Mkb
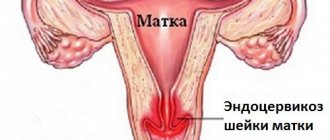
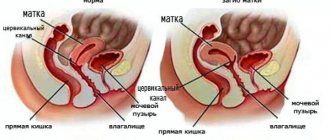
Cervicitis is a disease of the cervix in which inflammation develops. There are two similar concepts - exocervicitis and endocervicitis.
- The first disease is inflammation of the vaginal area of the cervix;
- The second is inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal of the cervix.
A disease such as exocervicitis according to ICD 10 refers to paragraph No. 72, which indicates inflammatory diseases of the cervix.
This diagnosis is made to women who seek medical help in 70% of cases.
Exocervicitis code according to ICD 10 No. 72 can be of different forms, these are:
- Acute;
- Chronic.
Exocervicitis ICD 10 – how is this diagnosis confirmed?
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures to the patient, which include:
- Microscopic examination;
- Bacteriological research;
- Cytological examination;
- Polymerase chain reaction or enzyme immunoassay.
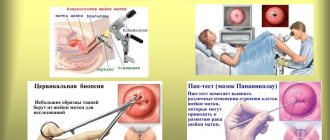
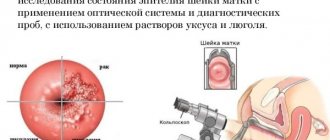
To obtain an accurate description of the disease, a woman needs to have a colposcopy. The results of such a study will make it possible to evaluate the following characteristics:
- The consistency of the discharge, which may differ depending on the type of pathogen;
- The presence of bright red dots on the surface of stratified squamous epithelium;
- The presence of an inflammatory process can be detected using the Schiller test. The lesions will be visible as light dots on a brown background;
- A purulent coating is visible on eroded surfaces.
To confirm or exclude oncological formations, an OMT ultrasound is performed.
The diagnosis of exocervicitis - ICD 10 code No. 72 is made after laboratory and instrumental studies
Before making a diagnosis, you need to undergo laboratory and instrumental studies.
Through microscopic examination, it is possible to identify the exact number of microorganisms, as well as determine what type they belong to.
With the help of bacteriological examination, it is possible to determine to what genus or species microorganisms belong. Their sensitivity to antibiotics is also determined.
Using the cytological method of research, it is possible to determine the structure and cellular level of tissue damage. It can also help you understand whether a particular treatment is effective.
Using colposcopy, you can also identify the type of pathogen and determine which treatment will be more effective.
In addition to laboratory diagnostics, an extensive examination of the cervix and instrumental examination of the pelvic organs are carried out. This should be done to exclude oncology.
ul
Treatment methods and drugs
Treatment of exocervicitis includes several stages. At the first stage, the pathogen is eliminated. Depending on what exactly is the causative agent, appropriate medications are prescribed:
- bactericidal;
- antiviral;
- antifungal.
If the inflammation is specific and the patient has a regular sexual partner, he, too, undergoes treatment at the same time. At the next stage, the vaginal microflora is restored. For these purposes, preparations containing lactobacilli are used. In most cases, forms of drugs that have a local effect are used, for example, suppositories, ointments. Most often, to restore intimate microflora, the following are prescribed:
- Acylact;
- Lactagel;
- Bifidumbacterin.
At the last stage of treatment, general and local immunity is strengthened. For this purpose, vitamin-mineral complexes and immunomodulators are prescribed. Also, a woman must follow certain rules regarding intimate hygiene so as not to provoke a relapse of the disease. This is all when it comes to the classical treatment of exocervicitis. But, surgical treatment can also be used. This is required when the disease has already caused serious complications, for example, in the form of erosion. When using a surgical treatment method, the following are most often used:
- cryodestruction;
- laser radiation;
- electrocoagulation.
If exocervicitis was diagnosed during pregnancy, surgical interventions are contraindicated. The doctor prescribes medications to get rid of the infection that caused exocervicitis. He selects them from the list of those allowed during pregnancy, taking into account its duration. This allows you to quickly and safely cure the disease without harming the fetus.
What you need to know about cervical diseases in the video:
Etiology
The reason for the appearance of nonspecific exocervitis is the growth of opportunistic flora, which does not manifest itself in a healthy woman. This condition can be caused by:
- Staphylococcus;
- Streptococci;
- Escherichia coli;
- Bacteroides and others.
The etiology of a specific exocervitis may involve infection with an STI, this is:
- Chlamydia;
- Fungus;
- Trichomoniasis;
- Gonorrhea;
- Mycoplasmosis and others.
There are also predisposing factors that can trigger the development of this disease:
- Inflammatory diseases OMT;
- Injury to the cervix during childbirth or abortion;
- Prolapse of the vagina and, accordingly, the cervix;
- Decrease in the body's defenses;
- Use of intrauterine contraceptives;
- Active sex life with different sexual partners.
Provoking factors also include menopause and menopause in women.
ul
Causative agents of cervicitis
Cervicitis is common among girls and women aged 16 to 35 years who are sexually active. The causative agents of the disease are nonspecific flora - opportunistic bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, enterococci, etc.) and sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia trachomatis, ureaplasma urealyticum, mycoplasma hominis, genitalium, trichomonas, gonococcus), sometimes viruses and anaerobic microflora (gardnerella , fusobacteria, bacteroides, etc.).
Conditional pathogens penetrate the vagina and cervix from the intestines or through the blood and lymph flow, and are specifically infected during sexual intercourse. Infections, especially hidden ones, sometimes remain in a woman’s cervical canal for years without causing inflammatory processes, but when the immune system is weakened, they can make themselves felt at any time in the form of colpitis, cervicitis, adnexitis, endometritis and other diseases of the pelvic organs.
Kinds
If we take into account the type of pathogenic bacterium that caused the inflammation, the types of exocervicitis can be as follows:
- A purulent disease develops due to infection with gonorrhea. Characteristic signs are accumulation of pus in the cervical canal;
- The viral disease is transmitted through sexual contact. The symptomatic picture is itching of the external genitalia, discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen;
- The bacterial type of the disease occurs against the background of existing gonorrhea, vaginal dysbiosis or bacterial infection. Characteristic symptoms include abdominal pain and suspicious discharge mixed with mucus or pus;
- The candida species differs in that the cause of inflammation is a fungal infection.
Atrophic exocervicitis is diagnosed at the site of the affected area after abortion, curettage, and uterine rupture during childbirth.
ul
Types and symptoms
Experts divide cervical inflammation into several types. The prescribed treatment depends on the exact diagnosis. Cervicitis occurs:
- Spicy;
- Chronic;
- Atrophic;
- Purulent;
- Candida.
Each type of disease arises from a specific pathogen and requires specific therapy.
| View | Pathogen | Peculiarities | Treatment |
| Spicy |
| It affects not only the superficial layers of the cervical mucosa, but can also affect the tissues of nearby organs |
|
| Chronic |
| It is often asymptomatic and can only be detected during examination by a gynecologist. If left untreated in time, inflammation can lead to the development of dysplasia. |
In advanced forms of chronic inflammation, surgical intervention may be necessary:
It is mandatory to use drugs that restore the natural microflora of the vagina |
| Atrophic |
| Occurs as a result of abortion or any other internal intervention in the uterus | The following groups of drugs are prescribed for treatment:
|
| Purulent | Sexually transmitted diseases. For example: urethritis, gonorrhea. | Before the appearance of purulent discharge, symptoms of pseudo-erosion may appear. After sexual intercourse, bleeding often occurs. |
|
| Candida | Fungal infections | In most cases, treatment is carried out with both sexual partners | Antifungal drugs (Diflucan, Pimafucin, etc.) |
Acute cervicitis
characterized by the presence of purulent vaginal discharge, elevated body temperature, pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region, difficulty urinating, and a feeling of hot flashes in the pelvic area. Modern diagnostic methods rarely determine this type of inflammation, so the main indicators for establishing a diagnosis are the results of culture and smear tests.
Important! Acute cervicitis occurs against the background of sexually transmitted diseases, to avoid this, both partners need to be examined by a specialist. If necessary, then two people should undergo treatment.
Chronic cervicitis
Most often it is asymptomatic. The main clinical signs of inflammation can be seen in the mucous discharge: it becomes cloudy, has a yellowish tint, the presence of pus is noticeable, and the discharge intensifies before and after the menstrual cycle. Pain occurs during urination and sexual intercourse.
Atrophic cervicitis
occurs when there is mechanical damage to the uterine tissue. This type of inflammation most often affects women from the following risk groups:
- Patients of childbearing age;
- Having promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Suffering from regular hormonal imbalances;
- During menopause and menopause.
Intervention in the internal structure of the uterus leads to a weakening of its protective function, thereby increasing the risk of inflammation. The main method of treatment is taking hormonal drugs containing estrogens.
Purulent cervicitis
affects tissue cells both inside and outside the cervix. This type of inflammation is transmitted sexually if the partner has urethritis. The main symptom of the diagnosis is bleeding discharge. A sign of the onset of this type of disease may be the presence of pseudo-erosion.
Candidiasis cervicitis
popularly called colpitis. The infection develops with severe immunodeficiency. Women who have HIV disease can receive this diagnosis.
Moderate exocervicitis
Many women who are faced with this diagnosis want to know whether moderate-to-severe exocervicitis - what does it mean? In fact, the moderate form of exocervicitis proceeds in the same way as the acute form of the disease, only the symptomatic picture is not so pronounced. The main manifestations of the disease include irritability, emotional instability and excessive nervousness.
Moderate exocervitis must be treated, and this will be effective if you seek medical help in time. In the worst case, infectious inflammation can affect the genital tract, which provokes the occurrence of other diseases.
Making a diagnosis of moderate exocervicitis
A woman who regularly visits a gynecologist knows what a cytogram means. For those who are not familiar with such a study, it is worth explaining that this is a kind of microscopic analysis that can be used to evaluate the sloughing off epithelial cells. Based on the results of the analysis, it is possible to understand what processes occur in the female genital tract or organs.
If the question arises of how to understand moderate exocervicitis and false erosion, then using a cytogram you can distinguish the presence of pathological inflammation from other diseases of the cervix.
Through this analysis, the disease is diagnosed at an early stage of its development. You can also accurately assess the condition of the cervix, namely:
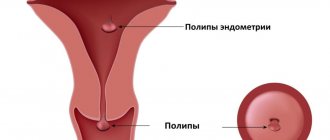
- Presence of oncological formations;
- Proliferation of polyps;
- Detection of leukoplakia.
The diagnosis of “exocervicitis – moderate severity” is made based on test results
A cytogram determines the distinctive features of the cell nucleus, as well as its cytoplasm. Using special techniques, cells are counted in the layers of the cervical epithelium. This calculation of indices helps to diagnose a pathological condition in a woman. Frequent inflammatory diseases due to exposure to various pathogens are taken into account.
A cytogram of inflammation against the background of herpes infection shows a sparse chromatin structure, its uneven distribution and an increase in nuclei in cells are also visible. Microscopic examination may reveal cells of irregular shape and size.
If the development of the disease is provoked by the human papillomavirus, then the analysis will show the presence of large nuclei in directional-shaped cells. Multinucleated cells and keratinized epithelial cells will also be visible. Based on such signs, the doctor cannot make a final diagnosis of “moderate exocervicitis,” so additional diagnostic methods are often prescribed.
A cytogram of moderate inflammation can detect cells with biological abnormalities in the superficial and intermediate layers of the cervical epithelium. Such cells do not spread to the lower layers of tissue, and the nature of their growth depends on the degree of the inflammatory process. If the inflammation is mild, then the woman is diagnosed with moderate exocervicitis.
The result of cytology is influenced by the age and hormonal background of the woman. If the diagnosis does not give accurate results, then a more informative study is prescribed - a biopsy.
If the exact type of pathogen is identified, and the inflammatory process does not stop, then the woman is prescribed a test to determine other sexually transmitted infections. Perhaps the cause of the disease lies in the spread of chlamydia, gonococci or ureaplasma.
If the result of tests for infections is negative, then bacterial culture from the cervix is prescribed, after which they begin to eliminate the identified pathological microorganism.
Moderate exocervitis - what are the complications if you refuse treatment?
If, as a result of the cytogram of inflammation, the causative agent of the disease was identified, then they begin to determine the treatment regimen. If treatment is not carried out for any reason, then due to inflammation and hardening of the tissues of the cervix, serious complications develop that can develop into a malignant disease, these are:
- Leukoplakia and pseudoerosion;
- Polyps and condylomas of flat type;
- Colpitis and ecropion;
- Salpingitis and endometritis;
- Cervicitis and endocervicitis;
- Dysplasia and so on.
Moderate exocervicitis is not accompanied by severe pain. In most cases, a woman feels only discomfort. For this reason, the disease is often not treated, which leads to the development of chronic pathology. As inflammation progresses, other genital organs suffer, which is why other diseases may be diagnosed against the background of this disease. As the inflammation progresses, the woman may experience increasing pain.
It is impossible to independently identify the disease and determine in advance the consequences of a long-term inflammatory process. Self-medication is highly discouraged, as the risk of complications is very high.
ul
Treatment of cervicitis
Treatment of cervicitis depends on the cause of its appearance, the causative agent of the disease and the severity of the inflammatory process. Typically, therapy consists of prescribing systemic or local antibacterial and antimicrobial, sometimes antiviral drugs to suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms and drugs to restore the intestinal flora and vaginal microbiocenosis.
For chronic recurrent cervicitis, the use of immunomodulators and physiotherapeutic treatment is also recommended. The hormonal cause of cervicitis requires correction of the hormonal status by a competent gynecologist-endocrinologist.
It must be remembered that the course of treatment for gynecological diseases must always be completed to the end, especially with regard to antibiotics. Many patients, having felt improvement, quit treatment, which is a big mistake. The infection is not killed, but acquires resistance (resistance) to the group of antibiotics used for treatment, which precludes the possibility of their use in the future.
Also, during treatment of an infectious-inflammatory process, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse, even using a condom, not only to avoid the risk of re-infection, but also since many vaginal suppositories have a destructive effect on latex.
Treatment methods for cervicitis in gynecology
1. Antibiotics and antimicrobials for the treatment of cervicitis.
With a slight inflammatory process in the cervix caused by nonspecific flora, it is usually sufficient to sanitize the vagina with anti-inflammatory antibacterial suppositories and broad-spectrum vaginal tablets (Terzhinan, Polizhinaks, Hexicon, Elzhina, Betadine, etc.)
If a patient is diagnosed with acute cervicitis, or cervicitis accompanied by a more severe disease (endometritis, adnexitis, etc.), after identifying the pathogen, systemic antibiotic therapy is prescribed. If opportunistic flora is detected, an antibiotic is prescribed according to sensitivity culture (most often these are Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone, Levofloxacin, Tsiprolet, etc.).
Vaginal suppositories include Hexicon, Macmiror complex, Elzhina, Fluomizin, Polygynax, etc. You can also treat the cervix with a diluted solution of Chlorophyllipt alcohol, Miramistin, Normoflorins. If cervicitis is caused by sexually transmitted infections, the patient is recommended to be treated together with her sexual partner.
Most often recommended are Vilprafen Solutab, Unidox Salutab, Levofloxacin, etc., depending on the pathogen. Trichomonas cervicitis is treated with Trichopolum, Klion-D tablets and Terzhinan, Fluomizin, Ginalgin suppositories. For cervicitis of a fungal nature, Flucostat, Mikosist and analogues are prescribed, as well as effective vaginal suppositories for thrush - Pimafucin, Neo-Penotran, Livarol, Ginezol, etc.
Herpetic inflammation is controlled by antiviral suppositories Viferon, Genferon, taking Acyclovir, vitamins, and immunostimulants. It is also recommended to irrigate the vagina with Miramistin, Panavir or Epigen-intim sprays. If HPV is detected after removal of condylomas, complex immunostimulating treatment (injections, suppositories) is carried out. As a preventative measure, the use of Epigen spray is recommended.
To treat allergic cervicitis, eliminating the allergen is usually sufficient. For swelling, you can take any antihistamine (Zyrtec, Suprastin, etc.). Atrophic cervicitis, caused by a lack of estrogen, involves the local use of hormonal ointments (for example, Ovestin), which restore the epithelium of the vaginal mucosa.
2. Preparations for restoring intestinal and vaginal microflora.
Vagilac, Provag capsules or Femilex suppositories with lactic acid, Latozhinal, Laktonorm, etc. will help restore the vaginal flora after treatment with antibiotics and antimicrobial suppositories. It is also worth taking care of the intestines; for this, Normoflorin, Bifiform, Hilak Forte and other drugs with beneficial bacteria are prescribed.
3. Immunomodulators for the treatment of cervicitis.
In the chronic course of cervicitis, to maintain immunity in the fight against infections, gynecologists prescribe immunomodulatory drugs to patients. The most popular among them are Galavit, Genferon, Polyoxidonium, and Epigen Intim spray to maintain the immunity of the mucous membranes of the genital organs.
4. Physiotherapy for chronic cervicitis.
For patients who are often diagnosed with cervicitis, or the disease is accompanied by complications, it is also recommended to undergo 7-10 sessions of physiotherapeutic treatment: magnetic therapy, laser, acupuncture, darsonvalization, mud therapy, etc.
5. Surgical treatment of cervicitis.
Advanced cervicitis sometimes requires surgical intervention - laser cauterization, cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation, etc. These methods of treating cervicitis are used after stopping the inflammatory process and eliminating the infection. At the same time, treatment of concomitant gynecological diseases is carried out.
Treatment of cervicitis in pregnant women
How to treat cervicitis during pregnancy? Treatment of cervicitis in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding is complicated by the fact that it is necessary to select drugs and suppositories that do not have a negative effect on the child. But nowadays, in principle, there are a large number of antibiotics and vaginal suppositories approved for pregnant and nursing mothers; the main thing is to correctly determine the causative agent of the disease and sensitivity to the drugs.
Most often, for the treatment of inflammation in gynecology during pregnancy and breastfeeding, vaginal tablets Terzhinan, Fluomizin, Polygynax suppositories (with caution), Hexicon, Pimafucin, Clotrimazole are prescribed. Among antibiotics, penicillins, some cephalosporins, and macrolides are allowed as prescribed and under the supervision of a physician. After completion of therapy, it is also necessary to restore the intestinal and vaginal flora with the previously listed drugs.
Causes
According to the nature of the pathology, there are only two forms of exocervicitis. A woman with a relatively healthy cervix may be diagnosed with an acute form of the disease. Most often, the provoking factors of such inflammation are gonorrhea and fungi. In such situations, the inflammatory process spreads very quickly to other pelvic organs.
Exocervicitis - causes, symptoms and treatment of the disease
Characteristic manifestations of the acute form of the pathology include pronounced vaginal discharge, pain in the lower abdomen and a feverish state.
The chronic form of the disease lasts approximately 2-3 months. Although the symptoms may be subtle, the inflammation will be more pronounced. It can spread to muscle and connective tissue. If the necessary medical care is not provided, exocervitis will progress. The reasons for such a process will be the omission of the disease.
Inflammation can progress for the following reasons:
- Failure to provide medical care in acute forms of the disease;
- Prolapse of the vagina and, accordingly, the uterus;
- Self-prescription of antibiotics and contraceptives;
- Promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules.
With chronic exocervicitis, the cervix increases in size and its tissues become denser. Rejection of the epithelium and formation of cysts also occur.
Exocervicitis - causes of the disease
Knowing what exocervicitis is, you need to figure out what causes can become a provoking factor. If a woman is notified about them, she will be able to take preventive measures to prevent the development of such a disease.
- The main causes of exocervicitis are sexually transmitted diseases that a woman becomes infected with as a result of unprotected sexual intercourse. Such diseases include gonorrhea, chlamydia, etc.
- When pathogenic bacteria multiply, exocervicitis can also develop. Most often, the female genital organs are affected by staphylococcus and E. coli.
- Often a fungal infection causes the development of this disease.
- Inflammation of the cervix can occur due to inflammatory processes occurring in the organs of the genitourinary system. In other words, this can occur against the background of cystitis, colpitis and other pathologies.
- Damage to the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix due to surgical intervention, that is, due to abortion or curettage.
- Prolapse of the cervix and the uterus itself.
- Incorrect installation of the intrauterine device, non-compliance with instructions when taking oral contraceptives.
- The causes of exocervitis may be hidden in hormonal imbalance, which usually occurs in women after menopause.
- Deterioration of the body's defenses and decrease in local immunity.
- Douching the vagina with aggressive solutions.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
To avoid complications and consequences of exocervicitis, you should seek medical help in a timely manner. It is also necessary to refrain from frequently changing sexual partners.
ul
Causes of exocervicitis
There are several factors that can trigger the onset of the disease:
- Promiscuous sex, unprotected sex.
- Decreased immunity due to renal or liver failure, HIV infection, diabetes.
- Abortion, childbirth, as well as the presence of injuries caused to the internal genital organs as a result of these processes.
- Prolapse of the cervix.
- Inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system (colpitis, cystitis, etc.).
- The presence of diseases during which microbes are spread throughout the body along with the blood (tonsillitis, various inflammations, etc.).
- Improper use of internal contraceptives (coils, vaginal suppositories) or frequent douching with aggressive drugs to protect against pregnancy.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body. Most often this occurs in postmenopausal women, when the production of female hormones significantly decreases and because of this, atrophic inflammation begins to develop in the mucous membrane. Another cause of hormonal imbalance may be improper use of oral contraceptives (birth control pills).
- Ignoring personal hygiene rules.
View gallery
Symptoms
Depending on the form of the disease, symptoms may be subtle or pronounced. Manifestations also depend on the type of pathological microorganism.
Complaints most often arise in patients with gonorrhea. And their absence may indicate the presence of hormonal imbalance and chlamydia.
Acute and chronic exocervicitis - what is it? Symptoms and treatment of the disease
In its course, this disease can be acute and chronic.
In the acute form, the symptoms of exocervicitis are quite well expressed. A woman should be alerted by the presence of purulent or mucous vaginal discharge, burning and toothache in the external and internal genital organs. Unpleasant symptoms may worsen with urination. In addition, pain in the lower abdomen may bother you.
Other signs of the disease may appear against the background of other pathologies, for example, cystitis. If a woman has inflamed appendages, then the pain in the lower abdomen will be more pronounced. Also, in frequent cases, body temperature rises. If there is erosion of the cervix, bleeding may occur after sexual intercourse. After menstruation, the symptoms of the disease become stronger.
Chronic exocervicitis - what is it? Symptoms, treatment and prevention of the disease
A characteristic feature of chronic exocervicitis is the absence of pronounced symptoms. Many women are interested in why exactly this happens?
In fact, this fact can be explained by the gradual subsidence of the inflammatory process and thickening of the cervix. After healing of the erosion, which may be a concomitant problem, small cysts form.
Based on its clinical manifestations, cervicitis can be confused with any infectious disease. Women should understand that they cannot self-prescribe antibiotics, since they only suppress symptoms and not treat the disease. If you are concerned about any suspicious symptoms or manifestations, it is better to seek qualified help from a gynecologist.
Exocervicitis - symptoms and treatment with drugs. What is an “appropriate treatment method”?
Based on the identified type of pathogen, various drugs can be used to treat exocervicitis, be it antibiotics, antifungals, antiviral drugs or other medications.
Not only laboratory tests, but also the symptoms with which the woman went to the doctor will help identify the cause of the disease. They can be like this:
- Nagging pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- Pain during sexual intercourse and the appearance of brown spotting after it;
- Pain, burning and stinging when urinating;
- Vaginal discharge may be mixed with blood, pus or mucus;
- Itching of the external genitalia.
These symptoms may be supplemented by general fatigue, increased body temperature, drowsiness and nervousness.
ul
What is cervicitis
This is an inflammatory process in the vaginal part of the cervix. Cervicitis is characterized by cloudy (purulent or mucous) discharge, dull or nagging pain in the lower abdomen, painful sexual intercourse and urination. A protracted chronic disease causes the development of hypertrophy, erosion of the cervix, and the penetration of infection into the upper parts of the reproductive system.
The uterine cervix serves as a protective barrier to infections, but under certain factors its protective functions are weakened and foreign microflora penetrates. This leads to the development of inflammation - cervicitis, consisting of exo- and endocervicitis. The latter is called damage to the inner lining of the cervical canal - the endocervix. Exocervicitis refers to inflammation of the vaginal segment of the cervix.
Causes
Cervicitis can develop due to a nonspecific infection, the causative agents of which are fungi, streptococci, staphylococci, and E. coli. An alternative option is the occurrence of an inflammatory process under the influence of a specific infection, for example, gonococci, chlamydia, syphilis, mycoplasma, trichomonas, gonorrhea, viruses, etc. Conditionally pathogenic flora, stimulating the development of cervicitis, penetrates the cervix by contact (from the rectum, through lymph and blood), and specific - exclusively during sexual contact.
The causes of cervical inflammation, in addition to those listed, include factors that contribute to the occurrence of pathology. These include:
- birth uterine trauma;
- previously performed diagnostic curettages;
- abortions;
- installation or removal of an intrauterine device;
- cicatricial deformities of the organ;
- decreased immunity;
- benign formations on the cervix;
- prolapse of the cervix or vagina;
- genital herpes;
- papillomavirus;
- vaginosis;
- chronic vulvitis;
- erosion or pseudo-erosion of an organ;
- amebiasis, other parasitic infections.
Cervicitis comes in different types - chlamydial, viral, atrophic, candidal, purulent, bacterial, herpetic, so it is extremely important to choose the right treatment, depending on the causative agent of inflammation. Sometimes the pathology of the uterine cervix develops in isolation, and it is accompanied by other diseases of the reproductive system (vaginitis, vulvitis, bartholinitis, cervical eversion). Inflammation of the organ is more often diagnosed in women of reproductive age, less often during menopause.
Classification
Depending on the type of infectious agent, the pathology is divided into several types. Each type is characterized by a specific set of symptoms, which, however, may overlap. The following types of nature of the inflammatory process are distinguished:
- viral (for herpes or human papillomavirus - HPV);
- purulent (with gonorrhea);
- candidiasis (with fungal infection of the mucous membrane);
- nonspecific (not associated with sexually transmitted infections).
In addition to the above classification, there is another one - according to the nature of the course of the disease. So, in the mucous membrane of the cervix the following pathological changes are distinguished:
- Atrophic cervicitis. Due to inflammation, the thickness of organ tissue decreases. As a rule, this occurs against the background of a chronic form of the disease. Often, atrophic cervicitis occurs with HPV, but can also develop in advanced cases of chlamydia or candidiasis.
- Diffuse inflammation. This is a lesion of the entire cervical canal.
- Focal inflammatory process. Occurs in certain areas of the cervical canal.
The inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the cervix goes through two stages of development. During the first, the vagina and cervix become inflamed. In this case, the infection is usually transmitted sexually and can occur without symptoms. The second stage is characterized by direct entry of pathogenic flora into the upper parts of the reproductive system. According to its form, cervicitis is divided into:
- Chronic. A common disease that occurs in the absence of timely treatment of acute inflammation. Chronic cervicitis affects women who are sexually active.
- Spicy. It is characterized by dull pain in the lower abdomen, copious discharge (may be purulent). During a gynecological examination, the doctor sees swelling of the opening of the cervical canal.
Diagnostics
Successful treatment of exocervicitis directly depends on the timely making of the correct diagnosis, therefore, when you detect the first suspicious symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for examination.
Differential diagnosis of exocervicitis
Before prescribing tests and laboratory tests, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints and studies her medical history. After this, a gynecological examination is performed to assess the condition of the external and internal genital organs. To examine the walls of the vagina and the walls of the uterus, the gynecologist uses special mirrors.
To diagnose exocervicitis, diagnosis in the gynecological chair is key.
To choose an effective treatment, one gynecological examination is not enough; you need to undergo several diagnostic procedures, these are:
- Taking a smear from the vagina for flora;
- Cytological analysis;
- Vaginal smear analysis to determine sensitivity to antibiotics;
- PCR to detect or exclude STIs;
- Testing for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B;
- Colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
If a protracted chronic disease is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed a biopsy of the affected area.
ul
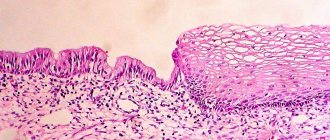
Cytogram
A cytogram of exocervicitis is changes observed in a smear that indicate the presence of inflammation in the cervical area. Cytological examination examines the cellular composition of the resulting sample. This analysis makes it possible:
- Determine the number of leukocytes, eosinophils and other blood cells;
- Study in detail the shape of epithelial cells;
- Clarify the location of chromatin in the nucleus;
- Determine reactive changes in tissue;
- Identify the presence of pathological microorganisms that could presumably be the cause of inflammation.
As a rule, such indicators are characteristic of all layers of the epithelium. They are important for calculating important indices:
- Maturation;
- Karyopyknotic;
- Eosinophilicity.
After analysis, it can be revealed that the cytogram corresponds to exocervicitis, which means the presence of an inflammatory process occurring in the area of the cervix. With this diagnosis, you need to take another smear to determine the sensitivity of the microflora to antibacterial agents.
After treatment of the disease with a previous diagnosis of exocervitis, the cytogram is repeated.
What is a “cytogram corresponding to exocervicitis” and how to prepare for the study?
In order for the cytogram result to be as reliable as possible, you need to follow simple rules for preparing for analysis:
- There should be no sexual intercourse two days before taking a smear;
- It is necessary to avoid douching and inserting medications into the vagina;
- Taking hormonal medications should also be stopped;
- Cytological examination is not done immediately after or before menstruation. The best time for analysis is the middle of the cycle;
- Inflammatory diseases of the cervix or vagina must be treated first, since when taking a smear, the risk of inflammation and pus spreading to other layers of tissue is very high. Based on this risk, a smear for cytology is taken in the absence of an active inflammatory process.
It is not possible to understand what the cytogram means corresponds to exocervicitis during pregnancy, since this cytological study is not carried out. This exception can be explained by the fact that in pregnant women the cervical canal is tightly closed with a plug of mucus. If you neglect this, the risk of damage to this plug will be very high.
You can take a smear for cytology after childbirth, when the birth canal and uterine tone are restored.
The cytogram corresponds to the inflammatory process of exocervicitis - what does this conclusion mean?
The most common conclusion of such a study is considered to be an inflammation cytogram. In fact, such a conclusion is not very dangerous.
Against the background of inflammation, cytological examination may reveal koilocytes, which indicate the presence of human papillomavirus. If such cells are detected, the woman will need to undergo additional examination to confirm the presence of such a disease.
The result of a cytological examination may also show cervical leukoplakia. This pathology can be detected even by taking a smear based on external signs. The doctor can see white areas of keratosis, which stands out perfectly against the background of the pink cervix.
Cytological analysis also reveals such atypical cells. As a result of their division, cells of irregular shape and size appear. If such cells are detected, the analysis is repeated to exclude an erroneous result. The presence of such cells indicates the development of a precancerous condition of the cervix. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the woman should undergo urgent treatment.
ul
Diagnosis of exocervicitis
After an initial manual speculum examination that suggests exocervicitis, the patient is referred for a battery of tests to confirm and clarify the abnormality.
Types of studies to clarify the diagnosis of exocervicitis
A woman is prescribed a number of tests:
- vaginal smear to detect pathogenic microorganisms;
- full colposcopy;
- cytological analysis;
- PCR analysis for the presence of infection;
- blood tests;
- sowing;
- biopsy to exclude the possibility of degeneration of malignant tumors.
- bacteriological tests
Bacteriological analysis is one of the most popular diagnostic methods due to its availability and lack of need for complex equipment. The study is carried out visually under a microscope. This same factor is negative, since the accuracy of the study depends too much on the competence of the personnel conducting the examination, taken from a vaginal smear. The purpose of the study is to count the number of leukocytes in the volume of the medium and determine the presence of fungal infectious agents. This preliminary analysis, although not directly related to exocervicitis, is necessary since the use of many drugs prescribed to the patient can cause exocervicitis or even erosion. If candidiasis, vaginosis and other bacterial diseases are determined, treatment is carried out.
Cytological analysis is a study that is recommended for every woman every year. This study of cells is carried out from the epithelium of several areas of the cervix, which gives a clear picture of the processes occurring in tissues at the cellular level. The result of the study is to identify cells with an altered state. All imaging methods depend significantly on the quality of tissue sampling for analysis. Deviations from normal development in this study are an important basis for further analysis, since they show changes in cell structure that may be a sign of tissue degeneration.
Colposcopy is another visual examination, but using a modern microscope with the help of chemical reagents. The purpose of this study is to determine the presence of altered cells and exocervicitis (erosion) within their localization. A procedure in which the doctor uses a speculum to examine in detail any suspicious areas of the cervix. The examination is accompanied by discomfort when the surface of the cervix is actually inflamed or there is exocervicitis or erosion. In this case, the patient will experience a slight burning sensation.
Biopsy is the examination of a tissue sample taken from a suspicious area on the surface of the cervix or inside its cavity. Colposcopy is often complemented by a cervical biopsy. Under the control of an endoscope, a microsurgery is performed - a sample of living uterine cells is taken for a detailed examination.
Histological examination - this analysis is the last in a series of studies in patients with suspected cervical cancer. A complete histological analysis takes up to two weeks and is the most accurate.
Prevention
Inflammation of the cervix is a very serious disease, which in an advanced stage can cause the development of various kinds of complications. To prevent such a situation, the following prevention of exocervicitis is required:
- You should visit a gynecologist twice a year;
- After birth, uterine ruptures are sutured;
- Abortion is not recommended;
- You should refrain from frequently changing sexual partners and sex without condoms;
- It is worth treating infectious and other sexual diseases in a timely manner;
- You need to periodically do exercises to strengthen the vaginal muscles;
- During menopause, hormone replacement therapy can be performed.
To eliminate the risk of developing the disease, it is also important to strengthen your immune system and lead a healthy lifestyle.
ul
Antifungal
A common cause of inflammation of the genital organs in women is candidiasis. It occurs as a result of infection or overgrowth of the opportunistic candida fungus. Normally, it is acceptable in small quantities in the vagina. With a decrease in immunity, poor personal hygiene, or unprotected sex, the fungus spreads to the cervix. A sign of the disease is the appearance of cheesy discharge, itching, and pain. The use of drugs with local action will minimize the negative impact of the active substance on the body.
Antifungal suppositories are intended to relieve thrush in pregnant women, women with gastrointestinal pathologies, and liver failure. The mild course of the disease also allows you to relieve inflammation without pills.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- Clotrimazole;
- Fluconazole;
- Livarol;
- Pimafucin.
Forum
Women who encounter exocervicitis for the first time do not always immediately consult a doctor. Many people prefer to find out more information about pathology on the Internet by visiting the “exocervicitis forum and reviews” sections. Of course, you can read the information, but only for informational purposes. It is better to begin treatment of the disease after a complete examination and an accurate diagnosis.
Exocervicitis - reviews of acute and chronic forms
If treatment of the disease at the initial stage of its development is not started in time, then there will be a high probability of serious complications. For example, an infection can enter the uterine cavity, resulting in damage to the inner layer of the endometrium. Due to chronic endometritis, the fertilized egg will not be able to attach to the walls of the uterus.
If a woman is planning a pregnancy, then she must cure all gynecological diseases, including chronic endometritis that appears against the background of exocervicitis.
Exocervicitis - treatment. Forum on the use of antibiotics
Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat the disease, but this is done only after the sensitivity of the pathogen to them has been identified.
If the cause of the disease is hidden in the spread of chlamydial infection, then the patient will be prescribed macrolides and tetracyclines. The next stage of treatment will be aimed at restoring the microflora in the vagina.
If inflammation of the cervix occurs due to the proliferation of Candida fungus, then antifungal medications are prescribed. This could be pimafucin or diflucan.
If there is a viral infection, treatment can take much longer and be more difficult. For therapeutic purposes, the woman is prescribed antiviral drugs. In exceptional cases, vaccination may be recommended.
If a woman in menopause is faced with such a diagnosis and has low estrogen levels, then she is advised to use special suppositories.
In addition to the listed drugs, immunomodulatory agents, vitamin complexes and, if necessary, hormone therapy are used to treat exocervicitis. If the disease begins to develop due to an STI, then both the woman and the man undergo comprehensive treatment.
Exocervicitis – how to treat it? Forum about traditional medicine
In the field of alternative medicine, there are special recipes for the treatment of such a disease, which are particularly effective. Despite this, such therapy should be an addition to drug treatment.
As folk remedies, baths of medicinal herbs or tampons prepared from them are most often used.
ul
Treatment
Treatment of cervicitis takes place in two stages. The first implies getting rid of the inflammatory process. The second is to restore the protective functions of the uterus and treat concomitant diseases.
Medications are prescribed depending on the causative agent of the infection. Bacterial or viral inflammation involves taking antiviral and antifungal agents:
- Diflucan (for candidal cervicitis);
- Azithromycin (for chlamydial cervicitis);
- Valtex, Acyclovir (for herpes cervicitis).
In parallel with them, antibiotics are prescribed:
- Tetracycline;
- Doxycycline;
- Maxaquin;
- Tarivid;
- Erythromycin.
Inflammation of the cervix is also treated with broad-spectrum drugs. Depending on the type of diagnosis, experts prescribe the following:
- Terzhinan;
- Betadine;
- McMiror.
Chronic inflammation involves the use of hormonal drugs: tablets, suppositories, creams. In some cases, surgical methods are prescribed. The most effective of them are:
- Cryotherapy;
- Laser therapy;
- Diathermocoagulation.
Surgical treatment is prescribed as a last resort - if drug therapy has not brought results.
In parallel with the use of tablets, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. The following will help alleviate the condition and speed up recovery:
- EHF;
- Electrophoresis;
- Ultrasound therapy.
Traditional medicine recipes will be a good help. At the same time, it is worth remembering that it is better to use them together with general treatment; they are additional means of therapy, and not the main ones. Decoctions and infusions are used for douching or wetting tampons, which are inserted into the vagina and help relieve inflammation. The following methods have proven themselves to be the best:
- Douching
can be done using a decoction of oak bark. 15 grams of the specified raw material should be poured with two glasses of boiling water and simmered over low heat for 10-15 minutes. The resulting broth is cooled to t35°, the procedure is done 3-4 times during the day; - Chamomile infusion
is suitable for both douching and wetting tampons. 30 grams of dried flowers of the plant need to be poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water and left for about 20 minutes. Cool the resulting liquid to t35°; it can be used to wet tampons no more than 3 times a day; - Douching can also be done with sage decoction. Pour 20 grams of dried plant into 0.5 liters of water and simmer for about 20 minutes. Leave the resulting mixture for 6-8 hours, then dilute with 0.4 ml of water at room temperature. Perform the procedure 2-4 times a day.
Important! Douching and tampons soaked in infusions should be used only after consultation with a specialist and with great caution - regular uncontrolled procedures can lead to disruption of the natural microflora of the vagina.
An infusion of eucalyptus leaves, yarrow grass, alder cones, tansy flowers, juniper berries, sage leaves and birch buds is taken orally for inflammation of the cervix. The indicated plant parts are taken respectively in the following proportions: 1:1:1:2:2:2:2. The resulting mixture is poured with boiling water at the rate of 2 tbsp per glass of water. Everything is boiled in a water bath for 8 minutes, cooled for about half an hour, filtered and taken 50 ml three times a day.
Therapy takes place at home under the supervision of a specialist, with the exception of the chronic form of cervicitis, in which surgical intervention is possible. When completing the course, you must strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and abstain from sexual activity.
Chronic cervicitis – what is it?
An undetected disease that lasts for a long time and has not been treated is called chronic. The symptoms are smoothed out so much that it allows the woman to lead a normal life and not experience discomfort or pain. Promotes this condition:
- low immunity, when the body is not able to cope with the infection on its own because it does not have the necessary resources (poor nutrition, smoking, drinking alcohol);
- concomitant diseases (lack of sex hormones, thyroid dysfunction);
- constant change of sexual partners, which contributes to an increase in the number of sexually transmitted infections;
- allergic diseases that reduce the body's protective potential;
- viral diseases;
- mechanical damage to the cervix;
- the presence of gynecological diseases and inflammation of the pelvic organs.
With inadequate sexual life (lack of orgasm), chronic cervicitis may develop due to blood stagnation, even in the absence of pathogenic specific microflora.
Important! Without going to a medical facility, without taking measures to eliminate the disease, a woman exposes herself to the risk of malignant neoplasms that develop as a result of the constant presence of infection and pathological changes in tissue.
ul
Etiology of cervicitis
Cervicitis is caused by infectious causes, that is, under certain conditions, the mucous membrane of the cervix and cervical canal is attacked by pathogenic microorganisms, causing an inflammatory reaction. The disease can be caused by both nonspecific microflora (opportunistic microbes) and specific microflora, which is sexually transmitted.
Nonspecific microflora
Opportunistic microbes enter the cervix through the blood and lymph or from the rectum:
- streptococcus;
- coli;
- Proteus;
- staphylococcus;
- mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- Klebsiella and others.
Specific microflora
Specific infectious agents enter the body, causing inflammation of the cervix, only through sexual contact:
- gonococcus;
- treponema pallidum (syphilis);
- Trichomonas;
- miko - and ureaplasma;
- chlamydia;
- protozoal infections (amoebiasis).
Predisposing factors
Inflammation of the cervical mucosa is provoked by the following factors:
- concomitant diseases of the genital area (cervical erosion and pseudo-erosion, colpitis, inflammation of the uterus or appendages);
- sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia and mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis, thrush, genital herpes, human papillomavirus); most often (25%) inflammation of the cervix occurs against the background of gonorrhea and trichomoniasis;
- nonspecific vulvovaginitis, enterocolitis, tonsillitis and other diseases caused by nonspecific microflora;
- prolapse of the genital organs (cervix, vagina);
- weakening of immune defense;
- frequent change of sexual partners or promiscuous sex life;
- endocrine pathology (metabolic disorders, thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus);
- ovarian dysfunction (the balance of sex hormones is disrupted, which causes a disorder in the protective function of the cervix);
- hormonal changes in the premenopausal and menopausal periods (a decrease in estrogen leads to thinning and vulnerability of the cervical mucosa - atrophic cervicitis);
- irrational use of local contraception (spermicides, acid douching);
- injury to the cervix (ruptures, cracks or abrasions) during childbirth, artificial termination of pregnancy, diagnostic curettage or during insertion/removal of an intrauterine device;
- vaginal dysbiosis (bacterial vaginosis).
Classification
By origin they distinguish:
- getting a sexually transmitted infection;
- structural changes in the tissues of the cervical canal;
- activation of opportunistic flora (thrush).
At the location of the inflammatory process:
- the entire mucous membrane is affected - a diffuse process;
- spotted (macular) chronic cervicitis, in which the formation of individual foci of inflammation occurs;
- exo and endocervicitis – either the vaginal part of the cervix or the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is affected.
There is an acute stage of the disease with characteristic symptoms and a remission stage.
ul
Complications and prognosis
Inflammatory processes in the cervix can lead to infertility.
Some types of infection affect not only the uterus itself, but also the organs adjacent to it (appendages, bladder, peritoneum). The presence of bacteria leads to the formation of adhesions, which is the main cause of loss of reproductive function. Chronic and advanced inflammation can lead to the development of the following dangerous diseases:
- Hypertrophy (thickening) or erythroplakia (thinning) of the uterine walls;
- Dysplasia;
- Cancer.
There are frequent cases of infection of the pelvic organs and urinary tract. The prognosis for treatment is favorable for all types of cervicitis; the main thing is to detect the disease in a timely manner and begin therapy on time.
Pathogenic organisms causing cervicitis
Among the infectious agents that cause inflammation of the cervix are:
- Specific microorganisms. These are chlamydia, ureaplasma, trichomonas, amoebas, tuberculosis bacilli, gonococci, genital herpes. In the presence of this infection, the process is acute and requires urgent treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, that is, chronic cervicitis of a high degree of activity is observed;
- Nonspecific. Candida fungus, gardnerella, E. coli. These microorganisms provoke chronic cervicitis of moderate activity.
In both cases, inflammation develops – this is how the body’s protective reaction to microbes manifests itself.
Bacterial nature of cervicitis
Bacterial cervicitis can occur against the background of an existing viral infection, which weakens the defenses. In this case, chronic active cervicitis occurs with periodic relapses and remissions, which is difficult to treat until the immune system is restored and the viral agent is eliminated.
Carefully! Against the background of viral infections, bacteria can transform into inactive forms, which, under favorable conditions, restore their activity. In this case, the woman will be a source of infection without even knowing it. Similar cases with Trichomonas are described in the medical literature.
Viral nature of cervicitis
With a low immune status, there is a high probability of developing sexually transmitted viral infections. These are:
- herpes virus;
- ureaplasma (intermediate microorganisms between bacteria and viruses)
- human papillomavirus;
- AIDS virus.
These pathogens weaken the body and create a favorable environment in which bacteria and fungi thrive, while actively reproducing.
Reasons contributing to the formation of a focus of inflammation
An exacerbation of a chronic infection can cause:
- abortion;
- hormonal disorders;
- damage to the cervix during childbirth;
- installation of an IUD;
- diagnostic examinations and microdamage to the epithelium;
- scars on the cervix.
When several factors are combined - infection, mechanical damage, low immunity - there is a high probability of an inflammatory process in the cervix.
ul
Causes of cervicitis, endcervicitis, exocervicitis
The occurrence of cervicitis is promoted by:
- concomitant inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. Quite often, cervicitis occurs against the background of cervical erosion, colpitis (inflammation of the vagina), endometritis, cystitis and inflammation of the appendages; - sexually transmitted diseases - chlamydia, gonococci, trichomonas, mycoplasmas, fungi and viruses can penetrate into the cervical canal. It should be noted that the most common of the listed infections, cervicitis, are provoked by Trichomonas and gonococci - in 25% of cases out of 100, cervicitis develops in patients with trichomoniasis and gonorrhea; - nonspecific infections caused by staphylococci, streptococci, intestinal flora and so on; - traumatic effects on the cervix contribute to the penetration of microbes: abortions and diagnostic curettages, cervical ruptures during childbirth; - prolapse of the cervix and vagina; - decreased immunity; - frequent change of sexual partners. In the vast majority of cases, cervicitis occurs in sexually active young women; - irrational use of contraceptives, use of chemical spermicides, douching with acids for the purpose of protection; - hormonal changes, in particular during menopause - due to a decrease in estrogen levels, atrophic cervicitis develops - the cervical mucosa becomes thinner and becomes easily vulnerable to various microbes.
Signs of chronic cervicitis
Highly active cervicitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- yellow-green purulent discharge in large quantities;
- presence of a specific odor;
- dysuria – painful urination;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- the presence of ulcerative lesions on the vaginal part of the cervix;
- painful sexual intercourse.
Chronic cervicitis is characterized by:
- cloudy mucous discharge;
- mild pain during sexual intercourse;
- There may be itching or a burning sensation in the vagina.
Important! Chronic inflammatory process on the cervix much more often develops into malignant tumors and poses a great danger to women of reproductive age.
ul
What is cervical erosion and exocervicitis?
A disease called “cervical erosion,” of course, exists in gynecological practice, but the doctor encounters this pathology quite rarely, and instead deals with ectopia or exocervicitis. The fact is that true erosion of the cervix is the absence of any epithelium on the surface of the organ, that is, an essentially bare wound. Usually the cause of such an event is an acute inflammatory process. Like any wound, erosion very quickly “heals”, that is, it is covered with new epithelium, and therefore the doctor simply does not have time to see it. If such a diagnosis is nevertheless established, one should always remember about oncological vigilance, especially in older women. It is in such cases that erosion exists for a long time, does not heal, and the likelihood that a specialist will detect it during the next examination is, of course, much higher.
Ectopia
Unfortunately, concepts are often substituted, and erosion is called a completely different condition, namely ectopia. The latter is a qualitatively different process - not the absence of epithelial tissue on the cervix, but simply the replacement of one type of epithelium with another due to a shift in the normal boundary between them. When a thin epithelium from the cervical canal with translucent vessels appears on the vaginal part of the cervix, clinically around the external pharynx a bright red area is found, somewhat reminiscent of a wound surface. Hence the misconceptions. Ectopia itself is not considered a pathological condition, and is usually associated with insufficiently regulated hormonal homeostasis (balance). This picture happens to about every tenth girl. Over time, the hormonal balance is established, the border between the two types of epithelium goes into the cervical canal, as a result of which the ectopia disappears without a trace. There is no need to treat it.
Diagnosis of cervicitis
Diagnostics consists of the following procedures:
- A smear from the vaginal part of the cervix to determine active or latent infection (in the acute phase of the disease and in latent cases).
- Histology in the form of a smear to identify atypical cells after examination of the smear and examination using mirrors.
- Biopsy. If you suspect cancer or if you have a human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk, you need to take a piece of tissue (or several) for examination under a microscope. Prescribed to clarify the diagnosis of dysplasia or cervical cancer after receiving poor results of a cytological examination.
To diagnose the uterine cavity, if endometriosis is suspected, the doctor may prescribe a hysteroscopy. This is a procedure in which a device with a camera is inserted into the uterus, which transmits an image to a computer monitor. Thus, it is possible to identify the pathology of the inner layer, various thickenings of the muscle layer.
Important! It is effective to use several types of diagnostics to accurately diagnose and prescribe productive treatment. All types of diagnostics are prescribed when it is necessary to exclude the occurrence of a rare type of cancer - for example, papillary.
When diagnosing HPV, the doctor must prescribe a biopsy in order to identify koilocytes - cells with modified enlarged nuclei. Koilocytic atypia is characteristic of papilloma viral infection: there are cells with two or more nuclei that have a peculiar glow around the center.
Koilocytosis is a long-term process of cell transformation. It is observed only in the active stage of HPV, which indicates unstable immunity and the need for treatment.
ul
Complications of cervicitis:
- transition from acute to chronic form; - cervical erosion; - development of an ascending infection (spread of the inflammatory process to the uterus, appendages, peritoneum, bladder). In 8-10% of cases out of 100, cervicitis caused by chlamydia or gonorrhea provokes an inflammatory process in the pelvic cavity; - in the presence of a sexually transmitted infection, bartholinitis may develop - an infectious inflammation of the excretory ducts of the Bartholin glands, which are located at the entrance to the vagina; - inflammation of the appendages; - development of Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome when cervicitis is combined with chlamydia; the most dangerous complication of this syndrome is the development of adhesions in the pelvis and abdominal cavity, which leads to infertility; - cervical cancer. The risk group is represented by patients in whom cervicitis is combined with a high-oncogenic human papillomavirus.