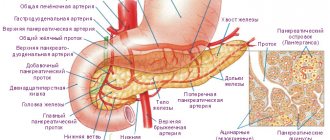
It makes sense to talk about a pseudocyst (literally “false cyst”) of the pancreas (PZ) only when it is already quite clear what a true cyst is.
Namely, this is how it is customary to call a cavity formed in the depths of a dense organ (brain, kidney, lung), which must certainly be filled with some kind of liquid - serous, mucous, blood, which resists its collapse, collapse - otherwise it cannot be called a cyst (translated from Latin as “bubble”).
But if a true cyst is a blind formation (without communication with any other cavity), then a false cyst is a bubble formed from a small duct of the gland as a result of “plugging” the exit from it.
As a result, a “flask” is formed, nominally connected to the adjacent duct by a narrow “neck” - but due to the presence of an obstacle in it, pancreatic juice cannot flow freely into the common line (it accumulates inside due to its continued production by the gland), but the duct stretches and expands evenly in all directions, forming a spherical “cave” with liquid contents (pseudocyst).
What it is
What is a pancreatic pseudocyst, and what to expect if it is present in the body? These questions are of interest to patients with a similar diagnosis.
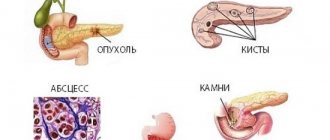
A pseudocyst that develops in the pancreas is a sac in the peritoneal cavity; inside it may be particles of dead tissue, liquid that consists of pancreatic secretion, organ parenchyma, blood and pus. A pseudocyst is formed as a result of pancreatitis, or due to insufficient pancreatic duct. A false pancreatic cyst is a real subtype of cyst.
The presence of a pseudocyst is a time bomb. Because today it may not show itself, and no one knows what will happen in a month. In any case, adverse effects will arise sooner or later.
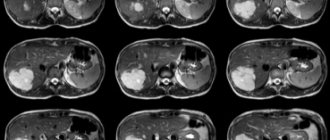
The tumor is fixed in any area of the pancreas, and the contents can reach up to 2 liters or more.
If you do not immediately start a therapeutic course, complications of the pseudocyst are observed.
- Swelling of the pancreas in the case of infected cysts.
- Suppuration.
- Internal bleeding.
- Rupture of formation and penetration of contents into the peritoneum.
- Compression of nearby organs.
internal bleeding
The reasons for the appearance of false cysts, as well as the factors for the development of gastric ulcers, are:
- alcohol abuse – most of the cases of false gland cysts;
- diseases of the bile ducts, the complication of which is a pseudocyst;
- complication of acute form and chronic type of disease;
- organ injuries;
- infectious diseases in children;
- uncontrolled use of enzymes of artificial origin;
- the appearance of the disease in children is associated with congenital anatomical changes.
The main symptom of a false cyst is acute pain. The larger the formation, the extent of its damage, the degree, the clearer and stronger the discomfort will manifest itself. Unbearable pain is felt at the stage of formation of the cystic sinus. After some time, the pain goes away, but not completely, but has a dull, aching course. Sometimes there is minor discomfort without pain.
If the pain is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, exudate into the pleura, increased temperature, bleeding from the pancreas, then the pseudocyst has become complicated and requires urgent medical intervention.
lack of appetite
Types of pancreatic pseudocysts
False neoplasms can be small or large, multiple or single. Their size depends both on the location (head, body, tail) and on the stage of the disease. Only a gastroenterologist can determine them correctly.
Half of all patients with acute pancreatitis have an additional diagnosis of “false cyst”. With chronic inflammation, a pseudocyst is found in 80% of patients.
In medicine, the following stages of pseudocyst formation are distinguished:
- Initial. At this time, the formation of the cavity of the future pseudocyst begins. This period lasts on average 1.5 months.
- Second stage. A connecting loose capsule appears. The process continues for about 3 months.
- Third. A fibrous capsule is formed. The stage can take six months, the benchmark is the beginning of the development of the disease.
- Last stage. The final development of a false cyst - a dense tumor.
Pseudocysts are also classified according to chronology, from the moment of appearance:
- acute course - if about three months have passed since the formation period;
- subacute - when the disease develops over 6 months;
- chronic course - if more than six months have passed.
The acute form is most sensitive to drug therapy; curing the chronic form already involves surgical intervention.
Formations are also distinguished by the nature of their occurrence: pseudocyst can be post-traumatic or post-operative.
Pseudocyst drainage
After diagnosing a false cyst, treatment of the patient begins with a conversation with a gastroenterologist. Based on the stage and development factor of the pseudocyst, the doctor prescribes medication therapy, surgical removal, and drainage of the pseudocyst. The first method is used if there is a formation of insignificant size; often the tumor diverges on its own. Surgery is performed if the formation is more than 6 cm and exists for more than 6 weeks.
Drainage is a method that is used when a pancreatic pseudocyst develops. There are two types of procedure – internal and external. Doctors often use the first method.
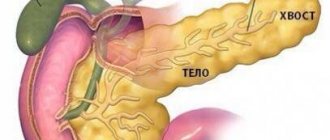
Based on the location of the tumor, a specific method of surgical treatment is selected. If the cyst is on the head of the pancreas, then cystoduodenoanastomosis is performed, and if it is on the tail, cystogastroanastomosis is performed.
These methods are more suitable, because they can resume the movement of pancreatic juice, reduce pain, and reduce the possibility of recurrences. There are complications.
- Penetration of intestinal contents into the sinus of the tumor with pus.
- Peptic ulcers.
- Bleeding into the cavity.
Peptic ulcers
The external method of drainage is rarely used. This operation is often used when:
- sinus suppuration;
- severe vascularization of the tumor;
Basically, such surgical interventions are of an emergency nature, due to the development of life-threatening conditions in the patient.
- Open bleeding.
- Rupture of a hollow organ.
After external surgery, the possibility of purulent inflammation increases and a pancreatic fistula is formed, which can subsequently lead to a more complex operation.
All types of intervention only on the condition that a non-tumor etiology is confirmed.
Clinical manifestations
The main symptom of the pathology is a painful sensation. The nature of this feeling can be different and depends on the stage of development of the formation, the degree of its growth, location and other factors.
Pain may appear already at the stage of formation of the parenchymal cavity. The strongest sensation is most often associated with the stage of “maturation,” that is, the full formation of the cyst capsule and they are associated with destructive processes in the affected organ.
Then the pain subsides, but does not disappear completely, but becomes dull. Some patients experience no pain at all and only complain of some discomfort. After complete formation of the pseudocyst, painful attacks are also possible, which are most often associated with increased pressure in the ducts of the organ.
The localization of sensations depends on the location of the neoplasm itself. If the pseudocyst is located in the area of the head of the organ, then pain will occur in the right hypochondrium. When the formation is located in the tail, they appear in the left hypochondrium or epigastric region.
Sometimes patients complain of constant pain. This may be due to the pressure of the tumor on the solar plexus. In this case, the unpleasant sensation intensifies when the body position changes. In addition, dyspeptic disorders in the digestive system are possible.
We suggest you read: You can treat a tumor in the pituitary gland with herbs
Minimally invasive methods and cyst resection
Before prescribing surgery, the doctor will tell you why the pancreatic pseudocyst appeared and what it is. Today, minimally invasive methods of drainage operations are achieving greater fame.
choice of treatment methods
The tumor is eliminated using the following minimally invasive methods:
- Drainage through the skin is an effective technique, but it has a high risk of causing problems;
- linear endoscopic echography - manipulation involves diverting the contents of the pseudocyst to the area of the stomach or intestines. Surgical treatment is prescribed if the formation is located remotely from the gastrointestinal tract;
- transpapillary drainage – cleansing the cyst capsule using a stent, which is inserted during the endoscopic examination;
- internal intervention – the presence of side effects, therefore it is used in rare cases.
Another way to eliminate it is excision. The operation involves removing part of the pancreas along with the tumor. The extent of resection is determined by the size of the formation and its condition.
The conservative method is possible if the size of the pseudocyst is insignificant, there are no signs or complications. Drug therapy includes taking:
- enzymes;
- anticholinergic drugs;
- histamine receptor blockers.
The use of medications is often combined with the installation of a catheter into the sinus of the tumor. This is how it is cleansed from the inside using antiseptic solutions from the inside.
Diagnostics
During a general examination, the doctor must pay attention to the asymmetry of the abdomen, its protrusion in the area of the growing pseudocyst. With palpation and percussion, the pain intensifies, the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall are tense. To confirm the preliminary diagnosis, additional instrumental and laboratory research is necessary.
In a blood test, leukocytosis, anemia during bleeding, increased concentrations of C-reactive protein, direct and total bilirubin, liver enzymes (AST, ALT), and increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be observed. In an acute inflammatory reaction, a specific symptom is an increase in pancreatic enzymes, for example, amylase, elastase.
If the clinical picture resembles obstructive jaundice, then the concentration of direct bilirubin in the urine increases, while stercobilin in the feces is several times lower than normal.
Structural changes in the pancreas, the location of the cyst, its size, tension, and concomitant diseases of neighboring organs can be seen using ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography, and radiography.
If an infection is suspected or an abscess is present, it is recommended to take a puncture from the neoplasm, conduct a bacterial culture, and determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibacterial agents.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are informative regardless of the timing of tumor development.
Treatment with diet
If the tumor does not manifest itself, doctors do not recommend undergoing any treatment for pancreatic pseudocyst. The operation is also not prescribed. There is a possibility that such falsehoods will resolve on their own, even if medications are not used.
Patients are often advised to adhere to a number of rules.
- Follow a strict diet plan.
- Systematic examination to monitor the condition of the pancreas.
- Get tested.
- Use folk recipes.
A strict dietary diet involves excluding the following products from the menu:
- fat meat;
- alcohol;
- fried, salty foods;
- margarine;
- spices, sauce;
- confectioner;
- sweet, carbonated drinks, coffee.
diet for pancreas
Before eating food, they are boiled and steamed. Do not eat hot or cold.
If you use folk remedies, you can remove excess bile and increase the activity of the pancreas.
Symptoms
In the early stages, the pathology does not have any symptoms. The neoplasms do not put pressure on surrounding organs and nerve endings and do not disrupt the production of digestive enzymes. As the pseudocyst develops, the following signs appear:
- Pain syndrome. It is most intense when a neoplasm forms against the background of acute pancreatitis, accompanied by destruction of pancreatic tissue. Over time, the pain becomes mild. When the ducts of an organ are blocked, the syndrome has a paroxysmal character. Cutting pain indicates rupture of the cyst or its suppuration. The burning nature of the syndrome is observed when the solar plexus is compressed.
- Indigestion. Nausea and vomiting appear, constipation is replaced by diarrhea. If the production of pancreatic enzymes is insufficient, the absorption of nutrients in the intestine stops, and the patient quickly loses weight.
- Obstructive jaundice (yellowing of the skin and sclera, severe itching). Occurs when there is a pseudocyst in the upper pancreas.
- Edema of the lower extremities. A characteristic sign of compression of the vena cava.
- Urinary retention. It is caused by a violation of the outflow of fluid through the ureters when a large pseudocyst of the pancreatic tail appears.
- Partial intestinal obstruction is a rare symptom of the disease.
As the pseudocyst develops, one of the signs of its deterioration appears as pain.
Traditional medicine recipes for treatment
Therapy of pancreatic pseudocysts using folk remedies gives results.
- For a medicinal drink you will need celandine, yarrow, and calendula in equal proportions. Measure out a spoonful of plants and pour in 250 ml of boiling water. The drink is left for 2 hours. Drink 2 tablespoons before meals.
- Take tansy, calendula, plantain inflorescences and combine. Pour boiling water over a large spoon of the mixture and let it brew. After cooling, the broth is filtered and drunk in ¼ cup. The course lasts a month.