What determines the size of the tumor?
Myoma appears for the following reasons:
- Excessive physical activity;
- Constantly being in a state of stress;
- Pathologies of the ovaries, due to which the functioning of the genital organs is disrupted;
- Problems with the endocrine system;
- Presence of chronic infectious diseases;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Problems with excess weight, obesity. In the photo you can see the degree of obesity, which can provoke pathology.
The size of uterine fibroids may be within normal limits, then a woman only needs constant monitoring by a gynecologist. But there are provoking factors that lead to an increase in tumor growth. These include:
- Frequent abortions. Sometimes a single abortion can trigger the development of a tumor, but this is extremely rare;
- No pregnancy or childbirth before age 30. The same applies to lactation;
- The constant presence of inflammation in the reproductive system of the body;
- Constant use of contraceptives that affect hormonal levels. What does it mean? Medications that prevent pregnancy work with a woman’s hormonal state. If such drugs are abused, hormonal levels can change forever;
- Excessive use of solariums or constant prolonged exposure to the sun. This especially applies to women with sensitive skin.
Uterine fibroids 38 mm on ultrasound
To understand how high the risk of surgical intervention is, you need to calculate at what stage the pathology is.
Why does uterine fibroid grow?
An increase in the size of the uterus with fibroids is due to:
- irregular sex life, taking oral contraceptives, which aggravate hormonal imbalance - estrogen levels
- continues to increase;
- frequent abortions;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- exacerbation of endocrine diseases - diabetes, obesity, hyperthyroidism;
- stress, nervous and mental overload;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- weakened immunity due to hypothermia, infectious and somatic diseases;
- intoxications of the body - alcohol, drugs, drugs, ionizing radiation.
Classification of fibroids by size
The size of fibroids is determined using ultrasound. It is described in weeks and centimeters. As the tumor grows, the uterus enlarges in the same way as during pregnancy. That is, in the case of an enlarged uterus at the 10th week of pregnancy, a woman is diagnosed with “fibroids at 10 weeks.” The sizes in weeks and cm are:
- Small – up to 2 cm or 20 mm. This usually corresponds to 4 or 5 weeks of pregnancy;
- Average - up to 6 cm or 60 mm. This indicator is considered normal for 6-11 weeks of pregnancy;
- Large - from 60 in mm or 6 in cm or more. Usually relevant at 12 weeks of pregnancy and beyond.
When the formation corresponds to 20 weeks of pregnancy, it can significantly affect the functioning of neighboring organs. Myoma is also dangerous because it can disrupt the functioning of neighboring organs without causing pronounced symptoms. But most often, minor symptoms are still present.
You can see photos of fibroids by size below.
How to cure pathology?
The doctor draws up a treatment plan based on the results of the patient’s examination. At the same time, he necessarily takes into account the size of the formation, clinical manifestations, course of the disease, the woman’s age, the presence of children and the desire to give birth to them in the future.
There are three methods of treating uterine fibroids:
- Medication. It is used rarely, mainly only in the treatment of small fibroids, in the presence of contraindications to surgery, and also after surgery. Taking medications is intended to control the development and growth of the tumor, as well as to suppress the symptoms that bother patients. Doctors prescribe hormonal medications and vitamins to women.
- Operational. This method is radical and is used in advanced cases. Based on how serious the situation is, the doctor decides whether to remove the uterus or just the tumor.
- Embolization. This method involves injecting the patient with a catheter into the uterine artery with a special substance that prevents blood circulation in the tumor. As a result, the fibroid cells begin to die. This method is preferable as it allows preserving a woman’s reproductive function.
Surgery is necessary in the following cases:
- The size of uterine fibroids coincides with 12 weeks of pregnancy, that is, more than six cm.
- There is a possibility that uterine fibroids will develop into a malignant tumor within 6 weeks.
- The patient suffers from regular and severe pain, which painkillers cannot cope with.
- The tumor puts excessive pressure on the internal organs located next to it, which leads to unpleasant symptoms.
- A woman often experiences heavy bleeding, which causes her to suffer from anemia.
- A pedunculated fibroid has been identified, resulting in a high probability of torsion or peritonitis.
- The pathology prevents the bladder from emptying normally, which leads to stagnation of urine.
- Due to the disease, there are problems with stool, which cause intoxication of the body, bloating and pain.
How to determine the size of a tumor in weeks
What to do when making an appropriate diagnosis? How do you know if you are being treated correctly? There is a table that shows the size of fibroids by week and what treatment method is used (table of correspondence between the height of the uterine fundus and the period):
| Size in weeks | Fundal height of the uterus | What type of treatment is used |
| 1-4 | 1-2 cm or 10-12 mm |
Hormonal and drug therapy
Surgical (operational) intervention
Depending on the stage of development of the pathology, its inherent symptoms make themselves felt.
Tumor treatment
Myomatous nodes are treated with various methods depending on their type and size in weeks:
- Hormonal therapy is applicable in cases where the size of fibroids does not exceed 12 weeks. Medicines act to inhibit the rate of progression of the pathological neoplasm and reduce its size. Hormonal treatment is widely used in case of detection of fibroids in women of younger and middle age who wish to have offspring in the future, as well as after surgery to prevent the formation of new nodes;
- Symptomatic treatment:
— Antispasmodic and painkillers (even nodes the size of 2-3 weeks can cause severe pain during menstruation);
— Hemostatic agents are prescribed for fibroids of the smallest size (a submucosal node with a diameter of 4 mm can sometimes provoke intense intermenstrual uterine bleeding) for appropriate indications: long and heavy menstrual bleeding, bleeding from the genital tract during ovulation;
- Surgery is indicated if the tumor has reached a size of 13 weeks or more:
— Vascular embolization;
— Removal of fibroids with laser;
— Myomectomy;
— Removal of the uterus, complete or partial, with or without a cervix;
- Unconventional methods:
— Traditional treatment;
— Physiotherapeutic treatment;
— Gymnastics;
- Treatment with leeches.
Symptoms
If the fibroid is at an early stage of development, that is, 10 mm-16 mm or 1-2 cm, it does not make itself felt in any way, that is, there are no symptoms at all. If the size reaches 3 cm, signs may appear, but not always clearly enough. But when the tumor grows and reaches 10 cm or more, or from 10 weeks onwards, the following symptoms make themselves felt:
- Menstruation, which is accompanied by severe cutting pain in the lower abdomen. Even the strongest painkillers do not help with this condition;
- As the tumor grows, the lower abdomen begins to swell. At the same time, the woman does not gain weight;
- In some situations, cutting pain in the abdomen begins with any physical activity. This can be not only playing sports, but also playing with a child on the street and similar situations;
- When the size has reached 13 weeks-15 weeks, the tumor can affect neighboring organs and disrupt their function. Because of this, constipation, problems with urination, pain in the lumbar region, heart, and lower extremities may occur;
- Numbness of the lower extremities;
- When fibroids from 13 weeks to 15 weeks and above form adhesions with neighboring tissues and organs, during any, even minor, physical activity, a person may feel pain and discomfort in the joints.
Fibroids are also dangerous during pregnancy. Usually, when the fibroid size is 2 cm-7 cm, the neoplasm does not interfere with the successful development of the child and the easy course of pregnancy. However, in other cases it is worth paying attention to this element.
How large fibroids affect other organs
The above-mentioned steal syndrome is characteristic not only of fibroids, but of all large tumors. Despite the benign course of the disease, 12-week fibroids are a large tumor that requires constant replenishment.
In other words, such a fibroid behaves like a parasitic organ, taking oxygen and nutrients entering the body from other systems and organs. As a result of this behavior, vital organs (pancreas, liver, kidneys) do not receive the substances they need. Due to impaired nutrition of important organs, metabolic failure occurs, which leads to rapid obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes.
Due to lack of oxygen, the heart muscle works poorly, and coronary artery disease develops, fraught with myocardial infarction. The respiratory system, the organs of which do not receive oxygen, suffers no less than other organs, which is manifested by rhinitis, laryngitis and bronchitis.
Stealing syndrome appears only when the myomatous formation is large - 12-14 weeks, and the maximum pathological symptoms appear when the fibroid size is more than 16 weeks.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy
A planned pregnancy may not occur if the formation has reached 16 cm or 11 weeks. The tumor can block the path of sperm to the egg.
Fibroids in the uterus during pregnancy
Uterine fibroids can also occur during pregnancy. The size for the operation is determined by the doctor, but the patient herself may encounter the following situations:
- The increase in uterine fibroids in the body can reach such a limit that the normal growth and development of the child is significantly hampered;
- At 12-15 weeks the size may become too large, leading to late miscarriage;
- If a fibroid of 5 cm-6 cm does not complicate the process of childbirth, then at later stages of the development of the pathology a cesarean section is possible;
- The size of uterine fibroids during pregnancy can quickly increase from 11 mm to 6 cm or more. This is facilitated by changing hormonal levels. This means that the woman must be under constant medical supervision during this period;
- In this case, it is impossible to do without medication support. Pharmaceutical drugs are necessary to keep the body in good shape until childbirth;
- If therapy does not bring positive results and negative dynamics are observed, then surgical intervention will be required. In especially severe cases, a caesarean section is performed, and after it the uterus is completely removed;
- If the size of uterine fibroids during pregnancy does not exceed 11 weeks, there are usually no symptoms of pathology, and the pregnancy itself proceeds successfully, resulting in the birth of a healthy child.
In general, pregnancy does not affect the number of centimeters added to the tumor. In addition to size, there are several other indicators that contribute to the operation.
How quickly does uterine fibroid grow?
Tumor development goes through three stages:
I. Formation - myometrial cells continuously divide, forming nodules. II. Maturation is a period of active growth: a nodule with a diameter of up to 30 mm grows and thickens. III. Aging - growth stops, degenerative processes occur in the node.
Depending on the growth rate, there are:
- simple small uterine fibroids - slowly progressing. More often it consists of one small node, the symptoms are erased or do not appear at all. Detected only on ultrasound;
- large proliferating uterine fibroids - rapidly increasing with the development of the clinic. It can be single or multiple, consisting of a large number of cells with a large nucleus and an increased concentration of DNA.
A neoplasm is considered to be rapidly growing if it grows by 5 weeks or more per year.
Slow growing - in 3 months it increases by no more than 1 cm.
When surgery is unavoidable
Is surgery necessary if the dimensions do not exceed the permissible limits? Yes, if the following factors apply:
- The neoplasm can develop into a malignant tumor;
- The size is insignificant, but pregnancy is planned soon;
- The patient feels unbearable pain for a long period;
- The tumor compresses nearby organs;
- Internal bleeding appeared;
- Myoma has an additional formation - a stalk;
- Problems with urination began.
What will happen without surgery?
If the patient is indicated for surgery to remove fibroids, it is necessary to adhere to this prescription, otherwise the outcome may be unpredictable. What does it mean? Possible consequences:
- If the inflammation spreads to a severe extent, severe kidney disease will result;
- A benign tumor will become malignant within a short amount of time;
- The growth of fibroids will continue, which will lead to even greater pressure on neighboring organs; the outcome of this process can be unpredictable, even fatal;
- Anemia will quickly develop;
- There is a risk of infertility.
If you regularly visit a gynecologist and follow all his requirements, the consequences of the problem will not affect you. Today there are many modern techniques that allow you to remove a tumor quickly and without consequences. Therefore, you should not be afraid of doctors; this pathology can be eliminated by living a full and rich life.
Video
Uterine fibroids are a hormone-sensitive benign tumor consisting of myometrial cells. Education occurs during the reproductive period and grows until menopause. The rate of tumor growth is variable and depends on various factors, including the woman’s age, pregnancy and childbirth, and other aspects.
The size of fibroids is traditionally measured in weeks of pregnancy and in centimeters. Tumor diameter is assessed during bimanual examination and ultrasound. The size of the formation affects the severity of clinical symptoms, determines the treatment method and prognosis for a woman’s reproductive health.
More information on the topic of uterine fibroids:
Submucosal uterine fibroids, Subserous uterine fibroids, Removal of uterine fibroids, Removal of the uterus for fibroids, Author's treatment methods, Laparoscopic myomectomy, Hysteroscopic myomectomy, Control hysteroscopy, Pregnancy after laparoscopic and open myomectomy, Uterine artery embolization (UAE), Multiple fibroids, Large uterine fibroids sizes, Why are uterine fibroids dangerous?
Hysterectomy
Enlarged fibroids carry the highest risk of complications and require constant monitoring and immediate intervention. Based on the fact that the enlargement of the uterus during the development of fibroids corresponds to its growth during pregnancy, the size of fibroids is usually determined in weeks of pregnancy. A fibroid that has reached the size of 12 weeks of pregnancy is considered large.
What determines the size of fibroids and what affects its growth
Before talking about the diameter of a benign tumor and deciding on treatment tactics, you need to understand what exactly influences the development of this pathology. Why do some women not even know about the existence of fibroids, while according to autopsy (post-mortem) data, the disease is detected in 80% of the fair sex? And why, while some patients benefit from a course of hormones, others are preparing for surgery, and sometimes surgery has to be performed more than once. Why does fibroid grow?
The diagram shows the main reasons for the growth and development of fibroids.
The development of a tumor in the muscular layer of the uterus is influenced by the following factors:
- Woman's age. Clinically significant formations are detected mainly in women of late reproductive age, that is, at 35-45 years of age. The older the woman, the higher the likelihood of detecting large and giant tumors. During menopause, fibroids may regress or remain unchanged;
- Reproductive status. Previous traumatic births, abortions and miscarriages contribute to the growth of the node. Conversely, the timely birth of a child reduces the risk of developing the disease. The optimal age for the birth of your first child is considered to be from 22 to 30 years;
- Taking medications. Some drugs accelerate the growth of the node, while others inhibit its development;
- Endocrine pathology. It is believed that obesity and thyroid disease provoke the proliferation of leiomyoma.
If an asymptomatic tumor suddenly begins to grow and menstrual irregularities appear, you must report your complaints to your doctor and undergo an examination. The growth of fibroids is always an alarming sign, especially during menopause. This symptom may hide uterine sarcoma.
You can see what a woman with a large uterine fibroid looks like in the photo below.
If there are large fibroids, a woman will experience an enlarged abdomen.
Uncontrolled growth of the tumor leads to an increase in the size of the abdomen, and often such a patient can be mistaken for a pregnant woman, but this is not the case. Nodules measuring 12 weeks or older, that is, extending beyond the pelvis, require mandatory treatment.
Size diagnostics
Symptoms of fibroids vary depending on their location and size.
Prescribed if the size of the tumor has reached 12 weeks. Drug treatment is aimed at stopping growth and reducing size. This treatment is carried out for women who are going to become mothers and after surgery to prevent the appearance of new tumors.
Conservative treatment of uterine fibroids helps prevent the growth of fibroids and helps preserve the uterus, allowing you to have a child in the future. Conservative treatment of uterine fibroids is possible in the case of a small size of the uterus (up to 12 weeks), slow growth rates of fibroids, when the fibroid node is located in the middle of the muscular layer of the uterus (interstitial fibroids) or under the superficial lining of the uterus (subserous uterine fibroids). The basic principles of treating uterine fibroids without surgery are the use of hormonal drugs, as well as symptomatic treatment (treatment of anemia, pain relief, etc.). The following hormonal drugs are used in the treatment of uterine fibroids:
Possible causes leading to the development of uterine fibroids include:
- subserous - the tumor grows subperitoneally.
- irregular sex life, especially from the age of 25; disharmony in sexual life - an interesting fact is that women who have problems achieving orgasm are more likely to develop uterine fibroids;
In this case, the uterus can be saved. A conservative myomectomy, possibly via a laparoscopic approach, is suitable for you.
Uterine fibroids are a disease of the female genital area, which is characterized by the appearance of a benign tumor in the muscle layer of the uterus. The main symptoms of uterine fibroids are: uterine bleeding (heavy, prolonged menstruation), pain (pulling pain) and heaviness in the lower abdomen, frequent urination, stool retention, and, in some cases, infertility. Diagnosis of uterine fibroids is based on a gynecological examination and confirmed by ultrasound examination (ultrasound of the uterus). Treatment for uterine fibroids depends on the woman's age, the size of the uterine fibroids, and the woman's desire to have children in the future. In some cases, treatment of uterine fibroids is carried out with the help of hormonal drugs, in other cases surgical intervention is necessary (removal of the tumor - myomectomy, removal of the uterus - hysterectomy, etc.)
For this reason, patients with uterine fibroids often turn to urologists and proctologists.
Traditional treatment of uterine fibroids
The basis of conservative treatment is the use of hormonal drugs.
To accurately determine the size of fibroids, it is necessary to do an ultrasound. It is generally accepted that for large tumors that exceed 60 mm or 6 cm (12–16 obstetric weeks), surgery must be performed. Benign neoplasms are dangerous for a woman’s life when there are many of them. Fibroids 20–60 mm or 2–6 cm (10–11 weeks) are treated with medications, diet and physical therapy. That is, conservative treatment is carried out.
The causes of uterine fibroids are currently not completely known. There are several factors that contribute to the development of uterine fibroids, these include:
Content
- hysteroscopy - the method is informative for recognizing submucosal and interstitial myomas with centripetal (cavity-deforming) growth. During hysteroscopy, the gynecologist takes a biopsy (a piece of tissue) from the uterine cavity for further histological examination;
— miscarriage, hypoxia and fetal malnutrition;
How is the size of a benign tumor determined?
Assessing the size of fibroids is carried out in several stages:
Gynecological examination
The primary diagnosis is made during bimanual examination. The patient is positioned in a gynecological chair, and the doctor, having inserted two fingers of one hand into the vagina, assesses the condition of the uterus and appendages with the other hand. The doctor pays attention to the size of the reproductive organ and determines it in weeks, as during pregnancy, and evaluates the surface of the uterus (smooth or bumpy). At this stage, the diagnosis has not yet been made. The doctor cannot see whether the uterus is enlarged due to fibroids or another pathology. For further diagnosis, the patient is sent for an ultrasound examination.
You can determine the enlargement of the uterus with your hands starting from 7-9 weeks. The uterus, the size of a goose egg, is easily palpable and clearly differs from the norm. With subserous myoma, you can palpate the nodes through the abdominal wall (the surface of the reproductive organ becomes lumpy). With smaller formations, the uterus is enlarged quite slightly, and the possibility of a diagnostic error cannot be excluded.
Large subserous nodes located in the fundus of the uterus can be palpated through the anterior abdominal wall.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound is the main method for diagnosing uterine fibroids. On ultrasound examination, a benign tumor appears as a hypoechoic formation. The heterogeneous structure of the node may indicate the inclusion of calcifications. During ultrasound, three parameters are assessed:
- Size of formation in millimeters. For each node, the diameter (for example, 35 mm) and location in relation to the walls of the uterus are determined;
- Size of the uterus (length and width);
- The presence of changes in the structure of the tumor: degeneration, formation of calcifications, cystic cavities.
Ultrasound is the “gold standard” for detecting fibroids and assessing their condition.
The blood flow around the fibroid is necessarily assessed, and the thickness of the endometrium (M-echo) is determined to identify concomitant pathology.
Histological examination
Accurate data about the fibroid can only be obtained after its excision. The removed node is sent to the laboratory, where its diameter is measured and also weighed. It is not so important how much the tumor weighs - this parameter is not important for further tactics and is only of scientific interest.
The weight of the largest fibroid in the world was 63 kilograms.
Histological examination evaluates the structure of the fibroid and the cells of which it consists - to exclude oncological processes.
Classification of fibroids: size matters
The diameter of fibroids in centimeters and the size of the uterus in weeks are the leading criteria for classifying pathology. The characteristics of this tumor depending on its size are presented in the overview table:
| Up to 7 | 3-7 cm or 30-70 mm |
| Up to 9 | 8-9 cm or 80-90 mm |
| Until 11 | 10-11 cm or 100-110 mm |
| Up to 13 | 10-11 cm or 100-110 mm |
| Up to 15 | 12-13 cm or 120-130 mm |
| Up to 17 | 14-19 cm or 140-190 mm |
| Up to 19 | 16-21 cm or 160-210 mm |
| Until 21 | 18-24 cm or 180-240 mm |
| Up to 23 | 21-25 cm or 210-250 mm |
| Up to 25 | 23-27 cm or 230-270 mm |
| Up to 27 | 25-28 cm or 250-280 mm |
| Up to 29 | 26-31 cm or 260-310 mm |
| Up to 31 | 29-32 cm or 290-320 mm |
| Up to 33 | 31-33 cm or 310-330 mm |
| Up to 35 | 32-33 cm or 320-330 mm |
| Up to 37 | 32-37 cm or 320-370 mm |
| Up to 39 | 35-38 cm or 350-380 mm |
| Up to 41 | 38-39 cm or 380-390 mm |
| Myoma and its characteristics | Tumor size in centimeters | Enlargement of the uterus in weeks of pregnancy | Leading symptoms | Treatment approaches |
| Clinically insignificant | Up to 2 cm | Up to 4-5 weeks | Asymptomatic | Dynamic observation |
| Small sizes | 2-2.5 cm | Up to 5-6 weeks | Menstrual irregularities, moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen | Hormone therapy |
| Medium size | 3-6 cm | 6-12 weeks | Menstrual irregularities, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, acyclic bleeding | Conservative myomectomy, uterine artery embolization |
| Large sizes | More than 6 cm | More than 12 weeks | All symptoms of medium-sized fibroids plus compression of the pelvic organs | Myomectomy or removal of the tumor along with the uterus (hysterectomy) |
Classification of uterine fibroids by size allows you to understand what to expect from such a tumor and what complications it may be accompanied by. For example, if a doctor tells a patient that she has fibroids for 7-8 weeks, then we are talking about a medium-sized tumor - up to 4-5 cm. Is this too much? Yes, such education will no longer go unnoticed. Most likely, the patient came to the appointment with complaints of heavy and prolonged menstruation - the most common symptom with medium-sized tumors. The best option would be to remove the tumor, possibly with preliminary preparation with hormonal drugs.
Photo of a medium-sized leiomyoma.
Myoma myoma - discord
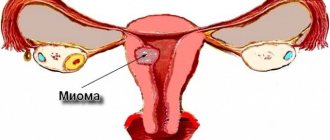
Myomatous nodes in the uterus can occupy different positions, and the symptoms and the need for treatment depend on this. The wall of the uterus consists of three layers: the mucous membrane, the muscular layer and the outer serosa. Myoma grows from muscle tissue; it can be located deep in the muscles (intramural), inside the uterus under the mucosa (submucosal), outside under the serous membrane (subserous).
In terms of symptoms, submucosal and subserous nodes are the most harmless. They often grow very large and are diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound.
The situation is different with submucosal fibroids. After all, during menstruation, the uterine mucosa is torn away and bleeding develops. Submucosal fibroids stretch it and prevent it from contracting, so bleeding will be longer and stronger. Submucosal fibroids with dimensions of more than 4–5 cm protrude into the uterine cavity, interfere with the attachment of the fertilized egg, the development of the fetus, “rob” it, drawing blood flow towards itself. Find out more about the types of fibroids.
What influences the size of a uterine tumor?
The size of the myomatous node determines not only the features of the clinical picture of the disease. The size of the tumor determines the likelihood of complications, as well as the choice of treatment tactics.
Conceiving a child and the course of pregnancy
Small fibroids, especially those located subserosally, usually do not interfere with the course of pregnancy. A node measuring up to 2 cm does not require treatment. During pregnancy, ultrasound monitoring of the tumor condition and correction of emerging complications if necessary is indicated.
Pregnancy can affect the growth of myomatous nodes and the development of complications, so ultrasound monitoring of the tumor is mandatory.
A formation measuring 2-3 cm can prevent the conception of a child, especially if the tumor is located in the submucosal layer of the uterus. Hormonal therapy is indicated to reduce the size of the tumor or removal of the node using endoscopic access. For multiple fibroids, uterine artery embolization is effective and is the best option for women planning pregnancy.
Medium-sized benign tumors can become an obstacle to motherhood. Gynecologists recommend removing the nodes before conceiving a child. This will reduce the risk of complications and bring the baby to term.
Large and giant nodes are a contraindication to pregnancy. Such formations are usually accompanied by infertility. Even if a woman manages to conceive a child with fibroids of 6 cm in diameter, the chances of a successful outcome are low. Spontaneous miscarriage, improper attachment of the placenta, delayed fetal development - this is just a small list of problems that await the patient during pregnancy against the background of large fibroids.
If a woman has uterine fibroids, she should undergo examinations before pregnancy to avoid the development of complications.
Complications of the disease
The larger the tumor size, the greater the likelihood of developing undesirable consequences:
- Compression of the pelvic organs - bladder and rectum - with the appearance of corresponding symptoms (impaired urination, constipation);
- Heavy uterine bleeding leading to anemia. Massive blood loss threatens the woman’s life;
- Malnutrition of the node with subsequent necrosis. Degenerative changes can be tracked by ultrasound, but not all women regularly visit the doctor. Necrosis of fibroids makes itself felt by acute pain in the lower abdomen. The condition is life-threatening and requires urgent surgery;
- Tumor infection. It occurs against the background of necrosis and is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Is an indication for surgical treatment;
- Torsion of the legs of submucosal or subserous fibroids with impaired blood flow in it. Accompanied by severe pain and bleeding and requires emergency surgery;
- Tumor malignancy. The fact that fibroids have degenerated into sarcoma has not been proven, but oncological alertness remains. Large formations with rapid growth, especially in menopause, require close monitoring, since this symptom may hide a malignant tumor.
This is what a subserous necrotic myomatous node looks like.
Large fibroids must be operated on to avoid the development of dangerous complications. Before surgery you should follow some recommendations:
- Do not create conditions to increase blood flow in the tumor. You cannot engage in heavy physical work and sports (do exercises to strengthen the abs and pelvic muscles), or get carried away with visiting the sauna and bathhouse;
- A doctor of any specialty who sees a patient with fibroids must know that she has this disease. Some medications accelerate the growth of the node;
- Do not self-medicate. Folk remedies will not help remove the tumor. Natural dietary supplements based on phytoestrogens can even provoke its proliferation.
Uterine fibroids measuring 12 weeks or more cannot shrink on their own and disappear without leaving a trace. It is impossible to do without surgery for large nodes. The disease must be treated on time, this is the only way to avoid the development of complications.
To date, there are no methods that can reliably stop the growth of myomatous nodes. The use of hormones provides a temporary effect, but after stopping the drug, the fibroids begin to grow again. Radical removal of the tumor solves the problem, but the possibility of relapse cannot be ruled out. A 100% positive result is achieved only by removal of the uterus along with the tumor, but this is not the method that young women dream of. The issue of treating fibroids is finally decided after a full examination and assessment of all risk factors.
Myoma is a benign tumor that is localized in the myometrium of the uterus (muscle layer). In medicine, the pathological formation is also called leiomyoma and fibromyoma. The age of patients who face this diagnosis varies from 20-70 years. Most often, tumors are found during reproductive age. To prescribe treatment, the doctor needs to determine the size of the growths, their number, location, type, etc. Let's figure out what size uterine fibroids require surgery and when conservative treatment is prescribed.
Complications
Multiple large fibroids can be especially dangerous. In this case, the gynecologist has to monitor several nodes at once, sometimes there are more than a dozen of them. If a woman is pregnant, but the placenta is affected by a myomatous node, this greatly increases the risk of miscarriage.
Large nodes put pressure on internal organs and can interfere with the normal functioning of the kidneys, promote the formation of stones and the development of infectious and inflammatory diseases. The functioning of the digestive system may also be disrupted: constipation develops.
The rate of growth is also important: it is considered accelerated if during the course of a year the tumor has increased by the gestation period corresponding to 5 weeks.
Impaired blood supply to fibroids can cause necrosis, and torsion of the tumor stalk is also possible. In some cases, the formation may prolapse from the uterus into the vagina, which is accompanied by severe pain and bleeding. In approximately 2% of cases it can develop into cancer.
Briefly about the disease
A benign neoplasm has the shape of a ball of varying sizes.
The seriousness of the disease lies in its asymptomatic course. The first discomfort appears at the moment when the tumor has reached a medium or large size and progresses further. The pathological process is caused by hormonal imbalances. According to statistics, multiple fibroids are most often diagnosed.
To identify formations, examination and ultrasound examination are performed. Knots are measured in mm, cm and weeks. The process itself is very similar to the development of a baby in the womb. As the tumor grows, the uterus enlarges and bleeding, pain and other discomfort may occur. If there is an excess of estrogen in a woman’s body, the pathology will progress.
According to medical data, large nodes (12-16 weeks), which reach 6 centimeters or 60 millimeters, require surgical treatment. Medium tumors (10-11 weeks) are not always removed. Small formations (4 weeks) 2 cm or 20 mm are treated with medications, physiotherapy, etc. The main danger of the process is the possibility of degeneration into cancer.
Sizes of fibroids and their symptoms
Every woman should understand at what size of the nodes surgery is needed, and when drug treatment is needed. Doctors compare the development of a tumor with an embryo, so the size of the uterus is determined in weeks, as in pregnancy, as well as in millimeters and centimeters. Nodes are divided into 3 categories based on size, and various symptoms appear according to size:
- Small - such tumors measure no more than two cm. The formations are discovered by chance; normally they do not cause pain or other signs of the pathological process. Fibroids cannot be removed for 7 weeks; hormone therapy and observation are prescribed.
- Medium – from 20-40 mm to 60 mm, but not more than 7 cm. The patient experiences heavy menstruation with pain that cannot be suppressed with painkillers. If the fibroids are more than 11 weeks old, the woman experiences bloating in the lower abdomen due to an enlarged cervix.
- Large - over 60-70 mm. This is a serious condition that requires surgery; medications are ineffective. The nodes compress the organs that are nearby, which disrupts the process of defecation and urination. The patient complains of pain in the heart muscle and lumbar region. There is numbness in the legs, as the formation presses on the nerve endings near the rectum.
Indications for removal
To find out whether surgery is needed or not, a thorough examination of the patient is carried out. Doctors identify several main indications for surgical interventions:
- Heavy bleeding - most often, excessive bleeding is caused by nodes for 15 weeks or more, if it is not stopped, anemia appears;
- The size of the fibroids is 12 weeks (in centimeters this is more than 6). If multiple medium-sized nodes are detected, the woman must be operated on. Such tumors threaten the patient's life. If the fibroid is less than 5 cm, but there are still medium and large ones nearby, concomitant drug therapy is indicated;
- Planning pregnancy - medium fibroids can cause infertility or miscarriage. After fertilization, the level of hormones changes, which can stimulate the growth of nodes. They may grow slowly or too quickly, causing the baby to suffer;
- Risk of oncology - if the tumor grows rapidly, malignancy occurs;
- Regular pain syndrome – pain occurs with medium and large nodular growths. They compress neighboring organs, stool and urination are impaired, which can cause intestinal inflammation or intoxication of the body.
New growths smaller than 4 cm are usually not removed.
Surgery is indicated when fibroids are diagnosed after 9 weeks of menopause. Menopause stops the development of nodes, as the production of estrogen is inhibited, but the patient must be monitored. As an alternative, a radical method of therapy is used - removal of the uterus.
How big can tumors be?
The size of uterine fibroids directly depends on the state of the woman’s hormonal balance and the amount of estrogen contained in her blood.
If too many sex hormones are produced, the tumor begins to grow rapidly. Gynecologists determine the size of uterine fibroids by comparing them with the size of the uterus at a particular stage of pregnancy. True, medicine is developing and offers hardware diagnostics, so this method is considered outdated. But it still exists and it’s worth telling a little about it.
In order to determine the size of the tumor in weeks, doctors must have a special table. It contains the period, how many weeks the pregnancy lasts, and the volume of the reproductive organ corresponding to this time.
Based on the above table, doctors have identified several categories of uterine fibroids depending on size:
- A small formation is a 6-week fibroid that does not exceed 2 cm.
- The average tumor is uterine fibroids up to 9 weeks, the size of which varies from 2 to 5 cm.
- A large neoplasm is when the size of the fibroid is 12 weeks in centimeters exceeding 6 cm.
Also, when identifying the disease, it is important to take into account not only the size, but also the rate of increase in fibroids. When a woman’s small or medium-sized tumor grows for more than five weeks over the course of a year, for example, a fibroid of 7 weeks has increased to 15 mm, then doctors say that the growth rate is high. Factors that can provoke this may be frequent disruptions in the hormonal balance in the female body.
It is very important to know what size the fibroids are if the patient is expecting a child. If the neoplasm is small, approximately 6-7 weeks, then the baby will be born safely and no problems will arise. If fibroids are diagnosed for 12 weeks or more, then women are practically unable to give birth.
This happens because the uterine tubes are blocked by a tumor, often causing miscarriages or premature births. Often, when a patient is diagnosed with uterine fibroids for 10 weeks, during labor there is heavy bleeding, complications of childbirth, the development of pathologies of an infectious or inflammatory nature, and other negative consequences.
Abdominal operations
The golden rule for successful treatment of pathology is that a formation that has reached the size for surgery must be removed.
If you start the process, the node grows to the size of a child and can weigh up to 7-8 kg. Today there are many methods, both traumatic and gentle. In cases where the condition is complicated by tissue necrosis or torsion of the leg, it is decided to operate in the traditional way; abdominal surgery is chosen. To do this, incisions are made in the peritoneum, through which the tumor will be removed. There are 4 types of such interventions, let's look at them.
Laparotomy
It is used in cases where fibroids have reached a size of 14 weeks and are pressing on neighboring organs. The operation is performed through small incisions in the abdominal wall, which are then sutured. This method of removal requires long-term rehabilitation, more than one month. During the recovery period, you should not overwork yourself, lift heavy objects, etc. You can leave the hospital after a week, when the stitches are removed.
https://youtu.be/YYx_EkhvilM
Hysterectomy
This technique is used if the node has reached gigantic proportions, is rapidly growing and is prone to degeneration into cancer. Intervention is also prescribed during menopause and in the presence of multiple tumors. Hysterectomy is the complete removal of the uterus, so it is used in extreme cases. The recovery period is 2 months, the first few days they take painkillers. An antibiotic is then prescribed. During the rehabilitation period, the risk of bleeding increases.
If a woman notices bloody discharge, you need to call an ambulance.
Hysteroresectoscopy
The operation is performed using a special device. A hysteroscope is inserted into the vagina and penetrates the uterus. The method is used for single formations of 15 mm or more, if they are localized on the front or rear wall. The intervention is prescribed in the first week of the cycle.
This method has received many good reviews; it can be performed even on an outpatient basis.
Myomectomy
Removal occurs through punctures in the peritoneum using a laparoscope, so there are no noticeable scars. The advantages of laparoscopy include a short recovery period, approximately 7 days. The method is used to remove several formations of 9-11 mm, but not more than 15. In this case, the uterine cavity should not exceed 8 weeks. The organ suffers virtually no damage, and the risk of adhesions is minimal.
After the operation, the patient retains reproductive function.
Diagnostic methods
Only a doctor can diagnose uterine fibroids.
However, you should pay attention to the appearance of the following symptoms, which may be signs of tumor development. Symptoms:
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Heavy menstruation mixed with blood clots.
- Development of anemia due to frequent blood loss.
- Pain at the location of the tumor.
- Impaired urination and defecation due to tumor growth.
- Shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat are characteristic of enlarged fibroids.
- Increased belly size without overall weight gain.
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
To accurately diagnose fibroids, there are a number of medical measures:
- Examination on a gynecological chair - by palpation of the lower abdomen, the doctor can detect a medium or large tumor. Using mirrors, an experienced gynecologist can easily detect the formation of fibroids on the cervix.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvis is one of the most accessible and effective studies in the diagnosis of fibroids. Currently, there are 2 forms of pelvic ultrasound examination: abdominal - performed through the abdominal wall and transvaginal - performed directly through the vagina. Transvaginal ultrasound is the most preferred form for diagnosing a uterine tumor. This type of study allows us to identify the entire clinical picture of the disease. Using an ultrasound, the doctor will be able to determine the location of the tumor, its size, and also rule out pregnancy.
- Laparoscopy is performed using a special laparoscope device. The essence of the procedure is to examine the organs and tissues of the pelvis through a puncture of the abdomen. It is prescribed in case of fibroid formation on the outside of the uterus and its growth into the pelvic area or abdominal cavity.
- Hysteroscopy is performed using a special hysteroscope apparatus. The device is inserted into the cervical canal and transmits an enlarged image of the internal organs of the small pelvis to the monitor, enlarged several times. Thanks to this study, it is possible to establish the degree of damage to the uterus by myomatous formations.
- Colposcopy is performed using a special optical device – a colposcope. The device enlarges and illuminates the body of the uterus several times, thanks to which the doctor can detect a neoplasm.
- X-ray – the essence of the procedure is the introduction of a special reagent into the uterus, after which the uterus is examined under X-ray radiation.
- Computed tomography is performed when a tumor is rapidly increasing in size. Allows you to identify its location, exact size and number of nodes in multinodular fibroids.
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to examine the uterus in a three-dimensional image from all sides. Helps detect fibroid development at an early stage
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine allow us to exclude other diseases of the genitourinary system with similar symptoms. A blood test for hormones allows you to study a woman’s hormonal background.
- Scraping of uterine biomaterial is carried out in case of insufficient information obtained from other studies. The essence of the procedure is that the doctor, using a special instrument - a curette, scrapes the surface of the uterus in order to send the resulting sample for histology. During the procedure, the patient is under general anesthesia.
A large tumor can be identified by a gynecologist during examination in a gynecological chair.
Additionally, the woman undergoes the following diagnostic procedures:
- Ultrasound;
- laparoscopy;
- hysteroscopy.
After confirming the diagnosis, you should not get upset and panic. It is necessary to think about how to treat this pathology of the uterus.
Other treatments
If the fibroids are no more than 12-13 weeks old, hormonal therapy is used. Such drugs inhibit the production of estrogen and the rate of progression of nodes, and also reduce their size.
UAE and laser removal are also prescribed. Gentle methods have a number of advantages:
- There are no large scars left, usually they do not exceed a diameter of 2 centimeters.
- The ability to bear children is preserved.
- Short rehabilitation – up to 14 days.
- Minimal risk of bleeding and complications.
Expensive operations are not affordable for everyone, so you can apply for a state quota. This will take time; you will have to prove that other methods will not work.
Conservative treatment
The therapy is relevant for young women who are planning a pregnancy in the future. Hormones are often used, sometimes after surgery, to prevent recurrence. Oral contraceptives are effective for infertility caused by fibroids. Doctors use Femoden, Novinet, etc. The drugs contain gestagens that stop the growth of tumors.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists work well for sizes from 10 mm to 30 mm. Zoladex, Lucrin-depot and others are prescribed. The course of therapy does not exceed 6 months, since long-term use of such drugs causes menopause.
GnRH reduces tumor formation by 2 times, pregnancy can be planned immediately after treatment. Some patients report increased sweating, mood swings and hot flashes during therapy.
If the fibroid does not reach 7 mm, it is monitored. Removal or other treatment is not appropriate until the disease has progressed. However, during menopause, small nodes, for example, about 9 mm, are sometimes removed.
Embolization
If conservative therapy does not produce the desired results, UAE is prescribed. The size of the nodes should not exceed 3 centimeters. The technique copes with pathology at any stage. In the process, the arteries are blocked with a special substance, causing the tumor to die, finding itself without proper nutrition.
The woman retains reproductive functions, since the uterus does not suffer. The procedure takes up to 50 minutes and no anesthesia is required. After the operation, the patient remains under observation until the morning, then goes home. After a while, mild pain is possible, which is eliminated with painkillers.
Recovery occurs after seven days, improvements are noticeable already in the next menstrual cycle. Discomfort and heavy discharge are eliminated. In the first week after UAE, weakness, fever and chills are possible. Soon the unpleasant symptoms will disappear.
Laser removal
Laser beams are used for tumors up to 4 centimeters. The beam hits the affected area in doses, maintaining optimal depth. In this case, neighboring tissues and cells are not affected. The therapy has a number of advantages, including:
- Speed of implementation;
- No pain, no scars, no anesthesia;
- Reproductive function is preserved;
- During the intervention, bleeding stops;
- Possibility of outpatient implementation.
The postoperative period does not exceed 2 days. As a result of this treatment, menstruation is normalized, well-being improves, and the ability to bear children returns. Disadvantages include a high risk of relapse and the impossibility of intervention in large-scale tumor growths.
Treatment of fibroids measuring 5 centimeters
For fibroids measuring 4.5.6 cm (age 8-12 weeks), there is treatment with alternative methods.
- Laser treatment (FUS ablation) – elimination or reduction of fibroids without incisions and damage to healthy tissue. The procedure involves “burning out” the tumor using a laser beam. The operation is carried out under the control of a magnetic resonance imaging device, which makes it possible to perform manipulations as clearly as possible and completely eliminate injury to the pelvic organs and preserve reproductive function.
- The method of uterine artery embolization involves blocking the blood flow to the fibroids. A small incision is made in the area of the right femoral artery, through which a catheter is inserted into the artery up to the vessels of the uterus. With the help of a specially developed drug, the blood vessels are blocked, after which the blood supply to the neoplasm is stopped and its gradual death occurs. The uterine fibroids are then eliminated from the body during menstrual bleeding.