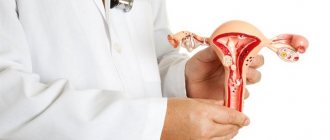
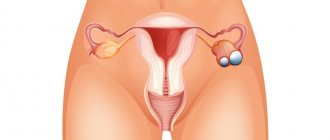
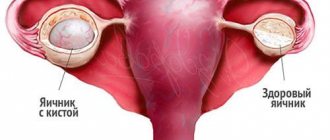
Early diagnosis of cancer of the female reproductive system is extremely important. Ovarian tumors rank first in mortality from malignant neoplasms of the female genital area due to the long period of asymptomatic development. In 70% of cases, the tumor is detected at stages three or four. At this stage, the cure rate is less than 25%. If a tumor is detected at the first stage, the chances are 80-90%.
Primary diagnosis includes a blood test for tumor markers. This allows you to determine the quality of the neoplasm: benign, borderline (low-grade malignancy), malignant. Blood is examined both for a single tumor marker and for their combinations. One of the complex indicators is the ROMA index.
Tumor markers - what are they?
Tumor markers are protein structures present in the blood that confirm the occurrence of an oncological process in the body. Based on the presence of a specific marker, it is possible to determine where the malignant neoplasm is localized. Also, by analyzing the blood for tumor markers, the oncologist determines how effective the therapy is.
The synthesis of tumor markers is directly proportional to tumor development. In a healthy person, protein structures are present in the blood in minimal quantities. In a cancer patient, the concentration of markers in the blood is high.
Types of tumor markers for ovarian cancer
The production of tumor markers begins when normal ovarian cells are replaced by malignant ones. A significant amount of protein formations ends up in the bloodstream and other biological fluids of the body. As the tumor grows, the synthesis of marker proteins increases.
To diagnose ovarian cancer, the following markers are determined:
- CA125 and HE4 are the main ones;
- APF and REA are secondary;
- HCG is additional.
Based on the values of these markers in the blood, the patient is diagnosed. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may send the woman for additional instrumental and laboratory tests.
It should be noted that isolated CA125 is not suitable for detecting cancer at the initial stage, as it has low sensitivity. Therefore, in a blood test, CA125 is determined in combination with HE4. With a comprehensive accounting of markers, the reliability of the blood test is 90%.
Preparing for analysis
To obtain reliable results, preliminary preparation is necessary, excluding a number of factors on the eve of venous blood collection:
- fatty, fried and sweet foods;
- alcohol;
- smoking;
- heavy physical activity;
- stress and anxiety;
- sexual intercourse - 2 days before the analysis;
- taking medications is agreed with the attending physician.
It is advisable to get a good night's sleep, at least seven hours. The study is carried out in different phases of the menstrual cycle, but more reliable indicators were noted in the first days after bleeding.
An increased ROMA index does not mean the presence of ovarian cancer, which shows the use of this method as a screening test. It also does not detect all types of cancer, only serous and endometrioid. Age and menopausal status also affect the value of the index. To confirm the diagnosis, additional studies are required: ultrasound, laparoscopy with biopsy to identify the morphology of atypical cells under a microscope.
Analysis for CA125
Used to detect gonadal cancer. Through analysis, in 80% of patients, the oncological process is detected at the initial stage.
CA125 is a structure that is a combination of a complex protein and a polysaccharide. This is the only marker that most accurately signals the development of a malignant neoplasm in the epithelial tissues of the ovary. However, the protein can be present in the blood of a healthy woman, but in small quantities. The substance is distributed throughout the body through blood plasma and other biological fluids.
You should not try to decipher the results of the CA125 analysis yourself. You should consult a medical specialist, since an increased marker value is not always a signal of cancer development. The provocateur of an increase in the indicator may be a cyst or a benign tumor.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor sends the patient for additional diagnostic tests. There is a high probability of cancer if the CA125 value is twice as high as normal.
To monitor the course of the pathological process, prevent relapse or the appearance of metastases, analysis for CA125 is carried out repeatedly.
Decoding the results
The diagnosis is made by a gynecologist or oncologist based on the data obtained. The Roma index is calculated using special formulas. They vary depending on the phase of menopause and the age of the woman. It is quite difficult to make calculations on your own. An increase in the indicator does not always indicate the presence of cancerous tumors. The following factors can provoke an increase in CA125:
- liver diseases;
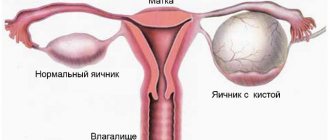
- cystic formations in the ovaries;
- pregnancy;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- infections in the genital tract;
- endometriosis;
- appendicitis.
An increase in HE4 almost always indicates the presence of malignant tumors. But in some cases it is the result of impaired kidney function, cirrhosis of the liver or the formation of fibroids. A diagnosis cannot be made based on data from one of the indicators. Both parameters need to be assessed. A false negative result is rare. It is possible only in the early stages, when the malignant tumor does not produce cells.
The doctor makes a conclusion about the patient’s health only after receiving the results of other studies. These include ultrasound monitoring of the pelvic organs, biopsy and gynecological examination. If the study was carried out in preparation for surgery, then the woman’s hereditary predisposition to cancer is determined. Surgical intervention is possible only if the woman does not have any problems.
Analysis for HE4
Carried out in addition to the analysis for CA125, it allows you to clarify the diagnosis.
HE4 is a protein included in the second number in the WFDC category. Localized in the epithelial tissues of the accessory portion of the gonads. Normally, in a woman, it activates the interaction between the egg and the sperm and has an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect. Protein synthesis increases with malignant ovarian lesions and spreads throughout the body through biological fluids.
Indications
In most cases, neoplasms of the gonads in women are benign - abscesses, adenomas, cysts. The ROMA algorithm is used to differentiate benign and malignant tumors and allows identifying patients at risk for the development of cancer pathology. Based on the study data, the question of the advisability of invasive interventions - diagnostic surgery and biopsy - is resolved.
- Clinical examination. Lumps may be detected during bimanual rectovaginal or vaginal examination.
- Instrumental procedures. Diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound, less often - MRI, CT.
The study is not indicated if the clinical and instrumental data are normal. It is also important to note that it is designed to assess the risk of developing epithelial tumors only. Germ cell and granulosa-stromal cell neoplasias do not affect the final POMA value.
Tumor marker values in normal and pathological conditions
CA125 in a healthy woman does not exceed 35 U/ml. A slight increase in protein is observed during pregnancy and on menstrual days.
On average, the normal value is 12 – 13 U/ml. If the protein gradually increases, with each new analysis its concentration in the blood becomes greater, then an oncological tumor develops in the gonads. If the indicator increased again after cancer therapy, then the disease recurred.
The HE4 marker has different normal values for women of different ages. So, for the patient:
- up to 40 years of age, the normal value is 60.5 pmol/l;
- 40 – 50 years – 76.2;
- 51 – 60 years old – 74.3;
- 61 – 70 years old – 82.9;
- after 70 years – 104.0.
If HE4 increases regardless of age, then we can confidently talk about ovarian, uterine or breast cancer.
AFP protein should normally range from 5 to 10 IU/ml.
CEA in the blood of a healthy woman is not higher than 3 ng/ml. With a benign neoplasm, the rate may increase to 10 ng/ml. With a malignant neoplasm, the protein is significantly higher than normal, and in most cases, an increase signals damage to the lymph nodes by metastases.
HCG outside pregnancy is normally 6.2 mU/l. In pregnant women, the value of the substance is different in different trimesters of gestation.
What the ROMA analysis shows
The cost of a blood test for tumor markers ranges from 550 to 1000 rubles. It includes the price of reagents and the work of medical personnel. Research is not carried out in government institutions. Blood sampling is carried out in the treatment room of specialized clinics. The patient is placed in a chair with an armrest. Using a sterile syringe, blood is drawn from a vein. For 15-20 minutes after the procedure, you must keep your arm bent.
The test is not prescribed for cancer patients, persons under 18 years of age, and those with a rheumatoid factor level of 250 IU/ml. The test result will be ready 1-3 days after blood sampling. It is carried out using the immunoelectrochemiluminescence method for assessing blood serum. The reliability of the data depends on the qualifications of the personnel and the serviceability of the test systems. If a questionable result is obtained, the analysis is repeated. To prevent errors, the study is carried out in the same laboratory.
Medical experts cannot recommend one specific medicine that will help get rid of cancer. In this case, early diagnosis and timely seeking help play a significant role. The early stage of a pathogenic disease can be treated.
In order to defeat ovarian cancer, the Roma tumor marker is important. The situation is aggravated by the fact that there are no symptoms until stages 3–4.
According to statistical studies, up to 90% are cured of the disease if treatment begins from stage 1 of development. In later stages, the percentage is much lower, 20%.
Thanks to Roma's tumor markers, it is possible to calculate the risk of developing cancer in the future, which helps save and protect thousands of women.
The work of tumor markers
It is worth noting that the Roma tumor marker is a protein indicator. With its help, you can determine the likelihood of the disease occurring and the structure of the future neoplasm. By assessing a given tumor marker, the approximate stage of development can be calculated, which also helps in treatment.
The tumor marker Rom index is calculated from two other protein markers - CA 125, HE 4. Their ratios are also taken into account. By calculating this index, you can estimate the likelihood of a person developing a malignant tumor in the future.
Important! When using this technique, specialists divide women into two groups. The first category includes those with a low incidence of the disease. The second group will include those individuals who have a high risk of developing a pathogenic disease in the area of the female reproductive glands and the pelvic cavity.
The main indicator during the procedure is the prognostic index. It helps in calculating the Roma index to identify the likelihood of developing the disease. It is worth considering the age category. In particular, menopause can be divided into postmenopause, for which Roma 1 is used. For those representatives of the fair sex who are premenopausal, Roma 2 is calculated.
To determine the normal level of tumor markers, a blood sample is taken (necessarily on an empty stomach). The optimal time for this is from 7 to 11 am. No specific preliminary preparation is required. It is enough to follow generally accepted recommendations:
- 5 days before the scheduled test, do not drink alcohol;
- 12 hours before the test - do not drink herbal teas, give up nicotine;
- 24 hours before the test - abstain from sexual intercourse;
- during the period of drug therapy for the treatment of diseases of the reproductive system, the analysis is not performed (you must notify the attending physician);
- 72 hours before the scheduled analysis, MRI, ultrasound, and x-rays should not be performed.
It is also recommended to consult a psychotherapist before taking the test, since the psycho-emotional factor has a significant impact on the final result.
Calculation of the ROMA index is used not only to assess the effectiveness of treatment and monitor the patient in remission, but also for screening for ovarian cancer. The use of antigens separately is not recommended by experts as an accurate test, especially if the woman is at risk for this disease.
The main indications for testing for the POMA tumor marker include:
- early diagnosis of malignant ovarian tumors (the index increases due to an increase in HE 4, while in benign tumors the concentration of CA 125 or both tumor markers increases);
- predicting the degree of malignancy of a neoplasm in the pelvic area (for benign tumors, the ROMA index does not exceed the reference values, is consistently slightly increased or decreases over time in the absence of therapy);
- determining the effectiveness of surgical treatment of malignant ovarian tumors (in combination with other tests).
To check the effectiveness of a course of treatment, the dynamics of one of the indicators is monitored, but in some cases a full study and calculation of ROMA is used. A decrease in this index demonstrates the effectiveness of the chemotherapy course.
As with other types of studies for which venous blood is taken, patients are prohibited from eating any food for 8 hours before taking biomaterial and are advised to report all medications they are taking. If they are not vital medications, you should completely avoid their use 2 days before the test.
Within a few days, a woman needs to stop drinking alcohol and eating foods that irritate the gastrointestinal tract (spicy, fried and fatty foods, smoked foods). Immediately before the test, you can drink only still water. You must stop smoking 3 hours before blood sampling.
The analysis should take place in a state of physical and psycho-emotional peace. It is recommended to eliminate heavy physical activity and stress for 1-3 days.
Despite the fact that the POMA analysis is often performed after detection of neoplasia in the pelvic area, in parallel with other clarifying studies, it is necessary to take a break for the test. For 1-3 days before laboratory diagnostics, MRI, CT, ultrasound, radiography and physiotherapeutic procedures cannot be performed.
Timely diagnosis using the highly accurate ROMA algorithm is a chance to detect a malignant tumor at an early stage and increase the patient’s chances of survival. A woman’s task is to regularly undergo preventive examinations (studies) and follow all the rules of preparation for them.
Published at Tue, 07 Nov 2020 16:31:10 0000
ROMA is an acronym that stands for Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm, that is, an algorithm for determining the risk of ovarian cancer. Thus, ROMA is rather not the name of analysis, but rather the name of a method of mathematical data processing. The basis for calculating the risk of ovarian cancer using the ROMA algorithm is the determination of a special prognostic index (PI).
It is also worth paying attention to the fact that the ROMA algorithm is effective only for epithelial malignant tumors; other types of ovarian cancer are not diagnosed using this technique. The reason for this is the characteristics of tumor markers used in calculating the prognostic index. HE-4 and CA 125 are specific only for neoplasms that develop from epithelial tissue.
To calculate the risk of ovarian cancer using the ROMA algorithm, a woman must donate venous blood. This must be done on the day prescribed by the laboratory, in the morning, on an empty stomach. This study does not require any special preparation; the only thing it is advisable to pay attention to is the inadmissibility of smoking and drinking alcohol, as well as medications (this point is agreed upon with the attending physician) on the eve of blood donation.
Before the procedure, it is important to learn how to properly test for this tumor marker. Preparing for the analysis is not difficult.
Blood for analysis is taken from a vein from 7 to 10 am. When donating blood to determine CA 125, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach; you cannot eat anything 8 hours before the procedure;
- In about a week you need to stop drinking alcohol and reduce the frequency of smoking;
- The day before, it is not recommended to drink drinks containing caffeine (tea, coffee);
- Two days before the test, you need to completely remove fried, spicy, salty foods from your diet;
- You need to take the blood test with a positive attitude; anxiety can increase your CA 125 level.
By following all the recommendations, you can achieve the correct CA 125 level in the patient’s blood. Only a highly specialized doctor should interpret the CA 125 blood test. Many women, seeing increased indicators, independently pronounce a death sentence on themselves. But it is worth remembering that without a full diagnosis it is impossible to confirm oncology.
Women of menopausal age are primarily at risk, since after 50 years the likelihood of malignancy of pathological formations increases significantly. During menopause, it is possible to increase the level of CA 125 not only in the presence of a cyst, but also in various other diseases. Therefore, if the tumor marker is elevated, it is important to immediately undergo a full examination and begin the necessary treatment on time. Ignoring doctor's recommendations can have serious health consequences and can be fatal.
What diseases cause elevated tumor markers?
The presence of tumor markers in the blood is necessarily a sign of a pathological process. But the process is not necessarily malignant. By analyzing the above tumor markers, you can identify:
- oncological pathologies of the ovaries (especially the epithelial form);
- malignant neoplasms in the uterus and fallopian tubes;
- cancer of the liver and digestive system;
- malignant neoplasms in the mammary glands.
In addition, an increase in tumor markers is observed in inflammatory reactions, benign formations in the uterus and appendages. Proteins may be elevated in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases.
To make sure that an increase in tumor markers is not a sign of an oncological process, the patient should undergo additional diagnostic tests.
Normal values
The normal limit may vary somewhat among laboratories, since the level of tumor markers depends on the characteristics of the reagents and equipment. Reference values are indicated in the corresponding column on the result form.
The value of the ROMA index test is extremely high. In almost 80% of cases, ovarian cancer is found in advanced stages. An analysis to determine the level of tumor markers in the blood detects cancer at the earliest stages of development.
According to WHO statistics, the prognostic indicator of ovarian cancer still remains unfavorable, despite all the advances in medicine:
- at stage 1, about 30% of cases of the disease are detected and there is the most favorable prognosis for five-year survival - 90%;
- at stage 2, approximately 15% of cases are detected, survival prognosis is 70%;
- at stage 3, more than half of the patients consult a doctor, survival rate is about 35%;
- at stage 4, up to 15% of cases are determined, the prognosis after 5 years is less than 20%.
Tests for the ROMA index are done in biochemical laboratories, oncology and diagnostic centers. Currently, the immunoelectrochemiluminescent method is used, which is highly accurate.
Price of tests to determine the level of tumor markers in Moscow clinics:
- CA-125 – 1550 rubles;
- HE-4 – 3000 rubles.
Roma Index – what is it?
If the tumor marker values are normal, then the patient can relax: she definitely does not have cancer. But if the indicators of protein markers are such that cancer is suspected, then the Roma index is calculated. This index is a digital indicator that predicts ovarian cancer. When predicting, the patient’s age is taken into account.
In premenopausal patients:
- index above 11.4% - the likelihood of developing cancer is high;
- below 11.4% - the probability is low.
In postmenopausal patients:
- index above 29.9% - the likelihood of oncological pathology is high;
- below 29.9% - the probability is low.
The index is calculated by a medical specialist using a complex formula.
Women experiencing perimenopause have a high risk of developing malignant tumors of the reproductive system. During the premenopausal period, hormonal levels change, which is why cysts appear in the ovaries and other benign formations in the genitals, which can turn into malignant tumors.
Norm of the ROMA index for women, table and explanation
According to the current instructions of the World Health Organization, the ROMA index is deciphered as follows:
- Roma index 1 - premenopause (age of reproductive activity) - permissible rate up to 7.39%;
- Roma index 2 - postmenopause (after the extinction of reproductive activity) - the permissible rate is up to 25.29%.
That is, in premenopausal women, an index below 7.39% indicates a low risk of epithelial (superficial) ovarian cancer, above 7.39% indicates an increased risk .
Similarly, in postmenopausal women, an indicator of up to 25.29% indicates a low risk, and above 25.29% indicates a high risk. Naturally, these indicators are not a reason for making a final diagnosis, but in 90% of cases the preliminary result is subsequently confirmed.
(The picture is clickable, click to enlarge)