Oncocytological smear is used as a screening method for assessing the reproductive system. Unlike flora analysis, which evaluates the composition of the biocenosis of the vagina and cervical canal, cytology shows changes at the cellular level, the presence or absence of atypical elements. Interpretation of the results of oncocytology of the cervix allows one to determine the degree of damage to the integumentary epithelium in various pathological processes. However, patients are often interested in what exactly this or that abbreviation means in the decoding.
Indications for cytological examination
The main goal of implementing cervical cytology analysis is the early detection of cancer. Timely detection of atypical cells in the biomaterial is necessary to be able to block the cancer process. Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancer pathologies among women. Its danger lies in its asymptomatic course, which is why regular preventive examinations and studies are so important.
Pap smear analysis of the cervical canal is an accurate and quick way to obtain reliable data on the presence or absence of atypical cells with precancerous or cancerous changes. In addition, the technique allows us to identify some underlying diseases, the etiology of which is not tumor.
Cytological examination of cervical smears is the standard for detection and follow-up of the following pathological conditions:
- presence of pathogenic microflora;
- disturbances in the menstrual cycle (duration, intensity);
- viral diseases (genital herpes, infection by the human papillomavirus - HPV);
- infertility (impossibility of conception);
- erosive changes in the cervical epithelium;
- pathological vaginal discharge.
A cytology smear is also necessary as a screening test in the following cases:
- Pregnancy planning.
- Several births in a row.
- Early age of a woman during her first birth.
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
- Postmenopause.
- Planning for placement of an intrauterine device.
- Visible changes of a pathological nature when examining the cervix in the mirrors.
- Family history (cases of cervical cancer and other cancer pathologies among relatives).
- Long-term hormone therapy.
- The previous cytology study was carried out for a long time.
Ultrasound of the cervix: methods and procedures during pregnancy
Papanicolaou smear with acceptable staining.
Cytological examination of cervical smears is recommended annually for preventive purposes, and if any pathological abnormalities are detected, at least twice a year to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
When and how often should I have a smear for oncocytology?
Starting from the age of 18, every girl must undergo this type of diagnosis once every year. The frequency of analysis increases for women who are at risk:
- age exceeds 35 years;
- abuse of tobacco smoking, psychotropic drugs and alcohol;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- girls who had sexual intercourse very early;
- frequent change of partner;
- positive HIV and HPV status;
- STD;
- when identifying erosion or endometriosis;
- often recurrent inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- often recurrent genital herpes or cytomegalovirus infection;
- identification of oncological episodes in the pedigree;
- if the menstrual cycle fails.
Oncocytology for pregnant women
During pregnancy, the frequency of analysis can increase up to three times. This fact is due to the need for early detection of pathological processes that may threaten the mother and child.
Important: the procedure is performed only if the pregnancy is normal and the patient is in complete health.
If pathological conditions are detected, the study is postponed until complete recovery.
If the biomaterial collection technique is implemented correctly, the procedure does not harm the woman, is painless and does not affect the course of pregnancy.
Oncocytology for older women
It is a mistake to believe that during postmenopause women have a reduced risk of developing gynecological diseases. Oncology affects people at any age. Moreover, against the background of concomitant diseases, the risk of pathologies of the internal genital organs increases. That is why women over 55 years of age are recommended to undergo this test at least twice a year.
The procedure for collecting material for research and the algorithm for conducting the research itself is similar to that for young girls. This does not cause any discomfort or pain to elderly patients. Timely diagnosis of any pathological condition will allow treatment to begin as early as possible, achieving the most favorable outcomes, including complete recovery.
Preparation for the biomaterial collection procedure
In order for the result of cervical cytology to be reliable, it is necessary to take into account the rules of preparation for collecting biomaterial. They are as follows:
- Elimination of hygiene procedures in the form of douching (sanitation).
- Abstain from sexual activity for three days before the procedure.
- Temporary refusal to use tampons, vaginal suppositories, tablets, creams and gels.
- Refrain from urinating two hours before taking the material.
In addition, you need to know about the following nuances:
- obtaining a smear from the cervical canal is possible only outside of menstrual bleeding, the optimal period is 10-12 days of the cycle;
- smear cytology will not be reliable in the acute phase of an infectious disease, so it is carried out after a course of therapy;
- intravaginal administration of any kind of medication should be stopped in consultation with the attending physician no less than five days before the procedure for collecting the material.
Additional conditions and rules that the patient must take into account must be clarified with the gynecologist.
How to take a smear
When performing a smear for cytology, the immediate object of attention of the gynecologist is the cervical canal - the mucous part of the internal reproductive organs that connects the uterine cavity and vagina.
The length of the cervical canal is, on average, 3-4 centimeters, while the canal is conditionally divided into 3 zones:
- external os or ectocervix - extends into the vagina and is covered with squamous epithelial cells;
- internal pharynx or endocervix - located on the side of the uterus, covered with glandular epithelium;
- transitional, inner part of the channel.
There are two ways to carry out the procedure:
1. Standard smear for cytology. Using special instruments (Eyre spatula, Volkmann spoon), the gynecologist takes smears from the vagina, external os of the cervix and directly inside the cervical canal. For this, a special cervical brush is used, which does not injure the narrow canal and does not cause any discomfort during the procedure.
The biological material is placed on sterile glass, fixed with a special solution and dried, after which it is sent to the laboratory.
2. Method of liquid cytology (LBC, Liquid Based Cytology). A more modern and accurate way to study the mucous membrane of the cervical canal.
To obtain biological material, the gynecologist uses several types of brushes (endocervical, Wallach brush), after which the tips are removed from the used instruments. Next, the brushes are placed in a bottle (vial) with a special liquid for preserving biological material.
The bottle is labeled and sent to the laboratory. The liquid cytology method allows you to obtain more accurate results and the ability to conduct additional examinations of the epithelium if necessary.
Material collection technique
Schematic representation of the collection of biomaterial for a smear
To obtain material that will be subjected to cytological examination, the doctor makes a scraping from the exocervix - the outer part of the cervix - and from the mucous lining of the vagina using an Eyre spatula. To obtain a scraping and subsequent examination of a smear from the cervical canal, a special probe is used - endobrush. Its use makes it possible to obtain biomaterial in quantities sufficient for analysis.
A gynecologist’s set of tools for obtaining material may include:
- Air spatula;
- spirette - an instrument for aspiration of material from the endocervix;
- endobrush;
- tweezers;
- gynecological speculum;
- Volkmann spoon.
The sequence of actions during the procedure includes:
- Gynecological examination of the cervix in the speculum. At the same time, the vaginal walls are expanded and scraping is performed, which can cause a feeling of slight discomfort.
- At the same time, material is collected for microflora analysis.
- The resulting samples of biomaterial are applied to glass and fixed, then labeled and sent for analysis to the laboratory.
Cervicometry during pregnancy: features of its implementation
The procedure for obtaining biomaterial takes no more than 15 minutes.
Analysis for oncocytology of the cervix
The procedure for taking a smear for oncocytology is completely painless and does not cause any discomfort. This is a standard procedure when visiting a gynecologist. The algorithm for taking a smear for oncocytology consists of the following steps:
- insertion of a speculum into the vagina;
- collecting biomaterial (smear; scraping) with a special spatula or cytobrush;
- additional collection of cell samples from the cervical canal with a cotton swab.
The taken biomaterial is spread evenly in a thin layer over the glass slide. The specimen is then stained with Leishman or Papanicolaou and then examined in detail under a microscope. In the case of liquid-based cytology, the glass slide is first placed in a special liquid.
Taking a smear for oncocytology
In rare cases, taking a smear for oncocytology is accompanied by subsequent light bleeding, lasting no more than 2 days. Such manifestations are normal and do not require seeing a doctor.
Important: inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs are a limitation for this type of analysis.
This fact is due to the possibility of obtaining distorted and unreliable results, which will entail making an incorrect diagnosis and prescribing the wrong treatment. Therefore, the cause of the inflammatory process in the body is first diagnosed, followed by its relief. Only after this is it possible to cytologically examine the cervix.
How long does it take to prepare a smear for oncocytology?
The duration of cytogram preparation varies from 3 days to 2 weeks, not counting the day of taking the biomaterial, depending on the workload of the laboratory. In private clinics, results are usually provided within 3-4 working days. Ready results of liquid cytology are issued within 10-14 days.
Interpretation of research results
Indicators of normal cytological examination of the cervix
The normal balance of microflora and the absence of pathological changes when analyzing a smear for cytology confirm the healthy state of the cervical canal. When studying, the cells in the smear are compared with the morphological standards of the norm, that is, their size, shape, and structure should not have abnormal deviations.
The doctor confirms that the study results correspond to a healthy state in the following cases:
- Cytology smear includes cylindrical single-layer epithelial cells.
- When taking a smear from the transition zone or vagina, it is normal to detect stratified epithelial cells.
Even minor deviations in cell morphology are reflected in the laboratory report. Changes may confirm inflammatory diseases or the presence of benign abnormalities. Most often noted:
- inflammatory atypia;
- atypia due to the presence of HPV;
- mixed atypia;
- atypia of unknown etiology, which require further diagnostic appointments.
Oncocytology smear - interpretation and normal values
Analysis of the mucous epithelium located on the cervix is extremely informative for the practicing physician. However, often the gynecologist does not provide a complete transcript to each patient individually.
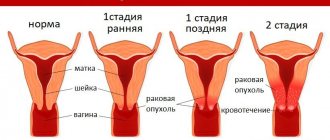
As a result of interpretation of the results of a cytological study, 5 classes of the condition of the epithelial tissue on the cervix are distinguished:
- Class 1 – normal condition without inclusions of cells with pathologies. Absence of inflammatory and oncological processes;
- Class 2 – questionable data, in which isolated modifications of individual sections of the epithelium were identified. This may indicate the manifestation of an infectious disease or an inflammatory process of a different etiology. If a smear for oncocytology shows an inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed additional diagnostic procedures (biopsy, colposcopy). After 3 months, the cervix is re-examined for cytology. After which a final diagnosis is made;
- Class 3 – dysplasia or hyperplasia in some areas of epithelial tissue. The patient must additionally undergo microbiological and histological diagnostics. After a control smear for cytology 3 months later, a diagnosis is made;
- Class 4 – tumor cells with abnormal DNA structure were detected. The woman is sent for a comprehensive diagnosis to the oncology center, based on the results of which the treatment tactics for the precancerous condition are determined;
- Class 5 – the number of tumor cells significantly exceeds the number of normal ones. In this case, a diagnosis is made - cancer of the internal genital organs.
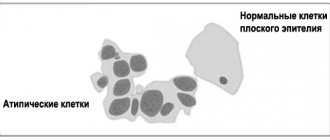
Normal and cancer cells of the mucous epithelium
Indicators of a smear for oncocytology, which are indicated in the results:
- level of cleanliness of the internal genital organs: 1 and 2 – normal microflora, 3 and 4 – the presence of parasitic microorganisms that provoke inflammation and need to be eliminated;
- C – taking a smear from the cervical canal, U – urethral canal, V – vagina;
- the concentration of epithelial tissue cells in a healthy woman does not exceed 10 units;
- leukocyte level;
- the fact of having an STD that requires immediate treatment;
- detection of mucus, a small amount of which is normally found in all examined patients;
- the level of content of all types of epithelium (cylindrical, squamous and glandular) with pathologically altered cells, which may indicate a precancerous condition. Each of the abnormal cells is assigned a specific abbreviation indicating the degree of change and number.
Normal values typical for healthy patients are presented in the table.
| Indicators | Normal values | ||
| V | WITH | U | |
| Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-30 | 0-5 |
| Flat epithelium | 5-10 | ||
| Gonococci | — | — | — |
| Trichomonas | — | — | — |
| Key cells | — | — | — |
| Yeast | — | — | — |
| Microflora | The predominant number of gram-positive Dederlein rods | — | — |
| Slime | Moderate amount | Moderate amount | — |
What changes are possible?
Benign changes may include:
- Detection of trichomonas, candida fungi, coccal infections, anomalies caused by infection with the herpes virus.
- Cellular atypia provoked by inflammatory reactions: metaplasia, parakeratosis, keratosis.
- Atrophic changes in epithelial cells in combination with inflammation: hyperkeratosis, colpitis, metaplasia.
Dysplastic changes and atypia suggest the following conditions:
- Atypia of unknown origin (ASC-US).
- High risk of presence of cancer cells in the material (HSIL).
- Precancerous atypia: varying degrees of dysplasia.
If cancer cells are detected, it is necessary to prescribe additional examination methods and a subsequent course of therapeutic correction (conservative or surgical treatment) with constant cytological monitoring.
Mixed flora: a variant of the norm or a violation?
Oncocytology during inflammation
A smear for oncocytology is sometimes performed during the inflammatory process that is present in the cervix. This happens if the woman has not properly prepared for the procedure, she has chronic inflammation, which she tried to treat, but without success, or there is resistance to therapy.
Carrying out analysis during the inflammatory process is not recommended, because during this period leukocyte cells and debris from dead cells make it difficult to determine whether there are cells affected by cancer pathology.
Pathogenic microflora that cause infectious inflammation (Trichomonas, fungi, chlamydia or gardnerella), in the normal state in the microscope lens, differ in appearance from cancer cells, and during a long-term acute state of infection they are modified and similarities with oncological ones are observed, which misleads the specialist who deals with research.
As a result, this may result in a false positive response.
Labeling of cytology results
Changes in the results of cytological analysis of the designation presented in the table below.
| Designation (class) | Decoding |
| Poor quality biomaterial, unsuitable for analysis. | |
| 1 | The results are normal. |
| 2 | Atypical changes are present. |
| 3 | Confirmation of dysplastic changes. |
| 4 | Precancerous condition. |
| 5 | Invasive cancer. |
Any degree of dysplastic changes is a signal confirming the need for further research and the appointment of adequate therapy.
Oncocytology for older women
The onset of menopause is not a sign that cancer in the cervix will not occur in women in this category. Reducing the production of female hormones reduces the risk of dyshormonal disorders, which allows women 50 years of age and older to be classified as a low-risk group.
But at the same time, against the background of other diseases of the body, the risk of pathological processes in internal organs increases.
For these reasons, there are 2 options for obtaining analysis:
- If the patient does not have pathologies of other internal organs, if she has had a smear for oncocytology once a year over the past 3 years and no abnormalities in the structure of the cells were found, then a woman who has entered menopause can now take the test once at 2 years old.
- If a woman does not visit a gynecologist regularly, if previous results revealed pathological processes of inflammation, then it is necessary to carry out oncocytology sampling every year until no changes are detected and confirm the result with positive tests for 3 years.
Atypical cells detected: what does this mean for the patient
Regular medical consultations are the key to the effectiveness of both treatment and prevention.
The gynecologist must conduct a detailed consultation, during which he will explain what it is in a particular case and explain the advisability of conducting an additional examination. Additional diagnostic search methods will allow you to correctly determine the most effective course of therapy.
For diagnosis when atypical cells are detected during a cytological examination in gynecology, the following are additionally prescribed:
- repeated cytological analysis of the cervical epithelium;
- colposcopy;
- biopsy;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- test for detecting human papillomavirus.
It is important to follow all medical recommendations and prescriptions; this will allow the pathological process to be identified and corrected in a short time. The effectiveness of the course of treatment should be regularly monitored using cytological examination. Therapy will be considered complete when cytology results confirm the healthy state of the cervical epithelium.
Examination of scrapings from the cervix is an important diagnostic procedure that should be carried out regularly for preventive monitoring of a woman’s health. An annual visit to a gynecologist for an examination and diagnosis of possible pathologies should be a rule of life for everyone, because early diagnosis of any disease is the key to timely initiation of treatment and its high effectiveness.
Types of research
There are various methods of smears for oncocytology with varying degrees of accuracy.
- The Leishman method is an old, traditional method of painting and fixing elements. It is used in district clinics and is the least expensive. Decoding consists in determining simple oncocytological transformations.
- The Papanicolaou method or PAP test is a more common procedure. The accuracy of the smear for oncocytology is higher than that of the previous method. The biomaterial of the cervix is smeared onto a glass slide, fixed with a special solution and sent to the laboratory. The doctor studies the composition of cellular elements in the form of a polychrome micropreparation. Instant fixation and new staining methods make it possible to qualitatively decipher the analysis of oncocytology of the cervix and identify precancerous conditions in the early stages.
- Liquid cytology is the most modern analysis of cervical cells for oncocytology and has the highest accuracy. Due to the high cost of the equipment, it is not used in all clinics. Once received, a smear for oncocytology is immediately placed in a liquid medium. Using special devices, the material is cleaned of foreign elements and placed on the glass in a thin, even layer. There is no loss of elements during transportation. Decryption is expensive and requires a highly qualified specialist.
According to European recommendations, liquid oncocytology is a more sensitive method. A significant advantage is the fact that after deciphering the results, the smear can be used for molecular studies of proteins, the breakdown of which indicates dysplasia and cervical cancer.
Methods for treating atrophy of the vaginal mucosa
Treatment consists of mandatory elimination of the inflammatory process.
At the moment, in modern medicine there are a huge number of methods for treating this disease.
1. Cryodestruction (exposure to low temperature on the affected areas); 2. Treatment with conization (partial removal of the uterus);3. Cauterization with a laser beam;4. Diathermocoagulation (use of high frequency current);5. Treatment of erythroplakia with loop electroconization.
Important! Never treat with folk remedies, this is a disease that does not forgive mistakes. Only a doctor should prescribe treatment for you after all the tests have been received.
The main and only way to treat the oral cavity is to perform surgery to remove the affected tissue. Drug therapy does not give the expected result. To prevent relapse of the pathology, it is necessary to eliminate the traumatic causes.
If erythroplakia of the cervix is diagnosed, treatment consists of surgery. The extent of the operation performed will depend on many factors:
- size of the affected area;
- histology results;
- woman's age (especially reproductive age).
Based on these factors, the doctor selects one of the removal methods:
- minimally invasive, preserves reproductive organs.
- conization of the cervix.
In parallel with surgery, antibacterial agents and probiotics are used. The latter help stabilize the vaginal microflora. The doctor prescribes vitamin complexes and drugs to boost immunity.
Replacement therapy is carried out using oral hormonal agents (containing synthetic hormones progesterone and estradiol, such as Ovestin), suppositories and creams (containing gestagens - synthetic progesterone). Doctors also prescribe medications containing phytoestrogens, but they are less effective.
Hormonal treatment has been carried out for several years, but the result itself is noticeable after a month of use. The attending physician records the results during the diagnostic process, however, even with a positive result, it is worth remembering that atrophy is an age-related manifestation and can recur several times.
Methyluracil suppositories are also popular among women, stimulating tissue regeneration and helping to get rid of colpitis.
Sampling process
The ascus procedure is performed in a gynecologist's office on a chair. For testing, you need to prepare a spatula, a mirror and a brush. The doctor should take three swabs in 10-15 minutes. These are the strokes:
- From the walls of the uterus.
- From the cervix.
- From the cervical canal.
We suggest you read: Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus
Typically, such an event does not cause negative feelings in the patient. But there are two points to pay attention to:
- If there is inflammation in the uterus, then any intervention can cause pain.
- For full testing and accurate results, it is important to take those tissues that are deeper, and not from above. Therefore, the doctor will have to apply some effort along the mucous membrane and pinch off part of it. This can usually cause discomfort.
The fabrics obtained in this way are dried and sent to the laboratory for testing. There they are examined by a specialist under a microscope.
Negative results
If an oncocytology test shows the presence of cancer cells, first of all, you need to not panic. A deviation from the norm most often does not mean that a woman is developing malignant neoplasms and that the situation cannot be corrected.
Studies show that a bad smear for oncocytology occurs quite often, and cervical cancer is much less common.
A qualified doctor will explain what type of abnormalities have been identified and prescribe additional tests, such as colposcopy or biopsy.
In any case, it should be remembered that an abnormal smear for oncocytology is not always evidence of the presence of cancer in a woman.
Every modern woman should be informed about the importance of such an analysis as oncocytology, what it is and why the analysis is so necessary for the timely detection of cancer
Most read:
Genitourinary systemLiveInternetLiv…
Miscarriage: causes, diagnosis and treatment of pathology Miscarriage…
What does a smear on the flora show in women - deciphering the gynecological analysis. A smear on the flora...
Brown (dark) spotting in the middle of the cycle: causes Reasons for appearing...
Ectopic pregnancy - Causes, symptoms and treatment Ectopic pregnancy...
Painkillers for menstruation: choosing the best by properties Which painkillers...
How to take Vikasol tablets during menstruation: instructions and reviewsHow to take V...
What menstrual cycle is considered normal for women, how many days? Norm and deviation…
Pink discharge: before and after menstruation, after sex, orange, yellow, mucous Pink discharge...
The most effective remedies for thrush in women: a review of medications for thrushChoosing a remedy...
Thrush after antibiotics: how to treat and how to prevent How to treat thrush...
Intermenstrual and dysfunctional bleeding Intermenstrual…
Pros and cons of an intrauterine device for pregnancyPros and cons...
Is scarlet blood dangerous during menstruation? Menstruation is scarlet...
Tampons or pads: which is better to choose: Intimate healthTampons or pro…
Culture of urine for flora: how to test and normsFlora of urine and its...
Urine culture tank for analysis: what it shows, how to give it, explanationUrine analysis for...
The main options for how to get rid of pregnancy and whether it can be done at home. Methods that ...
Medical abortion - indications and contraindicationsMedical abortion...
When your period comes after an early miscarriage without cleaning When should you…
When do periods start after an abortion and how long do they last? When do they come...
Brown, spotting discharge instead of menstruation: why does it happen? Why does it appear...
Termination of pregnancy (abortion), methods, consequences of termination of pregnancy (abortion) Consequences of…
Discharge after medical abortionDischarge after...
Cells without atypia: what are they?
Cells without atypia retain their structure and functionality. Columnar epithelium without atypia and squamous epithelium without atypia continue to perform their functions without changes.
The result of a cytogram without atypia does not always indicate the absence of any disease that reduces the patient’s quality of life. Indeed, the presence of columnar cells without signs of atypia, squamous epithelial cells without atypia, and normal mucus are a good result. However, any gynecological diseases should not be left unattended. If atypia is not detected today, this does not mean that after some time cells without signs of atypia will not degenerate into precancerous ones.
«>
Oncocytology and pregnancy
As a rule, this analysis is taken from the expectant mother when registering with the antenatal clinic. During pregnancy, if there are no contraindications, a smear for atypical cells is recommended to be done 3 times (every trimester).
The period of bearing a child is considered a responsible and important stage in the life of every woman. All the forces of the mother’s body are aimed at the needs of the baby. Due to hormonal changes and constant stress, the risk of normal epithelium degenerating into a pathological type increases. And if a woman had a precancerous condition before pregnancy, then against the background of a surge in hormones, a sharp progression of the process is possible.
If the procedure for collecting cervical epithelium is associated with possible complications and negative effects on the fetus, it will be postponed until a more favorable period. Gynecologists advise women planning a pregnancy to undergo a comprehensive examination in advance to identify possible pathologies.
Cytological diagnosis of the epithelium of the vagina and cervix requires a minimum of effort from the patient and provides the doctor with maximum information. Any disease has a characteristic microscopic picture. After receiving the cytologist's conclusion, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment.
Since the incidence of cervical cancer is steadily increasing, every woman should know about this method. A systematic visit to the gynecologist will help maintain health and life.
Summarizing
To summarize, it is worth emphasizing the following important points:
- It is recommended to conduct the study at least 5 days after the start of the menstrual cycle, and also no later than 5 days before the expected start;
- before taking a smear, you must abstain from sexual intercourse for at least 1 day, and from lubricants, tampons, douching procedures, the use of medicated suppositories and spermicidal preparations - 2 days before;
- if there is an acute infectious process in the body, it is necessary to first stop it, and then take a control test at least after 2 months;
- false negative results and erroneous classification of the studied material as class 1 are allowed, which is why it is important to conduct a control examination annually.
Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova)
Certified specialist, in 2019 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiologist. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University.
In 2019 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”.
Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the category “Biological Sciences” 2019.
What is meant by “atypical” in gynecology?
When speaking about atypia, gynecologists mean a variety of disorders that occur in the tissues of the female reproductive system at the cellular level. Essentially, this is the formation of abnormal cells, which manifests itself in a distortion of their structure and is accompanied by a number of signs indicating problematic malfunctions in the body, improper functioning of an organ or the entire reproductive system.
Most often, pathology develops on the cervix, because this part of the organ is primarily exposed to the adverse effects of external factors (viruses, bacteria, infections), the development of inflammation and other damage. As a result, when normal cells divide, atypical ones are formed, i.e. having an irregular structure, abnormal shape and size.
Cellular disorders in the tissues of the cervical walls and cervical canal can provoke the rapid development of abnormal layers. This in turn causes disturbances in the functioning of the organ. In addition, there is often a deterioration in blood circulation in these areas, which leads to the occurrence of such a type of atypia in gynecology as vascular, i.e. to distortion of blood vessels, which can enlarge and proliferate.
The described pathological processes often develop directly in the uterus; they can be closely related to endometrial hyperplasia (the internal mucous membrane of the organ).
Scheme of oncocytology
The method of taking a smear is painless. The procedure is performed by a doctor during an examination of the patient by a gynecologist in a gynecological chair. Initially, specialized magnifying mirrors are inserted into the vagina, then a piece of epithelium is removed from the membranes of the uterine cervix using a small spatula or using a special cytobrush. A cell sample is then taken from the cervical canal using a small cotton swab. The shelf life of the biological tissue is 14 days.
The collected material is applied to a special glass for further microscopic manipulations (Pap test) or placed in a special liquid for liquid-based cytology. The analysis has no painful symptoms and is absolutely painless. During the study, the tissues of internal organs are not injured. The initial examination may be accompanied by slight discomfort.
Oncocytology shows small discharge with blood clots. Bleeding goes away within two days and does not require treatment. When a woman passes childbearing age, diseases of the genital organs do not disappear. Seeing a doctor and undergoing diagnostics at this age reveals advanced and irreversible pathological processes. It is difficult to cure cancerous tumors in the later stages of development.
Pregnancy is a serious stressor on the female body. Increased hormonal levels and stress activate the progression of many oncological and non-oncological diseases. When registering a pregnant woman, the doctor must take a smear for oncocytology. If the pregnancy is stable, tests are performed again in the second and third trimesters. It is recommended to undergo examination during pregnancy planning. This will allow you to accurately prevent disturbances in fetal development.
In developing inflammatory processes, a smear is not taken after oncocytology to avoid obtaining distorted information. In such situations, the doctor takes a smear and scraping to check the development of viral infections and pathological diseases transmitted through sexual contact. The patient then undergoes a course of therapy. After recovery, oncocytology tests are repeated.
Types of atypia
Functional atypia is the development of a tumor, even if its cells do not receive oxygen. Hypoxia does not stop tumor growth. Anaerobic glycolysis increases, the breakdown of glucose in tumor cells in the absence of oxygen supply proceeds, as in the case of an oxygen supply. This makes tumor cells resistant to oxygen deficiency.
Glycolytic processes in the tumor predominate over oxidative ones. Lactic acid accumulates in the tissues, they become similar to embryonic tissues. The cytoplasm of tumor cells contains a large amount of proteins, under-oxidized metabolic products, neutral fats, phospholipids, glycogen, nucleic acids, and cholesterol. With functional atypia, the cell contains a lot of water, calcium and sodium ions; it contains less magnesium and potassium than normal.
Structural atypia is divided into cellular and tissue atypia. Structural (morphological) atypia is a violation of the structure of the cell, starting from the molecular level and ending with the type of cell, that is, ultrastructural, cytotypic and histotypic differentiation is impaired. Even within the boundaries of one tumor, there may be cells that differ from each other in structure and shape.
Cellular (cytological) atypia is a change in the appearance of a cell, its shape, size, that is, a tumor manifestation at the cellular level. In some malignant tumors monomorphism occurs, but in most tumors the atypical cells are polymorphic. Atypical cells are characterized by nuclear atypism - an enlargement of the nucleus.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xRBGo50ppMQ
The nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio is disrupted, more and more division figures appear, and pathological mitosis occurs (the chromosomal distribution between daughter cells and continuity over a number of generations are disrupted). Polymorphism of cell nuclei causes changes in color density, changes and diversity in the size of the nucleus and its shape, which greatly distinguishes them from the norm.
Cellular atypia can be strongly or weakly expressed; sometimes cells lose their resemblance to the original tissue, which makes it impossible to determine their tissue origin. In the extreme state of biological atypia of the tumor, its structure becomes simpler and more uniform in cellular composition. Neoplasms consist of cells in which the number of free ribosomes has increased, which are not associated with the endoplasmic reticulum.
Tissue atypia is a violation of the arrangement of cells that does not correspond to the order of location in a given tissue. Tumor cells are characterized by chaos - the cells are located in the form of random clusters, chaotically oriented. Malignant tumor cells penetrate the lymphatic bed, blood vessels, and metastasize to other organs and tissues.
What is oncocytology?
Cytological examination is a microscopic examination of cellular material obtained during diagnostic or therapeutic manipulation. More often this term is used in relation to screening for precancerous and malignant diseases of the cervix.
Oncocytology analysis is performed to obtain and interpret smears from the vagina and cervical part of the reproductive organ in a woman. The biopsy sample is taken with a special instrument. As a rule, the manipulation is performed at an appointment with a gynecologist. The method is accessible and inexpensive. The examination is carried out in any antenatal clinic or other medical institutions.
The main objective of the method is the early detection of atypical changes in the cellular composition of the vaginal epithelium and cervical zone of the reproductive organ. The analysis also allows you to detect dysplasia, inflammatory diseases, and other pathologies. It is used by doctors to evaluate the treatment provided and track the dynamics of the disease.
The resulting cellular material is sent to cytologists for study. They examine the preparations under a microscope and issue a conclusion.
Interpretation of a cytological examination of a cervical smear
- Do not douche.
— Do not use topical medications (suppositories, ointments, etc.).
- Wait until your period ends.
- Do not urinate three hours before taking a smear.
— Abstain from sexual intercourse for two days before the study.
If there is an inflammatory process in which a lot of secretion is released, the disease must be treated and a control smear done to confirm recovery. And only after this does it make sense to perform a cytological analysis.
An oncological smear is taken by a gynecologist when examining a patient. First, using mirrors, the doctor examines the condition of the vagina, examines the entrance to the cervical canal and the mucous membrane of the cervix.
Then, material is taken for analysis from three areas (vagina, cervical canal, cervical inlet) using a special brush. The procedure takes very little time and does not cause patients any pain.
The collected material is placed on a glass slide, evenly distributed and, after drying, transferred to a medical laboratory. There, the smear is stained with special substances and examined under a microscope.
— Cell sizes and their structure.
— Number of cells (per certain unit of area).
- Mutual arrangement.
- Shape of the epithelium.
— The presence of pathological changes in cells.
Structures of stratified squamous epithelium of the cervix
Structures of multilayered squamous epithelium of the vaginal mucosa
A - basal layer (a - basal cells, b - parabasal cells) B - intermediate layer, C - superficial layer; on the right are individual cells of the corresponding layers of the vaginal epithelium.
After the material collection procedure, the patient can immediately return to her normal activities. Normally there should not be any discomfort, since the brush cannot injure the tissue.
True, there is a possibility that a small blood vessel will be affected. Then, within 1-2 days after the analysis, slight bleeding (streaks) will be observed. This phenomenon should not cause concern to a woman.
If this is vaginal candidiasis (thrush), then local treatment with antifungal drugs, for example, Clotrimazole, will be required. Medicines with active ingredients are also used against thrush: isoconazole, miconazole, natamycin, nystatin.
If this is bacterial vaginosis, key cells and coccal flora are found in smears from the cervical canal, then antiseptics like Hexicon (chlorhexidine), metronidazole or a complex drug - Terzhinan will be prescribed.
If urogenital trichomoniasis is detected, drugs from the nitroimidazoles group are prescribed: Metronidazole, Ternidazole, Neomycin, Nystatin.
For chlamydial cervicitis, take tetracycline, doxycycline and or erythromycin orally.
For actinomycosis caused by wearing an intrauterine device (IUD), you must first remove the intrauterine device. And then, there are options. These may be penicillin antibiotics:
- tetracyclines; cephalosporins (cefaclor, cephalexin); aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin, tobramycin).
Broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs:
- metronidazole (metrogyl, trichopolum, efloran); clindamycin (dalacin, climycin, clindamycin).
If relapses of the disease are frequent, the same medications are prescribed in the form of tablets for oral administration.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for HPV. But within 1-2 years after the manifestation of the disease, the immune system overcomes the virus, and it ceases to negatively affect the cervix. The main thing is to hold out for these few months.
For atrophic colpitis (atrophic type of smear, ATM), treatment is carried out with antibacterial agents, usually of complex action, and then the woman is prescribed hormone replacement therapy (HRT) if necessary and if there are no contraindications for it.
Cytogram of inflammation: the lesser of evils
An inflammatory cytogram indicates the development of a serious gynecological lesion in the area of the uterus and appendages.
Cytology analysis allows us to determine not only the presence of inflammation, but also a number of concomitant pathologies, including the development of cancer. Also, the method of cytological diagnosis effectively determines cervicitis and other pathologies of the female reproductive system of an infectious nature.
With an inflammatory type of smear, cytology is one of the main diagnostic methods. The inflammation cytogram procedure is characterized by a specific algorithm:
- the biological material taken for analysis is placed on a specially treated glass surface;
- the material is processed with special means in order to preserve the cell structure;
- Using Nikiforov’s mixture, the tissue under study is fixed;
- To identify foci of inflammation and other pathological lesions, PAP testing or Papanicolaou staining is used.
The result of the cytogram of inflammation obtained after staining allows one to accurately determine the presence of pathological manifestations in the tissue being examined.
Cytological studies are an effective diagnosis of the inflammatory process in the uterine cavity. Against the background of inflammation in the uterus, other pathologies that threaten the life and health of a woman can also develop.
The cytogram corresponds to the main vital signs of the uterus and related organs of the female reproductive system.
The inflammatory process of the mucous membrane corresponds to a number of characteristic symptoms:
- painful manifestations localized in the groin area and lower abdomen;
- bloody vaginal discharge not associated with the menstrual cycle;
- increased body temperature;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
A cervical cytogram allows you to timely determine the development of the disease and prescribe effective treatment.
If the patient has moderate inflammation, this is a reason to conduct a cytological examination. However, it is not yet a critical diagnosis.
This type of inflammation rather corresponds to the presence of a certain imbalance in the body, and indicates the need to identify and eliminate the causes of the inflammatory process.
However, if a cytology smear shows a more serious and deep damage to the uterine tissue, urgent and comprehensive treatment measures are necessary, which can only be prescribed by the attending physician after a complete and objective examination.
Deciphering test results is a simple matter for a doctor, but for a patient it is incomprehensible letters and terms.
- Latin letters U, C, V are a symbol for collecting secretions from the urethral, cervical canal and vagina, respectively.
- The number of leukocytes – a number of up to 15 units is considered normal.
- The presence of trichomonas, gonococci, and fungi indicates an infection of the genital organs that needs to be treated.
- Gardnerella in combination with fungal mycelium are signs of vaginal candidiasis, which can cause inflammation.
- The presence of glandular, flat, columnar epithelium in large quantities with signs of atrophy and pathological changes indicates possible signs of the development of cancer. Such cells are carefully studied and described in detail in the comments. The type and nature of changes are established.
- Degree of purity - 1, 2 degrees indicate a good vaginal environment, 3, 4 requires additional research and treatment.
- Flat epithelium normally comprises up to 10 units. An excess indicates a possible disease of hyperkeratosis - a benign formation of the cervix.
- Mucus in moderate quantities is a normal state of the vaginal environment.
If atypical cells are found in the smear, the laboratory technician will write about this in the conclusion and also determine the type of changes. Therefore, if the transcript of the cytology smear does not contain any special notes, then, most likely, no pathologies were found.
The time required for a smear test for cytology is from 1 to 5 days. Pathological changes in the cells of the cervical canal and cervix on the way to the diagnosis of cancer go through several stages, and not in 1-2 days.
Cytological examination makes it possible to identify atypical cells at the initial stage and begin treatment, which in most cases leads to complete recovery.
Therefore, cytological examination has been widely introduced into medical practice as a quick, painless and inexpensive way to diagnose cancer cells at an early stage.
The cervix of a healthy woman is covered with columnar epithelium, and the vagina is flat. As for the vaginal microflora, it is not cocci, but rods.
Some indicators depend on the phase of the cycle - karyo-pyknotic and acidophilic indices, basal and parabasal cells, the number of leukocytes. They provide information about the functioning of the ovaries.
Class 1. Absence of pathological changes in the examined material. The cells are of normal size and shape and are correctly located.
Class 2. The morphological norm of some cellular elements is reduced, which is a sign of inflammation or infection. This result may be a sign of vaginosis.
Class 3. The material contains single cells with disturbances in the structure of the nucleus and cytoplasm (dysplasia or hyperplasia). The number of such pathological cells is small. The patient is sent for repeat cytology.
Class 4. The examined smear reveals cells with malignant changes in the nucleus, chromatin and cytoplasm. These pathological changes indicate that the patient has a precancerous condition.
Class 5. The presence of a large number of atypical cells in the smear (they are much more than normal). In this case, the initial stage of cancer is diagnosed.
- Normal. The absence of pathology does not have any special designation.
— Vaginosis, koilocytosis – HPV.
- Cervical dysplasia depending on the degree - CIN I, CIN II or CIN III.
— Cervical cancer — Carcinoma (pax).
— CBO. Normal indicators, no pathological changes.
- Cytogram of inflammation. Indicators indicating the development of the inflammatory process (cervicitis).
— Leukocyte infiltration – increased number of leukocytes. This is a sign of vaginosis, exocervitis or endocervitis.
— Koilocytes – the presence of cells indicating HPV.
— Proliferation – acceleration of cell division. This condition is typical for the inflammatory process in the uterus. With strong proliferation, advanced inflammation occurs.
— Leukoplakia – the smear contains pathologically altered (but not cancerous) cells.
- Metaplasia - one type of cell is replaced by another. It is considered normal for patients who were treated for non-cancer pathologies of the uterus during menopause.
— Dysplasia is a precancerous pathology.
— ASC-US – the presence of altered squamous epithelial cells of unknown etiology. It most often occurs in patients over 45, when estrogen production decreases.
- AGC - changes in cylindrical cells, which may indicate vaginosis or some other diseases. This result requires additional clarifying diagnostics.
— L-SIL – the presence of a small number of atypical non-cancerous cells. In this case, the patient is referred for further examination (biopsy and colposcopy).
— ASC-H – pathological changes in cells that indicate a precancerous pathology or an incipient oncological process.
- HSIL is oncocytological (modified squamous cells present). Such patients are given immediate treatment to prevent degeneration into a malignant tumor.
- AIS - This abbreviation indicates that cylindrical malignant cells have been identified. With such results, urgent treatment is necessary.
If pathologically changed cells are detected in a smear, the laboratory assistant will definitely indicate this in a written report specifying the type of changes. If there are no special designations in the analysis transcript, then, in all likelihood, the smear corresponds to the norm.
An accurate diagnosis cannot be made based on this test alone. To determine the nature of the pathology, the gynecologist needs to compare the results of different examinations.
A cytogram in gynecology is a cytological examination of a cervical smear, or, to put it simply, an analysis of the “imprint” from the cervix to determine the condition of the cells of its surface layer - the epithelium.
Another name for the analysis is oncocytology or cytology. Performed to identify precancer and cervical cancer. For reference: there are about 80 signs of an atypical (cancerous) cell, but cytologists mainly use 10 of them.
But sometimes the result does not sound entirely clear to the patient - “a cytogram of inflammation with reactive or degenerative changes in the epithelium”... What does this mean and how is it treated?
This is type 2 Papanicolaou smear (Pap test), class 2 - ASCUS - atypical squamous cell undetermined significance. Speaking in Russian, cells of undetermined significance were discovered, most characteristic of an inflammatory process.
Usually, with such decoding, there is also a mention of a significant number of leukocytes. That is, all that is required of a woman is to undergo anti-inflammatory treatment, but not with folk remedies. Which one exactly? Depends on the infectious pathogens and symptoms.
Possible complications
Complications of erythroplakia are:
- Malignancy of the transformation zone (development of oncology).
- Chronic inflammation.
Complications after drug and hormonal therapy may be due to the characteristics of the woman’s body and its perception of the drugs taken.
Diathermocoagulation causes the most complications. The scar left after treatment narrows the uterine canal, which can subsequently lead to rupture during childbirth. In addition, the risk of developing problems such as bleeding, endometriosis, infections and even infertility increases.
Infection and inflammation can also appear after laser destruction if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations.
There are no symptoms of erythroplakia in the classical sense. This is most often an accidental discovery during a routine examination. Since the disease develops as a consequence of chronic inflammation, signs characteristic of cervicitis, colpitis, and vaginitis may be observed:
- discharge from the genital tract of varying intensity, which intensifies during periods of exacerbation and before menstruation;
- feeling of itching and burning of the vulva, vagina due to irritation from discharge;
- Pain in the lower abdomen in the chronic course of the pathology rarely appears, there is a feeling of discomfort;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse - dyspareunia, which can occur both in the vagina and in the lower abdomen.
With advanced erythroplakia and extensive damage to the cervix, contact bleeding may occur after sexual intercourse. It is not long-lasting and does not lead to massive blood loss.
The presence of atypical cells allows us to classify erythroplakia as a precancerous disease. Without treatment and when exposed to additional damaging factors, the most dangerous consequence is the degeneration of the process into a malignant one. Other complications include the presence of a permanent focus of inflammation, which is provoked by local immunity.
How to take a smear for cervical cytology
- Shape of the epithelium.
For women who are regularly examined by a gynecologist, this procedure will not be fundamentally new. The only difference is that the smear is taken with a special brush, and not with a Volkmann spoon, as during the usual smear procedure.
The brush is inserted into the cervical canal and scrolled several times clockwise and counterclockwise. After this, the taken material is applied to a glass slide and fixed with a special solution to keep the cells from drying out.
Then, the resulting preparation is placed under a microscope for a detailed study of the cellular composition.