Hydronephrosis of the kidneys: what is it?
What is kidney disease hydronephrosis? Hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney or renal hydronephrosis is a serious pathology consisting in increased fluid content in both or one kidney. The normal outflow of urine is disrupted, and this leads to inflammation of the renal tissue - parenchyma, followed by its atrophy and deterioration of the filtering and excretory function of the kidney.
As a result of this, partial, and then, as the disease progresses, complete renal failure may occur.
In medical practice, hydronephrosis of the right and left kidneys occurs equally often. As for bilateral hydronephrosis, it is recorded in 5-9% of identified cases. Hydronephrosis can be not only congenital, but also acquired. Moreover, congenital hydronephrosis occurs against the background of urinary tract dyskinesia, an anomaly in the placement of the renal artery (possibly its branches), which compresses the ureter.
Why does hydronephrosis of the right kidney occur?
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis consists of 2 parts “hydro” and “nephro”. “Hydro” can be deciphered as “water”, “nephro” is translated as “kidney”.
The whole paradox is that during the disease, the concentration of fluid in the kidneys is infinitely high, and the outflow of urine from the organs is disrupted.
Anyone who has encountered this dangerous pathology at least once in their life, or those who have already contracted it, needs to understand the nature and causes of the disease.
Find out which physiological processes fail during the rapid development of pathology.
Average statistical calculations by scientists have provided information that a lot of fluid passes through the kidneys per day - about 2 thousand liters.
All this liquid is transformed into 1.5-2.5 liters of urine, along with which harmful wastes, toxins, and even salts are removed from the body. People in the age group of 18-45 years are most susceptible to the disease.
Hydronephrosis is a serious pathology, which, depending on its origin, can be:
- Congenital. Incorrect placement of arteries in the kidneys is the main stumbling block due to which the organ cannot function in infants. This is the main ambush, as a result of which the organ compresses the ureter, causing stagnation of urine. The list of congenital renal anomalies includes dyskinesia, urinary tract obstruction, and stricture.
- Acquired. Some renal pathologies will provoke the occurrence of others. The occurrence of hydronephrosis often provokes stagnation of urine in the kidneys. Against the background of the acquired disease, cicatricial narrowings, chronic inflammatory renal processes develop, and damage to the spinal cord occurs.
Hydronephrosis is an “insidious thief of health” that rapidly develops, despite any obstacles.
Provoking factors for the development of pathology:
- Urolithiasis. It causes blockage of the ducts, which leads to the development of hydronephrosis.
- Presence of an accessory artery in the kidneys.
- Anomalies of the ureter, which are characterized by narrowing of its lumen.
- The presence of cancerous formations, which are a harbinger of compression of the ureter. A complete outflow of urine cannot occur.
- The presence of relapses that occurred due to surgery.
All these factors influence complexly. But the mix of these reasons with an unhealthy lifestyle creates a similar pathology.
Causes of hydronephrosis
The disease develops due to a violation or absolute cessation of the movement of urine from the kidney to the bladder, which occurs due to a number of physiological or anatomical factors. The disease can also be caused by an accessory renal vessel passing to the bottom of the kidney from the aorta. This additional vessel crosses the ureter and puts pressure on it, which leads to narrowing.
The factor that provokes the development of kidney hydronephrosis is an obstacle to the natural outflow of urine from the organ. The reason for this may be any pathological process occurring both in the kidney and outside it - in nearby organs and tissues:
- stricture (narrowing) of the urinary tract,
- congenital or acquired nature;
- various stones in the genitourinary system;
- benign neoplasms;
- malignant tumors;
- retroperitoneal fibrosis.
As a result of urinary retention and expansion of the calyces and pelvis of the kidney, the parenchyma and muscle fibers of the organ atrophy. This leads to deterioration of kidney function, up to complete loss of function.
Depending on the causes of the development of the disease, its forms are distinguished:
- Congenital – hydronephrosis develops in utero or immediately after birth.
- Acquired – hydronephrosis appears as a result of damage to a previously healthy kidney.
The acquired form of hydronephrosis can have both anatomical causes of impaired urine outflow from the renal pelvis, and physiological ones (arising against the background of diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system).
In total, there are five main groups of pathological conditions that create mechanical obstacles of an anatomical nature in the urinary system:
- Thickening of the walls of the ureter or pelvis as a result of tumors.
- The presence of tumors in surrounding organs and tissues that compress the ureter, kidney or urethra.
- Violation of the normal location of the ureter or kidney (prolapse of the kidney, bending or torsion of the ureter).
- Blocking of the internal lumen of the ureter and pelvis with formed kidney stones.
- Compression or damage to the lower organs of the urinary system as a result of cancer and other diseases or injuries.
Quite often, women experience hydronephrosis during pregnancy. Its cause is mechanical compression of the ureter and other organs of the urinary system by the enlarged uterus.
Stages of pathology
Depending on the underlying cause, primary and secondary renal hydronephrosis are distinguished. That is, diseases can be congenital (due to the presence of a developmental abnormality) or acquired (the result of nephrolithiasis, traumatic exposure or tumor disease) etiology. Both types can be aseptic even in the presence of infection.
During kidney hydronephrosis, several stages are distinguished (according to N.A. Lopatkin’s classification):
- I – predominant damage to the pelvis with insignificant initial processes in the renal parenchyma – pyelectasia;
- II – involvement in pathological changes in the calyces and a decrease in the amount of parenchyma – hydrocalycosis;
- III – significant atrophy of the parenchyma; at this stage, the organ essentially looks like a bag.
The mechanisms underlying obstructive uropathy are the same and are not determined by a specific factor. In all stages, except for terminal function, the organs are preserved, but not in full. There is a lag between the processes of reabsorption and secretion, which determines stagnation in the underlying tissue. The transformation affects first the medulla, then the cortex. Significant changes also occur in the vascular apparatus of the kidney.
Degrees of the disease
Doctors distinguish several degrees of development of this disease, which have individual characteristics.
| 1st degree | the first degree of hydronephrosis is characterized by: slight accumulation of urine in the pelvis, slight stretching of the walls of the pelvis, kidney functionality is not impaired; |
| 2nd degree | for the second degree of kidney hydronephrosis: due to excessive stretching of the pelvis, the organ tissue becomes thin and the functionality of the kidney suffers. If kidney hydronephrosis is present in only one organ, then the main burden of work falls on the healthy one; |
| 3rd degree | in the third degree of hydronephrosis, it is noted: the diseased kidney completely stops functioning, the healthy organ experiences excessive stress, which causes kidney failure. With such symptoms, without proper treatment, renal hydronephrosis can be fatal. |
Hydronephrosis is also classified according to the type of development. If the disease is complicated by an associated infection, then it proceeds according to the infected type. If not, such a disease proceeds aseptically, the symptoms in these two cases will be slightly different.
General information about the disease
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney is one of the most common diseases in urologists. The disease develops according to several “scenarios” and can become a sign of abnormalities in the structure of the organ or acquired changes leading to impaired urine outflow.
If you understand the anatomical features of the kidney structure, the disease occurs due to narrowing of the ureter and accumulation of excess urine in the kidney. This happens because the outflow of fluid is disrupted. Difficulty in excreting urine leads to the development of hydronephrosis.
The pathological process also develops if the outflow of urine is disrupted due to blockage of the ureter by a calculus. The stone blocks the ureter partially or completely, thereby impairing the flow of urine.
Urine accumulates, expansion of the pelvis is observed, which leads to the appearance of characteristic signs.
Nominally, hydronephrosis is considered a harmless disease; it rarely leads to the development of complications, but it all depends on what led to the narrowing of the ureter and the appearance of arterial stenosis.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis
In the photo on the left there is a healthy kidney, and on the right there is hydronephrosis.
Often the development of kidney hydronephrosis occurs unnoticed. The disease has no specific symptoms. In the early stages, the clinical picture is determined by the cause that caused the development of hydronephrosis. For example, with urolithiasis, attacks of renal colic may occur, characterized by severe acute pain along the ureters.
As the pathology progresses, the patient complains of the following problems:
- dull pain in the lower back,
- independent of the time of day and body position;
- painful sensations are most clearly manifested in the area of the affected kidney: if the left side of the lower back hurts, then the left kidney is affected and vice versa;
- in some cases, pain appears in the right side of the abdomen;
- often painful sensations are accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
If renal hydronephrosis progresses and there is no treatment, then the following symptoms of hydronephrosis appear:
- pronounced pain from the problematic kidney;
- a painful attack is accompanied by nausea, and in some cases, vomiting;
- blood pressure increases;
- flatulence increases, the patient complains of discomfort due to bloating;
- when infection penetrates the kidney, body temperature rises - the most dangerous sign;
- there is blood in the urine - this applies to those patients who have been diagnosed with urolithiasis.
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney is one of the most common complications of urolithiasis, which can also occur on the right. Hydronephrosis of the left kidney increases the internal pressure of the calyces and pelvis. The walls of these organs “fight” high pressure for some time. Unable to withstand the pressure, the pressure gradually acts on the kidney itself, which in turn prevents urine from being released. This process can affect the tissue of the left kidney. The tubules and glomeruli atrophy and shrink. As a result, the layer of the organ in which urine was formed decreases.
The first symptoms of urinary stagnation are: acute pain in the lateral abdomen, radiating to the leg on the affected side. If hydronephrosis of the left kidney is observed, the pain will radiate to the back area.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis of the left kidney:
- pain in the kidneys, intensifying towards the damaged area;
- nervous overexcitation, anxiety;
- symptoms of intoxication of the body with nitrogenous products - loss of appetite, dizziness, migraines, vomiting and nausea, insomnia;
- back pain that radiates to the groin and under the shoulder blades;
- pain in the abdomen (stretching of the walls of the ureter due to the size of the stone);
- small amount of urine excreted per day.
- There may also be a small amount of mucus and blood when urinating.
If the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner, as well as unqualified treatment, the tissue of the left kidney can be severely damaged. This process leads to partial loss of organ functionality or even complete loss of the ability to perform its functions.
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney must be treated. If this is not done, kidney failure may develop. Stopping kidney function can lead to intoxication and result in the death of the patient. Another possible outcome is urolithiasis, which can be made worse by infection. The most common complication in this case is cup rupture.
Depending on the level at which the long-term blockage occurred, hydronephrosis of the right kidney occurs with various symptoms. The most common cause is urolithiasis. Urinary stones, larger in size than the natural tracts of the excretory system, get stuck in places of narrowing, and therefore completely or partially disrupt the outflow of urine.
Symptoms and signs:
- At the initial stage of the disease, a person usually complains of renal colic; In the evening, as a rule, there is a dull pain in the lumbar region, which goes away by night.
- Attacks can be caused by physical exertion or general fatigue.
- The presence of blood in the urine is observed with increased pressure in the calyces, as well as with the presence of kidney stones.
- Another characteristic sign is an enlarged kidney. In people with an asthenic physique, it can even be felt through the anterior wall of the abdomen.
Most cases of hydronephrosis (more than half) are left-sided; in approximately 40% of cases, the pathology affects the right kidney and only 5% of hydronephrotic transformation is bilateral.
Characteristic symptoms and clinical signs
The symptoms of right-sided hydronephrosis can be multifaceted, and everything depends directly on the stage of the disease.
At the initial stages of development of the pathology, the symptoms are not bright, in other cases they may be completely absent, which is a call to delay diagnosing the pathology.
In the initial stages, the pathology is almost asymptomatic, and it can make itself felt when a person is mentally and physically exhausted.
The terminal stage is characterized by severe impairment of kidney function. With urolithiasis, the patient may inevitably suffer from attacks of renal colic.
This disease is hidden under the mask of nagging pain in the lumbar region.
The patient experiences classic symptoms:
- Aching, nagging, unbearable pain, which can be of varying degrees of intensity depending on the position the patient takes and how great his activity is;
- Increased pain threshold - mainly in the afternoon, at night this pain transforms into a quieter, less noticeable manifestation;
- An increase in size of the organ, the doctor determines this by palpation;
- With right-sided hydronephrosis, symptoms similar to cholecystitis are observed, the pain is intense, the pain is localized in the right side of the abdomen, the patient complains of excessive bloating, diarrhea, and the urge to vomit;
- Urine mixed with blood acquires a cloudy, golden hue, which should arouse suspicion in the patient and become a reason to immediately contact the right address - a urologist.
Complications
A dangerous complication of hydronephrotic transformation is renal failure and atrophy. Due to changes in tissues, the kidney loses its functionality, and death occurs from intoxication of metabolic products.
Due to renal dysfunction, the content of residual nitrogen and other substances in the blood that are normally excreted through the kidneys in the urine increases.
To avoid fatal intoxication, patients are advised to remove the affected organ, after which patients undergo hemodialysis with an artificial kidney machine or receive an organ transplant from a donor.
Treatment
With hydronephrosis, the main goal of treatment is to preserve the functional ability of the kidneys by eliminating the cause of the disease. The development of complications in the form of episodes of pyelonephritis should not be allowed. For this, patients are prescribed antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, leflobact, amoxiclav, ceftriaxone) and herbal preparations (urolesan, cystone, canephron). The duration of treatment depends on the stage and results of examination during therapy.
The drugs eliminate the main manifestations of pathology, which significantly reduce the standard of living of patients. Pain is the leading symptom. To get rid of unpleasant sensations, use drugs from the group of analgesics and antispasmodics (analgin, baralgin, spasmalin, halidor, no-spa, papaverine, atropine).
You can improve the flow of urine from the bladder with the help of alpha-blockers (omnic, doxazosin, focusin). As a rule, the prescription of these drugs is justified in the presence of bladder outlet obstruction, that is, an obstruction localized in the bladder cavity.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the doctor can preliminarily diagnose hydronephrosis through palpation. There is compaction in the area of the organ. The patient's symptoms and general health are also taken into account.
Ultrasound of the kidneys for hydronephrosis
To make an accurate diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- X-ray examination of the kidneys.
- If the results of previous examinations are equivocal, the patient may be referred for an MRI or CT scan.
Hardware diagnostic methods help determine and compare on which side kidney damage is present or predominant. Thus, hydronephrosis of the right kidney has a larger size of the pelvic region compared to the healthy left kidney. Or vice versa, hydronephrosis of the left kidney has a larger pelvis compared to the right kidney.
There are also many additional methods by which pathology is detected. But they are not that common. The appropriateness of using one or another individually or many in combination is determined by the attending physician.
Life forecast
The prognosis after treatment will always depend on how early the disease was detected and how quickly treatment was started. In advanced stages, when atrophic changes have already occurred in the parenchyma, the restored flow of urine through the affected area may no longer help restore the lost functionality of the kidney.
Important! If an ultrasound showed an increase in the calyces or pelvis, an urgent consultation with a professional - a urologist or nephrologist - is necessary.
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney during pregnancy significantly complicates its course, the birth process and the postpartum period. The prognosis with timely treatment is favorable.
The outcome of the disease in patients with hydronephrosis of the right kidney, if it is diagnosed in time and the operation is carried out successfully, has a positive result, which occurs in 90 percent of cases.
Treatment of kidney hydronephrosis
The course of treatment that the doctor will select has three directions: relieving symptoms, eliminating the cause and reducing the load on the kidneys. The goal of treatment for hydronephrosis is to:
- remove accumulated urine and reduce the pressure it puts on the kidneys;
- prevent irreversible deformation;
- eliminate the cause that caused hydronephrosis.
Drug treatment
Often the use of medications precedes surgery. At this stage, the symptoms of hydronephrosis are eliminated, urination is stimulated, and side pathological processes, for example, foci of infection, are removed.
The doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- painkillers – to relieve pain in the patient;
- antibiotics – if there are signs of infection in the body;
- drugs that lower blood pressure; anti-inflammatory drugs;
- other medications, depending on the patient's symptoms.
Operation
If the condition of the kidney worsens over time, then treatment of hydronephrosis with surgical intervention is necessary.
There are two types of operations aimed at improving function in hydronephrosis:
- creation of an additional channel for urine output,
- narrowing of the dilated pyelocaliceal system of the kidney.
As a rule, radical surgery is preceded by drainage of the kidney. They are also used to treat hydronephrosis during pregnancy, which is caused by compression of the ureter by the growing uterus.
| Type of operation | Brief description and features |
| Anderson-Hines operation | Open surgery is performed on adults and children. Effective in narrowing the area of the ureter near the kidney. Performed under general anesthesia. Complications are observed in 10% of patients. |
| Bougienage | An endoscopic method of surgical intervention based on the introduction of special rods - bougies - into the ureter. Used to dilate the ureter. |
| Balloon dilatation | Under X-ray control, a special balloon with markers is inserted into the ureter. The doctor expands the area with the stricture by applying pressure, and the contrast agent enters the ureter. The operation is performed endoscopically. |
| Endotomy | A modern and most effective method of endoscopic surgery for renal hydronephrosis. It is based on the use of electric current of the required frequency, laser radiation or a “cold knife”. |
| Laparoscopic surgery | It is performed under general anesthesia. The doctor will make 4-5 punctures (ports) in the abdominal wall. Endoscopic equipment is inserted into one, and special surgical instruments are inserted into the others. The operation involves a low degree of tissue trauma and sutures are usually not required. |
| Nephrectomy | It is carried out as a last resort in case of unilateral hydronephrosis (affecting only the left or right kidney). The indication for kidney removal is complete atrophy of its parenchyma. |
Causes
The main cause of hydronephrosis is the presence of an obstruction to the outflow of urine from the kidneys, which can be localized in any part of the urinary tract. More often it is located at the junction of the pelvis and the ureter. Sometimes obstructions occur along the urethra or bladder.
The most common causes of pathology are the following diseases:
- Urolithiasis, stones of the pelvis, ureter, bladder, urethra,
- pyelonephritis,
- large prostate adenoma,
- cancer, prostate tuberculosis,
- tumors of the urinary system,
- chronic cystitis with damage to the ureteric orifices,
- metastatic lesions of the lymph nodes of the retroperitoneal space,
- some inflammatory bowel diseases,
- iatrogenic injuries after surgical, urological and gynecological interventions in the pelvis,
- accessory vessel of the kidney, which can block the flow of urine,
- consequences of radiation therapy,
- abnormal development of the ureters, their kinks, diverticulitis,
- hypotonicity of the urinary system,
- underdevelopment of the muscular apparatus of the ureters,
- megaureter (wide ureter),
- high discharge of the ureter from the pelvis, etc.
Separately, it is worth highlighting hydronephrosis of the kidneys during pregnancy. More often it occurs on the right side, which is caused by compression of the ureter by the pregnant uterus.
Diet
Diet plays an important role in treatment. The diet is prescribed by a doctor individually. The diet should be such as to help restore the flow of urine and kidneys.
The following foods should be excluded from the daily diet:
- salty;
- fat;
- smoked;
- sweets;
- alcohol;
- fried meat and spicy dishes.
Instead, the diet should include the following:
- vegetables and fruits;
- dairy products;
- proteins.
This diet, combined with proper treatment, gives positive results. By the way, diet can help improve metabolism, which is beneficial for the whole body.
Nutritional features and therapeutic diet
Doctors require switching to a balanced and high-calorie diet, including enough amino acids and vitamins.
As with other kidney diets, the menu is selected to reduce the load on the kidneys.
Only then will they be able to perform functions and use their reserves of strength to fight hydronephrosis naturally. It is important to exclude the consumption of dangerous microelements from the diet.
The attending physician can correctly create a menu, taking into account:
- Presence of swelling;
- Arterial pressure;
- General state;
- Accompanying illnesses;
- Urine tests;
- The effect of medications taken.
Nephrologists pay attention to 2 important elements that can aggravate the patient’s condition with hydronephrosis:
- Protein. Its processing requires serious work from the kidneys. Violation of the excretory function does not allow the body to get rid of toxins remaining as a result of metabolic processes. But the complete exclusion of protein foods causes even greater harm to a person. Recovery (especially in old age) is long and associated with many problems. Doctors agree that patients should focus on easily digestible proteins (lean meat, dairy products) and limit their daily dose to 0.5 grams per kilogram of body weight.
- Salt. In each specific case, the norms of its daily consumption are calculated individually.
Patients with hydronephrosis need nutrition that promotes urine excretion, so their diet should include fasting days with:
- Compote diet: compotes from fresh berries or fruit are prepared by adding sugar (drink every 3 hours);
- Fruit diet: every 3 hours eat 300 grams of fresh fruit (particular preference is given to watermelon);
- Vegetable diet: all 5 meals during the day are replaced with a 300 gram portion of salads.
List of harmful and healthy foods
Each patient who wants to restore health must give up various broths, chocolate, legumes, fatty meats and fish, canned foods, carbonated drinks and alcohol.
For successful treatment you need to prepare dishes from vegetables. Spinach, pumpkin and cauliflower are healthy.
It is useful to include rice and buckwheat porridge in the menu. It will be cooked in water or milk with the addition of pieces of pumpkin and fruit.
Lean meat, fish and poultry remain in the diet only if they are served boiled. Sugar in reasonable quantities and dairy products are not prohibited.
Diet taking into account concomitant disease
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys is accompanied by other pathologies of the organ.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, adjustments are made to his menu:
- Combination with pyelonephritis during an exacerbation. The consumption of fresh berries and fruits is increasing. The amount of liquid you drink per day is at least 2 liters.
- Combination with uremia. The emphasis is on the consumption of baked potatoes and eggs. Protein and sodium intake are kept to a minimum. High blood pressure requires complete exclusion of salt during treatment.
- Development against the background of kidney stones. You need to drink plenty of fluids.
- With phosphaturia, it is necessary to limit the consumption of fruits and dairy products due to the high calcium content and alkalizing effect. Increased urine acidity is achieved by eating cereals, bread with lean meat.
- With uraturia, foods that are sources of purines are prohibited. Their most prominent representatives are coffee, cheese, and poultry.
- For oxaluria, reduce calcium intake with ascorbic acid. Chocolate, milk, legumes, and sorrel are subject to serious restrictions.
Kidney hydronephrosis is a dangerous pathology. Following a diet for kidney hydronephrosis can reduce the rate of its progression, reduce the damage caused, and help the body recover during and after therapy.
How to treat hydronephrosis with folk remedies
Traditional methods are recommended to be used as additional to the main drug treatment after consultation with the attending physician. In this case, one kidney must be healthy.
Treatment with folk remedies involves the use of various herbs and medicinal preparations that improve kidney function and alleviate the condition of patients with hydronephrosis. For this purpose the following is used:
- Pumpkin, namely the stalks. To prepare the medicine, the stalks are crushed, 500 ml of boiled water is poured in and infused in a water bath for 20 minutes. After this, the infusion must be removed, wrapped in a warm towel and left for about 2 hours. Take 4 times a day, half a glass per dose.
- 150 gr. birch leaves, 50 gr. nettle leaves, 50 gr. Adonis herbs, 50 gr. oat grains, 50 gr. bearberry and 50 gr. horsetail.
- In equal proportions take black currant leaves, raspberry leaves, calamus roots, kidney tea, string grass, chamomile flowers.
- Herbs for hydronephrosis are used in the form of preparations, which are recommended to be used for no longer than 3-4 months. It is necessary to change fees, after each course, waiting approximately 2 weeks. Plant infusions are taken on an empty stomach, approximately half an hour before meals.
- Chopped parsley root, 1 tbsp. l., pour 100 ml of boiling water. The product is infused all night. Carefully drain the liquid in the morning and drink 1 tbsp. l. on an empty stomach during the same day. If it is not possible to purchase plant roots, you can also use seeds. However, they give a less pronounced positive result. In the same way, you can prepare infusions for hydronephrosis from caraway seeds.
Clinical picture of the disease
Often, signs of hydronephrosis do not appear at all and the pathology is detected as an accidental finding. Only at the early stage of the disease, when blockage of the urinary tract suddenly occurs, do symptoms similar to renal colic develop. These include:
- severe pain in the lumbar region on the affected side,
- weakness,
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain,
- urinary disorders (cramping, frequent urge),
- blood in the urine,
- chills,
- increase in body temperature.
Blood is a characteristic sign of hydronephrosis. It is released when intrapelvic pressure drops due to a short-term restoration of urine outflow. The pain is intermittent. As the body adapts to new pathological conditions, the symptom subsides until it disappears completely.
Signs of intoxication of the body occur if an infection occurs. In this case, pyelonephritis develops with its characteristic symptoms: fever, weakness, pain when urinating, etc. The further course of renal hydronephrosis inevitably leads to renal failure with its characteristic symptoms of uremia, which include:
- Lack of appetite,
- bitterness in the mouth,
- unpleasant odor from the mouth,
- nausea, vomiting after eating, loose stools,
- drowsiness, apathy,
- dry skin, itching,
- decreased visual acuity, etc.
In order not to lead to renal failure, it is necessary to eliminate hydronephrosis in a timely manner.
Prevention
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys, if acquired, occurs only under certain conditions. Doctors recommend adhering to the following preventive measures to avoid its development:
- empty the bladder in time - frequent artificial retention of urine can lead to some of it spilling back into the pelvis;
- limit the consumption of salt and water - a violation of the salt and water balance leads to excessive production of urine in the kidneys;
- Avoid hypothermia - this can provoke the development of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
Treatment of hydronephrosis occurring after surgery
Hydronephrosis that occurs after surgery is treated with the mandatory use of medications. The patient is vulnerable to attacks of infection and pain.
He is prescribed analgesics, and, if necessary, narcotic substances, and given antibiotic therapy.
In case of uncomplicated hydronephrosis of the first degree, the patient should be treated conservatively with constant monitoring by a specialist. An important condition for this is normal kidney function and the patient’s well-being.
If necessary, surgery is performed. A special indication for surgical treatment is a high risk of developing a urinary tract infection or kidney failure, and unbearable pain.
Doctors try to use the laparoscopic method so as not to create additional stress on an already weakened body. Thanks to this approach, it is possible to avoid the development of inflammatory processes in the postoperative period.
Complications and prognosis
The prognosis for treatment of hydronephrosis is determined by a specialist individually. Operations aimed at eliminating obstructions to the outflow of urine are successful only in half of the cases.
In 10–18% of cases, the narrowing of the ureter forms again.
The prognosis for life with a unilateral process is favorable, since one healthy kidney can completely cleanse the body of waste and toxins. With bilateral hydronephrosis, the prognosis is serious. The following complications often develop:
- renal failure,
- formation of stones in a kidney affected by hydronephrosis,
- bleeding after surgery,
- repeated narrowing of the ureter after the intervention.
Who should I contact and how to diagnose?
If pathological changes appear, you should contact a nephrologist. But since the pathological process develops too quickly, it is better to call an ambulance, the doctors will take the patient to the intensive care unit.
The disease can be diagnosed using a number of diagnostic procedures:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and ureters;
- extensive urography;
- urine analysis for biochemistry and tank culture (if urine is passed).
In most cases, an ultrasound scan of the urinary system is performed on an emergency basis. This study will be sufficient to make a diagnosis. Less commonly, an MRI or CT scan is required. Only if there are signs of urolithiasis.
Degrees of hydronephrosis
ICD-10 code: N13
Taking into account atrophic processes in the kidney parenchyma, 4 degrees are distinguished:
• hydronephrosis 1st degree: no changes in the structure of the renal parenchyma; • hydronephrosis 2 degrees: damage is minor; • grade 3 hydronephrosis: pronounced changes in the structure of the parenchyma, • grade 4 hydronephrosis: kidney function is lost, the parenchyma is completely destroyed.
Hydronephrosis during pregnancy
During pregnancy, pathology develops due to compression of the ureter by the growing uterus. Hydronephrosis of the right kidney in pregnant women develops more often than the left, this is due to the peculiarities of the change in the position of the internal organs. The condition is often transient and the first-time disorders disappear on their own after childbirth. True hydronephrosis in pregnancy is not an indication for termination of pregnancy. To facilitate the outflow of urine and eliminate pain, the knee-elbow position is recommended 5-6 times a day for 10-15 minutes and herbal remedies, for example, Canephron.
The knee-elbow position during pregnancy helps improve urine flow and reduce stress on the kidneys
Chronic hydronephrosis, which existed in a woman before, can worsen during pregnancy and lead to serious complications, including rupture of the thinned wall of the renal pelvis or atrophy of the parenchyma with the development of renal failure.
The question of the possibility of pregnancy in chronic hydronephrosis is decided by specialists on an individual basis, taking into account the preservation of renal functions.
Video: hydronephrosis during pregnancy
Classification of hydronephrosis
First of all, it is worth noting that hydronephrosis can be a congenital or acquired pathology. Congenital hydronephrosis is caused by various changes in the anatomical structure of the structures or vessels of the kidney itself. In children, only congenital forms of this disease are diagnosed and they speak of primary hydronephrosis. Secondary forms of this pathology arise as a consequence of inflammatory processes of various etiologies in the urinary system and other diseases (prostate adenoma, prostate cancer, etc.). Secondary nephrosis is more common in men over 60 years of age.
According to the nature of the clinical course, this disease can be acute or chronic. If a pathological acute condition is stopped in time, it is possible to completely restore all kidney functions. If the disease becomes chronic, then the pathological processes become irreversible.
It is customary to distinguish between unilateral and bilateral hydronephrosis. The bilateral form of the pathology is quite rare; hydronephrosis of the right kidney or hydronephrosis of the left kidney is more often observed.
Hydronephrosis, according to the severity of the pathological process, can have the following forms:
- mild form, in which only the renal pelvis expands, and renal function is not impaired or slightly impaired;
- a moderate form, which is characterized by an increase in the pelvis by 15-20%, and a significant thinning of its walls is observed. The functions of the organ are significantly reduced;
- a severe form of hydronephrosis, in which the kidneys increase in size by approximately 2 times, and the pelvis and cups are significantly dilated. Kidney function decreases by 70-80% or the kidneys lose their ability to function. This condition is life-threatening for the patient.
Hydronephrosis, the degree of which determines the medical prognosis of the disease, can have both reversible and irreversible consequences.
It is also customary to distinguish between infected and aseptic types of the disease.
Diagnosis and treatment
If the patient has hydronephrosis of the right or left kidney, then the diagnosis must first be confirmed. Usually the disease can be detected at the second stage. It is at this time that patients already turn to the doctor with complaints of pain and nausea. But such signs can also indicate other ailments.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- Ultrasound. On the screen you can see whether the pelvis is greatly enlarged and how much it is filled with urine.
- X-rays make it possible to identify stones in the urinary ducts. Often this disease occurs together with hydronephrosis.
- Urography of intravenous type. During this procedure, a contrast agent is injected. It remains in the kidneys and is then excreted through the ureters. Periodically, pictures are taken that allow you to see changes in the tissues of the organ.
- Radionuclide scanning.
Hydronephrosis is treated using several techniques. Both traditional therapy, surgery, and folk remedies are used. However, the latter option is used only as an auxiliary option in the early stages. The doctor chooses the therapy.
- Drug treatment. Antibacterial therapy is required if the disease develops along with inflammation. For example, this happens when pyelonephritis progresses in parallel. Products with analgesic properties are also used. For example, antispasmodics are suitable. They are able to relieve attacks of severe pain. Alkalinization therapy is also required if the patient has stones.
- Surgical intervention. If medications do not cope, then surgery for hydronephrosis is prescribed. This is required in order to drain excess fluid from the pelvis. The pelvis itself is also sutured in the place where it is too dilated. Typically, such operations are practiced at the third stage of the disease. If the organ does not function, it is completely removed. In this case, at the last stage of development of the disease, the kidney is an ordinary tissue sac that does not perform its functions.
- Traditional medicine. This technique helps only in the early stages, when the kidney is functioning, but there are minor problems with the outflow of urine. Doctors recommend using a special herbal mixture for the kidneys. It can be purchased at a pharmacy. If there are contraindications, the product should not be used. This applies to the presence of stones. Liquid can also be removed using decoctions and tinctures that have diuretic properties. In this case, the diet for kidney hydronephrosis must include rosehip decoction. By the way, the diet itself helps prevent the development of the disease, so you need to limit yourself in salt and liquid if necessary.
Methods for diagnosing fluid in the kidneys
The diagnosis is made by a nephrologist or urologist. To assess the degree of kidney dysfunction, a comprehensive examination is performed, which includes:
- taking anamnesis;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- lab tests;
- hardware examination.
The defining methods for diagnosing urological disease are:
- Ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys;
- excretory urography;
- renal angiography;
- nephroscintigraphy;
- Kidney MRI.
To visualize the area of the urinary tract in which there are obstacles to the movement of urine, urethroscopy or cystoscopy is performed. Kidney dysfunction is determined by biochemical urine analysis. It contains high concentrations of protein, creatinine, potassium, and uric acid.
When making a diagnosis, hydronephrosis is distinguished from diseases with a similar clinical picture - nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis, prolapse, polycystic disease and kidney carcinoma.
What is hydronephrotic transformation
Hydronephrosis is a disease in which fluid stagnates in the kidneys. The organ consists of:
- parenchyma - tissue that cleanses the blood of toxins and produces urine;
- cavity system - consists of small cups that form large pelvis.
The cavity system is a reservoir for storing liquid. Outside, it is shrouded in parenchyma. If the passage (passage) of urine through the urinary tract is disrupted, the pelvis dilates. Subsequently, the pyelocaliceal system (PSS) becomes deformed, and the viability of the renal tissue decreases.
Deterioration of urine outflow from the renal cavity system leads to:
- violation of the filtration function of the organ;
- slowing down the circulation of blood and lymph in the parenchyma.
The outcome of the disease is the death of nephrons - structural units in which blood filtration and reabsorption of various substances occur.
Hydronephrosis is more often found in women 20-55 years old, which is associated with pregnancy and gynecological pathologies. And after 60 years, men with sluggish prostatitis and prostate adenoma suffer more from the disease.
Diagnosis of hydronephrosis according to ICD
Diagnosis of hydronephrosis is primarily based on laboratory and instrumental data. Objective data (that is, patient complaints) are not very informative, since in the early stages of the disease the clinical picture of hydronephrosis is very poor.
Periodic dull pain and blood in the urine (complaints with which the patient goes to the doctor) are not sufficient to make a diagnosis. Therefore, the doctor prescribes special tests and analyses.
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), hydronephrosis is coded N13. 6
Tests for hydronephrosis
To make a diagnosis, a urine test and a blood test are prescribed.
Urinalysis indicators for hydronephrosis
| Laboratory sign | Description |
| Hematuria | The presence of red blood cells in the urine. |
| Proteinuria | The presence of protein in the urine; in the last stages of hydronephrosis, the loss of protein in the urine exceeds 3.5 grams per day. |
| Cylindruria | The presence of casts (substances of protein origin) in the urine. |
In parallel, the patient experiences severe edema (due to loss of protein) and persistent arterial hypertension.
Blood test indicators for hydronephrosis
| Laboratory sign | Description |
| Hypoproteinemia | A decrease in the concentration of total protein in the blood of less than 65 grams per liter. |
| Hypoalbuminemia | A decrease in predominantly albumin (high-density proteins), less than 25 grams per liter. |
| Hyperlipidemia | An increase in cholesterol levels of more than 6.5 millimoles per liter. |
There is also an increase in the levels of urea, creatinine and nitrogen in the blood. All these substances, when retained in the body, cause endogenous intoxication.
Complications of hydronephrosis
A pathological condition such as hydronephrosis is quite dangerous to human life and health. Due to pathological disorders, the kidneys lose their ability to function normally, and the following complications may arise that threaten the patient’s life:
- renal failure is a syndrome of dysfunction of all kidney functions, which leads to disruption of all metabolic processes in the patient’s body. In this situation, the development of severe general autointoxication of the body is possible, which can cause the death of the patient;
- sepsis (or blood poisoning) can occur against the background of infected hydronephrosis;
- hypertonic disease;
- urolithiasis disease;
- inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis);
- sudden rupture of the pelvis, leading to spillage of contents into the retroperitoneal space. This condition is characterized by high mortality.
How to treat the disease?
When hydronephrosis is detected, treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating the cause that caused its development. For example, if these are stones due to urolithiasis, then they are crushed, and congenital anomalies are eliminated using plastic surgery.
Depending on the stage of hydronephrosis, treatment can be either active surgical or conservative medication.
If renal function is not impaired and there are no complications, then the condition of the kidney is monitored over time and no treatment is prescribed. The localization of a unilateral process does not affect the choice of patient management tactics, i.e. For hydronephrosis of the left kidney, treatment is the same as for the right one.
Nutrition for hydronephrosis
Regardless of the chosen treatment tactics, hydronephrosis requires a diet that involves consuming about 3,000 calories per day. The diet must include proteins containing essential amino acids. However, meat and fish with hydronephrosis must be excluded from the diet. Egg dishes are acceptable and the basis of the diet should be vegetables and fruits. The patient needs to limit salt intake and drink at least 2 liters of liquid every day.
Treatment with folk remedies
Only first degree hydronephrosis can be treated using traditional methods.
In folk medicine, various herbal preparations are used to treat hydronephrosis.
The most effective are the following:
Kidney tea, string herb, raspberry leaves, chamomile flowers, currant leaves, calamus root, meadowsweet flowers and knotweed herb are taken in equal parts and finely crushed. Then an infusion is prepared: 2 tablespoons of the collection are poured into a glass of boiling water. Drink 50 ml of infusion 3 times a day. The herbs of knotweed, mint, waterweed, fireweed and celandine, marshmallow root, alder cones and coriander fruits are taken in equal parts, the infusion is prepared in the same way as the previous one. The treatment method is also similar.
Both collections are used alternately: after a course of treatment with one collection for 2-3 weeks, a two-week break is taken, after which they begin to take the second collection.
Drug treatment
If the pathology is complicated by infection and the development of pyelonephritis, then antibacterial therapy is necessary. If there are stones in the kidney consisting of uric acid - urates, alkalizing therapy is carried out. Pain syndrome is also relieved with medication. And in cases where retroperitoneal fibrosis leads to the development of hydronephrosis, hormonal treatment is prescribed.
Diagnosis of bilateral hydronephrosis
The diagnosis of this disease is usually made based on the results of excretory urography, as well as after retrograde pyelography. On a clear and clear image of the urinary tract, you can notice the shadow of enlarged kidneys. A doctor can judge the functional state of the affected kidneys based on data from so-called isotope renography.
Bilateral hydronephrosis is usually differentiated from kidney stones, as well as nephroptosis. In a patient with nephroptosis, the painful sensations subside in a horizontal position. A palpable tumor-like formation should be differentiated from polycystic disease, kidney tumor, or solitary cyst.
In cases where the main symptom of hydronephrosis is pyuria or hematuria, a correct diagnosis can only be made on the basis of a complete urological examination.
Classification and degrees of disease
Modern classification involves dividing hydronephrosis according to certain characteristics:
- by origin: congenital (primary) - arising from various anomalies in the development of the urinary organs, including due to intrauterine damage to the neuromuscular apparatus of the ureter or pelvis (dynamic hydronephrosis);
- acquired (secondary) - developed as a complication of another pathology leading to obstruction (obstruction) of the urinary tract;
- open - the outflow of urine is partially preserved;
- aseptic - without an infectious-inflammatory process;
- unilateral - right or left kidney - occurs equally often;
- acute - characterized by the possibility of complete recovery of the kidneys, develops over several days or weeks;
Hydronephrosis is classified according to the nature, origin, localization and course of the process.
According to the degree of severity, urologists divide the pathology into 3 degrees:
- lung, which is characterized by the following signs: the size of the organ is not changed;
- the pelvis is slightly dilated, its walls are thickened;
- some cups may be slightly expanded;
- changes in the structure of the kidney are minimal (the parenchyma is preserved, the interstitial tissue is edematous, the renal tubules are dilated);
- functions are preserved, there is some impairment of the evacuation ability of the pelvis;
- changes in the structure of the organ are more pronounced - the thickness of the parenchyma is reduced to 8–10 mm;
- severe (often irreversible) dysfunction and structure of the kidney;
In its development, hydronephrosis goes through 3 stages - from minimal changes to pronounced disturbances in the structure and functions of the kidney
Symptoms of the disease
At the first stage, hydronephrosis occurs without pronounced symptoms and is often discovered by chance when examining a patient in connection with various complaints. At this stage, the symptoms directly depend on the causes of the pathology. For example, if hydronephrosis appears as a result of the formation of stones, then the accompanying symptom will be sharp, acute pain along the ureters.
As the pathology progresses, the patient complains of the following problems:
dull pain in the lower back, independent of the time of day and body position; painful sensations are most clearly manifested in the area of the affected kidney: if the left side of the lower back hurts, then the left kidney is affected and vice versa; in some cases, pain appears in the right side of the abdomen; often painful sensations are accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
The patient may experience increased blood pressure and bloating. When an organ becomes infected, the body temperature rises. In some cases, the only symptom of hydronephrosis of the left or right kidney is the presence of blood particles in the urine. This situation is possible if the problem is caused by the development of urolithiasis. Stones leaving the bladder injure the walls of the ureters and impede the outflow of urine.
At the last stage, signs of chronic renal failure appear, edema develops, blood pressure rises and anemia. The patient should definitely seek help from a doctor if lower back pain begins. Hoping for self-medication, the patient misses the favorable time to start treatment. The outcome in this case can be disastrous: from removal of the affected kidney to death.
Stages of hydronephrosis
There are several stages in the development of hydronephrosis. The duration of these stages depends on the severity of the underlying disease and the presence of concomitant diseases. The final or terminal stage of hydronephrosis, as a rule, coincides with renal failure.
The stages of hydronephrosis include:
- initial stage of hydronephrosis;
- early stage of hydronephrosis;
- terminal stage of hydronephrosis.
Stage 1 hydronephrosis
At this stage, the pyelocaliceal apparatus of the kidney is enlarged, but this is not accompanied by an increase in the organ itself. Kidney function is preserved; the clinical picture can manifest itself with symptoms such as aching pain in the lumbar region. Sometimes hematuria (blood in the urine) may occur. In the tests, protein may be slightly increased; with hematuria, red blood cells will also be present.
Stage 2 hydronephrosis
At the second stage, simultaneously with the pelvis, the kidney itself enlarges. On average, it increases by 10 - 20 percent of its original volume.
However, it is worth understanding that the enlargement of the kidney does not occur due to an increase in its tissue or function, but due to the stretching of the pelvis and the accumulation of urine in them. The kidney function itself is reduced by 30–40 percent.
Protein (proteinuria) begins to appear in the urine, and toxic metabolic products - creatinine and urea - increase in the blood. At this stage, the first signs of renal failure begin to appear - blood pressure rises, and renal edema appears in the morning.
Stage 3 hydronephrosis
Represents renal failure. At this stage, the kidneys almost double in size, while their function decreases by more than 60 to 70 percent.
The kidney parenchyma (its tissue) almost completely atrophies, and large cavities form in its place. The kidney takes on the appearance of a multi-chamber cavity, which, in turn, is filled with urine residues.
Arterial hypertension becomes resistant (difficult to treat) and blood pressure is constantly elevated. Protein continues to be lost by the body; at the terminal stage, proteinuria reaches 3 grams per liter of urine.
Such a massive loss of protein provokes large swelling. Patients at this stage are very swollen, swelling is observed not only in the eye area, but throughout the body.
In its development, pathology can go through several stages:
- 1st degree. In most cases, identifying grade 1 hydronephrosis at the very beginning of its development is quite problematic, since it occurs in a latent form and does not cause the appearance of pronounced symptoms. In addition, the clinical picture at the first stage of development is quite blurred and identifying the disease is quite problematic, but still possible. In addition, there is an accumulation of a small amount of water in the organ, which causes a slight stretching of the pyelocaliceal system, but its work is not disrupted.
- 2nd degree. At this stage of progression of the pathology, a strong thinning of the wall of the renal pelvis is observed and the consequence of this is a disruption of the normal functioning of the organ. In addition, grade 2 hydronephrosis is accompanied by serious impairment of renal function.
- 3rd degree. The final stage of the disease is considered life-threatening, because the kidney transforms into a multi-chamber organ filled with urine. The prognosis of the pathology at this stage is completely unfavorable, because the organ completely refuses to work and chronic renal failure is detected.
Each stage of the pathology is accompanied by the appearance of certain symptoms that must be paid attention to.
- In the first degree of hydronephrosis of the kidney, the functions of the organ itself are not impaired, only an enlarged pelvic system is observed.
- At the second stage, the expansion of the pelvis is quite significant, its walls are thinned, and kidney function is reduced by an average of 20%.
- At the third stage, a multi-chamber cavity filled with urine is already detected in the kidney. The decrease in the functional capacity of the entire organ reaches 80%.
This disease, regardless of its classification, has several stages.
Table No. 2. Stages of hydronephrosis in children.
Symptoms of pathology
As mentioned above, hydronephrosis is dangerous, among other things, because its symptoms in the initial stage (in the so-called first period) are not pronounced.
Experienced doctors carefully collect anamnesis, including specifying how the patient sleeps. Often with hydronephrosis, the patient prefers to sleep on his stomach - this makes it easier for fluid to drain out. It is especially difficult to identify hydronephrosis in children - it happens that symptoms do not appear either at the first or even at the second stage. The difficulty of diagnosis also lies in the fact that the disease manifests itself differently depending not only on the stage, but also on the type of pathology, its nature, and course.
So, for example, acute hydronephrosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the side or back;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased pain after drinking liquids;
- manifestation of pain on the side where the kidney is affected (or on both sides, if both are affected);
- sometimes the pain goes to the vagina (women) or testicles (men);
- if the urine is infected, fever and chills develop;
- if there are kidney stones, there may be blood in the urine;
- in severe cases, the kidneys are enlarged, this can be determined by touch.
In the case of chronic hydronephrosis, symptoms may be as follows:
- the same as for acute;
- do not appear at all;
- back pain that comes and goes;
- urination is rare compared to usual.
If we talk about the symptoms of unilateral hydronephrosis, then they include constant fatigue, discomfort in the lumbar region, which over time turns into aching pain, which intensifies with increasing physical activity or taking a significant amount of liquid. There is also a clear decrease in performance and swelling.
Sometimes the patient's blood pressure increases. If the outflow of urine is seriously impaired, the person feels nauseous and even vomits, the pain becomes paroxysmal, as with renal colic, and blood appears in the urine. Then we are talking about the second period of development of hydronephrosis, when the clinical picture is clear. At this stage, dyspepsia often occurs, which sometimes interferes with the correct diagnosis of hydronephrosis, especially in young children.
Symptoms with bilateral hydronephrosis are more obvious, because kidney dysfunction increases, azothermia occurs, that is, an increase in the amount of nitrogen in the blood. This threatens kidney failure.
If the disease is complicated by an infection, purulent pyelonephritis has developed (this happens), chills and fever occur.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of this disease is considered to be a decrease in passage in any part of the urinary tract. Experts distinguish between congenital and acquired hydronephrosis, and the first type can occur for the following reasons:
- obstruction of the urinary tract;
- incorrect localization of the ureter;
- taking medications.
As for the acquired form of pathology, it usually occurs against the background of the following diseases:
- urolithiasis;
- damage to the spinal cord, which provokes problems with the outflow of urine;
- malignant neoplasms in the abdominal cavity and the appearance of metastases;
- tumors of the reproductive organ, ovaries, prostate and urinary tract.
The most common cause of kidney pathology is urolithiasis, so it is important to diagnose it in a timely manner and not wait for complications to develop. In addition, disturbances in the process of natural outflow of urine can be caused by anatomical features.
Treatment of hydronephrosis and management tactics
Most pathologies require minimally invasive or open surgical treatment. The exception is conservative therapy that prevents the formation of uric acid stones and the prescription of steroids for retroperitoneal fibrosis.
The management of children with congenital hydronephrosis is based on confirmation of the diagnosis, taking into account prognostic factors:
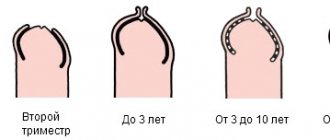
• Bilateral fetal hydronephrosis with dilatation greater than 15 mm during the 3rd trimester poses the greatest risk for the development of significant renal failure.
• Hydronephrosis of a single kidney.
An ultrasound examination is performed on the first day after birth.
Bilateral hydronephrotic transformation involves an obstructive process at or below the bladder: urethrocele or posterior urethral valves in boys, which may be associated with impaired renal function and further progression of renal failure. If persistent hydronephrosis is present in the dynamics of ultrasound, voiding cystourethrography is performed.
Children with mild or moderate hydronephrotic transformation of the kidneys are examined using ultrasound over time after 7 days of life.
Severe unilateral hydronephrosis
In newborns with severe congenital unilateral hydronephrosis, ultrasound is performed after the return of body weight at birth (after 2 days, but no later than 2 weeks).
Moderate and mild unilateral hydronephrosis
In newborns with minor unilateral hydronephrosis (diameter