Is Utrozhestan hormonal or not?
Many patients are concerned about the question of whether this drug is hormonal. According to its composition, Utrozhestan is a hormonal drug used in cases where the amount of necessary hormones in the body increases from the outside. Hormones are not vitamins; they cannot be replaced with special nutritional elements; when doctors see a deficiency of a certain hormone, they immediately prescribe hormonal medications.
The main difference between this drug is that Utrozhestan is a hormone extracted from the natural environment, while analogues are synthetic and are prohibited for use in European countries.
When to see a doctor
Ideally, your period comes after stopping the drug for 1-3 days. However, according to the instructions, an interval of a week is allowed. With extremely irregular menstruation, a delay of up to 10 days is possible. In case of major violations, you should consult a doctor. Depending on the existing pathology, the doctor will prescribe additional treatment or order an examination.
We recommend reading about pills that induce menstruation. From the article you will learn about the main reasons for delayed menstruation, hormonal contraceptives and folk remedies that improve the menstrual cycle. And here is more information about how your periods go after Duphaston.
Utrozhestan is a modern natural progesterone that is widely used to correct the menstrual cycle and to maintain pregnancy in women at risk. Schemes, doses and indications for treatment are determined by the doctor. The nature of menstruation after taking the medicine largely depends on the cause of the delay.
https://youtu.be/mxPgHtMZkNU
Utrozhestan (progesterone)
The active substance of the drug interacts with the following hormonal classes of the body:
- Gestagen. A subclass of steroid hormones responsible for a woman’s ability to conceive and subsequently maintain pregnancy.
- Estrogen. These hormones enhance the physiological effects of progesterone. Only with the combined influence of estrogen and progesterone on the body does the lobuloalveolar formation of the mammary glands and the appearance of milk for feeding the baby occur.
- Chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). A hormone that is produced 6 or 8 days after the egg has been fertilized. Correct indicators affect the successful development of the fetus, and if the level is low, a miscarriage or pregnancy outside the uterus is expected.
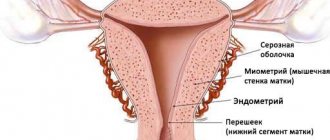
The drug has a preparatory effect on the uterus, helps the egg to be fertilized and develop after that. While the gestation process is ongoing, it reduces contractility and excitability in the muscles of the uterus and fallopian tubes, thereby preventing miscarriage. In addition, it promotes the formation of the endometrium, induces the lactation process, increases fat reserves and promotes the removal of nitrogen from the body. You should not take the medicine as a contraceptive; it has no contraceptive properties. When using Utrozhestan, you need to know exactly what it is prescribed for and in what situations the medicine should not be used.
Compound
Utrozhestan is produced in the form of capsules and vaginal suppositories. The composition of the drug includes:
- Natural micronized progesterone is the active component of the drug.
- Gelatin. It partially helps restore the elasticity of cellular tissues; soy lecithin, which accelerates tissue regeneration.
- Peanut oil, it increases the absorption of medicinal components.
- Glycerol. This product helps to activate metabolic processes.
- Titanium dioxide It has a stabilizing effect on the main substance and auxiliary components of the drug.
Utrozhestan application
The following are diseases for which Utrozhestan is prescribed vaginally:
- in the treatment of cysts;
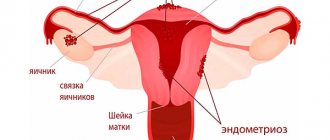
- in the treatment of endometriosis (also for the prevention of the disease);
- in the treatment of endometritis (for chronic endometritis, preventive, hormonal treatment with an anti-inflammatory effect is prescribed);
The medicine is administered in the same way for:
- adenomyosis (as a preventative);
- adnexitis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- hormonal imbalance;
- ovarian cyst(s);
- multifollicular ovaries;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- uterine polyp;
- PCOS (full name: polycystic ovary syndrome);
- fibroadenoma;
- follicular cyst;
- endometrioid ovarian cyst.
In the treatment of infertility and in the early stages of pregnancy, Utrozhestan is used in the following cases:
- with androgenism, hyperandrogenism (increased number of male hormones in a woman’s body);
- during an anovulatory cycle ( anovulation);
- to preserve the fetus with antiphospholipid syndrome (APS);
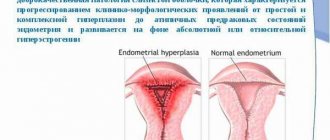
- elimination of endometrial hyperplasia (the main consequence of the disease, the inability of a woman to become pregnant);
- to prepare the endometrium for the time of embryo implantation;
- after insemination (the process of introducing sperm into the uterus without sexual intercourse);
- with icn (isthmic-cervical insufficiency), when the cervix opens too early;
- in cases of mastopathy, including fibrocystic mastopathy;
- with fibroids, including fibroids;
- with insufficiency of the corpus luteum in the ovaries;
- with low progesterone in the body;
- in pregnancy planning, to increase the chances of egg fertilization;
- with thin endometrium;
- in case of threat of miscarriage (termination of pregnancy);
- in the case of IVF, when the embryo is grown in a test tube and then placed in the uterus;
- with cervical erosion.
For oral administration in connection with menstrual irregularities (sometimes to induce menstruation), Utrozhestan is prescribed for:
- amenorrhea, secondary amenorrhea (menstruation does not occur; their absence is noted for three cycles in a row);
- ovarian dysfunction;
- long cycle (long periods);
- menopause;
- disturbance (failure) of the menstrual cycle (periods): with an irregular cycle, with a short cycle, with a long cycle (long periods);
- cases of luteal phase deficiency;
- prolonged absence of menstruation;
- lack of ovulation;
- early ovulation;
- early menopause;
- PMS (facilitates the occurrence of premenstrual syndrome).
The body's reaction to Utrozhestan may vary
Usually the substance is well tolerated, but side effects occur when taken in tablets, for example:
- cycle disorders and lack of menstruation;
- acyclic bleeding; mammalgia;
- headache, drowsiness, dizziness;
- bloating, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea;
- depression;
- cholestatic jaundice;
- urticaria, itching, acne;
- chloasma.
When taking Utrozhestan, dizziness and drowsiness occur as a reaction to the oral route of administration. These unpleasant symptoms are mitigated by reducing the dose after consultation with a specialist, as well as the vaginal method of administration. If you feel sleepy after a dose of the medicine, take it just before going to bed.
Women are usually interested in whether Utrozhestan and thrush are related or not? Indeed, in gynecological practice there have been cases when, while taking the medicine Utrozhestan, thrush manifested its symptoms, but the effect was short-lived. The balance of vaginal microflora largely depends on hormones, and the addition of hormonal medication affects the overall hormonal balance of the body. At the same time, a drug consisting of micronized progesterone is not capable of causing candidiasis by itself. Utrozhestan is often prescribed for thrush just to treat this condition as part of complex therapy. WHO advises choosing natural neutral progestogens for pregnant women, which are similar in structure to endogenous progesterone.
If a woman has previously experienced tachycardia against the background of diagnosed cardiovascular diseases, she should be periodically observed by a specialized doctor while taking medication. Concomitant complaints from patients in Urozhestan are often related to the breasts: someone’s breasts are growing, sometimes the breasts hurt, but when the correct dose is prescribed, the breasts do not hurt. After stopping the course, everything usually returns to normal.
Frequent urination is not included in the list of side effects, but may be associated with pregnancy.
Drugs for the treatment of adenomyosis
The main task of the gynecologist is to select the most suitable drug to restore hormonal balance and suppress the growth of endometriotic lesions.
Medicines are taken according to a strict regimen, which is selected individually for each patient. The effectiveness of treatment is monitored using ultrasound examinations every three months.
If there are no positive results, other tablets are selected. Hormone treatment is considered the most effective. In medicine, drugs used to treat adenomyosis are divided into several groups, differing in the spectrum of their effects.
Oral contraceptives
To treat adenomyosis, hormonal drugs are usually used. The gynecologist selects combined oral contraceptives (COCs) individually.
Among the popular drugs: Silhouette, Yarina, Janine, Qlaira, Regulon.
These tablets contain synthetic hormones that help normalize the menstrual cycle, reduce the severity of symptoms, and stop the growth of pathological lesions. Taking COCs helps normalize the level of female hormones, due to which the lesions regress. When treating uterine adenomyosis, medications are taken for 3-6 months, then an ultrasound examination is performed to check the result.
Judging by the reviews, the most popular drug is Yarina. These tablets are slightly cheaper than similar drugs, but are more effective in the fight against adenomyosis.
Antigonadotropins
This category includes the following drugs: Danazol, Danol. When taking medications, the activity of the ovaries is inhibited, the ovulation process is suspended, which causes endometrial atrophy. With adenomyosis, the pain syndrome decreases, the growth of endometrial tissue decreases, due to this, regressive changes occur in pathological foci.
The medications included in this group have a number of contraindications, so taking the medications requires constant medical supervision!
Progestins (gestagens)
This group includes: Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Norkolut. Progestin drugs reduce the production of the hormone estrogen, suppress ovulation and stop the growth of the endometrium. They are prescribed for all stages of adenomyosis and are taken continuously for 6 to 8 months.
Not recommended for use by women who are planning pregnancy.
Medicines cause the effect of drug-induced menopause, due to this, proliferative processes in endometriotic lesions are restrained.
Antiestrogens
These include: Gestrinone, Medroxyprogesterone. These drugs reduce the production of the hormone estrogen, which promotes endometrial growth. Medicines cause an artificial onset of menopause, so they are most often prescribed to women after 40 years of age. As a result of long-term therapy (5-6 months), menstruation completely stops, the clinical symptoms of the disease are eliminated and the growth of the endometrium is blocked.
Read more Balanoposthitis in a 2 year old child
GnRH analogs
The drugs are prescribed for the treatment of infertility, preparation for IVF, before and after surgery for adenomyosis. Often used: Buserelin, Zoladex, Decapeptyl. Medicines are available in the form of injections and tablets. Therapy is carried out under strict medical supervision, since during the treatment period hormonal levels change sharply, which can provoke an exacerbation of the disease and increase the severity of symptoms. The drugs create an artificial menopause, therefore they are used to stop severe bleeding from adenomysis.
Important! All medications have their contraindications and side effects. Therefore, treatment of adenomyosis is carried out strictly under the supervision of a doctor, who must select the right medicine and monitor the effectiveness of therapy. Self-medication is unacceptable!
Utrozhestan temperature
Since the drug resembles endogenous progesterone, Utrozhestan can raise body temperature and also have a sedative effect. With a body temperature reaching 37.0 ⁰С - 37.4 ⁰С, a woman should not worry: the so-called “progesterone” temperature can be an indirect sign of the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy. Utrozhestan and basal temperature, respectively, behave in a similar way - it may be normal or slightly elevated, but the artificial hormone does not directly affect it.
Utrozhestan and weight
Some girls are worried when taking Utrozhestan, is it possible to gain weight? Does it make you fat? Indeed, weight gain when taking hormonal medications can be observed, but this is not a direct effect of artificial progesterone, but only a consequence of a general imbalance of hormones in the female body. Weight gain, especially during pregnancy, is normal. Excess weight is removed after the course or after pregnancy is resolved. Whether your weight gain is acceptable or not, decide with your personal doctor on an individual basis.
Utrozhestan for discharge
Pink discharge after menstruation is known in gynecological practice, including due to the use of hormonal drugs (the so-called “spotting” - mini-bleeding with oral contraception based on hormones). Mucous pinkish discharge, similar to raw egg white, which is observed in the middle of the cycle, is usually harmless and is associated with increased progesterone levels and the onset of ovulation.
Utrozhestan with spotting has the ability to increase the amount of discharge. It is recommended to wear a pad if a large therapeutic dose is prescribed. Spotting during pregnancy can have several shades; it is necessary to check if there is thick, cheesy discharge; dangerous symptoms are bright scarlet blood, brown, copious watery fluid.
Contraindications and side effects
It is not recommended to use Utrozhestan in the treatment of endometriosis in the presence of the following conditions and pathologies:
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology.
- Liver diseases.
- Predisposition to thrombosis or the presence of thrombophlebitis.
- Increased blood clotting.
- Neoplasms that can develop into cancer.
- Severe mastopathy.
- Impaired kidney function.
- Individual intolerance to the drug.
Treatment with this drug is usually well tolerated, but the following negative effects are possible:
- Impaired concentration.
- Daytime sleepiness.
- Dizziness.
- Spotting.
- Nausea.
- Allergic manifestations.
If unpleasant signs appear, you should inform your doctor in order to adjust the dosage or select a different drug.
Utrogestan and menstruation (menstruation)
When taking Utrozhestan, your periods may behave in an unusual way. In particular, your period does not come, and this may indicate either pregnancy or a delay (usually it is believed that you can wait up to 5 days). Did your period start early? Sometimes, under the influence of the hormone, there is a shortening of the cycle, as well as slight uterine bleeding between menstruation. When acyclic bleeding occurs, it is better to stop taking it and find out the cause of the bloody discharge as accurately as possible. If progesterone is normal, and this is indicated by the test results, do not self-medicate so as not to upset the hormonal balance in the body.
How does the drug affect the cycle?
Utrozhestan is necessary in a non-pregnant state in the second phase of the cycle. It is on this basis that his appointment is carried out - from 16 to 25 days. During pregnancy, it is prescribed continuously. There are two forms for use - tablets and vaginal capsules. When taken orally, the drug acts more systemically, and in the form of suppositories, the main substance accumulates in the uterus. In different cases, preference should be given to one form or another.
The drug directly affects the endometrium, promoting its growth and further rejection. Menstruation when taking utrozhestan begins within a few days after discontinuation of the drug.
Thus, using this medicine, the woman’s cycle normalizes. The likelihood of failures is also reduced due to the fact that utrogestan, like an endogenous hormone, competes with receptors for male sex hormones, thereby ultimately leading to a decrease in their production.
Many women are interested in what kind of menstruation occurs after the morning: as usual or with some deviations. Several options are possible:
- Standard menstruation in terms of amount of blood lost and duration.
- Heavy periods with clots, but in rapid succession after stopping the medication. This is due to the fact that during the delay the endometrium grows excessively, and then, when rejected, the inner layer of the uterus has larger volumes than usual. This phenomenon is observed (menstruation comes in clots after morning use) in most cases in the first month of taking the drug.
- Menstruation varies in nature, but longer than 10 days after the last pill. This is due to deep disturbances in the body, or the reason lies in the wrong dose or prescription regimen of the drug.
- The delay in menstruation after the morning is very long. This can sometimes be observed, if the endometrium has not grown at all in the first phase, more time is required. Also, a small dose of progesterone may not have a complete effect. And it is necessary to exclude pregnancy first.
Utrozhestan: complications
The drug should be prescribed taking precautions:
- with thrombophilia;
- with infection;
- with gastritis;
- with varicose veins;
- with multiple sclerosis;
- in diabetes mellitus, reduces glucose tolerance;
- with thrombosis;
- with cystitis.
The thyroid gland, as well as the stomach (if consumed orally), must be healthy. For all potential complications, especially if the patient is pregnant, it is necessary to arrange monitoring of the condition.