Causes of follicular ovarian cyst
Pathological cell division is usually not observed in a follicular cyst. It is filled with liquid viscous contents, similar in properties to blood plasma. Such cysts can appear even in newborns, and with the onset of puberty, the risk of development is one fifth of all gynecological diseases diagnosed in patients before menopause.
Doctors identify two main factors that trigger the formation of a follicular ovarian cyst:
- excessive blood supply to the ovaries;
- variability of hormonal levels.
Girls suffering from infectious diseases of the urinary system are at risk. Infections that progress in the pelvis provoke intense blood circulation in the walls of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. As the disease progresses, congestion begins in the female genital organs, which in turn leads to damage to neighboring tissues.
With the onset of ovulation, menstruation or conception, blood flow in the tissues of the pelvic organs increases several times. Increased blood circulation is also observed during the postpartum and lactation periods.
Abundant blood flow to the ovaries, which increases the likelihood of follicular cyst formation, is caused by the following subjective factors:
- interrupted sexual intercourse;
- frequent lack of orgasm with strong arousal;
- prolonged refusal of sexual relations;
- tumor formations in the uterus;
- adhesions in the fallopian tubes;
- passive lifestyle;
- abdominal organ injuries;
- tendency to constipation;
- instrumental abortions;
- obesity.
A follicular cyst, provoked by variability in the hormonal balance in the body, can be a complication of nervous system disorders or a single-phase menstrual cycle, in which systematic anovulation is observed. Sometimes infertility treatment is carried out with strong stimulating drugs that cause ovarian hyperfunction, which provokes the formation of bilateral follicular cysts.
When diagnosing neoplasms of the pelvic organs, factors such as:
- nicotine addiction;
- being in a constant stressful situation;
- infectious lesions of the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- frequent hypothermia of the lower extremities and abdominal cavity;
- stimulation of ovulation for IVF;
- ignoring barrier contraception during sexual relations with new partners.
With stable ovarian function, a dominant follicle is produced in which the egg grows. With the onset of the middle of the cycle, the follicle bursts - the ovulation phase begins. The mature egg ends up in the fallopian tube, where it is ready to meet the sperm if conception is planned.
A follicular cyst is formed when the follicle is unable to complete its full cycle and ultimately release an egg ready for fertilization. Secretory fluid from granulosa cells accumulates in the resulting capsule. In addition, the cyst is filled with fragments of blood and lymph. Thanks to this content, the color of the neoplasm becomes light yellow, pink or light brown.
Follicular cysts in newborns are most often caused by the stimulating effect on the embryo of hormones circulating in the mother’s blood.
https://youtu.be/-18NP8nPopQ
What is this?
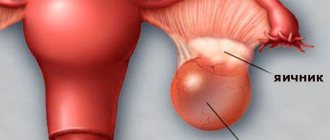
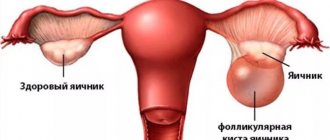
A follicular cyst is a benign ovarian formation consisting of a capsule and fluid accumulated inside. It is called follicular because it is formed from a follicle.
Normally, a woman's ovaries begin to grow several follicles every month. These are bubbles with liquid inside. In each such bubble an egg matures. A few days after the start of the menstrual cycle, one follicle becomes the leader in size. It's called dominant. The remaining follicles cannot withstand the competition and begin to decrease in size until they completely disappear. This process is called atresia.
By the middle of the cycle, the follicle reaches a diameter of about 2 cm. Then it ruptures and the egg is released into the abdominal cavity. There it is captured by the fimbriae, penetrates the fallopian tube, is fertilized and moves towards the uterus. But sometimes the follicle does not rupture. Instead, it continues to grow in size. This is how a follicular cyst is formed.
Is a cyst dangerous?
A follicular cyst is not considered a disease. It is one of two types of functional cysts (along with the luteal cyst, which is also called a corpus luteum cyst). In most cases:
- the appearance of formation does not require treatment;
- it does not cause pain or cause other symptoms;
- disappears after 2-3 months.
If the cyst becomes complicated, becomes too large or does not disappear after 3 months, it is removed.
Education often occurs against the background of delayed menstruation. Then comes heavy periods. Sometimes there are no symptoms at all. Such cysts can grow up to 10 cm, but generally do not exceed 6 cm. With a cyst larger than 6 cm, the risk of complications increases, so the question of surgical treatment is raised. Malignancy (malignancy) of follicular cystic formations is impossible because they do not contain adenogenic epithelium.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is the main method for diagnosing follicular or any other cysts. Ultrasound can reliably distinguish a liquid formation from a solid (solid) tumor. In most cases, with the help of ultrasound, the doctor can differentiate a functional cystic formation from another tumor.
Typically a functional cyst is round. Less often it is oval. The wall is thin, usually not more than 1 mm. The internal contents are always homogeneous. Diameter may vary. Usually it is at least 3 cm. The largest cysts reach 10 cm. A follicular formation less than 3 cm is not considered a cyst. It is called the dominant follicle.
Differences between other cysts:
Corpus luteum cyst. Often has a thick wall, from 3 to 6 mm. The size rarely exceeds 7 cm. Accordingly, if a cyst of 8 cm in diameter is detected, it is unlikely to be luteal. The content is heterogeneous. It looks like a spider web or mesh on ultrasound. There may be partitions inside. Such a cyst disappears much faster, on average after 2 weeks.
Thecal lutein cyst. Occurs with hydatidiform mole and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (one of the main complications of IVF). Formations often appear on both sides. They can be multi-chamber. At the same time, there are many signs that are similar to follicular cysts. This is a thin – about 1 mm – wall, homogeneous content. The sizes are comparable - theca lutein cysts have a diameter of 4-8 mm.
Endometrioid cyst. It is located mainly behind the uterus. Often the cysts are multiple, while the follicular one is single. Cysts do not move during palpation due to the adhesive process in the pelvis. Such women have a history of endometriosis. The size of cysts varies significantly. They can be from 1 to 8 cm. The wall thickness is greater than that of a follicular cyst and is 2-6 mm. The main difference lies in the content. In a follicular cyst it is anechoic, in an endometrioid cyst it is medium or highly echogenic. This means that it is denser. When the formation is percussed, there is no vibration of the fluid. A pathognomonic (unique, different from others) ultrasound symptom of an endometrioid cyst is a double wall contour.
Paraovarian cyst. The only way it differs is that it is located not in the ovary, but separately from it.
Teratoma. The contents inside can be quite varied. It is rarely a clear liquid. Such a cyst can contain anything: fat, bones, hair, etc.
Cystadenoma. The most common true ovarian cyst. May be serous or mucinous. The latter is divided into papillary and smooth-walled. Smooth-walled cysts are practically indistinguishable from follicular cysts. Sometimes they are larger in size; in 25%, partitions are identified inside. But if there are no partitions, and the size is up to 10 cm, then it is impossible to reliably distinguish such a cyst from a follicular one using ultrasound. Papillary cystadenoma is characterized by higher echogenicity (density) of the contents. The wall may be slightly thicker than that of a follicular cyst - up to 2 mm. The main distinguishing feature is the presence of growths inside.
Alternative diagnostic methods that are used much less frequently:
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Symptoms of follicular ovarian cyst
In most cases, the follicular cyst does not reveal itself in any way. It can even be argued that the pathology is “hidden” in nature. In adolescence, it is possible to track that the menstrual cycle occurs with a significant delay. Typical symptoms include the following:
- moderate pain in the lower abdomen;
- nagging pain in the groin area;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- low-grade fever;
- spotting between periods;
- discomfort in the vaginal mucosa.
Some girls complain of prolonged delays in menstrual flow, which last from several weeks to several months. The onset of menstruation after such a delay is characterized by a large amount of secreted uterine contents and increased pain. The more menstruation is delayed, the higher the risk of complications such as:
- cyst rupture;
- hemorrhages in the ovary or abdominal cavity;
- torsion of the cyst stalk.
Complications in the form of adhesions in the pelvis occur with dull nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Torsion of the cyst leg provokes venous stagnation, damage to nerve endings and small blood vessels. The next stage of the disease is an increase in the volume of the organ and increased swelling of the soft tissues around it.
Acute painful symptoms are caused by rupture of a follicular cyst, which occurs during high physical activity, sudden movements or sexual intercourse. When the torsion of the capsule leg bursts, the woman experiences high-intensity pain in the lower abdomen. The following discomfort sensations are also observed:
- "acute" abdomen syndrome;
- attacks of nausea;
- vomit;
- increased sweating;
- high anxiety;
- blackout;
- high body temperature;
- false urge to urinate;
- disturbance of intestinal motility;
- bloody discharge from the vagina.
The pain from a burst cyst does not decrease even with complete rest. The danger is ovarian apoplexy - hemorrhage from the cystic capsule into the organ itself. Signs of this pathology:
- unnatural pallor of the skin;
- anemia;
- rapid pulse;
- decreased blood pressure;
- loss of ability to work;
- delusional states;
- profuse cold sweat;
- numbness of the limbs.
Ignoring the initial symptoms of a ruptured follicular cyst carries mortal danger.
Symptoms
According to a survey of patients, this functional neoplasm is asymptomatic in most cases.
On ultrasound, it is very often discovered by chance during a routine preventive examination. If the size of the cyst is large enough or it continues to grow, then the woman already feels alarming symptoms, which include the following clinical signs:
- Delayed menstruation.
- Intermenstrual bleeding.
- Pain on the right or left side, a feeling of heaviness and discomfort.
- Heavy, painful or prolonged periods.
- The occurrence of pain after sex, sudden movements, heavy lifting and physical activity.
- Asthenic syndrome.
Symptoms appear in all patients individually, depending on the size of the cystic formation. In any case, you should immediately consult a doctor, as there is a high risk of complications such as tumor rupture or torsion.
If this does happen, then the woman experiences acute and unbearable abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and a sharp rise in temperature. In such a situation, you should immediately call an ambulance, as urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
IMPORTANT! Pain that occurs as a result of the progression of a follicular cyst usually manifests itself in the luteal phase of the cycle, when hormonal changes inevitably occur. This is a reason to be wary and do a control ultrasound of the pelvis
Follicular cyst of the right and left ovary
A follicular cyst of the left ovary is identical in symptoms and characteristics to a cyst that can form on the right ovary. The prevailing opinion that the right ovary is most susceptible to cyst formation is a myth.
The right ovary takes a more active part in the functioning of the reproductive system. In fact, it more often produces dominant follicles that produce an egg ready for fertilization. The main aorta and artery more intensively supply blood to the right ovary, having a direct connection with it. The left ovary receives blood from the renal artery in a bypass way.
However, apoplexy of the right ovary is diagnosed more often. Perhaps it is the proximity of the passage of the aorta and artery that is the stimulating factor in the pathology. But the frequency of cyst formation in both ovaries is not the same.
The anatomical features of a woman’s pelvic organs often make it difficult to make a diagnosis of inflammation of the appendix. The reason for this is the proximity of the caecum to the right ovary. When a follicular cyst of the right ovary ruptures, the same symptoms are observed as with acute appendicitis:
- feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity;
- cutting pain in the groin;
- temperature increase;
- false urge to urinate;
- constipation;
- attacks of nausea;
- tachycardia;
- profuse cold sweat;
- pale skin;
- fainting conditions;
- dizziness;
- loss of ability to work.
It is possible to determine the most likely cause of severe symptoms after an ultrasound scan.
Local treatment with folk remedies
It is advisable to combine a complex of traditional therapy with local baths and compresses. For a sitz bath, you can use the following composition of herbs: boron uterus, tansy, mantle, chamomile and celandine. The raw material in the amount of two tablespoons is poured with boiling water and left to cool completely. Then, after filtering the broth, the volume is increased to two liters. The resulting warm mixture should be poured into a small bowl and sit in it for 20 minutes. This procedure must be done daily for a week.
Treatment of follicular cysts can be carried out using local compresses. A ten percent salt solution resolves the tumor quite effectively. A moistened piece of cloth is applied to the lower abdomen for 30 minutes 4 times a day.
You can also prepare a compress from baking soda (1 tbsp), apple cider vinegar (250 ml), vodka (250 ml). The ingredients must be diluted with three liters of water.
Wormwood is often used to eliminate cystic formation. A handful of dry raw materials is brewed with hot water. Then the steamed herb is wrapped in cloth and applied to the right or left ovary.
Pregnancy with follicular ovarian cyst
Follicular cysts that remain on the walls of the ovary for several years increase the risk of developing adhesions in the abdominal cavity. This complicates the process of conception, acting as the root cause of female infertility.
Ovulation can only occur in a healthy ovary, so the chances of getting pregnant in patients with a follicular cyst are significantly reduced. Even when conception occurs, the risks of spontaneous miscarriage due to complications of the neoplasm are high.
After removal of the follicular cyst, in most women, reproductive function is fully restored. Cysts of large proportions, sometimes reaching 10-15 centimeters in length, pose a threat to the fetus.
When a cyst is diagnosed after successful conception and embryo development, a decision is made to remove the tumor by laparoscopy in the second trimester of pregnancy. By this time, the placental barrier is fully formed and provides protection to the fetus. However, medical statistics indicate that cystic neoplasms on the ovaries do not pose a high danger after conception.
During embryonic development, the mother's body produces increased prolactin. Thanks to this hormone, the production of further follicles in the ovaries is inhibited, which excludes a new conception against the background of an existing one, and, accordingly, follicular cysts.
Treatment
In 80% of cases they are eliminated on their own: they undergo reverse development. This process takes on average up to 3 menstrual cycles, after which it is necessary to undergo a control ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages. Large ones are eliminated by laparoscopy. This is one of the few methods that helps get rid of a tumor without extensive dissection of the skin. An additional advantage of the intervention is a rapid postoperative recovery period.
If a follicular cyst provokes ovarian rupture, the woman undergoes emergency surgery: the organ is removed or sutured, depending on the degree of damage. In both cases, after surgery, the patient undergoes hormone replacement therapy.
If the neoplasm appears against the background of oophoritis, in addition to the tumor, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of its development – inflammation. For this purpose, the woman undergoes antibacterial therapy. When a tumor occurs while taking contraceptives, treatment begins with stopping their use and selecting an alternative type of contraception. If the neoplasm is associated with constant exposure to stress, the woman will need to take sedatives and will additionally need to consult a psychologist.
Methods for diagnosing follicular ovarian cysts
When examined by a gynecologist, a follicular cyst can be felt when it is located in front or to the side of the uterus. It usually has a soft pliable consistency, a rounded top and a relatively smooth surface. The tumor moves easily with finger pressure. In rare cases, the cyst becomes painful when complications do not occur. Its dimensions range from 5-6 centimeters in diameter.
When the examination is performed two-handed, there is a high risk of cyst rupture and complications.
An informative diagnostic method is ultrasound examination, which is carried out with color Doppler mapping. Thanks to this, the doctor examines all the walls of the follicular cyst, determining its proportions and the place of attachment to the ovary.
If a specialist doubts the results obtained, laparoscopy, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the affected organ is prescribed.
It is not possible to diagnose a follicular ovarian cyst in utero. As soon as the baby is born, the pediatrician conducts monthly monitoring. In most girls, the cyst resolves without additional therapy after the first few months of life. Rarely, complications arise that require urgent surgical resolution. This:
- torsion of the cyst pedicle;
- ovarian ischemia;
- necrosis of the tissues of the pedicle and walls of the ovary.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods require special treatment tactics, which are divided into three periods:
- Expectant;
- Conservative (medicinal);
- Surgical.
If we talk about traditional methods, then such treatment does not require division into periods and can be applied from the first days of diagnosing the problem. It would be wrong to expect that visible results will appear fairly quickly. Treatment with natural remedies involves a long course of treatment, in which the emphasis is on regularity and method. Patient application of the prescribed procedures will certainly lead to a positive result.
When treating follicular cysts, various methods of alternative traditional medicine can be used. Depending on the degree of development of the disease, the following procedures are considered the most popular and effective:
- Internal herbal treatment based on normalizing hormonal levels and boosting immunity;
- Herbal medicine aimed at restoring the nervous system;
- Baths with herbal solutions, douching, tampons.
The use of all procedures in one therapeutic complex will allow you to solve your gynecological problem as quickly as possible.
Treatment of follicular ovarian cyst
In most patients, the effect on the follicular ovarian cyst is carried out with medication. The growth of atypical neoplasm cells is effectively suppressed by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Sometimes they resort to hormonal drugs.
In young girls, the follicular neoplasm resolves on its own after 1-3 menstrual cycles.
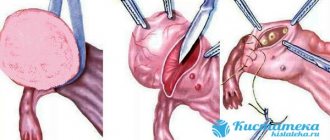
If conservative treatment of the cyst does not bring the expected effect, laparoscopy is prescribed, followed by enucleation of the capsule along with the pedicle. Before the operation, bed rest and cold compresses on the lower abdominal cavity are required.
During laparoscopy, a special probe is used that inserts a video sensor into the abdominal cavity through an opening in the abdominal wall. To preserve the ovary and reproductive function, the follicular cyst is enucleated.
When dealing with severe complications of an ovarian follicular cyst, accompanied by intra-abdominal hemorrhage, the ovary may be completely removed to save life. After menopause, the ovary on which the follicular cyst has grown is recommended to be removed.
Postoperative rehabilitation is reduced to restoring stable ovarian function. The body must receive the required amounts of microelements and vitamins. After surgery, temporary abstinence from sexual relations, full sleep and minimal physical activity on the abdominal organs are indicated.
There are often cases when, after getting rid of a follicular cyst, it appears again. It is extremely important to identify the root cause of the development of functional tumors in the body. The key to women's health will be regular gynecological examinations and preventive measures:
- rejection of bad habits;
- balanced diet;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- preventing infection with infections transmitted through sexual contact;
- compliance with the rules of daily intimate hygiene;
- exclusion of excessively active sports;
- long walks in the fresh air.
Relaxation procedures, massage, and spa treatment will have a beneficial effect on the female body. Hot baths, saunas and solariums, prolonged exposure to the sun, hypothermia of the pelvic organs and lower extremities are contraindicated.
To stimulate regression of the follicular cyst, some gynecologists recommend physiotherapeutic procedures:
- electromagnetophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- electrophoresis.
Physiotherapy without additional injections deliver fractions of drugs to the cells of the pituitary gland, adrenal cortex and ovaries, stabilizing their basic functions.
Oxygen therapy is effectively used to treat follicular ovarian cysts, which often recur. Oxygen administered intravenously saturates the meninges, cells of internal organs and tissues by 25-30%. One procedure is equivalent to a two-hour walk in a forest belt.
The use of hormonal contraceptives should only be regulated by a doctor. Gynecologists try to prescribe new drugs to prevent unwanted conception every two months. If the anamnesis does not allow preventing unwanted conception with hormonal contraception, it should be abandoned altogether, replacing it with a barrier one.
Options for ultrasound examination and features of its implementation
In gynecological practice, three types of ultrasound of the pelvic organs are used:
- Transvaginal ultrasound involves examining the reproductive organs through the vagina. The method is considered the most informative, since the distance to the internal organs is reduced. Allows you to identify small cysts. Not used in virgins;
- Transabdominal ultrasound is performed through the anterior abdominal wall. The distance to the pelvic organs is quite large, so the method is not very informative for small cysts;
- Transrectal ultrasound. The sensor is inserted into the rectum. In terms of information content, it is comparable to a transvaginal examination. It is used in virgins in cases where the transabdominal method did not produce results.
Scheme of transvaginal ultrasound.
The ultrasound procedure lasts from 5 to 15 minutes. This is enough for the doctor to detect an ovarian cyst or other pathology. All information about the examination is provided on the form. The ultrasound results are interpreted by a gynecologist.
Ultrasound data is not a diagnosis yet. The final conclusion is made by the attending physician after a complete examination.
Ultrasound examination in women of reproductive age is carried out on the 5-7th day of the menstrual cycle. If your periods are short, you can do an ultrasound earlier; if your periods are long, the examination will be postponed to a later date. During menstruation, ultrasound is performed only for emergency reasons. Before the onset of puberty and during menopause, an ultrasound examination can be done on any convenient day.
How to treat a follicular cyst
- Waiting tactics
Most often, when diagnosing a follicular cyst, treatment is limited to regular observation and expectant management for 2-3 cycles, while changes in the size of the tumor should be monitored over time using ultrasound.
- Homeopathic treatment, herbal medicine, folk remedies
If the cyst is no more than 6 cm, it resolves in 2-3 months; at the request of the woman, this process of reverse development of the cyst can be supplemented with treatment with homeopathy, folk methods (see treatment of ovarian cysts with folk remedies, homeopathy)
- Progressive modern physiotherapy treatments
To stimulate the regression of such a cyst, the doctor can refer the patient to physiotherapeutic procedures - ultraphonophoresis, magnetic therapy, electromagnetophoresis, SMT phoresis. These modern progressive physical procedures make it possible to painlessly deliver medications to the tissues of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and ovaries, normalizing metabolic processes in them.
- Oxygen therapy
When treating ovarian cysts, recurrent (repeating after a certain time), persistent cysts, it is very important to restore the harmony of brain activity and help the woman form the right way of thinking. A treatment method such as oxygen therapy, that is, oxygen therapy, can be carried out with modulation of the patient’s brain rhythms, which helps to normalize processes such as excitation-inhibition in the cerebral cortex, and also has a general healing effect. Oxygen saturates the patient’s brain, tissues and organs by 30%, which is equivalent to walking in the forest for 2 hours.
- Hormone therapy, vitamin therapy, anti-inflammatory treatment
Gynecologists recommend taking oral contraceptives for 2 months, but taking any hormonal drugs should be done after blood tests for hormones - FSH, LH, progesterone, estrogen (see the harm of oral contraceptives for a woman's health). The doctor may also prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy and vitamin therapy.
- Surgical treatment (see preparation and after laparoscopy of ovarian cysts)
Of course, if the tumor progresses, the diameter is more than 8 cm, it will not regress within 3 months, and in cases of recurrent cyst, doctors will insist on surgical intervention. Surgical treatment consists of laparoscopy, enucleation of the cyst, resection of the ovary, or suturing its walls.