Every year more and more people suffer from cardiovascular diseases. And many of them are prescribed the drug “Asparkam” by doctors. Not everyone understands why it is needed, because it is believed that such a cheap medicine, containing only potassium and magnesium, cannot have a serious effect. But actually it is not. Potassium and magnesium ions are necessary for the normal functioning of the body. True, it is not recommended to take even cheap and seemingly harmless drugs without a doctor’s prescription. Therefore, you need to know what Asparkam is needed for, so that the use of this drug brings only benefit to the patient.
Analogs
Medicines such as Mexorhythm, Rhythmocard, Propanorm, Inosine, Riboxim have a similar therapeutic effect. A complete analogue in composition is Panangin, which contains the same amount of active substance in the form of potassium and magnesium.
It is distinguished by the presence of excipients, of which there are slightly more in Panangin tablets.
What is better to choose for treatment, Asparkam or Panangin, consult your doctor. Doctors prescribe based on individual tolerance to the drug, taking into account the use of other drugs in therapy.
Important! For better absorption, it is recommended to combine both drugs with vitamin B6.
An important difference between Panangin is its higher cost. Certain advantages of this product include the presence of a film shell. When taken orally, such tablets do not harm tooth enamel and the gastrointestinal mucosa. For this reason, patients suffering from gastritis or peptic ulcers are often recommended to use this particular analogue.
In some cases, healthy people who are constantly engaged in vigorous activity need additional potassium and magnesium. In this situation, the drug is recommended to be used to eliminate heart rhythm disturbances that athletes experience. Asparkam is used in bodybuilding for prophylactic purposes.
The medicine provides athletes with:
- normalization of metabolism,
- successful muscle building,
- ridding the body of excess fat and water,
- replenishment of potassium and magnesium reserves,
- increasing endurance and reducing fatigue.
Only a specialist can recommend an appointment. In most cases, the standard dosage is used - 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. The drug is taken after meals. The duration of use of the medicine is 1 month. In some cases, the doctor may recommend a different dosage and duration of use of the product. The appointment is made after studying the anamnesis and conducting research, including an evaluation of an extended blood test.
Analogues of "Asparkam"
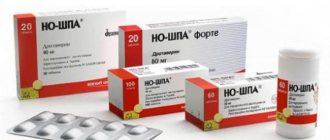
Like many other drugs, Asparkam has analogues. For example, doctors very often prescribe Panangin. This is a time-tested and very high-quality Hungarian drug. Of course, this product is more expensive than Asparkam, but at the same time it has a large number of positive reviews from specialists and patients.
"Panangin" is available in the form of tablets and solution for intravenous injection. 1 tablet of "Panangin" contains magnesium aspartate 140 mg, and potassium aspartate 158 mg. There is also an increased dosage - forte: potassium aspartate 316 mg, and magnesium aspartate 280 mg.
Cardiologists prescribe Panangin for:
- chronic diseases of the heart muscle;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- treatment with cardiac glycosides;
-replacement therapy for lack of potassium and magnesium in food.
Recently, the manufacturer released a new form of “Panangin”, enriched with vitamin B6. It contains magnesium aspartate 140 mg, potassium aspartate 158 mg, plus pyridoxine hydrochloride 0.6 mg. This dietary supplement is intended as an additional source of vitamin B6, potassium and magnesium.
As a result, the tone of the heart muscle and blood vessels is normalized, the risk of developing atherosclerosis is reduced, resistance to stress increases, the functioning of the nervous system improves, and anxiety decreases.
Which is better Asparkam or Panangin
Asparkam and Panangin are drugs of the same action and purpose. One Panangin tablet contains 140 mg of magnesium aspartate and 158 mg of potassium aspartate.
The concentration of these elements in Panangin in injections per 1 ml is 10.33 mg of potassium and 3.37 mg of magnesium, respectively.
Recently, doctors have given preference to Panangin, a more expensive drug compared to Asparkam. Therefore, which drug to give preference to and what to choose depends largely on the dosage of the active ingredients.
Panangin is produced in the form of film-coated tablets and for some patients this type of drug is easier to swallow.
However, judging by the reviews of doctors and patients themselves, there is not much difference between them. Some patients report less drowsiness when taking Panangin. Again, this may vary depending on the individual. From the point of view of medicinal action, these are analogues.
The drug "Asparkam" and its analogues
Medicines containing potassium and magnesium are often prescribed to heart patients as part of complex therapy.
But recently, doctors have begun to recommend more expensive analogues of Asparkam. Their differences often lie only in the manufacturer and price, but there are also different contents of active ingredients. Therefore, the question of the advisability of replacing the drug can only be decided by a doctor. Although many patients with “experience” trust Asparkam more, it is also the cheapest of the drugs in this group: a pack of 50 tablets can be purchased for only 20-50 rubles. A more expensive medicine is Panangin. Its composition is similar, although the active ingredient is contained in a lower dosage, so the drug is considered safer. This medicine is foreign-made and costs about 150 rubles per package. A lesser known medicine is called Potassium and Magnesium Aspartate. They are produced by different pharmaceutical companies, and their price depends on this.
Contraindications to taking the drug
Not everyone can take this cheap and effective medicine. Particularly serious contraindications to taking Asparkam are for diseases accompanied by fluid retention in the body and slow excretion of potassium. In this case, taking the drug can lead to excessive accumulation of this trace element, which is also harmful to health. When should you not drink Asparkam?
— with kidney dysfunction and insufficient urine formation;
- in case of impaired cardiac conduction function;
- damage to red blood cells or acute blood acidosis;
- in a state of shock, with severe myasthenia gravis or dehydration;
- in case of severe metabolic disorders;
- allergic intolerance to the components of the drug.
Injections of the drug are contraindicated in case of low blood pressure and pregnancy.
Contraindications and method of use
There are few contraindications, but they are important:
- Individual intolerance or sensitization of the body.
- Impaired function of the adrenal glands and kidneys.
- Myosthenia.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Blockade 2-3 degrees.
- Metabolic acidosis.
- ARF and chronic renal failure, anuria.
- Hemolysis.
- Dehydration.
- Age up to 18.
The effect of Asparkam on the body has not been studied in detail. For this reason, it is used with caution during pregnancy and is not prescribed to children. Elderly patients are also at risk, since their metabolism is a priori slowed due to age-related changes. However, for diseases of the cardiovascular system, the drug can be taken without restrictions. The usual method is a couple of tablets three times a day after meals.
Asparkam composition
In the dry language of the instructions, 1 tablet of the drug contains:
Potassium aspartate – 175 mg
Magnesium aspartate – 175 mg
1 ampoule of 10 ml:
Potassium aspartate – 0.45 grams
Magnesium aspartate – 4 grams
Auxiliary elements for tablets are talc, starch, usually corn, calcium stearate and Polysorbate-80.
For injections - sorbitol and distilled water.
As you can see, this drug contains only two main active elements: potassium and magnesium. But they are the ones responsible for normal electrolyte balance, participate in the conduction of nerve impulses and maintain normal heart rhythm.
These two elements are very important for health. Moreover, potassium is considered the most effective. Magnesium primarily serves as a conductor of ions into cells. The required amount of these elements provides:
Normal conduction of cardiac impulses;
Elasticity of blood vessels;
Reduced blood viscosity;
Adjustment of metabolism in the heart muscle;
Proper functioning of myocardial muscle contractions.
Their functions in the body are strictly distributed. Potassium helps provide a variety of nerve endings in the form of impulse signals, organizes muscle function, and promotes the normal functioning of the heart muscles.
With a lack of this macroelement in the body, the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted. The use of potassium in a small dose helps to dilate arteries, and in large doses, on the contrary, narrows them. Potassium has a weak diuretic effect.
Magnesium is the main component, which, in combination with other compounds, is responsible for the energy balance of the body, normalizes the balance of electrolytes, membrane permeability and neuromuscular excitability. In addition, magnesium is involved in cell division and growth. Its deficiency leads to lethargy and other side effects.
Why is there not enough potassium in the body?
Not everyone knows why Asparkam is prescribed. And this is done mainly for patients who have a deficiency of potassium ions. Why might this happen?
- even with proper nutrition, microelements enter the body with food in very small quantities;
— a lot of potassium and magnesium are lost during heavy sweating in hot weather and with increased physical activity;
— the absorption of microelements is impaired due to hormonal imbalances, diabetes mellitus or metabolic diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases, for example, gastritis or pancreatitis, also lead to a deterioration in potassium absorption;
— loss of these necessary elements often occurs with stomach disorders and intestinal infections, especially accompanied by diarrhea;
- Drinking alcohol, foods containing caffeine, and certain medications also contribute to excess potassium excretion. Therefore, for such conditions, the drug “Asparkam” is often prescribed. Why it is needed will become clear when you understand the consequences of a lack of these microelements.
Asparkam analogues
Some people want to know if there is anything they can do to replace the drug. Pharmacies offer a wide range of analogues of this medicine.
In the domestic pharmaceutical market, analogues of Asparkam include drugs that also contain potassium aspartate and magnesium aspartate as active substances. Such analogues of Asparkam include the following drugs:
- Aspangin;
- Asparkam –UBF;
- Asparkam Avexima;
- Pamaton;
- Panangin;
- Panangin Forte;
- Potassium and magnesium aspartate.
Most often they buy Asparkam or Panangin. What makes the products distinctive is the dosage of active ingredients. Although the effects of the drugs are the same, Panangin does not cause drowsiness, which is an important point for some people. At the same time, the price of Asparkam is slightly lower. The advantage of an expensive analogue is a special shell that facilitates the swallowing process. Therefore, everyone chooses for themselves whether it is better to buy Panangin or Asparkam.
Many athletes prefer to take Riboxin Asparkam, which they need during periods of intense physical activity. Thanks to this drug, the myocardium is pumped and the heart becomes more resilient.
"Asparkam" for heart diseases
Potassium and magnesium salts are vital for the normal functioning of the heart muscle. Therefore, many heart patients are prescribed Asparkam. Why it is needed is often not explained, so some patients treat the drug frivolously, believing that such a cheap medicine cannot have a serious effect. But in fact, Asparkam is very effective in helping with the following conditions:
- for heart rhythm disturbances;
— for rehabilitation or prevention of myocardial infarction;
— when metabolic processes in myocardial cells are disrupted;
— for angina pectoris and coronary heart disease, they also drink Asparkam.
Why is this drug used in complex treatment? It is effective for various vascular pathologies, for example, epilepsy, glaucoma or simply circulatory failure.
Potassium and magnesium
Cardiologists constantly talk about the importance of these microelements. There's nothing surprising about this
The rhythm of heart contractions is determined by the quality of the conduction system of the myocardium, in which impulses are generated independently and, passing through bundles of special nerve fibers, activate the periodicity of contraction of the atria and ventricles in a certain sequence. The normal conductivity of these fibers depends on the concentration of magnesium and potassium in them.
The heartbeat is normal, which means the person feels good, since each organ receives appropriate nutrition and oxygen on time and with a clear sequence. With a lack of magnesium, problems begin in the coronary vessels. They soften and become wide. As a result, the blood slows down, the organs begin to experience discomfort, and the patient begins to feel worse.
The opposite effect is observed with excess potassium: the coronaries become fragile and narrow. But this also brings nothing but trouble to the bloodstream, since blood cannot enter the main lines in normal quantities and be pumped to the organs. The loss of magnesium by cells, its release into the intercellular space entails the destruction of complex carbohydrates, and hyperkalemia occurs.
Magnesium takes part in all metabolic processes without exception. It is a catalyst for cell division, RNA synthesis, and provides the laying of hereditary information. But if its concentration decreases, the cell membrane becomes an insurmountable obstacle for the trace element. Magnesium Asparkam helps get into it with an additional amount of the element.
The concentration of potassium and magnesium in the cell is especially important during pregnancy. They ensure stable development and growth of the fetus
But Asparkam is prescribed to pregnant women with great caution, preferring German Panangin, a vitamin for the heart. Symptoms of overdose are fatigue and dysuria
Another nuance: a lack of potassium changes nervous excitability, and a deficiency of intracellular magnesium causes an imbalance in the generation and expenditure of energy, which stimulates convulsions, numbness of the limbs, and lethargy.
Composition and properties
The drug is produced in two forms: tablets and solution for injection. The tablets have a specific odor, are white in color and have a smooth surface. Available in packs of 50 pieces. The tablets contain 0.175 g of magnesium and potassium, as well as a number of excipients, such as talc, corn starch, polysorbate and calcium stearate.
The solution is white or yellowish in color. Available in ampoules of 5 or 10 ml. The active components of the drug are anhydrous magnesium and potassium aspartate; the solution also contains an auxiliary component in the form of sorbitol and purified water.
As mentioned above, Asparkam is a reliable source of magnesium and potassium. It provides restoration and support of electrolyte balance in the body. Magnesium takes part in many enzyme reactions and also helps potassium penetrate cells. Potassium prevents arrhythmia and maintains the normal functioning of the heart and other organs of the cardiovascular system.
After administration, the active components of Asparkam are absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. Residual substances are eliminated through the kidneys. The maximum level of concentration of active substances is achieved 1-2 hours after taking the drug.
Reviews about Asparkam are mostly positive.
How to use
To ensure that the tablets do not cause harm, follow the instructions and adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations. How to take the medicine depends on the specific diagnosis.
In case of illness, the course can last a week. Appointments are resumed after consultation with a doctor. The drug is also taken intramuscularly and intravenously, but only as prescribed by a specialist. For injection, 30 ml of medication is used, which is diluted with glucose solution and saline solution.
The dosage for an adult varies between 10-20 ml. Intravenous procedures are performed only by medical professionals. When taking medications for a long time, it is important to control the content of active components in the body
Microelements, when used in combination, normalize the water and salt balance in the body, which allows you to cope with swelling.
At the same time, weight may decrease, but this only happens due to getting rid of excess water. In general, follow these rules:
the price of the drug is small, but the prescription is carried out by a doctor, since this is an individual process; with long-term use, monitoring of substances in the blood plasma is necessary; intravenous injections require precautions. First of all, the drug should not have any cloudiness
After opening it must be used immediately. It must be administered immediately to avoid overdose.
How to take Asparkam tablets
Human bodies, like the rest of the world around us, contain a wide range of elements from the periodic table. The ratio of these elements, both in macro- and microdoses, affects the vital functions of the body. Both potassium and magnesium are macroelements - this means that more than 0.01% of them are found in the human body.
Potassium, together with sodium, is responsible for the water-salt balance. Therefore, potassium preparations or medications that affect the level of potassium in the body should be used with great caution - because an excess of potassium can cause an imbalance in this very balance and many unpleasant consequences. Potassium also promotes the transmission of nerve impulses and affects the condition of the heart muscle.
Magnesium promotes the transmission of nerve impulses, energy production and takes part in protein synthesis. Even the width of the lumen and the tone of muscle tissue depend on the magnesium content in the body. Due to its sedative effect, it is often used in neurology and psychiatry; for this reason, it should be taken with caution, especially if you need to perform activities that require increased concentration.
Both potassium and magnesium work together in the body - magnesium helps the human body absorb potassium and maintains its cellular concentration at sufficient levels. That is why Asparkam contains two active substances. And aspartate is a means by which potassium and magnesium ions enter the body and penetrate through the cell membrane into the intracellular space. There are many potassium and magnesium salts, but it is aspartic salt that most effectively delivers potassium and magnesium ions inside the human body.
If the patient has no contraindications to the use of Asparkam, and for some reason he does not receive enough potassium and magnesium from food, it is theoretically possible to take Asparkam tablets for preventive purposes. However, if normal nutrition is possible, it is recommended to compensate for the lack of macroelements with foods containing increased amounts of potassium and magnesium, for example, prunes, nuts, baked potatoes with skins, rye bread, and so on.
When taken prophylactically, 1 tablet of Asparkam is taken 3 times a day after meals; The duration of treatment is determined individually.
There are two forms of release - tablets and ampoules (injections). And, in my opinion, the more popular form is obvious. As a rule, this drug is used after three main meals, 2 tablets each, that is, only six tablets per day. This course lasts three to four weeks. Further, if a maintenance regimen is necessary, the dosage is reduced to one tablet per dose: a total of three tablets per day, one after breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Such a dosage may seem large (as many as 6 tablets), but this is due to the fact that the drug is not covered with any protective coating, which leads to the destruction of its active substances at the stage of digestion: they do not achieve the desired goal. And so, the more the drug gets inside, the more active ingredients will reach their desired goal. Therefore, 2 tablets at a time is optimal.
And, by the way, athletes swallow even more of these pills per day, so 6 is not a lot.
Naturally, the medicine should be taken with water (200 ml): when digested, the tablets and water form a paste, which makes the components better absorbed.
In addition, this drug is quickly eliminated from the body, does not cause any serious side effects and is safe for both young and elderly people.
Why do athletes use the drug?
Athletes, including bodybuilders, take Asparkam, according to reviews, in order to support the heart muscle during prolonged heavy physical activity. In addition, the cause may be arrhythmia, neurocirculatory dystonia, as well as maladaptation (conditions caused by overtraining).
In this case, the use of the drug is determined by the fact that athletes often develop hypokalemia, expressed by convulsions, muscle weakness and cardiac arrhythmia. Also, potassium loss in athletes can develop due to dietary habits, namely a protein diet: the breakdown of proteins potentiates the release of toxic substances in the body. This process negatively affects the functioning of the liver and kidneys. Large amounts of fluid are required to remove toxins. Accordingly, not only toxic substances are excreted in the urine, but also trace elements, including potassium. This is confirmed by the instructions for use and reviews for Asparkam.
Another cause of potassium deficiency is excretion through sweat during exercise. It turns out that for many athletes who cannot eat foods rich in potassium due to their eating behavior, Asparkam is the only opportunity to replenish potassium reserves in the body
It is also important for athletes that the drug promotes the process of relaxation of muscle tissue, relieves tension and cramps, which allows them to achieve better results. The condition of the heart improves, its productivity and readiness for high loads increases
As a result, taking this drug reduces the risk of sudden death from cardiac arrest during intense exercise. In many cases, the tablets are taken immediately before exercise as it is believed to help replenish potassium lost through sweat. Often this drug is prescribed together with Riboxin.
Reviews
Reviews are 98% positive. This is due to obvious clinical indicators that are not long in coming and appear after the first course of treatment. There are also negative reviews, but almost all of them are based on incorrect self-administration of the drug without taking into account the maximum permissible dosages.
According to patients' reviews, heart function returned to normal, convulsions disappeared on the second or third day of taking Asparkam. The lion's dose of reviews was given by patients who underwent a complex therapeutic drug complex course of treatment after or during severe heart diseases: coronary and heart failure, and various other heart pathologies.
In these cases, Asparkam had a powerful positive effect in combination with other drugs: the heart rate returned to normal, the work of the heart muscle became stable. All tests after the course of treatment came back to normal.
Additional Information
Diacarb is a medicine that is often prescribed in cases of increased intraocular or intracranial pressure. Often in the recipe there is a combination of “Diacarb and Asparkam” - doctors prescribe them together. The fact is that the second drug helps prevent the side effects of the first.
When treated with Diacarb, the body loses a large amount of sodium ions and, accordingly, potassium, which can lead to negative consequences.
Potassium is a vital element involved in cellular metabolism. The myocardium – the heart muscle – especially needs it. The body also needs magnesium, which takes part in carbohydrate metabolism and transports energy to each cell to carry out biochemical reactions.
Normal heart rhythm is characteristic of the myocardium when it responds to an increase in magnesium concentration by decreasing excitability and conductivity. But with a large amount of potassium, the contractility of the heart muscle is inhibited, which can lead to cardiac arrest. This effect is possible with an overdose of Asparkam administered intravenously.
If the potassium content in the blood is low, then the acid-base balance in the body is disturbed. This is facilitated by an increase in blood alkalinity and an increase in acidity inside the cells, which leads to increased secondary absorption in the kidneys from primary urine of bicarbonate. In general, the formation of general metabolic alkalosis occurs.
Potassium deficiency is accompanied by lethargy, muscle weakness, heart rhythm disturbances, and decreased performance.
Asparkam restores the content of potassium and magnesium and promotes the rapid penetration of these substances into cells. Thanks to taking Asparkam with Diacarb, the osmotic pressure in the cells is restored, providing them with sufficient energy. Also, the combination with Asparkam increases blood acidity and removes bicarbonates from the body.
The simultaneous use of Diacarb and Asparkam allows you to compensate for the side effects of the former in the form of loss of potassium ions and an increase in blood alkalinity.
Neurologists often prescribe these drugs to patients to reduce intracranial pressure in various diseases and the consequences of traumatic brain injuries.
Properties
They are caused by the combined effect of potassium and magnesium on the heart muscle and help restore it after a heart attack. K+ improves the contractility of the heart, reducing excitability and improving muscle conduction. It expands the lumen of the great vessels of the heart. Magnesium stimulates the synthesis of amino acids necessary to compensate for the defect in muscle tissue and stimulates cell division, promoting rapid regeneration.
These properties are used in the treatment of glaucoma and high intracranial pressure. Normalization of metabolism and electrolyte balance relieves almost all negative symptoms associated with vascular overload. A side effect is accelerated muscle growth, which has proven important for athletes. Therefore, Asparkam is quite popular in strength sports.
Drug interactions
Compatibility information
| Product name | Possible impact |
| Potassium-sparing diuretics Beta blockers ACE inhibitors Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Immunosuppressant Cyclosporine | Risk of developing hyperkalemia, impaired intestinal perilstatics |
| Anesthetics | CNS depression |
| Antidepolarizing muscle relaxants Atracurium Dexametonin Suuxametonin | Increased neuromuscular blockade (Asparkam in ampoules) |
Possible influence on other medicinal substances
| Name of drugs | Possible effect |
| Stimulators of trophic processes in the myocardium | Strengthening the action |
| Streptomycin Neomycin Tetracycline Polymyxin B | Reduced effectiveness of drugs |
| Corticosteroids Saluretics | Preventing low blood potassium levels Reducing the risk of toxic effects from the use of these products |
| Iron supplements Tetracycline Sodium fluoride | Slow absorption |
| Cardiac glycosides | Reduced cardiotoxic effects |
| Calcium preparations | Reducing the effect of magnesium ions (for Asparkam solution) |
Pharmacological group
Thanks to the active components of the drug, Asparkam functions as an intracellular cation, has a positive effect on the heart muscle, and takes part in enzyme reactions in the body.
- ensures the conduction of nerve impulses;
- improves the elasticity of blood vessels;
- reduces blood viscosity;
- normalizes metabolic processes;
- improves myocardial muscle contraction.
This mechanism of action of the drug occurs due to the composition of the drug. The presence of potassium in the composition of the medicine provides the nerve endings with the necessary impulses, stimulates the heart, increases the supply of oxygen to the myocardial cells, which improves its functionality. Magnesium, which is also the basis of the drug, is responsible for the energy balance of the body, normalizes the balance of electrolytes, stimulates membrane permeability, and takes part in cell division.
The action of the drug “Asparkam”, which helps with potassium and magnesium deficiency in the body, is based on the ability of aspartates to move potassium ions into the intercellular space. In addition, active elements are involved in metabolism. The use of the drug allows you to normalize electrolyte levels, restore the deficiency of potassium and magnesium, and reduce the excitability and conductivity of the heart muscle.
The medicine creates a moderate antiarrhythmic effect, restores metabolic processes in the myocardium, and normalizes blood circulation. The medication reduces the sensitivity of the heart to glycosides and reduces their toxic effects. The product is well absorbed by the body, fills the blood with potassium and magnesium ions for 2 hours. Excreted through the kidneys.
Comparison with Panangin
Potassium and magnesium are part of another popular medicine. We are talking about Panangina. Comparative characteristics of drugs are presented in the table.
| Component | Pills | Solution | ||
| Panangin | Asparkam | Panangin | Asparkam | |
| Potassium aspartate | 160 mg | 180 mg | 45 mg/ml | |
| Magnesium aspartate | 140 mg | 10 mg/ml | ||
| Conversion to K+ ions | 36 mg | |||
| Conversion to Mg+ ions | 12 mg | 3.5 mg/ml | ||
| Aids | Silica, povidone, talc, magnesium stearate, starch, macrogol, titanium salts, methcric acid copolymers. | Starch, talc, calcium stearate, Tween-80. | Injection water. | Water for injection, sorbitol. |
Obviously, the active substances in both drugs are identical, the difference is in the cachet, which does not affect the medicinal properties of the drugs. However, Panangin has a film coating that protects the gastric mucosa and teeth from the chemical toxicity of the product. Therefore, Panangin is recommended to everyone who has problems with the digestive system, the price of which is several times higher than the cost of Asparkam.
Author Maria Ladygina
Scientific consultant of the project. Physiologist (Faculty of Biology, St. Petersburg State University, bachelor's degree). Biochemist (Faculty of Biology, St. Petersburg State University, Master's degree). Hatha yoga instructor (Institute of Human Resource Development Management, GENERATION YOGA project). Researcher (2013-2015 Ott Research Institute of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductology, work with markers of female infertility, analysis of biological samples; 2015-2017 Research Institute of Highly Pure Biological Products, drug development) Author and scientific consultant of websites on healthy lifestyle and science (in field of life extension) Since 2019, scientific consultant of the Cross.Expert project.
Aspark for children and infants
This drug is prescribed in children in exceptional cases when there is a clear lack of potassium and magnesium ions in the child's blood. Only Asparkam tablets are prescribed to children. Injections can only be used if the child’s life is at risk. The dosage is prescribed only after examination by a doctor, and for each child the dosage and duration of the course of treatment are individual.
Thus, for children under one year of age, the maximum dose of the drug can be up to 1/4 tablet per day; older children, depending on age, can be prescribed from ½ to 1 whole tablet per day. The dosage may be adjusted depending on repeated results.
Side effects of Asparkam
The instructions for Asparkam indicate that side effects develop extremely rarely. However, taking the drug can lead to malfunctions of the digestive system, namely nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, gastrointestinal bleeding, discomfort in the epigastric region, dry mouth, ulcers of the mucous surface of the gastrointestinal tract.
Allergic reactions in response to taking the drug can manifest as redness of the skin, itching and rash.
According to reviews of Asparkam, some patients complain of convulsions, paresthesia and hyperreflexia, which is a disruption of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
Rarely, respiratory depression may occur due to hypermagnesemia. In addition, some reviews of Asparkam talk about such a side effect as a feeling of heat.
As for drug overdose, to date no such cases have been recorded. However, according to the instructions, Asparkam in large quantities can theoretically lead to the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, metallic taste in the mouth, abdominal pain, weakness, bradycardia, muscle paralysis, disorientation, paresthesia of the limbs, thirst, redness of the facial skin, arterial hypotension, convulsions, impaired neuromuscular transmission, arrhythmia. In this case, it is necessary to stop taking Asparkam and undergo symptomatic therapy, including intravenous administration of a calcium chloride solution at a dosage of 100 mg/min. If the need arises, the patient undergoes hemodialysis.
Side effects
Asparkam has not only positive side effects, but also negative ones. They are visualized by the following symptoms:
Feeling weak, tired, dizzy.
- Muscle weakness.
- Skin rashes.
- Nausea.
- Dyspepsia.
- Dry mouth.
- Bloating.
- Hypotension.
- Hyperhidrosis.
- Dyspnea.
- Vein thrombosis.
In addition, an overdose is possible, which manifests itself:
- hyperkalemia;
- hypermagnesemia;
- crimson cheeks;
- thirst;
- arrhythmia;
- convulsions;
- arterial hypotension;
- heart blockades;
- depression of the respiratory center in the brain.
These symptoms require consultation with a doctor. In general, long-term use of Asparkam requires monitoring of electrolyte levels, because:
- the absolute safety of the drug has not been proven;
- when combined with tetracyclines, iron and fluorine, the medicine inhibits their absorption (the interval between medications must be at least three hours);
- there is a risk of developing hyperkalemia.
Compatibility
It has a different focus. From a pharmacodynamics point of view, combination with diuretics, beta blockers, cyclosporines, NSAIDs, heparin stimulates the development of asystole and arrhythmia. The combination with hormones stops this situation. Potassium ions reduce the negative effect of cardiac glycosides. Magnesium ions – neomycin, streptomycin, polymyxin
Calcium reduces the activity of magnesium, so such drugs should be combined with great caution, according to health indications
Pharmacokinetics warns about the incompatibility of Asparkam with astringent and enveloping drugs, since they reduce the absorption of the drug in the digestive tube and recommends, if necessary, maintaining a three-hour interval between doses.
Dosage for use
As with other drugs, there is a certain dosage that must be observed in order to avoid unwanted irreversible consequences. So, Asparkam, its indications for use in the following doses for adults and children:
- Tablet form - one or two tablets twice or three times (maximum) daily half an hour before eating. Children from three years old - a quarter of one tablet, the maximum dose per day is 175 ml. The course of treatment is up to 10 days.
- The solution for infusion is administered intravenously by drip up to two times daily for adults and children. The method of administration is slow (25 drops/min). For adults, dilute with glucose, drop up to 20 ml of Asparkam per day. And for children - up to 10 ml at the same speed.
- If you are using injection ampoules, then Asparkam is administered intravenously at a rate not exceeding 5 ml/min. Up to two times a day for adults and children.
Analogues and substitutes
Main analogues:
- Panangin.
- Panangin Forte.
- Plus Vitamin B6 Panangin.
- Potassium and magnesium aspartate.
What is better - Asparkam or a substitute and how much it costs - a comparison will show.
Comparative characteristics of tablets
| Name | Manufacturer | Content of the main active ingredient in 1 table. (mg) | Content of excipients in 1 table. (mg) | Tablets, pcs. | price, rub. |
| Asparkam | Pharmapol (Russia) | Potassium aspartate (175), magnesium aspartate (175) | Talc (10), potato starch (135), calcium stearate (5) | 60 | 38-41 |
| Health (Ukraine) | 50 | 43-47 | |||
| Medisorb (Russia) | Potato starch, sugar, polyvinylpyrrolidone, calcium stearate | 50 | 42-54 | ||
| Pharmstandard (Russia) | Potato and corn starch, talc, calcium stearate | 20 | 30-48 | ||
| Asparkam avexima | Avexima (Russia) | magnesium aspartate tetrahydrate (175) potassium aspartate hemihydrate (175) | potato starch (88), stearic acid (5), macrogol 4000 (7), colloidal silicon dioxide (50) | 56 | 73-110 |
| Panangin | Gedeon Richter (Hungary) | potassium aspartate (in the form of hemihydrate) (166.3), magnesium aspartate (in the form of tetrahydrate) (175) | colloidal silicon dioxide (2), magnesium stearate (4), povidone (3.3), starch: (corn-86.1), (potato – 3.3), talc (10) | 50 | 132-148 |
| Panangin forte | Gedeon Richter (Hungary) | potassium aspartate (hemihydrate) (316), magnesium aspartate (tetrahydrate) (350) | Talc (20.0), corn starch (172.2), potato starch (6.6), magnesium stearate (8.0), colloidal silicon dioxide (4.0), povidoneKZO (6.6) | 60 | 323-376 |
| Plus Vitamin B6 Panangin | Gedeon Richter (Poland) | magnesium aspartate tetrahydrate (140), potassium aspartate hemihydrate (158), vitamin B6 (0.6) | Microcrystalline cellulose, talc, magnesium stearate, potato starch, EudragitE-100, polyethylene glycol 6000, silicon dioxide, titanium dioxide, crospovidone. | 60 | 334 |
Comparative parameters of solution for injection
| Name | Who produces | Content of active substances, (g/l) | Excipients, (g/l) | Solution | Cost, rub. |
| Asparkam | Farmak (Ukraine) | Potassium L-aspartate anhydrous (45.2), magnesium L-aspartate anhydrous (40.0) | Sorbitol (50), water for injection – about 1 liter. | 10 ml (10 ampoules) | 78-100.20 |
| 5 ml (10 pcs.) | 53-71.90 | ||||
| Asparkam-L | Biosynthesis (Russia) | 5 ml (10) | 45-67 | ||
| Bottle 400 ml (12 pcs.) for infusion | 1281 | ||||
| Panangin | Gedeon Richter (Hungary) | Potassium aspartate hemihydrate (45.2), magnesium aspartate tetrahydrate (40.0) | Water | 10 ml No. 5 | 135-172 |
| Potassium and magnesium aspartate | East Farm (Russia) | Potassium L-aspartate (anhydrous) (10.02), magnesium L-aspartate (anhydrous) (7.86) | Sorbitol (20.00), water for injection (up to 1 l) | Bottle 250 ml | 89.70-90.00 |
| 500 ml | 167.20-169.00 | ||||
| Potassium and magnesium aspartate Berlin-chemi | (Germany) Berlin-Chemie AG/ Menarini Group | D,L-aspartic acid (15.16), potassium hydroxide (3.854), magnesium oxide (1.116) | Xylitol (16.7), water for injection (976.2) | Bottles 250 ml | 261.00 |
Release form
Asparkam is available in several forms:
- Tablet form. One tablet of the drug contains up to 175 mg of the active substance (magnesium aspartate with potassium aspartate). One package contains 10 or 50 tablets.
- Solutions for administration of infusions (droppers). Contains up to 11.6 g of active ingredient. Available in 400 ml glass bottles.
- Ampoules for injections. The content of the main active agent in each ampoule (10 ml) of the drug is up to 0.4 g. Packaged in cardboard packs of 5 or 10 ampoules (5, 10 or 20 ml each).
- Indications for use of panangin
- Medicines for the treatment of increased intracranial pressure - a list of the most effective tablets
- Sparex - instructions for use, composition, release form, indications, side effects, analogues and price
Asparkam instructions for use
Depending on the form of release, as well as the problem, the dosage and methods of using the drug vary.
Asparkam tablets must be swallowed without chewing. You just need to fill them with a small amount of water. Usually, when prescribing treatment, doctors recommend taking 2 tablets three times a day. The course lasts a month. Then you need to take a break for 2-3 months and repeat the intake again. When using the drug for preventive purposes (for potassium and magnesium deficiency), you need to drink 3 tablets a day immediately after eating. How long this course will last depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Some athletes take this remedy on an ongoing basis. At the same time, you need to take tests every month to monitor the level of potassium and magnesium in order to exclude an overdose of the drug. There is no point in taking more than 6 tablets per day, since the excess is simply excreted from the body along with urine, and is not absorbed by the body. This increases the load on the kidneys, which does not always have a good effect on this organ.
The dosage of the drug and the duration of use depend on the form of release of the drug. Asparkam in tablet form is prescribed in the amount of one or two tablets three times a day, the duration of administration is about three or four weeks
While Asparkam tablets can be used as prophylaxis, intravenous solutions are prescribed only for treatment. The medicine is administered using a syringe or as a dropper directly into a vein. After opening the ampoule, the solution should be used immediately.
The instructions for Asparkam indicate that in case of heart disease, the solution is administered intravenously at 10-20 ml for the first 5 days. In this case, the medicine is mixed with saline or dextrose. For a dropper or intravenous drip, use a 300 ml jar (2 times a day for 5 days).
Why is Asparkam prescribed?
1. Most often, this drug is used in the treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system. This may be arrhythmia, angina or heart failure. Sometimes Asparkam is also prescribed along with certain medications. What is it for? Some medications can cause arrhythmia or abnormal heart rhythms, as well as contribute to excessive potassium excretion.
2. To strengthen the nervous system, with nervousness, irritability and stress.
3. To normalize the functioning of the gallbladder and gastrointestinal tract.
4. In the complex treatment of certain diseases associated with a lack of potassium and magnesium.
5. When recovering from binge drinking, treating alcoholism.
6. Why else is Asparkam taken? Some conditions cause potassium deficiency, such as excessive sweating, bowel disorders, or taking diuretics. Recently, it has been recommended to take this drug while following weight loss diets. It helps replenish micronutrient deficiencies and accelerates weight loss.
Indications for taking Asparkam
The main function of Asparkam is the transport of microelements into the cell. The drug is prescribed in the following cases:
- Deficiency of K+ and Mg+ in the body.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
- IHD, post-infarction condition.
- Ventricular extrasystole.
- Foxglove intolerance.
- State of shock.
- Chronic circulatory disorder.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Heart failure.
- From 4 months it is recommended in combination with Diacarb to correct intracranial pressure. This combination treats glaucoma, epilepsy, edema, and gout.
Sport
It cannot be said that Asparkam has a significant effect on muscle growth. Therefore, in theory, this is not the drug of choice for sports. But, nevertheless, its popularity among athletes is great. This is explained simply: when gaining extra pounds, athletes eat a large amount of calories in the form of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. At the same time, microelements account for a very small part of the diet. It is clearly not enough for normal cardiac activity. Moreover, a lack of potassium and magnesium leads to high fatigue due to metabolic imbalances. Asparkam in this case is irreplaceable.
Compact, easy to take and rich in essential K+ and Mg+ preparation:
- Relieves the feeling of fatigue.
- Replenishes micronutrient deficiencies.
- Relieves muscle weakness.
- Makes myocardial function stable.
- Stimulates endurance.
- Prevents AMI and stroke.
Body-building
As for bodybuilding, here Asparkam acts as an excellent metabolite. It is during strength training that its side effect of building muscle mass is in demand. Potassium has a positive effect on the speed of metabolic reactions, magnesium is involved in protein metabolism. In this case, cell growth occurs without fat accumulation and fluid retention in the body. This is a very important point, since during training athletes consume large amounts of water, which washes away microelements. This means that their replenishment becomes an urgent necessity.
Weight loss
The rationality of taking the drug is based on the same already familiar properties of magnesium and potassium. Mg+ is needed by the central nervous system, and K+ helps all muscles in the body. Together they correct the water-salt balance and remove swelling. Because of this feature, Asparkam is used for weight loss: removing fluid from the body allows you to lose weight. At the same time, the amount of fat deposits remains unchanged, so the drug has never been classified as a means of helping to lose weight. Taking it thoughtlessly is dangerous, since it is a metabolite, and metabolism is a very delicate substance. An excess of microelements has undesirable consequences, but in no way accelerates metabolic processes.
Indications
The drug is prescribed as an additional drug in the treatment of conditions and diseases such as:
- Disturbed heart rhythm, manifested in the form of paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial or ventricular extrasystole. The causes of these conditions may be an overdose of cardiac glycosides, myocardial infarction, etc.
- Intoxication of the digitalis type, caused by intolerance or poisoning with drugs related to cardiac glycosides.
- Heart failure.
- Rehabilitation period after a heart attack.
- Ischemic heart disease.
“Asparkam” is also used as an independent drug. In this case, it is prescribed for hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia of various origins. In case of deficiency of potassium and magnesium, the drug is prescribed to restore the concentration of ions of these elements in the blood.
Asparkam is used to restore magnesium and potassium levels after frequent vomiting and diarrhea, taking diuretics, laxatives and glucocorticosteroids.
We will consider reviews of the use of Asparkam below.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the drug, sorbitol, hyperkalemia, hypermagnesemia, acute renal failure, adrenal insufficiency, atrioventricular block of II and III degrees, impaired amino acid metabolism, hemolysis, myasthenia gravis, dehydration; Addison's disease, age under 18 years (the effectiveness and safety of the drug have not been established).
With caution: Severe liver dysfunction, metabolic acidosis, risk of edema, chronic renal failure, if regular monitoring of magnesium levels in the blood serum is impossible (risk of accumulation, toxic magnesium levels), cardiogenic shock (systolic blood pressure less than 90 mm Hg), hypophosphatemia, urolithiasis associated with impaired metabolism of calcium, magnesium and ammonium phosphate, first degree atrioventricular block.
Interaction with other drugs
Asparkam can be used in combination with other medications. You should be careful, since the active substance of this drug is not compatible with all medications. This can cause many undesirable consequences and side effects. Therefore, read in detail the list of medications, combining asparkam with which is possible or strictly contraindicated:
- Asparkam is not required if you are using diuretics that contain potassium-sparing medicinal components.
- "Cyclosporine." It also contains potassium-sparing components, therefore it is incompatible with Asparkam.
- Beta blockers (same as the previous drug).
- Asparkam can be combined with drugs that contain digitalis or strophanthin.
- If you combine it with medications that contain tetracycline, sodium fluoride, iron, you will get the effect of reducing the toxic effects of cardiac glycosides on the myocardial muscle.
- The central nervous system is depressed if you combine asparkam with anesthetic drugs.
- The effectiveness of antibiotics is significantly reduced if a person takes asparkam at the same time.
Myths about aspartame
In the long debate about whether aspartame is harmful or beneficial for the body, the main argument is the chemical nature of the substance. It consists of three components, into which it breaks down in the body: amino acids - aspartic acid (40%) and phenylalanine (50%), as well as toxic methanol (10%).
Potential toxicity has given rise to many myths around the ill-fated sweetener. Here are the most popular ones:
- Methanol in sweetener poisons the body and can cause temporary blindness.
- The additive causes a whole range of neurological disorders: insomnia, depression, problems with memory and attention, panic attacks, ringing in the ears, severe headaches and convulsions.
- Aspartame increases appetite and causes excess weight.
- During pregnancy, consuming a sweetener can cause birth defects in the fetus.
- Toxic substances in aspartame can provoke the growth of various types of tumors.
What are the restrictions on the use of the medicine?
Contraindications to the use of Asparkam injection tablets are:
- Impaired kidney function in acute or chronic form;
- Hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia;
- Dehydration of the body;
- High susceptibility of drug components;
- Amino acid metabolism disorder;
- Addison's syndrome;
- Adrenal insufficiency;
- Myasthenia gravis in severe form;
- Hypotension;
- Hemolysis;
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In some cases, Asparkam therapy is allowed during pregnancy or breastfeeding. This happens in the following cases:
- Increased uterine tone;
- Miscarriage;
- Uterine gestosis;
- Swelling of the extremities;
- Heart diseases;
- Lack of potassium and magnesium in a woman’s body;
- Irregular bowel movements.
During drug therapy, driving a car and other mechanisms is allowed.
The risk of developing hyperkalemia, which will be accompanied by arrhythmia and asystole, increases several times with the simultaneous use of beta-blockers, cyclosporines, NSAIDs, and diuretics that accumulate potassium.
Be sure to read: One of the best remedies for fighting stretch marks - Bepantol Emulsion
With the simultaneous use of glucocorticosteroids, hypokalemia is eliminated. The effectiveness of drugs such as Neomycin, Polymyxin, Streptomycin, and Detracycline decreases. When taking muscle relaxants with Asparkam, the neuromuscular blockade increases.
It is impossible to simultaneously carry out therapy with antibacterial and painkillers. The effectiveness of Asparkam is increased by products containing foxglove or strophanthin.
Do not take the medicine together with alcoholic beverages. This is due to many reasons:
- Development of vasospasm;
- Circulatory disorder;
- Brain hypoxia, which leads to serious and dangerous complications;
- Disorder of water-salt balance;
- Removal of potassium and magnesium from the body in the urine;
- Possible death.
Before using the drug, it is important to consult a doctor, who can refer you for additional examinations, and based on their results, he will determine whether Asparkam Avexima can be used as therapy in a particular case.
Medicinal properties
Insulin aspart is a drug based on natural short-acting insulin. It interacts with a number of receptors located on the outer cytoplasmic cell membrane, resulting in the formation of the so-called insulin receptor complex. The drug helps to activate the production of the enzymes hexokinase, glycogen synthetase, and pyruvate kinase.
The hypoglycemic effect is due to improved intracellular transport and normalization of glucose absorption within tissues. In this case, activation of glycogenogenesis and lipogenesis is observed, and the rate of glucose production by liver cells is significantly reduced.
Insulin aspart acts much faster than human insulin, as it lowers glucose levels more effectively - for 4 hours after meals. After administering the drug under the skin, the therapeutic effect appears after 10-20 minutes, the highest effectiveness is recorded 1-3 hours after the injection. The duration of exposure is 3-5 hours. It is worth noting that during antidiabetic therapy, the likelihood of nocturnal hypoglycemia is significantly reduced.
Biphasic insulin aspart is characterized by the same principle of pharmacological effects on the body.
The effect of using the drug is registered almost immediately after administration (within 10 minutes), and 70% of the drug remains in reserve subcutaneously. Biphasic insulin is released gradually, the duration of action is up to 24 hours.
What is this drug for?
Potassium and magnesium are the main intracellular ions that play an essential role in regulating body functions. Potassium is involved in the regulation of the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers, muscle contraction, myocardial function and much more. Magnesium activates about 300 enzymes in the body, is a physiological antagonist of calcium and helps to inhibit spontaneous contractions of isolated smooth and transverse muscles. Both ions, potassium and magnesium, support the polarization of cell membranes.
The occurrence of a deficiency of these ions is associated with their increased excretion due to diseases of the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract, the use of diuretics and cardiac glycosides, alcohol abuse, etc., as well as due to a decrease in the intake of potassium and magnesium from food. The consequence of a deficiency of potassium and magnesium ions in the body is, first of all, disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and the occurrence of arrhythmias. Particularly dangerous, requiring intravenous administration of potassium and magnesium preparations, are arrhythmias and conditions during and after myocardial infarction.
The drug is used for arrhythmias caused by hypokalemia, intoxication with cardiac glycosides, and ventricular extrasystole; circulatory failure. The use of Asparkam-L is recommended for the correction of hypokalemia when using loop diuretics. In the treatment of angina pectoris as an adjuvant, during cardiac surgery, during myocardial infarction and in conditions after a heart attack. It will also help to quickly and effectively deliver potassium and magnesium ions into the intracellular space.
Why Asparkam-L?
Similar, well-proven drugs are widely known on the pharmaceutical market, such as “Panangin” from Gedeon Richter (Hungary), “Asparkam” from Farmak (Ukraine) in the form of solutions for intravenous administration, a solution for infusion “Potassium-magnesium asparaginate” (Berlin -Hemi, Germany). These drugs contain potassium and magnesium salts of D,L-aspartic acid.
Asparkam-L is obtained from pure L-aspartic acid. It is known that only L-amino acids are absorbed by the body, which have special transport systems into the intracellular space and are effectively included in cellular metabolism. L-Aspartate binds metal ions and transports them into the cell through its own transport system. D-enantiomers of amino acids are inactive for most of the body's enzyme systems and are practically not absorbed by it. Studies have shown faster saturation of erythrocytes and myocardium with potassium and magnesium ions when using L-aspartic acid salts compared to racemate (D,L-aspartate). It has also been shown that D-aspartate is excreted in the urine and is a ballast impurity that increases the load on the body's excretory system.
Clinical studies of the drug showed
- When used in patients with myocardial infarction (as part of complex therapy), it helps restore and maintain normal levels of potassium in the blood serum and magnesium in the blood serum and red blood cells (tissues).
- Improves the clinical status of patients and exercise tolerance. Significantly reduces the frequency and severity of anginal attacks. Helps reduce the frequency of arrhythmias and improve the Quality of life of patients.
- During a course of treatment at the recommended dosage, it is a safe and well-tolerated drug.
- In a comprehensive comparative assessment, the effectiveness and safety of Asparkam-L is comparable to Panangin and KMA, and in terms of the dynamics of improving clinical status and preventing the development of recurrent acute infarction, it is superior to comparison drugs.
Also, our study drug:
- reduces severe heart rhythm disturbances,
- improves the tolerance of cardiac glycosides,
- reduces the incidence of arrhythmias and mortality when administered prophylactically, and prevents recurrent arrhythmias.
Dynamics of ischemia parameters in patients with myocardial infarction after 10 days of therapy with Asparkam-L
Dynamics of rhythm disturbances in patients with myocardial infarction after 10 days of therapy
Aspartame myths, beneficial properties and contraindications
Aspartame is a low-calorie artificial sweetener that is almost 200 times sweeter than sugar. This substance was accidentally discovered in the 60s of the last century. Today, aspartame is the second most popular sweetener in the world and is actively used in the production of food and medicine. It is approved for use in more than one hundred countries around the world.
Myths about the dangers of aspartame
Aspartame only came onto the market as a dietary supplement in 1981. It has passed many tests that have proven its complete safety. But 15 years later, an article appeared in the press that the use of aspartame was associated with an increase in the number of brain tumors. It was at that moment that panic arose around this sweetener. People were afraid. It took many years to dispel the myth about the carcinogenicity of aspartame and its side effects.
In particular, the US National Cancer Institute published information according to which the increase in the number of brain tumors began already in 1973, that is, long before aspartame appeared on the market. In addition, this disease was most often diagnosed in people over 70 years of age, who were not the main consumers of products containing aspartame.
Numerous studies have found no connection between aspartame and cancer, behavioral disorders, poor health, or even the headaches that consumers often complain about. As it turned out during the tests, headaches appeared in anxious and suspicious people and were not associated with the amount of aspartame in the product.
During its use, aspartame has been studied so thoroughly that further research simply does not make sense. Like any other food additive, if aspartame has been approved for use in food and beverages, it is safe to use.
Does aspartame turn into poison?
Unlike other synthetic sweeteners, aspartame is completely metabolized by the body during digestion. It breaks down into three components: aspartic acid, phenylalanine and methanol.
Aspartic acid and phenylalanine are common amino acids that are part of proteins and perform an important function in the nervous system. Both amino acids are necessary for our body, and they can only be obtained from food. One liter of carbonated drink with aspartame contains a negligible amount of these substances. Much more aspartic acid and phenylalanine are found in the most common foods - meat, fish, eggs and milk.
So much controversy about the safety of the sweetener is caused by the third component - methanol, which is released when aspartame is broken down. The fact is that this sweetener is thermally unstable. Some believe that this is precisely the reason for the recommendation to drink carbonated drinks chilled. But that's not true. Cooling just improves the taste of the drink, and methanol is formed in the body regardless of whether you drink soda cold or warm.
Methanol is a strong poison and turns into formaldehyde. There is a misconception that the latter accumulates in the body and leads to disease. If this were true, we would all have died long ago, since methanol is found in the vegetables and fruits that we eat every day. Moreover, from them we get methanol (and formaldehyde), many times more than from products containing aspartame.
To exceed a safe dose of methanol, you need to drink more than 30 liters of soda with aspartame per day. Agree, this is an unrealistic amount.
Properties of aspartame
Aspartame is popular as a sugar substitute because it has a zero glycemic index. This makes it possible for people with diabetes to use the substance. In addition, products with aspartame do not contain calories, which makes it possible to include the sweetener in a weight loss diet.
Externally, the substance appears as white crystals. Aspartame has a good taste, similar to the taste of sugar, without unpleasant overtones or aftertaste. The sweetness of aspartame develops more slowly but lingers in the mouth longer. This is the main property due to which the substance is included in chewing gum.
This sugar substitute is available on sale in tablets, powder or liquid form. Aspartame is included in sugar substitute mixtures. The substance is often used in conjunction with acesulfame potassium. This combination improves the flavor and increases the sweetness quotient of the finished product.
This sweetener is marketed under the names: Milford Suss Aspartame, Novasweet, NutraSweet, Canderel, NatraTaste, AminoSweet, Equal. Included in the mixtures: Sladis, Slastin.
Uses of aspartame
Aspartame is actively used:
- in the food industry for the production of dietary products and general products
- in confectionery products for diabetics
- in chewing gum
- in medicines to give them a sweet taste. For example, vitamin complexes contain
- aspartame, including those intended for children
- in sports nutrition to improve the taste characteristics of protein
Aspartame in products
Products with aspartame can be found on the shelves of any store. The substance is included in:
- non-alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks
- chewing gums and lozenges
- chocolate, sweets, lollipops
- yoghurts, curd cheeses
- ice cream
- jelly
- instant drinks: hot chocolate, coffee, cocoa, tea
- toppings for desserts
The taste of products with aspartame differs from similar ones with sugar in the composition; they are more sweet and somewhat cloying.
Benefits of aspartame
Aspartame has no nutritional or energy value and does not have a healing effect. The benefits of this substance boil down to its safe use as a sweetener and sugar substitute for diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Useful properties of aspartame:
- has a zero glycemic index
- can be used in the fight against excess weight, as it contains few calories
- does not destroy tooth enamel
- not carcinogenic
Instructions for use of aspartame
Although aspartame is primarily used in industrial products, it can also be used in home cooking. Since this sugar substitute is not suitable for heat treatment, it is used in cold dishes. For example, aspartame is added to chilled drinks, desserts, dairy products, and salads.
Aspartame is considered safe when taken within daily limits. In Europe, the maximum dose is 40 mg per kg of body weight per day, in the USA - 50 mg/kg.
When consuming aspartame, you must follow these recommendations:
- use only cold, as when heated the substance loses its properties
- do not consume on an empty stomach
- recommended single dose – 18–36 mg per 250 ml of liquid
Making yogurt with aspartame
Aspartame is added to fermented milk products as a sweetener. This is a good option when you need to reduce or eliminate your sugar intake.
To make yogurt you will need:
- 1 liter of milk
- 1 g starter or 100 ml natural yoghurt
- aspartame to taste
The milk is pre-boiled and then cooled to 37-40 degrees. When the milk has cooled to the desired temperature, add starter (or natural yogurt) and mix thoroughly.
The future yogurt is placed in a warm place for 8 hours. You can prepare a fermented milk drink in a yogurt maker or multicooker using the appropriate mode. After the time has passed, aspartame is added to the yogurt, everything is mixed and put in the refrigerator to ripen for two hours.
Side effects and contraindications
Aspartame should not be used for:
- phenylketonuria
- epilepsy
- hypersensitivity to the substance
Aspartame or xylitol
Aspartame is an artificially synthesized substance, xylitol is a natural sweetener. Both sugar substitutes are widely used in the health food industry. Aspartame and xylitol are especially often added to chewing gum and carbonated drinks.
| Properties | Aspartame | Xylitol |
| Sweetness factor | 180 | 1 |
| Calorie content per 100 g | 400 | 243 |
| Glycemic index | 0 | 7 |
| Heat treatment | No | possible |
| Negative effect on teeth | No | No |
According to the table, aspartame is more suitable than xylitol for nutrition for people with endocrine diseases and excess weight.
Features of aspartame:
- zero glycemic index
- Products with aspartame contain negligible calories
- much higher degree of sweetness
- short shelf life
- increases appetite and thirst
- impossibility of heat treatment
Features of xylitol:
- has a beneficial effect on the condition of the oral cavity
- has a gentle effect on digestion
- has a choleretic effect
- has a laxative effect
- the substance can be added to hot drinks and cooked with it in various dishes
Aspartame or stevia
Both sweeteners are effective and safe alternatives to sugar. According to the characteristics of stevia, it is more suitable for use in everyday life than aspartame. A comparison of the properties of aspartame and stevia can be seen in the table:
| Properties | Aspartame | Stevia |
| Sweetness factor | 180 | 300 |
| Calorie content per 100 g | 400 | 0 |
| Glycemic index | 0 | 0 |
| Heat treatment | No | possible |
| Negative effect on teeth | No | No |
Features of aspartame include:
- no aftertaste
- low cost
- impossibility of heat treatment
Features of stevia:
- higher degree of sweetness
- zero calorie content
- Can be used in hot dishes and drinks
- specific taste
Stevia is considered safer because it is natural and traditionally used. But this is a stereotype, since often products of natural origin are more harmful to health than artificially synthesized food additives. Aspartame has undergone many tests over the years to prove its safe use in products.
What is the dosage regimen?
Diacarba and Asparkam tablets must be used correctly and in accordance with the instructions for use, which will ensure the effectiveness of the drugs without the development of side effects from treatment. The choice of dose depends on the patient’s age, his weight and the underlying pathology for which it is necessary to take these drugs. In case of a lack of microelements in the body due to long-term use of these substances, Panangin is prescribed. It saturates the body with magnesium, sodium and potassium, promoting the normal functioning of all cells in the human body.
How to take for adults with ICP?
Patients over 18 years of age can take 1 tablet of Diacarb, which contains 250 mg of active ingredient, up to 4 times a day. The maximum dose of the product over 24 hours should not exceed 1 gram. This will help prevent the development of side effects. For high intracranial pressure, most often take 2 tablets in the morning and evening. The course of treatment lasts 4 days, after which you need to take a 3-day break. This will prevent the leaching of microelements from the body and provide a pronounced therapeutic effect.
A single dose of the drug for an adult should be 2 tablets.
One Asparkam tablet contains 250 milligrams of active substance, half of which is magnesium and the rest is potassium. The maximum dose of the drug during the day should not exceed 9 tablets. For ICP, adults are prescribed 2 tablets. 3 times a day, which provides the body’s needs for microelements, which are washed away due to the use of Diacarb.
How is it prescribed to children?
The dosage regimen for Diacarb and Asparkam depends on the age and weight of the child. Infants are advised to use syrups and suspensions that contain the same active ingredient, and the drugs are taken at a dose of 50 mg per day. After 3 years, children, like adults, can take capsules. “Asparkam” and “Diacarb” are indicated for children with congenital cerebrospinal fluid hypertension, as well as excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles.
Why do healthy people need Asparkam?
This drug has long been popular not only among cardiologists. It is prescribed by therapists for decreased performance and frequent seizures. Sports medicine doctors also paid attention to this remedy. Now the drug is actively used by athletes, especially in bodybuilding. It neutralizes the negative effects of a special protein diet for muscle building and prevents potassium and magnesium deficiency. “Asparkam” increases performance, eliminates fatigue, and prevents the occurrence of cramps.
In addition, recently it has become popular to take this drug for weight loss. After all, it normalizes metabolic processes, prevents fluid retention in the body, and strengthens the heart muscle. Asparkam alone will not help you lose weight, but it can be an addition to diets and sports training. Although, even healthy people can take this drug only after consulting a doctor.
What are the contraindications
Now let's look at the contraindications.
Here they are:
- Individual intolerance.
- Kidney problems.
- Excess potassium.
- Excess magnesium.
- Pathologies of metabolic processes.
- Problems with the genitourinary system.
- Concomitant use with diuretics.
- Rarely prescribed to children. Especially babies.
- Not recommended for pregnant and lactating women.
During the course of treatment, you should not drink alcohol, which will negatively affect kidney function. There are certain restrictions for older people.
What a joint action
"Diacarb" is a diuretic drug with a moderate effect and helps reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain. This is due to the inhibition of a specific enzyme that is involved in the reduction of carbon dioxide from carbonic acid. This reduces the reabsorption or reabsorption of microelements, primarily potassium and magnesium, which retain fluid in the body.
The drug reduces the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid, thus reducing ICP. Due to the accumulation of carbon in the brain, excessive paroxysmal discharges of neurons are inhibited, causing the antiepileptic effect of the drug. When used together with Asparkam, the preservation of microelements important for life and their direction into the cell is ensured. This leads to the removal of excess fluid from the body without loss of magnesium, sodium, K and Ca, which are necessary for normal metabolism, primarily the heart.
Indications for use
Both drugs can be taken by people with ari and its substitute “Asparkam” is used in the treatment of such pathologies as:
- hypopotassium and magnesemia;
- chronic cardiovascular failure;
- states of shock;
- cardiac ischemia;
- arrhythmias;
- secondary cardiomyopathies.
Clinical data confirmed a decrease in pathological metabolic changes caused by deficiency and impaired oxygen utilization by tissues. "Panangin" maintains the metabolism of the heart muscle at an adequate level even in conditions of deterioration of coronary circulation and hypokalemia, provoked by prolonged and uncontrolled use of diuretic pharmaceuticals from the saluretic group.
Comparison of pharmaceuticals
Composition and pharmacological effects
“Asparkam” and “Panangin” contain one active substance - magnesium and potassium aspartate. The use of the drug replaces the deficiency of electrolytes in the heart cells. Both pharmaceutical products are sold in the form of tablets and ampoules for intravenous administration. The content of active metabolites does not differ. A comparison of the action shows that both “Asparkam” and “Panangin” are equally beneficial for the heart. Potassium and magnesium help restore metabolism in cardiomyocytes. Electrolytes take part in neuromuscular conduction, the processes of cell growth and division, as well as tissue respiration.
Overdose
Symptoms: hyperkalemia (bradycardia, arrhythmia, drop in blood pressure, vascular collapse, diastolic cardiac arrest, neurotoxic symptoms) and hypermagnesemia (nausea, vomiting, lethargy, bladder weakness, deterioration of atrioventricular conduction and ventricular propagation of excitation, at higher concentrations of Mg++ ions in plasma - drop in blood pressure, respiratory paralysis, "magnesium anesthesia", at extremely high concentrations - diastolic cardiac arrest).
Treatment: intravenous administration of solutions of calcium and sodium salts, intravenous drip administration of glucose with insulin (1 unit of insulin for every 3-5 g of glucose). For peripheral paresis caused by the toxic effect of Mg++ ions, especially with paralysis of the respiratory muscles, physostigmine can be administered. In the presence of renal failure, extrarenal elimination can be achieved by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
The drug Asparkam: indications for use and contraindications
In case of disturbances in the functioning of the heart and hypokalemia, the doctor may prescribe Asparkam.
Indications for use of this drug, which are indicated in the instructions:
Insufficient blood supply to organs in heart failure. Atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease, which developed due to insufficient oxygen supply to the heart. Heart rhythm disturbances of various etiologies. Previous myocardial infarction. Complications from an overdose of glycosides.
Asparkam is available as a solution in glass ampoules. Their volume can be different: 5 ml, 10 ml, 20 ml. They are packed in a thick cardboard box, lined with corrugated paper. The drug is accompanied by instructions that provide information about indications and contraindications for taking the drug.
You can also find Asparkam tablets at the pharmacy. The indications for the use of this form of medication are similar, but it is not suitable for people with gastrointestinal problems.
Asparkam is prescribed if the patient is diagnosed with potassium and magnesium deficiency, as well as for heart disease. It is used if the patient has had a heart attack and with coronary heart disease, as well as with rhythm disturbances. It will be useful for chronic circulatory failure, and after conditions that lead to a lack of potassium and magnesium in the body.
The use of this drug can improve metabolic processes. It is used in the complex treatment of edema and cramps together with diuretics.
The effect of the drug on the body occurs due to its constituent potassium and magnesium, which have the ability to penetrate into the intercellular spaces.
Use for various purposes not indicated in the instructions is permissible if you know the principle of action of the medicine and the characteristics of your body.
Asparkam can be used both in sports and for weight loss alone or in combination with other medications:
Asparkam and Riboxin. Asparkam is a drug that helps quickly restore electrolyte balance. In addition to therapeutic and preventive purposes, it is used in bodybuilding. It can reduce fatigue, which promotes faster muscle mass gain. Magnesium, which is part of it, is involved in protein metabolism and is a supplier of energy for muscle building. With the help of Asparkam, athletes have the opportunity to eliminate the lack of magnesium and potassium salts, the loss of which occurs during forced drying and weight loss. To increase endurance in bodybuilding, Asparkam is often used in combination with Riboxin. This complex of drugs allows you to increase the effectiveness of training, protects and increases the productivity of the heart muscle. They are also used to prevent cardiac arrest from overload and myocardial diseases. Asparkam may be useful for weight loss. In order to free the body of toxins, it is recommended to drink a lot of fluid, which flushes out not only harmful substances, but also useful ones. With Asparkam you can replenish this supply and regulate metabolism. Of course, before using the drug, it is better to consult a doctor, since it is not a dietary supplement. Asparkam can be used for hangovers , especially if alcohol abuse is constant.
When taking the drug in order to replenish the ions of salts washed out of the body during training, poisoning and weight loss, it is better to take the medicine in tablets. Droppers and injections of the drug Asparkam, indications for the use of the drug are more related to the treatment of diseases and arrhythmias.
Prices for Asparkam, unlike Panangin, are much lower. It is an analogue of this medicine and there are many positive reviews from people who have used it. Dr. Komarovsky’s forum also mentions the use of potassium and magnesium aspartate in pediatrics for infants in the presence of cysts and cerebral edema.
Do you still think that it is difficult to cure hypertension?
Enter your pressure
130
on
90
Search in progress Not found
Judging by the fact that you are reading these lines now, victory in the fight against pressure is not yet on your side...
The consequences of high blood pressure are known to everyone: these are irreversible damage to various organs (heart, brain, kidneys, blood vessels, fundus of the eye). In later stages, coordination is impaired, weakness appears in the arms and legs, vision deteriorates, memory and intelligence are significantly reduced, and a stroke can be triggered.
window.RESOURCE_O1B2L3 = 'kalinom.ru'; var m5c7a70ec435f5 = document.createElement('script'); m5c7a70ec435f5.src='https://www.sustavbolit.ru/show/?' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '=' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '= 13698&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000) + '=' + document.title +'&' + Math.round(Math.random()*100000); function f5c7a70ec435f5() { if(!self.medtizer) { self.medtizer = 13698; document.body.appendChild(m5c7a70ec435f5); } else { setTimeout('f5c7a70ec435f5()',200); } } f5c7a70ec435f5(); (function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-336323-4', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-336323-4', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks '); (function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-336323-3', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-336323-3', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks '); (function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-336323-2', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-336323-2', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks '); (function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-336323-8', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-336323-8', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks '); (function(w, d, n, s, t) { w = w || []; w.push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: 'RA-336323-1', renderTo : 'yandex_rtb_R-A-336323-1', async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName('script'); s = d.createElement('script'); s.type = 'text/javascript '; s.src = '//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js'; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this, this.document, 'yandexContextAsyncCallbacks ');
VseDavlenie.ru » Drugs for blood pressure » Combined drugs
Instructions
- Russian
- Kazakh
Tradename
International nonproprietary name
Dosage form
Solution for injection, 100 U/ml
Compound
1 ml of the drug contains
active substance - insulin aspart 100 units (3.5 mg);
excipients: glycerol, phenol, metacresol, zinc, sodium chloride, sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, sodium hydroxide 2 M, hydrochloric acid 2 M, water for injection.
One bottle contains 10 ml of solution, equivalent to 1000 units.
Description
Transparent colorless liquid.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Medicines for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Insulins.
Insulins and fast-acting analogues. Insulin aspart.
ATX code A10AV05
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacokinetics
After subcutaneous administration of insulin aspart, the time to reach maximum concentration (tmax) in blood plasma is on average 2 times less than after administration of soluble human insulin. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) averages 492 ± 256 pmol/l and is achieved 40 minutes after subcutaneous administration of a dose of 0.15 U/kg body weight to patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Insulin concentration returns to the original level after 4– 6 hours after drug administration. The rate of absorption is slightly lower in patients with type 2 diabetes, resulting in a lower maximum concentration (352 ± 240 pmol/L) and a later tmax (60 minutes). Interindividual variability in tmax is significantly lower with insulin aspart compared with soluble human insulin, while the reported variability in Cmax is greater for insulin aspart.
Pharmacokinetic studies have not been conducted in elderly patients or in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function.
Pharmacokinetics in children (6-12 years) and adolescents (13-17 years) with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Absorption of insulin aspart occurs rapidly in both age groups, with a tmax similar to that in adults. However, there are differences in Cmax in the two age groups, which emphasizes the importance of individual dosage of the drug.
Elderly patients (≥65 years)
NovoRapid® can be used in elderly patients.
In elderly patients, blood glucose concentrations should be monitored more carefully and the dose of insulin asprate should be adjusted individually.
Patients with renal and liver failure
In patients with renal or hepatic impairment, insulin requirements may be reduced.
In patients with impaired renal or hepatic function, blood glucose levels should be monitored more carefully and the dose of insulin asprate should be adjusted individually.
Pharmacodynamics
NovoRapid® is an analogue of short-acting human insulin, produced by recombinant DNA biotechnology using a strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, in which the amino acid proline at position B28 is replaced by aspartic acid.
Interacts with a specific receptor on the outer cytoplasmic membrane of cells and forms an insulin-receptor complex that stimulates intracellular processes, incl. synthesis of a number of key enzymes (hexokinase, pyruvate kinase, glycogen synthetase, etc.). The decrease in blood glucose levels is due to an increase in its intracellular transport, increased uptake by tissues, stimulation of lipogenesis, glycogenogenesis, a decrease in the rate of glucose production by the liver, etc.
Substitution of the amino acid proline at position B28 with aspartic acid in the NovoRapid® drug reduces the tendency of molecules to form hexamers, which is observed in a solution of regular insulin. In this regard, NovoRapid® is absorbed much more quickly from subcutaneous fat and begins to act much faster than soluble human insulin. NovoRapid® lowers blood glucose levels more strongly in the first 4 hours after a meal than soluble human insulin. In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, lower postprandial blood glucose levels are detected when NovoRapid® is administered compared to soluble human insulin.
The duration of action of NovoRapid® after subcutaneous administration is shorter than that of soluble human insulin.
After subcutaneous administration, the effect of the drug begins within 10–20 minutes after administration. The maximum effect is observed 1–3 hours after injection. The duration of action of the drug is 3-5 hours.
Clinical studies in patients with type 1 diabetes have demonstrated a reduced risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia with insulin aspart compared with soluble human insulin. The risk of daytime hypoglycemia was not significantly increased.
Insulin aspart is equipotential to soluble human insulin based on molarity.
Adults Clinical studies involving patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus demonstrate lower postprandial blood glucose levels when administered with NovoRapid® compared to soluble human insulin.
Children and adolescents The use of NovoRapid® in children showed similar results of long-term glucose control when compared with soluble human insulin.
A clinical study using soluble human insulin before meals and insulin aspart after meals was conducted in young children (26 patients aged 2 to 6 years); and a single-dose PK/PD study was conducted in children (6–12 years) and adolescents (13–17 years). The pharmacodynamic profile of insulin aspart in children was similar to that in adult patients.
Pregnancy: Clinical studies of the comparative safety and effectiveness of insulin aspart and human insulin in the treatment of pregnant women with type 1 diabetes mellitus (322 pregnant women examined, of which insulin aspart: 157; human insulin: 165) did not reveal any negative effect of insulin aspart on pregnancy or fetal/newborn health.
Additional clinical studies of 27 women with gestational diabetes receiving insulin aspart and human insulin (insulin aspart in 14 women, human insulin in 13) show comparable safety profiles along with significant improvements in postprandial glucose control with insulin aspart.
Indications for use
– treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 2 years and older
Directions for use and doses
NovoRapid® is intended for subcutaneous and intravenous administration. NovoRapid® is a fast-acting insulin analogue.
Due to its faster onset of action, NovoRapid® should usually be administered immediately before a meal; if necessary, it can be administered soon after a meal.
The dose of the drug is determined by the doctor individually in each specific case, based on the level of glucose in the blood. NovoRapid® is usually used in combination with intermediate-acting or long-acting insulin preparations, which are administered at least once a day.
The individual daily requirement for insulin in adults and children over 2 years of age is usually from 0.5 to 1.0 U/kg body weight. When the drug is administered before meals, the need for insulin can be met by NovoRapid® by 50-70%, the remaining need for insulin is provided by long-acting insulin. The temperature of the administered insulin should be at room temperature. NovoRapid® is injected subcutaneously into the area of the anterior abdominal wall, thigh, shoulder or buttock. Injection sites within the same body area should be changed regularly to reduce the risk of developing lipodystrophy. As with any other insulin preparations, the duration of action of NovoRapid® depends on the dose, injection site, blood flow intensity, temperature and level of physical activity.
Subcutaneous administration into the anterior abdominal wall provides faster absorption compared to administration to other sites. However, the faster onset of action compared to soluble human insulin persists regardless of injection site location.
If necessary, NovoRapid® can be administered intravenously, but only by qualified medical personnel.
For intravenous administration, infusion systems with NovoRapid® 100 U/ml with a concentration of 0.05 U/ml to 1 U/ml insulin aspart in 0.9% sodium chloride solution are used; 5% or 10% dextrose solution containing 40 mmol/L potassium chloride, using polypropylene infusion containers. These solutions are stable at room temperature for 24 hours. Blood glucose levels must be constantly monitored during insulin infusions.
Special patient groups
As with other insulins, in elderly patients and patients with renal or hepatic impairment, blood glucose concentrations should be monitored more closely and the dose of insulin aspart adjusted individually.
Children and teenagers
It is preferable to use NovoRapid® instead of soluble human insulin in children when a rapid onset of action of the drug is necessary, for example, when it is difficult for a child to maintain the required time interval between injection and food intake.
Transfer from other insulin preparations
When transferring a patient from other insulin preparations to NovoRapid®, a dose adjustment of NovoRapid® may be required
and basal insulin.
Instructions for patients on the use of NovoRapid®
Before using NovoRapid® Check the label to make sure the correct type of insulin is selected.
Always check the bottle, including the rubber plunger. Do not use if it is visibly damaged or if there is a gap between the plunger and the white stripe on the bottle. For further instructions, refer to the instructions for use of the insulin delivery system.
Disinfect the rubber membrane with a cotton swab soaked in rubbing alcohol.
Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent infection.
Do not use NovoRapid® if
the insulin bottle or system has been dropped, or the bottle is damaged or crushed, as there is a risk of insulin leakage;
storage conditions for insulin did not correspond to those specified, or the drug was frozen;
insulin is no longer transparent and colorless.
NovoRapid® is intended for subcutaneous injections or continuous infusions in an insulin pump system (PPII). NovoRapid® can also be used intravenously under strict medical supervision.
You should always change injection sites to avoid the formation of lipodystrophies. The best injection sites are: the anterior abdominal wall, buttocks, anterior thigh or shoulder. Insulin will act faster if it is injected into the anterior abdominal wall. Infusion sites should be changed periodically.
NovoRapid® in a bottle is used with insulin syringes with a corresponding scale in action units.
If NovoRapid® and another insulin in a Penfill® vial or cartridge are used at the same time, it is necessary to use two separate insulin syringes or two separate injection systems for administering insulin, one for each type of insulin.
NovoRapid® bottle cannot be refilled.
As a precaution, always carry a spare insulin delivery system with you in case your NovoRapid® is lost or damaged.
How to give an injection
Insulin should be injected under the skin. Use the injection technique recommended by your doctor or nurse, or follow the instructions for injecting insulin in the instructions for your insulin delivery device.
Hold the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to ensure that you have injected the full dose of medication.
After each injection, be sure to throw away the needle. Otherwise, fluid may leak out, which may result in incorrect insulin dosage.
For use in an insulin pump system for continuous infusions
When used in a pump system, NovoRapid® should never be mixed with other types of insulin.
Follow your doctor's instructions and recommendations for using NovoRapid® in a pump system. Before using NovoRapid® in a pumping system, you should carefully read the complete instructions for use of the system and any steps to take if you are ill, have too high or too low blood sugar, or if your CSII system is malfunctioning.
Before inserting the needle, wash your hands and skin at the injection site with soap and water to avoid any infection at the infusion site.
When filling a new reservoir, check to see if there are any large air bubbles left in the syringe or tube.
The infusion set (tubing and catheter) must be replaced in accordance with the user manual included with the infusion set.
To ensure optimal compensation for carbohydrate metabolism disorders and timely detection of possible insulin pump malfunction, it is recommended to regularly monitor blood glucose levels.
What to do if your insulin pump system is not working
As a precaution, always carry a spare insulin delivery system with you in case it gets lost or damaged.
Precautions for use and disposal
NovoRapid® should only be used with products that are compatible with it and ensure its safe and effective operation.
NovoRapid® is intended for individual use only.
NovoRapid® can be used in insulin pumps. Tubing with an internal surface made of polyethylene or polyolefin has been tested and found suitable for use in pumps.
Solutions for infusion in polypropylene containers prepared from NovoRapid® 100 U/ml with a concentration of 0.05 to 1.0 U/ml insulin aspart in 0.9% sodium chloride solution, 5% dextrose solution or 10% dextrose solution containing 40 mmol/l potassium chloride, stable at room temperature for 24 hours.
Although stable for some time, a certain amount of insulin is initially absorbed by the infusion set material.
During insulin infusion, blood glucose levels must be constantly monitored.
NovoRapid® cannot be used if it is no longer transparent and colorless.
Unused product and other materials should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Side effects
Adverse reactions observed in patients using NovoRapid® are mainly dose-dependent and due to the pharmacological effect of insulin.
Insulin aspart is a drug that is used for antidiabetic treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Prescribed for insulin-dependent forms of diabetes type 1, as well as type 2 (when there is resistance to hypoglycemic drugs or partial resistance to these drugs during combination antidiabetic therapy, intercurrent illnesses are diagnosed).
“Asparkam” in sports: how and why they use the product
The official instructions for Asparkam indicate that the drug is indicated for replenishing potassium and magnesium deficiency. In athletes, this condition develops after prolonged grueling training. The drug is taken to normalize the balance of electrolytes, maintain heart function under conditions of increased stress, maladaptation (overtraining) and vegetative-vascular or neurocirculatory dystonia.
Another reason for the lack of K and Mg is the frequent loss of electrolytes through sweat and the nutritional habits of athletes: a strict protein diet that allows you to control the growth of muscle mass and the burning of fat deposits. During the metabolism and breakdown of amino acids, nitrogenous bases are released, which are excreted by the kidneys and liver along with potassium and magnesium. This leads to electrolyte imbalance, which is manifested by typical symptoms:
Athletes and bodybuilders are not always able to compensate for the lack of microelements with food due to dietary restrictions. The only way to regulate the balance of K and Mg is to take medications. "Asparkam" allows you to eliminate the symptoms of overtraining, increase tolerance to physical activity and increase endurance.