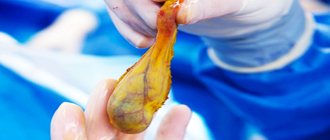
Removal of the gallbladder is most often prescribed for recurrent gallstone disease or after the occurrence of complications associated with cholelithiasis. After surgery, the patient must follow the principles of the rehabilitation period and eat properly so as not to cause a deterioration in health. Sometimes there are cases that after cholecystectomy the right side hurts. It is necessary to analyze the main causes of this condition.
Pain after cholecystectomy
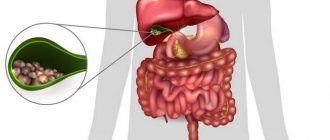
Removal of the gallbladder is prescribed in the presence of diseases that contribute to functional disorders of the hepatobiliary system against the background of the development of a life-threatening condition. Absolute indications include:
- Acute and recurrent cholecystitis.
- Gallstone disease.
- The appearance of polyps in the gallbladder.
The gallbladder is removed using two methods: open abdominal surgery and laparoscopy. Laparoscopic surgery is a more gentle method that allows you to remove an organ from the abdominal cavity with virtually no incisions. The advantages of laparoscopy are that the recovery period is faster, the operation causes few side effects, and the patient can be discharged from the hospital within a few days. Puncture sites heal quickly.
Today, conventional abdominal surgery is rarely prescribed, only in extreme cases, if the patient is hospitalized and there is an urgent need to save a life (for example, a complete blockage of the bile ducts, a perforated hole, or bleeding in the gallbladder caused by damage by the sharp edge of a stone). During abdominal surgery, a large incision is made, and large blood loss is possible. On average, the recovery period for surgery is approximately one month.
During the recovery period, some patients may experience discomfort in the right hypochondrium. This condition is associated with the absence of the gallbladder, because significant changes occur in the functionality of the digestive system. The body must adapt to a new way over time, so initially a discomforting state is observed.
Nature of pain
In the absence of a gallbladder, bile goes directly into the intestines. This is a continuous process. Previously, there was a sphincter in the area of the gallbladder, which regulated the amount of bile secreted. After removal, bile continuously flows from the liver through ducts into the duodenum. This is the cause of discomfort. The pain is not sharp, but nagging, without shooting. The nature of the pain is tolerable. An unpleasant sensation usually occurs after eating.
The patient also has irritation of the intestinal walls due to the action of acid in the bile secretion. Now bile will be present in the intestines constantly. The condition is unpleasant, but solvable. Medicines prescribed by a doctor, diet and exercise will help alleviate the patient’s condition.
Localization and time of occurrence
Unpleasant sensations occur in the area of the right hypochondrium and lower abdomen. Also, pain in the right side in the postoperative period is associated with the type of operation that was performed:
- Using small punctures performed for laparoscopy, the abdominal cavity is filled with an inert gas - carbon monoxide. This gas allows you to easily remove the diseased organ. Excessive accumulation of gas can cause unpleasant pulling sensations not only in the right hypochondrium, but throughout the entire abdominal region. As the inert gas evaporates from the abdominal cavity, the patient feels better.
- During abdominal surgery, severe pain often occurs in the rib area. An unpleasant sensation is associated with the cutting of a scalpel and the removal of an entire organ. The tissue is damaged and the cut takes time to heal. About a month after surgery, the pain should subside.
For severe pain, painkillers are prescribed and should be taken for a week.
In the postoperative period, discomfort may bother the patient constantly and subside only after taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If the pain is caused by errors in the diet or a period of adaptation, then unpleasant sensations in the right side will occur mainly after eating. The attack lasts 20 minutes or more. On average - about an hour. The length of the attack also depends on the amount eaten and the severity of the food (fat content, satiety).
Drug therapy
After removal of the gallbladder, the doctor prescribes antibacterial medications. They are necessary to eliminate complications. They are taken during the first three days after surgery. Next, antispasmodics are prescribed for a course of ten days - No-shpu, Drotaverine, Buscopan. After the patient is discharged, treatment continues. At home, he needs to take medications containing ursodeoxycholic acid. This is necessary to reduce the risk of stone formation. Ursofalk is considered one of the effective medications. It is produced in the form of a suspension and capsules. The course of treatment is prescribed by the attending physician. If necessary, it can be two years. To speed up the process of food digestion, which is disrupted after surgery, medications containing enzymes, bile and bile acids are prescribed. These medications also prevent the formation of stones, which is very important. These include: Cholenzym, Allohol, Liobil.
For intensive production of your own enzymes, the following are prescribed:
- Ursosan;
- Hepatosan;
- Cyclovalon;
- Ursofalk.
Due to the low concentration of bile, problems with stool appear. To do this, you need to take medications that have a beneficial effect on the intestinal microflora:
- For constipation - lactulose disaccharide.
- In case of disorder - antidiarrheal and antimicrobial medications that improve intestinal function.
- For gas formation - Dimethicone, Simethicone.
- For problems with peristalsis - Domperidone.
- In case of intoxication - enterosorbents.
- Heartburn is relieved with medications that neutralize excess acid.
Associated symptoms
If pathological pain occurs, additional symptoms may occur:
- The pain can radiate from the right hypochondrium to the area of the shoulder blade, back or shoulders, behind or in front.
- The appearance of loose stools due to accelerated evacuation of bile without retention in the gallbladder. Bile in a similar consistency dilutes stool, causing mechanical diarrhea.
- Flatulence. It often occurs during the period of adaptation to life without a gallbladder.
- Nausea. In more severe situations, it is accompanied by vomiting.
- There is a bitter taste in the morning.
- Lack of vitamins, especially fat-soluble ones. This condition is associated with decreased absorption of vitamin and mineral supplements in the small intestine.
- Weight loss. Associated with hypovitaminosis and lack of nutrients.
- Against the background of reduced absorption of nutrients, decreased performance, weakness and drowsiness.
This condition develops gradually and requires additional correction from medications, including parenteral forms of vitamin supplements.
ethnoscience
After undergoing cholecystectomy, the patient must protect his liver. To do this, you can seek help not only from medications, but also from folk remedies. In herbal treatment, substances are used that help prevent stagnation in the bile ducts and the re-formation of stones in the liver. Birch buds and leaves have a choleretic effect and normalize metabolism - pour two tablespoons of the raw material into one glass of boiling water and leave for an hour. Strain and drink half a glass four times a day before meals. Milk thistle is a unique plant; the main thing is to follow the correct dosage. With the help of Milk Thistle, you can cleanse the liver of toxins and remove thickened bile. The herb can be made into powder, extract and oil. To treat the liver, grind 2 tablespoons of fruits and pour half a liter of water, put on low heat. Evaporate to half the original volume. Strain and drink one tablespoon every hour throughout the day. To prevent the formation of stones, reduce pain and inflammation in the liver and ducts, use Knotweed. Pour two tablespoons of crushed raw materials into 0.5 liters of hot water and boil for a couple of minutes. Leave for four hours, strain and drink 20 minutes before meals, half a glass three times a day.
Causes
If the pain is constant, it can be caused by the following reasons in a patient who has undergone cholecystectomy:
- The emergence of postcholecystectomy syndrome.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Errors in diet.
- Exacerbation of concomitant chronic diseases.
- The presence of postoperative complications, including medical errors.
There are also a large number of other, less serious reasons. This may be a normal variant or a pathology. It is necessary to find out the reasons individually, through diagnostics. Even in the practice of doctors, there are cases of phantom pain - when the patient feels unpleasant sensations at the site of a removed organ, which should not normally exist.
What pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract system and concomitant diseases may occur:
- History of pancreatic inflammation.
- Exacerbation of gastritis or gastric ulcer.
- Exacerbation of duodenal ulcer.
- Presence of liver diseases.
Doctors can introduce infection into the body if surgical instruments are not sufficiently sterilized. Therefore, after removal of the gallbladder, you need to monitor temperature readings. If severe hyperthermia develops (indicators rise from 38 degrees), then the patient is immediately prescribed antibiotic therapy. Such situations are extremely rare, because according to the protocol, hospitals immediately begin to use antibacterial agents within 5-7 days from the date of surgical manipulation of any complexity.
Another point is the appearance of adhesions after surgery. Adhesions are extensions of connective tissue that arise in response to inflammation or damage to internal organs. This connective tissue often causes discomfort if there is a lot of it and it begins to stick together the internal organs.
When removing a gallbladder with stones, the release of the stone into the bile duct may not be noticed. If this happens, the patient will soon feel worsening and acute pain in the right hypochondrium. If there is a risk of blockage of the bile ducts, then they are also amputated.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome
After removal of the gallbladder, postcholecystectomy syndrome may occur after some time, pain in the right hypochondrium. Discomfort may occur almost immediately after surgery, or it may occur later, even six months later. The exact causes of this condition have not yet been identified.
The main cause of the condition is dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi. After removal of the gallbladder, the sphincter functions are disrupted and hypotension occurs. Normally, the sphincter of Oddi reacts to the incoming amount of bile and unclenches. After removal of the gallbladder, the need for this function disappears, because now bile flows continuously. This causes pain at the site of the removed organ. The second cause of postcholecystectomy syndrome is the cystic duct left by doctors after the operation.
Excessive physical activity
During the recovery period, the patient is given complete rest. The first weeks of the patient's life should be spent in bed rest. Otherwise, the risk of internal bleeding increases, and the discomfort is manifested by a dull pain on the right. Once the two-week period has passed, the patient can gradually return to normal physical activity, provided there are no complications. Light to moderate intensity exercise is also allowed over time. Daily walking at a slow pace prevents the appearance of bile stagnation.
Poor nutrition
If the patient does not follow the principles of diet No. 5, then the patient will soon have a stabbing pain in the right side. The tingling sensation is caused by a spasm of the bile ducts, in which thickened bile secretions accumulate. Abuse of flour, fatty, spicy and sweet foods causes a painful condition in the patient. Treatment consists of normalizing the diet, adhering to the principles of fractional nutrition, excluding non-recommended foods.
Function of an organ without a gallbladder
When, after surgical intervention during rehabilitation, bile continues to be produced by the liver and there is no stagnation, there is no reason to worry. Bile continues to flow into the intestinal lumen, fully performing its natural functions.
Although sometimes patients develop bile stagnation. Its first sign is slight pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. At the same time, the bilirubin level increases along with liver enzymes. Liver therapy in a similar situation after excision of the gallbladder consists of taking choleretic medications.
After a certain period of time, the functioning of the gland should be restored. The intrahepatic ducts will begin to perform uncharacteristic activities, becoming some kind of containers for bile. This does not harm the body at all.
First aid
If the patient is in severe pain, he needs to take actions that can alleviate the condition before the doctors arrive. First, loosen tight clothing. For severe shooting and aching pain, the patient is placed on the right side. As far as possible, the victim should relax and not think about bad things. To distract the patient’s negative thoughts, it is necessary to talk to him, encourage him, and distract him in every possible way.
If the pain is unbearable, you can take a warm bath, and after it put a bag of ice on your right side. Perhaps after these actions the condition will improve significantly and you will not have to call an ambulance. In any case, you need to visit a specialist to find out what caused the discomfort in order to prevent future attacks.
Diet food
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of the liver after surgery. The main point is to eat regularly. The amount of food taken should be small but frequent - from 4 to 6 times a day. In this case, food will act as a stimulant for the formation and excretion of bile. This will avoid stagnation in the ducts. Olive oil is considered a good choleretic product. It must be included in the diet. From the diet you need to remove foods high in animal fats and carbohydrates - baked goods, sugar, potatoes, pasta and confectionery, fried and spicy foods, cold and very hot. The consumption of all carbonated drinks is prohibited. It is recommended to drink up to two liters of drinking water per day. It promotes normal bile secretion. The diet of a patient who has undergone removal of the gallbladder and is undergoing liver treatment should consist of first courses - low-fat meat broths and vegetable soups, stewed vegetables, low-fat fermented milk products, day-old white bread, protein omelettes and porridges. Eliminate semolina porridge.
Diagnostics
The patient should contact a local physician, who will conduct a general examination, collect complaints and give a referral to see a gastroenterologist. This is a specialist who deals with gastrointestinal disorders. You may need to consult a more specialized specialist - a hepatologist.
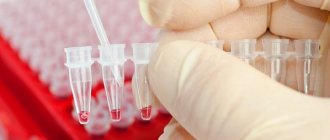
The patient is prescribed a general and biochemical blood test to check how the hemostasis system works and whether there are any manifestations of abnormalities in the functioning of the organs according to the analysis. If everything is normal, then the patient will probably be referred for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. If an unspecified diagnosis occurs, additional abdominal CT or fibrogastroduodenoscopy may be required.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome
Postcholecystectomy syndrome is a combined concept that includes organic and physiological disorders of the digestive organs after resection of the gallbladder. The symptoms are varied, and in five percent of patients it is impossible to identify the causes of the syndrome. Predisposing factors for PSEC include:
- Incorrectly performed operation.
- Insufficient or incorrect examination.
- Insufficient production of bile acids.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- Infections of the duodenum or gastrointestinal tract.
- Adhesions localized under the liver.
Pain treatment
Therapy depends on the diagnosis. Typically, complex treatment is prescribed using medications. The drugs temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition and normalize some biochemical parameters if they are not normal. Nutrition correction is the most important stage. Without following a diet, there will be no result in therapy. If pathological changes occur that threaten the patient's health, surgery may be required. Numerous reviews indicate that postcholecystectomy syndrome can be managed without resorting to surgery.
Drug therapy
Treatment with drugs is an important stage at first. They normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and relieve pain in the right hypochondrium. The main list of appointments includes:
- Analgesics or NSAIDs are needed in the acute period, when the patient is in severe pain. They are not suitable for long-term use as they have an impressive list of side effects.
- Enzymes. Necessary for improving liver and pancreas function.
- Antibiotics - if a complication occurs in the form of an inflammatory process.
- Prebiotics are necessary to normalize intestinal function and treat diarrhea.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodics, like NSAIDs, are used short-term to relieve a painful attack associated with spasm of the bile ducts and intestines, including the duodenum. Examples of drugs are No-shpa, Papaverine. These medications selectively act on the smooth muscles located in the uterus and intestines, relaxing them.
Choleretic agents
Choleretic agents facilitate bile outflow. They help if the patient has an accumulation of bile secretion in the lumen of the tubes due to errors in the diet. The drugs are taken in courses to alleviate the condition or prevent the occurrence of cholestasis. Medicines act quickly. Usually the patient feels relief within a few days of starting choleretic therapy.
Proper nutrition
Diet recommendations for a person who has had their gallbladder removed include eating foods allowed in diet menu number 5. The basis of the diet is porridge with water or skim milk, lean meats, poultry and fish. Protein and fats are consumed in moderation. Recommended carbohydrate values are 4 g per 1 kg of body weight. For proteins and fats – 0.8 g per kg of body weight. Vegetables are first eaten boiled and pureed. Dried fruits are consumed in moderation. The patient should eat in small portions, 5-6 times a day, if he does not have diabetes. The drinking water norm is from 1.5 liters per day.
Choleretic products
There are foods that promote the active secretion of bile. This includes vegetable oils rich in omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (olive or flaxseed oil). Food additives – turmeric, herbal mixtures based on immortelle sandy, corn silk, dandelion. It is useful to drink chamomile tea and rosehip compote.
Prohibited components
The patient should avoid foods that cause accumulation and thickening of bile secretions in the lumen of the bile ducts. These include:
- coffee, strong tea, chocolate, cocoa;
- fatty, spicy, salty and fried foods;
- flour, dough baked goods made from white flour;
- sweets, cakes;
- alcoholic drinks;
- semi-finished products, fatty meat, mushroom or fish broths.
If over time the patient gets better and relapses of pain stop completely, then occasionally (no more than once a month) and in small quantities you can afford to eat the forbidden food.
Surgery
The bile ducts are removed if there is a blockage with stones or cholestasis causes complications (infection, the appearance of stones). Therefore, in some cases, the bile ducts are removed immediately with the gallbladder (with frequent relapses of cholelithiasis).
Why is bile needed in the digestive system?
The formation of bile is a multi-level complex process, and the substance is multicomponent. It contains bile acids, minerals, bile acids, hormone breakdown products, cholesterol, toxins, metabolites and other active substances. Most of the bile is water, which is why the substance is quite liquid and can flow through the ducts without delay. Bile secretion has a dissolving effect, neutralizing toxins and toxic substances that are filtered by the liver and excreted into the intestinal tract. About a liter of bile enters the body per day.
Read also: Basics of proper nutrition for gallbladder inflammation
The main tasks of bile:
- participation in the digestive process, emulsification of fats, preparation and breakdown of food for further absorption;
- activation and enhancement of the action of pancreatic enzymes. These are lipase, trypsins, amylases;
- neutralization of the action of pepsins. The stomach environment is acidic, the intestinal environment is alkaline, it is bile that transforms digestion in the stomach to absorption in the intestines;
- improvement of intestinal motility, which facilitates the digestion and pushing of food masses;
- removal of metabolic hormones and active substances of drugs, toxins and poisons;
- participation in the transformation of fats from food masses, carbohydrates and protein, improving the absorption of minerals and vitamins;
- normalization of intestinal microflora, preventing the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Bile is not only a digestive secretion, but also a catalyst for the removal of various substances that enter the body.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of complications, patients must follow preventive measures. Organizing proper nutrition is a key point in prevention. It is recommended to follow the diet until two years after surgery. The body needs this period to adapt to the new functioning of the digestive system.
Attention! The diet strictly limits carbohydrates, fatty foods, alcohol, herbs, spices, canned food, onions, celery, basil, and garlic.
You should eat raw vegetables and fruits with caution. It is better to eat often, in small portions. Puree soups, boiled meat and fish, steamed cutlets, baked vegetables, juices diluted with water, weak tea and decoctions are allowed.
Liver pain that does not go away during the recovery period should be diagnosed by doctors to prescribe the correct therapy. To avoid complications, a gentle regimen is maintained until complete recovery. Gastrointestinal diseases require a special attitude of the patient towards his body.
Indications for surgery
Doctors say that recently only complete resection of the gallbladder is performed using laparoscopy. This is despite the fact that the procedure is also suitable for removing formed stones. When large stones are detected, surgeons believe that the structure and functions of the organ itself are significantly impaired. After removing the stones, there is a high probability of relapse or other problems with the gallstones. Since the bladder is not a vital organ, its complete removal is possible, although it leads to some restrictions for the person in the future. Laparoscopic surgery to remove the gallbladder is prescribed for the following conditions: Chronic cholecystitis. Detected polyps. Acute inflammation. Cholesterosis (accumulation of cholesterol in the walls of the bladder). In case of obstructive jaundice due to stones in the ducts, laparoscopy is also performed, which helps to get rid of stones and free the bile ducts.