Urine smells like rotten eggs, ammonia
Causes of ammonia odor
Normally, urine has no odor. The strong smell of ammonia in urine occurs due to a number of factors. Common causes of ammonia odor in urine:
- abstinence from urination;
- insufficient amount of fluid consumed throughout the day;
- the presence of various infections in the genitourinary system;
- unhealthy diet, abuse of spicy foods;
- taking antibiotics and other medications.
It is important to drink enough water. How many? The daily norm is 1.5 liters. Water helps flush toxins from the body. The kidneys regenerate the entire process and are responsible for the smooth functioning of the body. If your daily fluid intake is below normal, a strong and unpleasant smell of ammonia appears from your urine.
Why is there an odor of ammonia in urine in women and men?
The ammonia smell of urine appears in adults for general reasons, although it happens more often in the fair half of humanity. But why does urine smell like ammonia in women more than in men? The genitourinary system of men and women is different, so women are more prone to a variety of diseases. The period of pregnancy and menopause has a very strong odor.
A specialist can determine the exact diagnosis.
An unpleasant odor of hydrogen sulfide in urine indicates the following diseases:
- Urethritis. The disease occurs due to viruses and bacteria. Cutting pains are felt when you urge and blood is observed when taking tests.
- Cystitis is an inflammatory process in the bladder. There is a frequent urge to go to the toilet, pain when urinating, and fever.
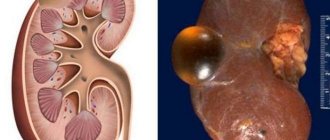
- Pyelonephritis. The disease indicates inflammatory processes and problems with pressure in the circulatory system of the kidney. A high temperature rises, chills and purulent discharge appear.
- Chlamydia and any sexually transmitted diseases, under favorable conditions, progress and create a chain of other pathologies. Symptoms vary and depend on the type of pathogen.
Features of a child
A child's urine changes color and smell as he or she ages. The smell of ammonia in a child's urine is temporary. But prolonged urine odor raises the suspicion of a serious illness, especially if there is weight loss, dry skin, lack of vitamin D, extreme thirst and frequent urination. When baby urine smells like rotten fish, there is a risk of a genetic disease. And if acetone is used, the child does not eat properly, severe emotional, physical or mental stress is possible. The smell is especially noticeable after sweets.
Certain foods can give your urine an unpleasant odor, but sometimes this is a symptom of an illness.
A healthy person's urine should be light yellow in color and, if fresh, should have virtually no odor. The smell appears only after alkaline fermentation, when urine is in contact with air for some time. Therefore, if you notice that your urine has an unpleasant odor of ammonia, this is an alarming signal of a disease.
However, there are reasons that do not indicate the disease:
- prolonged abstinence from urination;
- eating spicy foods, asparagus;
- lack of water in the body;
- taking certain medications.
If a person has excluded all these facts from his list, but the aroma of ammonia is present in the urine, then he should urgently consult a doctor.
Discharge from a healthy woman
Mucus is considered a natural defense reaction of the body. It is produced by special glands of the reproductive system. Depending on the period of the cycle, the intensity of secretion varies significantly.
In the absence of health problems, the smell of the discharge is barely perceptible. They are in most cases colorless and have a slimy consistency. With the onset of the second phase of the cycle, an increase in volume is noted.
The following characteristics are considered signs that white discharge with an odor without itching is normal:
- a spot appearing on a panty liner with a diameter of no more than 5 cm;
- the consistency is thick, but not excessively;
- barely noticeable sour aroma;
- the presence of lumps up to 4 mm in size is acceptable;
- no discomfort or pain.
Such symptoms are caused by physiological reasons. If there are no associated clinical manifestations, then there is no cause for concern.
Variant of the norm
Sometimes this shade is explained by the peculiarities of the reproductive system and the ratio of hormone levels. Natural leucorrhoea, which has such a color and viscous character, should not be intense and cause discomfort.
White discharge in women changes to yellowish immediately before or immediately after menstruation. In the described case, the characteristic shade means the presence of traces of blood in the physiological secretion.
Abundant, odorless, transparent yellow secretion can occur in the middle of the cycle, when a woman is ovulating. Often at such times it is distinguished by a thick mucous character (the discharge looks like snot).
If a woman has recently started taking oral contraceptives, then this shade occurs due to hormonal changes. Often OK is accompanied by the appearance of scanty yellow vaginal discharge.
Often the cause of mucous secretion of this color is also unprotected sexual intercourse, when the partner’s seminal fluid enters the woman’s vagina. In this case, the appearance of the described secretion in the form of pale clots is natural. The situation returns to normal 8-10 hours after sexual contact.
A change in sexual partner can also explain specific secretion. Thus, the vaginal flora adapts to the unfamiliar microflora of the man.
A change in the color of the secretion of the sex glands, which is not accompanied by an unpleasant odor, sometimes indicates the action of unfavorable factors. Let's take a closer look at them.
- Colpitis often causes the described discharge. There may be no specific aroma. Inflammation of the mucous membrane is accompanied by itching, hyperemia, swelling of the vulva, and burning during urination. Both an adult woman and a teenager can suffer from inflammation.
- Andexitis is also often accompanied by a yellowish discharge that is odorless and itchy. Additionally, accompanying symptoms appear: pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, rise in body temperature, general malaise.
- Cervical erosion is another reason why this phenomenon occurs. Explains its presence in the physiological secretion of a small amount of blood or the onset of the inflammatory process. After the cauterization procedure for erosion, transparent ichor is considered normal. If the marks on the underwear do not stop, but look like pus, then we are talking about the addition of an infection.
- Some types of STDs are also accompanied by a similar symptom. Pathogenic pathogens can irritate the mucous membrane and cause severe itching and swelling of the labia. Examples of such diseases are ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, which in some cases are asymptomatic.
If there is not only the appearance of such a secretion, but also the addition of a specific aroma and other symptoms of trouble, then there is no longer any need to talk about a variant of the norm. All the signs of a pathological process are present.
Causes of unpleasant odor
Why might there be an ammonia smell in my urine? One of the reasons is damage to the genitourinary tract by bacteria. This is what indicates pyelonephritis.
- This is one of the common diseases that people face. It affects the kidneys. It can be recognized by other symptoms, such as lower back pain and fever. In this case, a person should contact a specialist.
- When bacteria enter the excretory tract, it causes an infection of the genitourinary system. Such bacteria may be gardnerella or chlamydia.
- Urethritis is also one of the diseases that is accompanied by damage to the walls of the genitourinary canal by bacteria, which in turn causes inflammation. In addition to the unpleasant odor, you may see blood or pus in the urine.
There are other diseases not associated with the presence of bacteria in the human body:
- cystitis, in which bladder function is impaired due to inflammation. This disease occurs more often in women than in men. However, it is easier to recognize than other hidden diseases. After all, it is accompanied not only by a change in the smell of urine, but also by severe pain during urination. Urine may also have sediment, and the feeling of constant desire to visit the toilet does not leave the person;
- Diabetes mellitus can cause ammonia-like odor in urine. This condition is dangerous for a sick person, so it is urgent to tell your doctor about it;
- acidosis is a lack of carbohydrates in the human body, which, in turn, begins to absorb fatty acids. This causes hypoglycemia, which is responsible for the appearance of ketone bodies in urine. They are the ones that cause the ammonia smell.
In what pathologies does the discharge smell like ammonia?
The causes of discharge with the smell of ammonia in women are also pathological.
- Urethritis, in which the urethra becomes inflamed, develops due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses into the microflora. The symptoms include the smell of ammonia, cutting pain when urinating, discharge from the urethra appears, and urine may have a brown tint and contain mucus.
- Cystitis is another inflammatory process of the bladder. It develops due to harmful microorganisms and due to hypothermia, and in menopause cystitis is an even more frequent “guest” due to age-related changes. Symptoms of urethritis may include fever and general malaise.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys and their pelvis, which gives such an odor and is accompanied by frequent urination, lower back pain, chills, weakness, increased sweating, and dizziness.
- In diabetes mellitus, ketones - acetone compounds - are present in the urine in excessive quantities. In high concentrations they can give a similar fragrance.
- If white lumps in the mucus begin to stand out or they become yellowish, the described smell appears, and unbearable itching and burning are felt, then this is a fungal disease called Candidiasis, popularly known as thrush.
- Bacterial vaginosis may be a prerequisite for the appearance of discharge with an ammonia odor. This aroma of discharge is diluted by the smell of rotten fish, and the mucus takes on a grayish tint. She can express herself with particular force after sexual contact. Symptoms are also expressed by a burning sensation with itching.
- Any other sexually transmitted infections, such as trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gardnerellosis and others can provoke such a fragrance from the vagina.
Find out in the article at the link why it can be painful to go to the toilet during your period.
A woman may confuse vaginal secretion with minor urine leakage, which is a sign of overactive or neurogenic bladder syndrome.
Causes of ammonia smell in urine in children
If an abnormal odor is detected in the urine of children, then you should not self-medicate. The reasons why a child may smell ammonia in their urine are the same as in adults. Therefore, there is no reason to postpone the problem until “later”. The only thing that may be different is a lack of vitamin D, the symptoms of which are:
- excess weight;
- sweaty palms;
- poor appetite;
- frequent whims.
If changes in the urine occur to the baby, then you should pay attention to the food consumed by the mother. When this is the only reason, then the nursing mother should stick to a diet.
How to eliminate the smell of ammonia from discharge?
If the discharge begins to smell like ammonia, you should contact a medical professional. It’s worth starting with a gynecologist to rule out female diseases. Also consult a urologist and endocrinologist, because most often such a symptom is the result of these specialists.
For the above diseases, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs are used, and in severe cases, antibiotics. These medications are supplemented with immunostimulants and restoratives.
Treatment is possible at home. Local suppositories, douching with solutions with the mentioned medications, baths based on medicinal herbs, and warming are suitable. But under no circumstances self-medicate. First of all, contact a competent specialist.
To prevent the disease, follow simple preventive measures:
- Eat a balanced diet, avoid strict diets and bad habits.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Don't get too cold.
- Do not neglect colds, as they are often the cause of diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Keep your blood sugar levels under control at all times.
- Maintain intimate hygiene, wash yourself often, paying attention to the groin area.
- Choose genital care products correctly: without fragrances, dyes, plant-based, maintaining ph balance.
- Eliminate synthetic underwear from your wardrobe, leaving only natural, comfortable shapes.
- Protect yourself with condoms if you do not have a regular sexual partner.
As numerous reviews show, colorless, white and yellow discharge with the smell of ammonia in women is a common problem that can be eliminated quite easily. It is important to notice in time, find out the cause and receive the correct treatment. Be healthy!
Vaginal discharge is present in all women of reproductive age. This is a physiological norm. The secreted mucus maintains the necessary balance of vaginal microflora, protecting against the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and the development of bacterial infections.
Normal secretion has virtually no aroma. The mucus produced may be completely odorless or slightly sour. Disturbances in discharge, characterized by changes in the discharge, indicate the development of pathology.
The discharge in women with the smell of ammonia deserves special attention. This does not apply to acceptable standards and requires consultation with a gynecologist.
Changed odor of urine in pregnant women
During pregnancy, the smell of urine should be like that of a completely healthy person, that is, without any strong odor. Also, the urine should be almost clear. If the smell of ammonia is observed, this may indicate alarming points:
- dehydration of the body;
- toxicosis;
- lack of carbohydrates in the body;
- diabetes;
- increase in leukocytes;
- sexual infections;
In any case, the expectant mother needs to talk to her doctor about her condition. We must not ignore the signals sent by the body, because not only the health of the mother, but also the health of the baby is at stake.
Prevention and treatment
In order to prevent unpleasant odor in urine, you need to drink at least one and a half liters of water per day. Also monitor your diet, exclude fatty, fried, spicy and smoked foods, as well as alcohol. Natural yoghurts and cranberry juice are very healthy.
If you discover an unpleasant odor in urine, it is better to consult a specialist rather than self-medicate. It is necessary to undergo tests and do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. After the conclusion, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment. Perhaps the patient will be prescribed medications that have diuretic, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, and cleansing effects.
If the smell of ammonia in the urine does not go away within 3 days, and even more so when any pain, discharge or temperature is observed, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Fresh normal urine from a healthy person has a light, slightly yellowish color and a slight sour odor. Over time, oxidation and proliferation of pathogenic microflora in urine provoke catabolic processes, which causes the urine to smell of ammonia. Additional provoking factors that cause the ammonia smell of urine may be:
- prolonged abstinence from urination: the processes of urine decomposition begin in the urinary system, which, with forced stagnation of urine, causes a strong odor of ammonia when urinating;
- dehydration of the body: lack of moisture in the tissues leads to slagging of the ureter organs, which disrupts the natural processes of urine formation and can lead to a change in the smell of urine;
- Abundantly flavoring food with aromatic seasonings or eating certain foods (asparagus, horseradish, garlic) can cause unpleasant odor in urine.
If, against the background of other symptoms (pain, vaginal discharge, skin reactions, elevated body temperature, general malaise, etc.), the smell of ammonia appears in the urine, then you should immediately seek a comprehensive diagnosis. After all, such signs, as a rule, indicate serious pathological processes developing in the body.
Treatment with folk remedies
The external genitalia should be washed regularly with mild soap. Loofah sponges cause fine scratches and increase the risk of infection. Routine cleansing will get rid of dead skin cells, sweat and dirt.
Do not use perfumed soaps and foams for this case. Fragrances and the chemicals in them can upset the acid balance in the vagina. Bar soap can be softer than foam soap.
Some hygiene products help restore the natural acidity of the vagina. If you use any product and the smell does not change or worsens, be sure to visit a doctor. You may need treatment.
Some women notice a stronger vaginal odor during their period. Some women smell iron, which is similar to a metallic odor, while others smell like ammonia.
Some menstrual products trap odor, exacerbating this effect. To reduce odor:
- Try wearing internal products. Moisture from maxi pads can contribute to odor. Sitting on something wet can also cause infection.
- Change your menstrual products frequently.
What diseases are characterized by an ammonia smell in urine?
So, if you notice that the urine has a strong smell, is cloudy, contains foreign impurities, and causes pain when urinating, then the probable causes of the abnormalities may lie in the following pathologies of the genitourinary system.
- Urethritis: develops against the background of damage to the mucous membrane of the urethra by a bacterial infection. Often, blood clots can be seen in the urine, and the process of urination itself is accompanied by cutting pain in the lower abdomen.
- Cystitis: a fairly common disease in women, which is explained by the proximity of the internal organs to the urethral opening, through which the infection enters. As a rule, the disease develops against the background of reduced immunity due to hypothermia, taking certain medications, or damage to the body by bacterial/viral/fungal infections. Irritation of the bladder leads to a frequent urge to urinate, a feeling of incomplete emptying, and itching of the labia.
- Pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys) or pyelitis (inflammation of the adrenal pelvis). Inflammatory processes of the urinary organs develop, as a rule, in the form of a secondary infection against the background of weak immune defense (as a result of hypothermia or infection of the body with pathogens). Often, the strong smell of urine appears against the background of acute pain in the lumbar region.
- Infectious diseases (chlamydia, gardnerellosis, vaginosis). Genital tract infections are common reasons why urine smells like ammonia. The proximity of the vaginal and urethral openings leads to the migration of pathogenic microorganisms and the spread of infection, resulting in changes in the color, smell and consistency of urine.
- Systemic diseases (diabetes, kidney and liver failure, hepatitis, tuberculosis, etc.) against the background of general malaise are manifested by cloudy urine and the appearance of a strong odor from the vagina.
- Malignant neoplasms. Tumors of various etiologies and localizations can cause urine to smell like ammonia and change color and consistency. Associated symptoms include: sudden weight loss, loss of appetite, general weakness, exacerbation of chronic diseases, etc.
- Prostate adenoma/prostatitis. In men, inflammation of the prostate gland can provoke a change in the smell of urine. As a result of the pathology, urine stagnation occurs and urination becomes difficult.
Due to the fact that the etiology of unpleasant urine odor is usually pathological in nature, you should not self-medicate, regardless of whether these symptoms manifest themselves in a child or an adult. Basic diagnostics (urinalysis) will allow you to identify the disease in the early stages and deal with it in a timely manner.
Ammonia is a toxic waste product of protein metabolism. To prevent it from causing poisoning of the body, ammonia is neutralized in the liver and excreted in the urine in the form of urea and ammonium salts. These metabolic products normally smell very faintly if they are sufficiently diluted in urine. If for some reason their amount in the urine increases, then the olfactory cells of our nose begin to perceive the strong ammonia smell of urine.
Types of yellow discharge
Yellow discharge can be divided into natural - considered by gynecologists as an acceptable norm - and pathological. The latter come with or without scent.
Without smell
Yellowish, odorless discharge may indicate the development of diseases of the female reproductive system. The causes of the condition can be:
- Colpitis. Physiological secretion increases, but does not change the color or smell. Typical manifestations are itching, burning in the area of the external genitalia, swelling and hyperemia of the tissues of the vulva, discomfort when urinating.
- Adnexitis (combined inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes). Additional signs are pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the lumbar region, poor health, and increased temperature.
- Cervical erosion.
Damage to the vaginal segment of the cervix may also be accompanied by the appearance of yellow leucorrhoea. This sign indicates the appearance of an inflammatory process and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection. After treating erosion, the presence of yellowish impurities in the mucus is normal. - Sexually transmitted diseases. The introduction of pathogens (infectious agents) into the mucous membrane causes not only a modification of the physiological secretion, but is also accompanied by such conditions as swelling of the labia majora and minora, severe itching, etc. An example of such pathologies is chlamydia.
With smell
Discharge in women of a yellowish color, accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant aroma, cannot be a variation of the norm. This symptom indicates the development of some pathological process.
Yellow discharge in women with a specific odor may be a sign of the following diseases:
- Vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis). Leucorrhoea with this pathology takes on a characteristic fishy amber and becomes more watery in consistency. Pathology is an inflammatory process that forms in the vaginal mucosa against the background of a violation of the natural balance of microflora. The cause may be taking medications from the group of antibiotics, changes in hormonal levels, violation of intimate hygiene rules, etc.
- Endometriosis. A hormonal disease accompanied by pathological proliferation of uterine endometrial cells and its exit beyond the organ. An additional sign of the disease is the appearance of profuse vaginal leucorrhoea of dark yellow or brown color. It has a consistency similar to water and has a very unpleasant, pungent stench.
- Cancerous tumors of the female reproductive system.
For such diseases, the development of bleeding is typical, as is the appearance of a red-yellow secretion. A yellow tint indicates the presence of purulent components in the leucorrhoea. The smell of the secretion becomes very unpleasant (contains notes of rot). Additional signs are pain spreading to the lower abdomen and sacral region, general weakness, apathetic mood, weight loss. Thick yellow discharge in women, which acquires a heavy foul odor, in the presence of cancer pathology, accompanies the formation of a fistula canal connecting the organs of the female reproductive system with the rectum or bladder. - Thrush (vaginal candidiasis). White-yellow mucus of a cheesy nature with the smell of sour milk indicates the development of thrush. Additionally, symptoms such as swelling and severe itching appear. In the absence of treatment for this gynecological pathology, leucorrhoea transforms into greenish-yellow. Erotic areas appear on the surface of the mucosa.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. Most often, such secretion, of an unnatural yellow color and with an unpleasant odor, accompanies decompensated diabetes mellitus. In this case, the mucus develops a characteristic odor of acetone and painfully severe itching of the vulva.
- STD. Not all diseases from this group are accompanied by daily odorless leucorrhoea. The vast majority of vaginal mucus begins to emit an uncharacteristic aroma. The following symptoms may indicate an STD - severe discomfort in the external genital area, swelling of the mucous membranes, redness of the tissues. Gonorrhea, gardnerellosis, and trichomoniasis occur with the appearance of an unpleasant odor of leucorrhoea.
Yellowish discharge that appears during the period after an abortion/diagnostic curettage in women indicates infection and the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
Natural causes
The odor is often described as a strong odor like rotten eggs or rotten fish, or urine is said to smell like bleach. The main thing is that such a change in aroma always raises the suspicion that something is wrong in the body. Let's try to understand the causes and treatment of this phenomenon in an adult. Even if the urine smells like ammonia or ammonia, this is not always a symptom of the disease. Before you panic, you should check for physiological factors that change the smell of urine:
- Mainly protein diet. Proteins consist of amino acids, from which ammonia is formed during metabolism in the liver. This means that the more protein you eat, the more waste in the form of ammonia must be removed from the body through urine and the stronger the urine will smell.
- Not drinking enough or being dehydrated. If you have drunk little fluid in the last few days or have been sweating excessively, the amount of water in your urine will be less, resulting in a relatively higher ammonia content. This concentrated urine is darker in color and has a strong odor.
- Female body. There are a number of reasons why urine smells like ammonia in women more often than in men. The proximity of the vagina with its specific microflora to the urethra facilitates the penetration of bacteria that produce ammonia. The number of these bacteria depends on the presence of an imbalance in the vaginal microflora (vaginosis). The main hormone that regulates vaginal microflora and protects against genitourinary infections is estrogen. A decrease in its amount is observed during menstruation, pregnancy and menopause due to hormonal changes in the body.
- Prolonged retention of urine. If the urine is fresh? then it has almost no smell. If you do not empty your bladder in time, the urea will begin to break down into ammonia particles, and the urine will smell of hydrogen sulfide.
- Taking some vitamins (especially group B), dietary supplements, using hot herbs and spices (garlic, horseradish, asparagus).
- If the urine collected for analysis is not covered with a lid, it will begin to oxidize and begin to smell as if it is “rotten.”
Usually, a physiological reason increases the smell of urine only for a short time. When urine smells like ammonia for a long time, this may mean that the function of some organ in our body is impaired.
How to treat abnormal vaginal discharge
Treatment of problematic discharge should always be carried out with the participation of a doctor after a thorough diagnosis.
For bacterial infection and inflammation associated with it, antimicrobial drugs are prescribed. Antibiotics are prescribed orally and locally in the form of suppositories, creams, and ointments.
For fungal infections, antifungal drugs are prescribed. It is worth remembering that thrush is a local manifestation of extensive fungal damage to the body, and its treatment is not limited to suppositories and creams.
For viral infections, antiviral drugs are prescribed. Viruses are dangerous organisms, and doctors have not yet learned how to effectively treat them. Increasing immunity plays a vital role here.
If tumors appear, they can be treated conservatively or removed. Here, the decisive role is played by the nature of the neoplasm - benign or malignant - and the speed of its development.
In case of intrauterine pregnancy with a threat of miscarriage, the patient is sent to the hospital, the condition of the uterus, placenta, and fetus is examined. In case of an ectopic pregnancy, immediate removal of the fertilized egg from the woman’s body is required.
In any case, when unhealthy discharge appears, very careful hygiene is required, since many pathological discharges corrode the skin of the genitals. Sometimes the doctor prescribes baths with medicinal solutions and douching.
There are many traditional methods for treating discharge. They sometimes help, but sometimes they can blur the clinical picture and complicate the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. Among the folk methods, washing with herbal decoctions is considered safe and useful.
Chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort relieve inflammation, increase local immunity and soothe irritated skin. Under no circumstances should foreign objects be inserted into the vagina, as some folk recipes advise.
Urogenital infection and unpleasant odors in urine
Pathogenic bacteria decompose urea and “release ammonia,” and some are able to produce it themselves. Therefore, with acute or chronic inflammation or infection of any part of the genitourinary system, the smell of ammonia increases in the urine. The following diseases may be the causes:
- Urethritis, which causes pain and pain during urination, sometimes bleeding at the very beginning - initial hematuria.
- Cystitis (pain and frequent urge to urinate, feeling of incomplete emptying, blood at the end of urination - terminal hematuria). It is important to know that with mild to moderate cystitis, an increase in body temperature is not observed if there are no other infections in the body. The fact is that the mucous membrane of the bladder prevents the penetration of microorganisms and their toxins into the blood.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidney, where urine is secreted. Complaints with pyelonephritis are quite typical: aching, dull pain in the lower back (usually one-sided, spreading towards the thigh), painful urination (concomitant cystitis). There is foul-smelling cloudy urine, sometimes with the smell of rot, signs of intoxication of the body (high temperature, chills, transient fever may be observed with periods when normal body temperature is recorded), bloody urine (blood is released during the entire act of urination - total hematuria).
- Infection of the genital organs, incl. and specific (gonorrhea, chlamydia, tuberculosis), can spread to the urinary system. At the same time, it smells rotten not only from urine, but also from discharge from the genitals.
- Bacterial vaginosis (gardnerellosis) and thrush (vaginal candidiasis) are not infections, but only dysbacteriosis of the vaginal microflora. However, they also manifest themselves as discharge that smells “fishy.” When the prostate gland is inflamed in men, the urine smells like rotten eggs.
What non-infectious diseases cause urine to smell bad?
The unpleasant odor of ammonia in the urine in women and men can occur due to the following disorders of protein or fat metabolism in the body:
- Liver diseases
(disruption of the process of formation of urea from ammonia, and the release of free ammonia in the urine). - Diabetes
. Diabetic urine begins to smell like acetone or sour apples. Why is there so much acetone in urine? Acetone is the end product of fatty acid metabolism and its amount in urine increases if the body switches to using fatty acids as an energy source (instead of glucose, which it can no longer absorb). The same thing happens if we fast or eat a lot of fatty foods and few carbohydrates. - Genetic diseases
, when the body has a deficiency or complete absence of any enzyme that takes part in the metabolism of amino acids (phenylketonuria).
Strange smell of urine in pregnant women
Why does ammonia-smelling urine occur in pregnant women? The enlarged uterus during pregnancy puts pressure on the ureters, and the hormone progesterone relaxes the muscles of the ureter and bladder. This causes stagnation of urine, and such urine is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria and the development of urinary tract infections. But urine smells like ammonia in pregnant women not only during infections. Almost all hormones released for the growth and development of the fetus inhibit the activity of insulin, which disrupts the absorption of glucose and its metabolism in the body. This condition is called gestational diabetes. It goes away after childbirth. In addition, during pregnancy, a woman may experience an exacerbation of chronic liver diseases, which is responsible for the conversion of ammonia into urea.
What to do?
Strong and strong-smelling urine and other symptoms do not always allow for an accurate diagnosis. The sudden onset of the disease and the putrid odor of the excreted urine almost always indicate a serious disorder. But there are cases when an infection or metabolic disorder proceeds sluggishly for a long time, without obvious signs. With this course of the disease, you can lose vigilance and miss the moment when the disease can be most effectively cured. That is why it is recommended to take a urine test in any case. With an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, microscopic examination of urine sediment reveals the following changes:
- Leukocyturia (increase in the number of leukocytes to 50 in the field of view). Normally, their number during microscopic examination is no more than 5 in the field of view. More than 50 leuktocytes are pyuria (discharge of pus).
- Bacteriuria, when 1 ml of urine contains more than 100,000 bacteria.
- Hematuria (as a symptom accompanying inflammation).
- Acid ammonium urate.
- There are many transitional epithelial cells that line the mucous membrane of the bladder, ureters and renal pelvis.
It is not recommended to treat the cause of unpleasant urine odor at home, because It is not the phenomenon of unpleasant smell of urine that needs to be eliminated, but its cause. If the doctor determines that the urine smells of ammonia due to chronic inflammation, then you need to support your immune system and avoid hypothermia and infections. During pregnancy, it is important to drink a lot of water and maintain good hygiene, do not hold back urine, and be able to go to the toilet when you have the urge to urinate. If the cause of the unpleasant odor is a malnutrition, then you should follow a diet, eat less spicy foods, and do not use aromatic spices.
Moderate discharge in women indicates the functioning of the reproductive system. They protect the vulnerable mucous membranes of the vagina and uterus from pathogenic viruses, microbes, fungi, and bacteria. But an ammonia smell indicates trouble. If such a manifestation was an unpleasant episode, you can forget about it. If the smell is felt constantly or periodically, this is a reason to contact a specialist.
Our article will not replace professional advice, but will help you understand in general terms what causes the ammonia smell.
The urine of a healthy person is clear and does not smell when fresh. Normally, a woman produces 1.5 to 1.8 liters of urine per day. Ammonia is a by-product of metabolism, the production of amino acids. A well-functioning liver converts it into urea and excretes it in the urine. The smell is a signal that for some reason the liver has not coped with its work, and ammonia, a toxic substance, remains in your body.
Women are much more likely to suffer from ammonia odor, since their genitourinary system is more vulnerable, and the vagina has specific microflora designed to protect the “cradle of life” - the uterus.
Non-pathological causes of the phenomenon
Ammonia-smelling discharge may occur if:
- There is too much protein in your diet
; your liver cannot process it into amino acids. Write down everything you eat for a week and check the protein content in the food charts. It’s even easier to take a simple urine protein test - You don't drink much.
You need to drink 2-2.5 liters of water per day (not counting other liquids - juice, soup, tea, etc.) Another reason for the smell is holding back urination. This should not be done under any circumstances. You risk damaging your liver and kidneys - You go through puberty, pregnancy, menopause
, when hormonal levels and vaginal microflora change. For some time, these changes may be accompanied by an ammonia smell. - Your period has started.
The pad smells like ammonia for the first 1-2 days - the reason is the same hormonal changes - You take medications
with calcium or iron, multivitamin complexes - Improper care of the genitals.
It sounds harsh, but, unfortunately, this is the reality that gynecologists face. As a child, many mothers are embarrassed to teach a girl how to wash herself properly. Sometimes this inability remains in adult women. You need to wash your precious, vulnerable genitals in the direction from the vagina to the anus (the other way around - you can’t!), with warm water (not hot or cold!) and using a detergent with a neutral pH. Do not use the same towel for body and face
Thus, if the discharge smells like ammonia for a short time, without pain or other alarming signs, and the normal state quickly returns after eliminating the causes, there is nothing to worry about.
Why can the smell be bad?
The natural odor is practically imperceptible and is normal when a woman does not experience any discomfort and a constant desire to wash herself.
However, if pathogenic flora enters the body, the vaginal odor changes and becomes more pungent and unpleasant. With the development of infectious diseases, a woman may feel a sharp, cheesy or putrid odor in her vagina, which almost always indicates the presence of infection, inflammation, thrush or other, more dangerous diseases.
If a man, during sexual intercourse, suddenly felt that his beloved clearly had not a rose between her legs, but something else, more unpleasant, he should try to tell her about it, as delicately and gently as possible.
However, rude words like “hey, something stinks there” will only offend the girl. This, of course, will make her, at a minimum, think about her own health, but the relationship with the guy may deteriorate.
Gynecologists, after conducting a huge amount of research, have proven that the smell in itself is not a pathology, but if rotten, fishy or sickly sweet is mixed with the normal aroma, you should definitely take tests for microflora and consult a doctor.
The most dangerous is the “fishy” aroma. This is a manifestation of bacterial vaginosis, which can occur in women at any age, both before sexual activity and after menopause. Poor intimate hygiene, improper wiping - all this leads to infection.
A yeasty odor is common in women with diabetes, and a rotten odor often indicates that a tampon or other foreign object was left in the vagina.
poor nutrition and eating spicy foods, weak immunity, abnormal, pathological structure of the vagina, as well as the use of certain medications and refusal of contraception.
Sex fact
In addition, an unpleasant odor may be present after childbirth, or some time after sex if the partners did not use protection.
The presence of a specific odor in vaginal secretions is normal if it is not accompanied by discomfort. Bad and uncharacteristically smelling discharge should be alarming.
Among the main factors that provoke the appearance of an unpleasant aroma from the vagina are:
- insufficient hygiene of intimate places by a woman;
- frequent douching;
- use of medications;
- using panty liners;
- recent intimate intercourse;
- incorrectly selected underwear (synthetic, excessively tight).
If a woman who carefully observes hygiene suddenly develops a stench in the external genital area, she should visit a doctor. This may be a symptom of a serious illness.
The appearance of a sour, unpleasant odor from the intimate area indicates a problem called thrush. This disease is provoked by the rapid proliferation of fungi in the vaginal microflora. In addition to the smell, the following symptoms will indicate a fungal infection:
- the presence of a sensation of itching, burning of the mucous membrane;
- the appearance of reddish rashes in the external genital area;
- the problem of difficulty and pain when urinating;
- pain during sex;
- the appearance of thick, cheesy vaginal secretion.
If a woman feels a rotten smell (stench) from the vagina, this indicates either an advanced thrush or the presence of a more serious pathology.
The appearance of a fishy odor from the intimate area may indicate the incidence of chlamydia. Symptoms of this disease include copious vaginal secretions that are yellow in color and have a putrid aroma characteristic of decaying fish.
However, chlamydia does not always manifest itself so clearly. In many cases, the disease is asymptomatic. It is transmitted sexually. Dangerous with complications. Chlamydia threatens inflammation of the uterus and appendages, problems with conception, and infertility. It must be treated promptly and competently.
The appearance of a garlic odor from the vagina and discharge of women indicates a problem called dysbiosis. We are talking about a disease caused by an imbalance of vaginal microflora. The predominance of pathogens in it leads to the appearance of a sharp unpleasant odor from intimate places. Among the pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the disease, you can see pathogenic ones like:
- staphylococci;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- cryptococci;
- coli;
- Klebsiella
In addition to the unpleasant odor, dysbacteriosis is indicated by symptoms in the form of the appearance of thick vaginal secretion, which has a yellowish or gray-green tint, and uncomfortable cutting and itching sensations in the area of the external genitalia. The doctor will answer the question of how to treat dysbiosis. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Ureaplasmosis
The appearance of an onion smell in vaginal discharge is a symptom indicating ureaplasmosis. Vaginal secretions with this disease smell bad due to the activity of a microorganism called ureaplasma and causing non-gonococcal urethritis.
Among the main signs of a problem are the following:
- the appearance of thick mucous vaginal discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urge to visit the restroom for minor needs, uncomfortable painful sensations when emptying the bladder;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle (the symptom appears rarely).
The incidence of gardnerellosis is manifested by the appearance of a strong odor, reminiscent of dried fish, in the vaginal discharge and external genitalia. It is not possible to get rid of it with soapy water. On the contrary, it intensifies when washing, as well as after sexual intercourse.
The disease tends to be asymptomatic. In advanced cases, it makes itself felt by stench, itching, pain and the appearance of vaginal discharge that has a gray or greenish tint.
One of the symptoms of Trichomonas colpitis is a discharge with a strong smell of iron (or rotten eggs). The disease can be acute or chronic. This is an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix, and urethra.
Infection with pathogenic microorganisms, called trichomonas colpitis, manifests itself in addition to the unpleasant odor with the following symptoms:
- observation of abundant foamy vaginal secretion with a yellowish or greenish tint;
- hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia, itching sensations and increased temperature;
- severe pain when emptying the bladder;
- increased symptoms during menstruation.
If the disease is not treated, it becomes chronic with vague and mild symptoms. The chronic form is dangerous due to complications.
An unpleasant specific odor in the intimate area may be a symptom of gonorrhea. This disease is transmitted through unprotected sex.
It appears along with the following symptoms:
- copious vaginal discharge of a yellowish tint;
- soreness in the lower abdomen, increasing during emptying of the bladder;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Symptoms of the development of gonococcal infection are also considered periodic soreness in the throat and a rise in temperature to 37.2. The main threat of gonorrhea is a decrease in immune defense, which leads to secondary infection.
When the reproductive system, including the uterine appendages, is affected, the female body loses the ability to procreate. The infection can affect the entire body, blood vessels, penetrate the respiratory system and the heart lining.
READ MORE: After severe stress, spotting