Treatment of genitourinary infections in women
Male infectious diseases, like female ones, are treated according to a strictly established scheme.
Among purely female diseases caused by infectious agents, there are 3 most common diseases, which we will consider further.
Modern medicine offers a wide range of drugs of synthetic and semi-synthetic origin that have a suppressive effect on pathogenic microorganisms. The following types of antibiotics are used to treat genitourinary tract infections:
- oral cephalosporins;
- inhibitor-protected penicillins;
- fluoroquinolones;
- nitrofurans;
- macrolides;
- phosphonic acid.
The use of a particular drug must be agreed with a doctor after all the necessary tests have been carried out to determine the sensitivity of the microflora to the effects of different types of antibiotics. In the acute form of cystitis, it is allowed to take new generation antibiotics without identifying the pathogenic microorganism.
However, in order to avoid the inflammatory disease becoming chronic, you should go to the hospital and undergo a full diagnostic examination.
Oral cephalosporins
The most popular group of antimicrobial drugs in terms of frequency of clinical use are cephalosporins. The widespread use of drugs of this type for inflammation of the bladder in men and women is due to the high efficiency and low toxicity of these drugs:
- name: Cephalexin;
- description: the activity of this antimicrobial drug is aimed at destroying the cell walls of streptococcal bacteria and methicillin-sensitive staphylococci, the drug relieves inflammation of the bladder mucosa;
- Method of administration: the drug should be taken every 6 hours, 1 capsule containing 250 mg of the active substance;
- advantages: low degree of toxicity;
- disadvantages: narrow spectrum of action, low level of activity.
When taking antibiotics, one should take into account the fact that the effectiveness of antibacterial drugs increases with each generation, but their toxicity also increases. A representative of the 3rd generation of cephalosporins is Ceftibuten:
- name: Ceftibuten (Cedex);
- description: an effective drug that inhibits the biosynthesis of cell walls of pathogenic microorganisms, has the highest index of resistance to beta-lactamases among antibiotics in this group, and is used to treat urinary tract infections in adults and children;
- Method of administration: 1 capsule with a dose of 0.4 g of the substance is taken once a day at any time;
- pros: rare occurrence of side effects;
- cons: aggressive effect on intestinal microflora.
Inhibitor-protected penicillins
To treat acute bacterial infections in women, short courses of antibiotic therapy using inhibitor-protected penicillins are used. This is a group of products containing compounds that inactivate beta-lactamases. The sensitivity of bacteria to the effects of drugs increases due to the suppression of their resistance to penicillins:
- name: Amoxicillin;
- Description: affects gram-positive and gram-negative infectious pathogens, as well as E. coli. Effective in the treatment of bladder inflammation, including urethritis, cystitis;
- Method of administration: for mild forms of the disease, the drug is taken orally, 0.5 g three times a day; severe cases of the disease require doubling the dose;
- advantages: quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract;
- cons: may provoke an exacerbation of infections.
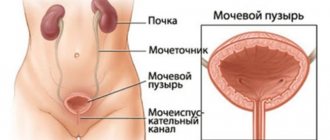
Infections of the genitourinary system in women are pathological effects caused by specific harmful microorganisms. Urinary tract diseases are characterized by inflammation, which is easy to cure in the initial stage or, if the signs are ignored, becomes chronic.
Which doctor treats diseases? The answer depends only on the area of the genitourinary system and its stage. This could be a therapist, urologist, gynecologist, infectious disease specialist, or even a surgeon.
Medicines for genitourinary tract infections: when and which ones are used
The most common complaints from patients when visiting a urologist are genitourinary infections, which can occur in any age category for various reasons.
A bacterial infection of the urinary system is accompanied by painful discomfort, and untimely treatment can lead to a chronic form of the disease.
To treat such pathologies in medical practice, antibiotics are usually used, which can quickly and effectively relieve the patient from infection due to inflammation of the genitourinary system.
The use of antibacterial agents for MPI
Normally, the urine of a healthy person is almost sterile. However, the urethral tract has its own flora on the mucous membrane, so the presence of pathogenic organisms in the urinary fluid (asymptomatic bacteriuria) is often recorded.
This condition has no symptoms and treatment is usually not required, except in pregnant women, young children and immunocompromised patients.
If the analysis shows entire colonies of E. coli in the urine, then antibiotic therapy is mandatory. In this case, the disease has characteristic symptoms and occurs in a chronic or acute form. Treatment with antibacterial agents over long courses in small dosages is also indicated to prevent relapses.
The following are antibiotic treatment regimens for genitourinary infections for both sexes, as well as for children.
Pyelonephritis
Patients with mild and moderate stage pathologies are prescribed oral fluoroquinolones (for example, Zoflox 200-400 mg 2 times a day), inhibitor-protected Amoxicillin, or cephalosporins as an alternative.
Pregnant women and children under 2 years of age are hospitalized and treated with parenteral cephalosporins, then transferred to oral ampicillin with clavulanic acid.
Cystitis and inflammation in the urethral canal usually occur synchronously, so the same antibacterial agents are used.
| Infection without complications in adults | Infection with complications | Pregnant | Children | |
| Duration of treatment | 3-5 days | 7-14 days | Prescribed by a doctor | 7 days |
| Preparations for primary treatment | Fluoroquinols (Ofloxin, Oflocid) | Treatment with agents used for uncomplicated infection | Monural, Amoxicillin | Antibiotics of the cephalosporin group, Amoxicillin in combination with potassium clavulant |
| Reserve medications | Amoxicillin, Furadonin, Monural | Nitrofurantoin | Monural, Furadonin |
Additional Information
In case of complicated and severe pathological condition, mandatory hospitalization is necessary. In a hospital setting, a special drug treatment regimen is prescribed using the parenteral route. It should be taken into account that in the stronger sex any form of genitourinary infection is complicated.
If the disease is mild, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, with the doctor prescribing medications for oral administration. It is permissible to use herbal infusions and decoctions as additional therapy on the recommendation of a doctor.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics in the treatment of MPI
Modern antibacterial agents are classified into several types that have a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect on pathogenic microflora. In addition, drugs are divided into broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum antibiotics. The latter are often used in the treatment of MPI.
Penicillins
Semi-synthetic, inhibitor-protected, combination drugs of the penicillin series can be used for treatment
- Ampicillin is a drug for oral and parenteral use. It has a destructive effect on the infectious cell.
- Amoxicillin - the mechanism of action and the final result are similar to the previous drug, it is highly resistant to the acidic environment of the stomach. Analogs: Flemoxin Solutab, Hiconcil.
Cephalosporins
This species differs from the penicillin group in its high resistance to enzymes produced by pathogenic microorganisms. Cephalosporin-type drugs are prescribed for both floors. Contraindications: pregnant women, lactation period. The list of common therapeutic agents for MPI includes:
- Cephalexin is an anti-inflammatory drug.
- Ceclor is a 2nd generation cephalosporin, intended for oral administration.
- Zinnat – available in different forms, low toxicity, safe for infants.
- Ceftriaxone is a granule for a solution that is subsequently administered parenterally.
- Cephobid – 3rd generation cephalosporins, administered intravenously, intramuscularly.
- Maximim - belongs to the 4th generation, the method of application is parenteral.
Fluoroquinolones
Antibiotics of this group are the most effective for genitourinary infections and are endowed with a bactericidal effect.
However, there are serious disadvantages: toxicity, negative effects on connective tissue, and can penetrate into breast milk and pass through the placenta.
For these reasons, they are not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women, children under 18 years of age, and patients with tendinitis. Can be prescribed for mycoplasma.
These include:
- Ciprofloxacin . It is perfectly absorbed in the body and relieves painful symptoms.
- Ofloxin . It has a wide spectrum of action, due to which it is used not only in urology.
- Nolitsin.
- Pefloxacin.
Aminoglycosides
A type of medicine for parenteral administration into the body that has a bactericidal mechanism of action. Aminoglycoside antibiotics are used at the discretion of the doctor, as they have a toxic effect on the kidneys and negatively affect the vestibular apparatus and hearing. Contraindicated for pregnant women and nursing mothers.
- Gentamicin is a drug of the 2nd generation of aminoglycosides, poorly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract, for this reason it is administered intravenously, intramuscularly.
- Netromycin - similar to the previous medicine.
- Amikacin is quite effective in the treatment of complicated MPI.
Nitrofurans
A group of antibiotics with bacteriostatic action against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. One of the features is the almost complete absence of resistance in pathogens. Furadonin may be prescribed as treatment. It is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation, but can be taken by children after 2 months of birth.
Antiviral drugs
This group of drugs is aimed at suppressing viruses:
- Antiherpetic medications - Acyclovir , Penciclovir .
- Interferons – Viferon , Kipferon .
- Other drugs are Orvirem , Repenza , Arbidol .
Antifungal drugs
There are 2 types of antifungal agents used to treat MPI:
- Systemic azoles that suppress fungal activity - Fluconazole , Diflucan , Flucostat .
- Antifungal antibiotics - Nystatin , Levorin , Amphotericin .
Antiprotozoal
Antibiotics of this group help suppress pathogens. Metronidazole is most often prescribed in the treatment of MPI. Quite effective for trichomoniasis.
Antiseptics used to prevent sexually transmitted infections:
- Iodine-based - Betadine in the form of a solution or suppositories.
- Preparations with a chlorine-containing base - chlorhexidine solution, Miramistin in the form of gel, liquid, suppositories.
- Products based on hibitan - Hexicon in suppositories, solution.
Other antibiotics for the treatment of genitourinary tract infections
The drug Monural deserves special attention. It does not belong to any of the above groups and is universal in the development of the inflammatory process in the genitourinary area in women. For uncomplicated MPI, an antibiotic is prescribed once. The medication is not prohibited during pregnancy; it is also permitted for the treatment of children over 5 years of age.
Drugs for the treatment of the female genitourinary system
Infections of the genitourinary system in women can cause the following diseases (the most common): pathologies of the appendages and ovaries, bilateral inflammation of the fallopian tubes, vaginitis. For each of them, a specific treatment regimen is used using antibiotics, antiseptics, painkillers and flora and immune support agents.
Antibiotics for pathology of the ovaries and appendages:
- Metronidazole;
- Tetracycline;
- Co-trimoxazole;
- Combination of Gentamicin with Cefotaxime, Tetracycline and Norsulfazole.
Antibiotic therapy for bilateral inflammation of the fallopian tubes:
- Azithromycin;
- Cefotaxime;
- Gentamicin.
Broad-spectrum antifungal and anti-inflammatory antibacterial agents prescribed for vaginitis:
Antibiotics for the treatment of the genitourinary system in men
In men, pathogenic microorganisms can also cause certain pathologies, for which specific antibacterial agents are used:
- Prostatitis – Ceftriaxone, Levofloxacin, Doxycycline.
- Pathology of seminal vesicles – Erythromycin, Metacycline, Macropen.
- Epididymal disease – Levofloxacin, Minocycline, Doxycycline.
- Balanoposthitis - antibiotic therapy is based on the type of pathogen present. Antifungal agents for topical use - Candide, Clotrimazole. Broad-spectrum antibiotics – Levomekol (based on chloramphenicol and methyluracil).
Herbal uroantiseptics
In urological practice, doctors can prescribe uroantiseptics both as primary therapy and as an auxiliary treatment.
Canephron
Canephron is a proven remedy among doctors and patients. The main effect is aimed at relieving inflammation, destroying microbes, and also has a diuretic effect.
https://youtu.be/rJtJ2sJPbGc
The composition of the drug includes rose hips, rosemary, and centaury herb. It is used internally in the form of dragees or syrup.
Phytolysin
Phytolysin is able to remove pathogenic microorganisms from the urethra, facilitates the passage of stones, and relieves inflammation. The drug contains many plant extracts and essential oils, and is available in the form of a paste for preparing a solution.
Urolesan
Herbal uroantiseptic, produced in the form of drops and capsules, is relevant for cystitis. Ingredients: extract of hop cones, carrot seeds, essential oils.
Medicines to relieve symptoms of inflammation of the genitourinary system: antispasmodics and diuretics
It is advisable to begin treatment of inflammation of the urinary tract with medications that relieve inflammation, while restoring the activity of the urinary tract. Antispasmodics and diuretics are used for these purposes.
Antispasmodics
They can eliminate pain and improve urine flow. The most common medications include:
- Papaverine;
- No-shpa;
- Bencyclane;
- Drotaverine;
- Canephron;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ketanof;
- Baralgin.
Diuretics
Diuretics to remove fluid from the body. Used with caution, as they can lead to kidney failure and complicate the course of the disease. Basic medications for MPI:
- Aldactone;
- Hypothiazide;
- Diuver.
Today, medicine can quickly and painlessly help treat infections in the genitourinary system using antibacterial agents. To do this, you just need to consult a doctor in time and undergo the necessary examinations, on the basis of which a competent treatment regimen will be drawn up.
We recommend other articles on the topic
Source: https://UroHelp.guru/lekarstva/pri-infekcii-mochepolovoj-sistemy.html
Antibiotics for cystitis during pregnancy
If it is necessary to prescribe an antibiotic for inflammation of the genitourinary system in women during pregnancy, one should take into account not only the activity of the drugs, but also their safety for the fetus. Complaints of frequent urination can be caused by many factors, so before making a diagnosis, doctors prescribe pregnant women to undergo a full examination of the body.
If the assumptions are confirmed, treatment must be started immediately to eliminate the risk of complications due to the spread of infection.
The following list of antibiotics meets safety requirements and can be used throughout pregnancy:
- aminopenicillins (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin);
- cephalosporins (Cefixin, Ceftibuten);
- Fosfomycin;
- Trometamol;
- Nitrofurantoin.
What symptoms accompany this inflammation?
Signs of the disease appear some time after the infection enters the body. They have some specific features, depending on the pathogen and location. However, we can say that there are general symptoms of inflammation of the genitourinary system in women.
These include:
- Urinary disorders - frequent urge, difficulty emptying the bladder, pain and stinging. Sometimes itching, heaviness and burning are observed. Change in color and odor of urine, bloody spots.
- Genital organs – rashes and neoplasms on the mucous membranes, atypical vaginal discharge with a pungent odor, swelling.
- Pain is localized in the lumbar back, lower abdomen, and appears when urinating.
- Common signs of intoxication are fever, weakness, headaches, sleep disturbances, nausea and dizziness.
Many women experience discomfort during sexual intercourse and lack of desire.
Diseases that are classified as inflammation of the MPS can be divided into two groups:
- The most common pathologies of the urinary tract:
- Common diseases of the reproductive system: vaginitis, vulvovaginitis;
- thrush;
- adnexitis;
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis.
These and some other, less common diseases are classified as inflammation of the MPS.
To prescribe effective treatment for inflammation of the genitourinary system in women, it is not enough to determine the symptoms; it is necessary to identify the causative agent and the location of the process.
Diseases of the genitourinary tract are characterized by certain symptoms. In inflammatory processes, diagnosis is necessary. All diseases progress differently, but the main manifestations are:
- pain;
- discomfort and anxiety that disturb the genitourinary tract;
- itching, burning and tingling;
- discharge;
- problematic urination;
- rashes on the genitals;
- neoplasms (papillomas and condylomas).
Inflammation of the urinary tract begins to be treated with medications that relieve inflammatory symptoms and restore the functionality of the urinary tract. The main medications for the genitourinary system are Papaverine and No-shpa. Doctors recommend using antibacterial agents after a course of antispasmodics. At the same time, they are treated with tablets that do not have nephrotoxicity.
For diseases of the genitourinary system, paracetamol is used. The daily dose is 4 times 650 mg.
When taking paracetamol, drink plenty of water to ensure normal hemodynamics. Instead of paracetamol, Ibuprofen is indicated.
The daily dose is 4 times 1200 mg. Other medications for symptom relief: Ketanov, Nimesulide, Cefekon and Baralgin.
The decision in therapy with nephrotoxic drugs is justified, and therapy is prescribed only after consulting a doctor.
What are the types of diseases of the genitourinary system?
The most common ailments of the genitourinary system among men are:
- urethritis . It is an inflammation of the urethra. As it progresses, the patient experiences redness, sticking and discharge from the urethra, frequent urges and painful urination;
- prostatitis _ Covers mainly men over 30 years of age. The disease is an inflammation of the prostate gland. With it, the patient feels spasms in the groin and perineum, the temperature rises, and chills appear.
The most common diseases in the female half are:
- pyelonephritis . The diagnosis is inflammation of the kidney cavity. With it, the following symptoms are observed: spasms in the sides and lumbar region, pain above the pubis, aggravated by urination, frequent urges, which are accompanied by small discharge, fever;
- cystitis . The disease is very common and causes inflammation of the bladder. During its course, cloudy urine, frequent urge to urinate with small discharge, accompanied by pain are observed;
- urethritis . It occurs in the same way as in men.
Diagnostic procedures and tests
It is easy to prevent diseases of the kidneys and urinary organs in humans; you need to take a general blood and urine test at least once a year. Harmful bacteria will initially be visible in the urine.
Diagnostics will help to identify or prevent infection and disease in advance. If there is a deterioration in health, a specialist should immediately examine the person.
Ultrasound and X-ray examination of the kidneys and bladder will also help to identify structural changes. This can be ultrasound, urography, cystography, nephroscintigraphy, cystoscopy and tomography.
Antibacterial drugs for a single dose
The good quality of such drugs is that they can be used once for treatment, and the disease will recede. These are new drugs in medicine, but have proven their effectiveness in getting rid of the disease. The advantages of these drugs are:
- speed of healing;
- virtual absence of side effects;
- low costs for their acquisition.
It is quite possible to get rid of bladder inflammation at one time by using antibiotics, but if the disease is not in a complicated stage. For one-time use the following drugs are used:
- Amoxicillin;
- Cefixime;
- Co-trimoxazole;
- Cefuroxime;
- Ceftibuten.
Depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease, the dosage is selected individually.
Treatment with folk remedies
Diagnostics allows you to identify the causative agent of the infection and select drugs to eliminate it. Taking antibiotics is mandatory.
Drugs for inflammation of the genitourinary system in women:
- antibiotics - to suppress the pathogen. These are Augmentin (Amoxicillin), Ceftriaxone, Monural;
- diuretics – Canephron;
- antispasmodics and analgesics to reduce pain No-shpa, Baralgin;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – Ibuprofen.
Attention: during treatment it is necessary to take blood and urine tests to determine the effectiveness of the drugs used and timely adjustment of methods.
For cystitis, which often develops in women, drugs from the penicillin group (Amosin), fluoroquinolones, and the tetracycline group are prescribed. The course of treatment is 5-10 days, depending on the amount of inflammation.
In severe cases, if paresis (partial muscle paralysis) of the bladder develops due to inflammation of the genitourinary system, antibiotics can be replaced during treatment with more effective ones.
For pyelonephritis, cephalosporins (Cephalexin), fluoroquinolones, and penicillins are prescribed.
Inflammation of the genital organs:
- For adnexitis, antibiotics from different groups are often combined, prescribed in pairs. Local antiseptics for baths and compresses.
- For salpingitis, the combined use of drugs (Gentamicin, Cefotaxime) is also used. Anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin E, anti-adhesive agents – Lidaza.
When treating inflammation of the genitourinary system in women, suppositories are often used - rectal and vaginal.
They are an additional means of local therapy. Suppositories reinforce the action of antibiotics and have the following effects:
- Antiviral and antimicrobial - act on infectious agents and prevent their spread.
- Anti-inflammatory – reduce the intensity of the process, relieve swelling and pain.
They are recommended to be used at night, but in severe cases, during bed rest, administration every 4 hours is possible. Using suppositories instead of taking oral medications reduces the load on the digestive tract.
Only a doctor can decide whether it is worth replacing tablets and injections with suppositories.
Medicinal herbs, as well as fruits, vegetables and berries, are widely used in folk medicine to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Watermelon rind is dried and added in small portions to drinks and decoctions to improve urine excretion.
- Pour a glass of boiling water over the decoction of birch leaves (4 tablespoons) or buds (2 tablespoons), leave for an hour, adding soda on the tip of a knife. Take 0.5 cups 3 times a day.
- Drink 0.5 cups of pumpkin juice 3 times a day.
The doctor may recommend taking pharmaceutical herbal teas that will help speed up recovery and reduce discomfort.
Contents: [hide]
- Features of each pathology
- Similar and distinctive signs of diseases
- Features of taking antibiotics
- Dosage of drugs
- Contraindications for use
- Possible side effects
- Effective antibiotics for inflammation of the genitourinary system
Antibiotics for pyelonephritis and cystitis are indispensable components for the successful treatment of these diseases of the kidneys and genitourinary system. These ailments are quite widespread, and according to statistics, representatives of the fair sex are most susceptible to them.
Such inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system are quite dangerous and, in the absence of timely and competent therapy, can cause numerous complications in the form of irreversible changes in internal organs and the development of various pathologies.
The clinical pictures and symptoms of these diseases are quite similar, so they are often confused with each other. How to distinguish between cystitis and pyelonephritis?
Cystitis is an inflammatory lesion of the bladder. The characteristic symptoms of this disease are the following:
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- Painful sensations when the muscles of the bladder are tense.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease that affects the renal calyces and pelvis. The following symptoms are typical for this kidney disease:
- Painful sensations in the lumbar region.
- Increased sweating.
- Significant increase in body temperature.
- Nausea.
- Attacks of vomiting.
- Increased fatigue.
- Insomnia.
- General weakening of the body.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Increased protein content in urine.
Treatment of the genitourinary system consists of mandatory use of antibiotics. The specialist always determines an individual approach, so you need to strictly adhere to the recommendations in order to avoid possible side effects.
For treatment, a complex technique can be used, for example, medications and herbs. It is necessary to follow a diet that excludes the consumption of irritating elements.
During treatment, it is important to maintain a drinking regime.
For inflammation of the urinary tract, antibiotics of the cephalosporin group are used - Cephalexin, Cefaclor, Cefepime, Ceftriaxone. For kidney inflammation, semi-synthetic penicillin is also used - Oxacillin and Amoxicillin.
But it is better for genitourinary infections to be treated with a fluoroquinolone - Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin and Gatifloxacin. The duration of antibiotic use for kidney diseases is up to 7 days.
For complex treatment, drugs with sulfenylamide are used - “Biseptol” or “Urosulfan”.
Broad-spectrum antibiotic for genitourinary infections
Urogenital infections are common among both men and women, as well as among adolescents. These pathologies require long-term observation by a urologist and constant monitoring of blood counts. In the long term, untreated infections can threaten life and provoke the development of chronic renal failure.
Prescribing antibiotics by a doctor for genitourinary infections is a necessary step; it is impossible to get rid of the disease in any other way. No methods of traditional therapy can neutralize microscopic bacteria that have settled in the urethra, kidneys, bladder and genital mucosa.
Only broad-spectrum antibiotics for genitourinary infections will help get rid of discomfort and return to work.
You should be wary and contact a urologist or nephrologist as soon as possible if you have the following symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back (can be present on only one side, or on both sides at the same time);
- high temperature and fever - in some cases the indicator can rise to forty degrees (in this case, you should not self-medicate, but call an ambulance as quickly as possible);
- chills - tremor of the hands can become so severe that the patient is unable to press buttons on the phone to call for help;
- the chronic course is accompanied by lethargy, asthenia, low performance, and lack of desire to do anything;
- the presence of blood and ichor in the urine;
- urethritis (infectious inflammation of the urethra) is accompanied by severe pain when urinating.
Therapy involves not only taking antibiotics for genitourinary infections, but also maintaining bed rest, as well as eating according to the principles of medical diet No. 7 for kidney diseases.
You should temporarily reduce your protein intake, as its metabolites put a strain on your already weak kidneys and bladder.
While the organs are fighting the infectious process, you should forget about harmful and heavy food and give preference to fermented milk products, boiled vegetables, and fresh fruits.
Bed rest is very important. The patient will have to take sick leave during antibiotic therapy for the treatment of genitourinary infections. You will have to forget about physical activity for a month or two.
And even with all the desire, most likely, you simply won’t have the strength to exercise: almost all patients during the period of exacerbation of genitourinary infections feel severe weakness. This condition most often lasts about ten days.
Then, provided that properly selected antibiotics are used for genitourinary infections, your health improves. The patient recovers after an average of three weeks: he can return to his work duties and becomes cheerful and cheerful.
Common causes of pathologies
With inflammation of the genitourinary system, the cause of the problem in most cases is staphylococcus or streptococcus. Less commonly, E. coli disrupts organ function.
In men, urogenital diseases most often appear after severe hypothermia, unprotected sex, regular alcohol abuse in parallel with malnutrition.
In women, urogenital infections are often associated either with a diagnosis of chronic pyelonephritis or with non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. Also, “fertile ground” for genitourinary infections is low immunity, autoimmune diseases, diabetes, vaginitis and often recurrent cystitis.
If a genitourinary infection has taken hold in one of the organs - for example, in the bladder - we can confidently say that very quickly (within a few days) it migrates through the ureters higher - to the kidneys. And this is already very dangerous for the patient’s life in general: very often the disease develops into chronic pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis.
And these ailments, in turn, sooner or later lead to the development of chronic renal failure. That is why it is very important to select a universal antibiotic for genitourinary infections in men and women as soon as possible, already at the first symptoms, and complete the full course of treatment.
If you do not do this, the disease will not go away on its own, but will only move to an increasingly more serious stage and affect more and more organs.
Rules for the use of antibiotics for genitourinary infections
There are several basic rules on how not to harm your general health when taking antibiotic drugs. Some patients are afraid of taking such strong drugs - these are groundless fears. Antibiotics for genitourinary infections are usually prescribed a new generation. If the rules of administration are followed, they do not pose a toxic threat to internal organs.
- In parallel with the course of antibiotic drugs, you should definitely take probiotics. This is necessary to prevent pathogenic intestinal microflora from multiplying. A broad-spectrum antibiotic for genitourinary infections destroys almost all pathogenic bacteria indiscriminately. As a result, healthy intestinal microflora suffers and diarrhea develops. This condition cannot be left without treatment: it will take a very long time to recover on its own. The drugs “Linex”, “Bifidumbacterin”, “Lactobalance” will come to the rescue.
- Women should use suppositories in parallel with a course of antibiotic drugs to prevent the development of thrush. During the period of exacerbation of genitourinary diseases, the immune system weakens greatly, and the candida virus (which is present in the body of almost every person) becomes more active. As a result, after a course of treatment, 80% of women suffer from vaginal candidiasis, or, as this disease is popularly called, thrush.
- For pathologies of the kidneys and bladder, you should temporarily limit the amount of protein in the diet. This is medical diet No. 7. It involves reducing the load on the kidneys. You can eat raw and boiled vegetables, porridge with water, lean turkey and chicken meat. Such a gentle diet helps reduce the load on kidney tissue, and recovery proceeds faster. But you should not starve or refuse food: this will not benefit the immune system. It’s just worth switching to diet food for a while.
List of broad-spectrum antibiotics in suspensions
Antibiotics in the form of a suspension are effective for genitourinary infections in men and women:
- “Amoxicillin.” Also available in tablet form. Can be used to treat children. It has been actively used in nephrology since Soviet years. The disadvantage of Amoxicillin is that some bacteria are resistant to its action. The drug is prescribed only after an analysis has been carried out and the bacteria that have caused the urinary tract pathology have been identified. If you treat it yourself, you may not get results.
- "Augmentin". For genitourinary infections in women, the antibiotic shows a good effect, as well as in the treatment of almost all genital infections. Produced in capsule and suspension form. Can be used to treat children and pregnant women (the dosage is discussed with the attending physician - self-medication is strictly prohibited). Before using Augmentin, the exact diagnosis must be known and general urine blood tests must be taken, which will help the nephrologist formulate the correct clinical picture.
- “Suprax” is an effective antibiotic for infections of the genitourinary system in women from the cephalosporin group. Refers to modern third generation antibiotic agents. Also suitable for therapy of ENT organs, upper and lower respiratory tract. It is also often used to treat children six months and older. If the disease is caused by staphylococcus, then Suprax may be ineffective.
- Cefixime is a fairly mild antibiotic drug. Effectively destroys the cellular structure of bacteria. Relief occurs after the first pill taken - the patient’s temperature drops, his mood improves, and he feels a surge of strength. However, do not delude yourself and abandon the treatment you have started: the full course of therapy is at least seven days. You cannot prescribe Cefixime yourself; it must be prescribed by a nephrologist or urologist after drawing up a clinical picture based on the patient’s tests. The doctor will select the appropriate dosage based on the patient’s weight and general health.
- Unidox Solutab. An effective tablet antibiotic for genitourinary infections in women. The product belongs to the latest generation tetracycline group. It is actively used in the treatment of colds, acute respiratory viral infections, intestinal infections, and urogenital pathologies. The main active ingredient is doxycycline. During pregnancy and lactation, as well as for the treatment of children, use is not recommended, but is possible after the approval of the attending physician.
- “Rulid” refers to fourth generation antibiotic drugs. It is actively used in medicine in the treatment of infectious pathologies of the urinary system and upper respiratory tract. “Rulid” has a rather narrow antibacterial effect. It is not recommended to use it yourself: you may simply not notice the result. Admission is possible only after identifying the name of the pathogenic bacteria due to the action of which the disease arose.
The injectable form of antibiotics for infections of the genitourinary system in women and men has proven to be safe in comparison with tablet preparations. When administered intramuscularly or intravenously, the drug enters almost immediately directly into the blood.
Tablets are almost always very aggressive towards the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach (which is why they are usually advised to be taken after meals). Injection administration does not have these disadvantages. Rarely anyone knows how to give themselves injections, so such products are used mainly only in hospital settings.
In addition, for self-administration of injections, the sterility of the room is very important.
- “Cefoperazone” belongs to the group of cephalosporins. the drug is produced only in the form of ampoules for injection, which should be administered once or twice a day, depending on the pathology. “Cefoperazone” is used for infectious inflammation in the respiratory, urinary tract, and for dermatological pathologies. It has proven its effectiveness as an antibiotic for infections of the genitourinary system in men and women. In some cases, use in the case of gynecological infectious inflammation is justified.
- “Lincomycin” is a universal antibiotic. For genitourinary infections, the latest generation can be used both intravenously and intramuscularly. It is often prescribed for the treatment of the development of infectious pathologies after abdominal operations. The exact dosage and frequency of administration is determined only by the attending physician.
List of modern broad-spectrum antibiotics in suppositories
Rectal and vaginal administration, to the same extent as injection, reduces the load on the organs of the digestive tract. Some patients are confused by this release form.
Meanwhile, antibiotics for genitourinary infections in children in the form of rectal suppositories are among the best. Depending on the chosen dosage, they can be used in children, adolescents and adults.
When treating urogenital infections in women, vaginal suppositories with antibiotic action can be used.
https://youtu.be/nsQemuoQrW8
If we talk about specific suppositories, it is worth noting such suppositories as:
- “Indomethacin” in the form of rectal suppositories;
- “Methyluracil” in the form of vaginal suppositories;
- “Terzhinan”;
- “Pimafucin”;
- Diclofenac suppositories - can be used both rectally and vaginally.
Antibiotic drugs for cystitis and kidney inflammation
Cystitis most often inevitably leads to pyelonephritis. And the reason lies in the fact that women, for one reason or another, put off visiting a doctor and try to be treated with folk remedies or homeopathy.
As a result, the infection rises through the ureters and chronic pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys and pelvis) develops. This is a very serious condition that after several years (and in some patients even faster) leads to the development of chronic renal failure.
And this disease is already fatal and requires either a donor kidney transplant or attending hemodialysis procedures for the rest of your life.
The most effective antibiotics for pyelonephritis and cystitis:
- “Cefotaxime”;
- “Amoxicillin”;
- “Lincomycin”;
- "Augmentin".
The patient cannot prescribe these antibiotics on his own, since if the type of bacteria that provoked pyelonephritis is outside the “action zone” of the drug, then the therapy will be in vain. Only after passing tests and drawing up a complete clinical picture of the disease is it permissible to prescribe treatment.
What antibiotic is the most effective for genitourinary infections?
There is no exact answer to this question, since depending on the general health and level of immunity of the patient, therapy will be different in each case.
for example, if a urinary tract infection also spreads to the genitals, complex treatment with several antibiotics will be required.
Such complex cases should be treated in a hospital setting, constantly undergo tests and monitor which antibiotic had the best effect on the clinical picture.
Based on the test results, an experienced urologist or nephrologist can accurately prescribe the most effective medicine with antibiotic action. In each specific case, the treatment regimen will be different.
Methods for preventing genitourinary infections
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. If you follow simple rules, you can prevent the development of genitourinary infectious diseases, and antibiotic therapy will not be needed.
- Do not sit on a cold floor, on concrete, do not allow the lumbar region and legs to become hypothermic. In rainy, cold weather, wear only high-quality, warm, waterproof shoes.
- Watch your diet. Avoid starvation and avoid strict diets. The quality of the immune system, and therefore its ability to resist various infections, depends on the quality and quantity of food taken. Once a quarter you should take a course of a high-quality vitamin and mineral complex.
- Do not swim in ponds with dirty water, do not stay in cold sea water for a long time. It should be noted that swimming in water in which other people are located often causes infection with various infectious diseases.
Source: https://fb.ru/article/407154/antibiotik-pri-mochepolovoy-infektsii-shirokogo-spektra-deystviya
Features of antibacterial therapy
The main goal of antibiotic treatment is to destroy certain pathogens identified during diagnosis.
After diagnostic studies such as polymerase chain reaction, bacteriological culture, DNA and antigens to the pathogenic bacterium are detected. During the examinations, the sensitivity of the pathogen to various antibacterial drugs is also recognized, which determines the course of treatment.
Antibiotic therapy makes sense for inflammatory processes characterized by urination disorders, purulent discharge, and redness of the genital mucous tissues. Their use helps relieve inflammation, pain and prevents further spread of infection to nearby organs and systems of the body.
A noticeable and fairly rapid result of antibacterial therapy depends on the early treatment of the patient, when the disease is at the initial stage.
Infections of the upper BMD include pyelonephritis, which comes in two forms - complicated and uncomplicated. With pyelonephritis, the kidneys, bladder, and urinary tract are affected.
Antibacterial therapy regimen for pyelonephritis:
- “Ampicillin”, “Amoxicillin” 600 mg three times a day for up to 10 days;
- "Solyutab" 1-2 tablets twice a day for 6-8 days;
- "Ciprofloxacin" 1 tablet 2-3 times a day. Complete recovery occurs after 7-10 days of taking the antibiotic;
- "Ofloxacin" 1-2 tablets twice a day. Course up to 10 days;
- Pefloxacin 400 mg 2 times a day for severe pyelonephritis;
- Levofloxacin 250 mg once a day – course 7-10 days. For severe forms, 500 mg 2 times a day for a week;
- Lomefloxacin 400 mg once for up to 9 days.
Antibacterial therapy for genitourinary tract infections can be carried out at home, provided that the disease is mild and the doctor has selected medications.
After treatment and rehabilitation therapy, the genitourinary system begins to function normally, and health improves. Antibiotics are the main link in the fight against diseases of the genitourinary system caused by a bacterial strain. They suppress unpleasant symptoms and destroy pathogens.
In order for the treatment to be effective and recovery to occur as quickly as possible, medications are selected as follows:
- The medicine must be excreted by the kidneys - this is necessary so that its concentration in the urine is high.
- The product must destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
- A particular drug should bring a positive result and at the same time cause a minimum of negative consequences.
Antibiotics are prescribed for diseases affecting the kidneys and urinary tract. They relieve inflammation and pain, preventing further spread of infection. Therapy with antibacterial agents is carried out for diseases such as cystitis, pyelonephritis, pyonephrosis and renal tuberculosis. The sooner treatment is carried out, the faster recovery will occur.
Antibiotics are an effective remedy against all pathologies affecting the kidneys and urinary system.
Price of antibiotics for cystitis
You can purchase medications for the treatment of cystitis in pharmacies by presenting a prescription. Average prices for popular antibiotics are shown in the table:
| Name | Country of origin, amount of active substance | price, rub. |
| Levofloxacin | Russia, 250 mg | 132 |
| Cephalexin | Serbia, 250 mg | 68 |
| Tsedex | Russia, 400 mg | 753 |
| Ofloxacin | Russia, 400 mg | 62 |
| Amoxicillin | Serbia, 500 mg | 105 |
| Ampicillin | Russia, 250 mg | 45 |
| Furagin | Latvia, 50 mg | 244 |
| Furadonin | Latvia, 100 mg | 164 |
| Monural | Italy, 3g | 501 |
| Roxithromycin | Russia, 150 mg | 125 |
| Sumamed | Israel, 500 mg | 500 |
| Trometamol | Russia, 1 g | 397 |
sovets.net
Infections of the urinary and genital tract are closely interrelated and are caused by the same type of infectious agents: bacteria, viruses, protozoa, fungi. There are both nonspecific inflammation activated by saprophytic or obligate flora (staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, fungi of the genus Candida albicans) when general or local immunity is weakened, and specific processes due to infection with bacteria such as mycoplasma, ureoplasma, gonococci, and spirochete pallidum. Also specific processes include chlamydia, when the culprit is a protozoan that has the properties of a bacterium and a virus at the same time. Viral lesions are represented by human papilloma virus and genital herpes. Lesions of the genital tract in women are represented by vulvitis, colpitis, cervicitis, endometritis, oophoritis. In men - balanitis and balanoposthitis, urethritis, prostatitis, orchitis and epididymitis. Urinary tract infections occur more easily in women due to the anatomical structure of the perineum. In men, urethritis is the most common, and lesions of the overlying sections (cystitis), as a rule, are secondary and occur against the background of disturbances in urine flow (anatomical abnormalities, prostate adenoma, urolithiasis). The main symptoms of this group of diseases are pain when urinating, burning and itching in the genital area, which intensifies during sexual activity. Also, pathological discharge from the genital tract (purulent, mixed with blood in a bacterial process, curdled in fungal infections, mucous in a viral infection) and changes in urine: darkening, turbidity and impurities of protein and (or) blood. Diagnosis of infections is carried out on the basis of bacteriological research methods (culture of scrapings on nutrient media) and serological blood tests (determining the titers of specific antibodies of classes M and G, which give an idea of the acute or chronic process). Of course, treatment can begin only after diagnosis and verification of the pathogen. Otherwise, the acute process quickly becomes chronic and can lead to severe complications and a long-term course.
Drugs for the treatment of genital and urinary tract infections.
I. Antibiotics. 1. Medicines are bactericidal as a result of disruption of the synthesis of microbial wall proteins. A. Semi-synthetic drugs: oxacillin, amoxicillin (flemoxin), ampicillin, ticarcillin, carbenicillin. B. Inhibitor-protected drugs: amoxicillin clavulonate (flemoclav, panclave, augmentin, amoxiclav), ampicillin sulbactam (unasin, sultamicillin, ampiside), B. Combined (ampiox). 2. – lactam-free with a bactericidal effect. 1st generation: cefazolin, cephalexin; 2nd generation: cefaclor, cefuroxime; 3rd generation: ceftriaxone, cefixime, cefazidime, cefoperazone, ceftibuten, cefotaxime; 4th generation: cefepime. 3. . Due to disruption of microbial DNA synthesis, they are bactericidal. Ofloxacin (zanocin, qirol, glaufos,), lomefloxacin (lomacin, xenaquin, lomeflox), norfloxacin (quinolox, loxon, negaflox), ciprofloxacin (ificipro, quintor, zindolin,), lefloxacin, gatifloxacin, sparfloxacin (sparflo), moxifloxacin, levoflox qing . 4. . Clarithromycin, azithromycin (azitral, sumamed. chemomycin), josamycin. 5. 1st generation: streptomycin, kanamycin, neomycin; 2nd generation: sisomycin, netilmicin, tobramycin, gentamicin; 3rd generation: amikacin. 6. Tetracycline, oxytetracycline, chlortetracycline. The choice of antibiotic looks something like this. Chlamydial infections are predominantly macrolides and fluoroquinolones. Mycoplasma – tetracyclines. Gonococci – azithromycin, cephalosporins, penicillins (piprax), fluorochlorine (norilet, raksar), aminoglycosides (netromycin). Ureoplasma is sensitive to doxycycline or azithromycin.
II. Nitrofurans disrupt oxidation processes in microbial cells. Used to treat urinary tract infections. They can be both bacteriostatic and bactericidal. Nitrofurantoin (nifurtoinol, furadonin), furazidin (furomax, furomag),
III. Antiviral drugs. 1. A. Antiherpetic. Acyclovir (Zovirax), valacyclovir (Valtrex), penciclovir (famciclovir, famvir). B. Ion channel inhibitors (orvirem). B. Specific chaperone GA. (arbidol). D. Neuraminidase inhibitors (peramivir, Repenza, Tamiflu) D. NP protein inhibitors (ingavirin). 2. Alpha and gamma interferons block the translation of viral RNAs and the presentation of viral antigens. Viferon, interferon, gripferon, kipferon. 3. trigger the synthesis of their own interferon. Amiksin, cycloferon, kagocel.
IV. Antifungal drugs. 1. Fungistatic effect. A. Imidazoles. Ketoconazole (oronazole, nizoral). B. Triazoles. Irunin, diflucan, fluconazole, flucostat, itraconazole (orungal), mycosist. 2. Antifungal antibiotics. Amphotericin B, pimafucin (natamycin), levorin, nystatin.
V. Antiprotozoal. Metronidazole. Effective for trichomoniasis.
VI. Antiseptics used to prevent sexually transmitted infections. 1. Based on iodine - betadine in suppositories or solution. 2. Based on chlorine-containing preparations: chlorhexidine in solution, Miramistin (solution, suppositories, gel). 3. Based on gibitan - Hexicon solution and suppositories.
The main forms of release of drugs for the treatment of genitourinary infections are tablets and injection solutions. Except in cases of fungal infections of the external genitalia, external treatment is not very effective and systemic medication is required. Violation of treatment regimens, inadequate dosages or attempts at local treatment of urinary and genital tract infections contribute to the chronicity of inflammatory processes. Self-medication for sexually transmitted infections and urinary tract infections is not acceptable. Treatment should be carried out as prescribed by a doctor and monitored by laboratory tests.
instructions-from-tablets.rf
Herbal preparations
| Name | Country of origin, amount of active substance | price, rub. |
| Levofloxacin | Russia, 250 mg | 132 |
| Cephalexin | Serbia, 250 mg | 68 |
| Tsedex | Russia, 400 mg | 753 |
| Ofloxacin | Russia, 400 mg | 62 |
| Amoxicillin | Serbia, 500 mg | 105 |
| Ampicillin | Russia, 250 mg | 45 |
| Furagin | Latvia, 50 mg | 244 |
| Furadonin | Latvia, 100 mg | 164 |
| Monural | Italy, 3g | 501 |
| Roxithromycin | Russia, 150 mg | 125 |
| Sumamed | Israel, 500 mg | 500 |
| Trometamol | Russia, 1 g | 397 |
sovets.net
There is no universal cure for kidney disease. In each specific case, the treatment regimen is determined based on the results of tests and a comprehensive examination. It is important to make a correct diagnosis, only after that a specialist prescribes medications. Among the most popular means are:
- Classic antibiotics - Azithromycin, Furadonin, Furagin, Palin.
- Antibiotics used in hospital. First of all, these are amioglycosides. They have a powerful antibacterial effect, but some have many contraindications. Most often, patients are prescribed Amikacin.
- Herbal decoctions and tinctures are used to prevent possible exacerbations.
- Vitamins and immunomodulators - complement and enhance the effect of other medications.
Treatment for men and women is almost the same. The only exception is diseases occurring during pregnancy and lactation. In this case, Amoxicillin and herbal medicine are prescribed. Phytolysin and Canephron are effective for cystitis. In severe cases of genitourinary infections in women, the antibiotics Levofloxacin and Ofloxacin may be prescribed.
Traditional medicine recipes help eliminate unpleasant symptoms and make you feel better. They are indicated for chronic diseases and for the prevention of possible relapses. Such products are available in the form of tablets or drops. But you can use them only on the recommendation of a doctor. The following herbs are widely used:
- Cranberry juice will help relieve inflammation of the genitourinary system. It acts as a diuretic and prevents bacterial growth.
- Unrefined coconut oil is used to kill urinary tract infections. Use 2 tablespoons of oil. in a day. Coconut milk contains good medicinal substances; you should drink it on an empty stomach in the morning and a glass before bedtime.
- Asparagus relieves inflammation of the urinary tract. When eating asparagus, the color of the urine darkens, which should not be alarming.
- Garlic is good for kidney diseases. Peel 2 cloves of garlic, crush and add 1 glass of water, leave for 5 minutes and drink. The procedure is repeated 3 times a day until the symptoms disappear.
- Onion is an antibacterial and diuretic, promotes rapid recovery of the kidneys and urinary tract. The onion is cut into 4 equal parts, 0.5 liters of water are added and boiled for 20 minutes over low heat, left for 8 hours, filtered and drunk.
- Inflammation of the urinary tract is treated with celery. Beat the stems, add pineapple and 200 ml of chamomile infusion. The mixture is drunk in the morning on an empty stomach. Celery seed is also used. The seed is steamed in 1 cup of hot water, left for 10 minutes and drunk 2 times a day.
- A good infusion of basil. Add 2 tbsp to 1 glass of water. plants, leave for 10 minutes. Drink for 2 days, 2 times a day.
Treatment of ureaplasma in women: groups of drugs, their action and rules of use
Ureaplasmosis is an inflammatory disease in the organs of the genitourinary system. A woman becomes infected during sexual intercourse, and the disease is transmitted when the newborn passes through the birth canal.
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day...
Read more "
Ureaplasmosis will not go away on its own.
Basics of therapy
Treatment for women is carried out according to a scheme that complies with the standards of the International Classification of Diseases:
- antibiotics;
- antimicrobial agents;
- suppositories;
- restoration of microflora;
- means for correcting immunity.
Treatment for ureaplasmosis is prescribed not only to the infected woman, but also to her partner.
Antibiotics for infection
It is impossible to do without antibacterial drugs in the treatment of inflammatory pathology. Before prescribing a medication of this group to a patient, a drug sensitivity test is performed.
How to treat pathology?
Treatment of ureaplasmosis in women is carried out using three groups of antibiotics:
- macrolides;
- tetracyclines;
- fluoroquinolones.
These drugs are selected based on the course of the disease. When the inflammatory process is sluggish, one antibacterial drug is prescribed. In severe cases of the disease, 2 types of medication are prescribed.
Table. Treatment of ureaplasma in women: drugs and regimen:
| Group | Name of the medication | Frequency (number of times per day) | Dose per day | Duration of therapy | Peculiarities |
| Macrolides | Vilprafen You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of regular... Parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach... | 3 | 1.5 g | 5 days | They accumulate inside cells, the optimal concentration of medications is maintained for 3 days. |
| Azithromycin | 1 time 1.5 hours before breakfast | 1000 mg | 5 days | ||
| Day 11 | |||||
| Day 16 | |||||
| Clarithromycin | 1–2 | 200–900 mg | 5–15 days | ||
| Josamycin | used similarly to Vilprafen | ||||
| Macropen | 1–2 | 1.5 g | 7 days | ||
| Tetracyclines | Doxycycline | 1, after eating | 200 mg | 2 weeks | Medicines of this group are prescribed together with drugs of another group. |
| Unidox | 2 | 200 mg | 1 day | ||
| 1 | 100 mg | 6 days | |||
| Fluoroquinolones | Avelox | 1 | 400 mg | 3 weeks | They do not accumulate and are not stored in cells. Take the medications for at least 21 days, first the main medicine, then its analogue. |
| Ofloxacin | 2 | 800 mg | |||
| Moxifloxacin | 1 | 400 mg | 2 weeks | ||
| Tsiprolet | 1 | 250 mg | 5 days | ||
| 1 | 500 mg | 10 days | in case of chronic course | ||
Antibacterial drugs negatively affect the functioning of the digestive system and liver. Therefore, on the 5th day after taking medications, they begin to use probiotics and hepatoprotectors.
Probiotics include the following:
- Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin dry, Colibacterin dry, Biobakton dry, Narine and Primadophilus capsules.
- Flonivin BS, Baktisubtil, Sporobacterin, Bactisporin, Enterol.
- Linux.
- Bifiliz, Linex, Bifiform, Atsipol, Atsilakt.
Hepatoprotectors restore liver function. Fosphonciale, Essliver Forte, Gepagard, Phosphogliv, Rezalut, Sirepar, Hepatamin, Hepatosan, Heptor are usually prescribed.
Vaginal and rectal suppositories
Antibacterial therapy is not always sufficient to cure inflammatory pathology. Ureaplasmosis in women should be treated with vaginal and rectal suppositories.
Suppositories are included in the treatment regimen for severe inflammatory processes, as well as if other harmful microorganisms have joined the main pathology.
For ureaplasmosis, two types of suppositories are prescribed:
- antiseptic and antibacterial;
- immunomodulatory.
Antiseptic and antibacterial suppositories for ureaplasma in women are used for 10 days. The drugs are administered 2 times a day, after hygiene procedures and an enema.
Suppositories do not replace antibacterial medications; they should be used in combination with these drugs.
Antiseptic and antibacterial suppositories include the following medications:
- Chlorhexidine is an antiseptic. With regular use, the number of dangerous bacteria decreases.
- Hexicon-D restores damaged vaginal microflora, kills chlamydia, ureaplasma and herpes virus.
- Betadine gets rid of many harmful microorganisms. The medicine should not be used by children under 12 years of age or by pregnant women. The drug should not be used for more than 12 days, since Betadine provokes renal dysfunction, hyperthyroidism, and anaphylactic shock.
- Klion-D has an antifungal effect. Vaginal tablets are prescribed for other infections. They must be moistened with water and placed in the vagina overnight.
- Polyjanx is used to prevent relapse after treatment for ureaplasma. Can be used in the 1st trimester of pregnancy; further use is discussed with your doctor. It is not recommended to buy Polizhansk suppositories when breastfeeding.
| Ureaplasma in children: causes, treatment of ureaplasmosis, diagnosis, complications |
| Treatment of ureaplasma in men - drugs: application regimen |
| Antibiotics for ureaplasma: types and use, cost |
| Ureaplasma during pregnancy: symptoms and consequences, treatment |
In the presence of ureaplasma parvum, the use of immunomodulating suppositories is mandatory. Antibiotics cause severe damage to the immune system and microflora; these suppositories restore the vaginal microflora, prevent re-infection and reduce the negative effects of other drugs.
The most effective are:
- Genferon;
- Hexicon;
- Viferon.
The duration of treatment is 5 days.
Immunomodulators should not be used during lactation or for autoimmune diseases.
Methods of therapy in pregnant women
Ureaplasma parvum in pregnant women is treated with other drugs. Therapeutic measures should be taken immediately after the patient has learned the diagnosis.
Ureaplasmosis in pregnant women is treated with antibiotics, agents for restoring intestinal microflora, suppositories, and a vitamin complex.
Lack of timely treatment leads to termination of pregnancy, premature birth, infection of the amniotic membranes and the unborn child.
Table. Treatment regimen for the disease in women in the following position:
| Type of medication | Name of drugs | Dosage, frequency of use | Side effects |
| Antibiotics | Vilprafen, Josamycin. | 1–2 g of the drug is divided into three doses, duration is 10 days. | Lack of appetite, heartburn, vomiting, flatulence, cramps, swelling of the feet, candidiasis, rash, fever. |
| Suppositories | Viferon | Allowed for use from 14 weeks of pregnancy. Application regimen: 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day for 10 days. | Allergic reaction. |
| Probiotics | Linex, Lactovit. | Linex take 2 capsules 3 times a day. Lactovit is consumed 2-4 tablets per day. The duration of treatment is 4–6 weeks. | Itching, rash. |
| Vitamins | Antioxidant complex (vitamins E and C). | Vitamin E is prescribed 100 mg 1-2 times a day. Vitamin C is taken 70 mg. | No. |
Mineral complexes are also prescribed. Vitamins and minerals restore the pregnant woman’s immunity and strengthen the body.
Some pregnant women require sanitation of the genital tract. This procedure is necessary to protect the child from infection as the baby passes through the mother’s genital tract.
Means for correcting immunity
Immunomodulators should be taken with caution and only as prescribed by your doctor. Despite the fact that medications increase the defenses of the female body, they should not be abused.
Pharmaceutical factories produce many immunomodulators. Doctors often prescribe the use of the drug Ureaplasma Immun. The medication was developed specifically against ureaplasma parvum.
Method of use of the drug:
- administered intramuscularly 3 ml 1 time every 3 days;
- Duration of therapy - 7 injections.
The drug is contraindicated for intravenous administration. Ureaplasma Immun is prohibited for patients with severe allergic reactions to protein medications in human blood.
No side effects were found after using the drug. Hyperthermia is possible at the injection site and an increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees during the first day after use.
The use of the drug Immunomax or Cycloferon is also prescribed. Medicines are administered intramuscularly according to the following scheme: 1, 2, 3, 8, 9, and 10 days of the main therapy for ureaplasmosis.
Preventive measures
To avoid relapse of the disease, precautions must be taken. Knowledge about prevention will help with this.
Compliance with the following recommendations will help prevent the development of ureaplasmosis in women:
- exclude accidental contacts;
- always use a condom if your partner is not permanent;
- take medications for prevention after consulting your doctor;
- after oral-genital sexual intercourse, the oral mucosa should be treated with an antiseptic;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- undergoing an annual examination by a gynecologist.
Ureaplasma is a disease that begins to develop after treatment of another pathology with antibacterial agents. When using these medications, be sure to take immunostimulants so that your immune system is not damaged.
Patients with this diagnosis will have to learn to cope with stress, eat right, avoid hypothermia, and treat other diseases in a timely manner.
Before pregnancy, a woman should be checked for ureaplasmosis. If bacteria are found in too large quantities, it means that you will first need to undergo treatment, and then you can think about conceiving a baby.
https://youtu.be/esz3hqQOxD4
The media and information boards in hospitals warn us about a host of dangerous sexually transmitted diseases. Any adult woman should know how you can notice your ill health, what to do in case of illness and what its consequences may be. Let's talk about the most common sexually transmitted disease of the 21st century - chlamydia.
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia (chlamydial infection) is a group of infections caused by the activity of bacteria of the genus Chlamydia. Chlamydia is an intracellular parasite that is transmitted from person to person in various ways. Chlamydia exists in several forms, depending on the type of bacteria and the affected part of the body, and in addition to sexually transmitted diseases, it causes trachoma and conjunctivitis (inflammation of the lining of the eye). This article will focus on the urogenital (genitourinary) form, most often observed in women.
You can become infected with genitourinary chlamydia through sexual intercourse (anal, vaginal, less commonly, oral). Previously, it was believed that chlamydia was also transmitted through underwear, toilet seats and common things, but such cases are possible only with reduced immunity (HIV), since a sufficient amount of chlamydia must enter the body to initiate an infection. In addition, bacteria are not adapted to survive outside the human body. Chlamydia is transmitted sexually even more often than gonorrhea (the incidence of the disease is 1 in 4 people), and women are more susceptible to this pathogen than men. Chlamydia can also be transmitted from mother to child, causing serious damage to the latter's internal organs.
Chlamydia is a direct threat to women’s health, the health of the patient’s sexual partner and her unborn child, so it is necessary to detect the disease and engage in timely treatment to avoid dangerous complications.
Why is chlamydia dangerous in women?
If a woman becomes infected with chlamydia, the bacteria begin to actively parasitize the epithelial cells of the genitourinary organs. Through their vital activity, chlamydia damages internal organs, causing damage to the vagina, cervix, uterus and appendages. Often because of this, a woman develops infertility or spontaneous abortions occur. Due to chlamydial infection, a woman may develop concomitant diseases: trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis and bacterial vaginosis.
The most common consequences of advanced chlamydia are:
- cervical erosion (cervicitis);
- inflammation of the vaginal mucosa (colpitis);
- inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis).
Cervicitis
With cervicitis, detachment and inflammation of the epithelium occurs and the cervix turns into an extremely vulnerable part of the female genitourinary system. Bleeding, burning, itching appears, or the disease is asymptomatic. The danger of cervical erosion is that if left untreated for a long time, tumors often form on the cervix, which can later become cancerous.
Erosion occurs not only due to chlamydia, so there is also an inverse relationship: if a woman has cervical erosion, the risk of becoming infected with chlamydia (and any other) infection increases sharply. Cervicitis is especially dangerous for nulliparous young women, as this disease causes complications during childbirth.
Colpitis
This is an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa or the vaginal part of the cervix. Symptoms also include vaginal discharge, burning, and itching. Without timely treatment, inflammation can spread to other organs of the genitourinary system: the cervix, the uterus itself and the appendages are especially vulnerable. The development of the disease leads to infertility and the risk of developing concomitant infections.
Salpingitis
The most common and at the same time serious complication of chlamydial infection is inflammation of the fallopian tubes. Inflammation can also spread to the cervix, causing erosion. Women are worried about pain in the lower abdomen, high temperature, and this is a direct threat to health. As a result of untimely detection and lack of treatment of this disease, infertility may develop as a result of adhesions of the fallopian tubes.
Ureaplasmosis
This is another infection that can develop against the background of chlamydia. It is caused by ureaplasma bacteria, which can normally be present in the body without causing ureaplasmosis. Urogenital infection ureaplasmosis can occur due to damage to the epithelium by chlamydia. In this case, in women it causes inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, urolithiasis, miscarriage or infertility. It is almost impossible to become infected with ureaplasmosis through everyday contact, but do not forget that about half of women are carriers of ureaplasma. Ureaplasmosis can also be dangerous for the sexual partner of an ill woman.
How to identify chlamydia in women?
Often, chlamydia occurs in the complete absence of symptoms; a woman simply has no tangible reasons to worry about her own health, which poses a danger to herself and her sexual partner, since without timely diagnosis and treatment, the infection can go from acute to chronic, and then into neglected To identify this disease in time, a woman needs to go to an appointment with a gynecologist in cases where:
- there is a feeling of discomfort in the vaginal area; vaginal discharge has appeared;
- periodically there is pain or pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, which intensify before menstruation;
- intermenstrual bleeding appears;
- there is pain or burning during urination;
- there is general malaise and fever (sometimes significant) for no obvious reason.
In addition, even if there are no unpleasant sensations, if you have an active sexual life with several partners, you should regularly take special tests for chlamydial infection to identify its chronic (asymptomatic) form. This is a concern for both the woman’s health and the health of those who are intimate with her.
Sexual life with chlamydia
When chlamydia is detected in sexually active women, the question arises about the health of their sexual partners. If you are diagnosed with chlamydia, convince your partner to get tested for this infection: tell about the consequences, show a photo with characteristic complications. If chlamydia is found in your partner, do not hesitate to get tested yourself, even if you are sure that you do not have chlamydia and do not have any symptoms characteristic of it. So, if you or your partner has chlamydia, take these steps:
- Stop sexual intercourse or use a condom for the duration of treatment;
- stop drinking alcohol and dairy products;
- carry out tests to detect chlamydia in all sexual partners of the carrier of the infection.
As mentioned earlier, chlamydia is not only transmitted through sexual contact, so get tested for HIV infection. If a guy is nevertheless diagnosed with a chlamydial infection, then he faces the same serious complications as a girl (especially if he is a carrier of other infections, such as ureaplasmosis). All partners need to undergo treatment at the same time, otherwise the risk of re-infection is inevitable.
In conclusion, let us recall the general rules of behavior that reduce the risk of sexually transmitted diseases to nothing: a limited number of trusted partners, trust, accuracy in contraception, cleanliness and marital fidelity.
- Bactefort
- Roundworms
- Other parasites
- Other parasites (bacteria)
- Giardia
- Opisthorchiasis
- Pinworms
- Parasites in animals
- Preparations for parasites
- Miscellaneous
- Trichomoniasis
- Chlamydia
- Tapeworm
Contraindications
Antibiotics for cystitis in women should be used after studying the clinical picture of the disease, conducting diagnostic studies and decoding tests for the susceptibility of the pathogen to the effects of a certain group of substances. Self-medication with antibiotic therapy is unacceptable. Most antibiotics for women have the following contraindications:
- severe liver dysfunction;
- kidney inflammation;
- pregnancy;
- the presence of allergic reactions;
- problems with the functioning of the heart muscle.
Prevention
Tips for the prevention and treatment of cystitis are as follows. You can’t get too cold or swim in cold water. If there is a desire to harden the body, then these procedures should be carried out with caution, starting with rubbing the body. When treating cystitis, you need to drink plenty of fluids (at least 2 liters of water), this helps to quickly remove the infection. It is recommended to drink slightly alkaline mineral waters (without gas), fruit drinks with cranberries or lingonberries, and dried fruit uzvars. When taking antibiotics, we must not forget about drugs that support microflora in order to avoid dysbacteriosis.
During treatment of acute or acute chronic forms of cystitis, rest and bed rest are needed, this helps reduce symptoms. You should avoid spicy, salty, spicy, fried and smoked foods. Do not drink strong tea, coffee, or alcoholic drinks.
It is recommended to give preference to a therapeutic diet containing a large amount of potassium, which can increase urination. The diet should consist of fermented milk products, fruits, vegetables, cereals, vegetable oil, fish and steamed meat with a low salt content and a complete rejection of marinades and seasonings.
For the prevention and treatment of cystitis in women, antibiotics alone are not enough. Recovery depends on what methods of therapy are used; an integrated approach to the disease is encouraged.
Consequences and possible complications
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner and poor quality treatment can lead to dangerous diseases. Women often refuse to take antibiotics for inflammation of the genitourinary system, hoping to get by with folk remedies.
However, these funds are not enough to destroy the pathogen. As a result, you may develop:
- renal failure;
- endomyometritis, panmetritis;
- infertility.
An untreated disease will certainly return again and may become chronic. After treatment with antibiotics, it is necessary to restore the vaginal microflora.
Neglecting recommendations leads to very big consequences. As a result, the condition worsens and chronic diseases occur, and if the disease is sexually transmitted, then in very severe forms, death is possible. Complications due to the disease manifest themselves as kidney failure and infertility. If this is an infectious disease, then the danger lies in further infection of partners.
Means for prevention
The prescribed treatment must be completed. Many women stop taking medications immediately after relief occurs, not wanting to overload the body with unnecessary chemicals.
However, you should know that the timing and dosage of the drugs are designed to completely extinguish the inflammatory process. Early refusal of treatment is fraught with the return of the disease.
In addition, women need to remember that after treatment for inflammation of the genitourinary system, extreme caution must be exercised. Prevention measures:
- Dress according to the season - overheating is also not good for the body. You should especially be wary of hypothermia. You need to wear warm boots, trousers, tights, preventing freezing.
- It is better to choose linen from natural fabrics. When wearing short skirts, it is better to choose closed panties rather than thongs. It is easy to catch an infection in public transport, a park, or a university. In addition, narrow strips injure the mucous membranes, opening the path to infection.
- When wearing pads, you should follow the rules for changing them. No matter how much manufacturers guarantee their antibacterial properties and convince them that they “breathe,” microbes multiply very quickly in them.
- Cleanliness is the key to health. It is necessary to observe hygiene requirements and wash regularly. Do not use other people's towels, washcloths, or clothes.
A good way of prevention is walking, exercising without fanaticism, light sports, and an active lifestyle. The overall tone of the body promotes good blood circulation, improved metabolic processes and resistance against infection. Then you won’t have to deal with inflammation of the genitourinary system and take antibiotics.
Prevention of diseases of the urinary system is that you need to monitor proper nutrition, lead an active lifestyle, and avoid hypothermia. From time to time you need to use diets in order to reduce the load on your organs.
Herbal teas will be useful for treatment and prevention. It is important not to forget about vitamins.
And most importantly, maintain personal hygiene and have order in your sex life.
Diet as a disease prevention
Diet is also disease prevention. It is important to exclude foods that contain purines and oxalic acid.
Also limit your salt intake. Make it a habit to drink water on an empty stomach in the morning; only after this small procedure can you eat.
Eat small meals 5-6 times a day. Usually, for diseases of the genitourinary system, diets No. 6 and 7 are used.
The main objectives of diet No. 6 are to reduce the amount of uric acid and salts formed in the body. You need to consume more liquid, vegetables and fruits, as well as dairy products.
And diet No. 7 is aimed at removing metabolic products from the body, combating swelling and unstable blood pressure. Here, on the contrary, liquid intake is limited, and cereals and salts, mainly plant foods, are excluded.