A burn is a serious injury caused by exposure to heat, sun, chemicals or electrical current. It causes damage to the skin and can lead to infection and disruption of internal organs. To assess the clinical picture, it is important to correctly determine the degree of burns. The treatment tactics and method of rehabilitation depend on this.
Classification of burns by degree
The list of the international classification of diseases includes burns of varying degrees of severity. They have ICD 10 code T20-T35.
Doctors systematized burn injuries. The most common is the division by depth and type of lesion. There are different types of burns. Among them:
- thermal;
- radial;
- electrical;
- chemical.
Health care providers believe it is important to classify burns according to the extent of injury, which helps determine the level of severity.
First
Diagnosed with minor trauma when the superficial layer of skin is affected. The main causes of this unpleasant phenomenon are:
- ultraviolet;
- contact with hot objects, hot water or steam;
- contact with the body of aggressive chemical elements.
Stage 1 is characterized by a mild course of the disease. In the field of injury, a slight burning sensation occurs. The skin becomes red and swollen. If you touch the damage, the symptoms worsen.
After a few days, the painful symptoms disappear. The tumor is going down. The epidermis begins to peel off. Damaged cells are restored. After recovery, there are no scars left on the body.
Second
The second stage is observed when others are added to the above symptoms, indicating the depth of the lesion.
- Bubbles filled with a cloudy liquid form on the skin, which gradually turns yellow.
- It contains a high percentage of leukocytes, which protect the wound from infection and promote tissue regeneration.
- Blisters cannot be pierced: by violating their integrity, you can provoke the penetration of microbes that cause suppuration.
With a 2nd degree burn, a person feels:
- severe pain;
- burning and itching;
- swelling.
With extensive trauma, body temperature rises and blood microcirculation is disrupted. Such wounds are provoked by prolonged exposure to:
- hot items;
- fire;
- acids and alkalis;
- steam and boiling water;
- sun rays;
- X-ray radiation.
If you follow the specialist’s instructions, the treatment proceeds without complications. The pain gradually disappears, and healthy skin begins to form under the blisters. Within 2 weeks, the redness subsides and the person recovers.
Suppuration prevents wounds from healing and can cause scars and pigmentation.
Third
At grade 3, all layers of the epidermis are affected. The skin dies and a dark scab appears. The affected area becomes inflamed, purple and swollen. There is pain and an unbearable burning sensation.
The third stage is divided into subgroups A and B.
- In grade A, partial damage to the dermis occurs. Hair follicles remain intact. Along with the scab, dense blisters with blood particles may appear. If infection is prevented and proper treatment is carried out, the integrity of the skin is restored in a few weeks.
- In grade B, the epidermis and dermis die. The lesion reaches the fatty tissue. The blood vessels are damaged, the skin looks lumpy and heterogeneous, and becomes covered with scabs and bloody blisters.
Such injury is caused by prolonged exposure to concentrated chemicals, flames, boiling water, and electricity. It brings severe intoxication and fever. The victim needs urgent medical attention and hospital treatment.
Fourth
Stage 4 damage threatens a person’s life. This is a dangerous condition when all layers of the skin are damaged:
- muscle;
- tendons;
- nerve endings;
- capillaries;
- vessels;
- bones.
The body becomes charred and blackened. Dead tissue peels off. Regeneration takes a long time. Various complications arise that complicate therapy.
With a favorable prognosis, rehabilitation is delayed for several months. After healing, deep scars remain on the skin, requiring surgical intervention.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of 3rd degree burns is carried out exclusively in a hospital under the supervision of a specialist.
The consequences of self-medication are too serious to neglect medical help. Scar formation, low joint mobility, incomplete restoration of body functions, the occurrence of sepsis - this is an incomplete list of complications caused by unqualified treatment. Burns of such intensity can lead to disorders of the respiratory, cardiovascular, immune, and endocrine systems, and cause problems with the kidneys, liver, and gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment for 3rd degree burns begins with painkillers. Analgesics in most cases do not provide the patient with relief from pain, so stronger drugs such as Promedol or Morphine are used. However, the use of narcotic drugs can lead to anaphylactic shock, so together with them, the prescription of “Suprastil”, “Diphenhydramine” or other similar antihistamines is required. To relieve inflammatory processes and accelerate skin regeneration, hormonal medications can be prescribed.
Thermal skin damage of the 3rd degree is often accompanied by increased excitability, so the patient must take sedatives and sedatives. In case of intoxication of the body and to prevent dehydration, droppers with appropriate medicinal solutions are prescribed. In some cases, antibiotics or antitetanus serum are additionally prescribed. In addition, the wound is treated with anti-burn drugs, cleansed of mucus, pus and dead skin.
Surgical treatment of burns
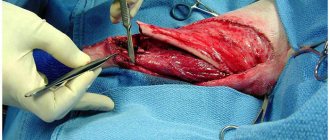
If, with a large area of skin damage, with deep burn wounds, the body’s ability to recover independently may not be enough, despite all therapeutic measures, then only a skin graft or other types of surgical intervention can fully cure a burn. For serious burn skin lesions, several types of operations are performed:
- Decompression surgeries are performed for deep tissue lesions that can lead to subfascial edema.
- Necrectomy cleans the wound of necrotic tissue; amputation of limbs also belongs to this type of operation.
- So that the wound after healing can look as aesthetically pleasing as possible, dermatoplasty is performed to get rid of rough scars and eliminate cosmetic defects.
Determination of severity
The etiology and pathogenesis of the disease depend not only on the severity, but also on the area of affected tissue.
Superficial and deep damage is dangerous. A 1st degree burn, if about 90% of the skin is injured, poses a serious threat to the patient’s life. Various techniques are used to determine the area of injury.
Palm rule
In 1953, scientists calculated that the open palm of an adult corresponded to 0.80 to 1.5% of the body, and began to use this to calculate the area of burn injury. The palm became a unit of measurement. It is equated to 1% of the surface of the human body.
To calculate the area, you need to place your palm on the sore spot. The number of times it is placed on the affected area is the percentage of skin damage.
This method has gained great popularity because it is simple and understandable for ignorant people far from medicine..
Rule of nines
The second common method is the rule of nines. It was proposed in the early fifties by A. Wallace. The scientist's invention provides an approximate calculation of the size of the injury. It is used to determine the severity of the situation in emergency cases.
The essence of the rule of nines is the conditional division of the body into zones, each of which is equal to nine or a multiple of this number from the total area of the skin.
Detailed characteristics of the method can be studied in the table.
| Percentage | Body area |
| 9 | Neck |
| 9 | Head |
| 9 | Hand |
| 9 | Hips |
| 18 | Chest and belly |
| 18 | Upper and lower back |
| 1 | Genitals |
Method of B. N. Postnikov
This system was common many years ago, but is now rarely used . Its use requires complex manipulations.
- First, the victim's body is wrapped in sterile gauze.
- Then the damaged areas are outlined with a special pencil.
- The gauze is carefully removed.
- The outlines of the drawing are transferred to graph paper.
- At the end, the doctor calculates the extent of the damage relative to the entire body.
Method of G. D. Vilyavin
To calculate the burn area, a silhouette of a human figure from the front and back, reduced by 10 times, is drawn on special stamps. The design is applied to a paper square grid. The side of each cell is 5 mm. The pure cells on the stamp are equal to the number of square centimeters of the total surface of the human body.
The cells in the places of injury are painted over with colored pencils in the schematic drawing. A 1st degree burn is shaded with a yellow pencil, a 2nd degree burn with a red pencil, a 3rd degree burn with a blue pencil, and a 4th degree burn with a black pencil.
Using this drawing, the physician determines the area of damaged tissue and the depth of the burn site.
What not to do for burns
When providing first aid, you should adhere to the rules of asepsis. Only sterile dressings are allowed. If it is applied incorrectly and is tightened too tightly, the patient's condition may worsen due to tissue compression.
When relieving their condition, patients most often make the following mistakes:
- Apply ice to the affected area. The consequence of this is frostbite and decreased blood supply to the affected area. For the same reason, you cannot cool the burned surface with frozen foods.
- Apply a rich cream or oil to the damaged skin. They create an airtight film over the affected area, which further increases the temperature in the specified area.
- Use alcohol or vinegar at the burn site. This leads to additional skin irritation.
- Apply urine to the affected area. This liquid irritates the skin even more because it contains salts. In addition, dehydration increases.
A burn may be accompanied by other injuries: dislocations, fractures, which is sometimes not taken into account when the patient is hospitalized.
Absolutely forbidden:
- puncture the resulting blisters, as this can lead to infection of the wound;
- comb the area of injury.
First degree
Surface damage often occurs from contact with hot objects or steam.
- First of all, the surface of the skin needs to be cooled by placing it under a weak stream of running water for 20 minutes. If severe pain is felt after this time, continue cooling until it goes away.
- Then the epidermis should be treated with an antiseptic. You can use Furacilin, a weak solution of manganese, Miramistin.
- If you have wound-healing ointment in your medicine cabinet, you can carefully apply it to the inflammation with a cotton swab, wait 10 minutes for the product to be absorbed, and apply a sterile bandage.
Subsequent treatment consists of regular treatment of the skin with ointments and creams. Doctors recommend Sudocrem, Bepanten, Rescue balm, Dexpanthenol. The dressings should be changed twice a day until recovery.
Second degree
For a second stage burn, the first aid algorithm is as follows:
- interrupt contact with an aggressive substance or a hot object;
- place the affected area under cool water for 20 minutes;
- disinfect the skin with Chlorhexedine or Furacilin;
- apply an anti-burn agent - you can use Panthenol, Levomekol, Olazol;
- cover the burn with a sterile bandage and secure with a bandage;
- take painkillers - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen;
- Consult your doctor regarding further actions.
Antimicrobial and healing ointments are used during the treatment process. Argosulfan, Solcoseryl gel, Dermazin performed well. To stop the inflammatory process, synthomycin and tetracycline ointments are used.
Third degree
If you receive a 3rd degree burn, you must urgently call an ambulance and carry out rescue measures.
- Eliminate the cause of injury.
- Remove damaged clothing from the victim. Do not tear off the adhered pieces of fabric, but cut them around the perimeter with scissors.
- Place the burned limb in a basin of cool water for at least 20 minutes. This will help reduce body temperature and prevent damage to the deeper layers of the skin.
- Apply a dry sterile bandage and wait for the doctor.
It is important for a person to ensure peace. It is advisable to lay it so that the affected area is on an elevated surface. This position ensures normal blood circulation and helps remove toxins from the injured area.
The patient requires plenty of fluids and, if necessary, anti-shock therapy.
At the hospital, a medical history is immediately taken and a diagnosis is carried out. Then the wound is disinfected, a pain-relieving injection is given and a treatment regimen is prescribed aimed at healing wounds, increasing immunity, and supporting cardiac activity.
Fourth degree
Extensive 4th degree burns are extremely dangerous. The person is in a state of shock and may lose consciousness. The patient needs access to fresh air and clean water to drink. You should lay it on its side, raising the affected area. If there is a disturbance in cardiac activity, artificial respiration and chest compressions are required. Cover the wound with a serial dry bandage and wait for the ambulance team.
Recovery from third and fourth degree burns occurs in a hospital setting. The patient requires a ward with a special microclimate, comprehensive care and treatment.
First aid for burns: general rules
When you receive a burn injury, the first thing you need to do is:
- Cool the affected area. It is enough to place it immediately after the injury in cool, but not icy, water. It takes about 10-15 minutes to relieve inflammation and swelling of tissues.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help relieve pain from minor burns. If the lesion is extensive, prescription analgesics are required.
If there is no improvement within a few days after receiving a burn injury and the wound does not heal, you should seek medical help.
After this, it is recommended to apply any medication to the skin that relieves inflammation and accelerates tissue restoration. For this purpose, drugs containing Pantheon or solcoseryl are used. These medications relieve pain and reduce burning sensation.
If there are no medications in your home medicine cabinet, aloe juice, a compress of raw pumpkin or potatoes, as well as raw egg white can help.
If a burning sensation appears in the burn area, it is necessary to take antihistamines.
Hospitalization of the patient is required if the face, eyes, genitals, or area near the joints are damaged. An ambulance is called when the area of the affected area is more than 7 cm or if the victim has difficulty breathing.
With a large number of victims, it should be taken into account that pain decreases with more extensive lesions. Victims may lose consciousness or experience painful shock, so the degree of tissue damage cannot be assessed by behavior. Often, patients who attract attention by shouting require much less assistance compared to those who remain calm.
What burns can be treated at home?
Grade 1 and 2 injuries, when no more than 5% of the skin is affected, can be treated independently at home after consultation with a doctor. If you follow his recommendations, healing occurs quickly and without consequences.
It is worth contacting a medical institution if a person’s condition worsens during therapy: there is an increase in temperature above 38 degrees, swelling and pain do not go away, and signs of infection appear.
To prevent burns, prevention is important. It is necessary to take precautions when working with dangerous objects, boiling water and store aggressive substances in hard-to-reach places.
Symptoms of different types of burns
To be successful and effective, it is necessary to correctly assess the area and depth of tissue damage. A visual examination and subjective sensations of the patient help the doctor determine the type of burn and select the optimal set of treatment measures.
Thus, a 3A degree burn is characterized by prolonged severe pain, since the nerve endings are not affected. The surface of the burned skin has a heterogeneous structure, is burgundy or bright red in color, and numerous blisters filled with liquid are observed along the edges of the wound.
Pain from a 3rd degree burn, type B, disappears after 20-30 minutes. This is due to deeper penetration of thermal energy into the layers of the skin and destruction of nerve cells at the site of the lesion. The blisters are usually covered with a crust, the edges of the wound are framed by hanging areas of skin. During burn shock, the victim experiences a sharp increase in blood pressure, which a little later is replaced by a decrease in levels to critical levels.
Symptoms and periods
How to determine the area of damage to the body? It is calculated by the Postnikov method (to calculate the area, the dimensions of the gauze applied to the wounds are used, the value is expressed in square millimeters), the palm rule (for small injuries) or the rule of nines (the total surface of the body is divided into sections of 9%).
- Rule of nines for burns
Burn disease is divided into periods:
- shock;
- toxemia;
- burn infection (septicemia);
- recovery (convalescence).
The first period can last from several hours to a day and is determined by heart rhythm disturbances, chills, and thirst. During the period of toxemia, protein breakdown and exposure to bacterial toxins occur, with the temperature rising, appetite disappearing, and weakness appearing. A burn infection begins on the tenth day and is characterized by infection of the affected area with depletion of the body, which can lead to death. With positive results of treatment, a period of regeneration and restoration of the body begins.
To prescribe therapeutic measures, establish the scope of treatment, and identify the ability of regeneration without surgical implementation, it is customary to classify burns by severity, localization and area of damage.
Treatment
Inpatient treatment for 3rd degree burns begins with a tetanus vaccination and usually includes the following:
- Anesthesia;
- Application of aseptic dressings;
- Taking antibiotics and bronchodilators;
- Ensuring adequate gas exchange;
- Hormone therapy;
- Infusion detoxification therapy;
- Dehydration therapy;
- Subsequent skin plastic surgery.
Treatment of third degree burns is carried out in a combined manner and involves both open management and the use of bandages. At first, bandages with antiseptic agents and drugs are applied that increase the outflow of fluid from the wound. When the first traces of regeneration appear, which is possible thanks to intact hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands, ointments with reparative properties are applied to the bandages.
Treatment of deep third degree burns is aimed at preventing the formation of rough scars. In cases where tissue regeneration is impossible or the burn is localized to visible parts of the body and in the area of movable joints, skin grafting is recommended. For dermoplasty, both your own perforated and stretched skin flaps and alternative materials can be used: donor skin, xenografts, artificially grown fibroblasts or biological materials containing collagen.
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/eo86CxmsfWI
3rd degree burns represent deep damage to the skin and are characterized by death of the epidermis with complete or partial damage to the dermis. According to the accepted classification, such injuries are divided into two types: burn injuries 3A and 3B degrees. And if with 3A degree burns independent tissue regeneration is possible, then 3B degree burns lead to the formation of rough scars and require surgical intervention.
Tuberculous lupus: causes and factors in the development of the disease, its types, routes of infection, signs of pathology, diagnosis and treatment, preventive measures
Gneiss: causes of development, symptoms and features of the course, diagnosis, treatment and preventive measures
Pyoderma: causes and signs of the disease, classification, diagnostic methods, treatment and prevention
Panaritium - causes and signs of the disease, its signs and types, methods of treatment and prevention
Pityriasis versicolor: causes and signs of the disease, diagnostic methods and treatment methods
Pityriasis rosea or roseola rosea: causes, signs, diagnosis and treatment
Lichen planus: causes and types of disease, methods of diagnosis and treatment, prognosis
Ecthyma: causes and signs of the disease, risk flus, diagnosis and treatment
Melanoma: causes of neoplasm, classification, diagnosis and treatment
Rhinophyma: features and signs of the disease, its causes and forms, diagnosis and treatment
Possible complications
If you managed to avoid a state of shock, you should not calm down too much. With large areas of lesions, other complications may develop. Common consequences of burns include:
- the development of sepsis is typical for lesions with an area of more than 20%. With reduced immunity and wet tissue necrosis, an early stage may develop, accompanied by gastrointestinal pathologies, insufficient functionality of the renal system, and toxic hepatitis. With pulmonary edema and heart failure, there is a high risk of death;
- the development of pneumonia, often occurs with extensive and deep damage;
- the development of burn exhaustion occurs in conditions of ineffectiveness of therapeutic measures. It is characterized by dystrophic changes in all body systems, decreased immunity and metabolic processes.
The consequences of a burn can last for 3 to 4 years. In addition, at the late stage of healing, complications in the form of scars, eczema, dermatitis, nephritis, trophic ulcers and skin cancer are possible.
Tips from folk treasures
It should be noted that folk wisdom a very long time ago adopted the properties of vitamins from groups A, C, B, E, which have a positive effect on accelerating the healing process of wounds. Observation and experience have allowed us to collect many recipes for the treatment of 3rd degree burns in conditions where we have nothing else to use except the healing properties of some products and we cannot use anything else except home methods, as well as find ourselves in other conditions. We can only hope that you will never need our selection of recipes.
- Remove the thorns and skin from an aloe leaf well washed with clean water. Place the resulting pulp on a cotton cloth and apply it to the wound.
- We will need chicken eggs, pre-boiled. Having separated the yolks, fry them in a hot dry frying pan and on a regular sheet of iron, if you can only light an open fire. You fry the prepared raw materials well, and you can do it directly on the flame, if there is no equipment at all (the eggs themselves can also be kept in the coals for 15-20 minutes, instead of boiling them). Then take a clean cloth, preferably gauze or nylon, put the yolks into it and squeeze firmly so that the oil begins to release. The resulting substance is an ideal treatment for skin areas affected by third-degree burns. At home, making butter from egg yolks is generally very simple.
- In this recipe we will need:
- approximately 100 grams of grated peeled potatoes,
- Bee Honey.
Mix the resulting mixture with a teaspoon of unthickened honey. Used as compresses on burned skin areas
Important! Use chilled. Once the mixture has warmed up, it should be replaced with fresh
Therefore, we advise you to prepare the composition in the quantity you need. But keep in mind that peeled potato mixture tends to darken, and this should not be allowed.
The easiest way for which we will need strong, fresh brewed black or green tea. Therefore, it is recommended that five to seven minutes after pouring boiling water, forcefully cool it to about 15 degrees C. This can be done in the chamber of a regular household refrigerator, in a container with cold water, or in the cellar. Snow is great in winter. Water the resulting mixture or gently blot the affected areas. Quickly relieves pain when treating 3rd degree burns. Can be used both at home and in camping and field conditions. This remedy should be prepared in advance and kept in the refrigerator just in case. Its composition will not cost you much, so the annual update of such a medicine is completely invisible to the budget, but it can come in very handy in an unpleasant situation. Freshly cut St. John's wort inflorescences should be infused for three weeks in twice the amount of vegetable or olive oil. As an ointment for the treatment of 3rd degree burns, it is suitable for use at home and is recommended by doctors. If you receive a 3rd degree burn, you need to start preventing it and prepare for treatment immediately. If very little time has passed since you received it, the consequences can be reduced by using sour cream or any fermented milk products on hand. It has been noted that in this way it is possible to reduce the level of pain at home even before using other potent medications. If possible, try to take products with the highest fat content.
What is a thermal burn and what are its features?
These types of damage occur when the skin is exposed to high temperatures. This type of burn is quite easy to get if you are not careful when dealing with high temperatures. Children are especially susceptible to such injuries, but even adult men and women are not always careful and attentive.
Regarding complications, children and the elderly are most susceptible to them, while young and middle-aged people, on the contrary, more easily endure injuries. So, if with a thermal burn in children, complications can appear if 5 percent of the body is damaged, then in adults they can only appear if the damage is more than 20 percent of the body surface, but if the injuries are deep, then 10 may be enough to disrupt the functioning of internal organs. percent.
For pregnant women, receiving thermal burns can harm not only herself, but also the fetus, so it is strongly recommended that treatment be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Depending on what caused the damage, a burn has its own distinctive features. For example, an injury received from contact with boiling water is visually very different from that received from fire.
Further treatment in children and adults
The third degree involves surgical intervention - skin transplantation from healthy areas to affected tissue. Surgeries may also be aimed at preventing further spread of infection. The patient is prescribed treatment with hormonal, antihistamine, painkillers, and sedatives. If visible areas of the body, such as the face, are damaged due to injury, the patient is then advised to undergo surgical interventions to eliminate cosmetic defects.
If necessary, under anesthesia, the blisters are opened and dead tissue is removed. Independently replacing medications prescribed by doctors can cause undesirable consequences.
Hospitalization of children should be carried out if there is already a suspicion of stage 2, since the protective forces of the child’s skin are much more delicate and thinner. Parents cannot always assess the severity of injuries. Providing medical care for children is mandatory, and parental negligence can be fatal.