Health is an important thing for any member of the stronger sex, especially when it comes to the organs of the genitourinary system. Unfortunately, from time to time many people encounter problems in this area. For example, the fairly common, odorless white discharge on the glans in men may have different causes. You should figure out whether this is always a cause for concern.
Causes of male discharge
The mucous membrane produces the necessary amount of lubricant to protect the penis from infectious attack. If the integrity of the foreskin is damaged or pathogenic proliferation of microorganisms occurs, the amount of lubrication may increase.
Discomfort and wet underwear are a reason to consult a doctor. Perhaps an inflammatory or infectious process is developing in the body.
Among the causes of urethral discharge in men are the following diseases:
- prostatitis of acute and chronic type;
- venereal diseases;
- pathogenic fungal proliferation;
- spermatorrhoea.
However, in some cases, discharge is a normal indicator of the functioning of the mucous membrane of the genital organ. Deviations can be distinguished by accompanying symptoms and additional signs of the disease.
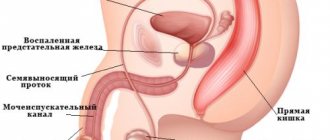
Prostate diseases
The most common cause of discharge from the penis is prostatitis. Inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system can provoke an increased amount of secretion. In the absence of adequate treatment for prostate diseases, there is a risk of decreased erectile function, up to its complete extinction, and difficulties with urination.
The nature of the discharge depends on the stage of development of prostatitis:
- Initial stage. The mucous secretion is released in the same volume, but the patient may experience additional difficulties with urination or pain in the pelvic organs.
- Acute form. Increased secretion of white (possibly with yellow spots) mucus from the penis. In the acute form, additional symptoms also appear. Urgent treatment is required.
- Chronic prostatitis. It can go into a remission stage, during which the symptoms of the disease practically do not appear. In advanced form, purulent or bloody spots appear.
Often the secretion is released during the treatment of prostatitis. This is a normal process that helps get rid of congestion in the prostate gland. After a massage or other physiotherapy, discharge is excreted along with urine.
Sexual infections
Sexually transmitted diseases occur due to promiscuity or unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected partner. The character, consistency and color depend on the microorganism that has infected the body.
Male discharge of an infectious nature:
- Trichomoniasis. There appears copious discharge from the glans penis of a foamy nature with an unpleasant odor. In this case, the man complains of pain and stinging during urination.
- Gonorrhea. The infection is transmitted during unprotected sexual contact with a sick woman or carriers of gonococcus. After infection, a man develops pain in the area of the glans penis, itching, burning, and purulent discharge from the urethra within 24-48 hours.
- Chlamydia. The color of the discharge may change, white liquid appears from the urinary canal in men, and the consistency changes. The disease can also be asymptomatic.
- Ureaplasmosis. Occurs due to increased activity of ureaplasma. In addition to the appearance of watery discharge, problems with urination appear, pain and burning occurs in the area of the excretory canal.
The nature of discharge for sexually transmitted diseases is similar in symptoms. With herpes, mycoplasmosis and other urogenital infections, pain appears in the urethra, the amount of mucus increases, color and consistency change. In advanced cases, there may be pus and blood present.
Candidiasis
Fungal diseases are less common in men. Women are more likely to suffer from candidiasis. However, after sexual intercourse with a partner suffering from thrush, a man may be a carrier of fungi.
The causative agents are microorganisms of the genus Candida. The disease can develop against the background of prolonged and uncontrolled use of antibiotics and other medications, as well as as a result of a decrease in the body's defenses.
Signs of candidiasis:
- white discharge in men from the urethra of the curd type;
- redness of the head of the penis;
- pain during urination and erection;
- swelling of the foreskin.
Only laboratory testing will help make an accurate diagnosis. A simple smear will help to detect a large number of fungi on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. Unlike the infectious type of discharge, with candidiasis the color is white and the consistency is thick.
Spermatorrhoea
Another pathogenic process that is considered one of the most serious disorders is spermatorrhea. In this case, pathology can occur at any age. The main sign of the disorder is the appearance of traces of sperm outside of ejaculation.
Seminal fluid can be found in urine or underwear even without sexual stimulation or contact. More often, the deviation is discovered in old age. Timely diagnosis allows you to find out the exact cause of spermatorrhea and take the necessary measures to eliminate this problem, otherwise there is a risk of developing infertility.
Signs of spermatorrhea:
- the presence of white spots of sperm on the underwear constantly or periodically;
- when pressing on the head of the penis, sperm is released;
- seminal fluid flows from the urethra without sexual arousal;
- erection and orgasm are absent.
When defecating or urinating, the amount of seminal fluid released increases. Untimely treatment can provoke the development of impotence and decreased fertility. The process can be stopped at an early stage of spermatorrhea when the main cause of the pathology is detected.
Variant of the norm
Not all discharges are signs of diseases of the genitourinary system. A variant of the norm is a clear liquid from the head (lubricant), which is necessary during sexual intercourse. Physiological secretions help protect the genital organ from pathogenic infection.
Normal processes include:
- discharge of lubricant (colorless liquid) from the penis during sexual arousal;
- smegma - accumulation of a mixture of secretion from the sebaceous glands of the foreskin, dead epithelial tissue and moisture;
- seminal fluid.
The release of semen is considered normal during orgasm and the remainder is removed through urination. Without an erection or arousal, the appearance of semen on underwear indicates a problem in the man’s body. Seminal fluid is released during orgasm during sexual intercourse or masturbation.
The secretion of the urethral glands, or lubricant, contains a small amount of sperm, so as a result of sexual contact with a woman, she can become pregnant. However, the likelihood of conception is very low. This is a clear discharge from the urethra.
Smegma is a small white discharge that is a mixture of sebaceous gland secretions, soap and other epithelial cells. It is not observed in circumcised men. If intimate hygiene is violated in the area of the foreskin, smegma can accumulate and provoke a number of unpleasant diseases. It is an excellent breeding ground for pathogens and serves as a prerequisite for the development of the inflammatory process - balanitis or balanoposthitis.
Other normal urethral discharge:
- Pollutions. They are especially typical for guys during puberty, when the body begins to produce large amounts of seminal fluid. Pollutions can be observed in adult men with prolonged sexual abstinence.
- Release of sperm during sexual arousal. This is possible if the patient has not had sexual intercourse for a long time and the sexual desire is too strong.
- Prostatorrhea. May be a normal process. There is a release of fluid from the excretory canal during defecation. This happens due to the pressure of feces on the prostate gland.
Your doctor will help you distinguish normal from pathology. The patient himself may suspect the disease if the process is accompanied by other symptoms.
Deviations from the norm
In addition to physiological discharge, which is considered normal, there are deviations. They can be easily identified by the structure of the secretion, color or smell:
- Bloody manifestations from the urethra indicate hemorrhea, a non-inflammatory disease that often develops due to trauma, for example, during a medical examination using an instrument.
- Spermatorea – the appearance of sperm without intercourse indicates a decrease in the tone of the vas deferens. The disease develops due to constant inflammation.
- White discharge in men on the head with a purulent-mucous structure is a sign of urethritis, which appears with chlamydia, mycoplasmosis and other infections. The problem is not accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, itching or stinging.
- A white foamy secretion appears during inflammation, which develops against the background of trichomoniasis. In addition, patients experience pain and burning, discomfort in the pelvic area.
- Yellow, green or brown manifestations of a thick consistency are a sign of gonorrhea. In addition, the patient has a number of other symptoms that cause discomfort.
- White or yellow mucus appears with prostatitis, inflammatory processes and other diseases occurring in the acute phase.
In addition to the described deviations, the shape of the urethral opening may change in patients, and the intensity of the transformation depends on the severity of the course and type of disease. Often the tissues swell and the color of the head changes.
What kind of discharge can there be?
Mucus can be different. Based on color, volume and consistency, the doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis and distinguish the physiological norm from a deviation of an infectious nature. To accurately diagnose the disease, laboratory diagnostics will be required.
By color
Discharge can be divided according to the presence of odor, color and consistency. If lumps appear that look like cottage cheese, then candidiasis can be suspected. An unpleasant odor indicates the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
The following normal discharges are distinguished by color:
- Yellow. If there is no odor and a thickened consistency, this may be normal - these are urine residues.
- White. Sometimes with a touch of yellowness. This is prostate secretion. They have the smell of seminal fluid.
- Gray. At the same time, the shade is unobtrusive and light, the amount of mucus is small - this is smegma.
If there is a change in volume and consistency, as well as the main symptom - an unpleasant odor - an infectious process can be suspected. But with ureaplasma infections, for example, the amount of discharge may be scanty, so color and stringiness are another sign of infection.
Pathogenic colored discharge:
- White curds. They talk about increased activity of candida fungi, which can provoke swelling of the foreskin and redness of the glans penis. If there is a “curd” on the penis and a characteristic fishy odor, there is a possibility of thrush.
- Cloudy and liquid. A sign of sexually transmitted diseases, dark green blotches may also be present. At the treatment stage, swamp-colored pus is released. The mucus may also be clear.
- Bright green and yellow. This is a sign of gonorrhea, which also has a strong putrid odor. Associated symptoms are severe pain and burning during sexual intercourse and when urinating.
- Red or brown. These are bloody spots that may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the pelvic organs or an advanced type of infection. The appearance of blood is a dangerous symptom that requires immediate treatment. Characteristic of hematorrhea (mechanical damage to the urethra).
It is easiest to cope with the disease at the initial stage of its manifestation. Chronic and advanced forms are difficult to stop, and in some cases they cannot be treated. If you experience an unpleasant odor from the genitals, a burning sensation in the urethra or redness, immediately seek help from a doctor.
By origin
Urethral mucus can be physiological (normal) or pathogenic. The appearance of an unpleasant symptom indicates the presence of a specific disease. A change in the nature of the discharge is a signal from the body that there is a problem.
Causes of the pathogenic process in the organs of the genitourinary system:
- infectious diseases;
- the appearance of formations (malignant and benign) in the pelvic organs;
- injuries to the penis or other mechanical damage to the genitals;
- inflammatory diseases (prostatitis, balanostitis);
- external factors (hypothermia, stress).
Pathology can also be identified by changes in the volume, consistency and nature of the discharge. In some diseases, mucus appears at certain times at night or in the morning, after drinking alcohol or during sexual arousal.
Opportunistic disorders include increased fungal activity. They are present in small quantities in any organism, but when the immune system is weakened, they begin to actively develop, causing thrush. Candidiasis most often appears against the background of other diseases or long-term use of antibiotics.
Non-venereal pathogens include:
- candida (fungi);
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- coli.
When the body's immune defenses are weakened, bacteria and fungi begin to attack the mucous membrane. External factors also have a special influence, which also provoke the proliferation of pathogens.
The risk of developing the disease increases if:
- carrying out chemotherapy treatment;
- taking antibacterial drugs;
- receiving an increased dose of radiation exposure;
- hypothermia;
- constant stress;
- unstable psychological states;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the pelvic organs.
Many people do not consider thrush a disease, but if not treated in a timely manner, candidiasis can become chronic. Also, a violation of the microflora of the genital organs provokes prostatitis and other inflammations of the prostate gland.
Natural manifestations
Natural discharge from the penis that is white or clear in color includes:
- libidinal urethrorrhea;
- smegmu;
- sperm.
These are the mucous secretions that are synthesized by the penis and glands related to the reproductive system. Their development is a natural process. Libidinal urethrorrhea is mucus from the penis, which is secreted during erection (sexual arousal) directly through the urethra. It is produced by special urethral glands. During erection, these secretions are used as a lubricant directly during sexual intercourse, thereby reducing friction and increasing the sensitivity of the head to any tactile touch (thereby accelerating ejaculation). Also, the function of this secret is to prevent damage to the female genital organs during quick fictions. Visually, libidinal discharge is absolutely transparent, when rubbed it can slightly foam, and has a specific smell (not causing disgust).
Smegma is a male discharge from the urethra, which is secreted by glands located in the part of the foreskin in contact with the head. The discharge is whitish in color, more like a greasy base. It accumulates in the folds of the foreskin and prevents excessive friction during walking or running, and also additionally protects the head of the penis from pathogenic bacteria. If the rules of individual hygiene are observed, smegma is removed in a timely manner, so its accumulations cannot be noticed. If you don’t wash yourself for more than 3-5 days, the discharge begins to smell unpleasant, and is already detected as papules, which are a mixture of smegma, dead cells and dirt. To prevent this, hygiene procedures should be carried out daily!
And the last type of natural discharge from the penis is sperm, which appears in portions directly during ejaculation, that is, when the peak of sexual arousal (orgasm) is reached. Physiologically, it is a mixture of prostate secretion, as well as sperm, which are synthesized in the testicles. The “excreting” organ in this case is the prostate gland, which contracts under the influence of the ejaculatory center (located in the spinal cord). It has a white-transparent tint and is released in small quantities (up to 8 milliliters, according to biological studies). Quite often it splashes out of the urethra in combination with libidinal urethrorrhea, which is why men mistakenly believe that sperm is released in huge portions.
https://youtu.be/yJ4Kvzhtm3c
It is worth noting that sperm can be released not only during sexual arousal. In biology, there is also such a thing as a wet dream - the unintentional release of prostate secretions during sleep. Mostly occurs in adolescents upon reaching puberty. Doctors cannot explain the exact cause of wet dreams, but many of them agree that in this way the body optimizes the functioning of the spermatic cords.
Associated symptoms
Excretory processes accompanied by an unpleasant odor or the appearance of other symptoms may indicate the presence of sexually transmitted or inflammatory diseases. You can suspect trichomoniasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis, balanoposthitis, gonorrhea or urethritis.
Associated symptoms:
- difficulty urinating;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- the appearance of pain syndrome;
- unpleasant odor;
- the appearance of pus and blood spots;
- itching and burning in the urethra, on the head or in the foreskin;
- erectile disfunction.
If you experience difficulty urinating, lack of sexual desire, increased urge to go to the toilet and a feeling of incomplete emptying, prostatitis can be suspected. Pain, burning and itching are common symptoms characteristic of any disease. The smell indicates the proliferation of microorganisms on the mucous membrane of the penis.
Symptom without inflammation
Discharge from the penis can appear without inflammation. This happens, for example, with spermatorrhea - the release of sperm without prior arousal (not associated with emission). Such a “defect” can be provoked by a violation of the peristalsis of the testes, as well as a disorder of the central nervous system, in which the process of ejaculation occurs unintentionally. The discharge from the penis itself has a natural hue, smell, density, but occurs on its own, without a provoking factor.
And we also need to mention about hematorrhea. This is a condition in which a man produces blood from the urethra due to mechanical damage to the soft tissues. This happens, for example, after a blow to the groin area or when an unsuccessful attempt to insert a foreign object into the urethra (a catheter or special instruments for examining the cavity). Such discharge from the penis is short-term and does not require any specialized treatment.
There is also such a thing as prostatorrhea. This is the discharge of seminal fluid from the urethra in a man without the inclusion of sperm, which occurs against the background of a malfunction in the functionality of the prostate. This condition may indicate pathological processes in the prostate gland, as well as improper functioning of the pituitary gland (it is responsible for the production of certain sex hormones and the regulation of sexual desire for women).
This kind of discharge from the penis does not indicate any serious illness, but you should still not put off going to the doctor. It is better to undergo a comprehensive examination in order to accurately determine the cause of the disorder.
When to see a doctor
It is recommended that men visit a urologist, venereologist and andrologist once a year, even in the absence of symptoms of disease. Many pathologies develop without symptoms. Detection of diseases at an early stage will eliminate long and difficult treatment.
Otherwise, there is a risk of the disease becoming chronic. If you notice any suspicious symptoms, contact a specialist immediately. With the normal development of men's health, underwear always remains dry.
When to see a doctor:
- when the color, consistency and volume of discharge changes;
- when an unpleasant odor appears from the genital organ;
- with a feeling of general discomfort and accompanying symptoms.
You can visit a specialist even after unprotected sexual intercourse, when there is a high probability of infection. The doctor will order a diagnostic test that will help determine the disease.
Symptoms of concern
The appearance of leucorrhoea outside of sexual intercourse should cause concern. If the penis is in a non-excited state, discharge may indicate the presence of a pathological process. Most often they talk about the presence of inflammation in the organs of the reproductive system.
Just like women, men's discharge can vary in color, clarity, and consistency. You can distinguish normal discharge from pathological ones by the following signs:
- Volume. Leucorrhoea caused by the disease may be too abundant or, conversely, scanty. Sometimes moderate discharge also indicates pathology.
- Consistency. The leucorrhoea may be very thin or too sticky and thick.
- By color and transparency. Cloudy discharge should cause concern. Their color can vary from white to yellow-green.
- By smell. Pathological discharge usually has a putrid, sour or fishy odor.
- Reasons for appearance. Discharge can be caused by sexual stimulation, urination, eating hot, spicy foods or drinking alcohol.
- By the presence of impurities. The discharge may contain blood, lumps of mucus, or pus.
The nature of the discharge directly depends on the state of the immune system, concomitant ailments and the causative agent of the disease.
Signs vary depending on the disease that caused the appearance of leucorrhoea. They are usually made up of a combination of mucus, cells and fluid. The level of transparency depends on the number of cells included in them. The level of turbidity also depends on this parameter. If the composition includes a large number of epithelial cells, the liquid becomes thick and acquires a gray tint. If the leucorrhoea is greenish or yellow, this indicates a predominance of leukocytes in it. Curdled discharge that is white in color indicates the appearance of candidiasis.
Usually men know their body well and pay attention to the slightest changes. The external genitalia are clearly visible and accessible for inspection by the patient himself. Therefore, a man often independently notices the beginning of the pathological process. The appearance of discharge, indicating the presence of a disease, is often accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the urethra. The patient may feel:
- cutting pain;
- itching;
- burning;
- discomfort.
Unpleasant sensations may intensify during urination or appear immediately after it. If blood is clearly visible in the discharge, this is a serious cause for concern. If there is an unpleasant odor coming from the penis, this indicates bacterial activity.
In some cases, pathological discharge may not differ from normal. This is possible, for example, with chlamydia. Because of these features, the patient may not pay attention to the course of the disease for a long period of time. This is dangerous because the pathological process can become chronic.
Diagnostics
First of all, the patient needs to contact a medical center. During the initial examination of the penis, the doctor will assess the condition of the penis, foreskin, and identify the presence of a rash, deformation of the organ, swelling and other signs.
The urologist will also assess the condition of the lymph nodes using palpation. The size of the prostate and the presence of an inflammatory process in the glandular tissue is indicated using a rectal examination.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Finger examination. Used to assess the condition of the prostate gland. Rectal penetration is sometimes used as a method of treating prostatitis. The doctor feels the presence of lobes, tissue density and size.
- Laboratory research. General tests are prescribed. Elevated white blood cell counts are a sign of infection.
- Smears for microscopic examination and culture. At the same time, the accuracy of the study is high; mycoplasma, candida fungi and other pathogens can be detected on the mucous membrane.
- PCR method (polymerase chain reaction). The study helps to detect sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), pathogens such as chlamydia, ureaplasma, and detect gonorrhea, herpes or syphilis.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. Helps detect inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. Ultrasound reveals the exact size and condition of organs and the presence of tumors.
- CT scan. It is prescribed to confirm or refute an existing diagnosis. Usually indicated for complicated and severe diseases.
- Biopsy. It is prescribed if a neoplasm has already been detected on the prostate gland or other organ. The study helps determine whether cells are malignant or benign.
Based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed. The more serious the problem with men's health, the more procedures you will have to undergo. It is for this reason that it is recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations in order to identify the disease in time.
Other inflammatory processes
Discharge from the penis can also occur against the background of non-infectious pathological processes in the urethra or urethra. The most common among them are stones (in the bladder, in the kidneys), as well as tumors (benign and malignant). In this case, the discharge from the penis acquires a predominantly transparent tint, but is sometimes complemented by brown, yellow, green inclusions, which are dead cells, stones and sand. The reasons for this are damage to the mucous and submucosal urethra, sphincters (located at the entrance of the bladder and urethra). Such symptoms are supplemented by sharp pain, which intensifies directly with urination. Discomfort in this case is caused by the passage of foreign bodies through elastic channels, in the process of which the ureters and urethra are mechanically damaged. It is the latter that leads to the appearance of blood flakes in the urine.
Transparent discharge in men without any pain may indicate pathological processes in the prostate gland. At the same time, the body’s hormonal levels and the process of prostate secretion synthesis are disrupted. The cycle of semen excretion itself is disrupted, which causes unintentional discharge from the urethra.
Why can tumors produce mucus? This is a kind of protective reaction of the body to inflammation of soft tissues. At the same time, blood flow increases to reject mutated cells, and the patency of the urethra may be partially impaired. In this case, mucus from transparent to yellow-green shades is released, and the concentration of leukocytes in the urine remains at a low level. It is possible to identify a tumor only after an ultrasound or other similar studies of the entire genitourinary system.
Treatment
Therapy is prescribed based on the diagnosis. Treatment methods can be divided into medicinal, conservative, folk and surgical. The latter are used only if other methods have not shown effectiveness.
Treatment of diseases:
- Candidiasis. Antifungal drugs are prescribed: Clotrimazole, Pimafucin or Exoderil. Tablets, gels and ointments are indicated for treatment. If thrush is detected, both sexual partners are treated.
- Prostatitis. It requires complex treatment, drugs from the group of alpha-blockers, herbal remedies and dietary supplements are prescribed. Among the popular ones are Prostamol Uno, Vitaprost, Omnic.
- Infections. White fluid from the urinary canal in men is treated only with antibiotics, which are prescribed depending on the pathogen. It is also recommended to additionally take medications to protect the liver (Essentiale), and douching with Chlorhexidine. Both sexual partners receive treatment.
- Spermatorrhoea. Leakage of seminal fluid is a dangerous pathology. It cannot be cured on its own; serious treatment is required. Most often, surgical treatment is prescribed. In some cases, exploratory surgery is performed followed by treatment.
- Oncology. If a cancerous tumor is detected, the patient will be offered several treatment methods: chemical castration, surgical removal of the affected organ, or radiation therapy. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages and is prescribed depending on the location of the tumor and the stage of the oncology.
Any deviations require immediate treatment. Traditional recipes can only be used as additional therapy. Do not take medications or use alternative medicine methods without a doctor's prescription. Self-medication can aggravate the disease and cause complications.
Allergic urethritis
In medicine, there is also such a thing as allergic urethritis. This is an inflammation of the mucous and submucosal lining of the bladder and urethra due to any allergic processes in the body. At the same time, transparent discharge from the urethra also appears, similar in its physiological qualities to libidinal urethrorrhea. This occurs against the background of an atypical protective reaction of the body to an allergen, which may be some food additive, medicine, preservative, bee venom, and so on. The discharge may also be white, which indicates an allergic reaction in other organs of the reproductive system (in particular, the prostate).
An accurate diagnosis in this case is only possible by taking a smear sample. And the so-called urethral collapse is eliminated by taking anti-allergic drugs (Diazolin, Cetrin and their derivatives). By the way, allergic urethritis, according to doctors, is mainly found in children under 5-6 years of age.
https://youtu.be/4iDXzsBfZbo
Consequences
Any disease, if left untreated, can cause problems with other organs. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, other unpleasant symptoms associated with urination or erectile function may appear.
Consequences:
- transition of the disease to a chronic type;
- spread of infection to other organs of the genitourinary system;
- chronic pain syndrome;
- the appearance of neoplasms;
- erectile disfunction;
- development of infertility;
- cancer.
The development of complications depends on the diagnosis. Along with chlamydia, urethritis or pyelonephritis may develop, and the functioning of the liver and kidneys may be impaired. At first glance, harmless discharge can cause significant harm to men's health.
https://youtu.be/doacSJ1IZ1Q
Passing the examination
If a man notices the appearance of atypical discharge, he should consult a doctor. Typically, the examination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The specialist examines the penis, perineum, glans and foreskin. The purpose of the procedure is to identify deformation of the genital organs, signs of injury, rash, discharge or signs of inflammation.
- Palpation of the lymph nodes in the groin and assessment of their condition. Enlarged, painful, inflamed lymph nodes indicate the course of the pathological process.
- Prostate examination. The specialist massages her through the rectum, and also obtains secretions for microscopic examination. Before the massage, it is recommended to refrain from urinating for one to two hours. If prostate adenoma is present, the increase in lobes is approximately the same. Dense strands can be felt. If a man is diagnosed with a malignant tumor, it usually grows evenly. During palpation, blood with clots may be released from the urethra.
- Smears are collected for microscopy and culture. During the examination, blood cells, fatty inclusions, and sperm are visible in the stained smear. The procedure can also help identify a number of pathogens. If there is an increase in the number of white blood cells, this may indicate the presence of chronic inflammation or urethritis. If too many eosinophils are detected, the man may have an allergy.
- Taking a general clinical blood and urine test.
Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis will be made and treatment will be prescribed. If there is not enough information to establish the pathology, the doctor may refer the patient for an ultrasound scan of the prostate, bladder and kidneys. Additionally, urography or CT may be performed.
Diagnosis and treatment
In order to establish an accurate clinical diagnosis, a specialist urologist must carefully interview the patient, collect medical history data and conduct an examination of the patient; only after this the patient is prescribed a set of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic tests. It is mandatory to take pathological discharge from the urethra for subsequent examination, which includes:
- Visual assessment of discharge;
- Microscopic examination;
- Bacteriological examination with inoculation of pathological discharge on nutrient media;
In addition, the patient undergoes a complex of instrumental studies, which includes: ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, cystoscopy and X-ray methods of examination with contrast.
Therapeutic tactics largely depend on the cause that caused the development of pathological discharge. If the secreted fluid is infectious in nature, a course of antibacterial therapy with a control bacteriological study must be carried out. You need to start treating the infectious-inflammatory process as quickly as possible. For any type of inflammation, be sure to use:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs from the NSAID group, these include (Baralgin, Diclofenac, Ketorol, Nurofen and other analogues). Also, drugs from this group have a pronounced analgesic effect. They can be used both topically and in tablet form;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. For the purpose of complex effects, procedures such as magnetic therapy and laser treatment of tissue are used in urological practice. Physiotherapeutic procedures help tissues involved in the inflammatory process to regenerate more effectively.
- Separately, it is worth mentioning about washing the urethral canal with antiseptic solutions. The most common and effective solutions include (Furacilin, Collargol, Miramistin, aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine). All these drugs have a pronounced bactericidal effect when douching the urethra, and also allow mechanical cleaning of the urethra from thick mucus or purulent masses.
Washing must be done at least twice a day to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. An alternative to the use of antiseptic solutions can be a variety of decoctions according to folk recipes.
In consultation with your doctor, it is possible to use some traditional methods of combating the infectious process. High efficiency is shown by freshly prepared oak bark decoction, which has a pronounced bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect.
Treatment is effective only when it is aimed at eliminating the main factor in the occurrence of pathological secretion.
In cases where a bacterial infection is known, antibacterial drugs sensitive to this species can be used. If urethritis is of a fungal nature (urethral candidiasis), then they resort to the use of antifungal systemic drugs, for example, Nystatin, Pimafucin or Levorin.
https://youtu.be/FkcjywRzK_k
ethnoscience
Many herbs have antiseptic properties. Therefore, it will be effective to wash the head with decoctions of oak, calendula, chamomile, and string. General strengthening drugs are taken internally. For example, honey with nuts, lemon and dried fruits, or garlic kvass. They will not only increase immunity, but also remove inflammation of the genital organs.
https://youtu.be/zeo8ETO7PJQ
Discharge indicators are within normal limits
A man can independently assess the degree of correspondence of discharge during arousal and the occurrence of an erection. The main evaluation criteria are the absence of a sharp unpleasant odor and impurities, transparent or whitish shades, and moderate density.
In case of minor deviations from the norm, it should also be taken into account that the nature of normal discharge depends on the frequency of sexual intercourse; with rare relationships, the amount of secretion increases. The norms for the amount of fluid released depend on the degree of excitement, and are also determined by individual characteristics. The spicy smell of discharge during an erection does not always indicate a disease. Eating salty, smoked, spicy foods can lead to changes. The presence of bad habits in a man reduces the amount of fluid released during erection, and also worsens biochemical and biological indicators.
Parents of teenagers should prepare future men for the fact that at this age nocturnal erections and emissions will begin, which will be accompanied by discharge. This is normal, should not cause concern or fear and has nothing to do with the guy's forbidden actions.
Yellow and green highlights
Purulent discharge of the named colors indicates a large accumulation of:
- epithelial cells;
- leukocytes;
- urethral mucus.
Yellow discharge, in which green specks are clearly visible, is a sure sign of the development of a sexually transmitted disease:
- gonorrhea;
- trichomoniasis.
Gonorrhea is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- release of a thick concentration throughout the day;
- unpleasant smell of rot;
- pain during urination;
- itching
Trichomoniasis most often has no characteristic symptoms. But if the disease is in an advanced stage, patients may note the following symptoms:
- burning and stinging when urinating;
- frequent urge;
- discomfort in the perineum;
- heaviness in the abdominal area;
- "smelling" discharge.
https://youtu.be/XVbFKcW9kkc
Prevention of discharge from the penis
To prevent discharge from the penis, you must:
- carefully choose sexual partners, avoid casual contacts;
- use condoms;
- if casual sex occurs without a condom, rinse the urethra with Miramistin or another antiseptic within 2 hours after contact;
- keep genitals clean;
- Avoid hypothermia, constant moisture in the genitals, and traumatic injuries to the penis.
https://youtu.be/eh5t8hXM08o
How is discharge treated?
If you notice the appearance of any uncharacteristic and alarming symptoms, immediately consult a venereologist. He will carry out the necessary diagnostic measures and prescribe a treatment program. However, regardless of the prescribed course, the patient must comply with the following instructions:
- Take only prescribed medications. In most cases, getting rid of discharge on the penis is achieved with the help of antibiotics.
- Do not self-medicate. The results of uncontrolled treatment can be completely unpredictable. There is no need to try to hide the symptoms of the disease or take the first antibiotics you come across, because... This can lead to complications.
- Maintain personal hygiene. If there is discharge on the penis, you should regularly wash it with warm water and soap.
- Don't infect other people. If you have symptoms of a sexually transmitted disease, you should avoid sexual contact without condoms.
https://youtu.be/9WVZKZwLAHA
https://youtu.be/9WVZKZwLAHA It must be remembered that discharge from the penis is by no means an accident or a temporary phenomenon. If you notice any unusual symptoms, contact your doctor immediately and begin treatment immediately, following the instructions prescribed by your specialist. Don't forget about your partner. Be sure to tell him about your illness and recommend that he see a doctor. Be healthy!
Discharge of blood with sperm
This process is described as hematospermia. It can be false and true. In false cases, sperm mixes with blood as it passes through the urethra. In reality, even before the sperm enters the urethra, it is excreted with blood.
Main symptoms of hematospermia:
- Ejaculation is accompanied by discomfort and pain;
- Irregularity of urination;
- Pain in the perineal area;
- Unpleasant sensation in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- Heat.
The main causes of pathology are associated with too frequent sexual intercourse. Sometimes, on the contrary, prolonged abstinence provokes the occurrence of hematospermia, as this leads to rupture of blood vessels.
Common causes of the problem
The most common cause of discharge is inflammation of the urethra (urethritis). The inflamed mucous membrane secretes more leukocytes and mucus in order to neutralize the effect of microbes as much as possible and quickly remove them from the body.
The causes of urethritis are divided into:
- Specific infectious diseases are sexually transmitted diseases (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, chlamydia).
- Nonspecific, when pathological growth of opportunistic microorganisms begins, which in normal times peacefully coexist with normal flora (candidiasis, gardnerellosis and others).
Inflammation can begin after damage to the urethra during the collection of a sample for analysis or when exposed to corrosive chemicals and salt crystals from the urine. Irritation of the urethra with food (mustard, sauerkraut, vinegar and beer) can also provoke discharge.
A more serious cause of fluid dripping from the urethra may be cancer of the penis or urethra. Due to erosions, ulcers and areas of necrosis of urethral tissue, inflammation and pathological production of mucus begins, sometimes mixed with blood.
https://youtu.be/w0U3saE-e74
Why is purulent discharge from the urethra in men dangerous?
The main danger of the condition is the development of infection and its spread to neighboring organs, such as the bladder and kidneys. In addition, in cases where treatment is chosen incorrectly, the disease can become chronic.
In such conditions, pronounced symptoms disappear, discharge stops, however, bacteria continue to live and develop in the body. In such cases, the man is a carrier of sexually transmitted diseases and can infect his sexual partner. The chronic condition of the disease is much more difficult to treat and can lead to erectile dysfunction.
When should you worry?
If a man monitors his health very carefully, he will immediately notice the slightest changes in urethral discharge:
- volume: abundant or insignificant;
- smell: putrid, sour, fishy stench;
- color and transparency;
- the appearance of impurities: mucous, purulent or bloody;
- consistency: thick or liquid.
If the above changes occur, a man needs to urgently consult a doctor for examination in order to avoid serious complications.
After all, urethral discharge can appear as a result of sexually transmitted diseases, neoplasms, injuries, inflammatory processes or after surgical operations.
The reasons for concern are:
- change in color of discharge to gray, green, brown or yellow;
- the appearance of a foul odor from the penis. This sign usually indicates the presence of bacteria;
- the appearance of blood impurities in the discharge.
In these situations, a man should urgently consult a doctor for advice. In certain situations, for example, with sexually transmitted diseases, discharge from the penis is similar to normal and therefore a man does not notice the development of pathology for a long period. At the same time, the likelihood of the disease becoming chronic increases.
Treatment of pathological discharge
Heterogeneous discharge from the urethra of an unnatural color is only a symptom of the disease. It is necessary to treat the pathology that caused changes in the secretion from the penis. Based on the type of negative processes in the urogenital system, doctors use several groups of medications:
- Antifungal drugs - Nystatin, Pimafucin, Fluconazole, Levorin. They are used for candidiasis.
- Antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins - used for gonorrhea, bacterial urethritis - Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin, Cefotaxime.
- Long-acting drugs - Bicillin.
- Anti-inflammatory antibacterial drugs - Sumamed, Azicide, Hemomycin.
Bicillin is prescribed for the treatment of pathological discharge
In addition to medications, the patient is given vitamin complexes and immunostimulating drugs.
Pathology therapy
Before prescribing medications, the doctor carefully examines the patient to identify the causative agent of the disease. In most cases, treatment consists of using products with antibacterial properties and a wide spectrum of action.
If there are parasites in the body, patients are prescribed antibiotics that are harmful to pathogenic microorganisms. To get rid of fungal infection, local treatment and antifungal medications are suitable. Sometimes therapy is supplemented with painkillers and non-steroidal drugs with anti-inflammatory effects.
If the appearance of white plaque and inflammation of the foreskin is associated with excessive accumulation of smegma, then treatment will consist mainly of improving the hygienic care of the male genital organs. It includes the following points:
- Wash the head daily with warm water and soap.
- Rinse the head once a day with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (it should be light pink).
- Lubricate the head at night with 1% tetracycline ointment or, even better, Malavit.
- If the problem is caused by phimosis, some men prefer radical treatment for this pathology - surgical circumcision of the foreskin.
https://youtu.be/SfOqJGV3KmQ
Treatment of thrush is aimed at suppressing the activity and eliminating the infection from the source of infection:
- First of all, you need to change your diet - exclude sweets, alcohol and flour foods from it, which will help avoid further development of fungi in the body. Instead, increase the amount of protein in the diet.
- General strengthening treatment and vitamins are prescribed, especially from group B and vitamin C.
- Local treatment consists of treating the head of the penis and foreskin 2 times a day with clotrimazole cream, which has an antifungal effect.
- Wash the head of the penis daily with a weak solution of baking soda.
Typically, a man’s recovery is observed within 1-2 weeks. If recovery does not occur during this time, then the man must be hospitalized in a medical facility. It is worth remembering the simple truth that the best way to be healthy and protect yourself from diseases is to prevent them in time. The best way to protect yourself from them is to maintain personal hygiene and keep your immunity at a high level.
Consequences of diseases
Any non-physiological discharge from the penis can cause a number of serious complications. If the cause is an STD or a specific infection, then late treatment and inaction will lead to the following results:
- development of prostatitis;
- inflammation of the seminal vesicles;
- inflammation of the testicles or foreskin;
- narrowing of the lumen of the urethra;
- infertility.
The risk group includes people who are promiscuous, do not use contraception, are often hypothermic and have a weak immune system.
Why is mucus formed?
Under normal conditions, discharge in men when an erection occurs is associated with the formation and release of pre-ejaculate - a clear, viscous liquid in a small amount. This has nothing to do with premature ejaculation, and the purpose of the lubricant is to neutralize the acidic environment in the urethra and vagina.
It is possible to restore erectile function! Proven FOLK CARE ... Reviews My story spotenciey.ru
Treatment of PROSTATITIS using a new method To restore the functions of the prostate, you need every day... Website Interview with a doctor bezprostatita.ru
The problem of the small size of the dignity has been solved. The mechanism of erection has been revealed... Official website Recovery bigbigrazmer.ru
The intended purpose of sexual intercourse by nature is the process of fertilization, and for normal movement and preservation of the functionality of sperm, certain conditions are required. It is to create an optimal environment that a transparent secret is released. A small amount of sperm is contained in pre-ejaculate, which should be taken into account to prevent unplanned pregnancy.
Mucus secretion occurs during erection during foreplay with a partner, during spontaneous night and morning arousal and masturbation. The second purpose of pre-ejaculate is to lubricate the mucous membrane of the urethra to facilitate the release and passage of sperm, so that the ejaculation process is not accompanied by unpleasant and painful sensations.
Thus, the discharge of a small amount of moderately viscous and completely transparent mucus during an erection is absolutely normal and indicates the correct functioning of the genitourinary system and a good level of potency.
Prevention
There are a number of preventive recommendations. First of all, you should take care of your personal intimate hygiene. A negligent attitude can result in the development of many dangerous diseases. It is necessary to wash the head of the genital organ daily with laundry soap, removing accumulated smegma from the surface. The procedure should be performed twice a day (morning and evening). To avoid contracting sexually transmitted diseases, you should use contraception when having sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner. In addition, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive medical examination at least once a year, which will help to promptly identify and eliminate possible health problems.
Principles of therapy for genitourinary infections
Treatment of diseases accompanied by the appearance of purulent discharge from the urethra depends on the causes that caused it.
Empirical (experimental, not confirmed by laboratory test data) prescription of antibiotics is practiced only in cases of severe manifestations of intoxication - high fever, chills, asthenic syndrome. For mild or moderate urethritis, it is recommended to wait for the results of a bacteriological examination before starting therapy.
For example, the drugs of choice for gonorrheal or chlamydial urethritis are
- Cefixime;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ofloxacin;
- Azithromycin;
- Doxycycline.
When treating chronic prostatitis, antibiotics from the pharmacological groups of aminoglycosides, cephalosporins and protected penicillins are most often prescribed. Depending on the microbial agent that became the causative agent and the characteristics of the course of the disease, the course of treatment can last from several days to 3-4 weeks.
In addition to antimicrobial agents, the following will help to quickly cope with purulent discharge:
- antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa), relaxing the smooth muscles of the urethra and promoting its sanitation;
- NSAIDs (Ketonal, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen), which reduce the activity of the inflammatory process and eliminate painful symptoms;
- medicinal/non-medicinal immunomodulators that increase the body's resistance to infectious processes.
Any discharge from the penis that has become different from normal in nature, quantity, consistency and color requires consultation with a doctor. Constraint and “hushing up” the problem in this case are bad allies. Timely treatment allows you to quickly and effectively cope with the disease and avoid the development of serious complications.
The physiological structure of the male reproductive organ is such that the urethra performs the function of removing urine and sperm from the body. In addition to these biological fluids, discharge from the urethra may have a transparent and slightly viscous consistency, or white and thick, but normally such discharge is insignificant.
If the secretion that comes out has a yellow or greenish color, a thick or viscous consistency, then most likely we are talking about purulent discharge. The amount of secretion released can vary, from a few drops to large volumes. This fluid consists of a large number of leukocytes and epithelial cells of the urethra. The appearance of this secretion is a symptom of various diseases of the genitourinary system.
Treatment methods
You should not self-medicate to eliminate symptoms, as this can lead to the disease becoming chronic. Drug treatment is based on the results of LBC culture and PCR diagnostics, and is prescribed by a doctor after the specific causative agent of the disease has been identified.
Treatment of the disease is based on the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Antibacterial agents . In cases where the cause of the disease is gonococcus or chlamydia bacteria, it is advisable to use the following drugs: Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Doxycycline, Metronidazole. These medications are available in tablet form. It is possible to use medications in the form of injections, for example: Ecmonovocillin, Bicillin-5. The specific type of antibacterial agent should be prescribed by a doctor, based on the results of tests of the sensitivity of bacteria to types of antibiotics. Uncontrolled, independent use of antibacterial agents has led to the emergence of bacteria resistant to certain types of antibiotics.
- Probiotics . Prescribed to restore intestinal microflora after taking a course of antibiotics, for example Linex, Bifiform.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs . Drugs such as Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are prescribed to relieve pain, lower body temperature and reduce inflammation.
- Antispasmodics . No-spa or Papaverine are used to relieve muscle spasm of the urethra, which promotes the outflow of urine and, accordingly, the removal of purulent discharge.
- Immunomodulators and multivitamins . For example, Viferon, Likopid are prescribed to increase the body's resistance to infection.
An integrated approach to treatment will not only reduce the symptoms of the disease, including in the form of purulent discharge, but also eliminate the main cause - bacteria.
Discharge from the urethra in men is quite common and can have a completely different nature of occurrence. In urological practice, this symptom comes first when patients seek medical help and provides important diagnostic information to a urologist when examining a patient.
Urethral discharge can be either physiological or have a pathological origin, and the pathology does not necessarily have to affect the urethral canal.
Preventive measures for the appearance of urethral compartments
Almost every representative of the stronger half of humanity has encountered similar phenomena. There was concern: the appearance of clear, odorless mucus-like discharge - what could this mean in men?
All male representatives secrete the following physiological fluids from the urethra:
- urine. Normally, urin is a transparent liquid of a yellowish color and almost odorless;
- secretion of the prostate. This viscous liquid is characterized by a whitish color and has a specific odor;
- ejaculate. Normal sperm is mucous and grayish-white in color.
In addition, the following are considered natural:
- Sperm. It is usually released during sexual contact. However, at a young age it can occur without sexual intercourse. The guy most often experiences wet dreams in the morning.
- Urethrorrhea. Colorless discharge in small quantities is characterized by a mucous consistency. They are secreted to protect the inner surface of the urethra and improve the passage of sperm. Urethrorrhea occurs with strong arousal.
- Prostatorrhea or defecation. With the first, there is a slight release of prostate secretion after the process of urination. And the second occurs as a result of tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall during defecation.
However, not in all situations the above discharge is considered the norm. It is important to monitor their color, volume, and frequency of appearance.
Quite often, during sexual arousal, taking certain medications or alcoholic drinks, some contents are released from the penis in the male half.
Urethral discharge, which differs in consistency, color and smell from the norm, often indicates the development of dangerous pathologies.
In the case of chronic chlamydia, mycoplasmosis or ureaplasmosis in men, slight transparent sections of mucous consistency appear. With exacerbation of the above ailments, mucous whitish discharge is observed. With chlamydia, sputum is usually localized on the head.
Gonorrhea discharge is accompanied by pain, itching and burning, which intensifies when the bladder is emptied.
Often a man’s body is affected by several infections. For example, gonorrhea or trichomoniasis is often accompanied by chlamydia, and ureaplasmosis can occur with mycoplasmosis. In these situations, pathologies manifest themselves uncharacteristically, thereby complicating diagnosis.
Inflammations of the genitourinary organs are usually formed as a result of changes in the microflora caused by impaired functioning of the immune system.
Streptococci, candida fungi, E. coli, and staphylococci are found on the mucous membranes and skin. Prolonged stress, frequent hypothermia, chemotherapy, uncontrolled use of antibiotics or radiotherapy provoke the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora.
https://youtu.be/p0RGAAytWk0
Common diseases accompanied by urethral discharge are listed in the table.
| Name of the disease | Short description |
| Nonspecific urethritis | The disease first affects the bladder and progresses with the appearance of minor mucous, purulent, cheesy discharge. The process of urination is accompanied by a slight burning sensation and itching. A man suffers from frequent urination. If the disease is not treated, the inflammation spreads to the kidneys and ureters. In these situations, bloody impurities are observed in the discharge |
| Gardnerellosis | The disease is accompanied by sparse greenish or yellowish discharge. I often consider this disease to be a venereal disease, however, infection with gardnerella usually occurs due to dysbacteriosis |
| Candidiasis | The disease affects the urethra and usually develops as a result of impaired immune function after antibiotic therapy, chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The disease occurs with cheesy discharge that has a sour odor. In addition, urination and ejaculation are accompanied by itching. In some situations, there is a dull pain in the groin or pubic area, or lower back. Soreness can radiate to the navel |
| Prostatitis | The disease is accompanied by cloudy discharge during urination. When the disease worsens, strong discharge occurs, and when it is chronic, the volume of discharge decreases. Difficulty urinating and weak erection are noted. If left untreated, anuria or impotence may occur. |
| Balanoposthitis | The disease is accompanied by copious discharge of purulent contents. In some situations, the discharge contains mucus impurities. Signs of the disease include swelling and redness of the foreskin, as well as pain in the head of the penis. Men with diabetes are often affected by the disease |
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: General urine analysis - mucus in the urine and the reasons for its appearance
Discharge from the penis is accompanied not only by sexually transmitted pathologies or inflammatory pathologies. They are also typical for the following conditions:
- Spermatorea. This situation is observed when the tone of the ejaculatory ducts is reduced and involuntary leakage of ejaculate occurs from the penis. Spermatorrhea is observed when a man does not feel orgasm. Often the causes of spermatorrhea are disorders of the nervous system, constant stress, spinal injuries, or long-term inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Hematorrhea. Bloody discharge is observed after injury to the urinary canal. The urethral canal is injured as a result of installing a catheter, bougienage, or taking biomaterial for a smear. The blood contains clots. If hematorrhea is caused by the passage of stones or sand from the kidney, the patient suffers excruciating pain. With the development of glomerulonephritis, bloody discharge occurs with increased pressure, edema, and the presence of protein.
- Prostatorrhea. The release of prostate secretion is characteristic of prostate adenoma, impaired intervention, as well as chronic prostatitis.
Brown-colored urethral compartments containing various impurities, as a rule, indicate malignant neoplasms. Brown mucus can also occur with polyposis.
It must be remembered that discharge from the penis can lead to irreversible consequences, for example, male infertility or impotence. And prostate tumors can cause kidney failure.
Many diseases accompanied by urethral discharge require long-term complex treatment. Patients who have undergone timely treatment leave positive reviews and photos on the forums.
You need to avoid masturbation and also observe personal hygiene rules to protect your body from pathogenic bacteria.
In some situations, discharge from the penis is considered normal. But sometimes they are able to warn a man about the development of dangerous pathologies. To find out the main reasons for the appearance of urethral discharge, a man needs to see a doctor and undergo an examination. Based on the test results, the doctor will determine effective treatment. There is no need to self-medicate so as not to aggravate the situation and avoid permanent consequences.
Increased leukocytes – acute urethritis, exacerbation of chronic urethritis.
Increased eosinophils – allergic urethritis.
Increased red blood cells – trauma, tumors, discharge of stones or sand due to urolithiasis, severe inflammation.
Epithelial cells in large numbers – chronic urethritis, urethral leukoplakia.
Spermatozoa – spermatorrhea.
Lipoid grains - prostatorrhea.
Mucus without blood cells is urethrorrhea.
Key cells (small rods on epithelial cells) with a small number of neutrophils – urethritis.
In a normal smear, up to 4 leukocytes are detected in the field of view, the bacterial flora is represented by single cocci and rods.