Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is becoming common today. Thoracic osteochondrosis is less often diagnosed than in other departments. The structure of the chest allows for limited mobility of the vertebrae, so they are less susceptible to injury. Previously, this disease manifested itself in older people, but over the past 20 years it has become “younger”. Now symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in women, men and children occur with almost the same frequency.
What is thoracic osteochondrosis?
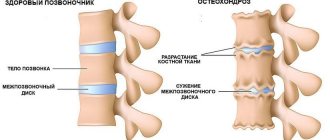
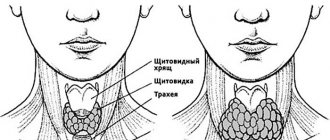
Thoracic osteochondrosis is a degenerative process that occurs in the spine between the 8th and 19th vertebrae. These vertebrae form the thoracic spinal column. And it is between them that changes occur in the vertebral discs when this type of osteochondrosis occurs. But due to the fact that this part of a person’s back is not as mobile as the rest, the changes that occur do not manifest themselves until it is too late and the disease progresses into an advanced phase, at which treatment becomes very problematic.
Therefore, it is so important that at the first symptoms of the disease, close attention is paid to them and measures are taken to prevent the development of the disease.
Why is thoracic osteochondrosis dangerous for women?
If treatment is not started in time, thoracic osteochondrosis in women can lead to the development of the following complications:
- intercostal neuralgia;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- VSD;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- intervertebral hernia in the thoracic region;
- proliferation of bone osteophytes;
- osteoporosis;
- mental illness;
- diseases of internal organs;
- spinal cord compression.
In its advanced state, the pathology leads to complete loss of mobility and disability.
Symptoms
It is worth remembering that the initial stages of thoracic osteochondrosis do not manifest themselves in any way. This is why this type of disease is dangerous. Therefore, it is very important that immediately when the first signs appear, or if there is a hint of them, you should consult a doctor and carry out all the necessary tests and examinations.
Osteochondrosis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Feelings of difficulty breathing.
- Feeling of tightness throughout the chest.
- It becomes more and more difficult to bend over. Moreover, this condition is progressing.
- Feeling of freezing of limbs. This occurs due to decreased blood circulation in them.
- Chest pain.
- There may be a burning sensation in the legs and feet.
- Keratin coatings (nails and hair) become brittle.
- Accompanied by thoracic chondrosis, the symptoms of which are similar to those of osteochondrosis.
- The gastrointestinal tract begins to work intermittently.
- Burning in the chest.
- Burning in the stomach area.
- Pectalgia – pain in the front of the chest.
- In men, potency decreases. The genitourinary system begins to malfunction.
- The person is feeling sick. Moreover, this condition also progresses.
- Headaches of varying severity, including migraines.
- Neuralgia of the chest, especially those localized in the ribs.
- On the left side of the body, pain may occur, similar to those that appear with cardiovascular disorders.
- Pain may affect the liver and gallbladder.
- Back and chest often reflexively.
- The appearance of herpes zoster (shingles).
- Signs of thoracic osteochondrosis in women include pain in the mammary glands.
- Discomfort in the throat and difficulty swallowing. A cough may appear, as if the larynx is irritated.
The appearance of several of these symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine requires an immediate and complete examination to clarify the diagnosis.
Dorsago and dorsalgia
Most often, thoracic osteochondrosis manifests symptoms and sensations in which the patient feels pain that varies in duration and strength. All pain symptoms are classified into two groups:
Dorsago - short-term acute pain. They occur when a person performs a monotonous load, that is, the muscles are in one position for a long period of time. The muscles become overstrained, causing sharp pain (neuralgia), which may also be accompanied by difficulty breathing. Dorsago occurs more often in women than in men.
Dorsalgia is prolonged pain. They become more pronounced when a person inhales. At first, the discomfort is mild and gradually intensifies. After 4 weeks, they become more pronounced and acute. The nature of the pain can be pulling, cutting, stabbing or some other type.
Pain due to osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is localized in the chest, shoulder blades, ribs, collarbones, and sides in the area of the ribs.
What happens at the very beginning of the disease
The initial stage of the disease does not manifest itself or does so in very mild, insignificant ways. You need to pay close attention to symptoms such as:
- I felt stiffness in my movements.
- The range of movements has decreased.
- There are signs of discomfort when bending, turning, bending or bending.
- Pain in the area between the shoulder blades in the chest.
These are sure signs of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, and to miss them means to transfer the disease to the next, more severe stage.
Chest pain
The main symptom that accompanies all stages of the disease is pain. It can be localized throughout the body to the waist area. So, the pain most often affects:
- The part of the back between the shoulder blades.
- Collarbones and areas below them.
- Ribs and parts of the body below them.
- Heart area.
- Pancreatic region.
Due to the fact that the pain affects vital organs, such as the heart, thoracic osteochondrosis is confused with other diseases and treatment is prescribed incorrectly.
The thoracic spine consists of 11 vertebrae. And each of them, when damaged and degenerative processes occur, causes a certain type of pain or negative changes in various organs. So, in order to distinguish pain in the sternum with osteochondrosis from cardiac problems, you should understand how pain differs in the two cases. In addition, when chronic diseases appear, a person must be aware that they could be caused by degenerative processes in the spinal column.
| Categories | Cardiac problems | Thoracalgia (pain in the thoracic spine) |
| Nature of pain | The pain has the character of an attack when the thoracic region is affected, but it can be either aching or pressing. | Shooting sensation, burning, aching pain. |
| Place where pain occurs | Soreness is felt on the back, pain is localized behind the sternum. But it can radiate in all directions, both to the shoulder and down under the ribs. | The pain is often either point-like or encircling. But in any case, it is localized precisely at the level where the vertebra in the chest area is affected. The pain radiates to the collarbone, shoulder blade, and back. Women are more likely to experience discomfort in the chest area. |
| Duration | It occurs spontaneously and does not last long, up to 15–20 minutes, but if it is a heart attack, it may occur over a longer period of time. | It can last for several moments or, on the contrary, have a monotonous, long-lasting character, which is very exhausting for a person. |
| Reasons for exacerbation of the condition | Stressful situations, increased stress on the heart during physical activity. Prolonged stay in a horizontal position. | Uncomfortable position, sharp turns, bends, bends, palpation of the ribs or those areas in which pain is felt. |
If your heart hurts, then in order to know how to determine that it is a cardiovascular problem, you should take the appropriate medications and see if the symptoms go away. If not, then these are most likely signs of osteochondrosis.
Feeling of tightness in the chest
This feeling is reminiscent of the feeling when you cannot take in as much air as you want. A so-called incomplete breath appears. A feeling of tightness in the chest may be accompanied by pain in this area. Shortness of breath occurs with osteochondrosis.
This tightness in the chest can also occur with other diseases, such as pneumonia or heart problems. And to understand why the compression occurred, it is worth measuring the number of heart beats per minute. If it is 100 or more, then most likely it is a pulmonary or cardiac disorder. But if there are less than 100 beats, then, with almost complete certainty, we can say that the cause of incomplete breathing is thoracic osteochondrosis.
Other symptoms
As osteochondrosis of the thoracic region develops, additional signs and symptoms of the disease are added to the pain syndromes, such as:
- Tingling in the upper and lower extremities - a sensation of goosebumps running across the skin.
- Then numbness occurs. It can appear in one limb or all at once.
- Excessive sweating appears, and it is situational in nature, regardless of external conditions.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Cold sweat may appear on the forehead and even on the body. This condition resembles panic attacks.
If such symptoms appear for the first time, then you should definitely take a calm and relaxed pose, drink nitroglycerin and call a doctor. Since these may be symptoms of a heart attack, especially if all of the above is supplemented by pain in the chest. It's worth listening to yourself. If after taking nitroglycerin the condition has improved, then this is most likely a heart problem, and if not, then most likely these are symptoms accompanying thoracic osteochondrosis.
In addition, symptoms such as:
- Digestive disorders - this can be irregular bowel movements, accompanied by both constipation and diarrhea.
- Abdominal pain of unknown etiology often occurs.
- Bloating and increased flatulence may also occur.
- Exacerbation of gastritis.
- Nausea appears and vomiting may even occur. All this may be accompanied by loss of appetite.
In addition to all of the above, symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in men include disorders of the genitourinary system, which manifests itself most clearly in a decrease in potency.
But the peculiarities of the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in women include pain due to pathologies of the mammary gland. If pain in the mammary glands torments a woman, then in order to exclude diseases of the mammary glands and confirm thoracic osteochondrosis, you need to visit a mammologist.
The appearance of pain and the occurrence of various diseases with damage to different vertebrae in the thoracic region is expressed as follows.
| Thoracic vertebra number | Accompanying pain |
| 1 thoracic vertebra | When the first thoracic vertebra is damaged or degenerative changes occur in it, numbness appears in the upper limbs of both one and two at the same time. The pain spreads to the shoulders and forearms. May radiate to the hands. The muscles of the back of the head become tense. |
| Second | A state of panic attacks may occur; a person is accompanied by a feeling of fear. The heart rhythm is lost. |
| Third | The pain may spread to different parts of the chest. Cough often occurs with thoracic osteochondrosis, bronchitis, asthmatic condition and other disorders in the respiratory tract appear. |
| Fourth | The functioning of the gallbladder and bile ducts is disrupted. Dyskinesia and gallstones may occur. There will also be pain on the right side in the shoulder and head. |
| Fifth | Problems with the liver, insufficiency of hematopoiesis and circulation. Hypotonic states and the associated feeling of chronic fatigue. Arthritis. |
| Sixth | Malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. Often problems with the sixth thoracic vertebra are accompanied by heartburn and diabetes. |
| Seventh | Gastrointestinal problems - duodenal ulcer, heartburn, increased acidity, hiccups, nausea. General weakness of the body. |
| Eighth | The spleen suffers in this case. The body's immune system malfunctions, resulting in immunodeficiency. |
| Ninth | Allergic manifestations. |
| Tenth | Violation of water-salt balance and associated malfunctions of the kidneys. The arteries become calcified, which sharply reduces their elasticity. |
| Eleventh | A wide variety of skin problems, from dryness to psoriasis. |
What other pain syndromes exist for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region?
It is important to realize that pain is the companion that always accompanies osteochondrosis. It can manifest itself either very weakly, or it can lead a person to a state in which he will experience constant stress, since the pain is so strong that he will not even be able to take a comfortable position.
Speaking in general about pain, it is worth considering that it must be divided into:
- Local (local).
- Distant.
Local pain occurs precisely around the area of the spine where degenerative changes have occurred. When a person is bothered by thoracic osteochondrosis, the pain will be localized in the back and neck. The amplitude of possible movements decreases, and stiffness appears. All this is accompanied by either short-term pain, or they are permanent.
With distant pain, areas of the abdomen, heart area, arms, even legs are affected. There may be squeezing sensations, burning, and tingling. It is very important that distant pain is accurately diagnosed so as not to confuse its occurrence with any other disease.
Neuralgia of thoracic osteochondrosis is characterized by such localization of pain that it is even difficult for the patient to take a breath. Intercostal neuralgia most often occurs precisely because of osteochondrosis in the thoracic vertebrae. But it is worth noting that there is no inverse relationship. That is, neuralgia does not lead to osteochondrosis. But neuralgia can be triggered by a rib fracture or other types of injury. In order to understand whether neuralgia arose precisely because of osteochondrosis, it is worth understanding how different the sensations are with these changes in the body.
| Main signs of neuralgia and osteochondrosis | Neuralgia | Osteochondrosis |
| Type of pain | The pain is sharp, piercing. Looks like an injection. | The pain is rather aching with a burning sensation. |
| Location of pain | On the sides of the body in the places where the ribs are located. | In the area and between the shoulder blades, in the back and in the armpits. |
| Time of onset of discomfort | The pain intensifies during a sigh or during a turn. | Pain with thoracic osteochondrosis occurs after prolonged stress on the body, that is, towards the end of the day. As a rule, it goes away or decreases after rest, either during the day or at night. |
Main symptoms and signs
The first characteristic symptom of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is acute pain in the sternum, similar to a heart attack.
Pain syndrome is also observed in the interscapular region, accompanied by discomfort throughout the entire back. In addition to pain, the following symptoms occur as the disease progresses:
- compression in the chest;
- pain, discomfort when taking a deep breath;
- pressure surges;
- coldness, numbness of the extremities;
- breast enlargement, tenderness;
- tingling, goosebumps;
- motor dysfunction;
- sensory disturbance;
- headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- noise in ears.
There may be a dysfunction of the respiratory system, manifested by the following symptoms:
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- cough, wheezing;
- pale skin;
- cyanosis.
The clinical picture of thoracic osteochondrosis in women can also be supplemented by a number of indirect signs:
- impaired gastrointestinal functions;
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- sleep disturbance;
- irritability;
- brittle nails;
- dryness, flaking of the skin;
- itching, burning in the legs or arms;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
During pregnancy, a woman may complain of frequent shortness of breath, swelling of the pelvis and thighs, rash, furunculosis, and pulsation in the fetal area. A woman’s feelings can be very different, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Causes
Thoracic osteochondrosis appears as a result of a number of the following reasons:
- Hereditary factor.
- Unnecessary and excessive physical activity.
- Lifting a weight from an incorrect position.
- Physical inactivity, which deprives a person of sufficient blood circulation in all tissues.
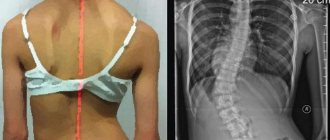
- Postural defects (curvature of the spinal column, for example, thoracic scoliosis).
- Injuries, damage or bruises to the chest and spinal column.
- Inconvenient shoes, especially those that lead to incorrect position of the spinal column - high heels.
- Bad habits.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Exhausting physical labor.
- Disruptions in the blood supply to the spinal cord.
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the bone structures of the spine.
- Changes in the cartilage tissues of the spine.
- Hypothermia.
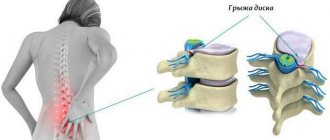
- Any changes in the intervertebral discs, including vertebral hernias.
The period of pregnancy in a woman can affect the formation of thoracic osteochondrosis. This is due to the fact that the load on the spinal column increases along with resource costs. As a result, there is a lack of micro- and macroelements, as well as vitamins.
Excess body weight. Moreover, it is enough to have 10% more than normal weight to increase the load on the entire spinal column.
Neuromuscular shock absorption disorders. This occurs when the muscle does not fully compensate for the shock loads that can affect the body. As a result, an intense “blow” falls on the human skeleton, namely the spine. As a result, damage occurs.
Osteochondrosis can occur only under the influence of several factors, as in principle any disease. Therefore, what can be excluded from the list of causes should be eliminated. For example, bad habits, physical inactivity or heavy lifting. Take control of stressful situations.
What is osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine of women
This disease characterizes dystrophic and degenerative disorders of the spinal column, changes in the structure and shape of the intervertebral discs. Thoracic osteochondrosis of the spine progresses by age 40, and many patients endure it on their feet. This cannot be done, because over time the intercostal nerves become pinched; disability is not excluded. The upper thoracic vertebrae are involved in the pathological process, and the patient guesses about the disease by the characteristic chest pain.
Signs in the subacute stage
The subacute stage occurs when the acute stage has passed. During this period, the person no longer experiences difficulty breathing. There is no pronounced pain, the symptoms become more subdued. A person falls asleep easier because it is easier for him to take a comfortable position while sleeping.
To prevent the subacute stage from becoming acute again, you should avoid:
- Lifting weights.
- Performing incorrect bends.
- Do not take static poses for a long time, especially if they are unnatural for the spine. These poses also include a sitting position.
- Hypothermia.
Usually the subacute stage lasts about 2 weeks. If the regimen and doctor’s recommendations are not violated, then most often a remission occurs, in which all symptoms disappear. Further, the patient’s task is to prevent the exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine by treatment, for example, with exercise therapy methods, folk remedies, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet.
But if during the subacute stage the following sensations arise, then you need to pay close attention to them:
- Renewed stiffness and inability to raise your arms, even if not accompanied by pain.
- Increasing pain if it has not gone away completely or pain attacks last longer.
- Dizziness and feeling of nausea.
As soon as this happens, it is possible that the subacute stage again turns into acute. You should consult a doctor and fully describe the sensations that arise.
Prevention
To prevent osteochondrosis, you should purchase an orthopedic mattress and pillow for correct body position while sleeping. You need to eat a balanced diet and consume as much fluid as possible. You need to try not to overload your spine and learn to sit correctly. For people driving, it is recommended to purchase an ergonomic seat and not drive for more than 3 hours.
Osteochondrosis is a serious disease that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. If you do not self-medicate and follow all the procedures prescribed by your doctor, you can get rid of this disease forever.
Degrees
After the symptoms have alerted the person and he has consulted a doctor, a comprehensive examination is prescribed. During which, if osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is confirmed, the doctor will determine the extent of the disease.
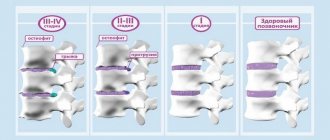
First degree
Osteochondrosis of the 1st degree of the thoracic spine is characterized by the onset of changes in the intervertebral disc. As a result, already at this stage protrusions may appear and the disc protrudes into the spinal canal. But at this stage there is no rupture of the fibrous ring. In the first degree of the disease, no pain syndromes appear.
Second degree
At the second stage, discomfort appears in the spine. There may be obvious pain, dizziness and a feeling of nausea. In the second stage, the discs protrude into the spinal canal so intensely that they lead to rupture of the fibrous ring, which leads to the formation of intervertebral hernias.
Third degree
The stage of active manifestation of intervertebral hernias with all the ensuing consequences, such as pain and limited mobility.
Fourth degree
The elasticity of the intervertebral discs is completely lost. In addition to pronounced hernias, destruction of the bone structures of the vertebrae also occurs. Bone growths – osteophytes – appear.
Symptoms of advanced osteochondrosis
The disease in an advanced stage leads to displacement of the intervertebral discs, disrupting the shape and structure of the spinal column. For the patient, this is acute pain that does not allow the body to turn, limits movement and physical activity, and is one of the main causes of an unstable emotional sphere. During the pathological process, systemic circulation is disrupted, and progressive symptoms of advanced osteochondrosis lead to the following health complications:
- dystrophy of the heart muscle;
- kidney dysfunction;
- intervertebral hernia;
- symptoms of decreased potency;
- shingles;
- dystrophy of other parts of the spine;
- extensive damage to internal organs.
Diagnostics
Many who first encountered the signs of this disease are concerned with the question - how to determine osteochondrosis in the thoracic region?
The disease is insidious, as it may not manifest itself for a long period of time or disguise itself as other diseases. In this connection, when the patient consults a doctor, he is already diagnosed with a progressive advanced stage of osteochondrosis.
Therefore, it is important, as soon as the first suspicions appear with the first symptoms of the disease, immediately consult a doctor and conduct a comprehensive examination in order to accurately diagnose, determine the stage and correctly prescribe comprehensive treatment. Even if the doctor prescribes only drug treatment, it is necessary to ask about exercise therapy, physiotherapy and other therapeutic actions.
When diagnosing, a neurologist can:
- Make a primary diagnosis based on the symptoms the patient describes.
- During the examination, the doctor palpates the areas that the patient points to and examines how severe the pain is.
- Certain functional tests help the doctor assess how intact reflexes and sensitivity are.
- X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs may be prescribed.
- A neurologist may prescribe an ECG in order to exclude interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
After a comprehensive examination has been carried out, the doctor, upon confirmation of osteochondrosis, prescribes treatment that is designed to alleviate symptoms, stop the development of the disease and, if possible, restore functionality to the body.
Risk factors
Thoracic osteochondrosis in women develops under the influence of the following factors:
- Heredity.
- Structural changes in discs that occur as a result of aging.
- Injury to the spine due to unsuccessful falls.
- Physical overload at work, playing sports at a professional level.
- Blood circulation pathologies in the thoracic spine.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis may appear due to insufficient mobility. To avoid its formation, you should perform moderate physical activity daily and train various muscle groups.
Other common reasons:
- Severe hypothermia.
- Chronic infectious diseases.
- Frequent stress.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Working conditions that do not comply with legal standards.
- Congenital or acquired spinal defects.
Area affected by thoracic osteochondrosis
Currently, the exact causes of the development of thoracic osteochondrosis have not been established. Experts have proposed many theories (infectious-allergic, hereditary, mechanical, hormonal, vascular), but none of them provides a clear and complete explanation of the pathological changes occurring in the spine and leading to tissue degeneration.
Factors causing such overloads are:
- abnormalities in the structure of the spine;
- asymmetrical arrangement of joint spaces in intervertebral joints;
- congenital narrowing of the spinal canal;
- spondylogenic muscular (myofascial, referred) and/or somatic (referred, arising against the background of a number of diseases of the blood vessels and internal organs) pain;
- prolonged exposure to vibration on the spine, for example, among vehicle drivers;
- physical stress;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle (hypodynamia);
- psychosocial factors.
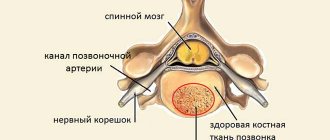
The mobility of the spine is ensured by intervertebral discs, which also play a shock-absorbing role. In their center there is an elastic gelatinous core, which contains large quantities of water. With osteochondrosis, the core begins to lose water as a result of demineralization of polysaccharides.
Over time, the nucleus becomes flattened, and along with it, the intervertebral disc itself becomes flattened. Under the influence of mechanical load, the fibrous ring protrudes, this process is called protrusion. Subsequently, cracks appear in the disc, through which fragments of the nucleus pulposus fall out, that is, the formation of a herniated intervertebral disc occurs.
The disease is quite rare. This is due to the fact that the spine, that is, the joints between the vertebrae, in the thoracic region are created almost motionless. And if a person makes some sudden movement, or often moves against the axis of the intervertebral joints (for example, digs or lifts a weight with only one hand), then all the thoracic vertebrae are activated at once. They do not work separately from each other.
The causes of thoracic osteochondrosis are:
- scoliosis in the thoracic or lumbosacral region;
- excessive or improper exercise;
- thoracic spine injuries;
- excess weight - more than 10% of what is expected according to body composition;
- metabolic disorders - as a result of endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, pathology of the adrenal glands and others) or inadequate nutrition;
- developmental anomalies of the thoracic spine;
- physical inactivity (the intervertebral disc - what is destroyed during osteochondrosis - is also nourished when the back muscles are working).
Remission
In the acute stage of the disease, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Cough with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine.
- Various symptoms of thoracic neuralgia.
- Pain syndrome that can manifest itself in different places of the upper body.
- Discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the chest area and directly in the middle between the shoulder blades.
- The temperature may rise with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine in an advanced form.
If proper treatment is carried out and the symptoms are relieved, then the remission stage begins. During this period, it is important to prevent the recurrence of all of the above symptoms.
As soon as the condition returns to normal, it is necessary to perform feasible physical therapy exercises; if the degree of the disease does not allow this, then at least do intense walking.
Dorsalgia and dorsago - what is it?
Pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is divided into two types:
- Dorsalgia - prolonged pain in the spine;
- Dorsago - acute short-term pain.
Dorsalgia develops gradually and unnoticed over two to three weeks. Its symptoms are mild pain of various localizations, aggravated by deep inspiration. The nature of the pain is varied (stabbing, cutting, pulling, burning). Beginning osteochondrosis in the thoracic region gives less pronounced symptoms than advanced ones, but this alarm signal is already a cause for concern.
- We recommend reading: why your back hurts when you inhale
Dorsago manifests itself in the form of acute pain during monotonous, monotonous work. Occurs when staying in one position for a long time (usually uncomfortable). Characterized by muscle tension, neuralgia, difficulty breathing. Worsened by sudden movements, relieved by walking. Dorsago with thoracic osteochondrosis in women manifests itself in a more severe form than in men.
Complications
The disease occurs infrequently, but has very serious consequences if it is not treated correctly, is misdiagnosed, or is inattentive to one’s health. Therefore, the doctor must carefully monitor the entire medical history and draw up a call card, especially if thoracic osteochondrosis cannot be stopped and it develops into more severe forms.
Sometimes the disease causes myositis of the chest muscles, when the muscular frame is so weak that it is unable to support the spinal column, and sometimes the patient even finds it difficult to perform the simplest self-care skills.
Radiculitis of the chest often occurs due to damage to the nerve roots.
A chest fracture may occur. The reason for this may be bruises and blows. Or it can arise in a completely “empty” place. In this case, signs of a chest fracture include difficulty and inability to take a breath and move. If the fracture occurred without external influence, then special attention should be paid to this, as this may serve as the first symptoms of cancer and osteoporosis. Chest cancer develops under the influence of many factors, but the main ones include heredity, stressful situations, obesity, unfavorable environmental conditions, etc.
It is necessary to monitor your health very carefully and lead an active and healthy lifestyle without bad habits.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in men
The disease can also develop in the male body, especially if you adhere to a sedentary lifestyle and choose hard physical work. Signs of thoracic osteochondrosis in men can be confused with acute pleurisy, angina pectoris, scoliosis, cholecystitis, and other myocardial pathologies. You can make sure that it is not a heart attack using medication, but heart pills are prescribed only by your doctor. Superficial self-medication is completely excluded. With this disease, not only chest pain occurs, but also other symptoms:
- numbness in the legs;
- crawling on the skin;
- increased muscle tension;
- symptoms of decreased potency;
- lumbago in the interscapular region.
Nutrition
The causes of chest pain can be caused not only by osteochondrosis, as discussed above. But in any case, despite your age, you need to pay attention to your diet.
Treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine must necessarily be accompanied by a balanced diet. It will allow the body to receive all the nutrients that the tissues of the spine and muscle corset need.
Nutrition for thoracic osteochondrosis can be divided into two categories of people who need it:
- Those who are not overweight.
- Those who are overweight.
For anyone who has developed osteochondrosis or has a tendency to do so, we can recommend regularly including the following foods in their diet:
- Nuts, seeds, eggs, high-quality dairy and fermented milk products, cabbage (broccoli, Brussels sprouts, kohlrabi), any leafy greens (cilantro, dill, parsley, celery). All of them are rich in calcium. Moreover, it is important to remember that calcium is better absorbed by the body if it has not been subjected to heat treatment.
- Nuts, bananas, dark chocolate, dill, parsley, cilantro, avocado, beans, chickpeas, lentils - they contain a lot of magnesium, and it affects the nervous system, reducing the manifestation of neurology in osteochondrosis.
- Sea fatty fish, different types of cabbage, hard cheeses and cottage cheese. They contain a lot of phosphorus, which is a building material for bones and cartilage.
- Fruits and berries, especially red or orange, especially peaches and apricots, also carrots and green peas. There is a lot of vitamin A, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of blood vessels.
- Meat, fatty cold-water sea fish, avocados, high-quality unrefined cold-pressed vegetable oils. These products will become a source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are a nutritional element for both blood vessels and cartilage tissue.
- The body will fully receive B vitamins from cereals such as buckwheat, millet, millet, kamut, and quinoa. It is worth considering that quinoa is an intense source of protein that can practically replace meat.
- Sour fruits, such as citrus fruits, rose hips, black and red currants, gooseberries, sea buckthorn, viburnum, sauerkraut will give the body the right amount of vitamin C, which, with its antioxidant properties, can have a rejuvenating and regenerating effect not only on blood vessels, but also on bone and cartilage structures.
These products should be the basis of the diet for both people with normal weight and those who are overweight.
Since excess weight is one of the factors that can provoke the appearance of thoracic osteochondrosis, in this case the diet should be aimed at reducing body weight.
The following foods and dishes should be completely excluded from the menu:
- fast food;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- ready-made breakfasts - due to the fact that they contain excessive amounts of sugar;
- confectionery products, especially industrial ones;
- products containing sugar should be kept to a minimum;
- pickles - since you need to try to remove excess salt from the body;
- overly spicy dishes - as they whip up the appetite.
You should also limit all baked goods. They do not carry any nutritional value other than energy. In addition, you need to be very careful with beef and pork fat, as they are refractory. Therefore, their consumption leads to the deposition of cholesterol plaques and blockage of blood vessels, which further reduces blood circulation and a general deterioration in the nutrition of the affected tissues.
In order to lose weight, you can try different diets. For example, rice or salt-free. But it’s always worth remembering that staying on a diet for too long can have negative consequences.
It is important that the entire daily diet includes more protein and plant foods and less carbohydrates. In addition, it is important that the calorie content is within the following limits:
- for men - 3 thousand kcal;
- for women - 2100 kcal.
The number of meals per day should be at least 4–5. And the volume of clean water drunk is about 2 liters. And do this fractionally and often throughout the day. This will flush out unnecessary salts from the body and give elasticity to the cartilage tissue.
Diet for thoracic osteochondrosis
To overcome pain due to thoracic osteochondrosis in women, you need not only to go for procedures, but also pay attention to proper nutrition. Here are some tips to help you cope more effectively with the disease:
- Include plenty of vegetables and fruits in your diet. Look out for cauliflower, eggplant, parsley and beets;
- Add foods high in magnesium to your diet. These are beans, seeds, nuts, avocados and spinach;
- Be sure to eat jellied meat, jelly or jelly. These dishes contain a substance that restores cartilage tissue;
- Don’t forget about calcium, which will help you cope with osteochondrosis faster. Consume dairy products, rose hips, nettles and almonds;
- Protein is also important in restoring strength and tissue. Eat lean meat, fish, soybeans and beans;
- It is best to include dishes that are steamed or boiled into your diet. Eliminate anything fried from your menu;
- Switch to rye and bran bread. It is much healthier for the body;
- Eat all salads with olive oil. It is rich in vitamins, which are important in treatment;
- Avoid sugar, baked goods and spicy seasonings. Also eat less salty and smoked foods;
- Add more buckwheat, millet and wheat to your diet. Porridge perfectly normalizes the digestive system;
- Pay attention to seafood. Crabs, oysters and lobsters are rich in vitamin B. It is this that will help restore spinal tissue;
- Doctors do not advise eating grapes and concentrated broths during treatment.
Recommendations
It is very important to prevent the disease from occurring. To do this, it is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle with a proper diet and nutrition, sufficient but not excessive exercise and the exclusion of stressful situations.
If the disease has already been acquired, then it is important to start treatment as early as possible. Therefore, you should treat your body with due attention so as not to miss the first bells signaling problems in the spine.
If a diagnosis is made of thoracic osteochondrosis, then you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations and take treatment seriously.
It must be remembered that the process of degenerative changes is considered irreversible by most doctors, therefore, for a quality life, it must be stopped as early as possible.
Attacks of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
With such an unpleasant disease, the nerve fibers are affected, so the attack is always accompanied by acute pain, which, at an early stage of development, has an unclear localization. At first, unpleasant sensations are observed with sudden movements, in case of increased activity, with coughing and sneezing, but then specific symptoms remind themselves even at night, when the body is relaxed and resting.
It is possible that attacks of pectalgia may become more frequent, when acute pain is concentrated in the front part of the chest, prevents you from inhaling and exhaling, literally paralyzes the entire body, and disrupts the usual rhythm of life. In the absence of timely treatment, such painful attacks of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region only increase, making a once healthy person disabled.
Drug treatment
It is impossible to cure osteochondrosis with medications alone, but it is on them that the scheme of influencing the pathology is based. They help improve the patient’s general condition, slow down or stop the degenerative process, and stimulate bone tissue regeneration. When prescribing medications, the doctor pays attention to the symptoms, since the main part will be aimed at relieving them.
Taking medications is the basis of treatment for osteochondrosis
The patient is usually prescribed the following groups of medications:
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs (Diclofenac, Celecoxib, Movalis, Ortofen). They are aimed at reducing the inflammatory process in tissues and stopping pain. Drink in courses for 8-12 days. The form of the drug: tablets, ointments, capsules, suppositories or injections, is selected individually, depending on the ease of use. In the acute period, injections are usually given, after which rectal suppositories are prescribed. Ointments are used for local impact on the diseased area.
- Painkillers (“Analgin”, “Novocain”, “No-shpa”). They are used to eliminate severe pain, which is the main symptom of osteochondrosis. Paravertebral blockades help well, but they are used in especially severe cases. In addition, “distracting” ointments with an irritating effect based on pepper extract, snake or bee venom are good.
- Muscle relaxants (Baclofen, Mydocalm, Sirdalud). Allows you to relieve muscle tension and improve blood flow, eliminate stagnation and blocks.
- Diuretics (Lasix, Desamethasone, Cyclo-3-fort, L-lysine escenate). Allows you to reduce or eliminate swelling of the nerve root.
- Chondroprotectors (Structum, Rumalon, Glucosamine, Arteparon) are used mainly when the acute condition has passed. Their main task is to improve metabolic processes in tissues and protect intervertebral discs and ligaments from destruction. In addition, they help restore cartilage cells and slow down the degenerative process. They are prescribed to be used for six months.
- Multivitamins (“Milgamma”, “Neurovitan”, “Neurobeks”). Preparations based on B vitamins are useful for osteochondrosis to strengthen the vertebrae. In addition to their general strengthening effect, they also anesthetize tissues and improve their nutrition.
In addition, such drugs as Complamin, Nicotinic acid, and Pentoxifylline are also used to treat thoracic chondrosis. They help improve blood circulation and nutrition at the cellular level and restore joint mobility. Many drugs are prohibited during breastfeeding, so treatment that occurs during pregnancy is difficult and is carried out only after consultation with a gynecologist and pediatrician.
What symptoms accompany the disease?
There are the following types of osteochondrosis - cervical, thoracic, lumbar.
Often they occur together and then they speak of a cervicothoracic or lumbar-thoracic lesion. Each type of disease is characterized by certain symptoms. Cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by:
- neck pain;
- numbness of hands;
- frequent headaches;
- dizziness;
- increased blood pressure.
Thoracic osteochondrosis is accompanied by:
- chest pain, which is often perceived as heart pain;
- numbness of hands;
- dull pain in the back.
In addition, changes in the functioning of internal organs are possible:
- nausea and heartburn;
- violation of stomach acidity;
- bloating;
- problems with bile secretion.
With cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, a combination of all the above symptoms is observed.
The signs of osteochondrosis are different, depending on the woman’s age.
At 30 years old
As a rule, at this age the first signs of pathology begin to appear. This can be caused by injuries, heavy lifting, and osteochondrosis can be an occupational disease.
At 30 years old, a woman may complain of pain in the cervical spine, frequent headaches, and a feeling of stiffness in the neck. These are the very first signs of osteochondrosis.
At 40 years old
By the age of 40, the pain becomes more acute, discomfort appears in the shoulders and fingers, there may be a decrease in the sensitivity of the hands and tongue, and the appearance of snoring, which was not there before.
Some women experience surges in blood pressure, nausea, and even bluish skin.
In addition, a woman may complain of weakness in the arm muscles, and insufficient blood circulation to the brain can cause not only severe and frequent migraines, but also loss of consciousness.
Important! Such symptoms require hospitalization - a lack of blood supply to the brain can cause a heart attack or stroke.
At fifty
During menopause, the female skeleton is negatively affected as a result of hormonal changes in the body. At this age, bone tissue density begins to decrease, which naturally has the most negative effect on the condition of the spine.
Osteochondrosis at this age is very dangerous - in addition to the fact that all its symptoms become more intense and painful, the risk of complications increases sharply.
Signs of spinal cord damage
Spinal syndrome is a rather dangerous consequence of osteochondrosis. Occurs when the spine becomes displaced or collapses, causing damage to the spinal cord. In this case it is observed:
- Loss of sensitivity, numbness, “lumbago”.
- Problems with movement, leg muscles sometimes relax or tighten on their own. With muscle wasting, the abdominal wall ceases to maintain its normal tone, and the abdomen sags.
- Paralysis of the upper or lower limbs is the worst symptom, which indicates that the spinal cord has stopped conducting nerve impulses, and the patient urgently needs surgery.
Damage to nerve fibers
When nerve fibers are damaged, the clinical picture is somewhat different. Characteristic manifestations of this are described below.
Pain syndrome
The pain can be episodic or acute, or it can be constant - chronic. It occurs in the neck area, affecting the back of the head and shoulder girdle. Painful sensations are caused by the fact that the nerve fibers become inflamed, and there is a spasm of the muscles innervated by these nerves.
Koreshkovy
With cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, all the main nerves of the upper extremities are affected. Depending on which root is damaged, certain symptoms appear. For example, the sensitivity of the fingers may decrease, and paralysis of one or a group of muscles may occur. All these symptoms are called radicular, and only a neurologist can recognize them.
Occipital neuralgia
If the damage concerns the 2nd, 3rd and 4th pairs of cervical vertebrae, they become inflamed, irritated or doubled, and pain occurs in the back of the head. This pain is called cranialgia. The attack occurs suddenly and is often unilateral.
Patients compare this pain to an electric shock. The attack lasts several minutes, but is repeated several times a day. A woman may also be bothered by numbness of the skin in the occipital region.
Cardiac syndrome
There is pain in the chest, which is easily confused with pain in the heart - hence the name of the syndrome. However, unlike coronary pain, cardiac pain can last for hours or even days. The pain intensifies with movement, coughing and sneezing, which also never happens with heart pain.
Such symptoms require careful differential diagnosis, since atypical variants of heart attack and angina are sometimes encountered.
The vertebral artery is affected
When symptoms of osteochondrosis appear only in the head area, this is due to compression of the large vertebral artery, which passes into the brain. There is pain in the back of the head, in the temples and above the eyebrow, dizziness, radicular syndrome, tinnitus, fatigue and adynamia.
Consequences
If left untreated, the consequences of osteochondrosis can be catastrophic. Degenerative changes provoke the appearance of a hernia of the spine . Compression of the nerves leads to loss of sensation in the limbs . The most serious complication is paralysis of the arms or legs.
In addition, the functioning of all internal organs and systems is disrupted : cardiovascular, urinary, digestive. The patient develops vegetative-vascular dystonia. The fact is that the spinal vessels are compressed, and the oxygen supply to the brain is disrupted. The patient experiences constant headaches, panic attacks, and sleep disturbances. Intercostal neuralgia is also a consequence of osteochondrosis.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of osteochondrosis is a process that requires an integrated approach.
In acute phases, drug therapy is prescribed, including the use of:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Meloxicam, Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ibuprofen);
- centrally acting analgesics (Katadolon);
- muscle relaxants that eliminate muscle spasms (Tizanidine, Mydocalm, Tolperisone);
- anticonvulsants that reduce compression of nerve endings (Gabapentin, Carbamazepine);
- drugs to improve peripheral circulation (Actovegin, Cavinton, Trental);
- B vitamins;
- sedatives that support the nervous system;
- chondroprotectors that stimulate the regeneration of cartilage tissue.
Therapeutic blockades help effectively relieve pain. The procedure involves injecting anesthetics or corticosteroids directly into the lesion.
For topical use, ointments, gels, and creams that have an irritating effect (Finalgon, Viprosal, Gevkamen) are indicated. The drugs have an analgesic effect and increase local blood circulation.
The treatment regimen and dosage are selected by the attending physician individually, taking into account possible contraindications.
Preventive actions
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is much easier to prevent than to treat. To do this, you just need to give up bad habits, avoid hypothermia, avoid excessive physical activity and eat right. This simple prevention will help you maintain your health for many years. Drivers and people with a sedentary profession need to be regularly examined by a specialist for timely diagnosis of the degenerative process.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region can be dangerous to humans, so it is better to start treatment at the first stage. Therapy is carried out comprehensively, using modern drugs, physiotherapy techniques, massage and therapeutic exercises. Strict adherence to all recommendations and treatment regimen increases the chances of successful restoration of health.
Treatment methods
Osteochondrosis cannot be completely cured, but most of its symptoms can be alleviated or eliminated conservatively or surgically. Treatment options for men and women with this disease do not differ.
Conservative treatment
Non-surgical treatments for thoracic osteochondrosis usually include a combination of several methods:
- A short period of rest (1 or 2 days) and physical activity modification (limiting activities that worsen or cause back pain). After this, the patient should gradually restore physical activity using light exercises such as walking.
- Apply ice to the sore area for 15–20 minutes several times a day.
- The use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (naproxen, ibuprofen) or painkillers (paracetamol) - these medications can effectively relieve the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis.
- Massage and manual therapy performed by an experienced specialist.
- Exercises to strengthen the back muscles, which can reduce the load on the spine and intervertebral discs.
- Introduction into the epidural space (the space between the hard shell of the spinal cord and the periosteum of the vertebrae, filled with connective tissue and venous plexuses) of drugs.
Administration of drugs into the epidural space
Surgery
Surgical treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is rarely performed.
Indications for surgery are:
- Spinal cord dysfunctions: impaired reflexes, nerve conduction. One of the functions of the spinal cord is the transmission of impulses from the periphery (from the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs) to the center (brain) and vice versa.
- The presence of a progressive neurological deficit: tinnitus, disruption of internal organs and other symptoms or intolerable pain.
Typically, these symptoms occur when the spinal cord is compressed by a herniated disc. Surgery is aimed at removing the hernia and eliminating this compression, thereby relieving the symptoms of osteochondrosis.
Surgery
Surgery is resorted to in cases of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region extremely rarely. This is usually necessary when a hernia begins to develop, compression of the spinal cord threatens the patient’s quality of life and health (complete or partial paralysis), there is constant muscle weakness, the functioning of the pelvic organs is disrupted, and the pain syndrome is not relieved by pills and injections.
Surgical intervention is required only if osteochondrosis has become complicated and a hernia has appeared
The disease itself is not fatal, but it significantly complicates the patient’s life, limiting his activity and causing severe pain. Since it is impossible to completely get rid of the disease, the process can be suspended or slowed down, minimizing all negative manifestations.
Prevention of pathology
Prevention of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis consists of following simple rules:
- do not overeat - obesity increases the load on the spine;
- swim more often and perform feasible gymnastic exercises;
- when working sedentarily, do a warm-up every 2 hours;
- do not carry a bag on only one shoulder;
- choose comfortable shoes;
- conduct back massage courses from time to time;
- watch your posture;
- do not sleep on a mattress or pillow that is too soft;
- eat a balanced diet.
Causes of the disease
Osteochondrosis in many cases does not develop on its own, but occurs due to the impact of negative factors and/or diseases on the spine.
Let's take a closer look:
- Passive lifestyle. A decrease in physical activity leads to poor circulation and weakening of the muscles that support the spinal column. Very often this is combined with incorrect posture and an uncomfortable position (leg behind the leg, leaning on the arm, etc.).
- Previous injuries, intense physical work (especially if improper lifting occurs constantly). Thus, the shock-absorbing function deteriorates, and changes in the structure of the disc occur (“drying out”, decrease in height).
- Curvature of the spine is one of the serious factors leading to osteochondrosis. These include lordosis, kyphosis and scoliosis (see photo below).
- Osteoporosis. This pathology occurs predominantly in middle-aged and elderly people (usually women). Osteoporosis can also form when the body receives insufficient vitamins and microelements necessary to “nourish” bone tissue (for example, due to diseases of the digestive tract or if you adhere to a strict diet).
- Carrying a pregnancy to term. A woman gains, on average, 16 kg (sometimes more) during pregnancy. At the same time, the spine experiences serious stress, which, in some cases, leads to osteochondrosis. You can also add provoking factors such as gait disturbances and a sedentary lifestyle.
Important! Hereditary predisposition plays a significant role. If anyone in the family has severe spinal diseases, then they should pay as much attention to their health as possible so as not to encounter an unpleasant pathology.
Factors that cause osteochondrosis are often combined. This significantly complicates treatment and further prognosis for recovery.
Treatment of breast osteochondrosis with medications
First of all, after diagnosing the disease, the doctor prescribes treatment that removes the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis.
First, the neurologist relieves the pain syndrome with the help of medications, and then proceeds to direct treatment.
Drugs that are used for osteochondrosis:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain in the thoracic region.
- Diuretics
Diuretics are prescribed when there is swelling on the nerve roots. Diuretics relieve swelling, thereby improving blood supply to the affected areas.
- Vitamins for nourishing nervous tissue
- Chondroprotectors
With the help of chondroprotectors, they are trying to restore the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc.
Antispasmodics relieve spasms from tense muscles and increase mobility of the thoracic region, thereby reducing pain syndromes.
Thoracic osteochondrosis symptoms and treatment do not always bring positive results, because if drug therapy does not have an effect, the doctor will suggest a surgical solution to the problem.
Treatment
The doctor will tell you how to treat osteochondrosis of the thoracic region - after confirming the diagnosis, determining the stage and nature of the disorders (hand sensitivity, breathing problems).
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugsThey are also painkillers. They can be taken in tablet form or applied as a patch (Olfen) - if the pain is tolerable. In the subacute period, they can be used as ointments for osteochondrosis. And in the acute period, with severe pain - only as injections.
|
Muscle relaxantsTheir task is to relieve spasm of the muscles that keep the spine from turning and compress the nerve endings and blood vessels. In the acute period, it is better to take them as injections for osteochondrosis, then switch to tablets.
|
ChondroprotectorsThese are drugs whose effectiveness is still disputed. However, many doctors recommend using them over a long period of time to give the intervertebral disc a chance to recover.
|
B vitamin preparationsThey are needed in order to improve the transmission of impulses from nerve to muscle. In the acute period, it is better to start with injections, for example, Neurorubin, then switch to Neurorubin, Milgamma, Neurovitan or others tablets. |
This treatment enhances the effect of medications. Applicable:
- Electrophoresis with anesthetics and drugs that improve local blood circulation. In this case, the medicine is carried out with an electric current directly into the back tissue.
- Magnetotherapy. Under the influence of a magnetic field, the functioning of pinched nerve endings improves and tissue swelling is relieved.
- Phonophoresis (injection of drugs with ultrasound) helps to better relieve back pain and eliminate inflammation of pinched tissues. It also has the ability to improve metabolism in the affected area.
- Acupuncture is the introduction of special sterile needles into active points that are responsible for the functioning of the thoracic spine.
- Laser therapy using an external method increases blood circulation in tense muscles and suffering intervertebral discs.
Massage
Massage for osteochondrosis is an effective procedure if performed by a specialist. A massage session can increase blood circulation in the affected area, relax cramped muscles, and improve the outflow of blood and lymph from this area. This speeds up healing and reduces pain.
To reduce the number of exacerbations, massage courses are recommended at least 2 times a year. It could be:
- therapeutic manual massage: applying hands to muscles that have become spasmed and have lost tone in order to normalize their condition;
- hardware: working out muscles with various types of exciting manipulatives. You can also resort to the services provided by cosmetologists: endosphere and LPG massage. They are also good for a sore back;
- point: in this case, biologically active points are manually worked out, as a result, the condition of internal organs compressed due to the rotation of the spine improves;
- cupping: the effect on muscles that have changed tone is carried out using a vacuum.
Exercises for osteochondrosis can be started only in the subacute period and in remission, as well as 2 weeks after removal of the disc herniation.
Exercise therapy is contraindicated if the back muscles are still very tense, one vertebra is pressed tightly against the other, which requires surgical intervention, if the pain is severe.
It is recommended to start gymnastics for osteochondrosis with self-extension of the spine. To do this, you need to take a wide and smooth board and attach one end to the wall - at a height of approximately 100 cm from the floor (to form an angle of 30-45°). The bottom edge lies on the floor. Two leather straps about 45 cm long are attached to the upper edge, on both sides, so that you can put your hands in them yourself, and then take your hands out.
The self-extension technique involves lying on this board with your back, head up, and your hands in the straps. Place a soft cloth under your knees, roll it into a cushion, and lie there for 10-15 minutes. It shouldn't hurt. If pain is present, increase the angle of the board. If this doesn't help, you'll have to do something different:
- make a cushion of blankets on the floor;
- lie down on the roller so that the blocked area is at the very top;
- spread your legs slightly;
- elbows and knees are bent, touching the floor, the body weight rests on them; the head should hang slightly or lie on folded hands;
- if you don’t feel like your spine is stretching, you can increase the load: move your legs back and your arms forward;
- 5 minutes while inhaling for 10 seconds, strain your back muscles, while exhaling - relax
- relax and breathe with your stomach – another 5 minutes.
Below, see a video with a set of the most important 7 exercises.
To treat the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis in women, conservative methods are used; in rare cases, surgical intervention is required. Traditional methods, manual and physical therapy are also often used.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is carried out on an outpatient basis. In case of severe pain, the patient is prescribed bed rest for 2-3 days. Traction of the affected segment of the spine is indicated, which eliminates compression of the nerve root and thereby relieves pain. In cases of severe pain, soft tissue infiltration is performed with a 2% novocaine solution. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed for a short course.
The complex treatment regimen for thoracic osteochondrosis also includes:
- antihistamines;
- B vitamins;
- tranquilizers;
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- manual therapy.
After the patient’s condition improves, he is referred to physical therapy classes. Regular exercise for thoracic osteochondrosis contributes to the formation of a well-developed muscle corset, which allows you to keep the spine in the correct physiological position and eliminates unnecessary static loads.
Of no small importance in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis is given to regular moderate physical activity (swimming, yoga, tai chi) and normalization of body weight. Jumping, running, weightlifting and other sports that involve increased stress on the spine are contraindicated.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis in women is selected by the doctor individually based on research results. The following methods of treating pathology may be recommended:
- Magnetotherapy. Exposure to a magnetic field stops the degenerative process in the spine, relieves inflammation, and improves immunity.
- Acupuncture. This is one of the best ways to treat osteochondrosis, which allows you to quickly eliminate pain and other symptoms without causing discomfort. Another advantage of acupuncture is a minimal list of contraindications.
- Electrophoresis with painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs. Helps improve blood supply to the tissues of the pathological focus, relieves inflammation, pain, and relieves neurological symptoms.
- Plasma injections. They help restore tissue around the spine, relieve pain, improve motor functions, increasing performance.
- Cupping massage. This type of massage action is aimed directly at the patient’s sore point, helping to relax muscles and relieve pain. The condition of the spine is also restored and immunity is increased.
- Spine stretching. This is a harmless method of therapy that helps increase the distance between the vertebrae, which leads to improved nutrition of the intervertebral discs and a reduction in protrusions.
- Spinal block. The essence of this method is to inject novocaine and/or lidocaine into the affected area. The blockade allows you to quickly relieve pain and restore the health of the spine.
Drug therapy aimed at eliminating symptoms (NSAIDs, antispasmodics, chondroprotectors and others), some folk remedies, manual therapy, and exercise therapy are also prescribed. In the most severe cases, surgical intervention becomes necessary.
The fight against pathology requires an integrated approach. Trying to cope with the disease on your own will not bring the desired result, and may even cause complications. Only after an examination and confirmation of the diagnosis, a number of medications are selected for the patient. In severe cases, surgery is used.