Indications and prohibitions for examination
Ultrasound allows you to examine the ovaries, uterus and cervix, fallopian tubes, genitourinary system and kidneys. Such scanning is always performed at least three times during pregnancy. List of main indications for ultrasound:
- inflammation in the genitourinary or reproductive system;
- constant pain in the lower abdomen;
- suspicion of conception (including ectopic);
- bleeding;
- pathologies of the ovaries, fallopian tubes or uterus;
- urinary disturbance;
- find the uterine device;
- various pathologies suffered in the first trimester;
- tumors (or suspicions of them);
- checking the length of the cervical canal;
- cystic formations;
- oncology;
- cycle disruption;
- abnormal development of organs;
- abortion or complicated childbirth.
If the examination is carried out for the first time, then it can be done, regardless of the day of the cycle, but after the discharge has stopped. In some cases, ultrasound is prescribed strictly within a certain period of time. For example, with endometriosis, ovarian dysfunction, uterine fibroids, etc. There are no contraindications to ultrasound, except for open wounds or skin disorders at the site where the sensor slipped.
Ultrasound examination is now widely used in all areas of healthcare. To determine the presence of abnormalities or confirm their absence, a gynecological ultrasound is prescribed, which allows one to assess the current condition of the pelvic organs.
Indications for the study may be of different nature:
- Detection of structural changes in the uterus and appendages, inflammatory processes.
- Determination of the presence of fibroids, tumors, cysts, polyps.
- Establishing ovulation, diagnosing the course of pregnancy.
- Detection of signs of polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Research to determine the cause of infertility and others.
During the study, the condition of the uterine body, the presence of congenital or acquired pathologies, and the location of the intrauterine device are also diagnosed. When determining pregnancy, the location of the fertilized egg is determined. In case of development of the inflammatory process, the presence of adhesions is excluded or determined.
Even such a seemingly harmless procedure as ultrasound screening of the pelvic organs in gynecology has certain contraindications:
- progression of acute inflammatory processes;
- operations performed on the rectum or in the uterine cavity (performed transvaginally or transrectally, that is, interchangeable);
- pyoderma (purulent rashes on the skin);
- progressive infectious pathologies.
A referral for the procedure must be issued by a leading specialist, since he first conducts a full examination of the patient and pays attention to the presence or absence of prohibitions on ultrasound.
What can be seen during diagnosis
If a woman is prescribed an ultrasound after visiting the gynecologist, she will definitely be interested in knowing what screening of the pelvic organs can show. The presented diagnostic method is quite often used to confirm or refute various diseases, as well as body conditions.
During the examination, the following can be revealed:
- Type of pregnancy and location of the fertilized egg (in the uterine cavity, in the fallopian tube or on the cervix).
- Individual characteristics of the reproductive organ and developmental anomalies (bicornuate, saddle-shaped, double uterus).
- Progression of inflammatory diseases.
- Pathological proliferation of endometrial tissue.
- Determining the presence of purulent contents, fluid or blood in the fallopian tubes.
- Fetal remains after gynecological cleansing.
- The condition of the reproductive organs after childbirth.
- Tumor neoplasms with an approximate determination of the degree of their malignancy.
- The presence of polyps on the endometrial layer.
- Number, size and localization zones of myomatous nodes.
- Determination of cystic formations, including detection of pedicle torsion.
- The presence or absence of pathological fluid in the pelvic organs.
In gynecology, ultrasound is also actively prescribed to women who are about to undergo in vitro fertilization. Thanks to the study, it is possible to dynamically monitor the condition of the ovaries and determine the day of ovulation, subsequently monitoring the quality of embryo attachment and its stage of development.
Methods for performing the procedure
Before conducting a gynecological ultrasound, the specialist usually warns how the examination will be carried out. If the patient is a child or a girl who has not previously been sexually active, then a transabdominal sensor is used. In other cases, transvaginal is most often used. The first differs from the second in the way the study is carried out - through the stomach. In the second case, the sensor is inserted into the vagina.
If during the diagnostic process a specialist needs a more detailed study, then both sensors can be used alternately. There is also a transrectal probe, which is used by inserting into the rectum through the anus. This method is used if there are deviations in the development of the genital organs or if it is impossible to perform a gynecological ultrasound using the other two methods described above.
Depending on the purpose for which the patient is prescribed an ultrasound in gynecology, on what day of the cycle, what is her initial state of health, as well as the degree of complexity of the clinical case, specialists in the field of gynecology distinguish several types of diagnostics.
Ultrasound screening can be performed using several methods:
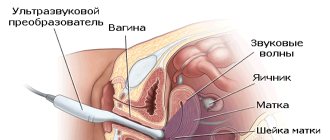
- transvaginally – provides the most accurate information if progression of pathologies of the female reproductive system is suspected (the sensor is inserted into the vagina);
- transabdominal – performed for patients who have not yet had intimate intimacy, as well as for diagnosing severe diseases (the sensor is in contact with the anterior wall of the abdomen);
- transrectally - in rare cases it is prescribed to virgins, and in terms of information content it is not inferior to the first method (the sensor is inserted into the rectum).
In gynecology, ultrasound is also prescribed to women when there is a need to assess the condition of the ovaries. This procedure is called folliculometry and is done transvaginally. During pregnancy, three routine screenings are always carried out. If the period is early (first trimester), then the sensor is inserted into the vagina; in later periods, an abdominal procedure is performed.
Gynecological ultrasound can be performed either as an independent examination or as part of an examination by a gynecologist. Very often, it is the gynecologist who performs the ultrasound examination. In this case, the ultrasound machine will be located in the gynecological examination room.
- Before the test, your doctor will ask you to empty your bladder if you are not a virgin. Before starting the procedure, you need to remove some of your clothes and lie down on the couch.
- A gynecological ultrasound is performed using a vaginal probe called an abdominal probe. This sensor is an elongated cylinder with a diameter of 2-2.5 cm. Before inserting the sensor into the vagina, the doctor will put a special nozzle or condom on it and apply a special gel that facilitates the passage of ultrasonic waves.
- After this, the sensor will be inserted into the vagina. This procedure is completely painless and should not frighten the patient. A gynecological ultrasound lasts only 10-20 minutes.
- At the end of the study, the doctor gives the patient a conclusion. Thanks to modern equipment, it is possible to shoot short films and take photographs, recording them on digital media. These images and films can be subsequently transferred to another doctor to review the patient’s medical history and obtain another independent opinion for a more complete picture of the condition of the female reproductive system.
At the Norma medical center, every woman will be able to undergo a gynecological ultrasound and learn everything about the state of her health. The clinic employs experienced specialists using modern equipment that allows for a complete diagnosis of diseases of the reproductive organs, based on its results, making an objective diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribing effective treatment.
Ask your question on the forum
Types of pelvic ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the pelvis can be of several types:
- transvaginal,
- transabdominal,
- transrectal.
The first type of procedure does not require any preliminary preparation. The bottom line is that a special sensor is inserted directly into the vagina. This technique allows you to collect the maximum necessary information, since the sensor is located in close proximity to the organs being studied.
The advantages of the transvaginal technique are as follows:
- the ability to obtain accurate visualization of the area under study;
- monitoring the condition of the internal organs of the reproductive system in real time;
- painlessness;
- the ability to conduct research in patients who have problems with urinary incontinence or other urological disorders.
Women are recommended to have a pelvic ultrasound once a year. Such preventive measures make it possible to identify gynecological pathology at the stage of its development, which means treatment will be faster and more effective.
Transvaginal ultrasound is also performed in the early stages of pregnancy. In this case, the procedure is needed for the following purposes:
- determination of intrauterine pregnancy;
- monitoring the condition of the ovaries and appendage area;
- observation of the embryo if a non-developing pregnancy is suspected;
- diagnostics for the risk of miscarriage.
Transabdominal examination is performed only on a full bladder. A few hours before the procedure, the patient needs to drink a liter of water and refrain from going to the toilet. Preparing for the study also involves a certain diet.
Important! A few days before the OMT ultrasound, you should avoid fatty and spicy foods, baked goods and drinks with gas.
Externally, the transabdominal version of the study resembles a regular ultrasound; the doctor passes a special sensor along the lower abdomen.
This method of ultrasound diagnostics has its advantages:
- the opportunity to see the condition of not only a specific organ, but also the entire small pelvis;
- a large tumor in the pelvis is clearly visualized;
- painlessness and harmlessness of the procedure;
- the opportunity to conduct an ultrasound examination of the pelvis in girls who have not started sexual activity.
Despite the large number of advantages, the transabdominal ultrasound scanning method has a number of disadvantages. The main disadvantages include:
- the image on the monitor will not be entirely clear, so the detail of the organs is quite poor;
- with a thickened abdominal wall or the presence of excess weight, problems may arise with visualizing the pathology of the uterus and appendages;
- adhesions in the pelvis can complicate diagnosis.
This scanning method is inferior in its information content to transvaginal ultrasound.
During transrectal ultrasound, a special ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum. The study is excellent for young girls (virgins), and is also used in studies of the male pelvic organs.
Diagnostic subject
There are several symptoms for which a gynecologist is required to write a referral for an ultrasound examination. You should check with your doctor in advance on which day of the cycle to perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. You can sign up for it without a referral if you:
- the lower abdomen hurts for a long time;
- there is vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor or an unclear consistency that has not previously been observed;
- bleeding that does not fit into the menstrual cycle;
- there are prerequisites for suspicion of the formation of tumors or cysts;
- diseases associated with inflammatory processes - infectious, sexually transmitted diseases;
- There is an inconsistent menstrual cycle or no periods at all.
It is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs before and after an abortion, as well as after surgery in the patient’s area of interest. During pregnancy monitoring, a woman visits the ultrasound therapy room 3-4 times. If the pregnancy is complex, then such diagnostics can be prescribed much more often.
According to the ranking of diseases, the most common diseases detected by ultrasound are:
- enlarged endometrial layer;
- cystosis, polycystic disease and ovarian tumors;
- corpus luteum cystosis;
- erosion of the uterus;
- uterine fibroids;
- pathology on the cervix.
If a cancerous tumor or uterine fibroids is suspected, in addition to external ultrasound (transabdominal), they also do hysterography - an ultrasound examination with the introduction of a lipid solution or water-soluble substance into the vagina. This diagnostic method allows you to thoroughly study the internal contours of the uterus.
When a woman cannot get pregnant for a long time, ultrasound is the first thing that helps the doctor determine the problem. He also paints the specialist a clear picture of the location of organs and possible pathologies leading to infertility. The answer to the question of which day of the cycle is best to do a gynecological ultrasound depends on what information the doctor or patient ultimately wants to receive.
For a woman planning a pregnancy, it is very important to know on what day of the cycle to do a gynecological ultrasound. In the best case, this is 3-5 days from the start of menstrual bleeding, but no later than the 7th day. This period is symbolic in that the inner lining of the uterus has a thin structure and clearly shows the presence of small tumors, polyps, and cysts. The thickness of the endometrium also allows you to determine the likelihood of successful conception in the current cycle.
Among the standard parameters for any girl or woman, the subject of research is the measurement of the thickness, width and length of the body of the uterus, the condition of its appendages. If the reason for performing an ultrasound is an inflammatory process, then the specialist additionally determines the structure, size and location of its focus.
Ultrasound after menstruation - when to do it, why there are restrictions
Ultrasound examination of the uterus is carried out to prevent gynecological diseases associated with endometrial disorders, if pathology in the genital organ is suspected.
Indications for ultrasound are:
- menstrual irregularities;
- absence of menstruation for a long time;
- infertility;
- menopause;
- heavy menstruation;
- the appearance of blood between periods;
- presence of pain in the lower abdomen.
As a result of the examination, specialists identify:
Gynecological diagnosis is carried out using several types of ultrasound examination.
Reasons for limitation
The second reason for gynecological ultrasound on certain days of the cycle is egg maturation. A follicle in the form of a cyst forms on one of the ovaries. Reaches a size of 3 cm. This is a normal natural process that is not a pathology. But this may also hide health problems. Since it is difficult to distinguish a pathological cyst from normal maturation of the egg in the follicle. After menstruation, the natural cyst disappears, but the pathological one remains. Therefore, it is very easy to diagnose it at the beginning of the next cycle.
The indication for a gynecological ultrasound in the middle of the cycle, at the end is to monitor the maturation of the egg, ovulation, in order to identify the causes of infertility and problems with conception.
Diagnosis of the uterus and other genital organs is carried out in 3 ways, selected based on the age, indication, and condition of the woman.
It is an indispensable method for identifying pathologies and diseases. The specialist inserts the sensor into the vagina. The woman does not experience any painful sensations, but there is a feeling of discomfort. The transvaginal sensor is located in close proximity to the uterus, ovaries, and other genital organs, allowing you to obtain a clear image on the screen. Internal ultrasound is performed by specialists to detect early pregnancy when other methods do not allow us to consider its presence. It is recommended to do an ultrasound examination on days 5–7 of the cycle. Transvaginal scanning is not performed for virgins, women with uterine bleeding, or heavy periods.
This examination method is performed extremely rarely when it is impossible to conduct a transvaginal examination. The specialist inserts a special sensor into the rectum. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and uterus is done on any day of the cycle according to indications.
To carry out a clear diagnosis, a specialist may recommend other examination methods: hysterography, Dopplerography.
Diagnosis is based on the administration of a special substance into the vagina. Then a regular external ultrasound is performed. It is recommended to undergo an examination if you suspect a cancerous tumor or uterine fibroids.
Preparatory activities
Diagnosis using ultrasound does not require any special preparatory measures. But some actions can improve the quality of the picture on the monitor screen, which will make diagnosis easier.
There is no need to do any other preparatory procedures. The entire diagnostic procedure takes from 5 minutes to half an hour. During the process, pictures are taken, the computer provides information about possible pathologies of the uterus, endometrium, other organs of the reproductive system, etc. After diagnosis, no measures need to be taken.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU HAVE A FIBROID, CYST, INFERTILITY OR OTHER DISEASE?
An effective remedy for the treatment of endometriosis, cysts, fibroids, unstable menstrual cycle and other gynecological diseases exists . Follow the link and find out what the chief gynecologist of Russia recommends to you
Did you like the article? Share with your friends!
In what cases is the procedure not recommended?
If a woman has an irregular cycle or the procedure was scheduled in advance under her health insurance policy, her period may start at the wrong time. This raises the question of whether it is worth undergoing an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, as well as other body systems.
There are a number of reasons why ultrasound diagnostics of the uterus and ovaries cannot be performed during this period.
Ultrasound during bleeding is performed not only in emergency cases. Some examinations give the most reliable results at this time. These include:
- menstrual flow is too heavy. May be a symptom of pathological changes;
- suspected ectopic pregnancy;
- critical days during an expected pregnancy with a short term;
- presence of bleeding between menstrual cycles;
- suspicion of the development of polyps, fibroids or endometrial hyperplasia. To clarify the situation, an ultrasound scan is necessary in the first couple of days of menstruation;
- Diagnosis of the condition of the follicle. In this case, several screenings are carried out in the first half of the cycle. This helps to understand the causes of infertility or menstrual irregularities;
- clarification of the type of cystic formations. For the study of small cysts (up to 10 mm), the first 5 days of the initial phase of the cycle are optimal;
- sharp pain like a woman during menstruation;
- acute inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs.
In gynecological practice, experts identify a number of diseases and conditions for which the patient may be prescribed the procedure in question.
The main indications are:
- Suspicion of pregnancy.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Determination of treatment tactics and control of drug therapy for endometriosis.
- Detection of tumors and other neoplasms.
- In preparation for the curettage procedure and after it.
- Scheduled preventive examination.
- Identifying the causes of infertility.
The indications presented are the most common, but according to medical opinion, the list may be expanded.
Optimal timing
The doctor makes the decision on which day of the cycle to do an ultrasound on an individual basis. In many ways, the period of the procedure depends on the goal being pursued.
Gynecological ultrasound is considered the best way to determine the period of ovulation. It is used for problems with fertilization, during preparation for IVF and during the diagnosis of infertility. The procedure is carried out several times. This is due to difficulties in identifying the dominant follicle.
As a rule, the first time the study is carried out on days 8-13 of the cycle. At this point, the size of the follicle reaches 15 mm. The second time, an ultrasound is performed on days 14-15. As a rule, with a stable cycle, ovulation occurs during this period. The size of the follicle reaches 20 mm. After this, its rupture and complete disappearance are noted.
The easiest way to identify cystic formations and fibroids is a few days after the end of the critical days. True, gynecological ultrasound is not always performed during this period. For example, if endometriosis is suspected, the procedure is performed twice. For the first time, it is prescribed 5-7 days after the arrival of the regulator. Repeated testing is recommended on days 26-28 of the cycle, immediately before the start of your critical days.
To determine the condition of the ovaries and identify disturbances in their functioning, ultrasound examination is performed repeatedly:
- Day 5 of the cycle. It is possible to measure reserves and evaluate morphology. The appendages are still at rest;
- 8-10 days. At this time, the late follicular phase is noted;
- 14-16 days. This period marks the early ovulatory phase;
- 22-24 days. Study during the luteal phase.
If you delve into the physiological characteristics of the female body, you can figure out on your own what day of the menstrual cycle to do a gynecological ultrasound. The favorable time for an ultrasound is the first 3-5 days after menstruation, counting from the very first day of the onset of menstruation. However, it is not recommended to conduct the study later than 8-10 days of the menstrual cycle. The appointment of gynecological ultrasound exclusively in the first phase of the menstrual cycle is not accidental.
This is due to the fact that it is during this period of time that the mucous membrane of the uterus, the so-called endometrium, has a minimum density. And with a reduced endometrial layer, pathologies of the uterine cavity such as fibroids, hyperplasia, cysts and polyps are quite easily visualized. Therefore, only a qualified specialist can correctly set the date for an ultrasound scan.
In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, a significant thickening of the endometrium occurs, therefore, the smallest pathologies may be hidden in its layers, which will go unnoticed in a given time period.
It is noteworthy that during the period from the middle and in the second phases of the menstrual cycle, small cysts with a diameter of about 2 cm can alternately form in the ovaries. As a rule, this is either a follicle that should ovulate in the near future, or a kind of corpus luteum cyst that forms on the spot ruptured follicle and can last up to two weeks.
The indication for an ultrasound before menstruation is the diagnosis of the formation and development of the follicle to ascertain the completed phase of ovulation. Typically, this procedure is performed to evaluate and treat women with infertility or in preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages, as well as the fallopian tubes, must be performed within the above-mentioned periods, namely, on days 6-8 of the menstrual cycle. But there are circumstances in which the doctor needs to assess the functionality of the ovaries, namely the development of the follicle and the subsequent formation of the corpus luteum. In such cases, the question arises when is it better to do an ultrasound of the ovaries.
If a patient who consults a gynecologist complains of pain in the lower third of the abdomen, purulent discharge or excessively heavy menstruation, then on what day of the cycle an ultrasound is performed is not significant. If menstruation is delayed, the procedure is carried out upon request to exclude serious pathological processes.
Ultrasound diagnostic device
Ultrasound examination of the ovaries
If we talk about determining the functioning of the ovaries, then on days 5-7 of the cycle, a gynecological ultrasound will be more effective. As a result of the study, the following information can be obtained:
- Dimensions - normally their length is 30-41 mm, thickness - 14-22 mm, width - 20-31 mm.
- The location of the organs should be on the sides of the body of the uterus, at a slight distance from it, while the ovaries should not be identical to each other, or have an oval shape.
- At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, follicles are visualized at different stages of maturity. If the study is carried out in the second phase of the cycle, then the corpus luteum should already be visualized, which will indicate the onset of ovulation.
On what day of the cycle is it better to do an ultrasound?
Many diseases of the female reproductive system develop almost unnoticeably.
For this reason, experts recommend examining the pelvic organs using ultrasound once a year. This procedure should be prescribed at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. Most often, doctors prescribe diagnostics on days 5–7 of the cycle. Why do specialists prescribe pelvic ultrasound for women after, and not before, menstruation? After menstruation, the endometrium (uterine lining) is very thin. This factor contributes to detailed visualization of possible pathology. By day 20, the mucous membrane will already be quite thick, which makes diagnosis difficult.
An ultrasound of the uterus is done 3-5 days after the end of menstruation. The optimal period is considered to be the 7th day of the cycle. Doctors recommend conducting the study no later than 10 days from the start of the critical days.
Ultrasound before menstruation, as a rule, is not performed. During this period, the study is not able to show the exact condition of the organs of the reproductive system. True, sometimes they resort to unscheduled examinations. Then the day of the cycle is no longer taken into account. Among the indications for its implementation are:
- infertility;
- delay or complete absence of menstruation;
- irregular periods;
- the onset of uterine bleeding;
- uncharacteristic vaginal discharge;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- excessive increase in size of the reproductive organ, revealed during examination in a gynecological chair.
Which day to choose
The first thing you should pay attention to when planning an examination is what day after your period you can do a gynecological ultrasound.
When asked on what day of the cycle to do an ultrasound of the uterus during the initial examination, any specialist will answer unequivocally - an OMT ultrasound is done on days 5–7 of the cycle. On the fifth day, when your period ends, you can see the formation of 6 or 7 follicles at once, then the dominant one will stand out among them. The next uterine examination will be scheduled on days 12, 13 or 14 - a couple of days before ovulation. A control, third ultrasound 3-4 days before the onset of a new menstrual cycle is also possible.
And also a pelvic ultrasound on days 5–7 of the cycle, after the end of menstruation, is done in cases where it is necessary to check the ovaries or conduct an examination of the fallopian tubes. By analogy with examination of the uterus, in the case of a thorough study, the ovaries are examined three times per cycle - at the beginning, before ovulation and after. The last time an ultrasound is done is on the 23rd day of the cycle.
This examination is carried out by:
- for menstrual pain in the lower abdomen;
- for painful sensations during sexual intercourse with a partner;
- in preparation for pregnancy.
On days 8 and 9 of the cycle, ultrasound shows possible problems with ovulation. During this period, ultrasound is prescribed for women diagnosed with infertility of unknown etymology. The gynecologist prescribes examinations on these days for patients with a standard 28-day cycle; if the cycle is longer or shorter, then the doctor will select the days individually.
If there are problems with conception, doctors often prescribe an ultrasound for the last week of the cycle. On day 19, ovulation has just ended and the body is prepared for the birth of the fetus. What will an ultrasound show on days 20, 21, 22 of the cycle? The sensor examines the amount of the endometrial layer - the biological material that covers the walls of the uterus for the comfortable existence of the fetus.
By this time, the endometrial “cushion” reaches its peak - from 11 to 20 mm. If the endometrium by this time is much larger than normal, this indicates endometriosis. If it is less, then the body malfunction most likely occurs at the hormonal level. The examination may reveal inflammation of the endometrial layer - endometritis. With advanced endometritis, it will not be possible to get pregnant, since the cushion of the endometrial layer becomes denser, and the uterus is not ready to accept the fetus.
In some individual cases, the gynecologist may prescribe an ultrasound on days 2–4 of the cycle - the stage when menstruation has not yet ended. This period is best for follicle examination. The study will help to understand whether a woman is planning to ovulate this month. Even these days, women undergo ultrasound diagnostics at the preparatory stage for in vitro fertilization (IVF).
A problematic pregnancy or lack thereof can be affected by problems with the kidneys, adrenal glands and ureters. These organs can indicate diseases of the reproductive system or determine the cause of hormonal imbalance. This explains why a gynecologist can write a referral for such an examination. Ultrasound of the kidneys is done in combination with other organs being examined using external scanning. The procedure can be performed regardless of the day of the cycle.
In order to track the appropriate date for conception, folliculometry is performed. As a rule, the doctor determines in advance on what day to do a gynecological ultrasound in order to obtain accurate information about the onset of ovulation. To monitor the maturation of the dominant follicle, a repeat study will be required on the 10-11th day of the menstrual cycle.
A mature follicle, ready for fertilization, is visualized in the second phase of the menstrual cycle (days 14-16). By the time of ovulation, its size is approximately 20-25 mm. During diagnosis, a specialist can determine the structure of its capsule; it is thin and contains liquid inside. Towards the end of the cycle, a third gynecological ultrasound is performed. It is done on the day of the cycle approximately 21-24, when it is already possible to establish the fact of implantation of the fertilized egg.
The universal time for carrying out various manipulations in relation to one or another pelvic organ is considered to be the first five days after the end of menstruation. Or is it the first 10 days of the general menstrual cycle. On days 5-7 of the menstrual cycle, it is possible and recommended to conduct examinations of the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes. Diagnosis of the ovaries is carried out several times throughout the entire cycle to obtain more accurate and reliable results.
In what phase of the menstrual cycle should a pelvic ultrasound be performed?
On what day of the cycle an ultrasound should be done is indicated by the doctor. The exact date depends on the expected diagnosis and the woman’s general well-being. For example, an emergency examination is carried out in case of bleeding or pain in the lower abdomen. In this case, the day of the menstrual cycle does not matter.
Reference! Most often, doctors recommend performing an ultrasound examination on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle.
If there is a suspicion of uterine fibroids, then the manipulation is carried out immediately after the end of menstruation. To diagnose endometriosis, an ultrasound is performed before the onset of menstruation. When planning a pregnancy, the patient undergoes research in the first and second phases of the cycle.
During pregnancy, ultrasound diagnostics are performed to confirm the fact of pregnancy and in each trimester. At 11-12 weeks, the doctor conducts the first fetal screening, and at 18-22 weeks - a second screening and 32-34 weeks - an ultrasound of the fetus. Every study is important because... allows you to identify a certain pathology of the fetus at each stage.
How to prepare properly
When a patient is prescribed a pelvic ultrasound in gynecology, preparing for this procedure will not be difficult, but there are some nuances, and they have a direct relationship with the method by which screening will be performed.
When carrying out transabdominal diagnostics, you need to stop eating foods that cause fermentation in the intestines (fatty foods, carbonated drinks, beans, legumes, cabbage, black bread) about three days beforehand. On the eve of the study, in the evening, dinner should be no later than 19:00, in the morning you are only allowed to drink clean water.
If a transvaginal ultrasound is prescribed, then it is also necessary to follow a diet; before diagnosis, you should refrain from eating for about 4 hours, and you must empty your bladder before entering the procedure room. In the case of a transrectal examination, it will also be necessary to perform a cleansing enema.
What does a normal uterus look like on ultrasound?
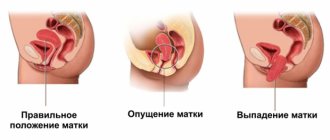
First of all, the doctor will analyze the position of the uterus: the tilt of the organ towards the bladder or rectum should be clearly visible.
The size of the uterus is assessed in this way: they must correspond to the age and condition of the patient. The following parameters are typical for nulliparous girls: length 42-48 mm, anterior-posterior size about 34 mm, width 42-50 mm.
In a patient in whose life there was at least one episode of pregnancy, but no childbirth (miscarriage or abortion), the dimensions will be different: length - 48-54 mm, approximately 37 mm - anteroposterior size and 45-55 - width of the uterus.
For those who have given birth, the dimensions are as follows: 48-60 mm - width, 55-61 mm - length, 38-42 - anterior-posterior dimensions.
Endometrial thickness indicator: on the 7th day of the cycle it should be 1-2 mm; after ovulation (when it is actively growing), its thickness can already reach 10-15 mm. It is good if the muscle layer is not involved in the tumor process and is homogeneous.
Some patients, out of ignorance, believe that a pelvic ultrasound can be done on any day of the cycle. This is wrong.
There are certain standards that are usually indicated in the transcript of the results. Average values depend on the patient’s age, the presence of pregnancies, childbirth, and the duration of menopause. Normally, the width of the uterus should be between 46-64 mm, thickness - 30-40 mm, length 45-70 mm.
It matters how and on what day a gynecological ultrasound is performed to measure endometrial thickness. Depending on the day of the cycle, it changes, from a lower value to a larger one. So, from the first to the fourth day from the beginning of menstruation it is 1-4 mm, from the fifth to tenth day - up to 10 mm, from the eleventh to fourteenth - up to 15 mm, from the fifteenth to twenty-third - up to 20 mm, from the twenty-fourth and until the end of the cycle - up to 17 mm.
To determine the condition of the endometrium, it is not enough to know its thickness; it is also important to determine its structure. Before ovulation, an ultrasound scanner can determine the degree of growth of the inner layer. It is noteworthy that when the egg is released, it stops growing and begins to thicken. If implantation does not occur, then endometrial rejection occurs.
There are certain M-echo norms, deviation from which may indicate the presence of deviations. Thus, hyperplasia is defined as a thickened and ovoid shape of the inner layer with smooth and clear contours. In this case, the resistive index deserves special attention. If its value is less than 0.6-0.8 mm, then there is a possibility of developing a neoplasm in the endometrium. An increase in M-echo by 1-3 mm is also subject to control, provided that its structure is within normal limits.
You should not look for an answer to the question: “Which gynecological ultrasound is better?” Because any method of conducting research can reveal certain deviations. Naturally, modern sensors are highly sensitive and can detect deviations in the photo. Which of these can be determined by ultrasound? For example, anomalies in the development of the genital organs, uterus, appendages.
Thanks to this study, its structure can be visually determined. It happens that a woman’s uterus has a septum, is divided into two or one part (bicornuate, unicornuate with one fallopian tube), is very small in size or is completely absent (agenesis). Without gynecological ultrasound, it would be difficult to detect such abnormalities. As well as the presence of fibroids, polyps, endometriosis and others.
Decoding the results
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women shows the presence of pregnancy at the earliest stage, allows you to determine the condition of the fetus and the degree of its development. Routine screening examinations make it possible to monitor the formation and growth of a child in order to take timely measures if any deviations from the norm are detected.
Ultrasound examination is a reliable method for the timely detection of ectopic pregnancy - a dangerous pathology that threatens a woman’s life. In this case, the fertilized egg is located in one of the fallopian tubes, and not in the uterine cavity.
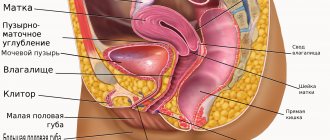
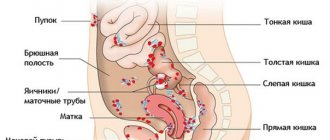
Pelvic ultrasound in women includes examination of the internal genital organs: the uterus and its cervix, ovaries, fallopian (uterine) tubes, bladder and rectum.
When interpreting the results, the uzologist must take into account the woman’s age, the structural features of the internal organs, the number of births and abortions performed. Despite all the advantages and informativeness of ultrasound, a specialist cannot make an accurate diagnosis based on examination data alone.
Uterus and cervix
Ultrasound examination of the uterus makes it possible to assess its position, shape and size, and identify the presence of structural changes. Normally, the body’s indicators should be as follows:
- length – about 7cm;
- width – about 6 cm;
- anterior-posterior indicator – 4 cm.
In addition, using ultrasound, the doctor examines the condition and thickness of the endometrium. These indicators of the mucous membrane should correspond to the day of the monthly cycle.
The study allows for the timely detection of diseases such as fibroids, endometriosis, malignant tumors of the uterine body and cervix, cervical erosion, and abnormal development of the genital organs.
The fallopian tubes
The fallopian tubes are hollow in structure, so in a healthy state they are not visualized on the monitor. They are mainly examined to check patency when a woman has problems conceiving. To do this, a contrast procedure is performed - a special substance is injected into the uterine cavity to assess the condition of the fallopian tubes and the presence of adhesions. Such an examination is prescribed on days 12-14 of the cycle.
Ovaries
Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the position, structure and size of the ovaries. Normally, the indicators should be as follows:
- length – about 3cm;
- width – about 2.5cm;
- thickness – about 1.5cm.
In women of childbearing age, the presence of follicular cysts in the appendages is a normal variant. Examination of the ovaries helps to identify the presence of cysts, polycystic disease, salpingitis and malignant neoplasms.
In case of problems with conceiving a child and treatment for infertility, folliculometry is performed - monitoring changes in the organs of the woman’s reproductive system throughout the entire menstrual cycle. Control is exercised over the formation and release of the follicle, and the correspondence of its size to the day of the cycle.
Bladder
The study allows you to determine the size, shape of the hollow organ and the patency of the ureters. Normally, the bladder should be free of stones, sand and tumor growths. After emptying, the organ should be completely freed from residual urine.
Deadlines
If women in menopause can undergo ultrasound examination on any convenient day, then with fertile patients the situation is more complicated. There is a clear dependence of pelvic ultrasound on menstruation. We will now discuss each option in detail.
A pelvic ultrasound for a routine examination is prescribed by a doctor without the patient’s complaints for a full examination, or the patient herself decides to have an ultrasound “for prevention.” This screening version of an ultrasound examination is performed on days 5-7 of the cycle - that is, on days 5-7 from the start of the next menstruation.
During this period of the cycle, women have a thin endometrium, the uterine cavity is clearly visible, the ovaries are calm, and there are no cystic formations or follicles growing for ovulation. These are the best days to perform a routine pelvic ultrasound in healthy women.
Pelvic ultrasound to assess ovulation and folliculometry. Most often, this type of examination is performed for women with unclear forms of infertility, menstrual irregularities, as well as in IVF and ovulation stimulation programs. The purpose of ultrasound examination in this case is to record the process of ovulation - the release of a mature egg from the ovary into the abdominal cavity for potential fertilization.
It is advisable to perform such an ultrasound to “search for ovulation” in the middle of the menstrual cycle. Many women a priori consider days 13-15 to be the middle of their cycle, but this rule only works for patients with the “classic” version of the menstrual cycle – 27-28 days.
However, there are many women whose cycle differs from the generally accepted one, more or less, and ranges from 21 to 40 days. In this situation, it is advisable to “look for ovulation” on individual days for each woman.
In addition to establishing the fact of ovulation and its presence, ultrasound is widely used for so-called folliculometry - measuring the size of the dominant follicle preparing for ovulation.
A mature follicle, ready for ovulation, is considered to be a full-fledged follicle measuring 18-22 mm. It is on the days it reaches this size that ovulation occurs and the likelihood of pregnancy increases significantly. This rule is widely used by gynecologists and reproductive specialists in sperm insemination and ovulation stimulation programs.
Pelvic ultrasound to assess the condition of the endometrium. The mucous membrane of the uterus - the endometrium - is also very susceptible to changes during the menstrual cycle. Ultrasound is used to assess the condition of the endometrium in two main cases:
- Diagnosis of hyperplastic processes of the endometrium - polyps, endometrial hyperplasia, as well as submucous fibroid nodes. In this option, ultrasound examination should be performed twice - on the 5-7th day of the cycle and on the eve of menstruation - 3-5 days before the expected menstruation.
- Assessing the condition of the endometrium in cases of pregnancy. In this option, it is better to perform an ultrasound of the uterus on the eve of menstruation - 3-5 days before the expected menstruation.
Pelvic ultrasound to assess the condition of the ovaries. The ovaries are also very, very variable throughout the menstrual cycle. Very often, during ultrasound examinations of the pelvis, various cysts are accidentally found. As a rule, the doctor invites the patient to observe the finding over time.
It is very important to assess the condition of the ovaries on the correct days of the menstrual cycle. The ideal time for this is days 5-7 of the cycle. On other days of the cycle, cystic formations can be represented by so-called functional formations - dominant follicle, functional cyst, corpus luteum, corpus luteum of pregnancy, corpus luteum cyst.
Pelvic ultrasound for diagnosing endometriosis. Endometriosis has become a real problem in modern gynecology. This diagnosis is very difficult to confirm. An ultrasound examination can only suggest this diagnosis, describing the picture as “ultrasound signs of adenomyosis” or “ultrasound picture of an endometrioid ovarian cyst.”
Performing it on days when the disease is at its peak can significantly increase the value of ultrasound. To do this, you can do an ultrasound on the first day of your period or immediately before it. These days, the picture of endometriosis becomes more vivid, typical, and it becomes easier to assume a diagnosis.
Pelvic ultrasound for diagnosing early pregnancy. As a rule, women initially learn about a suspected pregnancy through urinary pharmacy tests. If a woman feels well, has no complaints and does not have any complicated history, for example, a previous ectopic pregnancy, then such a pregnant woman does not need an additional ultrasound examination. Her first ultrasound will be at about 12 weeks - genetic screening for genetic abnormalities of the fetus.
If a woman is worried about something, the tests are questionable, terminations of pregnancy and ectopic pregnancies have been observed in the past, and if the patient is determined to terminate the pregnancy, then an early pregnancy can be determined by ultrasound.
It is important to understand that this is not necessary to do this too early - the fertilized egg may not have time to descend into the uterine cavity, the ultrasound doctor will not see it and will be forced to diagnose the patient: “Ectopic pregnancy” is in question.
The ideal option for early diagnosis of pregnancy is 5-7 days of delay of menstruation, subject to a positive test. If there is bloody discharge and pain in the lower abdomen with a positive test, the test should be performed immediately.
In what way, as well as on what day, a gynecological ultrasound will be scheduled is determined by the leading specialist. If the procedure is prescribed as planned, then the optimal time will be the first half of the menstrual cycle.
At this time, the endometrial layer is quite thin, so it lends itself well to visualization on the monitor, and the doctor can easily identify pathological abnormalities. Polyps, condylomas, and small tumors will be clearly visible on the mucous membrane. If you clearly answer on what day a gynecological ultrasound is performed, then this is the 3-5th day after the end of menstrual bleeding.
It is also worth noting that starting from the second phase of the cycle, a corpus luteum forms on the ovary, which can be mistaken for a pathological cystic formation. In addition, the question may arise as to when it is better to do a gynecological ultrasound if there are complaints about deteriorating reproductive health.
When a woman notices that her menstrual cycle has gone wrong, pain in the lower abdomen appears, and there is atypical vaginal discharge with a characteristic unpleasant odor, then the procedure can be performed on any convenient day. If there is a delay, diagnosis is made on the 5-10th day.
Optimal time for ultrasound, depending on the purpose of the examination
Ultrasound examination can be carried out in two ways:
- transabdominal (After lubricating the dermis of the abdomen with a special gel, the specialist places an abdominal sensor above the womb. An image of the uterus is displayed on the screen);
- transvaginally (The woman should take off her underwear and lie down. Her legs should be spread wide enough for the doctor to have access to the genitals. The specialist inserts a thin sensor into the vagina, on which a special condom is placed).
To do an ultrasound, you need to take with you a diaper, a towel, and a referral for diagnostics. If the examination is performed transvaginally, you need to take a condom. No special preparation is required.
What will a pelvic ultrasound show? If everything is normal for a woman, the uterus will be visible on the screen, which is small in size, has a well-developed muscle layer, and mucous membrane. The mucous membrane should correspond in thickness to the day of the menstrual cycle.
When examined, the fallopian tubes are similar to hollow cords that have oval cellular formations at their ends. These formations are ovaries.
Normally, there should be no formations or inclusions inside the uterine cavity (exception is pregnancy).
Pelvic ultrasound is very popular. This diagnostic method has some advantages over other methods of examining the pelvic organs. Its advantages are:
- absence of ionizing radiation;
- non-invasiveness;
- allowed during pregnancy;
- diagnosing various diseases of the reproductive system and urinary tract;
- image of tissues in “real time” mode;
- providing a clear image of soft tissues that are difficult to see with x-rays.
On what day of the menstrual cycle is it better to do a pelvic ultrasound?
During the study it is possible to determine:
- the structure, size and position of the reproductive organ, as well as the thickness of its walls;
- the number of follicles and their exact sizes;
- proliferation of tumors in the ovaries and uterus.
Any deviations from the norm indicate the presence of violations. Among the pathological signs that are detected during ultrasound are:
- thickening of the fallopian tubes. Indicates an increased risk of onset of a malignant process;
- oval or round objects. Most likely these are fibroids or cysts;
- reduction in the size of the reproductive organ and enlargement of the appendages. As a rule, such changes indicate polycystic disease;
- change in echogenicity. Fixed for endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
If you are recommended to have a pelvic ultrasound, when should you do the test? For standard manipulation, it is recommended to schedule the procedure for the first half of the cycle. Gynecologists advise going to a specialist immediately after the bleeding is completed. It simply doesn’t make sense to do an ultrasound before. During menstruation, the uterus is filled with blood. Diagnostics will not be able to provide reliable information.
Conducting research before menstruation is also not recommended. The fact is that in the second phase of the cycle progesterone is actively released. This hormone helps thicken the endometrium. If you visit an ultrasound room at this time, the specialist may simply not see minor defects in the mucous membrane of the reproductive organ. These may be polyps or fibroids.
The first half of the cycle is the best time to perform a pelvic ultrasound. When to do the procedure? In a normal cycle, this is day 5-7. If menstruation is short and the cycle is short, then this will be the 3-5th day. With a long female period, diagnostics can be carried out from the 5th to the 10th day.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is done on any day except menstruation. Usually 5–7 days after they start. During this period, the endometrial layer has a thickness of 3–6 mm, which allows you to see the most minor changes in the inner layer of the uterus: tumor processes, endometrial or corpus luteum cysts, polyps. Varying degrees of echogenicity enable the doctor to accurately make a diagnosis.
Research is also carried out on other days, but changes characteristic of a given period are taken into account. The endometrial layer thickens at the time of ovulation and can hide some processes in the uterus, so if you suspect a tumor, it is recommended to adhere to the time limits indicated by your doctor.
Fibroids are a benign tumor growing from the muscular layer of the uterus. It has a round shape and a denser consistency than neighboring fabrics. In the initial stages, the disease manifests itself poorly. To see a small tumor, an ultrasound examination is performed no later than the 7th day of the monthly cycle, when the endometrial layer is at its thinnest.
Myoma can be located in the muscular layer of the uterus, under the mucous membrane or along the outer contour.
- Subserous (external) tumor rarely manifests itself and is diagnosed during random examinations. It can cause minor discomfort if it has a large diameter and puts pressure on neighboring tissues and organs. It doesn’t really matter on what day of the cycle to do a pelvic ultrasound in women, since the inner layer does not affect the outer contour of the uterus.
- Intramuscular (intramural) fibroids affect the monthly cycle, causing disturbances and pain in the pelvis.
- A submucosal (submucosal) tumor grows in the deep layer of muscle. With this arrangement, the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves most clearly. An ultrasound is prescribed on days 23–25 of the cycle.
- Intermuscular (interstitial) myomatous growth causes heavy menstruation and pain if the node swells or necrotizes. It has a negative effect on neighboring organs - the bladder, rectum.
- Cervical fibroids grow in the lumen of the cervix. Detected in 5% of patients. The doctor prescribes a vaginal ultrasound if pain occurs during sexual intercourse and blood discharge from the vagina. The presence of fibroids in the cervix can be determined on any day of the cycle.
For endometriosis
A woman is examined for growth of the endometrial layer on days 24–25 of the cycle, that is, as close as possible to the beginning of menstruation. During this period, the endometrium is at its greatest thickness and is clearly visualized. The endometrium reacts to female sex hormones, so if there are lesions in other organs, they are also visible on the monitor screen.
The doctor’s task is to see lesions in the abdominal cavity or on the ovaries, which is an indication for surgical intervention. The disadvantage of ultrasound diagnostics for endometriosis is that the device poorly determines the initial stage of the disease. The only informative method in this case is the laparoscope.
Using ultrasound, the stages of endometriosis are determined:
- small lesions;
- deep lesions;
- multiple deep lesions with the formation of cysts;
- multiple lesions that grow into the walls of the bladder, ovaries, and vagina.
It is possible to accurately determine the presence of foci only at the second stage of the disease. Endometrosis is one of the causes of infertility, so not only the uterine layer is checked, but also the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and abdominal cavity.
At the beginning of the cycle, endometriosis is determined by the presence of lesions on the ovaries and fallopian tubes. An additional feature is the round shape of the uterus.
If pregnancy is planned, it is better to do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women before its onset. Some diseases can cause changes in blood flow in the uterus, which can lead to complications during pregnancy.
What an ultrasound examination reveals:
- congenital pathologies of the reproductive system - an underdeveloped uterus, partitions in the cavity, duplication of the genital organs (partial or complete);
- ovarian cysts, which can cause infertility;
- inflammatory processes in the fallopian tubes, as a result of which the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus, but is fixed in the tube and begins to grow;
- chronic endometritis - inflammation of the uterus, in which the cavity enlarges and gases accumulate in it;
- tumor neoplasms – benign or malignant.
When choosing an in vitro fertilization method, a woman is prescribed a number of diagnostic procedures and tests to determine the ability to carry an artificially implanted embryo. At the first stage, using ultrasound, the condition of the internal genital organs - the uterus and appendages - is determined. There should be no signs of an inflammatory process, as it affects the survival of the fertilized egg.
The patency of the fallopian tubes is assessed. Two methods are used: laparoscopic or ultrasound. The second one is safer and non-traumatic.
Inspection of the inner layer of the uterus is performed with a vaginal probe or hysteroscope. Both methods are informative, but there may be indications in favor of the first or second.
Before conception, an ultrasound is also performed on a man to rule out varicose veins of the scrotum. The quality of sperm in this case may be worse due to poor metabolism in the tissues.
During egg retrieval, an ultrasound machine is used to monitor the needle. After fertilization and transfer of cystoblasts into the uterine cavity, the woman begins to produce the hCG hormone, which determines the success of IVF. The first ultrasound is done a month after embryo transfer with a high level of hCG. An abdominal sensor is usually used, which detects the presence of a fetus in the uterus.
In what cases can diagnostics be performed?
Not in all cases, ultrasound during menstruation is contraindicated. In a number of situations it may well be carried out. These include the following types of diagnostics:
- An examination that does not involve the pelvic organs, for example, the abdominal cavity, kidneys, heart, etc.
- The need for emergency research of the reproductive system.
When planning an ultrasound examination of a particular body system, you should remember the essence of this procedure. Indeed, in a number of cases it is not only permitted, but also extremely necessary.
If the patient suspects that she is developing some pathological condition, then the day of the cycle does not matter. Ultrasound in gynecology is initially necessary for diagnosing diseases, so a woman should go to see a doctor as early as possible, where she will tell him all her complaints.
Depending on the method of the procedure, it will be carried out differently:
- Transvaginally. A woman needs to undress from the waist down, lie down on the couch, and bend her knees. After this, a sensor is inserted into the vagina, on which a condom is previously placed. The patient does not feel pain, but there is discomfort.
- Transrectal. This research method is carried out identically to the previous one. The only differences are that the sensor used is thinner and it is inserted into the rectum.
- Abdominal. During this procedure, the girl bares her stomach and lies on her side or back on the couch. The anterior abdominal wall is lubricated with conductive gel, after which the sensor is moved over the desired areas.
The ultrasound diagnostic procedure, regardless of the technique used to perform it, should not be accompanied by painful sensations. If they are present, then you must inform your doctor about this.
What indicators are assessed?
Without special medical education, it is unlikely that you will be able to understand what the results of the ultrasound screening indicate.
When decrypting, the specialist receives the following information:
- shape of the reproductive organ;
- uterine size;
- endometrial thickness;
- the presence or absence of neoplasms of various types.
In most clinical cases, based on the results of ultrasound, the gynecologist confirms the initial diagnosis.
When can pregnancy be detected?
Thanks to positive experience and reviews, gynecological ultrasound is safely performed in the early stages of pregnancy. It allows you to determine the location of the fertilized egg and eliminate the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy. Normally, it should be located inside the body of the uterus. At 6-7 weeks of gestation, the head, arms, legs, and torso of the fetus can be visualized.
The optimal time for the first study is 10 - 12 weeks, when it is already possible to determine the fetal heartbeat and the thickness of the collar zone. If there is a deviation from the norm, there is a risk of developing Down syndrome. Next comes the second screening at 22-23 weeks of pregnancy, when the likelihood of developing defects of internal organs is established or excluded. At this time, it is already possible to determine the sex of the child.
The third screening is performed upon reaching 31-32 weeks of pregnancy. At this time, it is possible to determine late developmental deviations, the degree of maturity of the placenta, the condition of the child and amniotic fluid. Ultrasound is performed using a transabdominal probe. Interim diagnostics are prescribed if there are indications or if the pregnant woman’s well-being worsens.
Patients' opinions on diagnosis
Those women who, for certain indications, were prescribed an ultrasound in gynecology, leave positive reviews. This is due to the fact that the procedure is not associated with painful sensations, and also does not require serious preliminary preparation.
The cost of diagnostics directly depends on the diagnosis made, as well as the level of the chosen medical institution. When conducting research using modern equipment, the level of effectiveness is quite high. Depending on the clinic and the completeness of the examination, the price for a pelvic ultrasound can vary from 1,500 to 22,000 rubles