The connection between a man and a woman cannot be imagined without intimacy, during which both partners receive not only physical, but also mental pleasure from the so-called merger.
If during sex there is pain in the vagina, then it is unlikely that a woman will be able to get her dose of pleasure. In such a situation, you need to go to the doctor so that he can help determine the cause of the discomfort and return to the fair sex the very sensations that are so important for the completeness of the relationship.
In addition to pain, discharge with itching may also appear if we are talking about a genitourinary infection. In this case, a consultation with a gynecologist is simply necessary.
General information
Sexual life is an integral and very important part of a relationship.
After all, regular sexual intercourse is not only an opportunity to obtain physical satisfaction, but also a prerequisite for psychological comfort. However, in order for both partners to be satisfied, it is important that during sexual intercourse neither of them feels discomfort or pain. In fact, pain during sexual intercourse is a typical phenomenon for women. If pain is a woman’s constant companion during sexual intercourse, then she, of course, will not be able to receive full pleasure. As a result, this will affect both her state of mind and her relationship with a loved one.
Dyspareunia is the medical term for a condition where women experience pain during sexual intercourse. This condition can develop at any age, and pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse is possible at almost any stage of intimate contact. The nature of this symptom can also be different, as well as its localization and severity.
Only a specialist can answer the question of why it hurts during sexual intercourse, having previously carried out all the necessary examinations. It often happens that the cause of such troubles lies in absolutely simple things - for example, incorrect body position during sex. Also, this may be due to no less “banal” reasons - vaginal dryness, the presence of psychological discomfort due to the inexperience of the partner.
But if dyspareunia manifests itself systematically, then it is likely that it is associated with more serious causes. This phenomenon can provoke diseases of the genitourinary or reproductive systems associated with infections and those of a non-infectious nature. The causes of dyspareunia will be discussed in this article.
https://youtu.be/-0Xbn42cQ1Q
Injuries
If a woman has recently suffered some kind of injury, childbirth or surgery, then for some time during sex there will be pain in the vagina.
In addition, the process of childbirth is sometimes accompanied by tears or cuts in the perineum, which require stitches. During healing, a scar may form and normal blood supply may be disrupted. This causes discomfort during sexual intercourse.
You can solve the problem with Kegel exercises. But it is very important to do them correctly. To strengthen the vaginal muscles, it is necessary to tense the pelvic floor muscles, while relaxing the stomach, hips and buttocks, and stay in this position for 3-10 seconds, depending on your physical fitness. You need to repeat the exercise no more than 10 times. The goal is to increase the long-term delay in tension.
Over time, the discomfort goes away because the tissues grow together and the tear site heals. The main thing is to prevent the appearance of rough scars, which can be caused by infection in the wound. If this cannot be avoided, then the help of a surgeon will be necessary to complete breastfeeding.
How does a doctor determine the causes of pain?
In the process of collecting anamnesis, the doctor asks a number of questions about the characteristics of the person’s health condition and more. During your consultation with a specialist, you may be asked the following questions:
- Are there other disorders associated with sexual activity, in particular poor hydration during arousal, lack of orgasm? Have there been any attempts to cure this condition?
- Do you have unusual discharge that is strange in color or has an unpleasant odor? Did you experience pain in the lower abdomen?
- Has the woman suffered from illnesses caused by sexually transmitted infections (including human papillomavirus , herpes )?
- Is there an aggravated obstetric history: were there any injuries during childbirth, incisions of the perineal tissue, use of forceps during childbirth?
- Has the woman previously been diagnosed with endometriosis , chronic pelvic pain, salpingitis , uterine fibroids , etc.?
- Have any surgical interventions been performed on the abdominal cavity or genitourinary organs? Has the woman undergone chemotherapy or radiation therapy ?
- What methods of contraception were used previously, and what contraceptives does the woman currently use? Have any intrauterine devices been used to prevent pregnancy ?
- Has the woman been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus or Behcet's syndrome ?
- Are you worried about skin diseases - eczema , psoriasis , etc.?
- Have there been any problems with the urinary system? Did the patient have urethritis , cystitis , did she have irritable bowel syndrome or colon disease?
- Is there high sensitivity to cosmetics and medications – ointments, creams, lotions? Does sensitivity occur when using colored or scented toilet paper or intimate hygiene products?
The specialist also asks about the nature of the pain that manifests itself:
- When exactly do pain sensations appear - before the start of the act at the entrance, immediately during movement, after contact?
- If the pain is deep, where exactly is it located? Which side exactly did the pain start on?
- The nature of the pain – sharp, aching, strong, burning?
- Are you bothered by unpleasant sensations - burning, itching?
- Are the pains generalized (that is, independent of the situation or partner) or situational (related to circumstances, partner, dependent on the monthly cycle)?
- Does pain depend on position during sex?
- Is there a connection between the manifestation of pain and the use of alcohol or drugs?
- Was the pain bothering you from the very beginning of sexual activity or did this symptom appear recently?
Psychosocial aspects are also discussed:
- Has the woman discussed this issue with her partner?
- Have similar manifestations been observed in intimate relationships with another partner?
- Has any concerted action been taken to overcome these manifestations?
- Has the woman experienced rape or assault before?
- Does the patient suffer from symptoms of depression or anxiety disorders ?
- Are there any stress factors in her life?
Associated symptoms
A burning sensation after sexual intercourse may be accompanied by other signs of pathology. The main symptom accompanying burning after ejaculation is pain. It is always a consequence of an inflammatory process that can develop in the testicles, prostate or bladder. Inflammation can begin in one place, and after localizing the inflammatory process, it can spread along the ascending line, affecting the urinary system: initially it stings after sexual intercourse in the area of the urethra, and then the pain can spread to the entire lower abdomen.
The second common symptom that accompanies discomfort during ejaculation in men is itching, which can be present constantly or occur from time to time, for example, the penis itches after sex or urination. In this case, it is most likely the presence of a sexually transmitted infection, which could be present in a latent form long before the onset of symptoms.
Itching and burning in the intimate area after intimacy appear with a decrease in local or general immunity. Thus, a factor provoking an exacerbation of the pathology can be acute respiratory infections or hypothermia.
Why does dyspareunia occur?
The reasons why painful sexual intercourse and discomfort during intimate contacts are noted are clearly divided into two groups by experts:
- Diseases of the genitourinary system associated with infections and having a non-infectious origin.
- The presence of psychological problems associated with the fear of experiencing pain again after an unsuccessful intimate experience.
If a specialist seeks to determine the reason why vaginal pain occurs during sexual intercourse, he initially needs to find out whether the patient’s arousal is sufficient before intimate intercourse.
Vaginal dryness associated with insufficient arousal is observed in unstable relationships in a couple and constant conflicts. A woman does not have time to become sufficiently aroused if her partners do not master the technique of foreplay or simply do not pay enough attention to them. As a result, a certain vicious circle gradually appears when initially a woman experiences insufficient hydration associated with psychological aspects or inexperience, and later this phenomenon repeats, and before each sexual intercourse the woman already expects the appearance of pain.
Diseases manifested by dyspareunia
The appearance of pain above the pubis, in the lower back, right or left side during each sexual intercourse indicates an organic pathology. If there are complaints about regular unpleasant, uncomfortable sensations during or after sex, a woman should consult a gynecologist, since diseases that cause these symptoms can lead to serious complications, including infertility.
Pain during intimacy is accompanied by the following pathologies of internal organs:
- Endometriosis. A disease characterized by the penetration of the uterine endometrium into the uterus, tubes, ovaries and other internal organs. During the entire menstrual cycle, these formations undergo the same changes as the uterine epithelium; under the influence of hormones they swell and may bleed. Pain in this disease is periodic, occurring and intensifying before and during menstruation. Without treatment, the painful sensations become even stronger, unbearable and become permanent. Doctors can provide specific assistance for endometriosis even in advanced cases; however, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor, since this disease can lead to anemia, chronicity of concomitant pathologies, and infertility.
- Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs - adnexitis, salpingitis, inflammation of the uterine membranes. This leads to pain of varying intensity (pressing, stabbing, cutting), which is localized in the right, left iliac regions, and in the pubic area. Acute inflammatory processes, in addition to discomfort during sexual intercourse, are usually accompanied by fever, the presence of pathological discharge, and deterioration in general condition. A gynecologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of these pathologies.
- Sexual infections - chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, thrush. The causative agents of these diseases can infect the sensitive mucous membrane of the genital tract. The friction that occurs during sexual intercourse leads to additional damage and a feeling of severe discomfort and burning in the vagina.
- Bartholinitis is an acute inflammation of the gland located at the vestibule of the vagina. An attempt at sexual contact with this pathology leads to hyperemia, increased swelling, and the appearance of unbearable pressing pain in the area of the affected labia. Diagnosis and conservative or surgical treatment of the disease are carried out by gynecologists.
- Genital warts are specific growths on the vaginal mucosa caused by the influence of the human papillomavirus. They manifest themselves as pain in the vagina during sex, and with intense friction they can become damaged and bleed.
The diagnosis and treatment of the pathology that led to the appearance of dyspareunia should be made by a specialist. To determine the cause of pain, the doctor needs to collect complaints and anamnesis, as well as conduct a number of additional studies (gynecological examination, ultrasound, take smears for flora and PCR).
During the period of bearing a child, intimate relationships between partners do not stop (until a certain period). However, intimacy is often overshadowed by the appearance of pain in a woman, frightening the expectant mother and father.
Discomfort during sexual intercourse during pregnancy is often associated with:
- Excessive worries about one’s situation, fear of harming the fetus. Because of this, spasmodic painful contractions of the vaginal muscles may occur, making sexual intercourse difficult.
- Uncomfortable pose. Starting from the second trimester, the expectant mother’s figure proportions change noticeably, which can cause discomfort and cause muscle pain in some positions.
- Increased sensitivity of the cervix, caused by the influence of changed hormonal levels.
- Reduced secretion of natural lubrication, irritation of the vaginal mucosa.
- A threat and an incipient miscarriage. Intense cramping pain, especially accompanied by spotting after sex, indicates a threatened or actual abortion. If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a specialist.
A woman’s well-being during sexual intercourse largely depends on her readiness for intimacy. Often in the early stages of pregnancy, the expectant mother suffers from toxicosis, which manifests itself as nausea, drowsiness, weakness, headaches and muscle pain, including during sexual intercourse.
Diseases that cause pain during sexual intercourse
Pain during sexual intercourse can be a symptom of various diseases. They can develop anywhere in the intimate area and have different origins. There are a number of the most common infectious and non-infectious diseases that may cause pain during sexual intercourse.
Infectious diseases:
- Endometriosis is a pathological change in the endometrium, in which particles of this tissue appear in various atypical places - the ovaries, serous and muscular layers of the uterus, peritoneum, etc.
- Vaginitis is an acute or chronic inflammation in the vagina, which appears due to exposure to trichomonas , chlamydia , gonococci , fungi, mycoplasma , and nonspecific pathogenic microorganisms. Sometimes vaginitis is associated with hormonal imbalances.
- Cystitis is an inflamed process in the bladder.
- Urethritis is an inflammation of the tissues of the urethra.
- Adhesions in the pelvis, manifested as a result of inflammation of the abdominal cavity, acute or chronic, develop after a previous acute or chronic inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity.
- Salpingitis , endometritis , cervicitis in chronic form.
Non-communicable diseases:
- Postpartum sutures, injuries, ruptures, as well as sutures after operations.
- Insufficient hydration - inactivity of the arousal phase in young women, lack of estrogen during menopause .
- Vaginal atrophy - a similar condition is typical during menopause; it is manifested by dryness of the vaginal mucous membranes due to a lack of estrogen in the body.
- Venous stagnation - this condition is observed when abstaining from intimate life or during irregular sexual intercourse, as a result of which stagnation of blood develops in the vessels of the small pelvis.
- Decreased pelvic floor tone leads to prolapse of the uterus .
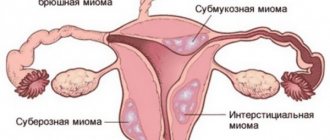
- Myomas , cysts are neoplasms that appear in the pelvic organs.
- Retroversion of the uterus - anomalies in the position of this organ (bending, deviation) in relation to other pelvic organs.
- Incompatibility of sizes, anatomical discrepancy is a rare phenomenon, since the female vagina is stretchable, and if there is sufficient hydration, then there are no problems. This is possible with gigantism in men.
Inflammatory processes
If during sex a woman experiences unpleasant sensations in the vagina, such as burning, pain, itching, this may indicate an inflammatory process. Then anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
In most all cases, the development of the inflammatory process is provoked by microflora that is natural for any organism: staphylococcus, E. coli, fungi.
Pain in the lower abdomen may be due to adhesions. Adhesions in all cases are a consequence of previous inflammatory processes in the intestines or appendages. They are present in most women in the pelvic organs. Most often, the problem can be solved with the help of physiotherapeutic treatment or selection of posture. If the adhesions are strong, surgery may be required.
Dyspareunia: what is it and how does it manifest?
Dyspareunia is a condition in which pain occurs during sexual intercourse. Symptoms of dyspareunia in women may appear before sexual intercourse, when the penis first penetrates the vagina. Dyspareunia can also occur with movement. Pain after sexual intercourse is also possible.
Each woman perceives such manifestations individually, feeling burning, pressure, discomfort or sharp pain.
If the pain is not severe or of moderate intensity, then most likely we are talking about an inflammatory disease.
Sharp pain may be a sign of acute inflammation of the ovaries, uterus, and appendages.
Psychological factors lead to pain of varying localization and intensity. They may disappear completely after a change of partner or environment.
Superficial pain
It appears at the entrance when the partner inserts the penis. They are often associated with diseases of the vestibule and lips, insufficient hydration, and vaginismus . The probable cause of such sensations may be vaginitis of fungal or bacterial origin, as well as vulvodynia , vulvar dystrophies, and mucosal atrophy. Superficial pain is also possible with genital herpes .
When a woman consults a doctor with such complaints, he may note the presence of ulcers or cracks in the vestibule of the vagina.
If pain appears during palpation along the urethra and bladder, then the cause is likely due to urethritis.
Herpeptic rashes indicate genital herpes, in which case the discomfort disappears after the course of treatment for the infection.
Deep pain
If sexual intercourse between a woman and a man causes deep pain, most often the reasons for this phenomenon are associated with adhesions and endometriosis . They can also be provoked by stagnation in the pelvis in women. Less common causes are endometritis, inflammation of the appendages, abnormal location of the uterus, weakened pelvic floor tone. A number of unpleasant symptoms, including dyspareunia, appear in diseases of the urinary system. The same thing happens with intestinal diseases. Therefore, dyspareunia can be caused by both colon inflammation and irritable bowel syndrome.
During menopause, deep pain manifests itself due to atrophic changes, insufficient arousal phase and associated dryness in the vagina. As a result, friction becomes difficult, and pain appears both at the entrance and inside the vagina. With certain positions, the pain intensifies, because the vagina does not lengthen or expand. Often a woman is interested, for example, in why pain appears in a position where the woman is on top, but not in other positions.
In this way, we can summarize what pain can occur in certain diseases.
Superficial
- Vulvodynia.
- Urethritis.
- Vaginismus.
- Vulvar vestibulitis.
- Vaginitis.
- Lack of arousal and, as a result, hydration.
Deep
- Adhesions in the pelvis.
- Inflammation in the pelvis.
- Endometritis.
- Endometriosis.
- Pathology of the appendages, urethra.
- Venous stagnation in the pelvis.
- Retroversion of the uterus.
- Chronic cervicitis
Both superficial and deep
- Vaginal atrophy and associated vaginal dryness.
- Insufficient hydration
- Consequence of childbirth , operations, injuries.
- Sjögren's syndrome.
Pain after pregnancy
The problem of pain during sex after childbirth very often worries young mothers. There is research data that after childbirth, about 40% of young mothers report non-localized pain, approximately 45% of women experience pain at the entrance. Directly during intimate contact, significant discomfort appears in 25% of patients who have undergone a cesarean section , and in approximately 40% of nursing mothers. However, the reasons for this phenomenon remain completely unclear to doctors to this day.
In most cases, the pain stops within six months after birth, but sometimes this condition can persist for a whole year.
Treatment tactics
If a man experiences cramps after sexual intercourse, they should not be ignored. As a rule, diseases do not cure on their own - they only become chronic. It can then be much more difficult to heal them.
The optimal tactics for eliminating an intimate problem are selected by a specialist in each case on an individual basis. Thus, when a penis injury is detected, the volume of intervention directly depends on the area of the lesion. Either anti-inflammatory therapy is recommended, or in combination with surgical suturing of the defect.
After confirmation of one of the sexually transmitted diseases, a set of measures is carried out to suppress the activity of the pathogen and remove it from the man’s body. Similar tactics will be taken if an inflammatory focus is diagnosed in the pelvic structures.
Reasons related to psychological factors
Not only physiological reasons can trigger the development of dyspareunia . This condition is often associated with psychological reasons, which is why a woman may refuse sexual intercourse.
Fear of sexual intercourse
Most girls are afraid of their first sexual intercourse due to the upcoming defloration and the pain associated with this process. During defloration, pain occurs due to tearing of the hymen . Many girls feel fear precisely because of this.
This disorder may be due to fear of the partner if he behaves cruelly. Also, a woman often fears an unwanted pregnancy, and this prevents her from relaxing. If you cannot overcome such fears on your own, a specialist psychologist or sexologist will help.
Pain during intercourse during pregnancy
When having sex during pregnancy, some women feel discomfort and pain at these moments. This condition develops at the level of the subcortical centers of the brain due to the risk of harming the fetus due to penetration of the penis into the vagina. However, some experts argue that dyspareunia cannot be associated with pregnancy, but is a consequence of gynecological diseases.
Vaginismus
Vaginismus is a condition that is often associated with complications of defloration. In this case, a woman for a long time cannot overcome the fears that are associated with sexual relations with a previous partner. Vaginismus is characterized by uncontrollable sharp spasms of the vaginal muscles, which causes pain and makes it impossible to fully complete sexual intercourse.
The presence of complexes and self-doubt
Often women believe that their body is imperfect, and this makes them doubt their own attractiveness and prevents them from focusing on sexual play. As a result, there is not enough arousal, and the partner feels pain during intercourse. This often happens to women who are overweight or have certain physical disabilities. Psychological complexes often become a serious problem, and only a specialist can help overcome them.
Common causes of pathology
Burning sensation in men after sex can occur for a number of reasons, but four can be identified as the most likely and most common.
- Candidiasis is a disease caused by pathogenic fungi called candida. Typically, a man’s body is not very susceptible to these microorganisms, but if immunity decreases during a cold, stress or hypothermia, infection can occur. However, sexual intercourse is not the only route of infection, since candida can be present on the hands and mucous membrane of the mouth. With candidiasis, burning in the urethra in men after sexual intercourse is one of the main symptoms.
- Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease that affects the urethra and prostate gland. Infection most often occurs during sex, less often through household means, for example, through towels. Symptoms include not only a burning sensation in the penis after intercourse, but also discharge from the urethra. The danger of the pathology is the high probability of complications - prostatitis.
- Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that causes damage to the urethra, rectum, tissues of the pharynx and eyes. Infection is possible only during intimacy, and even the presence of a condom does not always completely eliminate the risk of infection. The clinical picture of the disease depends on which organs are affected. Therefore, if a burning sensation in the urethra after ejaculation is accompanied by a sore throat, there is a high risk of gonorrhea.
- Balanoposthitis is an inflammation of the glans penis, which is caused by bacteria and fungi. People who already suffer from serious diseases, such as diabetes, or pathologies of the immune system, are especially susceptible to the disease. As a result of the disease, glandular secretions accumulate in the subcutaneous space, which provokes inflammation that spreads to the urethra, causing a person to experience a burning sensation during sex.
All these pathologies have a similar clinical picture, but each disease requires individually selected treatment.
How is dyspareunia diagnosed?
You can determine the causes of this condition by visiting a specialist - a urologist, gynecologist, psychotherapist, sexologist. First, the doctor carefully collects anamnesis, conducting a careful questioning of the patient about the characteristics of the symptoms and the circumstances under which pain appears. If the doctor suspects that the cause of unpleasant symptoms is gynecological diseases, he may prescribe a number of diagnostic and laboratory tests:
- Extensive or general clinical examinations of urine and blood.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs.
- Detection of infections, including those that are sexually transmitted.
Having received a complete picture thanks to the listed studies, the doctor will be able to confirm or deny that pain during sexual intercourse in a woman is associated with a certain disease. If it is not possible to identify clear reasons for the development of such a condition, then the psychological nature of dyspareunia is considered.
The table below shows the differentiation of those conditions in which dyspareunia manifests itself in a woman.
| Disease | Signs | Causes | Research results | Following actions |
| Dyspareunia of unknown origin |
|
|
|
|
| Vulvodynia |
|
|
|
|
| Vaginismus |
|
|
|
|
| Vulvar vestibulitis |
|
|
|
|
| Disturbed natural hydration, tissue atrophy |
|
|
|
|
| Diseases of the uterine appendages |
|
|
|
|
| Endometriosis of the uterus , adhesions |
|
|
|
|
| Uterine fibroids , its abnormal location, weakened pelvic floor tone |
|
|
|
|
| Venous stagnation |
|
|
|
|
| Endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, chronic cervicitis |
|
|
|
|
| Urethritis, cystitis, interstitial cystitis |
|
|
|
|
Diagnostics
Half of the diagnosis is a correctly and thoroughly collected medical history and life history. It matters when the pain appeared, what its nature is, whether it depends on the menstrual cycle, what diseases the patient suffered and how it was/was treated, whether there were any traumatic situations in the past. It is necessary to find out how the patient menstruates, whether the nature of menstruation has changed (duration, abundance, pain, the appearance of clots and intermenstrual spotting). Reproductive history, number of births, abortions, miscarriages, complications. The operation and method of contraception also plays an important role.
For a full examination, the patient must be undressed, so the condition of the skin and mucous membranes, the presence of enlarged lymph nodes and much more can be assessed. When examined in a chair, you can sometimes immediately find out the cause of the pain (colpitis, bartholinitis, condylomas are visible to the naked eye). The pain of a gynecological examination already indicates some deviation from the norm. If you feel pain during the examination, be sure to tell your gynecologist and specify the location of the pain (back wall, side wall, etc.), this will help in diagnosis.
Laboratory tests: - smear for flora and cytological examination of scrapings from the cervical canal - these are mandatory routine tests that are carried out during the initial examination; — examination for STIs is indicated if a specific type of inflammation in the vagina is suspected.
Instrumental studies: - ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs is the basic level of diagnosis. A good ultrasound specialist will see fibroids, signs of endometriosis, varicose veins of the small pelvis and much more, which will help the clinician in diagnosis. — MRI and CT of the pelvis are indicated if a mass formation or a common pathological process is suspected. — laparoscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure that is performed only in a hospital and according to strict indications.
You may need to consult a surgeon, coloproctologist, endocrinologist, dermatologist, allergist, psychologist or psychiatrist.
Pain in a man during sexual intercourse
Men rarely complain of discomfort during intimacy, which is due to the peculiarities of their psychology, physiology and anatomical structure of the reproductive organs. The appearance of pain during sex in representatives of the stronger sex indicates a serious pathology and the need for immediate medical intervention.
Let's consider the most common pathologies leading to this:
- excessively tight foreskin, phimosis;
- Peyronie's disease (change in the shape of the genital organ);
- frenulum injuries;
- sexually transmitted infectious diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhea), candidiasis;
- urethritis, balanitis, balanoposthitis, prostatitis.
During sexual intercourse, a man may experience pain in the head and base of the penis, scrotum, perineum, anus and lower abdomen. The appearance of any discomfort requires medical consultation, correct diagnosis and treatment. You cannot postpone a visit to a specialist, since many of the diseases that manifest as pain during sex can lead to complications such as impotence and infertility.
More information about pain during sex in this video.
Lifestyle and home remedies.
The following tips may help you manage the symptoms of vulvodynia:
*Use of cold compresses. Place them directly on the outer genital area to relieve pain and itching.
* Taking a sitz bath. Two to three times a day, sit in comfortable, warm (not hot) or cool water with Epsom salts (magnesium sulfate, at the rate of 0.5 - 1 kg per bath) or oatmeal infusion for 5 -10 minutes.
* Avoid tight tights and synthetic underwear. Tight clothing restricts air flow to the genital area, which often leads to increased temperature and humidity and can cause irritation. Wear white cotton underwear to increase ventilation and dryness. Try sleeping without underwear at night.
* Avoid hot baths. Prolonged exposure to hot water can cause discomfort and itching.
*Do not use deodorized tampons or pads. Deodorant can be irritating. If pads cause irritation, replace them with natural cotton gauze pads.
* Avoid activities that put mechanical pressure on your vulva, such as cycling or horseback riding.
* Wash yourself carefully. Over-cleaning the affected area or washing it too often can increase irritation. Use plain water, wash your vulva with your hand, and pat dry. After bathing, apply a preservative-free emollient such as Vaseline to create a protective barrier.
* Use lubricants (lubricant). If you are sexually active, apply lubricant before sex. Do not use lubricants containing alcohol, fragrances, or heating or cooling agents. Choose condoms whose lubricant does not irritate your mucous membranes and use only them.
Choice of contraception
Pain may occur due to too sudden or deep movements. Of course, you can ask your partner to be more gentle, but during sex the man gets into a rage and can unintentionally gain momentum, unwittingly causing pain to his girlfriend. In this case, find an option for yourself, because this way you can control the depth and speed of entry.
Speaking of positions: it happens that discomfort arises due to inappropriate posture. All people are individual, for example, a man’s penis can be sharply bent down or turned to the side, causing it to rest against the walls during penetration. Experiment and choose the most optimal body positions that minimize pain.
While condoms remain the leader when it comes to birth control choices, there are many others. Some may be allergic to latex or to the ingredients in tablets and suppositories. This can also lead to discomfort: itching, swelling, pain. Choose contraception wisely, taking into account the characteristics of your body.
Treatment of pain during or after sex
Sexual intercourse should give pleasure to both partners. However, unfortunately, there are some objective medical reasons why sex, instead of an activity that brings pleasure, can become an extremely unpleasant and painful process. The good news is that most often this problem is completely solvable if you find out and eliminate the reason that caused it. To do this, all that is required of you is to seek qualified medical help at a men's and women's health clinic. Here you will find out why you are experiencing unpleasant sensations and how you can eliminate them. Don't be afraid to see a doctor because this issue is really personal and sensitive. Remember that not only your relationship, but also your health may be at stake. Indeed, often after diagnosis in our clinic, the doctor reveals the presence of diseases that require immediate treatment.
Minimizing painful factors
Unpleasant sensations during sex can be associated with a full bladder or bloating (colic, flatulence). Before sex, visit the toilet and empty yourself completely. The optimal position for effective urination is the so-called. "eagle pose" No need to sit on the toilet seat. Stand over it, leaning slightly forward and bending your knees - this will help cleanse your urine better.
A well-thought-out diet will help you get rid of bloating. Often sex is preceded by a meal, but in this case you should think about choosing dietary dishes for a romantic dinner. Do not eat fatty foods before sex, avoid fast food and carbonated drinks.
Advantages of examination at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
- conducting a comprehensive survey;
- modern diagnostic equipment (video colposcope, three-dimensional and four-dimensional ultrasound);
- extensive experience as gynecologists;
- quick and accurate determination of the cause of pain during sexual intercourse;
- consultations with related specialists if necessary.
You can see prices for services
The article was checked by obstetrician-gynecologist N.K. Glukhova. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.