All articles by the author
Author of the article: Ekaterina Sergeevna Churaeva
Practicing obstetrician-gynecologist, ultrasound diagnostics doctor
A general urine test is often prescribed by doctors at an appointment if they suspect any disease, not related to the urinary system. Sometimes you can see in the results that the level of red blood cells in a woman’s urine is increased. Why is this happening? If there are elevated red blood cells in the urine, this in most cases means that changes are occurring in the body that require close attention.
Normal red blood cells in urine
During the day, about 2 million red cells in the blood are released in urine. This means that there are 1 - 2 red blood cells in the urine in the field of view. The normal level of red blood cells in the urine in women is up to 3. In the case of an increased level of red blood cells in the urine, they speak of hematuria. In urinary sediment, red blood cells are unchanged (i.e., those that contain hemoglobin) and lack this blood pigment.
The appearance of unchanged and altered red blood cells in the urine is of great diagnostic importance for many infectious and non-infectious pathologies.
Probable causes of red blood cells in urine
If there is a high blood content, the urine changes color
The most likely causes of increased levels of red blood cells in the urine in women:
- The effect of injuries on the organs of the urinary system. The most common injuries are to the kidneys, ureters and bladder. For example, a bladder injury is most often the result of a blow to the suprapubic area. If at this time it was empty, then a hematoma forms in the submucosal layer, diffuse pain appears, and blood may be found in the urine.
Kidney injuries usually occur due to falls. A blunt blow to the lumbar area is reflected by acute lumbar pain. As a result, there may be a decrease in the portions of excreted urine and a false urge to urinate. At the same time, the number of red cells in urine can vary significantly - it depends on the size of the injured vessels.
- The development of hydronephrosis is a pathology in which there is an expansion of the renal cavities that collect urine (pelvis, calyx), which leads to significant difficulty or complete impossibility of urinary outflow. Hydronephrosis can be a consequence of congenital anatomical abnormalities of the kidneys and ureters, or a consequence of acquired diseases and injuries.
Symptoms include dull pain in the abdomen and lower back and an increased number of red blood cells in the urine. With bilateral hydronephrosis, pressure rises, swelling of the kidneys and decreased urination are noted.
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory process in the kidney tissues. Mostly small vessels (glomerular) are affected. The disease is a consequence of streptococcal infection, as a result of which the body reacts by disrupting the immune response and damaging its own organs. Symptoms are manifested by the development of renal hypertension, swelling of the kidneys and the appearance of protein and red blood cells in urine tests. More often, the disease manifests itself in a latent form, in which the presence of only small inclusions of protein and blood is noted in the urine.
- Urolithiasis (urolithiasis) - penetration of blood into the urine occurs due to injury to tissues and blood vessels formed by stones. The larger the caliber of the vessel, the more red blood cells will end up in the urine.
- The development of pyelonephritis, manifested by damage to the extracellular renal matrix and renal cavities, due to bacterial infection. Characteristic symptoms include aching lumbar pain, fever and general weakness. As a result of damage to the kidney vessels, blood is found in the urine.
- Cystitis - as a result of the development of inflammatory reactions in the mucous lining of the bladder. Women are more often susceptible to this pathology. The symptoms are characterized by discomfort and dull pain in the lower abdomen, frequent and painful urination. When examined, an increase in red blood cells and white blood cells is found in the urine.
Such a combination as the loss of red blood cells together with leukocytes is very rare. Mainly as a transient (quickly passing) response to stressful situations. But in case of a significant increase in these indicators, urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary. Because a simultaneous increase in the analysis of white and red blood cells may indicate a chronic course of tumor processes in the bone marrow, or be a consequence of dehydration of the body.
Among other reasons, one can note quite banal ones that can be easily eliminated. This is the effect on the body of prolonged thermal exposure (bath, prolonged tanning, etc.), heavy loads, alcohol, salty or spicy foods. In addition, it is quite possible to cause irritation of the kidney tissue by long-term use of certain medications and abuse of vitamin complexes.
In addition to urological diseases, the presence of red blood cells and blood in the urine is noted when:
- prostatitis and the development of tumor processes in it (adenoma);
- gynecological pathologies caused by erosive lesions and hemorrhages.
- failure of cardiac and respiratory functions;
- chronic hemoblastosis;
- extensive burns.
What is hematuria
Hematuria (erythrocyturia) is the detection of red blood cells in the urine during analysis. Depending on its severity, microhematuria is distinguished when there are single red blood cells in the urine, which are detected by microscopy. With gross hematuria, urine acquires an unnatural shade from pink to dark brown.
There are different types of hematuria.
- Initial. Blood is found only in the initial portion of urine.
- Terminal. The color of urine is red in the last portion.
- Total. This means that the entire portion of urine changes color.
False hematuria
Some foods, such as beets, blueberries, blueberries, and rhubarb, change the color of urine. Certain medications - Cyclophosphamide, some penicillin antibiotics, Warfarin, Aspirin also cause the number of red blood cells in urine to increase. Its color will soon return to normal after the patient completes treatment.
Normal values
The norm of red blood cells and white blood cells varies according to the patient’s gender and age (in children and adults). The measurement value is a digital indicator per microliter (μl) of biofluid (in other words, how much is in the field of view). The OAM has adopted the following standards for the content of blood cellular elements for adults:
| Leukocyte cells | |
| men | women |
| ≤ 3 | ≤ 6 |
| Red blood cells | |
| men | women |
| 1–2/µl | ≤ 3/µl |
The difference in leukocyte parameters in women and men is explained by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the external genitalia. The female urethra is wider and shorter, and white blood cells contained in vaginal secretions easily penetrate into it. During pregnancy, red blood cells are allowed to increase by a maximum of 2 units (that is, no more than 5).
The norm of red and colorless blood cells in children's urine
| Leukocytes | ||||||||
| boys | girls | |||||||
| up to a year | 1–6 years | 7–17 years old | up to a year | 1–6 years | 7–17 years old | |||
| 1–7 | ≤ 2 | ≤ 3 | 7–8 | ≤ 3 | ≤ 6 | |||
| Red blood cells | ||||||||
| boys | girls | |||||||
| up to 1 month | 12 years | over 12 | up to 1 month | up to 12 years | over 12 years old | |||
| ≤ 7 | ≤ 4 | ≤ 4 | ≤ 7 | ≤ 4 | ≤ 2 | |||
In infants, a high rate of red blood cells is due to their accumulation during intrauterine development and the active destruction of red cells during the baby’s adaptation to the new environment. The average indicators of formed elements in the Nechiporenko test for adults and children are identical. The measurement is made in one milliliter (ml) of urine sediment.
Reference values (Nechiporenko test)
| Leukocytes | Red blood cells | ||||
| ⩽2000 | ⩽1000 | ||||
| Cylinders | |||||
| hyaline | erythrocyte | epithelial | grainy | waxy | |
| ⩽20 | not detected | not detected | not detected | not detected | |
Deviations from the norm of leukocyte parameters according to Nechiporenko (+2000/l) during the perinatal period in women are not considered pathological. This is due, firstly, to the double load experienced by the kidney apparatus of a pregnant woman. Secondly, with changes in hormonal levels. The acceptable value of leukocytes is considered to be 4000/ml.
In women, the reliability of the results may be affected by the presence of menstrual blood in the urine collected for analysis. During the period of bleeding, the study is not recommended. In urgent cases, before collecting urine in a container, it is necessary to insert a hygienic tampon into the vagina.
Rules for collecting urine for laboratory testing
Dangerous diseases that cause hematuria
A three-glass test helps determine the disease and the advisability of other examinations. The first portion of urine is collected in the first container, the average portion is collected in the second, and the residual urine is collected in the third. The kidneys begin to excrete a large amount of blood in such pathologies.
- Thrombocytopenia is a decrease in the concentration of blood platelets. When urine is excreted from the body, it may contain blood clots.
- With cancer, the kidney vessels are damaged, which causes bleeding. In this case, the urine takes on a rich red or dark red hue.
- Pyelonephritis is a nonspecific inflammatory disease of the pelvis, calyces, and renal parenchyma. Acute pyelonephritis sometimes leads to anuria and poisoning of the body with decay products. Advanced chronic pyelonephritis is dangerous for the development of chronic renal failure.
Causes of excess red blood cell levels
To understand the necessity of the presence of red cells in urine, it is necessary to find out why they are found in it. All reasons can be divided into several groups:
- physiological, which includes the temperature environment of the human body - being in a hot climate, in a bathhouse or sauna, active physical activity, acute stress conditions, excess alcohol or salty/spicy foods in the diet;
- diseases of the genitourinary system, accompanied by urolithiasis, renal failure, glomerulonephritis in any form, cystitis, the urge to decrinate and discharge in the urine with pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, any injuries, as well as malignant tumors and oncology;
- male diseases in the genital area, such as prostate adenoma, prostatitis;
- diseases in the field of female gynecology - uterine bleeding, erosion of the uterus or cervix;
- drug exposure, taking ascorbic acid, methenamine, anticoagulants and sulfonamides;
- any pathologies of the body, heart failure, thrombocytopenia, febrile conditions, hypertension, hemophilia, bacterial and viral intoxication of the body.
More on the topic: Causes of alkaline urine reaction
More generally, the reasons are divided into three categories:
- prerenal or somatic, absolutely not related to the urinary system (thrombocytopenia, hemophilia, toxic damage to the body);
- renal, arising from kidney pathologies and their dysfunction (kidney cancer, the presence of glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, kidney injury and urolithiasis);
- postrenal, directly related to diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, stones and formations in the bladder, trauma, bladder cancer).
Diagnosis of hematuria
If there are elevated red blood cells in the urine, you should consult a urologist as soon as possible. First of all, he analyzes a person’s lifestyle and nutrition. It is important for the doctor to know whether the patient has had scarlet fever, syphilis, typhus, or whether he is developing hemolytic anemia.
The doctor may be interested in the following questions:
- do pain occur during miction;
- how often is blood detected in urine;
- in what portion of urine does blood appear;
- whether blood clots are present;
- whether the patient is taking any medications;
- whether radiation therapy has ever been performed;
- whether the person experiences increased physical or emotional stress.
Tests that the patient needs to undergo:
- general urine analysis;
- urine test according to Nechiporenko;
- microscopy of urinary sediment;
- general blood examination.
Blood and red blood cells in urine - what does this mean?
Based on the state of the red cells themselves in the analyzed urine, one can judge the nature of possible pathologies. It is not uncommon for fresh, undamaged red cells to be found in the test material; they can be combined with the loss of white cells (leukocytes) into the urine. Such indicators are typical for calculus, polypous and cancerous neoplasms, for necrotic damage to structural tissues in the organs of the urinary system.
Damaged, so-called leached red blood cells, are often lost in the urine along with protein, indicating signs of extensive protein loss in the kidneys with the development of nephrotic syndrome. Be evidence of the course of acute or chronic processes of glomerular nephritis, the development of renal hypertension or toxic kidney poisoning.
Of great importance when deciphering a urine test is the color of the urine and the nature of the inclusions in combination with hematuria:
- If the urine is red or brown with the presence of bloody clots, this indicates a high probability of signs of blood disease, kidney bleeding, infection or poisoning.
- Scarlet urine, in combination with a painful syndrome, is evidence of tumor growths, or accumulation of stone formations in the urinary organs.
- Dark, brown color of urine appears due to glomerular nephritis. This can be noticed by the development of swelling, joint pain, and a sharp reduction in urine output.
What to do if red blood cells in urine are elevated?
Even the detection of a small number of red blood cells in the urine should not be ignored. To avoid a false conclusion, it is necessary to do a control analysis, observing all hygienic rules for collecting a sample. If hematuria is confirmed, an ultrasound examination of the urinary system is necessary. And the examination of ureters inaccessible to ultrasound is performed using an x-ray method with a contrast agent.
If a urological cause is not confirmed, it is necessary to conduct a full diagnosis. Only this will give the doctor the opportunity to draw up an effective treatment plan.
You should pay attention to the fact that hematuria cannot be treated on its own. Only additional diagnostic methods will allow the doctor to prevent serious consequences of such seemingly insignificant deviations in urine tests.
Tags:
urinary system analysis
Treatment
Hematuria cannot be eliminated with special therapy. To ensure that the blood in the urine disappears, treatment for the underlying disease is prescribed. If the level of red blood cells in the urine is slightly elevated, treatment may not be required at all.
For cystitis, patients undergo a course of antibiotic treatment. For prostate adenoma in men, the following is used:
- substances that inhibit 5 alpha reductase;
- alpha 1 adrenergic receptor inhibitors.
Therapy for urolithiasis is done using herbal medicine or physiotherapeutic procedures.
Pathology therapy
An increase in leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine is determined by diagnostic methods. For this purpose, a general urine test is always used at the beginning of treatment, since this method of detecting such disorders is the most accessible and informative. It allows you to determine the number of these structures in urine, as well as the presence of other components in it - proteins, bacteria, various salts. You can more accurately determine the number of red blood cells and white blood cells secreted in urine using the Nechiporenko test. By assessing the results of urine tests, the specialist determines the stage and nature of the disease. This further influences the choice of therapeutic tactics.
The main measures for the treatment of pathologies caused by the activity of infectious pathogens have general principles. In almost all cases, patients are prescribed antibacterial agents (Cefixime, Ampicillin). To eliminate concomitant symptoms, analgesics (Baralgin, Revalgin), antispasmodics (Platifillin, No-shpa), and anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac) are used. In special cases, only surgical intervention will help eliminate the cause of the increase in leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine (tumors, urolithiasis). The effectiveness of treatment increases with physiotherapeutic measures.
Patients are advised to follow a special diet during therapy. If a person is found to have an increase in red blood cells and leukocytes in his urine, he should exclude all smoked and salty foods from his daily menu. Excessively fatty or fried foods are not recommended for consumption in such a situation - they should be replaced with dairy products, healthy vegetables and fruits.
Interesting! With this disorder, the patient can also be helped by some alternative medicine recipes. In this case, their use has an anti-inflammatory effect. For this purpose, herbal infusions, decoctions of horsetail and chamomile, birch sap, and cranberry tea are used.
If leukocytes, protein and red blood cells are increased in the urine, such a deviation cannot be ignored! Any change in the composition of the discharge must be carefully studied in order to understand the cause of the violation and eliminate it in a timely manner. Treatment of the pathology is completed only when all urine indicators return to normal. This result indicates the correct choice of treatment tactics and the patient’s complete recovery.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely prevent hematuria, based on the many reasons that contribute to its occurrence. To prevent urinary tract infections you must:
- prevent dehydration by maintaining a drinking regime;
- fight bladder overflow;
- empty the bladder after coitus;
- For women, wipe the anus back away from the vagina to prevent germs from entering the urethra.
To prevent urolithiasis you need:
- drink more water;
- Do not eat many foods containing oxalic acid.
To prevent the development of cancer, it is important to avoid smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Hematuria is not a disease, but a symptom of many pathologies. He should force the patient to see a doctor as quickly as possible. Following the principles of a healthy lifestyle helps prevent kidney and urinary tract diseases.
Research methods
Hematuria in the results of a urine test requires additional research. In this case, it is necessary to do a three-glass analysis, in which 1 stream is collected in the first container, the middle one in the second, and the remainder in the third. An analysis is made of the presence of red blood cells in each of the glasses, and if their excess is found in 1 serving, then this characterizes diseases or pathologies of the urethra.
If an anomaly is detected in the third portion, this indicates a disease of the bladder itself. If the red blood cells in the urine are exceeded in all three glasses, then the ureters are damaged or kidney disease is present.
Exceeding hematuria by more than 1000 units per 1 ml of test fluid using the Nechiporenko method may indicate additional reasons for the appearance of the anomaly:
- unchanged may be combined with an increased number of white blood cells, which indicates cancer or polyps in the bladder or kidneys, possibly the formation of stones, prostate adenoma or necrosis in the kidney tissue;
- altered red blood cells in the urine, leached, often appear along with protein in the fluid, which often occurs with nephrotic syndrome, or with glomerulonephritis in acute or chronic form, toxic nephropathy or renal hypertension;
- if the indicators of erythrocytes and leukocytes are exceeded, in addition, protein appears - this characterizes the presence of inflammatory processes or microtraumas of the mucous membrane of the urethra or ureter. This can happen when stones or sand pass through the urinary tract.
More on the topic: In what cases do bubbles appear in the urine?
Cylinders in general urine analysis - characteristics and norms
The place of formation of the bodies in question are the renal tubules. The structure of these elements may vary, which is determined by the nature of the constituent components: red blood cells, protein, renal tubular cells.
The appearance of the cylinders is also different, due to which they are divided into granular (the basis of the structure is erythrocytes, renal tubular cells), hyaline (the leading role in the structure belongs to renal tubular cells + proteins), erythrocyte, waxy (granular + hyaline bodies), epithelial ( as a consequence of epithelial detachment).
What should be the level of casts in urine in children and adults according to the norms?
The presence of almost all of the above groups of cylinders in the urine is not the norm.
An exception is hyaline casts, the number of which in the urine of men, adults, and children cannot exceed 20 per 1 ml. urine.
Why does the number of casts in urine increase in children or adults - reasons
Factors that provoke the appearance of casts in the urine will depend on the nature of these casts:
Hyaline casts
The source of their formation is protein. Their presence in urine is possible in the following diseases:
Treatment with diuretics.
- Inflammatory phenomena that occur in the kidneys.
- Pathologies in the functioning of the kidneys, which are caused by urolithiasis, malignant tumors, injury.
- High blood pressure.
- Exhausting physical work.
Grainy cylinders
Their formation is associated with deformation of the cells that make up the kidney tissue. There may be several ailments that often provoke the appearance of granular casts in the urine:
- Intoxication due to lead poisoning.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the kidneys.
- Infection of the body.
Waxy cylinders
Their presence is the result of pathologies that deeply affect the kidneys during processes of a chronic, acute nature:
- Renal failure (chronic/acute).
- Malfunctions of the kidneys that are associated with amyloidosis, nephrotic syndrome.
Red blood cell casts
The formation of this type of cylinders is a consequence of numerous penetrations of red blood cells into the renal tubule, which provokes its blockage. The presence of red blood cell casts (even a negligible amount) in the urine is a defective phenomenon that can cause several diseases:
- The presence of blood clots in the cavity of the renal veins.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the kidneys.
- Heart attack/kidney cancer.
Epithelial casts
The presence of epithelial casts in the urine is evidence of serious malfunctions in the kidneys:
- Destruction of kidney tissue.
- Infection of the body.
- Intoxication as a result of poisoning with heavy metals and chemicals.
Salts in general urine analysis - characteristics and norms
When studying urine sediment, the salts present in it will be presented in small crystals. The presence of a limited number of such crystals, in the absence of other errors in the testing, is not always the result of violations, but such phenomena should not be ignored.
What should be the normal level of salt in urine in children and adults?
The presence of these substances in urine, even in small quantities, is not normal.
If crystals are detected in the urine, the doctor must take measures to eliminate this phenomenon: diet, adequate exercise, prescribing diuretics, etc.
Causes of increased salt in urine in children or adults
Often, factors that provoke the appearance of certain groups of salts in the urine are certain foods, drinking insufficient amounts of fluid, and inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system.
The most common types of salts present in urine are urates, oxolates, and phosphates.
Urats
There may be several factors that can provoke the appearance of these salts in urine sediment:
- Excessive consumption of certain foods (mushrooms, meat, fish), drinks (black tea, coffee, cocoa) + insufficient amount of fluid.
- Serious disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys (inflammatory phenomena, renal failure).
- Children under 6 months. This is due to the inability (at this age) of the kidneys to fully perform their functions.
- Gout.
- Excessive fluid loss due to vomiting and diarrhea.
- Increased urine acidity.
Oxalates
Their appearance in urine does not depend on its acidity, and may be due to several reasons:
Inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- The presence of stones in the urinary tract.
- Congenital diseases associated with errors in the metabolism of oxalic acid.
- Diabetes.
- An abundance of foods rich in oxalic acid (beets, sorrel, asparagus, spinach) and vitamin C (red currants, citrus fruits, tomatoes) in the daily diet.
- Chemical poisoning.
Salt crystals (phosphates)
The most popular reason for the appearance of salts of this group in the urine are foods rich in phosphorus (seafood, dairy products, eggs), and gastric lavage.
Other factors (of a pathological nature) that can cause the detection of salt crystals in the urine include:
- Diabetes.
- Constant disruption of bowel function.
- Inflammatory phenomena in the genitourinary organs.
- Liver failure.
What is the normal level of leukocytes in the blood?
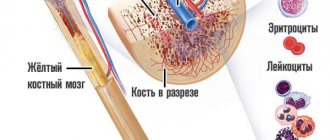
To talk about whether red and white blood cells are elevated in the urine, you should understand what norms for the content of these cells in the blood are acceptable for different age groups. The norm may vary depending on the age of the person being examined, as well as the rate of influx of cells from the bone marrow.
An increase in the leukocyte count above 10*109 indicates the development of a disease such as leukocytosis, and a decrease below 4*109 indicates leukopenia.
Mucus in a general urine test - characteristics and norms
The substance in question is created due to the functioning of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system.
How much mucus should there be in the urine of children and adults according to the norms?
The presence of a small amount of mucus in the urine of children and adults is allowed. If the recorded amount of mucus in the urine is quite extensive, the doctor prescribes repeated testing to eliminate possible errors during the collection of this biological material.
Why is the level of urine mucus increased in children or adults - reasons for deviations from the norm
Due to inflammatory phenomena that occur in the organs of the urinary system and other pathological phenomena, urine stagnation occurs, which provokes increased mucus production. This process complicates the drainage of mucus, which leads to its excretion in the urine.
The most common causes of increased mucus levels in the urine are:
- Venereal diseases.
- Infection of the body.
- Ignoring personal hygiene rules.
- Delaying the process of urination.
- Presence of stones in the urinary organs.
Normal composition of urine
In a healthy person who does not suffer from serious diseases of the internal organs, red blood cells in the urine are within 2-3 cells in the field of view. The rate of red blood cells in the urine does not change, and exceeding the established values is possible only under the influence of one or several negative factors at once.
The norm for leukocytes in men is 3-5 units per field of view. It is important to remember that for women it is not considered a deviation from the norm if the concentration of leukocytes in the urine is 7-8 units in the field of view. It is believed that the female body is more susceptible to hormonal changes that affect the level of these blood cells.
Protein and red blood cells in the urine are the first symptom of serious kidney disease, which developed under the influence of infectious microorganisms, chemicals with toxic properties, or prolonged hypothermia.
At least 97% of the total mass of urine is water, which took part in metabolic processes and blood purification, and the remaining 3% of the biological fluid is organic substances excreted by the kidneys as a result of homeostasis. These biochemical compounds include urea, creatinine, molecules of magnesium, calcium, sodium, potassium, uric acid salts, and protein particles. A small number of epithelial cells may be found shed from the surface layer of the renal tubules and bladder walls.
Bacteria, viral and fungal microorganisms, protein, mucus secretions, sediment and foreign impurities in the form of flakes should not be present in principle. The normal density of urine is 1.010 - 1.025 units. The color of a healthy person's urine is light yellow or bright, but without pink or red. The presence of the latter signs indicates that red blood cells have entered the urine.
What to do?
Even the slightest deviation in the normal level of red blood cells in the urine can indicate a possible disease that should be treated in traditional ways. As a rule, additional diagnostic methods should be used after identifying the results of the analysis. But you should also take into account that a slight increase in the number of red blood cells in the blood may indicate insufficiently good hygiene during the test.
Thus, the deviation in such a case occurs by 2-3 units. And if there are too many red blood cells, then this always indicates a disease that is observed in the body. In this case, additional urine tests are prescribed to identify the disease.
After an additional urine test confirms an increase in red blood cells, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys, as well as other additional examinations that will help determine the disease, based on which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. Typically, this state should not be triggered.
Thus, a person may miss the development of a serious disease, which he will only learn about when it is difficult to treat. Especially timely seeking help from a doctor concerns pregnant women, when the health of the baby completely depends on the expectant mother. Thus, a disease associated with an increase in the level of red blood cells cannot be treated on its own.
Other reasons
In addition to the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system, an increase in leukocytes in human urine can be caused by other reasons.
For example, white blood cells increase during pregnancy, which is completely normal. But if you are pregnant and your red blood cells are elevated, you need to be wary.
During pregnancy, the activity of a woman's hormonal system is activated. Therefore, there is an increase in leukocytes in the urine. However, it should not be high all the time. The norm is only those periods when the level of leukocytes fluctuates, that is, they either decrease or increase. A persistently high level of these cells indicates an infectious disease. Elevated red blood cells and white blood cells in the urine that do not decrease for a long time are a cause for concern.
What are leukocytes?
Leukocytes are formed elements of blood, namely white blood cells that have a nucleus. Their formation occurs in the bone marrow and lymph nodes. The main function of leukocytes is to protect the body from foreign agents. Leukocytes are phagocytically active, and in addition, they participate in the formation of immunity, as well as in the exchange of heparin and histamine, due to which such components of immune reactions as antibody-forming, antimicrobial, antitoxic and others are realized.
What are red blood cells?
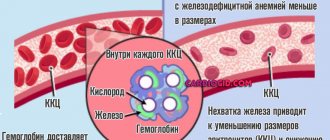
Red blood cells are the main elements of blood, their presence in the blood is significant, but they can also be contained in other formed elements. These blood cells look like a disc, which is slightly thicker at the edges. This structure allows them to easily and quickly pass through the circulatory system.
The task of red blood cells is to saturate organs and cells with oxygen. Their amount in the blood and urine should be normal, and if a person has increased protein, leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine, this may be an indicator of the development of a serious disease, such as pyelonephritis.
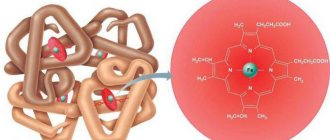
The formation of red blood cells occurs in the bone marrow. They include hemoglobin (two thirds). Each red blood cell functions for one hundred and twenty days.
What does an increase in red blood cells and white blood cells in a woman’s urine indicate?
If a doctor detects increased red and white blood cells in a woman’s urine, he may suspect a disease such as endometriosis. Also, an increase in blood cells sometimes indicates the presence of menstruation. In this case, a more detailed examination of the woman’s genitourinary system may be necessary. If there are no red blood cells in the urine collected with a catheter, this indicates a gynecological disease.
The causes of pathological hematuria are different. It may indicate diseases such as:
- Pyelonephritis, which provokes infection of the kidneys and blood vessels. This is where blood leaks through the urinary tract and walls.
- Kidney tumors that destroy blood vessels and cause bleeding.
- Kidney stones, which have a traumatic effect on organs and blood vessels.
- Glomerulonephritis, in which the organ completely loses its ability to filter substances.
- Hydronephrosis, in which there is stagnation of the excreted fluid in the bladder. The pressure increases, causing bleeding.
- Kidney injuries.
Also, red blood cells, white blood cells and protein in the urine can be increased in diseases of the bladder and urethra. We are talking about such ailments as:
- Cystitis is an infectious disease that affects the bladder, which reduces its strength, which allows blood particles to leak into it.
- Tumor of the urethra and bladder.
- Stones in the urinary canal.
Treatment methods
Therapy for unchanged red blood cells in the urine largely depends on the cause of the pathology. Conventionally, all treatment can be divided into medicinal and surgical.
Drug treatment is used for infectious inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, bladder and urethra. Thus, pyelonephritis, whistitis and urethritis are treated with antibacterial drugs.
For more serious pathologies, surgical intervention is resorted to. For example, the appearance of neoplasms requires their prompt resection. Rapid tumor growth can damage organ function. In this case, it will need to be completely removed.
The presence of unchanged red blood cells in the urine is a versatile symptom that can be a manifestation of many diseases. Therefore, if when urinating you notice a change in the color of the urine or the appearance of fresh blood clots, do not hesitate, consult a specialist!
Rules for collecting urine for laboratory tests
To accurately diagnose the parameters of proteins, red blood cells and leukocytes, there is a preliminary stage of urine collection. During pregnancy, monitoring the amount of protein is necessary; testing is prescribed before each visit to the doctor. To get reliable results follow simple rules:
- The day before the test, you should avoid salty and spicy foods, and do not overuse sweet and sour foods. Following a diet will help establish reliable data.
- To collect urine, use only a sterile jar; special containers can be purchased at pharmacies. If this is not possible, then treat the glass jar with boiling water.
- Urine is collected in the morning after sleep; the collection should not contain impurities.
- Doctors recommend taking a shower before getting ready; this approach will reduce the risk of foreign protein getting in.
- The collected analysis is delivered to the hospital no later than 2 hours after the procedure.
- In cold weather, the flask with urine should be wrapped to prevent it from freezing.
The result of the study allows you to monitor the functioning of the kidneys and bladder. The indicators are especially important for pregnant women, whose fetal development increases the load on the genitourinary system.
Character of red blood cells under microscopy
When performing microscopy, it is possible not only to identify their quantity in urine, but also to determine the shape and integrity of red blood cells. If leached (destroyed) red blood cells are observed in the smear, this indicates the presence of pathology in the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys. Glomerulonephritis leads to impaired filtration of blood in the kidneys, as a result of which red blood cells penetrate through a membrane that is normally impermeable to them and accumulate in urine.
If the red blood cells are of unchanged shape, they are called fresh. Such red blood cells indicate a violation of the integrity along the urogenital tract or cystitis. Fresh red blood cells appear as a result of a violation of the integrity of the vascular wall and the epithelial lining of the ureters, bladder or urethra.
Isolated microhematuria
Isolated microhematuria is a difficult condition to interpret, but is often discovered by chance during a regular preventive medical examination.
In this case, microhematuria can be repeated in each subsequent urine test of the patient (persistent), or disappear periodically (intermittent). In itself, such division of hematuria does not allow us to determine the localization of the pathological focus.
It is more informative to divide microhematuria into symptomatic and asymptomatic (that is, hematuria accompanied by symptoms and without any manifestations).
Criteria for isolated hematuria:
- 1 Urine red blood cells 3-5 in the subcutaneous region, without change in urine color in 2 consecutive urine tests;
- 2 Absence of any complaints from the patient;
- 3 Absence of obvious signs of somatic pathology;
- 4Proteinuria is absent or trace (the amount of protein in the urine ranges from 0.033-0.066 g/l).