During accidents, emergencies and natural disasters, people get injured. Most often these are fractures, which are accompanied by blood loss and painful shock. The success of further treatment largely depends on how timely and correctly first aid was provided for open and closed fractures.
Guidelines and a poster about fractures on the stand are available after the article.
Basics of first aid
Immobilization is achieved by applying medical splints or those made from materials available at hand. As such, it is permissible to use anything straight and strong, such as a stick, cane or skis. Small boards or plywood are also suitable for this.
Splints should be applied not only to the outer, but also to the inner plane of the injured limb. It is important that they provide complete immobilization of the two joints that are adjacent to the fracture area.
If splints are applied to a bare surface, they should be:
- cover with cotton wool or other soft materials;
- secure using a bandage, towel, thin scarf or belt. They should not dangle; it is important to attach them very firmly and securely.
For those who are faced with an open fracture, first of all, using a tourniquet, it is necessary to stop the bleeding, after which a bandage is applied to the wound. It is mandatory not only to disinfect the wound with iodine, brilliant green and even alcohol, but also to apply a pressure bandage or tourniquet. This will make it possible to avoid blood loss, the consequences of which can be no less serious than as a result of an open fracture.
Then the victim needs to take a painkiller (analgin, tempalgin) and ensure that the limb or part of the body is immobilized. If, upon a quick examination, it is impossible to distinguish dislocations or bruises from bone fractures, then assistance should be provided in the same way as for a fracture.
It would be wrong to make independent attempts to correct the position of a bone that has been damaged. Moreover, it is forbidden to set protruding bone fragments into the wound itself. Only professionals know how to do this correctly and with minimal harm to the victim.
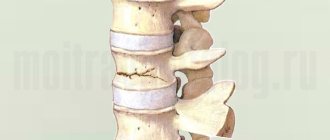
What to do if your spine is broken
Such injuries are among the most severe and can pose a threat to the life of the victim. It is necessary to immobilize the body as quickly as possible and fix it in one position.
If it turns out that the spine is broken, the sequence of actions will be as follows:
- The person is carefully lifted and transferred to any hard surface - a bed, couch, flat floor. Several people should do this, preferably three or four. The coordination of the assistants’ actions is very important; jerking and sudden movements are not allowed.
- The patient lies on his back, he is tied with belts, ropes or bandages to avoid displacement of bone fragments.
- A person should be placed on a stretcher face down, that is, on his stomach, but if a neck fracture is suspected, he is left lying on his back.
- If there are signs of a fracture of the pelvic bones, the legs are spread apart, like a frog.
REFERENCE: You cannot carry or shift a person unless absolutely necessary. These functions should be entrusted to doctors. The exception is in emergency cases when leaving the injury at the scene threatens life - for example, in case of a fire or earthquake.
For fractures of the cervical vertebrae, you need to make a tight and high collar to fix the neck. For this, a thick towel, gauze or fabric in which cotton wool is wrapped in a layer of 2-3 cm is suitable. The width of the collar should correspond to the height of the neck. To secure it, you can use Velcro, paper clips, clips, etc.
Transporting a victim with a fractured cervical vertebrae is a very responsible undertaking that requires at least 3 people
If a person is lying on his back, the collar cannot be put on, since it cannot be moved. In this case, a towel or other fabric rolled up in several layers is placed under the back of the head. Then two rolls are also twisted from a towel or gauze and placed on the sides of the head. To prevent them from moving, you can place books or other heavy objects next to the rollers.
Brief statistics on bone damage
More often, fractures occur in boys and young men. Representatives of the stronger sex work in industries where there is a risk of injury, drink alcoholic beverages more often, which is associated with drunken fights and drunk driving, and love extreme sports. Most often, men experience dislocations and fractures of the limbs (first aid should be provided immediately), ribs and bones of the facial part of the skull.
In women, due to osteoporosis that develops with age, the risk of injury increases by the age of 45-50. In addition to menopause, pregnancy and breastfeeding are dangerous periods, when the body experiences calcium deficiency, the center of gravity shifts, and visibility is limited by a large belly.
Similar injuries are also common in childhood. Fractures account for up to 20% of all injuries in children, who are by nature active, active and inquisitive.
Treatment
This type of fracture can only be treated in a hospital under the supervision of doctors. Due to the complexity, the period of time may drag on indefinitely. It all depends on the patient’s age, his immunity and the location of the fracture itself.
The first task of doctors is to prevent inflammation of the damaged area and the formation of suppuration in the soft tissues. For this, 3 methods are used:
- Immobilization method. Used in the treatment of fractures of the leg or shoulder.
- Extension method. A tension device is installed to align parts of the bone when they are displaced.
- Operative method. Used for fractures with a large number of fragments.
Principles of first aid (FAM)
Providing first aid for signs of a shoulder fracture involves the use of fixation of the damaged joint. For this purpose, a cotton swab is placed in the armpit area under the injured arm, securing it with a bandage through the area above the healthy shoulder. In this case, the arm should be pulled back slightly at the shoulder joint and bent at the elbow at a right angle.
To fix the fingers in a bent state, a rag roller is placed in the victim’s palm. Then a splint is applied using the traditional method, only the part on the shoulder is longer. After all, the damaged limb is securely attached to the body with a bandage.
Help depends on the cause of the injury, the nature of the injury, location and severity, but there are general rules that can be used regardless of the type of fracture:
- First aid for fractures begins with immediately calling an ambulance. During the conversation, you should clarify to the dispatcher about the general health of the victim, the approximate nature of the injury and the presence of bleeding. Thanks to such information, the operator will be able to understand the essence of the problem and send a group of doctors with the most appropriate equipment and drugs to provide medical care and subsequent hospitalization of the patient;
- if there is severe pain, the victim must be provided with any non-narcotic pain reliever to which he has access;
- Under no circumstances should you try to change the location of the victim without first fixing the injured bone in one position;
- in the event that it is impossible to do without transporting the patient, you need to help ensure that the load on the damaged area is minimal, there is no pain, and the fixator does not come into contact with the skin of the victim;
- Never try to compare displaced fragments yourself; this should be done by a qualified specialist, otherwise you may contribute to the emergence of many unpleasant complications.
First aid for bone fractures consists of treating the wound with antiseptics, pain relief and immobilization of the injured part of the body (transport immobilization). A wound is formed during open fractures, when the sharp edges of bone fragments break the integrity of the skin and come out. Such skin defects are susceptible to infection, which causes purulent complications in the form of osteomyelitis, phlegmon, and sepsis. The edges of the wound must be treated with a solution of brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide, iodine and a sterile gauze bandage applied.
It is forbidden to force bone fragments into the wound yourself. This will damage soft tissues and cause painful shock in the victim. If external bleeding occurs, apply a pressure bandage or a medical tourniquet. Arterial bleeding is characterized by a gushing stream of bright red blood.
In this case, the tourniquet is applied above the injury site. Bleeding from a vein is accompanied by the flow of a sluggish stream of dark cherry-colored blood, while a pressure bandage is applied below the site of the damaged vessel. Closed fractures are usually accompanied by internal bleeding. In such cases, an ice pack should be applied to the site of hematoma formation.
Cramer splint is used to immobilize limbs
We suggest you read: How to develop an arm after a fracture of the humerus at home
To reduce the intensity of pain, analgesics are given - ketorolac, maxicold, pentalgin. After treating the wound, stopping bleeding from the damaged vessel and anesthesia, they begin to apply splints to immobilize the deformed bones. Transport immobilization is an important part of first aid for fractures.
For transport immobilization, standard medical splints or devices made from scrap materials are used. Standard medical splints are in the arsenal of first-aid posts, emergency rooms, and ambulance teams. When providing emergency assistance, non-professionals often have to use improvised tires made from branches, ski poles, cardboard, skis, and planks.
More article: Displaced clavicle fracture and its treatment
Types of standard tires:
- plywood (Diterichs tires);
- wire (Kramer tires);
- vacuum (pneumatic).
Standard and improvised splints are placed over clothing, and soft pads are placed under the protrusions of the bones. If it is necessary to treat the wound, the clothing is cut over the skin defect. The basic principle of immobilization is the immobilization of two joints adjacent to the site of injury. After first aid is provided, the victim is taken to the emergency room in a half-sitting or lying position, depending on the location of the injury.
Comminuted rib fractures pose a risk of damage to the lungs and pleura. If the patient is not hospitalized correctly in the emergency room, pneumothorox may occur - accumulation of air in the pleural cavity or hemothorox - accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity. This impairs breathing and leads to deterioration of cardiac function.
Therefore, rib fractures require the application of a rigid circular bandage to the chest area. Bandaging is carried out while exhaling. After applying the bandage, the victim breathes using abdominal breathing. This eliminates pain and the risk of complications. For immobilization, you can use a sheet, bandage, towel and other available materials.
Position of the patient for hospitalization in case of a fracture of the pelvic bones
Proper first aid for spinal column fractures helps prevent disability. Spinal trauma carries the risk of damage to the spinal cord, which can lead to impaired movement (paresis) below the fracture site or complete immobilization (paralysis). The patient is transported to the hospital on a solid stretcher or board.
It is necessary to transfer the victim onto a stretcher with the help of several people who simultaneously support the shoulders, pelvis and legs of the injured person. Rigid cushions are placed under the neck, lower back and knees to maintain the physiological position of the spinal column. During long-term transportation, the patient is firmly fixed on the board.
First aid for bone fractures consists of anesthesia, stopping bleeding, treating the wound and providing transport immobilization. Correct provision of first aid prevents the development of hemorrhagic shock due to blood loss, painful shock as a result of soft tissue injury from sharp edges of bone fragments, damage to the spinal cord and the formation of paralysis.
If the bones of the forearm are damaged, then the limb at the elbow joint should be bent at an angle of 90 °C and pressed with the palm of the hand to the body. The splint must be of such length that any of its ends wraps around the fingers, and the next one reaches the elbow joint. In the presented position, the splint must be secured with a bandage, and the limb must be suspended either on a homemade bandage.
If the humerus is fractured, the forearm area will also need to be bent at an angle of 90 °C at the elbow joint.
Two splints are applied to the damaged shoulder bone:
- the first from the outer plane of the shoulder;
- the second - from the cavity of the armpit to the joint in the elbow area.
After this, each of the splints is first individually bandaged to the shoulder and then connected together. The forearm bent in this way should be hung on a wide belt or scarf. If a special splint or other similar means are not available, then it is recommended to hang the limb bent at the elbow on a scarf or belt and only then bandage it to the body.
The person is transported strictly in a sitting position so that there is no impact on the limb. The same is true for fractures of the collarbone and scapula. So, if the collarbone is broken, then a ball of cotton wool should be placed in the hollow of the armpit on the side that is injured. Next, the shoulder is firmly bandaged to the body. If we talk about the forearm, then it would be most correct to hang it on one scarf, with the help of which the limb is also tied to the body
To apply a splint bandage in case of a hip fracture, you need to have at least two large splints. The first of them is applied to the outer plane of the leg, with one of its ends located under the armpit. The second is to slightly protrude beyond the foot area. It is important that the second splint is applied strictly along the inner plane of the leg so that one end reaches the perineum, while the other protrudes beyond the foot itself. In this position, the splints must be bandaged to the body.
When special splints or similar devices are not available, the injured limb must be bandaged to the uninjured leg. In case of a tibia fracture, first aid is provided in the same way as for a hip injury.
A characteristic feature of pelvic bone fractures is that internal organs are damaged, and therefore bleeding and shock are likely. The victim’s pelvic bones should be placed in a position that will create a minimum of pain.
Most often this is:
- in a horizontal position on your back with a bolster under your feet;
- your hips should be slightly apart.
The cushion can be made from a pillow, outer or warm clothing, or any other fairly soft material. The victim can be transported only on a hard board or board. It would be best to carry out various anti-shock measures before this, for example, relieving pain or stopping bleeding.
One of the most common types of fractures is a leg injury. First aid consists of tying the injured limb to the uninjured leg. Preferably in a supine position to minimize movement. In this case, areas not only above, but also below the damage must be involved.
Diagnostics and therapy
There are several methods for determining a closed fracture. After first aid has been provided, the doctor collects the patient’s medical history; this is necessary to determine the cause of the injury and its nature. Next comes palpation - thanks to this method, the traumatologist determines the presence of bone fragments and whether they are displaced.
To make an accurate diagnosis, radiography is prescribed in two projections. After the specialist examines the images and confirms the diagnosis, the necessary therapy will be prescribed.
For complex fractures, diagnostic tools such as CT, arthroscopy and ultrasound are used.
Treatment of closed fractures begins with the provision of primary care. After this, the doctor prescribes treatment. The main treatment methods consist of:
- Conservative therapy.
- Surgical intervention.
What method the traumatologist will use to treat a closed fracture depends on which bone was broken.
If the medical indications of the victim indicate that the bone injury is of mild severity without displacement or the patient is not allowed to undergo surgery, then conservative treatment is used for therapy. With this method, bone repositioning is performed followed by fixation. The procedure is performed using local anesthesia.
After the reposition has been completed, plaster and other special fixing bandages are applied to the damaged area. For a crushed fracture, skeletal traction is used. The duration of therapy is controlled by a doctor.
The operational method is more effective. This treatment method is preferred for severe fractures, when it is necessary to use special means to secure the bones.
The basis of surgical intervention is that metal objects are introduced into bone fragments - knitting needles, pins, plates, screws, nails.
Some patients are prescribed bone grafting and endoprosthetics. In order for the bones to heal well, stimulation with anabolic hormones, mumiyo and an electromagnetic field is used.
There are absolute and relative signs of a fracture, which are important for diagnosis both at the time of injury and already in the hospital. Relative signs are necessary to suspect a fracture, and absolute signs help make an accurate diagnosis.
Relative signs:
- pain,
- swelling,
- hematomas,
- Impaired bone function, such as the inability to put weight on a broken leg.
Absolute signs:
- unnatural deformation of a limb,
- pathological mobility (in places where there are no joints),
- presence of signs of fracture on x-ray.
The complexity of a closed fracture is assessed by the general condition of the victim, the nature and type of bone damage. For example, a multiple fracture of the spine will always be more severe than a simple fracture of the little finger.
It is important! To exclude diagnostic error, usually radiography should be done in two projections, comparing with symmetrical intact bones (right rib with left rib of the same order, both legs, arms, etc.).
General symptoms
Fractures occur when a significant force is applied to the bone, exceeding the ultimate strength of the bone tissue. They can be both traumatic and pathological. In the first case, injury occurs during an impact, during a traffic accident or during a fall from a great height, when the traumatic factor affects a healthy bone.
We suggest you read: Treatment of a fracture at home
In the second case, bone deformation occurs under the influence of a slight force of a traumatic agent on a pathologically altered musculoskeletal system by various diseases, for example, osteoporosis, tuberculosis, and tumor. Pathological fractures are much less common than traumatic bone defects.
Depending on the severity, fractures are divided into several types:
- open – characterized by damage to the outer skin with the formation of a wound and or a skin defect with sharp bone fragments (you can read more about open fractures here);
- closed with displacement of bone fragments - a change in the anatomically correct position of bone fragments, which can injure the surrounding soft tissues, without damaging the external integument;
- closed without displacement of bone fragments - characterized by cracks in the bone tissue, the anatomical position of the bone and the integrity of the skin are preserved (you can read more about closed fractures here).
Intra-articular fractures are considered a special type of injury. They are accompanied by defects in the bone tissue that forms the joint. Such damage is characterized by the accumulation of bloody exudate in the joint cavity (hemarthrosis). They are difficult to diagnose without X-ray examination.
From left to right, an intra-articular open and closed fracture is shown.
Clinical manifestations of a fracture:
- intense pain in the area of injury;
- violation of the normal configuration of the limb;
- swelling of the injury site;
- lengthening or shortening of arms, legs;
- crepitus when palpating the injury site;
- impaired mobility of the affected part of the body or limb.
With open bone injuries, external bleeding often develops due to damage to an arterial or venous vessel. Closed bone injuries may be accompanied by internal bleeding of varying severity with the formation of hematomas.
When a shoulder is fractured, a Cramer's ladder splint is used, which is placed from the shoulder blade on the healthy half of the body to the middle of the forearm of the affected arm. At the same time, the shoulder and elbow joints are immobilized. The splint is modeled on oneself by the person who provides assistance to the victim, and then attaches the device to the affected limb using bandages.
Application of improvised splints: a – for a fractured shoulder, b – for a fractured forearm
The fracture of the forearm bones is immobilized using two wooden splints, which immobilize the elbow and wrist joints. After this, the arm is suspended on a scarf in a physiological position, bent at an angle of 90 degrees at the elbow joint. In the absence of splints, the arm with a fracture of the shoulder or forearm is bandaged to the body.
Emergency care for clavicle fractures requires immobilization of the arm on the affected side, which is suspended in a scarf. During long-term transportation to the hospital, a figure-eight bandage is applied - the forearms are pulled back as much as possible and fixed in this position with an elastic bandage or thick fabric. If fingers are broken, use a tight bandage or bandage the injured finger to a healthy one.
If the bones of the leg and foot are fractured, a Cramer's ladder splint is applied to the back and lateral surfaces of the leg, while the back splint captures the sole of the foot. The device is tightly bandaged to the lower limb, immobilizing the knee and ankle joint. Instead of standard devices, you can use improvised materials - boards, thick cardboard, sticks.
Application of a Dietirchs splint for a hip fracture
The hip fracture is immobilized with a Ditirichs splint, which is a set of plywood boards. The long part of the splint is applied to the outer surface of the leg up to the armpit. A short splint is placed on the inside of the leg from the foot to the groin area. In this case, three joints are immobilized - ankle, knee and hip, which is associated with the significant size of the thigh and the risk of damage to large arterial vessels and nerves.
When the toes are fractured, the injured toe is bandaged to the healthy one, placing a soft cushion between them. Victims with pelvic trauma are hospitalized in the trauma department on a rigid stretcher lying on their back. To reduce pain, the patient’s legs are slightly bent in ruts and spread apart, and a cushion of clothing is placed under the knee joints.
First aid for broken limbs largely depends on the nature of the injury. There are several criteria for dividing fractures into groups:
- Reason for occurrence: traumatic (caused by external influence) or pathological (internal factors contributed to the fracture: complications of various diseases, deficiency of certain vitamins and minerals)
- By severity: fractures are classified as displaced, when bone fragments can injure surrounding tissues, or without displacement, if bone fragments are held by muscles and tendons. There are also incomplete fractures, which are called chips or cracks.
- In terms of the integrity of the skin: an open fracture is characterized by a superficial wound, while in a closed fracture the bone fragments do not communicate with the external environment.
- According to the shape and direction of damage: helical, straight, longitudinal, oblique and transverse fractures.
If fractures of the limb bones occur, first aid can halve the likelihood of complications, and in some cases even save lives. The main thing is that all activities are carried out correctly and in a timely manner.
First aid for limb fractures includes a number of measures aimed at determining the type of fracture (the actions of the person providing first aid vary depending on what they are dealing with - an open or closed fracture, whether there is pain shock accompanying the injury, etc. complications) and directly providing the necessary assistance. Afterwards, you should take the victim to the hospital or ensure that doctors arrive at the scene of the incident.
How is first aid provided for broken limbs? In general, assistance is provided as follows:
- It is necessary to give an objective assessment of the victim’s condition, make sure that there is a fracture and determine the further course of action. First aid for limb fractures is carried out only if the patient is already safe.
- If the victim is unconscious and not breathing, the first step is to carry out resuscitation measures and bring him to his senses.
- For open fractures, you must first stop the bleeding and treat the wound with an antiseptic to avoid infection; if possible, it is advisable to apply a sterile bandage.
- If medications are available, you should numb the injured limb by injecting ketorolac (1 ampoule), novocaine (5 ml) or another suitable remedy.
- It is necessary to immobilize the limb and call an ambulance. In some cases, it is possible to independently deliver the victim to a medical facility.
We invite you to read: Closed fracture - first aid for a closed fracture and precautions, difference from an open fracture, main signs of a closed fracture
First aid for broken limbs is provided only if you are convinced that the victim received a fracture and not another type of injury. So, the absolute signs of a limb fracture are:
- visible deformation of the damaged area;
- in some cases - impossibility of movement;
- increased mobility, unnatural position of the arm/leg (or parts thereof);
- superficial wound and visible bone fragments in an open fracture;
- characteristic crunch at the moment of impact.
Relative signs of a fracture, i.e. symptoms that in some cases may accompany other injuries, are:
- pain in the damaged area, which intensifies during movement;
- hematoma, and throbbing pain indicates that internal bleeding continues;
- swelling and swelling in the area of injury, which can develop within 15 minutes after the fracture;
- limited mobility, the damaged limb, as a rule, does not function at all or partially.
First aid for limb fractures involves immobilizing the damaged area of the bone. The immobility of a limb can be ensured in several ways: tying the damaged lower limb to a healthy one, fixing it with improvised means, or bandaging a broken arm to the body.
When immobilizing, several rules and requirements should be taken into account:
- the splint must immobilize at least two joints to prevent additional damage to soft tissues from bone fragments;
- the size of the fixing splint should be comparable to the damaged area;
- Immobilization is usually carried out over clothing and shoes, but it is worth removing bulky items from the victim;
- First aid for fractures of the upper extremities (as well as the lower ones) is provided, if possible, with an assistant.
After carrying out all the necessary measures to provide first aid, you should definitely call an ambulance. The victim will require qualified medical assistance and care.
When applying transport splints to the lower limb, the leg should be in a straight position, and the foot should be at a right angle to the lower leg.
Shin
In case of injury to the bones of the lower leg, 2 adjacent joints are attached: the ankle with the foot and the knee. Moreover, the latter is fixed in an extended position, and the foot is attached to the lower leg at a right angle.
When transporting to a medical facility, a splint is applied from the upper third of the thigh to the fingers. They use cardboard, plywood, and strips of iron. First you need to cover the splint with foam rubber or cotton wool, bandage it to the injured limb with bandages, strips of rubber or cloth. If there is nothing at hand, then you need to bandage the injured leg to a healthy limb as a splint.
Signs of a closed fracture
The main symptoms of a closed fracture:
- bone deformation,
- the limb may be in an unnatural position,
- strong pain,
- there is no violation of the integrity of the skin at the fracture site,
- violation of the amplitude of habitual movements,
- on an x-ray, computed tomography or MRI - the presence of fragments, cracks, impacted bones, etc.
In addition, you may experience:
- pain shock,
- slight increase in temperature,
- signs of blood loss - weakness, dizziness, pallor, hematoma formation,
- in the area of the fracture - swelling,
- if nerves, ligaments, or muscles are damaged, sensitivity and the ability to make movements are impaired.
Note! Sometimes a closed fracture looks more like a dislocation or just a severe bruise, so in all doubtful cases, you need to take an x-ray and show the victim to a specialist.
Experts divide the signs of a closed bone fracture into relative and absolute. If the signs are absolute, no additional diagnostics are required. Relative signs are not enough to accurately determine a closed fracture.
Relative signs are the following symptoms:
- Pain increases with any movement.
- Severe pain at the time of injury.
- A sign of a fracture is the formation of swelling in the area of injury within 30 minutes.
- In the tissues surrounding the fracture, hemorrhages appear, turning into hematomas.
- The injured limb or part of the body partially or completely loses mobility.
An absolute sign can be considered:
- When moving or palpating, an obvious crunching or crepitation is heard.
- The limb begins to move abnormally.
- One of the symptoms of a fracture is deformation of the limbs.
With a closed limb injury, the main symptoms indicating the presence of this injury are the following indicators:
- When moving, loading or at the moment of palpation, the pain syndrome intensifies at the site of injury.
- The injured area is greatly deformed - if legs and arms are broken, they lengthen and change shape; if there is an injury in another place, protrusion of the bones is observed.
- Motor activity is significantly reduced - a patient with fractures can practically not perform usual functions, and with severe fractures the victim cannot move at all.
- Hematomas – internal bleeding manifests itself in the form of a bruise or hematoma.
- Swelling appears in the damaged area - this occurs due to problems in the functioning of the lymphatic system and local microcirculation.
- Hemarthrosis – occurs after injury to joints and ligaments.
- Crepitation - a damaged bone produces a characteristic crunching sound during movement.
Now that most of the main signs of this fracture are known, you can familiarize yourself with what to do with a closed fracture.
Assessing the victim's condition
First aid for an open fracture of a limb, closed injury, cracks or other injuries involves examining the victim, assessing his condition and the situation around the scene of the incident. If danger is still present, people should be evacuated to a safe place and only then begin providing first aid.
The victim must be examined for the presence of additional damage, bleeding, potential injuries, check the basic indicators of vital functions: the presence and frequency of pulse and breathing, the ability to respond to external stimuli (light, sound). If the person is conscious, you should establish contact with the victim, ask about complaints, location and nature of pain.
What is important is that it is unacceptable to move the victim unless absolutely necessary and without applying transport splints to the injured limb.
First aid for broken limbs involves bringing a person to consciousness and carrying out resuscitation measures if necessary. So, you should provide the victim with peace and try to bring the person to consciousness with the help of external stimuli - patting the cheeks, cold water or cotton wool soaked in ammonia and brought to the nose.
Healing
Fracture healing and complete recovery are divided into 4 stages:
- Preparatory stage - at this time the blood coagulates and forms clots that smooth the edges of the debris.
- The formation of new tissue from which future bone callus will be formed. It keeps parts of the bone from moving further.
- Ossification. A few weeks after the incident, the new connective tissue hardens. During this period, it becomes denser, with an increased concentration of calcium.
- Formation of a complete bone callus.
The volume of the callus is usually larger than the bone itself, but after some time it becomes smaller. Physiotherapy helps speed up this process.
Once the broken bone has healed, it is worth taking additional rehabilitation courses. They include: massages, physiotherapy, relaxation therapy. In this way, the period of complete recovery will be significantly reduced, and soon the patient will again begin to lead a full lifestyle.
Resuscitation measures
If there is no breathing or pulse, it is necessary to perform artificial respiration and cardiac massage. For successful resuscitation measures, the victim must lie on a hard surface. With one hand you should grab your chin, with the other you should pinch your nose. The victim's head is slightly tilted back, the mouth should be open.
The person providing assistance takes a deep breath and then exhales smoothly, tightly covering the victim’s mouth. Artificial respiration should be carried out through a napkin or a special device. Exhale into the victim’s mouth should be done every four seconds until spontaneous breathing is restored.
Indirect cardiac massage is carried out as follows: the person providing first aid places his hands crosswise on the victim’s chest and applies pressure (the chest should drop four to five centimeters). You should do 30 pushes, and then change compression to ventilation. Resuscitation measures are carried out in a ratio of thirty pushes to two breaths.
First aid for pelvic fractures
A fall from a height, an accident or an impact can cause a fracture of the pelvic bone. First aid in this case is provided before the arrival of the emergency medical service team. To do this you need:
- Take measures to prevent traumatic shock.
- Place the victim on a hard surface.
- Give your body a “frog” position. Bend your legs at an angle of 450 at the knees and hip joints, slightly apart to the sides. Place a soft cushion of clothing or blanket under your feet.
If necessary, a person can be transported in the “frog” position to a medical facility.
As is the case with other fractures, it is necessary to monitor physiological indicators, monitor the pulse rate and breathing. You need to talk to the victim, try to calm him down, and if he loses consciousness, turn his head to the side to prevent asphyxia from vomit.
Stopping bleeding and treating the wound
Providing first aid for an open fracture of the limbs involves stopping the bleeding and treating the wound. Firstly, the limb should be given the correct position and freed from clothing, since increasing swelling in the future may not allow this to be done. Next, you need to apply a tourniquet or tight bandage to the wound (preferably sterile) and treat the edges of the damaged skin with a disinfectant. Be sure to record the exact time the bandage was applied.
You can give the victim an analgesic to relieve pain. Analgin, paracetamol, Nurofen, Ketorol and the like are suitable. In a hospital setting, if necessary, stronger narcotic painkillers can be used. These include Fentanyl, Nalbuphine or Promedrol.
First aid for a skull fracture
During various accidents, fractures of the skull bones are possible, but at first it is difficult to understand whether the brain is damaged. Therefore, the victim must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible.
The sequence of care for a skull fracture is as follows:
- To create immobility of the head, use a cotton-gauze bag, a sling-shaped bandage or handy means (clothing, a blanket), forming them into a cushion around the head.
- If a person is unconscious, empty the oral cavity of vomit and begin resuscitation measures.
- To normalize heart function, if possible, give an infusion of Corvalol (up to 20 drops).
If the wound is in the back of the head or the victim is unconscious, he must be transported on his side. This position will prevent the development of suffocation due to vomit or retraction of the tongue.
If the victim has a fracture of the nasal bones, he must be transported in a “half-sitting” position. If the jaw is broken - in a sitting position, and for those who have lost consciousness - lying on their stomach. In case of a fracture, the lower jaw is immobilized with a sling-shaped bandage, and if the upper jaw is broken, a ruler or a piece of plywood is inserted between the jaws, which is fixed to the head.
First aid for fractures
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of the patient usually involves a long period of restoration of motor functions of the leg.
Massage is definitely included in the list of rehabilitation procedures after a fracture.
For this, the patient is shown the following procedures:
- Physiotherapy. Includes attending sessions of shock wave, laser, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and quartz treatment;
- Massage;
- Physiotherapy. Helps develop muscles and eliminate stiffness of movement.
All these procedures improve blood circulation and metabolism in damaged tissues, and also help enhance regeneration. However, for a noticeable positive effect, the patient must take the procedures in courses, at least 8-12 sessions from each prescribed type of treatment.
An immobilizing plaster cast or splint after fusion of the seam is worn for 2.5-3 months. After its removal, periodic use of an orthopedic bandage and special shoes is recommended for the next 1.5 months.
The load on the injured leg should increase gradually. However, this can be done no earlier than 6 months after the injury has healed.
How to distinguish from a bruise
In order to distinguish a fracture from a bruise, you need to pay attention to several key points:
- a bruise is just damage to soft tissue, and with a fracture, the integrity of the bone is disrupted;
- if soft tissues are damaged, the pain will gradually decrease, and if there is a fracture, it will be felt for quite a long time;
- these two injuries are accompanied by similar symptoms, so it is better to entrust their differentiation to a specialist;
- a fracture is characterized by the appearance of an unnatural position of the limb and a decrease in the normal range of movements;
- when a typical bone crunch (crepitus) appears, a fracture can be confirmed;
- treatment of bruises can be carried out without medical assistance, and for the rehabilitation of patients with a fracture, immobilization is mandatory.
Clinical manifestations
It is quite simple to determine the presence of an open leg fracture by the symptoms accompanying the injury. The main sign of damage is the presence of a bleeding wound, from which part of the broken bone is visible.
An open fracture is also accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Swelling of the leg and the appearance of an extensive hematoma;
- Severe sharp pain that intensifies when trying to move the injured limb;
- The mobility of the leg at the site of the bone fracture is unnatural.
In the case when an open fracture is accompanied by displacement of the damaged bone, the leg may become deformed, twisted and visually shortened.
General features of an open fracture
Open fractures are injuries to the bones of the skeleton, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin and underlying soft tissue, where the fracture area communicates with the external environment.
An open fracture is considered a complex injury, since such injuries increase the risk of infection of parts of the bone with microbial flora.
This is what distinguishes open and closed limb fractures. Characteristic of an open fracture is exposed bone, which significantly complicates treatment, as well as crushing and detachment of soft tissue in the area of damage, which increases the risk of an infectious process. When an open fracture occurs, bleeding and shock are considered life-threatening.
Consequences
If first aid was not provided on time, and the victim ended up in the hospital late to prescribe a course of treatment, irreversible consequences are possible. In the future, they will cause discomfort to the victim throughout his life.
If first aid was provided later than 6-8 hours after injury, sepsis or blood poisoning may develop.
If soil gets into the wound, it can lead to tetanus. Then, during surgery, the contaminated areas will be eliminated. Sometimes in such situations, muscles and even tendons can be removed to save the patient’s life. Then the person faces disability and complete or partial loss of ability to work.
An open fracture can happen to anyone and can have a wide variety of complications and consequences. First aid and prompt transportation of the patient to the hospital will help not only prevent many unpleasant factors, but also speed up full recovery and soon forget about what happened.
Complications
Complications of an open leg fracture include the following pathologies:
- Limited limb movements;
- Low sensitivity of the leg;
- Shortening or lengthening of a limb;
- Leg deformity;
- Lameness;
- Frequent pain in the limbs;
- Suppuration.
The most dangerous complications include an inflammatory process with suppuration in bone and muscle tissue. If this pathology is not treated in a timely manner, there is a risk of destruction and necrotization of the bone, as well as blood poisoning with subsequent amputation of the limb.
General information
A displaced fracture is a fracture in which the normal location of the fragments is disrupted. Displacement occurs due to traumatic effects or due to muscle traction. It can form on any part of any bone, it is almost always observed in fractures of the diaphysis of long tubular bones, and is often detected in intra-articular and periarticular injuries.
Displaced fractures can be either isolated or multiple. Often diagnosed as part of a combined injury (polytrauma), they can be combined with blunt abdominal trauma, head injury, kidney damage, chest injury, bladder rupture and other traumatic injuries. Sometimes they are complicated by compression or disruption of the integrity of nerves and blood vessels. Displaced fractures are treated by orthopedic traumatologists.
Basic methods of immobilizing fragments
It is necessary to immobilize the damage in any case. To do this, taking into account the indications, you should choose:
- plaster cast;
- skeletal traction;
- primary, delayed internal osteosynthesis with metal structures;
- external osteosynthesis with an external fixation device.
The plaster cast has good hygroscopicity, is suitable as a means of fixation for seriously ill patients, does not require technical skills, and allows gradual loading of the injured limb. However, the cast immobilizes adjacent joints and may compress the limb in the cast.
Skeletal traction allows you to observe the limb and make dressings. If there was an open fracture with displacement, then it is traction that allows the displaced fragments to be reduced. But this method of immobilization requires bed rest; the rest of the limb is not complete; it requires monitoring and adjustment. Osteosynthesis is performed for oblique, helical, comminuted, difficult-to-hold fractures, as well as for double and multiple fractures.