Conception and pregnancy planning if a polyp is removed
Modern methods of diagnosing the reproductive organs take care of the female body, but pregnancy after hysteroscopy occurs only after a certain period of time.
And this despite the fact that minimal harm is caused during the procedure. After all, the doctor is trying to carry out the most necessary manipulations so that they do not once again infiltrate the female body.
After completing the diagnosis, the woman must undergo a recovery period before pregnancy to prevent possible complications.
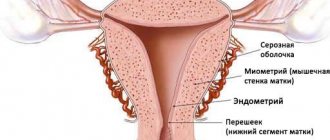
Hysteroscopy is a gynecological procedure in which a special device (hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterus. The video camera at its end allows you to examine the internal area of the cervix and, if necessary, remove polyps and neoplasms. The tool allows you to take material for further research.
This surgical intervention does not harm the body because it is performed without incisions or punctures through a natural opening. To avoid discomfort, a painkiller is administered.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is used to examine the female reproductive system. It is performed under local anesthesia in a gynecological office. In turn, invasive hysteroscopy is similar to surgery.
It is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia. Its purpose is to carry out medical manipulations: remove a polyp, another tumor, take a piece of tissue for examination; in some cases, these 2 types of procedures are combined.
The procedure is successful in cases of infertility. Pregnancy occurs after hysteroscopy in most cases. Although this manipulation is not performed specifically to get rid of infertility.
Hysteroscopy is performed for pathologies of the female reproductive system. Indications for the procedure may include:
- adhesions in the uterine cavity;
- unstable menstrual cycle;
- the formation of neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature;
- abnormal development of the genital organs;
- foreign object in the uterus;
- endometrial polyps;
- severe bleeding from the uterus;
- infertility for various reasons;
- hyperplasia of the mucous membrane;
- uncharacteristic discharge from the uterus;
- incorrectly performed abortion;
- complication after childbirth;
- the need to remove remnants of the intrauterine device;
- the presence of pieces of the fertilized egg during an ectopic pregnancy;
- carrying out sterilization;
- control of disease therapy.
After hysteroscopy (even if cells were taken for biopsy), the uterus quickly recovers. You can expect pregnancy in the coming months.
But its occurrence cannot be guaranteed, because much depends on the identified diseases.
If polyps or another problem are found in the uterine cavity, then you need to first undergo treatment and prepare for pregnancy so that nothing interferes with bearing the baby.
According to statistics, there are many who became pregnant after hysteroscopy within 2 months after it was performed. There is a definite connection between the desire to conceive a child and medical manipulation. There are often cases when infertility is diagnosed due to adhesions and polyps in the uterine cavity. These formations are successfully removed during hysteroscopy.
Medical manipulation forces the body to devote its strength to recovery. Perhaps this serves as an impetus for pregnancy after hysteroscopy.
You should plan such significant events in your life only after consultation with a gynecologist. Only he, after assessing the results of the examinations, can say whether the recovery process has ended.
To avoid negative consequences, it is better to follow your doctor's recommendations.
You should not immediately plan a pregnancy after the procedure. A woman needs to rest, restore strength and health. Sometimes you need to be treated for several months.
Almost always, after hysteroscopy, antibiotics are prescribed to avoid infection in the damaged uterine mucosa. Hormones are used to restore the general background and stimulate the ovaries.
Normal sexual relations begin 3 weeks after the manipulation. An ultrasound may be needed to confirm normal healing. It is recommended to plan pregnancy after hysteroscopy with or without curettage at least 6 months later.
With hormonal imbalances, specific growths on the mucous layer of the uterus - polyps - can occur. Sometimes they are the ones who do not give a woman a chance to get pregnant or the pregnancy ends in a miscarriage. Hysteroscopy allows you to remove such formations. Pregnancy after hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp occurs, in most cases, a year after the operation.
Since polyps arise due to a malfunction in the hormonal system, restoration of hormonal levels and proper treatment are required (usually lasts 2 months).
A woman should take tests and undergo routine examinations to prevent possible complications. If necessary, ultrasound examinations of the reproductive system are prescribed.
Approximately 1 month after completing the course of hormonal therapy, pregnancy may occur.
If a patient has serious pathological problems in the reproductive organs, LDV (therapeutic and diagnostic curettage) is prescribed.
During the operation, the uterine cavity is immediately examined and the necessary surgical removal is performed. During the process, the doctor uses a camera to monitor all actions.
Properly performed curettage helps to avoid complications and allows you to start planning a pregnancy within 1-2 months. The woman should contact her doctor, who will decide whether to conduct an additional examination. A competent specialist will help you determine the time when ovulation will occur.
Any interference in the functioning of the human body can lead to negative consequences. Complications are also possible after hysteroscopy. Incorrectly performed manipulations can lead to the following consequences:
- addition of infection;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- inflammation in the pelvic organs;
- cervical injuries;
- allergy to anesthesia - the gas used during the operation;
- vaginal cramps.
Before performing the procedure, the doctor must warn the patient what complication awaits her if the operation is unsuccessful and how this may affect a future pregnancy. Such consequences are rare; modern equipment allows all manipulations to be carried out at a high level.
Unpleasant consequences are bleeding. This is the norm after such a procedure, because the blood vessels are injured. The discharge should end after 2, maximum 5 days. If you continue for more than this period, you should consult a doctor. Particular attention should be paid to your health if there is an unpleasant odor from the discharge or a change in its color, for example, to a black tint.
After hysteroscopy, the lower abdomen may hurt, radiating to the lower back. The duration of such sensations sometimes extends to 10 days. If the pain increases from a more moderate degree to severe, you should complain to a doctor. You also need to consult a specialist if the nagging pain does not go away after the specified period.
After surgery to remove a polyp, a woman needs time to restore tissue integrity. The duration of the rehabilitation period depends on the extent of the surgery performed and the general health of the patient.
The main factors influencing the possibility of conception:
- presence of diseases of the reproductive system;
- restoration and duration of the menstrual cycle;
- state of the hormonal system;
- chronic pathologies and concomitant diseases.
Pregnancy after removal of an endometrial polyp is planned individually for each patient.
During this period, the integrity of the endometrium is restored, the body is mentally and physically prepared for fertilization. The treating gynecologist recommends pregnancy if the clinical picture is stable and according to the following indicators:
- results of ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) without deviations from the norm;
- absence of infectious processes according to blood tests;
- hormonal parameters are within normal limits;
- absence of inflammatory changes in the genitourinary system;
- According to the examination results, no pathological processes were detected in the body.
It is advisable to plan pregnancy after removal of a cervical canal polyp no later than 4-5 months after surgery. Conception may occur if laparoscopy was performed and the right or left fallopian tube was removed.
Cost of hysteroscopy
The cost of hysteroscopy depends on the purpose for which it is performed. Diagnostic or office hysteroscopy, respectively, is cheaper since it does not include surgery. Prices for surgical hysteroscopy vary according to the level of complexity of the operation, the qualifications and experience of the doctor and the quality of the equipment. Increases the cost of the procedure and the need (in some cases) for hospital stay. But, of course, the price of the service depends on the region and the level of the clinic.
For example, in Moscow, diagnostic hysteroscopy will cost 15,000 - 35,000 rubles, and the price for an operating room reaches 60,000 - 65,000 rubles. In the provinces, the price of office hysteroscopy ranges from 2,500 to 9,000 rubles, and the procedure with surgical treatment of intrauterine pathology costs from 3,500 to 25,000 rubles. The average price for a hospital stay is 1,500 – 4,000 rubles.
Removal methods
Once detected, the polyp is subject to observation until the patient undergoes menstruation. If the growth remains after menstruation, it must be removed.
Examinations, procedures and operations are selected by the doctor based on the following indicators:
- number of polyps;
- size of education;
- location;
- data from laboratory and instrumental examinations;
- accompanying illnesses;
- symptomatic manifestations;
- predisposition to malignant transformation.
| Surgery | Description |
| Polypectomy | Twisting and cutting off the build-up |
| Curettage | Removal of the pathological layer of mucous membrane |
| Hysteroscopy | Minimally invasive surgery under video surveillance |
| Cryodestruction | Exposure and freezing to low temperatures |
| Laser removal | Targeted laser beam |
| Diathermocoagulation | Cauterization with directed electric current |
| Radio wave removal | Vaporization of the affected area with high frequency radio waves |
| Laparoscopy | Removal through small punctures in the abdominal wall |
| Hysterectomy | Removal of the uterus and appendages in case of malignant cell degeneration |
Briefly about hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic manipulation that allows you to visually evaluate the uterus from the inside, identify pathological formations or anomalies in its structure and, if necessary, remove them promptly, that is, without penetrating the abdominal cavity. This method is endoscopic and is performed using a special optical device - a hysteroscope - by a trained specialist.
Translated from Greek, hysteroscopy means “to examine the uterus.” Manipulation can be diagnostic or therapeutic. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed not only to examine the internal uterine surface, but also to collect material (endometrium) for histological examination (biopsy). During therapeutic hysteroscopy, surgical interventions are performed, for example, removal of tumors or foreign bodies.
endometrium
Hysteroscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure. The purpose of which is to identify malignant tumors and pathologies of the female genital organs (such as the cavity and canal of the cervix, as well as the cervical canal) in the early stages of development for their subsequent treatment. This method of therapy can also be prescribed in cases where there is uterine bleeding, if uterine cancer, hyperplasia and other diseases are suspected. However, many patients have a natural question whether pregnancy is possible after hysteroscopy. Let's try to figure this out.
How does hysteroscopy help cope with infertility?
Pregnancy may not occur for many reasons, most often hormonal disorders are to blame. The imbalance does not ensure the safety of the fetus, and conception fails. Other common causes of infertility include:
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes. This may appear due to adhesions, fusion of the entrance to the canal.
- Abnormal structure of the uterus. It can be bicornuate, infantile, or have septa.
- Hyperplastic changes in the mucosa. The fertilized egg does not attach to the deformed endometrium.
- Adhesions in the uterine cavity. Because of them, the egg cannot penetrate inside and gain a foothold.
Before planning a pregnancy after hysteroscopy, you need to eliminate the listed obstacles, except for a bicornuate or infantile uterus. Polyps often prevent you from conceiving a child. These are small neoplasms inside the uterus, usually arising against the background of hormonal imbalance. Polyps sometimes act like a spiral. Especially if the education is large. Therefore, all polyps identified during diagnosis are removed.
The septums are easily destroyed, polyps and adhesions are removed, and the fallopian tubes are cleaned. To eliminate clogging, air is injected into the channels. If hyperplasia is detected, the uterus is curetted, but the mucous membrane is removed. In this case, complete restoration of the endometrium will require a longer time. If we take into account reviews of those who became pregnant after hysteroscopy, then this often happened without problems, after 2-3 months.
Principle of hysteroscopy
The essence of hysteroscopy is that with this type of medical intervention, an ultra-thin optical device called a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity. It is equipped with a camera with multiple magnification, which allows the doctor to diagnose the disease as accurately as possible. The mobility of the device, in turn, makes it possible, if necessary, to carry out surgical treatment immediately after the examination.
However, any woman who has been prescribed such manipulation must undergo a preparatory check. In particular, it is necessary to undergo general blood and urine tests, a cytology smear (taken from the cervical canal) and a vaginal smear (the purity of the microflora is checked), blood biochemistry (the content of glucose and bilirubin is checked), and also check the platelet content in the blood and blood clotting time.
Carrying out hysteroscopy
A woman sits in a gynecological chair for an examination. The most commonly used drugs are internal painkillers, which also act as a sleeping pill. A woman in a dream does not feel any manipulations being carried out. She wakes up after the procedure is over. This method of pain relief is the safest and most effective.
After the woman falls asleep, the uterine cervix is fixed with mirrors and then the hysteroscope is inserted. If necessary, the cervical canal is expanded with other instruments. The hysteroscope slowly moves to the desired location - into the uterine cavity. An examination of its walls begins to identify pathological growths and deformations.
During the procedure, a physiological solution is constantly poured into the cavity, washing away the removed fragments and ensuring maximum visibility. Sometimes insertion of a resectoscope is required. Using this device, polyps, other small tumors, septa, submucosal nodes and cauterization of tissue in specific areas are removed.
Sometimes after hysteroscopy, curettage of the uterus is performed, which is no different from the usual procedure. The biomaterial obtained during the procedure is sent for histology.
Uterine hysteroscopy and pregnancy are first discussed with a gynecologist. In some cases, examination or surgery is combined with laparoscopy. This may be necessary for infertility that has arisen for unknown reasons, endometriosis, polycystic disease, uterine fibroids and endometrial diseases.
Is it possible to get pregnant after hysteroscopy?
After such a procedure, you can get pregnant (if the nature of the disease allows it), and this is confirmed by many women who have undergone this procedure and subsequently experienced the joy of motherhood. But here is a clear answer to the question “how soon?” can't be given. In particular, one of the reasons for this is that the rate of onset of a new conception is influenced not so much by the procedure itself or the medical intervention accompanying it, although they also play an important role. And the very reason (read pathology) for which hysteroscopy was prescribed.
In addition, after such an effect, the female body is often weakened, and therefore pregnancy immediately after hysteroscopy is usually contraindicated. Everything is explained simply: if a woman has any disturbances in the functioning or structure of the organs of the reproductive system (for example, polyps, uterine fibroids, adhesions, etc.).
How a woman copes with recovery after treatment is also of great importance. Usually, after the procedure, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibiotics in order to avoid possible unwanted inflammatory processes. Or he will prescribe preventive treatment with hormonal drugs to stimulate the restoration of normal reproductive function of the reproductive system.
In accordance with this, the timing when you can plan a pregnancy after hysteroscopy also varies. Thus, some women managed to conceive two to three months after the procedure, while others became pregnant only six months later, or even more. However, doctors unanimously agree that you should start planning a pregnancy no earlier than six months after treatment.
This method of treating female infertility is good because with its help the existing problem is not simply temporarily suppressed (as is the case with antibiotics), but the factor itself is eliminated, due to which conception could not occur. In particular, some of the most common causes eliminated by hysteroscopy are a variety of polyps, as well as a phenomenon known as missed abortion. Accordingly, the indications for conception after their treatment will vary slightly.
Polyps are, in essence, overgrown mucous membranes, and they are dangerous because if not treated in a timely manner they can turn into malignant formations. Other complications include difficulties with pregnancy and infertility. After all, the presence of polyps in the uterine cavity leads to deformation of its mucous membrane, which significantly reduces the chances of normal conception.
After this type of procedure, pregnancy should be planned only after treatment with hormonal drugs under the supervision of a qualified doctor. During the treatment process, a woman must be registered at a dispensary, undergo regular ultrasound examinations and undergo the necessary tests. If the course of recovery is favorable, the patient can become pregnant within three months after stopping taking hormonal medications.
Something similar applies to cases where pregnancy is planned after hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp. In this case, malignant tumors spread along the walls of the uterine cavity and act like an intrauterine device, preventing the process of conception. After removal of the formations, restorative treatment can take up to two months - during this period the uterine mucosa completely restores its functions and ability to fertilize. Pregnancy in this case usually occurs within a year.
There is no need to rush in either case, since a woman whose body has undergone such an intervention needs time to recover. This involves drug treatment and (if necessary) hormonal or complex restorative drugs, depending on the nature of the detected pathology.
In some cases, hysteroscopy may be necessary after a frozen pregnancy. This is the name given to the cessation of fetal development followed by its death when a woman is up to twenty-eight weeks pregnant. Various factors can lead to spontaneous termination of pregnancy, from the negative influence of the environment (ecology, bad habits, emotional stress and stress) to genetic incompatibility of mother and fetus (for example, Rhesus incompatibility).
With a natural termination of pregnancy, it is often necessary to perform a hysteroscopy procedure with curettage of the walls of the uterus. The abortive material obtained in this way is examined in the laboratory in order to establish the reasons for the termination of pregnancy. Pregnancy after hysteroscopy with curettage is possible in principle, but planning can begin no earlier than six months after the previous one, or better yet even later, in order to give the woman time to recover not only physically, but also psychologically.
If the hysteroscopy procedure was performed successfully and the pathology was removed without any negative consequences or complications, then the woman can become pregnant again. This also applies to cases where this procedure is performed for the purpose of examination or medical abortion. In such cases, in a healthy woman, pregnancy can occur within two to six months after the operation/examination/abortion.
Usually, the attending physician will advise you not to rush and start planning a pregnancy after hysteroscopy at least six months after the procedure. This is necessary for the patient to undergo a course of rehabilitation therapy, as well as to return the female reproductive system and the body as a whole to normal.
Another important reason to pause is that in some cases (such as polyps) the disease tends to return periodically. In such cases, antibiotic treatment is used to restore and maintain the reproductive system, and at the same time eliminate hormonal imbalance in the body.
Such a break is also needed in order for the general hormonal background of the body to normalize, as well as to avoid possible infection in the inner lining of the uterus and stimulate the work of the ovaries. It is also worth abstaining from sexual relations, at least in the first three weeks after surgery (unless otherwise prescribed).
However, there are cases when re-conception occurs independently and earlier than planned, for example, in the first two or three months after the procedure. Much less often, but it still happens that pregnancy occurs in the next cycle after hysteroscopy.
If a woman nevertheless decides to become pregnant again, she will have to undergo serious and thorough preparation. One of the key points is compliance with all medical requirements in order to form a pregnancy after hysteroscopy whenever possible. First, after the operation, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound at one, three and six months to make sure that the healing process is proceeding without any deviations.
And only if all indicators of women’s health are normal can you begin to plan a new conception. In this case, the woman must be under regular supervision of a gynecologist in order to monitor the progress of pregnancy.
Perhaps information about caesarean section will also be useful for you; you can read more here.
Despite the fact that hysteroscopy is a safe procedure and the risk of complications after it is extremely small, but, like any type of treatment, it has its contraindications. You should definitely familiarize yourself with them before subjecting your body to such an intervention.
So, in what cases is it better not to use hysteroscopy? Doctors do not recommend this type of treatment if there are inflammatory processes in the genital organs, if there are tumors, or if cervical cancer has been diagnosed. It is also not used in cases where a woman is diagnosed with a disease such as cervical stenosis, diseases of the cardiovascular system, or if she is suffering from influenza, sore throat and ARVI.
Hysteroscopy is not performed even when the patient is diagnosed as pregnant, suffers from severe uterine bleeding, or has been diagnosed with a chronic disease of one of the internal organs (kidneys, liver, heart, and so on). Menstruation is another reason why your doctor may delay the procedure.
After the manipulation, an increase in temperature may be observed (on the third or fourth day, less often on the next day after the operation), but this is a normal reaction of the body, which the doctor must warn the patient about in advance. Bloody discharge is also considered normal - from two days during a diagnostic examination to six days during a major surgical intervention.
do not eat heavy, fatty foods, carbonated drinks, or smoke. Instead, you should limit yourself to fresh fruits and vegetables, weak tea and water. The day before the procedure and on the day of the procedure, you can perform a cleansing enema. Pregnancy after hysteroscopy may occur in the near future, so you should prepare your body and gain strength, and we wish you good health.
Possible consequences of hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy refers to surgical operations, but unlike abdominal ones, it is less traumatic. However, some complications may occur:
- the appearance of adhesions due to damage to the mucosa;
- perforation of the uterine wall;
- penetration of germs and infections into the genital organs;
- development of purulent processes;
- the appearance of uterine bleeding.
In the latter case, stopping is sometimes impossible and the organ has to be removed completely. However, such consequences appear very rarely. The cause of complications is the incorrect use of antibacterial agents, insufficient treatment with antiseptic drugs, and lack of experience on the part of the surgeon.
All of the above are extremely rare, and to prevent negative consequences, absorbable and hormonal anti-adhesive therapy is done. During the operation, an anesthesiologist is on duty in the office; the procedure is monitored visually from the very beginning. When pregnancy is planned after hysteroscopy: reviews indicate that there are no complications. Conception occurs quickly and without problems.
Hysteroscopy is a modern and low-traumatic way to cope with infertility. Often the cause is factors that are easily removed through the procedure. As a result, pregnancy after hysteroscopy can occur within three months.
- The test is positive, but the ultrasound does not show pregnancy
- Pregnancy after laparoscopy: when is conception possible?
- Recovery after hysteroscopy of the uterus. Polyp removal.
- Laparoscopy is a new method of diagnosis and surgery
- Laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
Infectious diseases
Possible causes of non-occurrence of pregnancy and forced delay of conception are infectious processes in a woman’s body. The penetration of pathogenic microflora can be provoked by insufficient sterility during manipulation, postoperative complications due to infection of damaged tissues.
Pregnancy against the background of an untreated disease causes the following possible complications:
- re-formation of polyps;
- penetration of infection into the amniotic fluid and the embryo;
- risk of miscarriage at any stage of pregnancy.
Before conception, after removal of the growth, it is necessary to donate blood to an infectious disease panel - an extensive study of infectious diseases in the body. If pregnancy occurs against the background of dangerous infectious diseases, the patient is recommended to have an abortion according to indications to prevent irreversible consequences for the fetus.
Possible complications
Hysteroscopy, like any invasive procedure, is fraught with complications.
Early complications
Among the early postoperative complications, the following should be noted:
- inflammation of the uterus and peritoneum of the small pelvis (endometritis, pelvioperitonitis) – accounts for 90% of all complications;
- intravascular hemolysis caused by the duration of the operation and the use of distilled water or electrolyte-free media or increased intrauterine pressure;
- bleeding – no more than 5% of all complications (observed after resection of fibroids, resection or ablation of the endometrium).
Late complications
Late complications include:
- formation of pyometra in postmenopausal patients (in case of rough manipulation);
- formation of hydrosalpinxes, especially with chronic adnexitis;
- deformation of the uterine cavity (after resection of the endometrium or removal of large myomatous nodes);
- exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes;
- incomplete removal of intrauterine formations.
Pregnancy after hysteroscopy - optimal timing for conception
In gynecological practice, hysteroscopy is a frequently used diagnostic method. It is also used to treat some gynecological diseases, including infertility.
However, this procedure is very traumatic and damages the uterine mucosa, which is necessary for the attachment of the fertilized egg.
How long before pregnancy can be planned after hysteroscopy so that it develops and proceeds without pathology.
Hysteroscopy is a type of endoscopic examination used in gynecology. Using a special device (hysteroscope), the doctor examines the uterine cavity and, if necessary, performs some medical manipulations.
The image is transmitted to the screen, so several specialists can monitor the manipulation at once. The procedure is painful, so it must be performed under general anesthesia.
Hysteroscopy is used to diagnose and treat many diseases of the reproductive system.
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding, which may be associated with hyperplastic processes.
- Myomatous nodes in the uterus.
- The presence of synechiae in the uterine cavity after inflammatory processes and operations.
- Diagnosis of polyps and endometrial cancer.
- The presence of intrauterine septa leading to infertility.
- Pathology of the development of the uterus and its appendages.
- The presence of a dead fertilized egg or its remains in the uterine cavity - after an abortion or frozen pregnancy.
- Foreign body in the uterine cavity.
- Impossibility of removing the intrauterine device due to its adherence to the walls of the uterus.
- Diagnosis of uterine infertility.
- Therapeutic manipulations for hyperplastic processes of the endometrium.
There are many indications for hysteroscopy, so this procedure is performed quite often. Despite the fact that hysteroscopy is used to treat infertility, the manipulation itself is traumatic. After it, time is needed to restore a normally functioning endometrium, which will be able to accept the fertilized egg and securely attach it.
Infertility can occur due to many reasons. They can be hormonal - when a woman’s body does not have enough hormones that are necessary to maintain pregnancy and preserve the fertilized egg. Infertility can also be caused by uterine factors:
- anomalies in the structure of the uterus itself - infantile, bicornuate, the presence of septa in its cavity;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes - due to adhesions, fusion of their cavity or entrance to the tube;
- the presence of adhesions in the cavity of the uterus itself - the fertilized egg cannot penetrate it and gain a foothold in the endometrium;
- hyperplastic changes in the endometrium - the fertilized egg cannot attach to such mucosa.
Hysteroscopy can help remove these barriers to pregnancy. With an infantile or bicornuate uterus, the procedure can only help establish the diagnosis, but treatment is not possible.
If there are partitions, they can be destroyed using a hysteroscope. The same applies to adhesive processes - any, even the densest synechiae can be destroyed and removed during this procedure.
You can also clean the cavity of the fallopian tubes. To eliminate their infection, pneumohysteroscopy is used - when the fallopian tubes are inflated with air and the adhesions are broken. For endometrial hyperplasia, complete curettage of the uterine cavity is performed, removing all the mucous membrane. After this, the woman is prescribed a course of hormonal therapy to restore normal endometrium.
Many women who have had the procedure note that it helped them get pregnant. Although before this, other methods of treating infertility were ineffective.
This procedure refers to surgical interventions. Its implementation is fraught with a number of complications. They can depend on the surgeons and on the woman’s body. What are the possible complications of hysteroscopy:
- perforation of the uterine wall;
- development of uterine bleeding - in some cases it is not possible to stop it and the uterus has to be removed;
- ingress of microbial flora and development of suppurative processes;
- Trauma to the mucosa can lead to the formation of adhesions.
Such consequences are quite rare. To prevent them, the following measures are taken:
- use of antibacterial drugs during and immediately after the procedure;
- visual control of the procedure;
- the presence of an anesthesiologist and surgeon in case of bleeding or perforation of the uterine wall;
- hormonal and resorption therapy to prevent adhesions and restore normal mucosa.
So, when can you get pregnant after hysteroscopy? This question worries all women who have undergone such a procedure.
The period when you can plan a pregnancy depends on the indication for which the procedure was performed.
If it was done to clarify the diagnosis or exclude other diseases, no traumatic manipulations were performed - pregnancy occurs almost immediately and no special preparation is required for it.
The optimal period for pregnancy after diagnostic hysteroscopy is considered to be an interval of 3–5 months.
If adhesions were removed or the endometrium was scraped, pregnancy cannot occur quickly. Getting pregnant becomes possible only after a full-fledged endometrium is formed.
How long this will take depends on the woman’s body. On average, with hormonal therapy, the endometrium grows within six months.
If after the procedure adhesions form again, the period increases for several more months until they are removed again.
There is no point in trying to get pregnant quickly after such a procedure. It is necessary to wait for a complete recovery and carefully prepare for pregnancy so that it proceeds physiologically and is not complicated in any way.
Reviews
Irina, 24 years old. I couldn't get pregnant for two years. Doctors discovered multiple polyps in the uterus. They recommended performing a hysteroscopy and removing polyps. After the operation I had to take hormonal medications for some time. But six months later the long-awaited pregnancy came.
Anna, 36 years old. After several ectopic pregnancies, adhesions formed in the tubes. Doctors recommended doing a hysteroscopy to try to remove them. The operation was performed under general anesthesia. Removal of adhesions was successful, and the endometrium was restored for several months. After this I managed to get pregnant.
Indications and contraindications for hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is usually used as a diagnostic method, but can also be used to treat pathologies of the reproductive system. Main indications:
- myomatous uterine nodes;
- polyps;
- irregular and painful menstruation;
- malignant process in the endometrium;
- hyperplasia;
- various vaginal discharge;
- uterine bleeding associated with hyperplastic processes;
- diseases of the appendages;
- biopsy;
- diagnosis of the causes of infertility;
- complicated pregnancy (ectopic);
- the presence of synechiae in the uterus after surgery or inflammatory processes;
- foreign bodies in the cavity;
- complications after childbirth;
- frozen pregnancy or dead embryo;
- intrauterine septums that cause infertility;
- removing the spiral;
- suspicion of a malignant tumor;
- sterilization;
- frequent pain in the lower abdomen;
- removal of fetal remains after abortion.
The operation is traumatic, so after the intervention it takes some time for the endometrium to recover and be able to firmly hold the fertilized egg.
Contraindications
Hysteroscopy is not performed in the presence of oncological processes in the female genital organs, stenosis, severe uterine bleeding, or during pregnancy. The method is not used for chronic inflammation, acute respiratory viral infections, respiratory infections and diseases of the cardiovascular system. To identify contraindications before hysteroscopic surgery, a full examination is prescribed, including biochemical analysis and consultation with other doctors.
Adhesive process
After surgery with damage to the epithelium, compaction and tissue growth occur during the healing process. Adhesions reduce the elasticity of the organs of the genitourinary system, impede the movement of sperm and eggs, and prevent the embryo from entering and attaching to the uterus after fertilization.
Ways to prevent and eliminate complications:
- careful adherence to all medical recommendations;
- attending physical therapy sessions: electrophoresis, therapeutic exercises, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, ultrasound;
- compliance with a therapeutic diet;
- reduction of physical and psychological stress.
Removal of adhesions can be done under hysteroscopy guidance to minimize damage.
EQUIPMENT AND INSTRUMENTS FOR HYSTEROSCOPY
Rice. 2. Instruments for hysteroscopy.
Equipment and instruments required for intrauterine interventions (Fig. 2.):
- laparoscopic complex;
- cold light source with a power of at least 150 W;
- apparatus for insufflation of liquid media – hysteromat;
- hysteroscope with viewing angle (0, 12, 30, 70 degrees) and outer diameter (1-2, 3, 4 mm);
- hysteroresectoscope;
- electrodes (loop with an angle of 90° and 45°, ball, L-shaped);
- vaginal speculum, lift, bullet forceps, probe, Hegar dilators up to No. 10, curettes.
An indispensable condition for performing hysteroscopy is stretching the uterine cavity, which makes it possible to examine its walls. Three types of media can be used during hysteroscopy:
- carbon dioxide;
- liquid high-molecular media (32% dextrans, 70% dextrose, rheopolyglucin);
- low-viscosity fluids (saline, Ringer's solution, 1.5% glycine, 5% mannitol, 5% glucose).
The choice of contrast medium for hysteroresectoscopy is guided by two factors: patient safety and optimal visualization. In accordance with this, the stretching medium of the uterine cavity must have the following properties:
- provide good visualization;
- create intrauterine pressure sufficient to stretch the uterine cavity;
- do not cause hemolysis and embolism;
- have minimal effects on plasma;
- do not increase osmotic pressure;
- be a dielectric.
Each medium has its own advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for a particular type of hysteroscopy. It is read that there is no ideal environment for stretching the uterine cavity. Most serious complications during hysteroscopy occur due to the careless attitude of surgeons to this issue.
Rice. 3. Instruments for diagnostic hysteroscopy.
For diagnostic hysteroscopy, especially in outpatient settings, carbon dioxide is widely used, which provides good visibility, is absolutely non-toxic, quickly resorbed, easy to use and available. Its injection is carried out using a hysteroinsufflator, which allows you to control intracavitary pressure within the range of 40-80 mm Hg. at a gas flow rate of 30-40 ml/min. It is an ideal environment in cases where there is no bleeding from the genital tract. Even with minor bleeding, the gas environment becomes cloudy, which makes it difficult to diagnose intrauterine pathology. CO2 cannot be used as a stretching medium during hysteroresectoscopy (an absolute contraindication), since the risk of embolism sharply increases with thermal energy effects on tissue (Fig. 3).
For intrauterine surgery, liquid media are preferred. Recently, the use of low molecular weight solutions has become increasingly popular. The flow-through design of a modern hysteroscope provides conditions for removing blood and tissue fragments, which creates clear visibility even in the presence of bleeding.
For operative hysteroscopy, it is important to distinguish low-molecular solutions according to their ability to conduct electric current: electrolyte (sterile water, saline, Ringer's solution) and non-electrolyte (glucose, glycine, sorbitol, mannitol). Procedures using electrosurgical techniques require the use of non-electrolyte solutions, as electrolytes undergo hemolysis and can cause electrolyte abnormalities. The advantages of bipolar resectoscopes include the ability to use electrolyte media, since the current passes between the jaws of the instrument and does not extend to the patient’s body.
Of course, an isotonic (0.9%) sodium chloride solution has certain qualities of an “ideal” medium for stretching the uterine cavity, since it does not irritate the tissue, is isotonic with blood plasma, is quickly removed from the vascular system and only temporarily increases the volume of circulating fluid.
Identical, including in optical properties, to a physiological solution of 5% glucose solution. However, it does not contain electrolytes, which allows it to be used for monopolar resectoscopy. The main disadvantage of solutions with low viscosity is the ability to cause overhydration and, accordingly, hyponatremia (water intoxication).
Laparoscopic assistance is used if necessary to monitor hysteroresectoscopy for the depth of tissue dissection and uterine perforation in the following cases:
- large size of the intramural component of the submucosal myomatous node,
- thick and wide intrauterine septum,
- pronounced cicatricial adhesive process (synechia) in the uterine cavity;
- proposed combined operations on the abdominal and pelvic organs (salpingo-ovariolysis, conservative myomectomy, ovarian resection, etc.).
Indications
As we have already understood, with the help of hysteroscopy you can assess the condition of the uterine cavity. This is a general characteristic of the procedure. Let's move on to specifics. Hysteroscopy is indicated in the following cases:
- Endometrial pathology detected by pelvic ultrasound or confirmed by other methods (MRI, CT) - endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial polyps. It is very convenient that simultaneously with examining the uterine cavity, you can remove a polyp, take a section of the endometrium for a biopsy, and coagulate or “cauterize” bleeding vessels.
- Suspicion of endometrial cancer. In this case, the endometrial biopsy is not taken blindly, but under eye control - that is, the doctor sends the most suspicious areas for histological examination.
- The presence of submucosal or cavitary fibroid nodes. In this case, through hysteroresectoscopy, it is possible to both remove the intrauterine nodes, assess their condition and determine a plan for further treatment.
- Suspicion of endometriosis or adenomyosis. Hysteroscopy is the only reliable confirmation of the diagnosis of adenomyosis, and also serves to determine the degree of adenomyosis, its prevalence and prevalence.
- Synechiae or Asherman's syndrome are thin connective tissue cords extending between the walls of the uterus. Often synechiae are the cause of infertility or miscarriage in young women. With the help of hysteroscopy, these cords can be cut, freeing the uterine cavity.
- The presence of foreign bodies in the uterine cavity is a rare but common phenomenon in gynecology. Foreign bodies can be represented by fragments of intrauterine contraceptives, fragments of medical instruments left over from previous intrauterine manipulations, and remnants of fetal tissue after abortion.
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology - that is, abnormal bleeding without an objective cause that was not detected by ultrasound or other diagnostic testing. Hysteroscopy followed by endometrial curettage is used to stop uterine bleeding or menorrhagia.
- Infertility. In this case, hysteroscopy is used to exclude chronic endometritis and endometrial deficiency as possible causes of infertility and miscarriage. The doctor can also find and examine the openings of the fallopian tubes - the orifices - and assess their condition.
- Preparation for ART or assisted reproductive technologies - IVF, insemination, ICSI. The purpose of hysteroscopy in this case is similar to the previous one - to assess the function and consistency of the endometrium, minimizing the risks of reproductive failures.
- Anomalies of the structure of the uterus - duplication of the uterine body, additional uterine horns, intrauterine septum. The procedure helps determine the condition of the cavity, assess the possibility of spontaneous pregnancy or the need for surgical correction of defects.
- Control studies after previous therapeutic and diagnostic procedures and to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. For example, using hysteroscopy, you can evaluate the dynamics of treatment for endometrial hyperplasia or the development or “growth” of the endometrium in pregnancy preparation programs.
Survey
Initially, when visiting a gynecologist, each patient undergoes a standard examination using medical mirrors. During the diagnosis, the doctor can also, if necessary, do a biopsy, taking a small piece of tissue from the affected area. Such actions make it possible to differentiate the pathology, as well as exclude deformation of the uterus and the presence of malignant or benign neoplasms on the ovaries.
The next stage of examination for the woman will be to undergo routine tests - blood and urine. If the information received is not enough, the specialist will prescribe an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs, which will make it possible to approximately determine the presence of foci of the disease.
However, ultrasound alone does not provide a complete picture of the condition of the reproductive organ, since it is impossible to examine areas with endometriosis that are less than two centimeters in size. This is precisely the main reason why a woman is prescribed hysteroscopy. Endometriosis is detected without any particular difficulties during this examination.
Such a study makes it possible to determine the location of even the smallest pathological areas. If the disease is found at an early stage of progression, then doctors have the opportunity to assess the condition of the surface of the uterus, if there is hyperplasia, and perform a diagnostic curettage.
Hysteroscopy of the uterus for endometriosis, although at first glance a complex procedure, does not require hospitalization of the patient in a medical hospital. Due to the fact that the device is equipped with high-quality optics, the doctor can perform a tenfold magnification of any area at which the camera is aimed and examine it from the most convenient angle.
Adenomyosis of the uterus - an indication for diagnosis with a hysteroscope
The main indications for hysteroscopy are:
- Suspicion of the development of endometriosis or adenomyosis;
- Various pathological processes in which endometrial damage occurs;
- The presence of polyps on the endometrium;
- Female factor infertility;
- Unstable menstrual cycle;
- The presence of adhesions in the uterus or abnormalities in the development of the organ;
- Inability to conceive a child naturally;
- The presence of foreign bodies in the body, for example, an intrauterine device.
The procedure is quite simple, and modern doctors perform it regularly, so there is no need to worry about anything going wrong. However, at the same time, understand the standard rules for preparing the body and follow them.
Endometrial hysteroscopy
Endometriosis is one of the most common and mysterious diseases of gynecology. The causes of its occurrence are not fully understood, and the consequences sometimes noticeably worsen a woman’s quality of life. About ten percent of women of reproductive age, which is from 18 to 40 years old, suffer from this disease. This problem negatively affects pregnancy; it can provoke adhesions, complicated pain, bleeding, and cycle disruption. Unfortunately, this disease is prone to relapse, that is, to repetition. And these numbers are quite serious:...
How to diagnose endometriosis?
Endometriosis is the most widespread disease, in terms of localization, of all female gynecological diseases. It is more common in girls of reproductive age.
The symptoms are very similar to other female diseases; to identify the disease, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination. Endometriosis is best treated at stages 1 and 2, so it is very important to identify the disease at an early stage.
In medicine, types of endometriosis are classified depending on its location:
- Genital: can be internal or external.
- Extragenital.
There are four stages of the disease, depending on the form and degree of its neglect.
https://youtu.be/QtXVBDGUd6c
Treatment at different stages
After examination, identifying the cause of the disease, an individual treatment method is prescribed:
- Conservative, with the help of medications;
- Surgical - they can remove foci of the disease while preserving the reproductive organs. Or radical - when the ovaries and uterus are completely removed.
- Combined.
Endometriosis is treated with medication in the first stages of the disease. Hormone therapy is most often used. Anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating drugs are also prescribed.
In the third degree, the disease manifests itself with more serious symptoms, severe pain, and heavy discharge during menstruation. The disease spreads to the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Growths and adhesions appear, which complicates the fertilization process. Endometriosis causes inflammation of the reproductive organs.
The disease can only be eliminated surgically by removing the tumors.
The most dangerous is the fourth stage of the disease. A woman's life is at risk.
Examination for endometriosis
First of all, you need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist with a speculum; he takes a biopsy from the affected areas of tissue.
This method will help eliminate deformation of the uterus and neoplasms on the ovaries. If foci of disease are detected on the cervix, a biopsy is taken from this area and sent for laboratory testing. Prescribes urine and blood tests.
An ultrasound examination of the pelvis is also performed, which makes it possible to identify suspicious lesions. But ultrasound does not give a complete picture, since small areas of endometriosis up to two centimeters cannot be seen during such an examination.
Having diagnosed the disease in the early stages, you can evaluate the surface of the uterus for endometrial hyperplasia and perform a diagnostic curettage.