Fibrosis (fibrogenesis) develops as a consequence of other diseases that affect the liver. This disease is one of the most common among the large list of complications of diseases that hepatologists or gastroenterologists have to deal with.
The most unpleasant thing about fibrogenesis is that it can slowly develop for several years completely asymptomatically, showing almost no signs of itself. In this article we will learn in detail what fibrosis is, how to diagnose it in time and what to do about it.
What kind of illness?
Hepatic fibrosis develops against the background of chronic inflammatory processes in the organ, as a result of which specific cells - hepatocytes - are destroyed. As a result, fibrotic changes in the organ are observed, in which functional cells are replaced by a fibrous structure, and activation of adipose tissue is also observed. In the initial stages of development, this liver disease can be successfully treated with medications. Otherwise, irreversible complications arise, leading to cirrhosis and death of the patient.
Treatment
For any degree and any type of fibrosis, therapy is prescribed that works in three directions:
- Elimination of the cause of changes in liver tissue and death of liver cells. A certain diet is prescribed, antiviral drugs are prescribed, and if medications were previously prescribed that caused tissue damage, they are canceled and detoxification is carried out.
- Reducing inflammation in the organ and combating symptoms caused by the disease: fatigue, depression, migraines, etc.
- Activation of the liver and restoration of all its functions.
What drugs and what type of treatment the doctor chooses depends, in addition to the degree of the disease, on other factors, such as the age or general condition of the patient. However, only early diagnosis of the disease can prevent serious health problems.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Under the influence of a number of factors, the organ is destroyed at the cellular level.
Under the influence of negative factors on the human body, the functional tissues of the liver are destroyed, as a result of which fibrous structures, namely the perivascular type, accumulate in the organ, disrupting its normal blood supply and function. The disease progresses, causing the patient to experience characteristic symptoms that cannot be ignored.
Acquired fibrosis
Diagnosed in adults, it progresses under the influence of such negative factors:
- Viral infectious diseases affecting the liver structures. These include hepatitis B, C, D, Epstein-Barr virus.
- Pathologies of an autoimmune nature, in which the body produces antibodies that attack and destroy its own cells.
- Ingestion of heavy toxins and chemicals into the body.
- Progression of systemic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, lupus erythematosus.
- Uncontrolled use of hormonal and steroid drugs.
- Amyloidosis, in which, due to metabolic disorders, protein is not fully absorbed by the body.
- Alcoholism. Abuse of alcoholic beverages provokes various liver diseases, since the breakdown products of alcohol have a destructive effect on hepatocytes.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system, under the influence of which cardiac fibrosis of the liver develops. If heart failure progresses, blood circulation in the internal organs is disrupted, causing hypoxia and acidosis to develop, provoking the destruction of functional structures.
Congenital fibrosis
Predisposition to pathology may be genetic in nature.
The development of this form of pathology is influenced by genetic factors, under the influence of which, even during the period of intrauterine development, the child’s liver tissue is incorrectly formed and developed. Even from the birth of the baby, all the symptoms of the disorder will appear in the form of pathological changes in the internal structures, fibrocholangiocystic disease. Periportal liver fibrosis also develops, in which fibrous tissue forms next to the vasculature, impairing blood circulation.
Congenital fibrosis in children occurs under the influence of the following factors:
- Budd-Chiari syndrome;
- alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease;
- hemochromatosis.
Forms and stages of fibrosis
The form of the disease is influenced by the perivascular layer of the liver, which is responsible for adipose tissue, as well as the disease that actually provoked the scarring. In addition to cardiac and congenital fibrosis, doctors distinguish:
- Focal fibrosis - scars appear on the site of liver nodules, as well as on injured areas of the organ.
- Septal or zonal. The scars are arranged in layers, which disrupts the segmental structure of the organ.
- Periportal liver fibrosis – connective tissue grows around the bile ducts.
- Perivenular - fibrous cells arise near the hepatic veins.
The stages of fibrosis are determined according to various scales. The Metavir system is most often used, which includes 5 stages:
- F0 – no pathology.
- F1 – connective tissue appears, leading to metabolic disorders between the liver and blood cells. The area of the healthy area of the organ is 85% or higher.
- F2 – bile ducts dilate, the amount of scar tissue is up to 50% of the total volume. The bile ducts expand, and the structure of the organ is disrupted.
- F3 – The amount of scar tissue is more than 70%. The liver is greatly enlarged in size, and all functions are impaired.
- F4 – scar tissue makes up more than 90% of the liver volume. Irreversible processes occur in the organ itself, and the risk of death is very high. It is impossible to reverse the process and return the parenchyma to its functionality.
Degrees of fibrosis
A timely visit to the doctor will help cure the disease completely.
To determine at what stage the pathology is progressing, a biopsy is performed. The results obtained are interpreted using the Claudel index or the Metavir scale. According to this technique, there are 5 stages of disease development, where a zero degree is allocated, indicating the absence of pathological changes in the organ. The characteristics of the remaining stages are as follows:
- Liver fibrosis of the 1st degree is diagnosed to patients in whom, during a diagnostic study, minimal damage to hepatocytes was detected and the functioning of the organ was slightly impaired. At this stage of development, the disease can be cured using a conservative method.
- Liver fibrosis of the 2nd degree is determined when fibrous structures grow over a large area. In this case, the functioning of the organ is noticeably disrupted, the person is bothered by characteristic symptoms, and the condition gradually worsens. Drug therapy may not bring the desired results, and the prognosis for a complete cure worsens.
- Focal fibrosis of the 3rd degree is characterized by the formation of pathological compactions in the structure of the organ. If treatment is inadequate, irreversible processes progress and the disease becomes incurable.
- At the last 4th degree, cirrhosis develops. People don’t live long with this diagnosis. The only option that can extend a patient’s life is liver transplantation, but such an operation is complex and has many contraindications, limitations and complications.
Symptoms of liver fibrosis
The main danger of fibrosis is that the pathology does not give specific signs. All the symptoms that the patient presents are specific to other liver diseases: hepatitis, hepatosis, liver failure.
If unusual sensations appear, it is necessary to be examined using instrumental and laboratory methods. This allows you to timely determine the nature and severity of health problems.
Subjective signs
Among the patient's subjective symptoms are general malaise, body weakness, and excessive fatigue. He is worried about lack of appetite, attacks of nausea, vomiting, headache, feeling of heaviness and bloating.
In addition, pain periodically occurs in the area of the right hypochondrium; it can be of varying degrees of intensity - from mild sensations to cutting, sharp sensations. Sometimes:
- body temperature rises for a long period;
- skin itching develops;
- gums bleed;
- nosebleeds appear.
The listed symptoms are associated with a gradual deterioration in liver function, accumulation of toxic substances, inflammation and impaired bile production. This also includes disorders of the digestive and hematopoietic functions, and an increase in bile acid levels in the bloodstream.
Objective signs
During a visual examination, the doctor discovers a number of signs that directly indicate pathological processes in the liver. The first symptom will be an increase in the size of the liver; changes are determined by percussion and palpation.
A significant increase in the filtering organ is manifested by right-sided asymmetry of the abdominal cavity and protruding edge of the liver. When, against the background of fibrosis, there is a difficulty in the outflow of venous blood, the patient’s spleen increases in size.
In the last stages of fibrosis, dilation of the veins on the abdominal wall is noted. A characteristic venous pattern appears on the skin of the abdomen, which shines through the integument. Dilated veins are medically called portal hypertension.
Fibrosis can be suspected by the appearance of spider veins. They look like purple tufts and appear in areas:
- neck;
- breast;
- stomach;
- face.
The formation of vascular spots is associated with the expansion of capillaries.
Liver diseases make themselves felt by yellowing of the skin and sclera. Usually the symptom appears already in the later stages of the development of the pathology. The cause of the color change is the accumulation of the yellow pigment bilirubin in the bloodstream.
This substance should normally be completely broken down by the liver. As the disorder progresses, the liver loses its functions, cannot cope with the evacuation of bilirubin, and the substance gradually accumulates in the mucous membranes and tissues.
With fibrosis, swelling forms in the area of the legs and feet; in some patients, the arms and thighs may swell. The severity of the symptom usually increases in the evening, especially in those people who are forced to remain in a static position for a long time.
Liver pathologies are characterized by darkening of the urine, and the discharge becomes the color of beer. The disorder is associated with an increase in the concentration of bilirubin, one of its intermediate breakdown products - urobilinogen.
Other signs of fibrosis
The process of formation of scar tissue occurs against the background of the formation of small subcutaneous formations of xanthoma, xanthelasma. Round or oval nodules are located in the eyelids, palms and other parts of the body. Xanthomas occur when fat metabolism is disrupted, fatty acids, low-density blood cholesterol levels increase, and its deposits in the skin area.
It is not uncommon for fibrosis to be accompanied by ascites, an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. The prerequisite for the development of the symptom is portal hypertension, a decrease in the level of albumin in the blood plasma. Due to the accumulation of fluid, the abdominal cavity increases to a significant size.
A particular danger is fraught with such symptoms as the appearance of mental disorders. When the cleansing functions are disrupted, neurotoxic breakdown products penetrate into the bloodstream, adversely affecting:
- brain function;
- nervous system;
- mental health.
With fibrosis, sudden mood swings, a constant feeling of depression, a pessimistic mood, increased anxiety, fatigue, and unreasonable fears become commonplace. The patient's concentration decreases, lethargy, insomnia appear, and in especially severe cases, there is a tendency to commit suicide.
Any symptom described above is a serious cause for concern. The sooner a patient seeks medical help, the greater the likelihood of a successful outcome of the disease.
Characteristic symptoms
For a long time, there is an inexplicable feeling of lethargy and fatigue.
At the very beginning of progression, there are no obvious signs of liver fibrosis, so it is extremely rare that the disease is diagnosed at this stage. As it progresses, nonspecific symptoms appear, such as:
- deterioration of general health, fatigue, drowsiness;
- decreased performance, stress resistance.
At the next stages, the patient notes a decrease in the body’s protective functions and the development of anemia. External changes are also visible in the form of bruises and spider veins on the skin. There is a high risk of developing internal esophageal bleeding, which occurs against the background of impaired venous circulation of the liver and digestive organs.
Cirrhosis of the liver
Liver pathology provokes the development of a disease such as cirrhosis. Liver fibrosis, which causes cirrhosis, is dangerous to human health and life.
At the first stage of the disease, the patient suffers from increased fatigue, dyspeptic disorders, weakness, and decreased performance. Belching, nausea, bitterness in the mouth, vomiting, intolerance to alcohol and fatty foods may also occur. In the epigastric region and in the right hypochondrium, abdominal pain and a feeling of heaviness are acutely felt. Signs of cirrhosis include redness of the palms, which are also called “liver signs.” Spider veins appear on the skin in the upper half of the body. Among the common symptoms that indicate serous liver diseases are periodic bleeding of the mucous membranes and hemorrhages into the skin.
With cirrhosis, libido decreases, hair loss decreases, joint pain and skin itching appear. Normal body temperature may rise moderately and return to normal. Patients' resistance to stress decreases and an overwhelming feeling of anxiety appears. Sleep disturbance is also a concern for patients with cirrhosis. Irresistible drowsiness during the day gives way to insomnia at night.
Alcohol consumption can significantly complicate the course of cirrhosis. Deterioration is also observed after a violation of the regime or previous colds.
Diagnostics
Laboratory diagnostics will help determine the presence of a pathological process.
Chronic liver diseases are treated by a hepatologist; if you suspect fibrosis, you should make an appointment with him. After an initial examination, palpation, and collection of important data, the patient is given a referral for a number of diagnostic procedures that will help confirm or refute the diagnosis. Laboratory diagnosis of liver fibrosis includes the following studies:
- general analysis of blood, urine, feces;
- tests for markers of fibrosis;
- blood biochemistry will show an increase in bilirubin, cholesterol, ALT and AST.
Instrumental diagnostics must be prescribed, which includes the following methods:
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the liver, stomach, intestines, pancreas;
- CT, MRI;
- elastometry.
Drug therapy for fibrosis
After diagnosing the disease, it is necessary to immediately treat liver fibrosis. The pathology does not tolerate delay, and within a short period of time it can already develop into cirrhosis if a set of therapeutic measures is not taken.
The primary treatment for liver fibrosis is diet. You need to exclude as much as possible from your daily diet those foods that negatively affect liver function. You should also limit your salt intake if possible. Under no circumstances should you drink alcohol (including low-alcohol drinks) if you have liver fibrosis. Medications that the patient was taking before the discovery of fibrosis should also be excluded, since some medications tend to affect the liver with particular aggressiveness.
Drug therapy should be primarily aimed at eliminating the root cause that triggered the development of the disease. Pathological processes should be minimized with the help of medications. Among the most common and popular drugs prescribed for fibrosis are immunosuppressants, immunomodulators and hepatoprotectors. Since liver fibrosis does not appear without any reason, it is also necessary to carry out a complex of treatment for concomitant diseases, including alcohol addiction, obesity, and disruptions in the functioning of the cardiac system. In some cases, it is allowed to take antibiotics, but only under the supervision of a doctor.
What treatment is prescribed?
Medicines
Treatment of liver fibrosis must be comprehensive. First of all, medications are prescribed that will help eliminate the root cause of the development of the pathology - the hepatitis virus and other pathogens. In addition, the patient needs to get rid of alcohol addiction and bad habits forever. The treatment regimen includes the following groups of drugs:
- hepatoprotectors;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- cytostatics;
- immunomodulatory medicine;
- vitamin and mineral complex;
- enzyme preparations.
What should the diet be like?
By adhering to the principles of fractional nutrition, you can reduce the load on the liver.
The diet for liver fibrosis is specific. Despite dietary restrictions, it is important to maintain a balanced diet so that a person receives all the necessary substances, vitamins and elements from food. The diet rules are:
- Limit the amount of fat in your daily diet to 90 g.
- Reduce consumption of salt and spices.
- Avoid foods containing oxalic acid.
- Prepare dishes in a gentle way - steam, oven, boil.
- Limit as much as possible foods that provoke fermentation, gas formation, and excessive secretion of gastric juice.
- Eat in small portions 5-6 times a day.
- Drink enough clean water - at least 1.5 liters per day.
Treatment with folk remedies
For liver fibrosis, it is recommended to consume 1 tbsp daily before meals. l. milk thistle seeds. A decoction prepared according to this recipe will help remove inflammation and improve the functioning of the organ:
- Combine 75 g of rose hips, 200 g of prunes, 30 g of buckthorn.
- Pour boiling water over the ingredients, place the container in a steam bath and simmer under a closed lid for 40 minutes.
- Remove from heat and leave to steep for 1 hour.
- Drink 0.5 tbsp before bed after meals.
It is contraindicated to treat the disease with folk remedies without a doctor’s permission.
Surgery
Radical surgical measures are taken if there is a threat to the patient’s life.
The operation is performed when fibrosis provokes a pronounced enlargement of the spleen. In such a situation, the organ is removed, after which a splenorenal anastomosis is performed in this place. If fibrosis is accompanied by dilation of the liver veins, an endoscopic sclerotherapy procedure is performed. Sclerotherapy will help prevent the development of internal bleeding and complications associated with it.
Treatment of fibrosis
Whether fibrosis can be treated depends on the stage of the disease.
Treatment of liver fibrosis is difficult, because There is still no drug that could completely prevent the formation of connective tissue.
Doctors prescribe medications to stop scarring. But to be effective, they need to be combined with lifestyle changes.
Medicines
Medicines are used for stages 1 and 2 fibrosis; at stages 3 and 4 they are no longer effective. Fibrosis should be treated with the following drugs:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs based on prednisolone (hormones). They block the development of inflammation and subsequent formation of scar tissue.
- Agents that restore parenchyma - Essentiale, Livodex, Ursoliv.
- Vitamins E, C, A. They are natural antioxidants and block cell oxidation.
- Cytostatics Methotrexate, Methodject. The drugs block the division of fibrous cells and the growth of connective tissue.
Effective treatment with folk remedies is impossible, since not a single herbal component can stop fibrosis.
A gentle diet is required, excluding fried, fatty foods, preservatives, and flavor enhancers.
In the fourth stage of fibrosis, the only chance to save a person is a liver transplant or part of it.
Prevention and prognosis
If fibrosis is diagnosed at the initial stage, the prognosis for successful recovery is as favorable as possible, otherwise complications and problems cannot be avoided. Acquired fibrosis can be prevented if you give up bad habits, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and monitor your health. There are no preventive measures to prevent congenital liver fibrosis. For a woman planning a pregnancy, it is important to eliminate predisposing factors from her life and promptly treat viral infectious pathologies.
Congenital fibrosis
This form of the disease occurs in most cases in children of early and preschool age. This is a hereditary disease that is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner. In the first stages, the liver retains its functions. The surface of the liver is not prone to changes, only slightly increases in size and may become covered with whitish star-shaped small spots. Fibrous tissue grows over time, and the portal tracts expand in histology. The structure of the lobules is not disturbed, cholestasis is not observed in them, there is also no damage to cells and regeneration nodes, functional tests do not change.
Quite often, gastric and esophageal bleeding is observed, which most often occurs in patients aged three years and can cause the death of the child. Liver fibrosis is sometimes combined with other congenital diseases. In particular, the kidneys may not function properly.
Congenital liver fibrosis, the symptoms of which may differ in individual cases, is divided into latent, portal cholangitis and cholangitis. Diagnosis is complex and includes biochemical blood testing, laparoscopy, liver puncture, rheohepatography, and echo scanning of the organ.
Reasons for development
Liver fibrosis is a consequence, in most cases, of pathologies such as hepatitis B, C, D, as well as the effect of toxic drugs on the membrane, including large amounts of ethanol.
In addition, one of the reasons for the development of fibrotic disease is congenital or acquired pathology of the gallbladder or excretory tract. Secretion stagnation forms in the ducts and hepatocytes become clogged with waste. In this case, they lose the ability to function normally and die; they are replaced by connective tissue.
Attention! If the mechanism of this disease starts, then it cannot be stopped; with timely diagnosis, you can only transfer the patient to a position of remission.
Kinds
Fibrosis is divided into types based on the area of localization of connective tissue scars in the liver.
Periportal
The proliferation of fibrous fibers causes an increase in pressure in the portal vein. With the periportal form, patients have dilated esophageal veins and may experience vomiting of blood even in the early stages of the disease.
Perivascular
Collagen formations are located around the vessels feeding the parenchyma. With perivascular fibrosis, hypoxia of the liver tissue occurs. The death of hepatocytes occurs due to oxygen starvation.
Focal
This type develops when a focus of necrosis appears in the liver due to inflammation or injury and a fibrous capsule forms.
Focal fibrosis can occur as an independent type of pathology, when several single scars are formed, or cause a diffuse process. In the latter case, fibrous tissue gradually grows from the lesion into nearby parts of the organ, destroying the parenchyma.
Cystic
Another name for the pathology is cystic fibrosis. When considering what cystic fibrosis is, it is important to note that it is a congenital disorder caused by a genetic mutation.
With cystic fibrosis, the transport of electrolytes is disrupted, bile becomes viscous and cannot fully circulate through the bile ducts. Stagnation of liver secretions provokes dehydration of the ducts, and this “triggers” the process of growth of fibrous tissue into the lumen of the bile ducts.
If the cystic form develops in children and is detected at an early age, then other types of pathology are usually diagnosed in adults. In this case, fibrosis manifests itself as a concomitant syndrome of another disease.
Diagnosis of liver fibroma
Diagnosis of this disease begins with the patient’s complaints (how long ago the symptoms appeared and what specific manifestations are there), then the patient’s life is analyzed (the presence of bad habits, lifestyle and nutrition, existing diseases), after which the doctor analyzes the family history for hereditary diseases and conducts an objective inspection. To clarify the diagnosis, laboratory blood test data (general, biochemical, tumor markers) must be used.
An ultrasound or MRI gives a clear idea of the presence of a tumor, its size and other parameters. In most cases, the histological material obtained as a result of a puncture biopsy of the tumor is examined. The examination may require procedures such as radiography, elastography, MRCP, additional consultations with a gastroenterologist and therapist. All diagnostic measures are aimed at providing clear evidence of the benign quality of the tumor being studied and identifying concomitant diseases.
Nuances of treatment table No. 5
The diet strictly distributes the use of various substances. You must eat according to special rules.
| Name | Quantity | Peculiarities |
| Fats | 50 – 120 g. | In case of pronounced fatty changes in the liver, insufficiency of its functioning or resection of the gallbladder, it is allowed to consume no more than 50 g (cow or olive oil, dairy products). In the presence of stones or a sharp deterioration in intestinal motility, up to 120 g per day is allowed. |
| Carbohydrates | 350 g. | It is allowed to be consumed mainly as part of sugar. With a rapid increase in the patient's weight, a restriction in the diet of bananas, pasta, honey, milk, and fruits is required. |
| Squirrels | 80 | It is better to give preference to plant proteins (legumes, buckwheat, mushrooms, seafood, nuts, cottage cheese). Fermented milk products are also recommended. |
Permitted and prohibited products
In order to slow down liver fibrosis, you need to strictly adhere to the restrictions and instructions included in diet No. 5. The patient is recommended to give preference to soups made from vegetables and oats, barley or rice. It is allowed to eat doctor's sausage, low-fat fish, lean meat, and poultry.
Season food with refined olive or sunflower oil. You can also add a small amount of cow butter. It is recommended to snack on day-old wheat bread or biscuits. Treatment table No. 5 includes the use of greens, cereals, low-fat dairy products, vegetables, and eggs.
Possible complications
If the process is neglected and you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, situations that are detrimental to the liver may occur. Complications result in the following pathologies:
- peritonitis and ascites;
- liver carcinoma;
- liver failure and cirrhosis;
- membrane encephalopathy and subsequent confusion.
It is important to know! It is worth considering that if the diagnosis is made in a timely manner and the patient receives proper treatment, then he can live for quite a long time.
Diet
Dietary nutrition for liver diseases should be complete, but with certain restrictions. It is impossible to improve the condition of a patient with this pathology without following a specially designed diet No. 5.
The principles underlying such therapeutic nutrition should be considered:
- limiting fats and carbohydrates;
- use of products from the approved list;
- cooking by baking, stewing, steaming;
- exclusion from the diet of spicy, smoked, fried, salty foods;
- frequent split meals;
- compliance with the drinking regime - daily consumption of at least 2 liters of clean water;
- ban on cold and hot dishes;
- a complete ban on alcohol.
In case of liver fibrosis of degrees 3 and 4, dietary nutrition is particularly strict. The daily diet is prepared by a nutritionist on an individual basis. Some products may even be excluded from the list of permitted products.
Patients are prohibited from eating foods that stimulate digestive secretion, containing coarse fiber, purines, and oxalic acid.
Causes of pathology formation
One of the most common causes of liver fibrosis today is excessive alcohol consumption and consumption of unhealthy foods. In addition, the following factors can be identified:
- long-term drug treatment;
- poisoning by toxins;
- congenital fibrosis;
- viral hepatitis;
- diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorder;
- deficiency of minerals and vitamins.
In some cases, the progression of liver fibrosis may be due to heredity. Also, if the patient has suffered or is suffering from group C hepatitis, liver fibrosis is practically guaranteed.
Folk remedies
In addition to the main therapy, you can use traditional medicine, before using which you should consult your doctor.
The following recipes exist:
- Oat based decoction. To prepare it you will need 1 cup of oatmeal and 1 liter of cow or goat milk. Mix the listed ingredients and place on low heat, then add a tablespoon of sugar and a pinch of salt. The resulting mixture should thicken, after which 50 g of butter is added. Then you need to leave the broth to infuse for 3 - 4 hours. It is recommended to use 2 times a day. The course of admission is 2 weeks, after which a break is taken for 10 days, then, if necessary, the course is repeated;
- Beetroot and carrot juice. Mix beet and carrot juice in a ratio of 1:10. Additionally, you can add sugar or honey for taste. It is recommended to use 100 ml 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is 4 weeks, then a break is taken for six months;
- To prepare the infusion, you will need the following components: milk thistle fruits (2 parts), dicotyledonous nettle (1 part), dry ground dandelion root (2 parts), birch leaves (1 part) and goldenrod (1 part). The listed components are thoroughly mixed, after which 100 g of the mixture is taken from the resulting mixture and poured with 2 cups of boiling water. Next, the infusion is infused for 2 hours, then carefully filtered. Should be taken 3 tablespoons 3 times a day after meals. The course of treatment is 2 – 4 weeks. It is recommended to repeat the course every 3 months;
- Decoction based on corn silk. To prepare it, take 1 teaspoon of raw material and pour 1 glass of hot water. Then place the resulting solution in a water bath and simmer for 30 minutes. Next, the broth is cooled and carefully filtered. It is recommended to consume 1 – 3 tablespoons before each meal. The course of treatment is 2 weeks;
- Turmeric based drink. To prepare it, take 1 teaspoon of turmeric, 2 tablespoons of dried cashew nuts and 1 glass of milk. Place all of the listed ingredients in a blender and mix thoroughly. The resulting drink is drunk in the morning on an empty stomach.
From the listed recipes, you can choose the one that suits you most, but it is worth recalling once again that before using any traditional medicine recipe, it is strongly recommended to consult with your doctor. This is necessary, since even the most seemingly safe recipe, if used incorrectly, can be harmful to the body.
Surgery for fibrosis
Treatment of liver fibrosis in late stages cannot be done without surgery. Endoscopic sclerotomy or gastrotomy is performed to prevent the flow of blood from the veins of the esophagus. Removal of the spleen is necessary in cases of severe hypersplenism. Liver cirrhosis is more dangerous to human health and life than fibrosis. In order to protect yourself from the development of cirrhosis, it is necessary to regularly carry out a number of therapeutic and preventive procedures. First of all, it is necessary to detect and eliminate the causes that, through their negative influence, can cause further progression of the disease. It is important to prevent fibrosis from progressing to the stage of cirrhosis, which can cause much worse consequences. To do this, you need to normalize metabolic processes in the body, lipid metabolism. If cirrhosis does develop, then only liver transplantation can protect the patient from death.
Treatment of liver fibroma
The course of the disease without symptoms requires constant monitoring by an oncologist, since liver fibroma has the ability to resolve on its own and there is no need for treatment. Canceling hormonal medications also contributes to regression. Surgical intervention is prescribed only if the fibroid grows significantly with symptoms, when tumor rupture may occur. Liver fibroma is extremely rare, grows slowly, and its cells cannot move to neighboring organs (do not metastasize).
There is no specific method for preventing liver fibroids. As preventive measures, it is recommended to follow certain nutritional principles: limiting animal fats, fried, spicy and smoked foods, banning fast food, increasing the consumption of foods containing fiber. It is advisable to stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages and, if possible, not to take medications containing hormones.
Causes of fibrosis
Fibrosis is primarily a consequence of liver damage from unfavorable factors. This can be either a disease or simply a harmful effect on the body, for example, alcoholism. Among the causes of fibrosis, the following pathologies can be identified.
Liver damage from hepatovirus
Hepatitis of various types contributes to damage to liver cells, causing suppurative processes in them. As a result, the body responds by producing fibrin and depositing it in the liver.
Toxic hepatitis
With toxic hepatitis, liver cells suffer primarily from the destructive effects of poisons and toxins. These may be products of alcohol decomposition, poisons from medications, or a toxic factor at work. When the liver is damaged by poisons, hepatocytes very quickly cease to perform their functions and die, and fibrotic foci take their place.
Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is a severe form of pathology when the body does not distinguish between “its own” and “foreign” cells. As a result of this, the body begins to attack its own liver cells, mistaking them for a negative factor, and the liver parenchyma is slowly replaced by fibrous tissue, almost completely.
Anatomy of the liver
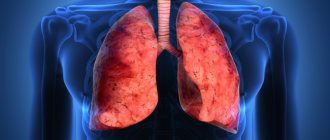
The liver is one of the largest human organs. Its weight is about one and a half kilograms. The liver has a red-brown color with a slight purple tint. In the human body, the liver performs vital functions - hematopoiesis occurs in it, the organ actively participates in metabolic processes, produces bile, and neutralizes toxins.
The liver is localized in the right hypochondrium, with its smaller part extending into the boundaries of the left side of the abdominal cavity.
When taking a deep breath, the liver may protrude from under the borders of the rib.
The liver is conventionally divided into two surfaces - diaphragmatic and visceral. The first, the diaphragmatic surface, is divided into two unequal lobes by the large falciform ligament. The visceral surface is facing down, and its surface is compressed by neighboring internal organs.
The liver ligaments provide attachment of the organ to the diaphragm. The grooves of the liver divide the organ into lobes. The organ is abundantly supplied with blood vessels, which are divided into smaller structures. The hepatic lobules, into which the liver is structurally divided, consist of hepatocytes - liver cells. Bile formation and metabolic processes occur in the liver lobules.
To remove bile, the liver has a mass of different-sized ducts that connect into one common bile duct. At the exit, the common duct flows into the duodenum.
The blood supply to the organ is mainly due to the portal vein, which carries two-thirds of the venous blood flow to the organ. The remaining third comes from arterial blood. The vessels branch throughout the liver from larger to smaller. They are designed so that each lobe of the liver receives both arterial and venous blood.
Symptomatic manifestations
Fibrous lesions are an insidious disease characterized by the fact that at the initial stage, with the possible effectiveness of therapeutic methods, the disease passes without symptoms. With liver fibrosis, symptoms become pronounced only at the third degree, when it is almost impossible to prevent the pathological process. In the first stages, general manifestations are observed:
- chronic drowsiness;
- constant loss of strength;
- weakening of psycho-emotional endurance.
The only sign that is not typical for most diseases is the appearance of multiple hematomas on the body, without physical impact on soft tissues. The longer the pathology develops, the more pronounced the symptoms become:
- bloody vomiting;
- sudden and significant weight loss;
- digestive problems;
- constant pain in the hypochondrium on the right.
At the last stage, the patient is diagnosed with jaundice, ascites, mental consciousness is disturbed, severe hyperthermia and itching of the skin appear, blood clots are present in the urine and feces.
Medical nutrition menu (Meal mode)
A diet for liver fibrosis is prescribed in addition to medications. A specially selected diet helps relieve the organ and normalize bile secretion.
A varied diet allows the patient not to feel discomfort.
Fibrosis is a disease characterized by the gradual replacement of hepatocytes (liver cells) with fibrous tissue. In fact, this is a natural process that is a consequence of inflammatory reactions occurring in the liver during various pathologies.
Fibrous formations are formed as a result of the activation of stellate cells (lipocytes), which in a healthy liver are in a “dormant” state.
As the liver parenchyma is damaged and destroyed, lipocytes begin to produce fibrogenic cells consisting of collagen and connective tissue fibers.
As the disease progresses, fibrous tissues grow, interfere with metabolic processes and blood circulation in the affected organ, the number of functional hepatocytes decreases, and the liver gradually loses its functions. In the initial stages, these changes can be stopped and reversed.
But with stage 3 liver fibrosis, this is almost impossible to do, since most of the gland cells are already replaced by scar tissue.
At this stage, competent complex therapy is very important, which will stop further progression of the pathological process and prevent the disease from progressing to the 4th stage, at which cirrhosis develops.
Causes of fibrosis
Many reasons can trigger the formation of fibrous tissue. The most common of them are:
- regular alcohol consumption;
- poisoning of the body with toxic, poisonous, chemical substances;
- hepatitis of various etiologies (viral, toxic, medicinal);
- congenital liver abnormalities;
- the presence of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine, biliary systems;
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of an autoimmune nature.
Hepatitis C is necessarily accompanied by fibrous changes in the liver tissue. But they are developing slowly. From the onset of the disease, it may take 5-6 years until the first pronounced symptoms of fibrosis appear. The course of the pathology significantly accelerates only at the late stage 3, when the functionality of the liver decreases and the organ can no longer function fully.
Symptoms
The initial stages of the disease do not have specific symptoms.
The patient may complain of weakness, chronic fatigue, increased irritability, decreased performance, but do not feel signs indicating organ damage.
Many consider deterioration in well-being to be a temporary ailment associated with intense work, but over time they notice that even a long rest does not bring relief.
As the disease progresses, symptoms become more severe and force the patient to seek medical help. At stage 3 of liver fibrosis, the following manifestations occur:
- Decreased appetite, nausea or vomiting that occurs due to dietary errors - consumption of fatty, spicy foods, smoked foods, marinades, alcohol.
- Dyspeptic symptoms - bloating, flatulence, rumbling, heartburn, belching, stool disorders.
- A feeling of heaviness and constant pain in the right hypochondrium of varying intensity - from pulling, aching, to sharp and unbearable.
- Excruciating skin itching, headaches and other signs of intoxication of the body with toxic products accumulating in the blood due to the loss of the liver’s filtering functions.
- Swelling of the limbs, which is most noticeable at the end of the working day.
- The appearance of nosebleeds, bleeding gums.
- Body temperature remains at 37-37.5°C for a long time.
Other characteristic signs that the doctor identifies when examining the patient include: an increase in the size of the liver, determined by palpation, yellowness of the skin, the appearance of spider veins or dilated venous vessels under the skin of the abdominal cavity on the skin of the face and body. Hematomas (bruises) appear on the skin spontaneously, in the absence of mechanical impact.
Diagnostics
Selecting the most effective treatment for stage 3 liver fibrosis is possible only after a full examination, including a set of diagnostic procedures. When collecting anamnesis, the doctor will listen to the patient’s complaints, ask about characteristic symptoms, and find out the presence of a genetic predisposition.
During palpation, the nature of the pain, the size of the liver, the condition of the skin, and the presence of accompanying signs (spider veins, venous pattern, xanthelomas) are determined. The psycho-emotional state of the patient must be assessed, since when the body is poisoned with harmful substances, hepatic encephalopathy develops, in which brain tissue is damaged.
Laboratory diagnostic methods include the following procedures:
- blood test (general) – determines the presence of an inflammatory process, hemoglobin level and other important indicators;
- blood test for biochemistry - in case of fibrosis, it shows an increase in the level of cholesterol, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, an increase in AST and ALT;
- coagulogram – allows you to evaluate blood clotting disorders;
- fibrotest is a specific blood test that allows you to accurately determine the degree of fibrosis;
- immunological study - helps to determine the cause of the pathology and the immune status of the body.
Among the instrumental research methods used:
- Ultrasound – an ultrasound examination procedure allows you to assess the condition of the liver and identify areas that have undergone fibrotic changes;
- CT – using computed tomography, it is possible to obtain multiple projections of an organ, build a three-dimensional model of it, and determine the presence of a tumor process.
- MRI is the most modern and informative diagnostic method, allowing you to determine the slightest changes in cells, clarify the degree of damage and the form of fibrosis.
- Fibroscan (elastography) is a procedure using modern equipment, with the help of which the stage of development of fibrosis is determined by assessing the elasticity of the liver parenchyma.
- Liver biopsy - the procedure is carried out under ultrasound control. Biological material for research is taken with a special needle, which is used to make a puncture in the abdominal cavity. Biological material is sent for histological examination.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and selects an effective treatment regimen.
At a doctor's appointment, patients ask whether stage 3 fibrosis can be cured? At this stage, pathological changes in liver tissue are already irreversible. In the liver parenchyma, the formation of multiple portocentral septa (connective tissue partitions) is observed.
They penetrate the thickness of the liver parenchyma, disrupt the structure of the organ and interfere with the normal functioning of the liver.
But even at this stage, properly selected treatment can stop the pathological process and prevent its transition to the next stage, which threatens the development of cirrhosis.
Therapy for late stages of fibrosis is long and complex, requiring the patient to be patient and strictly follow all medical recommendations. Complex treatment is aimed at achieving the following goals:
- elimination of the causes provoking fibrotic changes;
- suppression of the inflammatory process in liver tissues;
- taking medications that slow down the further formation of fibrous tissue.
If the pathological process develops against the background of viral hepatitis, antiviral therapy is prescribed. In the presence of concomitant diseases of the biliary system, the treatment regimen includes drugs that eliminate bile stagnation and suppress the inflammatory process in the gallbladder.
Additionally, digestive enzymes are prescribed to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. For concomitant diseases of the heart and blood vessels, anticoagulants, which thin the blood, and thrombolytics, which prevent the formation of blood clots, are prescribed.
DETAILS: Gynecology diseases of girls
If the development of pathology is facilitated by infection with parasites, anthelmintic and antiprotozoal drugs are prescribed.
The pathology is characterized by the replacement of ordinary organ cells with connective tissue structures. The main causes of the disease are usually:
- viral hepatitis;
- long-term alcohol abuse;
- autoimmune diseases;
- intoxication.
With fibrosis, both the liver parenchyma and the stroma are affected. Pathological changes dramatically disrupt the normal functioning of the organ. As a result, portal hypertension is formed, and subsequently cirrhosis develops.
When liver fibrosis occurs, diet becomes one of the most important components of treatment. It is used both at the very beginning of the development of the disease and in advanced forms.
Table No. 5 makes it possible to relieve the load on the damaged organ, improve digestion processes and slow down the onset of irreversible changes in severe liver damage. Therefore, the specifics of the diet can only be clarified by a specialist. You cannot prescribe your own diet.
It is important to know! The doctor will take into account not only the restrictions and prescriptions of the therapeutic diet, but will also take into account the wishes of the patient. He will also calculate in detail the number of calories needed, the composition of microelements and biologically active substances in the menu.
Nutrition for liver fibrosis must comply with special requirements. The basic rule is to completely avoid food that can damage the affected organ. Others include the following:
- Drinking a certain amount of liquid.
- Preparing food in a strictly prescribed manner.
- Salt intake is limited.
- The fractional power supply is used.
- Using special recipes that involve boiling or baking foods.
- Food should not be served too hot or cold.
- Limit on the consumption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
The diet strictly distributes the use of various substances. You must eat according to special rules.
NameQuantityFeatures
| Fats | 50 - 120 g. | In case of pronounced fatty changes in the liver, insufficiency of its functioning or resection of the gallbladder, it is allowed to consume no more than 50 g (cow or olive oil, dairy products). In the presence of stones or a sharp deterioration in intestinal motility, up to 120 g per day is allowed. |
| Carbohydrates | 350 g. | It is allowed to be consumed mainly as part of sugar. With a rapid increase in the patient's weight, a restriction in the diet of bananas, pasta, honey, milk, and fruits is required. |
| Squirrels | 80 | It is better to give preference to plant proteins (legumes, buckwheat, mushrooms, seafood, nuts, cottage cheese). Fermented milk products are also recommended. |
For liver fibrosis, use as little salt as possible
- strictly exclude prohibited foods and consume permitted ones;
- strictly adhere to the drinking regime prescribed by the doctor;
- be sure to control the amount of protein consumed per day;
- use only gentle heat treatment methods for preparing dishes;
- All food consumed should be at a suitable temperature - 36–40 degrees. Cold and too hot food negatively affects both the digestive system and the liver - spasms and colic may occur;
- use as little salt as possible;
- eat at least 4 times a day, in very moderate portions;
- the last meal should be no later than 3-4 hours before bedtime;
- Chop and puree all prepared dishes as much as possible.
Classification of pathology
There is a classification of fibrosis, which determines the origin of the pathology depending on the factors that provoked its appearance:
Table 1. Forms of fibrosis
| Form of fibrosis | Provoking factors | Localization and types of affected tissues | |
| Pericellular | Chronic alcohol intoxication, viral forms of hepatitis, especially severe form with hepatitis C | Pathology can be located in any part of the liver. Fibrous tissues create a sheath around each hepatocyte, causing its rapid degradation and disintegration | |
| Cardiac | Venular | Cardiovascular failure, ischemic diseases of the heart and vascular system, alcoholic hepatitis, hypertension, Budd-Chiari syndrome (blood stagnation in the liver) | Affects the central hepatic vein, replacing its tissue with connective vein |
| Perivenular | Occurs in tissues adjacent to the hepatic vein in the central lobes of the liver | ||
| Portal | Non-cirrhotic hepatoportal | Alcoholic, viral, toxic and autoimmune hepatitis, parasitic infestations (schistosomiasis), metabolic disorders | Develops in the area of portal tracts. Fibrous formations damage the hepatic artery, portal vein, all vessels and capillaries located in the affected area. Fibrous tissue also spreads to lymphatic vessels, nerve nodes and endings, intrahepatic bile ducts |
| Periportal | Fibrosis spreads to the entire area of the portal tracts, involving the portal and splenic veins, provoking the development of portal hypertension | ||
| Periductal | Various pathologies of the biliary tract associated with impaired outflow and circulation of bile (inflammation of the bile ducts, stone formation, congenital or acquired dyskinesia) | Connective fibrous tissue forms along the bile ducts, also penetrating into their walls | |
| Septal | All types of hepatitis | Focal death of hepatocytes leads to the formation of fibrous septa - false septa, which form pseudolobules in the parenchyma. Arteriovenous connections pass through the septa, disrupting the natural blood flow, which prevents proper blood purification and disrupts the nutrition of the parenchyma | |
| Mixed | Hepatitis, parasitic infestations, toxic liver damage | Combines features of two or more forms of fibrosis | |
| Congenital | Metabolic disorders | The growth of scar collagen tissue while the hepatic lobes are preserved in an unchanged form | |
The severity of fibrosis is assessed by the histological picture, which is obtained as a result of a complete diagnosis.
There are several systems that allow you to assess the complexity of the pathology and the extent of its spread:
- Metavir scale (Metavir), distinguishes 4 stages;
- Knodell, stages correspond to the Metavir scale;
- Ishak, 7 stages.
The main scale used in making a diagnosis is METAVIR. The table shows all stages with a decoding of the meaning.
Table 2. System for diagnosing fibrosis using the Metavir scale
| Disease code | Histological parameters after liver examination |
| F0 | The organ is without pathological changes, practically healthy |
| F1 | Slight stellate expansion of the portal tracts, in the absence of pseudosepta (fibrous septa) |
| F2 | Significant expansion of the portal tracts, accompanied by a small number of septa, transforming the perimedullary portion of the parenchyma into false septa |
| F3 | Fibrosis of liver tissue with multiple fibrous septa and growth of false lobules, without cirrhosis |
| F4 | Extensive cirrhosis of the organ |
Forms
Based on the degree of prevalence and localization of the pathological process, several main forms of the disease can be distinguished:
- venular – the focus is located in the central part of the organ;
- pericellular – inflammation is mainly concentrated around hepatocytes;
- septal – the presence of large necrotic areas, the formation of a large number of fibrous septa;
- periductal - characterized by constantly growing connective tissue located around the bile canaliculi;
- mixed form is the most common type of fibrosis, which includes all the signs described above.
The rate of development of fibrosis from the initial to the last stage is determined mainly by the type of pathology.
- The non-cirrhotic form can develop in various severe infectious diseases. In this case, sclerotic changes and thrombosis in the hepatic vessels may develop. This pathology is often the result of excessive alcohol consumption, the presence of hepatitis of various natures, exposure to toxic substances, and uncontrolled use of medications.
- The periportal form is complemented by potal hypertension and is characterized by an increased severity of the course. The disease begins with parasites, which occurs through contaminated water. This form is dangerous due to severe complications when the helminth enters the human body.
Causes
After identifying connective tissue scars in the liver, the doctor interviews the patient to find out what the cause of fibrosis is and how to treat it. The person is asked in detail about existing diseases, bad habits and lifestyle features.
The cause of fibrous scars can be:
- Hepatitis. The disease caused by the C virus is especially dangerous. Fibrosis in hepatitis C is a process that occurs under the influence of a virus, as a result of which hepatocytes die, which leads to the formation of collagen scars in their place. The disease has a chronic course with periodic exacerbations.
- Parasitic infestations. Penetration of small parasites (Toxoplasma, Echinococcus) into the organ causes an inflammatory process. If the source of inflammation persists for a long time, connective tissue begins to form.
- Drug intoxication. With prolonged use of medications or an overdose of drugs, an inflammatory process develops, which is accompanied by the death of liver cells.
- Amyloidosis. When protein metabolism is disrupted, pathological deposits appear in the liver - amyloids. The accumulation of protein provokes disruption of the organ structure and the growth of connective tissue.
- Unbalanced diet. Abuse of fast food and processed foods, excess fatty foods in the diet lead to metabolic disorders in the liver and deposition of fats in the parenchyma. Inflammation of adipose tissue provokes fibrosis.
- Alcoholism. Chronic intoxication with ethyl compounds causes the organ to work under increased load. Gradually, the liver cells are destroyed, and collagen fibers appear in their place.
- Work in hazardous production. If a person at work comes into contact with toxic chemical compounds (oil refining, production of industrial poisons), then some of the toxic compounds enter the blood and gradually settle in the liver, destroying the parenchyma. Connective tissue forms at the site of liver cell death.
- Endocrine diseases. With diabetes, hypothyroidism and other hormonal diseases, metabolic disorders occur. This can lead to the appearance of pathological deposits in the parenchyma.
- Oncological formations. Malignant cells grow rapidly and put pressure on the parenchyma, causing hepatocyte atrophy. The dead liver structures are replaced by fibrous formations.
- Pathologies accompanied by stagnation of bile (dyskinesia, cholangitis, cholelithiasis). The accumulation of bile secretion in organ tissues leads to the destruction of hepatocytes and the appearance of fibrosis.
- Heart diseases. Cardiac form of disorders, when weak work of the heart muscle provokes blood stagnation, increased pressure in the portal vein and liver edema. This causes periportal fibrosis.
- Autoimmune processes. The human body perceives liver cells as foreign structures and begins to produce antibodies to hepatocytes. A fibrous scar forms in place of the destroyed tissue.
The diagnosis of fibrosis will be made by a doctor after a complete examination.
Rapid destruction of liver structures occurs only with malignant neoplasms. During oncological processes, rapid development of fibrosis is observed.
If the cause of the growth of fibrous tissue is intoxication or non-cancerous diseases, then the pathology progresses slowly. Several years pass from the formation of the first collagen scar to the appearance of the first signs of deterioration in health.
Other scales
In addition to the METAVIR index, the stages of liver fibrosis can be determined using the Knodel and Ishak scales, which were originally invented to determine the degree of liver fibrosis in hepatitis.
The level of intensity of hepatitis is assessed by the Knodel system. It is more complex than METAVIR, but is characterized by higher accuracy for determining the severity of the inflammatory process accompanying liver fibrosis in hepatitis C.
The method is based on the use of four different scores, which together make up an overall index. The first block of the index (periportal necrosis) varies from zero to ten. The next two blocks (lobular necrosis and portal inflammation) vary from zero to four.
The combination of these three components determines the level of the inflammatory process:
- 0 (no inflammation),
- 1-4 (beginning of inflammation),
- 5-8 (slight inflammation),
- 9-12 (moderate inflammation),
- 13-18 (severe inflammation).
The fourth block indicates the level of organ compaction and varies from 0 (no scars) to 4 (cirrhosis).
Stages of liver fibrosis according to the Ishak scale:
- 0 – no fibrosis,
- 1 – fibrosis grows into several portal tracts,
- 2 – fibrosis grows into most portal tracts,
- 3 – fibrosis grows into many portal tracts and some portoportal septa,
- 4 – fibrosis covers the portal tracts and many portoportal and portocentral septa,
- 5 – incomplete cirrhosis,
- 6 – full-fledged cirrhosis.
Symptoms
As mentioned above, the disease does not manifest itself in any way for the first five years. At the end of this time period, the following symptoms of liver fibrosis can be observed:
- hepatomegaly;
- enlargement of the spleen;
- bleeding from the walls of the esophagus;
- bruising and dilated blood vessels;
- malaise, increased fatigue;
- instability to stress of any type - physical, mental.
It is worth noting that the severity of symptoms largely depends on the degree of the disease. In the early stages, the symptoms of the disease may be completely absent, but in the later stages they are very pronounced, so this condition causes significant discomfort to the person.
Symptoms of the disease
Like all liver diseases, fibrosis has a long asymptomatic course. The pathology can progress from 5 to 8 years without manifesting itself in any way. The first symptoms appear when the pathology already has a chronic status. In this case, the area of liver damage is quite significant.
Signs that tissue fibroids are developing in an organ may be as follows::
- lethargy, drowsiness, decreased ability to work;
- loss of concentration, anxiety, depression;
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, heartburn, bitterness in the mouth, belching);
- jaundice;
- hardening of the liver and enlargement of the spleen;
- vascular network and asterisks, most often on the abdomen, chest, arms and face;
- gynecomastia;
- fatty nodules under the skin (xanthomas);
- expansion and compaction of periportal tracts;
- internal bleeding from the esophageal veins.
Liver fibrosis is often accompanied by a symptom such as periarticular edema of the lower body (legs, feet). One of the dangerous symptoms is ascites, an accumulation of water in the abdominal cavity caused by portal hypertension.
Prevention
To avoid the development of fibrotic processes, it is necessary to eliminate provoking factors. Doctors recommend periodically undergoing control examinations of the gastrointestinal tract for preventive purposes. To prevent fibrosis it is necessary:
- normalize nutrition;
- follow a diet;
- promptly treat viral hepatitis;
- prevent the development of helminthiasis;
- cure inflammation of the digestive system (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gastritis).
Prevention to eliminate fibrosis and stop the progress of pathological processes includes the following measures:
- limitation of psycho-emotional, physical, sports stress;
- avoiding the use of alcohol and drugs;
- use of medications strictly as prescribed by the doctor;
- reducing exposure to toxic substances on the body at work and at home;
- smoking cessation;
- taking vitamins.
Does diet help?
An important part of the treatment process is dietary nutrition. A diet for fibrosis can reduce the load on liver cells and improve bile secretion.
Basic principles of nutrition:
- Fractionality. You need to eat often and in small portions.
- Good processing. It is recommended to boil or steam the products. For patients who cannot chew properly, food needs to be crushed.
- Moderate temperature. Food should be warm. You cannot eat hot or cold foods.
Fried, smoked, spicy and fatty foods should be excluded from the diet.
Following a diet helps reduce the digestive load on the liver and improve the production of bile secretions. This will improve digestion and reduce discomfort under the ribs. Fibrosis cannot be cured with diet alone.
Proper nutrition can improve organ function. To eliminate the consequences of the disease, drug treatment will be required.
Medicines
The main drugs used in the treatment of liver fibrosis are hepatoprotectors. These include:
- essential phospholipids (Essentiale Forte, Antraliv, Phosphogliv), which contain phosphatidylcholine and unsaturated fatty acids. The action of these drugs is to restore the cell wall of hepatocytes, which are largely composed of phospholipids. In addition, essential phospholipids enhance the detoxification function of the liver, prevent the appearance of connective tissue in the liver parenchyma, and also have antioxidant properties. To achieve the desired effect, you should use these products for at least six months. It is also worth noting that long-term use of essential phospholipids can provoke bile stagnation, which is why this phenomenon should be carefully monitored;
- amino acids (Heptral, Hepa-merz). They participate in the synthesis of phospholipids, which are a structural component of the cell wall of hepatocytes, and have a regenerating and detoxifying effect. It is recommended to use drugs in this group via intravenous administration, since when taken orally, amino acids are metabolized and reach the liver in small quantities;
- vitamins (B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine), B12 (cyanocobalamin), E (tocopherol)). Facilitate metabolic processes in the liver, thereby promoting the restoration of its cells. As a rule, they are not used as monotherapy, but complement other hepatoprotectors;
- inhibitors of lipid peroxidation (Tiogamma, Berlition). The action of the drugs is aimed at accelerating the removal of lactic acid from liver cells, which has a toxic effect. The formation of lactic acid occurs as a result of the combination of nitrogen with oxygen. These drugs can be prescribed either in the form of injections or in tablet form;
- ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk). Stimulates the removal of bile from the liver, thereby achieving a hepatoprotective effect.
There are also combination drugs that contain components belonging to several groups of hepatoprotectors. The following combination agents are distinguished:
- Essel Forte;
- Phosphonciale;
- Result Pro;
- Hepatrin;
- Sirepar.
Diagnostic methods
Early diagnosis and diagnosis using the latest methods will eliminate treatment errors and avoid life-threatening complications.
The presence of hepatic fibrosis can be checked using laboratory and instrumental methods.
Laboratory research methods include:
- general blood test: allows you to identify anemia, the presence of inflammatory processes in the liver, and determine a decrease in coagulation factors;
- blood biochemistry: helps determine the functionality of the liver and pancreas;
- liver decay tests - PGA index;
- general urinalysis: in case of liver fibrosis, it reveals autoimmune lesions;
- stool analysis: determines parasitic infestation, etc.
An informative instrumental method for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis is ultrasound examination, which makes it possible to detect pathological areas of connective scar tissue.
Important instrumental methods should be considered:
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy, in which internal organs are examined with an endoscope for the presence of venous expansion;
- computed tomography of the liver, identifying malignant formations and various damage to organ tissue;
- liver biopsy, which allows you to accurately diagnose hepatic fibrosis and its stage of development;
- elastography is the latest alternative research method, in which liver fibrosis is determined by ultrasound using a special Fibroscan device.
During diagnostic measures, the doctor must find out the conditions and lifestyle of the patient, the presence of liver diseases in his close relatives, examine and palpate the abdomen, and collect other important information.
Progression of fibrosis
The intensity of fibrosis progression varies significantly among different patients. It occurs most quickly in adult male patients with weak immune systems who often drink alcohol. Diabetes and excess weight also contribute to its development.
At the moment, there is no accurate method for predicting the rate of progression of necrosis in patients. A large amount of alanine aminotransferase in the blood can serve as a marker. Analysis for alt and ast, fibrotest, ultrasound fibroscan examination and biopsy can also help in predicting the development of events.
What tests confirm the presence of the disease?
Having read the information about what liver fibrosis is and how it is treated, perhaps someone has discovered similar symptoms. In this case, a person begins to look for what test for liver fibrosis needs to be taken to determine whether the disease exists. Let's consider the main methods for identifying fibrosis:
- Biochemistry of blood. Liver parameters (bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, AST) will increase.
- UAC. It will show a decrease in red blood cells and an increase in ESR.
- OAM. Protein or bilirubin is found in urine.
- Ultrasound. An ultrasound scan of the liver will show an increase in size and change in echogenicity of the parenchyma due to the formation of fibrous nodes.
These are the primary research methods to identify signs of liver fibrosis. If deviations are detected that allow one to suspect fibrous formations, then an additional examination is prescribed:
- CT or MRI. Tomography provides complete information about the condition of the bile ducts and allows you to assess the size and structure of the liver.
- Biopsy. One of the main methods to confirm the development of fibrosis. A biopsy is contraindicated only in cases of low blood clotting.
- Elastometry. A type of ultrasound that allows you to detect fibrous formations. Allows you to accurately determine the nature of the changes and the stage of the pathology.
Those looking to determine how to determine liver fibrosis should first give urine and blood, and then do an ultrasound. Simple and accessible methods will allow you to identify fibrotic changes at an early stage.
Features of treatment
After making a diagnosis and determining the stage of development of hepatic fibrosis, the specialist prescribes a set of therapeutic measures, including:
- Drug therapy.
- Special diet and lifestyle adjustments.
- Use of folk remedies.
- Surgical intervention.
Treatment of liver fibrosis is aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the disease, stopping the process of degeneration of the organ, and restoring its functions. When carrying out therapy at any stage of the disease, the following medications can be prescribed:
- heteroprotectors that help hepatocytes maintain viability (Heptral, Maksar);
- glucocorticosteroids;
- cytostatics that stop tissue scarring;
- immunomodulators, which help activate the immune system to fight the disease;
- choleretic drugs that eliminate bile stagnation (Allahol, Nikodin);
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diuretics, which remove fluid from the abdominal cavity;
- painkillers;
- antioxidants that neutralize the effects of toxins and poisons;
- enzymes that help digest food.
If fibrosis is caused by viral infections, then antiviral drugs are prescribed. If the cause of the disease is alcoholism, a complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages and normalization of lifestyle are necessary. Further treatment is selected for each patient individually. Therapy largely depends on the qualifications of the treating physician who knows how to treat liver fibrosis of any degree.
Severe cases of the disease may require surgery. Indications for it may be:
- schistosomiasis;
- preventing internal bleeding;
- hypersplenism;
- cirrhosis, etc.
When performing operations, a gentle laparoscopic method is often used. In case of cirrhosis of the liver, only an organ transplant will save the patient from death.
Traditional methods of treatment can be used as an effective addition to traditional treatment, but only after consultation with the attending physician.