What is laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a modern endoscopic method used in operative gynecology for the diagnosis and treatment of various pathologies. Its essence lies in the fact that through small incisions with an average diameter of 0.5 to 0.7 cm in the navel area, a special optical instrument called a laparoscope is inserted. Thanks to this, doctors have the opportunity to study the condition of the pelvic or abdominal organs, receiving a high-quality image on the monitor screen.
Sign up for an appointment with the doctor
How is diagnostic laparoscopy performed?
The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- The administration of anesthesia - general or local - is determined individually.
- Injecting gas into the abdominal cavity using a special instrument and a small incision (usually in the navel). The gas is completely safe and serves to lift the abdominal wall, providing volume for a good view.
- Insertion of the instrument and camera through two other miniature holes.
- After all necessary manipulations have been carried out, the instrument and gas are removed, sutures and bandages are applied.
- Most often, the patient can go home within a day after the operation.
Indications for implementation
Indications for laparoscopy are:
- diagnostic examination of the pelvic organs;
- uterine fibroids;
- genital endometriosis;
- idiopathic infertility;
- chronic pelvic pain;
- ovarian pathologies (cysts, space-occupying formations, sclerocystosis);
- pathologies of the fallopian tubes (obstruction, hydrosalpinx, sactosalpinx, tubal pregnancy, etc.), as well as tubal ligation for the purpose of sterilization;
- pelvic organ prolapse;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- adhesive disease of the pelvis.
Indications
Laparoscopy is performed both planned and emergency.
Indications for emergency operations
- Ovarian cyst with torsion, cyst rupture.
- Diagnosed tubal pregnancy.
- Necrosis of uterine fibroids.
- Traumatization of the uterus during medical procedures.
- Purulent formation in the pelvic cavity.
- Diagnosis of acute abdominal pain.
Indications for planned operations
- Tumor-like formation in the area of the ovaries, tubes or uterus.
- Taking tissues for histological and cytological examination (biopsy).
- Suspicion of ectopic pregnancy.
- Suspicion of congenital anomalies of the internal genital organs.
- Examination for patency of the fallopian tubes.
- Monitoring the dynamics of the disease during treatment.
- Surgery for uterine fibroids, endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, for removal of tubes or their ligation, adhesions in the pelvic cavity.
The operation can also be performed for the purpose of differential diagnosis. This may be necessary when laboratory and instrumental research methods do not allow making an accurate diagnosis and determining the cause of complaints.
Diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology
Diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology is used to assess the condition of the pelvic organs.
In the presence of pathological changes, we are able to effectively remove cystic formations and tumors of the ovary (including in the gestational period), myomatous nodes, and malignant neoplasms of the reproductive system. Diagnostic laparoscopy for infertility is used quite widely, since it makes it possible to identify many of the reasons underlying the decline in reproductive function. Based on the results obtained, the doctor at the laparoscopy center can recommend one or another treatment tactics and assess the extent of the required surgical intervention. The cost of diagnostic laparoscopy (including hysteroscopy and checking the patency of the fallopian tubes) at Nova Clinic ranges from 71,000 rubles.
Indications for diagnostic laparoscopy
Diagnosis using the laparoscopic method can be carried out in a number of cases:
- For gynecological disorders such as adnexitis, oophoritis.
- To identify the causes of infertility, if tubal obstruction is suspected.
- Acute organ diseases with vague symptoms.
- In acute pancreatitis to determine the condition of the pancreas and peritoneum.
- After spontaneous reduction of hernias.
- For differential diagnosis of jaundice, to monitor the outflow of bile and the appearance of obstruction.
- If there is a neoplasm in the pelvic area - ovarian cysts, tumors.
- After closed injuries to the abdominal organs, especially if the patient is unconscious and there are no obvious symptoms.
- In case of injuries, to determine hemorrhages and inflammations.
- With postoperative peritonitis.
- If there is ascites formed for an unknown reason.
- For the diagnosis of abdominal tumors.
Preparing for surgery
Ovarian laparoscopy or fallopian tube laparoscopy, as well as other types of minimally invasive surgery, can be performed on any day (except during menstruation). The diet before surgery involves avoiding foods that can cause increased gas formation in the intestines. These products include carbonated drinks, white cabbage, rye bread, and legumes. You will need to eliminate these foods from your diet for several days before surgery. The day before, you can have dinner (preferably liquid food) until 6 pm. You can drink water up to 22 hours. Your doctor may also recommend a colon cleanse with an enema.
Preparation for diagnostic laparoscopy
The preparatory stage includes a preliminary examination, as with any surgical intervention. This includes taking anamnesis, conducting blood and urine tests, taking smears, performing ECG and ultrasound. Before surgery, the patient must follow a mostly liquid diet and not eat foods that cause excessive gas formation. Taking special medications may be necessary depending on the nature of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies. When preparing, it is very important to follow all the doctor’s instructions so that the operation is as easy as possible and gives accurate results.
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications include:
- cancer of the ovary or fallopian tube;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular or respiratory systems in the stage of decompensation, as well as acute renal and liver failure;
- bleeding disorders that cannot be corrected;
- obesity degrees III and IV;
- any violations that prevent the patient from being in the so-called Trendelburg position during the operation, in which the pelvis is elevated in relation to the head (sliding hernia of the diaphragm, cerebral vascular pathologies);
- hemorrhagic shock.
In addition, there are relative contraindications, which include severe adhesions in the pelvis, acute infectious diseases and some other disorders.
Postoperative period after laparoscopy
At the end of the intervention, the patient can be left to regain consciousness directly in the operating room or transported to the ward. This is usually decided by the operating doctor.
After regaining consciousness, the woman needs to gradually return to activity. Doctors strongly do not recommend lying down after this intervention for more than 4 hours. Physical activity, even minimal, normalizes blood circulation.
Usually, provided there are no serious consequences, the woman is observed for 3 days. After which, recuperation can be done at home. Returning to a normal rhythm of life after laparoscopy is possible within a week.
But, physical activity in the postoperative period should be limited! Lifting weights and doing exercises, especially for the abs, remain prohibited for 2 to 3 weeks.
Now about nutrition. Immediately after the operation you cannot eat anything, you can only drink still water.
The next day the patient's menu consists only of:
- low-fat meat broth without any additives in the form of vegetables, cereals and other things;
- tea without sugar.
On the third day, a woman’s diet expands slightly and may consist of::
- lean liquid porridges;
- mashed potatoes;
- lean meatballs or steamed cutlets;
- natural yogurt prepared at home.
Dietary nutrition after laparoscopy must not be violated! You should still avoid foods that cause gas. Digestive problems and discomfort will worsen your well-being and increase the recovery period.
Additional recommendations
Another important point is sex life after surgery. The doctor will inform you about the period during which it is necessary to maintain sexual rest, taking into account the purpose and result of the operation.
- Often the period of abstinence can be from two to three months, until complete recovery. And until the wounds heal, the woman will be prohibited from any sexual contact.
- If the purpose of laparoscopy was to remove adhesions in the fallopian tubes, then sexual activity should be resumed as soon as possible to eliminate the risk of re-obstruction.
If we talk about well-being in general, then you need to remember that an operation was performed, which means you need time to recover. Wounds usually heal fairly quickly. In the first days, women usually complain of constant pain in the abdomen and lower back, but it quickly passes without the use of painkillers.
The temperature may rise to 37.5°C, and mucous and bloody discharge from the vagina may appear. But, as a rule, a woman’s condition becomes stable within 7 days.
If there is a sharp increase in body temperature and deterioration of the condition, the woman remains in the department for further treatment.
As for menstruation after surgery, its onset depends on the period of the menstrual cycle in which the intervention was performed.
- 7-10 days of the cycle - at normal times;
- the middle of the cycle is in 24-30 days.
In addition, a delay of one or two weeks is not uncommon.
Possible complications after laparoscopy in gynecology
Immediately after laparoscopy of the ovaries or fallopian tubes, women may complain of aching sensations in the neck, abdomen, and shoulders.
This is due to the fact that during the operation gas is injected into the abdominal cavity. Such sensations can be eliminated with the help of simple exercises. The risk of complications after laparoscopy is much lower than after abdominal surgery, since it is a minimally invasive method. As a result, there is less tissue injury and there are no postoperative scars. However, it must be borne in mind that performing laparoscopy requires great skill from the surgeon. Although laparoscopy is performed in many clinics in Moscow, it is recommended to go only to medical centers specializing in the treatment of infertility. This will help avoid potential complications associated with insufficient qualifications of the doctor (damage to blood vessels and internal organs, infection, tissue burns). In particular, all operating gynecologists at Nova Clinic have many years of successful experience in performing such operations. Complications after laparoscopy can also develop due to the fact that the patient does not follow the doctor’s instructions. Therefore, strictly follow the doctor's recommendations and observe restrictions related to physical activity, diet and intimate relationships for a certain time. Still have questions?
Preparation for laparoscopy and the principle of its implementation
Careful preparation for laparoscopy in gynecological practice identifies contraindications and ensures the body is prepared for surgical access. First of all, the following studies are carried out:
- a comprehensive blood test, which includes a general analysis, identifying the group and Rh factor, checking glucose levels, taking tests for blood clotting, syphilis, HIV and hepatitis;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- general urine analysis;
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorography;
- consultation with a gynecologist with taking a smear for flora and a cytological smear;
- consultation with a general practitioner to exclude contraindications for laparoscopy and the use of general anesthesia.
Further preparation consists of the following:
- Test results are brought back to normal if required.
- The end of food intake is 8 hours before the procedure, the last liquid intake is 3 hours.
- The intestines are cleansed. Use Fortrans or other laxatives. It may be necessary to use a cleansing enema.
- To use endotracheal anesthesia, the patient is given sedatives before being sent to the operating room (30 minutes before).
- To prevent problems associated with thromboembolism, compression stockings are worn or an elastic bandage is used.
Before performing the procedure, the doctor must explain to the patient the essence of the surgical intervention and its necessity. Consent for laparoscopy and anesthesia is signed.
What is the essence of laparoscopy?
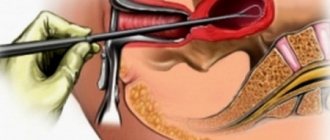
The essence of this diagnostic and treatment method is based on the introduction of special tubes into the abdominal cavity, through which the doctor manipulates cameras, lights and instruments. Thanks to this, the specialist has the opportunity to perform surgery on the patient’s internal organs without resorting to classical abdominal surgery.
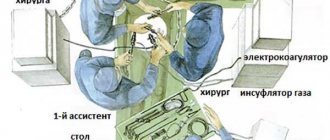
Laparoscopic surgery in gynecology is performed under general anesthesia using endotracheal anesthesia. A hole is made in the woman's abdominal cavity through which a certain amount of air mass is pumped into the peritoneal cavity. As a result, the abdomen increases in volume, which allows specialists to carry out the necessary interventions, avoiding injury to nearby organs.
Several small incisions (called micro-incisions) are then made into the cavity. The number of incisions depends on the complexity of the chosen manipulation. Through one incision, a laparoscope is inserted - a tube-shaped device with an eyepiece on one side and a lens or video camera on the other. A manipulator is inserted through the second incision. An operation begins, the duration of which is difficult to make any predictions about. It all depends on the severity of the disease. On average, for diagnostic purposes, laparoscopy in gynecology lasts no more than an hour, for therapeutic purposes - several hours. At the same time, doctors see their own manipulations and everything that happens inside the patient on a special screen.
After completing the procedure, surgeons conduct an additional video inspection of the operating area and remove the volume of biological fluid or blood that accumulated during laparoscopy. Oxygen or gas is eliminated, the closure of the vessel walls is checked, and the doctor makes sure that there is no bleeding. After this, all instruments are removed from the abdominal cavity, and suture material is applied to the site of their insertion on the skin.
Before and after diagnostic laparoscopy
Before a laparoscopic examination, it is necessary to undergo various blood tests, urine tests, a gynecological smear, an ECG, and additional studies are possible as prescribed by the doctor.
After diagnostic intervention, it is necessary to adhere to the recommendations of doctors.
You can start work in two days. Physical activity should be increased gradually, there are restrictions on heavy food intake, alcohol, and intimate relationships for two to three weeks.
If you follow the recommendations, recovery after the study will take place in the shortest possible time, and even subtle scars will not remind you of it.
Contact our specialists any day of the week.
Process
Before diagnostic laparoscopy, a comprehensive examination of the patient is performed by the attending physician and anesthesiologist.
Stages of preparation for surgery:
- Connecting the patient to an IV and a monitor that monitors the heart.
- The use of general anesthesia, intravenous or combined with endotracheal.
- Administration of drugs intravenously to completely relax the body.
- Insertion of an endotracheal tube and further connection to a ventilator.
The surgical intervention itself is carried out in the following sequence:
- The Veress needle enters the cavity, after which carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide penetrates into the space.
- Insertion of hollow tubes, the needle is removed.
- Dissection of skin tissue and puncture with a trocar.
- After removing the trocar, the laparoscope is inserted.
- Removal of found formations/suppurations, biopsy. This stage may be skipped in the case of pure diagnosis or detection of a cancerous tumor.
- Removing instruments from the cavity.
Positions of the operated patient during diagnostic laparoscopy:
- raised pelvis above the upper body;
- the torso is raised above the pelvis;
- on the side.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for laparoscopy in gynecology are:
- female infertility;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- adhesions or obstruction of the fallopian tubes (manipulation is carried out for diagnostic and at the same time therapeutic purposes);
- appendicitis;
- ovarian cyst;
- endometriosis;
- uterine fibroids;
- secondary dysmenorrhea;
- inflammatory process in the pelvic organs.
Contraindications to laparoscopy are classified into absolute and relative.
Absolute contraindications:
- decompensatory diseases of the respiratory system;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- poor blood clotting;
- cachexia;
- state of shock and coma;
- hiatal hernia;
- acute infections;
- bronchial asthma in the acute stage;
- severe degree of hypertension.
Relative contraindications:
- oncology of the cervix and ovary;
- obesity 3 and 4 degrees;
- a significant volume of pathological neoplasms of the pelvic organs;
- serious adhesive process formed in the abdominal organs after previous surgical interventions;
- significant hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity.