What is pelvic ultrasound
One of the most highly accurate and safe diagnostic methods used in gynecological practice is ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (USP). The essence of this method is the reflection of the sound wave sent by the sensors by the internal organs. The reflected radiation is converted with the help of technical instruments into a graphic image, which is interpreted by a diagnostician . Using ultrasound, you can track the pelvic organs over time, which allows you to make accurate conclusions.
Preparation for ultrasound diagnostics
Transvaginal method
Typically, diagnosis is prescribed on days 5–7 of the female cycle, that is, when menstruation ends.
You need to start preparing for this type of study 2 days in advance. Preparation consists of observing special nutritional standards. It is better not to eat vegetables and fruits that have not undergone heat treatment. It is necessary to limit the consumption of milk and products made from it, as well as meat, and do not drink soda.
All this is done to reduce the formation of gases in the gastrointestinal tract, since gases can reduce the accuracy of the data obtained. In the evening, the day before the examination, you should give an enema.
Transrectal method
You should also prepare for this type of examination: a diet that excludes foods that can cause increased gas formation. In the evening before the day of the examination, you need to do a cleansing enema. Before the examination, be sure to go to the toilet and empty your bowels.
Transabdominal method
If you choose this method, you need to prepare for 3-4 days. This is how long you need to follow a special diet of foods that will not cause increased gas formation. Let us remind you that the gases accumulated inside will prevent the doctor from seeing the exact picture and drawing the right conclusions. When preparing for the examination, you should avoid:
- sweets, buns;
- alcoholic drinks;
- fatty foods;
- beans, peas, legumes;
- spicy dishes;
- carbonated drinks.
It is important to come to the examination with a full bladder. An hour and a half before the appointed time, you need to drink at least a liter of water.
A moderate desire to visit the toilet should indicate that the organ is filled to the required level. This condition of the bladder will facilitate diagnosis - it will help the uterus take a place convenient for examination, and will displace the lower part of the gastrointestinal tract from view.
When should women undergo a pelvic ultrasound examination using this method? It is advisable to be examined on days 5–7 of the menstrual cycle.
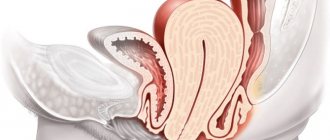
What is included in the female pelvic organs
The space that is limited by the pelvic bones is called the small pelvis. The organs located in it belong to the reproductive and excretory systems. The excretory system includes the bladder and rectum, which are the same in men and women. The organs of the reproductive system are individual for each sex, for women they are:
- vagina;
- uterus (cervix, cervical canal);
- ovaries;
- fallopian (or fallopian) tubes;
- rectum;
- bladder.
What can an ultrasound doctor see if you are not pregnant?
- Condition of the vagina;
- Condition of the uterus. Its structure, size, position, tissue structure, presence or absence of neoplasms in the cavity;
- The condition of the ovaries, or rather the position, size, presence of follicles in them and their maturation; the presence or absence of neoplasms, adhesions and constrictions;
- The position and size of the bladder, the presence or absence of stones or deposits inside the bladder;
- The position, size, structure of the intestine, as well as the presence or absence of tumors inside.
Ultrasound is prescribed during the period of preparation for pregnancy (through the abdominal wall or transvaginally), in the presence of complaints, often with chronic diseases in order to monitor the state of women's health. Also, ultrasound examinations of the pelvic organs are included in the calendar of mandatory examinations of pregnant women:
- In the first trimester, at 9-10 weeks. Allows you to see the fertilized egg, determine its size, and also distinguish the presence of genetic abnormalities;
- In the second trimester, at 16-20 weeks. On this ultrasound, you can already see the baby’s gender, body structure, the presence of major organs, the number of limbs, etc. The most important thing is that the ultrasound shows the condition of the placenta and umbilical cord, as well as blood flow and the amount of amniotic fluid;
- In the third trimester, from 32 to 34 weeks. On the third ultrasound, you can already see the features and structure of the face, the fetus is so large.
Ultrasound also monitors the condition of scars on the uterus resulting from cesarean section or other surgical interventions.
If necessary, additional examinations are prescribed during pregnancy - MRI diagnostics, CTG, Dopplerometry, etc.
Indications
It is recommended to undergo this procedure, regardless of the presence of indications (for preventive purposes), every year, since some diseases of the reproductive and excretory systems may be asymptomatic. The reason for prescribing an ultrasound examination after a gynecological examination is the gynecologist’s suspicion about the presence of neoplasms (fibroids, cancer, tumors, cysts). In addition, indications for the study are:
- menstrual irregularities;
- signs of inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- pregnancy (a cervicometry procedure is prescribed to assess the condition of the cervix);
- the presence of an intrauterine device (to control its position);
- past inflammatory diseases and other gynecological diseases (adnexitis, endometritis, cervicitis, vulvitis, colpitis);
- infertility (to determine the cause, folliculometry is performed, i.e., identifying disorders of the ovulatory mechanism);
- previous surgical interventions (to control the condition).
Timing of pelvic ultrasound in women
The time of the procedure depends on the indications. For example, if there are complaints of pain in the lower abdomen, problems with conception, menstrual irregularities and changes in the intensity of menstrual flow, an ultrasound scan is prescribed on days 5-7 from the beginning of menstruation.
To determine the functionality of the ovaries and their ability to form a follicle, pelvic ultrasound in women is performed several times during the menstrual cycle:
- on day 8-9;
- on day 14-15;
- on day 22-23.
During pregnancy, subject to its normal course, ultrasound is performed as planned approximately once every 3 months:
- at 11-13 weeks;
- at 20-22 weeks;
- at 32-36 weeks.
If necessary, the number and timing of diagnostic testing may be changed by the attending gynecologist.
What does it show
During the examination, the specialist performing the procedure evaluates the anatomical structure of the organs. The assessment is based on a comparison of the observed picture with established standards. Deviations cannot clearly indicate pathology; to confirm the diagnosis, the necessary tests must be taken . The following main indicators are used for diagnosis:
| Index | Meaning |
| Size | An increase in the size of the uterus occurs during the inflammatory process, a decrease occurs during fibrosis. |
| Form | A change in the natural shape may indicate structural defects of the uterus |
| Wall thickness | Thickening of the walls of the uterus may be a sign of the presence of malignant tumors or an inflammatory process |
| Echogenicity | Tissue density increases in the presence of pathology |
| Structure | Heterogeneity may indicate fibrosis of the uterus or prostate gland |
| Presence of neoplasms, compactions, stones | This indicator identifies tumors, stones |
Effective ways to examine female organs inside the pelvis
Ultrasound diagnostics is considered one of the most detailed, safe and highly accurate research methods. Ultrasound is performed on infants, pregnant and lactating women, and elderly people. Ultrasound does not require long or complex preparation, and its cost cannot be called high.
As for ultrasound of the pelvic organs, it is available for women in three methods:
- Transabdominal – through the abdominal wall, used mainly during pregnancy;
- Transvaginally;
- Transrectally - rarely.
Indications for ultrasound examinations during pregnancy and outside this period differ. During pregnancy, there are periods accepted and determined from an obstetric point of view when ultrasound is performed.
How to prepare
Preparation for an ultrasound for women depends on how the diagnosis will be carried out. The transvaginal method does not require preliminary preparation, but it is better that the bladder is emptied before the examination. Prepare for a transrectal ultrasound, which involves examining the pelvic organs through the rectum, and for a transabdominal ultrasound as follows:
- two days before the procedure, stop consuming foods and drinks that contribute to gas formation (legumes, dairy, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, fresh vegetables and fruits);
- eat in small portions;
- 3 hours before the procedure, cleanse the intestines (using an enema or taking laxatives);
- an hour before the diagnosis, you should fill your bladder (drink 1 liter - 1.5 liters of still water);
- On the day of the examination, you must refrain from smoking and taking medications.
Articles on the topic
- Libido in women - what is it, deviations, home correction methods
- Uterine fibroids - signs and types of disease, drug therapy, surgery
- Adhesions in the pelvis in women
Is it possible to eat before an ultrasound?
Eating on the day of a transabdominal examination is not recommended if the procedure is scheduled for the morning. If the study is scheduled to take place later than 2 o'clock in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed, which must be no later than 11 o'clock in the morning. During transvaginal examination of the pelvic organs, there are no restrictions on eating time.
Types of ultrasound in gynecology
Ultrasound in gynecology can be performed in three ways. The following types are distinguished:
- transrectal ultrasound (performed through the rectum in girls who are not sexually active);
- transvaginal ultrasound (carried out by inserting a sensor into the vagina for an accurate examination of diseases of the pelvic organs);
- transabdominal ( or simply abdominal) ultrasound , or simply abdominal ultrasound (performed through the abdominal wall when signs of inflammation of the pelvic organs are detected or in girls who are not sexually active).
For what indications is an ultrasound of the pelvic organs performed in women?
- identifying the causes of infertility;
- menstrual irregularities;
- assessment of pathology of the uterus and ovaries;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs: endometritis, parametritis, vulvovaginitis, salpingoopharitis;
- vaginal discharge;
- study of the nature of pelvic tumors (bladder cancer, fibroids, uterine cancer);
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis);
- study of the condition of the ovaries and uterus during IVF;
- surgical manipulation of the bladder, uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries;
- complications of pregnancy;
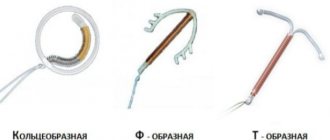
- monitoring the installed intrauterine device (see methods of contraception).
What diseases and conditions can ultrasound detect in gynecology?
- tumor processes in the pelvic area;
- torsion of ovarian cyst; ovarian cyst;
- complications after pregnancy and childbirth;
- pathology of the development of the uterus and appendages (duplication of the fallopian tubes, underdeveloped “infantile” uterus, bicornuate, saddle-shaped uterus);
- endometrial polyps;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes (formation of adhesions and constrictions);
- the presence of fluid in the pelvic organs;
- uterine fibroids;
- pelvic inflammatory diseases, endometriosis;
- pregnancy (uterine and ectopic).
A female ultrasound will help determine the following indicators:
- ovarian size;
- the presence and type of ovarian cysts (follicular, luteal, endometrioid);
- size and shape of the uterus;
- thickness of the uterine mucosa (varies depending on the day of the cycle);
- the presence of tumors of the uterus and appendages, their location and the nature of the formation (benign or malignant).
How to do a pelvic ultrasound
During a gynecological or urological examination, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan to identify possible abnormalities. The method of diagnosis depends on the expected diagnosis and can be transvaginal, transabdominal and transrectal. The ultrasound examination procedure lasts 10-20 minutes. and is carried out in the absence of direct contraindications, which may include an allergy to latex (for transvaginal) or open skin lesions on the abdomen (for transabdominal).
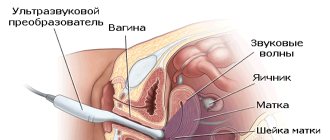
Transvaginal ultrasound
The transvaginal ultrasound procedure is practically painless (except in cases of acute inflammation of the genital or abdominal organs). The research proceeds as follows:
- The woman frees the lower part of her body from clothes and lies down on the gynecological chair.
- The specialist places a disposable condom on the tip of the vaginal sensor (transducer), lubricating it with a special gel.
- The transducer is inserted into the vagina.
- The sensor sends a signal to the device screen.
- The doctor deciphers the resulting picture, dictating his observations to the assistant.
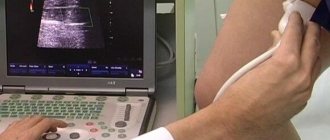
Transabdominal ultrasound
Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound is not prescribed for young girls whose hymen is not broken, so in such cases a transabdominal examination is used, which is indicated for both women and men. You must prepare for this procedure in advance by following your doctor's instructions. The sequence of actions when carrying out diagnostics is as follows:
- The person being diagnosed takes a horizontal position on the couch and frees the stomach from clothes.
- A conductive gel is applied to the skin of the abdomen and the sensor.
- The specialist moves the sensor over the surface of the abdomen, studying the indicators of the internal organs.
- After the procedure is completed, the remaining gel is removed and the patient can immediately return to their normal lifestyle.
Pelvic ultrasound during pregnancy
During pregnancy, women undergo ultrasound three times to monitor the health of the fetus and generally monitor the progress of pregnancy.
The first time a pelvic ultrasound is done at 10 weeks.
At this time, the doctor assesses the condition of the patient’s uterus, the site of attachment of the fertilized egg and counts the number of embryos. The first screening is the most important. During this period of time, the fertilized egg is still very small, and therefore, when determining an ectopic pregnancy, measures can be taken to preserve the life and health of the woman. In addition, during the examination, the doctor examines the embryo itself, measuring its size. One of the most important parameters is the thickness of the collar space, an increase in which indicates the presence of chromosomal abnormalities. The earlier a pathology is detected in a pregnant woman during pregnancy, the greater the chance of saving the life of her and her unborn child.
The embryo's heart is formed earlier than other organs, and its beating can be heard after the fifth week of pregnancy. To identify anomalies, an ultrasound is performed with Doppler measurements, that is, an assessment of the quality and speed of blood flow in the veins and arteries of the woman and the embryo. A Doppler study is usually done at the second and third screening, and if necessary, repeated before birth. An assessment of blood flow is needed to promptly notice congenital heart defects, compression of blood vessels or entanglement of the umbilical cord. All these pathologies, identified early, make it possible to take timely measures to treat the woman and child.
In the second and third trimesters, the doctor will examine the baby more carefully. If during the first screening more attention is paid to its size and location in the uterus, then later, during an ultrasound of the woman’s pelvic organs, the specialist will measure the size of the fetus from the crown to the tailbone, count the number of fingers and toes, estimate the length of the bones of the limbs, the thickness of the brow ridges, and more. several parameters. All results taken together make it possible to identify mutations and pathologies of pregnancy.
At the first screening, when the fetus is still almost invisible, the examination is performed transvaginally, and in the later stages, doctors recommend doing an ultrasound of the pelvis through the anterior abdominal wall. Using a transvaginal sensor in the last months of pregnancy may cause premature labor.
In addition to the usual standard ultrasound examination, a woman is often offered 3D or 4D diagnostics. These examinations allow the doctor and parents to examine the child’s appearance in more detail, but the condition of his internal organs can only be assessed on an ordinary flat black and white picture. Three-dimensional echography is performed using more sophisticated equipment, and is often combined with Doppler ultrasound. The essence of the 3D method is that the device, which is in continuous contact with the patient’s skin, records several two-dimensional “images” and builds a three-dimensional image on their basis. 3D diagnostics are often prescribed to pregnant women or patients with tissue and vascular pathologies.
4D diagnostics is rarely used in medicine, since this research method is not informative. Most often, 4D ultrasound is done in paid medical centers that monitor pregnant women. The difference between this method and 3D research is that with 4D the device not only builds a three-dimensional image, but also records a video clip of the child’s movements. This video is usually shared with parents who want to save their baby's first image.
Decoding the results
The patient has the opportunity to receive the results with their interpretation immediately after the end of the procedure. During the procedure, the diagnostician voices sonological conclusions regarding the observed picture, but an accurate diagnosis must be made by a gynecologist based on the diagnostic results. Deviations from the established norm may indicate both the individual characteristics of the subject and the presence of pathologies. During the examination of organs, their size, echogenicity, and structure are assessed:
| Organ | Norm | Deviations |
| Uterus | Dimensions (length, width) – 70, 60 mm, no thickenings | Thickening of the walls was noted, heterogeneity of the structure was revealed, the size was reduced or increased, there were abnormal formations, cavities |
| Ovaries | Dimensions (width, length, thickness) – 25, 30, 15 mm, uniform structure | Increased size, presence of cysts, fluid-filled cavities |
| Bladder | Free flow of urine through the ureters, complete emptying occurs after urination | Presence of stones, changes in size and position |
| The fallopian tubes | Not viewed | There are oval, round formations, adhesions, thickening of the walls |
For men
During an ultrasound scan of a man’s pelvic organs, the diagnostician determines whether the size and structure of the prostate gland and bladder correspond to normal values. When interpreting the research results, the following data is taken into account:
- The normal size of the prostate gland is 30/25/1.7 mm (length, width, thickness). An upward deviation in size may indicate prostatitis or prostate adenoma.
- The structure is homogeneous, there are no inclusions or compactions. The presence of compactions or thickenings indicates the possibility of tumor formations.
Preparation for the procedure
Many people are interested in how a pelvic ultrasound is performed on a woman. This procedure can be carried out using the following methods:
- transabdominal (through the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity);
- transvaginal (through the vagina);
- transrectal (through the anus);
- obstetric (in a pregnant woman).
Each research method requires certain preparation, which may differ depending on the research method. However, when performing an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women, preparation for any method has some similarities:
- Before doing an ultrasound, for several days you should avoid eating foods that can cause increased gas formation. These are legumes, yeast bread, fermented milk products, alcoholic drinks.
- Directly on the day of the examination, in preparation for the procedure, care must be taken to completely cleanse the intestines.
- If a diagnosis using barium or x-ray was carried out a few days before the ultrasound examination, it is recommended not to do a pelvic ultrasound in the near future, since the substance can greatly affect the results.
Price
The cost of an ultrasound examination procedure differs in different diagnostic centers in Moscow. This examination can be carried out at a price from 1000 to 6000 rubles:
| Medical institution | Cost of transabdominal examination, rub. | Cost of transvaginal examination, rub. |
| Affordable Health | 1700 | 1700 |
| MedicCity | 2500 | 3500 |
| SM-Clinic | 1450 | 1450 |
| Center V.I. Dikulya | 1000 | – |
| Best Clinic | 1800 | 1850 |
| Ramsey Diagnostics | 1500 | 2500 |
| Perinatal Medical Center | 5000 | 5000 |
| Eurasian clinic | 4000 | 4000 |
Where to do it and how much does it cost?
There are two options for pelvic ultrasound diagnostics:
- Free - carried out in a clinic at your place of residence if you have a compulsory medical insurance policy and a referral from your attending physician, provided that the clinic provides such services and is equipped with ultrasound equipment.
- Paid - suitable for those who do not want to waste time standing in queues and medical consultations, but just need to get the necessary information. You can undergo an ultrasound scan of any organs at private diagnostic centers and medical clinics for a fee.
Appendix 2. Male pelvic organs.
Keep in mind that the cost of the same procedure can vary significantly depending on a number of factors, including:
- Quality and modernity of diagnostic equipment. Thus, when using three- and four-dimensional scanning devices, more detailed information can be obtained, so the cost of such a procedure will be higher.
- Qualification skills of specialists conducting the examination. An ultrasound in a professor’s clinic will be more expensive than a similar procedure performed by a young specialist.
- Material base of the clinic. Equipment with medications, as well as auxiliary materials such as shoe covers, disposable sheets and napkins also affects the cost of manipulations.
- Region of the country and district of the city.
- Reputation of the medical center and patient reviews about it.
For example, the average cost of pelvic ultrasound in the two largest cities of our country:
- Moscow – from 1200 to 1500 rubles;
- St. Petersburg – from 600 to 1650 rubles;
- regions – from 600 to 1000 rubles.
How to choose a day for an ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is one of the few studies that takes place on a certain day of the monthly cycle. The timing of the ultrasound depends on the patient’s expected diagnosis.
For most cases, the first phase of the cycle, immediately after the end of menstruation, is considered ideal. The endometrial layer is only growing, so with echography it is very easy to see all the organs and detect possible pathology. At this time, ultrasound is performed if a uterine fibroid, tumor or cyst is suspected, while monitoring the condition of the uterine appendages. And also if this is a preventive examination.
In the second phase of the cycle, an analysis is done for endometriosis, the diagnosis of fibroids, and the study of the ovaries and fallopian tubes continue. If the patient has complications after a miscarriage, abortion or difficult childbirth, there are clear signs of pelvic inflammation, no matter what phase of the monthly cycle the woman is in.
And if ultrasound is required urgently, it can be performed absolutely any day - even during menstruation.
Methodology
Ultrasound is performed on an outpatient basis in an office specially equipped for this purpose by an ultrasound specialist. While viewing the image on the computer monitor, the doctor reads out loud the main characteristics of the internal organs and the detected pathologies. According to the doctor, the nurse present here makes notes on the examination form.
The ultrasound specialist can turn the monitor towards the patient so that she can see for herself the processes occurring inside her. Typically, this practice is used when diagnosing pregnant women, especially in the later stages, when the sex of the unborn child is determined.
How is a pelvic ultrasound done in women?
The patient is positioned on the couch lying on her back with her knees bent (to relax the abdominal wall muscles). The lower abdomen must be freed from clothing (for transvaginal ultrasound, remove underwear and slightly spread your legs, providing the doctor with access to the external genitalia).
Then the doctor lubricates the woman’s skin and the device’s sensor with medical gel and begins to move it over the abdomen, applying slight pressure in some places (transabdominal ultrasound).
If the examination is performed vaginally, a probe, which is much thinner than standard speculum, is inserted into the vagina. This type of examination does not cause pain or discomfort to the patient, with the exception of slight psychological inconvenience for particularly shy women.
Detection of female diseases
- Characteristic features of the structure of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle-shaped, with a partial septum, etc.);
- Dense round or oval formations - fibroids or vaginal cysts;
- Changes in the walls of the uterus - possible oncological problems, inflammatory processes;
- An increase in the size of the ovaries is often one of the signs of polycystic disease;
- Changes in the structure of tissues and walls of the uterus - possible endometriosis;
- The presence of foreign inclusions in the bladder cavity - stones and sand.
An ultrasound reveals some signs of the disease; if there is suspicion, the doctor conducts an additional examination and prescribes a number of tests. During the course of the inflammatory process in the pelvic cavity, adequate treatment is prescribed. Inflammation inside the bladder, uterine cavity, tubes or ovaries is always painful and is often accompanied by discharge. Vaginal diseases make sexual intercourse uncomfortable, and serious diseases can be fatal.
It is recommended to do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs for women of childbearing age at least once a year and immediately if there are complaints.
What are they watching?
Which is the best ultrasound? The gynecologist decides exactly how the study will be carried out: transvaginally or transabdominally (depending on the indications and characteristics of the medical history).
A transabdominal pelvic examination makes it possible to see the overall picture of the patient’s reproductive health. This method requires certain preparation from the patient in the form of a pre-filled bladder .
An examination using a vaginal sensor has its advantages: this method allows you to carefully examine areas of interest to the doctor , since the sensor is located directly near the female genital organs.
Due to the danger of cancer, many women may be interested, for example, in the question, are metastases visible on ultrasound?
During the manipulation, the diagnostician has the opportunity to examine in detail:
- parameters and features of the uterus, including anomalies of its structure;
- fallopian tubes;
- bladder and ovaries;
- rectum;
- number of follicles and their size;
- tumor formations of any quality;
- pregnancy, embryo location and development period;
- the condition of the unborn child and existing developmental pathologies;
- length of the cervical canal;
- localization of the spiral installed inside the uterus.
During the examination of a woman, the sonologist determines:
- the location of the uterus and its cervix relative to other organs;
- sizes of organs in centimeters, their general condition and integrity;
- the structure of the muscular and endometrial layer of the uterus;
- smoothness of the walls;
- structural features of the female reproductive glands and fallopian tubes.
Important! Suspicion of any inflammatory diseases of the uterus, including inflammation of the mucous layer, appendages or adjacent tissue, is a reason for the gynecologist to send the patient for an ultrasound examination of the pelvis.
In addition, the technique of examining the female genital organs using ultrasound provides an excellent opportunity to monitor the condition of a postoperative patient or monitor the location of the spiral in a gynecologically healthy woman.
Video
The video below gives an idea of what a pelvic ultrasound shows in women.
What can a pelvic ultrasound reveal?
When answering the question: “When is it better to do a pelvic ultrasound?”, it is worth remembering the indications for diagnostics:
- The presence of adhesions;
- Tumors of the female reproductive system;
- Diagnosis of pregnancy;
- Monitoring fetal development and its condition (conducting three mandatory screening studies);
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Frozen fruit;
- Diagnosis of the presence of genetic diseases of the fetus, as well as many other pathologies;
- Myomas and cysts;
- Endometriosis;
- Polyps;
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- Polycystic disease;
- Identifying the causes of hormonal imbalances and infertility.
Features of the diagnostic procedure
The study is prescribed to women to confirm intrauterine pregnancy, diseases of the uterus and appendages, and to identify pathological neoplasms.
The procedure takes 20-40 minutes, which is determined by the purpose of the examination.
Depending on the pathology, sexual activity, and condition of the patient, the following types of ultrasound scanning of the pelvic organs are prescribed:
- Transvaginal ultrasound. The most informative technique that allows you to diagnose any pathology of the reproductive system and determine pregnancy at an early stage. The study is carried out using a sensor that the doctor inserts into the vagina. The procedure is contraindicated for women during bleeding and virgins if the patient is allergic to latex;
- Transabdominal ultrasound. The most comfortable method, which involves examining the pelvic organs through the abdominal wall. Widely used in pregnant women when internal scanning is not possible;
- Transrectal ultrasound. The study is carried out by inserting a sensor into the rectum. The method is used quite rarely - for virgins and women during bleeding, when the most accurate results are needed. The procedure causes some discomfort to the patient.
For preventive purposes, the procedure can be performed on any day of the cycle, excluding menstruation. However, the most favorable period is considered to be the first week after the end of menstruation. To assess the condition of the ovaries, ultrasound is recommended to be performed on days 14-16 and 21-24 of the cycle.
The price of the study varies from 600 to 1200 rubles, depending on the clinic and locality.
What is visible on ultrasound at different periods of the cycle?
Normal values may vary depending on the period of the cycle. For example, interpretation of pelvic ultrasound in women during menopause: length, width and thickness of the uterus (in cm) - up to 4, up to 4.3, no more than 3. Depending on the cycle, the thickness of the endometrium will vary. Its norms and echogenicity (in mm):
- 1-4 days – 1-4.
- 5-10 days – 3-10 with an anechoic homogeneous structure, at the end it thickens to 8 mm.
- 11-14 days – 8-15, continues to “grow”, on average its value is 11 mm, echogenicity becomes average.
- Days 15-23 – 10-20, at first the growth of the endometrium slows down. In this case, echogenicity increases towards the center. The middle of the endometrium is visible in the form of a drop with a narrowing towards the uterine cervix. At first it is visualized unclearly, at the end of the period the thickness of the layer becomes maximum. In this case, the hyperechoic central line is almost invisible.
- 24-28 days – 10-17, the layer thickness decreases to 12 mm. The echogenicity is very high, the structure is heterogeneous, the lines of closure of the layers are not visible.
During menstruation, a hyperechoic streak or blood clots appear in the uterus. Sometimes the cavity expands slightly due to the contents. Many women are interested in whether it is possible to do an ultrasound before menstruation. Typically, the study is scheduled a few days after the end of the discharge. Accumulated blood before menstruation can distort the picture.
How to properly prepare for the procedure?
When you plan to conduct a study using the transabdominal method, you need to prepare for it in this way: about an hour before visiting the doctor, the patient should drink a liter of water. Please note that the liquid must be non-carbonated. After this, you cannot go to the toilet until the ultrasound. This will give the doctor a better look at the insides, because liquid is a favorable environment for ultrasound.
Before the study, which is done using the transrectal method, it is necessary to empty the intestines. An enema given the night before will help cleanse it.
If a transvaginal ultrasound examination is performed, then in this case, before the procedure, you definitely need to go to the toilet “in a small way.” The choice of day for an ultrasound using the transvaginal method is made taking into account the female menstrual cycle. It is usually prescribed on the 5-7th day of the cycle.
Decoding data on pelvic examination in men
If everything is normal, then when deciphering the ultrasound results, the prostate and seminal vesicles have normal parameters. No tumors, cysts or similar abnormalities are visible.
However, urological ultrasound in men sometimes reveals the following problems:
- Enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hypertrophy). This is one of the most common problems.
- A pelvic ultrasound may reveal stones in the urinary tract that have come out of the kidneys.
- The doctor may detect signs of abscesses or tumors in the internal organs of the pelvis.
- There is an abnormal amount of fluid inside the pelvis.
Decoding
If the results of an ultrasound of the pelvic organs are handed out, the patient will definitely look at them. The protocol will indicate the various sizes of organs and write a conclusion. If a woman does not have a medical education, then most likely she will not understand anything in this protocol.
Of course, any doctor will tell you that you shouldn’t decipher the ultrasound results yourself, much less try to prescribe treatment based on them. After the examination, it is recommended to go to a gynecologist, who will correctly evaluate the results and prescribe additional examination if necessary.
It must be remembered that a diagnosis cannot be made based on one analysis. The doctor must conduct an examination in a gynecological chair, direct the patient to undergo blood and urine tests, smears. Only a comprehensive examination allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. For reference, we present the norms for ultrasound of the internal genital organs in women for each organ examined.
Uterus
The location of the uterus should be without any peculiarities. The dimensions of the uterine body range from 4 to 7 cm in width. The anteroposterior dimension (thickness) ranges from 3 to 4 cm. The cervix is in the range of 2 to 3 cm, and the anteroposterior dimension is 1.5-2 cm. The thickness of the uterine walls should be uniform without formations.
Photos of an ultrasound scan of the uterus can be seen below:
Photo of ultrasound of the uterus. Source: medison.ru
An increase in the size of the uterus may indicate an inflammatory process, a neoplasm inside, or adenomyosis. A small uterus may be underdeveloped, for example, as a result of congenital pathologies or hormonal imbalance.
The thickness of the inner layer of the uterus, the endometrium, is also assessed; it should be uniform and correspond to the day of the cycle. During the menstrual cycle, this norm changes, since in every healthy woman the endometrium grows in the first half of the cycle. This is necessary so that the fertilized egg can attach to the uterus and begin to grow.
Normally, the thickness of the endometrium has the following dimensions:
- On days 1 and 2 of the cycle - from 5 to 9 mm. The endometrium is quite loose and is shed during menstruation.
- From 5 to 7 days of the cycle in the proliferation stage, when the endometrium begins to grow, it ranges from 5 to 7 mm. That is, on day 5 - 5 mm, on day 7 - 7 mm, respectively.
- On the 10th day of the cycle, the normal thickness of the endometrium is from 10 to 12 mm.
- from 10 to 14 days, the process of growth of the endometrium is completed, at this time its size is from 1 to 1.5 cm. At the end of proliferation, ovulation should occur.
If the endometrium grows in insufficient quantities, then infertility occurs, because the fetus will not be able to attach to the thin endometrium. If the endometrium is too thick and does not shed well, this may indicate hyperplasia or endometriosis.
What does ultrasound OMT include in women?
This ultrasound shows the functioning of organs in motion, which eliminates inaccuracies and distortions in the results. The procedure lasts only 10–20 minutes, depending on the chosen method.
To improve the passage of signals and ensure accuracy of indicators, a special gel is used.
Ultrasound diagnostics are carried out using echolocation. The device's sensor sends and tracks sound signals passing through body tissues, which have different acoustic properties. Ultrasonic waves undergo various stages of vibration and, depending on the density and elasticity of tissues, reflect echo signals of varying lengths and frequencies.
A graphic image is displayed on the screen through the tip of the sensor. After the procedure, the doctor describes the condition of the examined area and gives a conclusion to the patient.
Kinds
There are several types of ultrasound examinations in gynecology. The attending physician decides which procedure will be prescribed. The accuracy of the ultrasound results depends on the correctness of the study. Ultrasound examination can be carried out in the following ways:
- transvaginally;
- transabdominal;
- transrectally.
The first type of pelvic ultrasound is performed through the vagina. This method is very often used in gynecology because it is the most accurate. Using a vaginal probe, you can get as close as possible to the ovaries and uterus and get a good look at them. In addition, the vaginal wall, unlike the abdominal wall, is much thinner. Accordingly, the image with transvaginal ultrasound is clearer.
Transvaginal ultrasound. Source: simptomer.ru
Transabdominal ultrasound is a classic research method in which an ultrasound probe is applied to the abdomen. The disadvantage of this method is that only organs located close to the abdominal wall can be examined. Due to its low information content, transabdominal ultrasound is often supplemented with MRI, laparoscopy and other gynecological procedures.
Transrectal ultrasound involves inserting a probe into the anus. This method is used quite rarely in gynecology, only for virgins and in cases of urgent need. More often, doctors still choose transabdominal ultrasound.
Also, pelvic ultrasound can be performed in several modes:
- in two dimensions;
- three-dimensional;
- four-dimensional.
Let's take a closer look at these types of ultrasound.
2D
The most common in gynecology is two-dimensional ultrasound. With this examination method, an image appears in one plane. Using 2D ultrasound, you can evaluate the size and shape of the uterus, cervix, ovaries, and assess the condition of the organ lining.
Pathologies of the bladder can be assessed on a two-dimensional study only if the organ is sufficiently full. Also, this sonography method allows you to see tumors, cysts, and excess fluid in the abdominal cavity. The method is basic and is used everywhere.
3D
Three-dimensional ultrasound is more informative than two-dimensional ultrasound, as it allows you to obtain a clear image in several planes. The doctor can see the organ “in cross-section” by examining each of its layers.
Three-dimensional ultrasound allows you to obtain the following data:
- gender of the child and the presence of genetic abnormalities during pregnancy;
- congenital pathologies of the uterus;
- tumors;
- cysts;
- degree of endometriosis;
- adhesions;
- polyps;
- location of the intrauterine device.
Very often this method is used during pregnancy, as it allows you to examine the baby in detail from all sides, as well as get three-dimensional photos and videos of the child.
4D
4D ultrasound is as voluminous as 3D, but also with real-time audio. This method is used during pregnancy, it allows you to evaluate changes in the fetal heartbeat.
4D ultrasound allows you to assess blood flow in the pelvic area and detect varicose veins. This method is also used to diagnose inflammation, tumors and many other gynecological disorders.
In most cases, this method of ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women allows you to obtain a color image. But during the procedure, it may be necessary to combine transabdominal and transvaginal examination.
Which is better to do a pelvic ultrasound is decided by the attending physician. If it is possible to confirm the pathology transabdominally, then this type of study will be prescribed. But you should not refuse transvaginal or transrectal ultrasound. Doctors prescribe this method not to torment their patients, but to obtain the most accurate results. It must be remembered that the effectiveness of further treatment will depend on ultrasound.