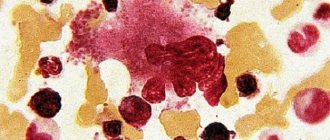
B-cell lymphoma is a neoplasm with a high degree of malignancy, in which cancer cells can rapidly spread throughout the body. The disease belongs to the non-Hodgkin type of lymphoma and is difficult to treat. In particular, therapy carried out in the early stages of the disease can be considered effective.
The danger of the disease lies in its sharp and rapid progression. Due to its rapid development, the disease can cause failure of vital internal organs within a short time.
Etiology of the disease
It is impossible to say exactly what causes the formation of this disease. In addition, each subtype has its own etiology; they are similar only in symptoms. However, the following provoking factors can be identified:
- mutagenic substances in production;
- hepatitis C virus;
- T-cell leukemia virus;
- AIDS virus.
A person who works for a long time in production with heavy chemicals is susceptible to this group of diseases. Also at risk are people who work with pesticides in agriculture and those who eat foods treated with chemicals.
It is worth noting the following reasons that can provoke the development of pathology:
- taking medications that suppress the immune system;
- diseases that are inherited;
- autoimmune diseases.
Causes of Hodgkin's lymphoma
It has not yet been clarified why exactly this disease develops. But there are a number of factors that provoke the appearance of this type of cancer:
• Heredity and genetic abnormalities;
• Decreased immunity due to HIV infection or due to organ transplantation, radiation and chemotherapy;
• Work in hazardous industries associated with constant inhalation of carcinogens;
• Diseases of the immune system.
Hodgkin's lymphoma cannot be transmitted from person to person through household or airborne droplets. But with this pathology there is a twin factor: such sisters and brothers have a very high risk of developing the pathology.
Types of lymphomas
Today in official medicine the following types of lymphomas are distinguished:
- B cell lymphoma;
- T-cell lymphoma;
- diffuse large B-cell lymphoma;
- follicular lymphoma.
It is worth noting that all types of lymphomas have not been fully studied, so in general they are classified into two types:
- Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The first type has 5 subspecies known to medicine. The second group has more than 30 subspecies. They can only be distinguished with the help of special laboratory and instrumental studies.
Diffuse large B-cell form of the disease
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma belongs to the group of oncological diseases. The risk group includes people aged 20 and 50 years. A malignant tumor can affect almost any internal organ.
T cell subtype
T-cell lymphoma most often affects older people and is very rarely diagnosed in adolescent children. In some sources, this disease is indicated as skin lymphoma, since the pathology affects the human skin. As a rule, the disease affects men; in women, skin lymphoma is diagnosed very rarely. At the initial stage of the disease, T-cell lymphoma manifests itself in the form of itching and redness of the skin around the lymph nodes.
B cell lymphoma
B-cell lymphoma is characterized as the most aggressive. Cancer cells develop very quickly. However, with timely treatment, a person’s life can be extended by 5–10 years. The causes of B-cell lymphoma are still unknown. Successful treatment is possible only at the first stage of development of the disease.
Follicular lymphoma
This subtype of cancer is one of the rarest subtypes. Follicular lymphoma is well treated, even in an advanced stage. Men over 60 years of age with a weak immune system are most susceptible to this type of disease. The pathology develops slowly, so it is much easier to diagnose.
Treatment of follicular lymphoma depends on the extent of the disease. Moreover, at an early stage the disease cannot be cured at all. This is necessary so that the disease moves to a new stage and the therapeutic course is more effective.
Most often, follicular lymphoma is treated through radiotherapy to stop the growth of a malignant tumor. It is worth noting that follicular lymphoma is the most “friendly” form of this group of diseases. A positive prognosis is given in almost 90% of cases. Provided that treatment is started in a timely manner and completed.
Causes
Since at the moment there are no reliable reasons for the development of lymphoma b, doctors have to be content with hypotheses and approximate data. In many countries around the world, studies are being conducted to determine the relationship between the development of lymphoma and exposure to carcinogenic and toxic substances on the human body.
Possible causes of the development of beta-cell lymphoma are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS);
- autoimmune diseases, including Crohn's disease, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, Sjögren's disease, etc.;
- consequences of hepatitis C and herpes;
- consequences of kidney and stem cell transplants.
In addition, hypotheses regarding the influence of external factors on the development of the disease are widespread in scientific circles:
- Epstein-Barr virus and diseases of similar etiology;
- exposure to carcinogenic substances, such as benzene, benzopyrene, formaldehyde, dioxins, etc.
One of the main reasons for the development of the disease is weakened immunity.
All of the factors described above in one way or another affect the structure of leukocytes, contributing to their uncontrolled division. The result is B-cell lymphoma.
General symptoms
Symptoms of lymphoma are almost the same for all subtypes. The general list can only be supplemented due to pathological changes in the affected organ. Common symptoms of lymphoma are:
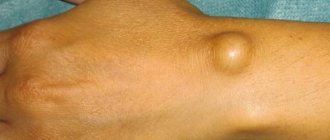
- enlarged lymph nodes (neck, groin, armpits);
- sudden weight loss for no apparent reason;
- sweating, especially at night;
- weakness and fatigue;
- cough;
- itching in the area of enlarged lymph nodes.
Enlarged lymph nodes are the first sign of the disease. In some cases, pain is felt in the lymph nodes after drinking alcohol.
At the same time, it is worth noting that the presence of slightly enlarged lymph nodes does not mean that it is an oncological disease. Even with viral diseases, such symptoms can be observed. If the clinical picture lasts several days, you should immediately consult a doctor.
It is especially difficult to identify follicular lymphoma, since in the first stages it practically does not manifest itself.
The above symptoms of lymphoma may be supplemented by other signs, depending on the location of the pathology.
Damage to internal organs
Since lymphatic tissue is located throughout the human body, the disease can develop in any area. The disease most often affects the following organs:
- stomach;
- mediastinal area;
- brain;
- spleen;
- lungs.
Mediastinal lymphoma
There are no exact reasons that provoke the disease in the mediastinum. But, as practice shows, most often pathology develops precisely in this place in people who work with pesticides or eat foods processed by this method.
Mediastinal lymphoma develops in people who work with pesticides
Mediastinal lymphoma manifests itself in the following ways:
- cough and frequent shortness of breath;
- chest pain;
- sputum mixed with blood.
In some cases, the esophagus may be damaged, making it difficult for the patient to swallow food.
The main course of treatment is chemotherapy. At the same time, the effects of drugs affect the entire body.
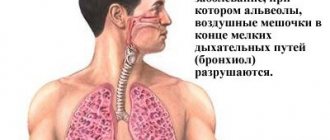
Lung damage
Most often, lung lymphoma affects older people. However, the secondary form can be observed even in infants. The pathology can develop as a result of internal organ transplantation or be hereditary.
Initial symptoms resemble a common cold. In this case, the lymph nodes become enlarged, and their palpation causes pain. If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, treatment can be successful. At the same time, it is worth noting that much depends on the general state of the human immune system.
Lymphoma of the stomach
All symptoms of gastric lymphoma indicate cancer. The disease can be accurately diagnosed only after laboratory and instrumental tests.
Lymphoma of the stomach develops slowly. At risk are people who are male and over 50 years of age. The development of the disease can lead to gastric stenosis and metabolic disorders. This entails other diseases and a greatly weakened immune system. But, if you start treatment in a timely manner, then gastric lymphoma can be treated quite well. The main thing is to diagnose the disease in time and begin the correct course of treatment.
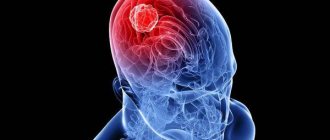
Brain damage
Lymphoma of the brain is a very rare disease. With this pathology, the lymphoid tissue of the brain is affected. As medical practice shows, the tumor rarely extends beyond the central nervous system and practically does not metastasize.
Drowsiness is a symptom of brain lymphoma
Most often, brain lymphoma affects people aged 50–60 years. The following is added to the general list of symptoms:
- blurred vision;
- drowsiness;
- speech disorders;
- frequent headaches;
- epileptic seizures.
In the later stages of the development of the disease, memory loss is possible.
Treatment of this type of malignant lymphoma is somewhat more difficult than other subtypes due to its location. Typically, chemotherapy and possibly surgery are used.
Pathology of the spleen
Lymphoma of the spleen is a malignant lesion of the tissues of this organ. Almost always at the initial stage it is asymptomatic. The main risk group is elderly people.
At the stage of active development, pathology can manifest itself in the following way:
- a sharp decrease in appetite;
- elevated temperature for no apparent reason;
- increased sweating, especially at night;
- heaviness on the right side of the hypochondrium;
- weight loss;
- anemia (anemia).
It is the progression of such symptoms that is a clear indicator not only of the pathology of the spleen, but also of gastric lymphoma. This can only be determined accurately after carrying out the necessary diagnostics.
Types, types, forms
The disease can vary in the nature of its course, and therefore it is customary to distinguish the following forms:
- Spicy. It is observed in 50% of cases, the pathological process progresses quickly, from the first manifestations to the development of all symptoms it takes about 2 weeks. Lymph nodes, as a rule, do not enlarge, and death occurs from complications that arise within 6 months after the onset of the disease.
- Lymphomatous. It has much in common with the previous form, with the exception of the dynamics of the growth of the lymph nodes - they increase to impressive sizes. Occurs in 20% of patients.
- Chronic. The lymphogenic process develops slowly, its clinical signs are mild. Despite this, at any time, for unknown reasons, the disease can become acute. Occurs in 25% of cases. Patients live up to 2 years.
- Smoldering form. It is diagnosed extremely rarely, in only 5% of cases. There are many times fewer atypical T-lymphocytes detected, and their division occurs slowly. Despite this, the skin symptoms correspond to the general picture of the oncological process. Average life expectancy is 5 years.
Types of T-cell lymphomas:
- Peripheral nonspecific. It develops against the background of mutations in T and NK cells, which form antitumor immunity. The oncological process changes the qualitative and quantitative composition of the blood, affecting the skin, bones and bone marrow. The tumor quickly metastasizes to internal organs. The main symptoms are enlarged lymph nodes, enlargement of the spleen and liver, and breathing problems. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma is rarely detected.
- Angioimmunoblastic nodal. Initially, the tumor process is represented by one lymph node, in which immunoblasts are concentrated. As the pathology progresses, the node disintegrates, and in its place vessels form, which contribute to the development of new complications. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma is characterized by an acute course and general symptoms such as skin rash, pyrexia and weakness. The prognosis is unfavorable.
- T-cell lymphoma of the skin (skin). It is characterized by an accumulation of damaged T-lymphocytes in the epithelium due to exposure to irritating factors such as radiation, viruses, etc. Polymorphic rashes appear on the skin (pictured), and as the pathology progresses, the patient’s well-being worsens. The rapid spread of metastases negatively affects life expectancy - on average it does not exceed 2 years.
- T-lymphoblastic. It is formed from immature T-lymphocytes and spreads throughout the surrounding tissues due to rapid cell division. The nature of the disease resembles acute lymphocytic leukemia. It is uncommon, but has a favorable prognosis if treated before bone marrow lymphoblasts are involved.
In addition to the above forms of T-cell lymphoma, a separate type of disease is damage to the mediastinum - the area where the chest organs are located. The pathology is dangerous due to rapid metastasis, since the altered cells move freely through the vessels that wash various internal organs.
When the mediastinum is affected, predominantly general symptoms are observed - shortness of breath, weakness, hyperthermia, etc. A specific symptom of the disease is the growth of the cervical and axillary lymph nodes, when pressed on there is no pain, which indicates not inflammation, but malignant changes in their structure.
There is also a classification of T-cell lymphomas of the skin. We invite you to consider it in more detail.
Aggressive lymphomas develop rapidly and spread metastases. These include:
- Sézary's syndrome. It is characterized by three main symptoms: erythroderma (rash in the form of large red spots), lymphadenopathy and the circulation of cells with folded nuclei in the blood.
- T cell leukemia. A disease caused by the retrovirus HTLV-1. Clinical signs: damage to the dermis and lymph nodes, bone resorption against the background of osteolysis, a condition caused by tumor metastasis.
- Nasal form of extranodal lymphoma or polymorphic reticulosis. Develops from NK leukocytes and affects the skin, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, facial bones and central nervous system. Rashes appear in the form of dense bluish plaques from stage III of the oncological process;
- Peripheral unspecified. It is characterized by the development of epidermal lesions, after which the malignant process rushes to the internal organs.
- Primary aggressive epidermotropic CD+8. outwardly manifests itself as polymorphic rashes with specific ulcerations in the center. Neoplasms affect the epidermis, mucous membranes and lungs, the central nervous system, and the external genitalia of men, in particular the testicles.
This is not the entire list of types of rapidly progressing T-cell lymphomas of the skin. In all of these conditions, human life expectancy does not exceed 2 years. Peripheral forms of lymphomas progress most quickly, most likely because the movement of lymph, enriched with diseased cells, occurs from the periphery to the center, thus, malignant elements quickly end up in the structures of healthy organs, where they can gain a foothold and begin increased division.
But the oncological process can also be sluggish. Let's look at the cases in which it occurs:
- Fungal form of mycosis. Most people confuse this disease with chronic dermatoses. In addition to skin symptoms resembling psoriasis, swelling, thickening of the soles of the feet and palms, eversion and inflammation of the eyelids are noted.
- Primary anaplastic. It is characterized by single rashes in the form of red nodules up to 10 cm in diameter, less often there are multiple rashes, which does not affect the course of the disease.
- Panniculitis-like subcutaneous. Develops in subcutaneous tissue. Main symptoms: skin rashes and itching, hyperthermia, swelling, jaundice, sudden weight loss.
- Primary CD4+ pleomorphic. It is characterized by the appearance of an infiltrate, the structure of which is composed of small-cell and large-cell components. The rashes are localized mainly in the face and chest.
With these T-cell lymphomas, a person can live for about 5 years.
Stages of development
According to the classification in official medicine, there are 4 stages of disease development:
- first stage - the pathological process is localized and does not spread to other parts of the body or internal organs;
- second - the lesion process affects two or more areas of the lymph nodes;
- third - the symptoms of lymphoma are more pronounced, the lymph nodes are greatly enlarged, damage to an internal organ is possible;
- fourth - damage to internal organs - kidneys, lungs, spleen, stomach. At this stage, the process of development of large cell lymphoma or any other type is irreversible.
Stages of lymphoma and areas affected
Accordingly, we can conclude that the earlier malignant lymphomas are diagnosed, the greater the chances of successful treatment.
Symptoms
When B-cell lymphoma affects the bone marrow, a person experiences severe headaches and dizziness
The manifestations of this disease are in many ways similar to the symptoms of other malignant neoplasms. The following signs indicate the development of large cell lymphoma in the body:
- weight loss that occurs suddenly and for no apparent reason;
- increased sweating at night;
- development of general malaise;
- increased body temperature;
- anemia and thrombocytopenia, causing increased bleeding and pale skin;
- rapid fatigue, and we are not talking about serious physical exertion;
- enlarged lymph nodes in groups.
In some cases, the pathological process spreads to nearby organs and bone apparatus. In this case, pain appears, which is accompanied by severe symptoms:
- If the respiratory system is damaged, the patient experiences a feeling of lack of air and coughing.
- If the pathology affects the bone marrow, then frequent dizziness, blurred vision and headaches occur.
- Damage to the intestines provokes the development of digestive problems and the urge to vomit.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of lymphoma is carried out using instrumental and laboratory tests. For example, follicular lymphoma practically does not manifest itself at the initial stage, unlike B-cell lymphoma.
A diagnostic plan is drawn up only after a preliminary examination of the patient has been carried out, the signs of the disease and possible causes of its formation have been specified. As a rule, the mandatory diagnostic program includes the following:
- blood test (general, biochemical);
- tissue biopsy;
- molecular genetic research;
- MRI;
- CT scan of the brain (if there is a suspicion of a tumor).
After this, additional tests may be prescribed:
- radiology diagnostics;
- cytogenetic study.
This is necessary in order to determine what type of lymphoma the patient has.
Relapses
Relapses with T-cell lymphoma can happen at any time in both a child and an adult, so you should not forget about this problem. After discharge from the hospital, neglect of one's own health and refusal of regular medical supervision contribute to the rapid return of the disease.
On average, relapses occur in 30-50% of cases within 5 years after the initial treatment of the pathology. The earlier they occur, the more unfavorable the prognosis for the patient. In the first 2 years after therapy, repeated oncological processes are characterized by a high degree of aggression, and therefore any therapeutic measures turn out to be practically meaningless - the patient dies in a short time.
In other cases, relapses can and should be fought. Most often, this happens with the help of high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation - this protocol is successful in 80% of cases, of course, in the absence of contraindications.
Treatment
In the early stages, radical treatment of lymphoma gives fairly good results. It all depends on the stage at which the disease is diagnosed and the state of the patient’s immune system.
Treatment of lymphoma is carried out using the following directions:
- radiotherapy - the tumor can be “neutralized”, that is, its growth can be stopped;
- chemotherapy - with the help of drugs, cancer cells are destroyed (especially effective for large cell lymphoma);
- Immunotherapy is the use of drugs to strengthen the human immune system.
Radiotherapy apparatus
The integrated use of such therapeutic courses gives positive results. As for folk recipes, for such cancer diseases they can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable here. Moreover, this can lead not only to complications, but also to death. Treatment of lymphoma requires strict adherence to all doctor's instructions. Only in this case can the prognosis for treatment of lymphoma be positive.
Treatment of T-cell lymphoma in Russia and abroad
We invite you to find out how the fight against T-cell lymphoma is carried out in different countries.
Treatment in Russia
Lymphoma is treated in any medical institution that has an oncologist on staff. When diagnosing lesions of the lymphatic system, this doctor puts the person on the register. Such specialists today work in public and private oncology hospitals.
After confirming the diagnosis, doctors select an individual treatment regimen, taking into account all the risk factors that affect the patient’s survival prognosis. Surgeries for T-cell lymphomas are rarely performed, only when single tumor foci are localized in the liver or stomach. The main treatments are chemotherapy and radiation.
If the patient chooses a private clinic, he pays the cost of medical services himself. Prices for chemotherapy in Moscow range from 12 thousand rubles. excluding medications per day. On average, the total cost of treatment for lymphoma costs a patient from 150 thousand rubles.
Which medical institutions can I go to?
- Clinic “Medicine 27/7”, Moscow. The clinic's oncology center provides assistance to patients with malignant diseases at any stage of development. It has intensive care, chemotherapy and palliative care departments.
- Medical, Moscow. Paid consultations by oncologists of the center are carried out daily, without holidays and weekends. Here you can get qualified help in the fight against lymphoma.
- City Clinical Oncology Dispensary (GKOD), St. Petersburg. It has a full range of necessary equipment to provide quality assistance to the population.
Let's look at the reviews of the listed clinics.
Alevtina, 56 years old. “I was treated for skin lymphoma at the State Clinical Hospital in St. Petersburg. I would like to thank the doctors at the dispensary for the organized care and treatment procedures. The disease has subsided, now we need to take care of ourselves.”
Margarita, 58 years old. “Life flew by in a flash when I found out about lymphoma and that it was a malignant diagnosis. I regret that I went to the doctors late, mistaking the skin rash for dermatitis. My daughter organized an appointment at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, where I was examined again and began treatment. The results are quite good, in general, I advise you not to give up!”
Treatment in Germany
Upon admission to a German oncology clinic, the patient again undergoes a comprehensive examination, even if it was previously carried out at his place of residence. This is due to the fact that German specialists trust only their own examination methods and focus on their professionalism.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, a treatment protocol appropriate for the specific case is formed. In most situations, the fight against lymphoma in German clinics begins with chemotherapy. In the case of an advanced form of pathology or lack of positive dynamics, specialists resort to a combination of cytotoxic effects with irradiation. In this case, patients are prescribed the strongest drugs developed exclusively for the treatment of lymphogenous lesions.
The most difficult treatment option is a bone marrow transplant, which, however, brings good results for most patients and a favorable prognosis. This procedure is not cheap, but the experience of doctors and the effectiveness of the event allow us to achieve the highest results.
The cost of oncology diagnostics in Germany ranges from 7 to 11 thousand euros, a course of chemotherapy - from 8 thousand euros, stem cell transplantation - from 100 thousand euros.
Which clinics can you go to for help?
- University Hospital of Heidelberg. By contacting this medical institution, patients can receive help in the fight against cancer of any kind.
- Clinic "Charite", Berlin. Within the walls of the medical institution, active scientific and practical activities are carried out, the tasks of which include high-quality diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the lymphatic and hematopoietic system.
- University Hospital of Munich. Recognized as one of the best in Europe. The medical facility provides treatment for lymphomas, leukemia and other malignant diseases.
Let's look at the reviews of the listed clinics.
Vlada, 32 years old. “I was examined at the University Clinic in Munich for lymphoma. The diagnosis was not confirmed; the tumor turned out to be benign. I’m glad I turned to professionals.”
Anna, 25 years old. “My father was treated for mediastinal T-cell lymphoma at the Charité clinic. The doctors did everything, including a bone marrow transplant, and it was this action that helped put him on his feet. I hope the disease has subsided.”
Treatment of T-cell lymphoma in Israel
The fight against lymphoma in this country occupies a leading position. Israeli oncologists use modern technologies and innovative drug formulas, thanks to which the prognosis for patients with early stages has increased to 98%. The results of remission among people with advanced forms of pathology have also improved.
Priority areas of treatment include:
- active surveillance;
- radiotherapy;
- targeted therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- immunotherapy;
- bone marrow transplantation.
The cost of treatment in Israel is 30% lower compared to European clinics. Let's look at the main price range to make sure they are democratic:
- consultation with an oncologist - $600;
- tests - $180;
- biopsy - $600;
- chemotherapy including medications - from $1100 + $360;
- stem cell transplantation - from $98 thousand;
- immunotherapy - from $2 thousand.
Which medical institutions in Israel can I go to?
- Medical, Tel Aviv. According to local residents, it is considered the best hospital in the country; they called it “the city of health.” Prices here are 20-50% lower than in other Israeli clinics.
- Clinic "Assuta", Tel Aviv. A private medical center, famous primarily for its surgical complex. Help is provided here for any malignant diseases, regardless of the stage of their development.
- Sheba State Hospital, Tel Aviv. Affordable prices and high-quality medical services are what the clinic is famous for among Israeli citizens and foreigners. By contacting here, you can not only save on treatment, but also receive high-quality oncological care for lymphoma.
Let's look at the reviews of the listed clinics.
Andrey, 45 years old. “For a long time I suffered from arthritis and painfully perceived enlarged lymph nodes as normal, until one day in 2013, after a standard X-ray, the doctor suspected lymphoma. The diagnosis was confirmed, and I decided to go to Israel, to the Assuta clinic. Here the treatment was so successful that remission occurred and continues to this day. I recommend this clinic for consideration.”
Inga, 34 years old. “Mom fell ill with skin lymphoma, so as not to waste time, we went to Israel, to the Sheba hospital. The whole family is happy with the results of the treatment, 2 years have passed since the trip, everything is fine.”
Traditional medicine treatment
In tandem with the prescribed course of treatment, folk remedies can significantly speed up the process of getting rid of the disease. But the use of any means should begin only after an accurate diagnosis has been made and treatment has been prescribed by a doctor. Diagnosing yourself using the Internet and outside advice is unacceptable.
Folk remedies for the treatment of lymphoma involve taking phytotherapeutic decoctions from the following herbs:
- celandine;
- sagebrush;
- Birch buds;
- aconite.
You can also prepare and use restorative spectrum tinctures. Such folk remedies help to restore the body relatively quickly and strengthen the immune system. But remember that any medications should be used only after consultation with your doctor. Not all folk remedies are universal and suitable for every person.
The point is that for proper treatment you need to know not only the signs, but also the causes of the disease. Therefore, it is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own based on symptoms alone.
Symptoms and signs of Hodgkin's lymphoma
The main manifestation of lymphogranulomatosis is associated with a significant enlargement of the lymph nodes, which can be either painful or painless. But due to the fact that lymphomas arise in a variety of organs, they may also have nonspecific signs associated with the location. When LGM affects the digestive system, the main symptoms are black stool, diarrhea, nausea and abdominal pain. In a quarter of patients, Hodgkin's disease is localized to the skin. In this case, it begins with such nonspecific symptoms as skin rashes and itching.
• A rash with lymphogranulomatosis forms in places of pathological proliferation of lymph nodes. Most often, it appears before the increase can be seen with the naked eye. The nature of the rashes in Hodgkin's disease is similar to urticaria or dermatitis, but cannot be quickly cured. Cancer can be suspected based on this symptom when the rash does not go away for more than 2 weeks;
• Itching in Hodgkin's lymphoma is not a necessary symptom. In many patients, it does not appear during the entire course of the pathology. According to statistics, only 25%-30% of patients suffer from this symptom, which appears long before the lymph nodes are affected. Skin itching can be localized in one place, mainly the surface of the chest and lower limbs, or spread throughout the body. In the latter case, it is accompanied by significant scratching;
• Blood with Hodgkin's lymphoma does not have specific changes that would indicate the presence of this disease. Sometimes there may be a moderate leukocytosis (slight increase in the number of white blood cells) with a shift to the left. This displacement shows the specialist that it was provoked by an inflammatory process. Also, some patients with lymphogranulomatosis may be characterized by a blood pathology such as anemia.
Hodgkin's lymphoma in children
Hodgkin's disease is rare in young patients. Sometimes it can develop in preschool age. The causes of this pathology in children are still unclear. Most often, Hodgkin's lymphoma is detected in boys. Symptoms of lymphogranulomatosis in children are accompanied by the following symptoms:
• Proliferation of lymph nodes;
• Night sweats and fever;
• Poor appetite, weight loss;
• Itching of the skin;
• Fatigue and constant drowsiness.
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the location of the primary lesion, at the initial stage the lymph nodes become enlarged and inflamed. The nodes can be located in the cervical, submandibular, inguinal or axillary areas.
The following symptoms may include:
- redness and large patches of skin;
- painful cramps in the abdomen, leading to a nausea reflex;
- shortness of breath and severe cough;
- itchy skin;
- poor sleep due to excessive sweating;
- lack of appetite and sudden weight loss, which can provoke the first signs of anemia;
- apathy, weakness, causeless fatigue;
- decreased performance;
- apathetic state, which leads to irritation and nervous breakdown.
What is lymphoma
With the onset of this disease, all patients are interested in the question: is lymphoma cancer or not? Unfortunately, this is an oncology that begins from lymphoid tissue, but sometimes a tumor can arise from degenerated lymphatic cells - lymphocytes. During the development of lymphoma, it is not only the lymph nodes that are affected. Lymphoma spreads throughout the human body through the lymph flow, affecting other lymph nodes. Gradually, important organs are involved in the process, and even bone marrow damage occurs.
During lymphoma, pathological lymphocytes begin to divide uncontrollably and accumulate in lymph nodes and organs, leading to their enlargement and impaired functionality. Lymphoma must be treated as quickly as possible.
This disease can occur in children and adults of any age, gender and race, regardless of their social status. The survival rate of patients with Hodgkin's disease (lymphogranulomatosis) is eighty percent; with cellular NHL (non-Hodgkin's lymphoma), twenty to twenty-five percent of patients survive.
How to treat lymphoma
The main methods of treating lymphoma are surgery, radiation and chemical therapy. Traditional medicine is used as an auxiliary therapy. The lower the degree of malignancy of the tumor, the higher the chance of recovery. Stage 4 lymphoma is practically untreatable and often recurs. The first stage is treated surgically, since the affected area is small. Chemotherapy for lymphoma is carried out at all stages. Some types of tumors cannot be treated with radiation.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for lymphoma involves taking antitumor medications that have a detrimental effect on pathological cells. Chemotherapy drugs are called cytostatics and are used to ensure long-term remission. Treatment of non-Hodgkin's tumor depends on the morphological appearance of the tumor and how malignant it is. Chemotherapy courses are given once every three weeks to give the body time to recover.
Radiation therapy
In radiation therapy, the patient is exposed to gamma radiation (X-rays). This method allows you to destroy cancer cells. If a patient is diagnosed with the most common Hodgkin's tumor, then the person is prescribed a radical radiation program, which involves irradiating not only the affected area, but also the adjacent lymphatic areas. This reduces the risk of relapse of the disease.
Operative method
Surgery is performed for a single tumor of internal organs. During the operation, the doctor excises the tissue affected by the tumor and nearby groups of lymph nodes. If a patient experiences severe splenism (a condition in which the functions of the spleen are disrupted, as a result of which it begins to destroy not only atypical but also normal cells), the spleen is also removed. Bone marrow transplantation has good effectiveness.
Folk remedies
Treatment of lymphoma with folk remedies is carried out as an auxiliary and preventive therapy against relapse. With the help of infusions, tinctures and decoctions, you can reduce the negative effects of chemicals and radiation. Treatment with folk remedies includes the use of goji berries and mushrooms - chaga, reishi, cordyceps. In dried form, these ingredients can be found in pharmacies and markets. The use of any traditional medicine must be agreed with the attending physician. It is important to remember that folk remedies cannot replace the main treatment - surgery, chemical and radiation therapy.
Stages of the disease and their features
Identifying the stage allows you to see the extent of the disease. This information allows you to prescribe the correct therapy. Treatment of local stages differs from treatment of common stages.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8BeHGI0L9Zc
When selecting therapy, not only the stage of the disease is taken into account, but also test results, the subtype of lymphoma, the person’s age and condition, the presence of other diseases, etc. But the main role in choosing the right treatment is still played by determining the stage.
There are 4 stages:
- I – one area of the lymph nodes is affected by the disease;
- II – the disease affects two or more areas of the lymph nodes on one side of the diaphragm;
- III – disease of the lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm;
- IV – the disease spreads to the organs.
Classification of non-Hodgin's lymphomas:
- B-cell.
- T, NK cell tumors.
The forms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma are divided based on the indolent and aggressive course of the disease.
Causes and risk factors
The exact causes of cell mutation and tumor formation have not been identified. Presumably, continuous antigenic stimulation of the body is a risk factor. The occurrence of the disease is facilitated by:
- Weakened immunity;
- Viral disease (retrovirus, herpes virus, HIV, hepatitis B, C virus);
- Exposure to external chemicals (carcinogens);
- Exposure to radiation (including sunlight).
Older patients and residents of cities with high levels of radiation are at increased risk. Agricultural workers are also at risk due to the use of pesticides and chemical additives. The immune system plays a decisive role in the body's resistance. Its suppression leads to a weakening of the defense, as a result, the virus easily penetrates the blood and cells. Transplantation of artificial organs, long-term use of strong drugs, antidepressants, tranquilizers, infection with concomitant diseases can also alleviate the occurrence of tumor processes.
How to diagnose skin lymphoma and not confuse it
Diagnosing the disease in the early stages of its development is quite difficult. This is due to the similarity of lymphoma to other skin diseases of the skin that have similar symptoms.
Diagnosis consists of identifying clinical symptoms:
• rashes that vary in size and color;
• the presence of progression and attenuation of different elements of the rash at the same time;
• intense itching;
• localization of the rash to areas that are hidden from the sun by clothing.
Specialists prescribe a histological examination to study the cells of the dermis. When lymphocytic accumulations inside the skin, swelling of the papillary layer of the dermis or other phenomena are detected, then it is worth talking about the diagnosis of lymphoma.
Clinical signs in the first stages of the disease are similar to other inflammatory skin diseases. These can be blisters on the skin, rosacea, acneiform dermatoses .
It often takes a couple of years for a correct diagnosis to be made.
B cell malignant lymphoma
Has a wide variety of manifestations.
The symptoms are:
• plaques appear ranging in size from 5 to 15 cm, which coalesce and enlarge;
• the color of the formations ranges from pink-blue to red-bluish;
• the disease is actively progressing;
• general weakness is observed;
• weight loss;
• the skin itches at an increasing rate;
• violet-red nodes appear, the size of which is about 8 cm, the nodes increase intensively.
In addition to external manifestations, this type of lymphoma leads to enlargement of the lymph nodes, as well as organs such as the liver and spleen.
Increased leukocyte cells
When lymphoma affects the fluid in the bone marrow, leukemia occurs. In this situation, there is an increase in leukocyte cells above 4.0 x 109/l. In this case, a special study will reveal quite a lot of abnormal cells. Such indicators make it possible to assume an oncological process of a generalized type. Treatment is carried out only through bone marrow transplantation. This is a complex and dangerous procedure, since the patient’s immunity is completely eliminated before transplantation. After surgery, the donor's bone marrow may not take root.
A decrease in hemoglobin according to the results of a blood test for lymphoma below 120 g/l may also indicate anemia. The latter is much more common, so there is no need to panic when your hemoglobin decreases. However, if anemia is accompanied by loss of appetite and nausea, further testing should be performed. With such a course of the disease, anemia can occur when serious changes occur in the protein components in the biological fluid.
Treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma in Israel
This disease is treated quite successfully in cancer centers in this country. According to statistical data, almost 80% of cases are characterized by a complete cure. This is especially often achieved in young patients. The rest of the people undergoing treatment for the disease in Israel experience long-term remission and significantly prolong their lives.
Treatment regimen for Hodgkin's lymphoma
Therapeutic regimens for this pathology in patients from 18 to 60 years of age depend on the stage at which the disease is located. Mainly 3 types of treatment are used: ABVD, BEACOPP and BEACOPP-esk. This abbreviation is the first letters of the names of drugs used for medicinal purposes.
Chemotherapy for Hodgkin's lymphoma
Chemotherapy is the main method of treating Hodgkin's disease, considered primarily by Israeli specialists. This method involves intravenous administration or oral administration of a complex of potent drugs. Medicines are delivered to the lesion through the bloodstream. Chemotherapy has been noted to be highly effective in the early stages of Hodgkin lymphoma. The best result is achieved when it is carried out in conjunction with radiotherapy.
Radiation therapy for Hodgkin's lymphoma
This type of treatment is effective in the early stages of the disease. Radiation therapy is designed to give the patient a specific dose of radiation that kills abnormal cells. It does not affect the entire body, but only reaches the area of the body affected by lymphogranulomatosis. This effect is achieved by the fact that during the procedure the patient is completely fixed on the table. Parts of the body not affected by Hodgkin's lymphoma are reliably protected by a special screen. The whole process is completely painless. Only in a small number of people it can cause some psychological discomfort. 1-2 weeks after the course of radiation therapy, medications are prescribed for oral or intravenous administration.
Drugs for the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma
Medicines used to treat this pathology are used in combination. Each drug has its own effect on abnormal lymph cells. It is their combination that increases the effectiveness of therapy. The greatest results are achieved when using the following combinations:
• For stages I and II of Hodgkin's disease, dacarbazine, vinblastine, bleomycin and doxorubicin are prescribed. These medications do not cause serious complications. For complete cure, which according to statistics is possible at these stages in 95% of cancer patients, at least 2 courses of these drugs are required;
• Stages III and IV of Hodgkin's lymphoma require 6-8 courses of treatment with a complex of drugs such as procarbazine, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, etoposide and blenoxane. They are also characterized by good performance, but when prescribed there is a risk of developing secondary cancer or leukemia.
Buy drugs for the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma
:
write us a letter or leave a request for a free consultation
Immunostimulants
Among immunostimulants in the treatment of diffuse large b-cell lymphoma, preference is often given to Interferon. Patients with a favorable prognosis for the development of this disease (that is, those who have the disease at the first or second stage) are treated in two stages according to a special scheme using drugs in the form of Bleomycin, Vinblastine, Dtoxorubicin and Dacarbazine. .
Patients whose disease has an unfavorable prognosis are prescribed intensive therapy in the form of treatment with drugs such as Oncovin along with Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin and others. In addition, if the prognosis is unfavorable, doctors prescribe chemotherapy for patients. Also in such cases, it is advisable to undergo radiation therapy, thanks to which tumor cells are destroyed using X-rays.
Classification
The largest subgroup of T-cell lymphomas, which primarily occur in the lymph nodes, are nodal tumors.
T-cell lymphomas, which affect the skin or appear primarily in the blood, have a special position in medicine. The most common subgroups:
- unspecified peripheral T-cell lymphoma;
- anaplastic large cell lymphoma;
- angioimmunoblastic T-cell type of lymphoma.
T-cell lymphomas are staged using the Ann Arbor classification. The classification takes into account the degree and prevalence of the disease in the body.
Ann Arbor classification:
- Stage I: involvement of one or more lymph nodes with or without organ involvement;
- Stage II: involvement of one or more lymph nodes on one side of the diaphragm with or without organ involvement;
- Stage III: damage to one or more lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm with involvement of organs outside the lymphatic system;
- Stage IV: involvement of one or more organs, lymph nodes.
The presence of symptoms of general intoxication and effects on organs outside the lymphatic system are also indicated. If there are no symptoms of intoxication, the letter “A” is added to the Roman numeral indicating the stage of development of lymphoma; if present, “B” is added. The letter "E" indicates the tumor has spread to organs outside the lymphatic system.
Stages
Stage is the stage of development of a tumor neoplasm. All stages of lymphoma have specific characteristics that indicate how old the tumor is, how far the tumor process has spread, and to what extent the body is affected. Determining the stage helps doctors select the optimal treatment tactics and make a prognosis for the patient’s life. In total, the disease has four stages.
- The first stage is the initial one. During it, one lymph node is affected (less often several located in the same area, for example, cervical or inguinal lymph nodes). Also, a tumor that affects one organ and does not affect the lymph nodes belongs to the first stage. Such tumors are local; they do not metastasize to other human systems, tissues and organs.
- At stage 2, the tumor process affects two or more lymph nodes located on one side of the diaphragm, with which doctors “divide” the human body into two halves horizontally. At this stage, the clinical picture begins to appear more clearly, forcing the person to see a doctor and undergo an examination.
- In stage 3 lymphoma, the oncological process affects two or more lymph nodes, which are located on opposite sides of the diaphragm. It is also possible that several lymph nodes and one organ or tissue area may be affected. Stage 3 is characterized by severe symptoms.
- Stage 4 lymphoma is a disseminated tumor, that is, one that has spread massively throughout the body. The last and most severe degree can be spoken of when the tumor affects several organs located far from the primary site of the oncological process.
How long do people live with lymphoma?
When lymphoma begins, life prognosis directly depends on its type:
- with follicular lymphoma, the prognosis exceeds 70%;
- with T-limblastic and peripheral T-cell NHL – 30%;
- with pathology of the lungs and salivary women - more than 60%;
- for cancer of the breast, bone tissue, central nervous system, ovaries and testicles - up to 20%.
In addition, the prognosis depends on how timely the treatment was started and what effect it had:
- with complete remission, the five-year survival prognosis is 50%;
- partial remission gives 15% percent;
- in cases with low-grade tumors, the prognosis is 80%, regardless of the result obtained with therapy.
Much depends on the degree of cancer percentage. Typically, at stage 4, survival rate is low because the tumor cells have spread throughout the body.
Prognosis and prevention
If diffuse lymphoma is detected early and a full course of therapy is carried out, the prognosis for the patient is quite favorable. In the case when the disease was detected already at stage 4, the chances of survival are insignificant. Unfortunately, due to the long absence of clinical signs, detection of lymphoma often occurs at later stages of development.
Since the exact causes of the formation of large cell lymphomas have not been studied, there is no specific prevention of this pathology. To reduce the risk of illness, you should follow some rules:
- get rid of bad habits;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- avoid contact with harmful substances;
- undergo regular medical examination.
We recommend reading Multiple uterine fibroids - causes, symptoms and treatment
The success of treatment largely depends on the timely detection of pathology, so if you regularly undergo routine examinations in the hospital, you can identify the disease in time, which will significantly increase the chances of recovery.