The human spine is a supporting and shock-absorbing system consisting of four curves: cervical and lumbar lordosis, thoracic and sacral kyphosis. However, not everyone has such an ideal spine. It happens that physiologically correct lordosis or kyphosis becomes pathological. In this case, it is appropriate to talk about a problem that needs to be clarified and cured.
The concept of spinal kyphosis
Kyphosis is a curvature of the spinal column in which the convexity is directed posteriorly. Physiological, that is, normal for a person, kyphosis begins to form in the first months of a child’s life and ends around the age of seven. In this case, the angle of inclination will be determined in the range from 15 to 30 degrees.
If the examination reveals a deviation from the norm, then we are talking about a pathological curvature, requiring the selection of special conservative or surgical treatment.
Pathological kyphosis is often also called stooping.
Causes
Determining the cause of the disease in most cases helps to choose the optimal treatment method and quickly cope with the problem. The development of curvature can be caused by a number of provoking factors. Let's highlight the main ones:
- hereditary predisposition;
- pathologies of intrauterine development;
- birth injuries;
- rickets;
- prolonged sitting in an incorrect position;
- unsuccessful back surgery;
- obesity;
- age-related changes;
- polio;
- bone tuberculosis;
- osteoporosis;
- oncological processes;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- injuries;
- active growth in adolescence;
- degenerative diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, scoliosis).
Incorrect posture at the table causes curvature of the spine
Types and degrees
There are several classifications of kyphosis used in medicine. In form, such a pathological curvature can be:
- Angular.
- Arched.
In the first case, with a pronounced degree of curvature, a hump is formed in a person. Based on etiology, there are several types of pathological kyphosis.
- Postural, postural kyphosis is formed as a result of weak posture. It is more often detected in adolescents and young people under 30 years of age; females are more susceptible to such curvature of the spine. Occurs when the spinal ligaments are overstretched.
- Scheuermann-Mau disease or juvenile kyphosis. The deformity begins to appear during the period of greatest skeletal growth, that is, in adolescence. Often this pathology is combined with scoliosis.
- Congenital kyphosis is determined during the neonatal period. The cause of the disease is certain disturbances during the formation of the bone skeleton. It is often combined in a child with congenital anomalies of the urinary organs.
- Paralytic kyphosis is the result of paralysis of a group of muscles in the back.
- Post-traumatic kyphosis is one of the most common; it is determined in almost 40% of cases in people with this disease.
- Postoperative kyphosis is a consequence of incorrect surgical technique or non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations after surgery on the spinal column.
- Degenerative kyphosis is diagnosed when the main cause of its development is diseases of the spine, which include osteochondrosis.
- Senile kyphosis occurs in old age, and more often in women. The disease is caused by the aging of all anatomical components of the spinal column.
- Rachitic kyphosis is often detected in children suffering from rickets. Such a bend can begin to form after the first six months of life.
In the process of diagnosing a pathological curvature, it is important to find out its degree; this is necessary for selecting treatment.
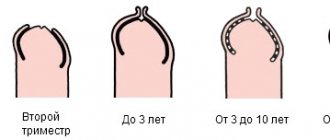
The photo shows a normal spine and with kyphosis of 1, 2, 3, 4 degrees of deformity
- The first degree is set when the deformation angle is in the range from 31 to 40 degrees.
- The second degree is a deformation greater than 41, but less than 50.
- The third degree of kyphosis is an angle from 51 to 70 degrees.
- The fourth degree is the most pronounced deformation; it is set when the angle reaches 71 degrees and above.
Consequences of surgical interventions
This type of surgery cannot be considered safe, as there is a high chance of neurological complications. Due to the use of implants that may not take root or simply break.
During the rehabilitation period after surgery, the patient feels pain and discomfort, so he is injected with painkillers. And just a couple of days after the operation, a course of physical therapy is prescribed, which may last longer than a stay in the hospital. When prescribing these courses, an individual program is used for each patient.
Symptoms
Pathological kyphosis can be in the chest, back, neck. Symptoms of the disease can be divided into external, that is, visible to strangers, and internal, that is, those about which the patient complains. Sensations and changes in well-being will depend on the area in which the pathological protrusion is formed.
Most often, kyphosis of the thoracic spinal column develops. In the first stages of the formation of pathological curvature, you can pay attention to a slight stoop; when the back is straightened, it disappears. Further progression of the disease leads to the fact that a person has a noticeable defect in appearance.
This is expressed by moving the shoulder girdle forward, shortening the collarbones, rounding the back, and compressing the chest. In the final stages, due to the displacement of the ribs and sternum, the functioning of the heart and lungs of the stomach begins to change. All this will be manifested by corresponding symptoms.
Kyphosis of the lumbar region leads to disruption of the pelvic organs, curvature in the neck changes the nutrition of the brain. With pathological curvatures, long-term lack of treatment leads to the fact that the defect only grows and this is reflected in changes in a person’s posture and gait. Flat feet often develop, and the knee joints change their normal position.
With pathological curvatures of the spinal column, a person is periodically bothered by fatigue and pain. This is due to tension in all ligaments and muscles of the back, destruction of the vertebrae themselves and changes in the functioning of many organs of the chest and abdominal cavity.
Clinical picture of kyphosis and diagnosis
The clinical picture of kyphosis is very varied and depends on the complications that arise. Lumbar kyphosis, which occurs most often, can be complicated by sciatica and lumbago, while sacral kyphosis can manifest itself as dysfunction of the reproductive organs - oligomenorrhea, dysmenorrhagia, decreased fertility and even infertility. Leukocyturia of unknown etiology can be caused by pyelonephritis, which developed as a result of a violation of the physiological lumbar lordosis. When the thoracic region is affected, respiratory failure occurs, and in more acute cases, pneumothorax.
During a general examination, depending on the degree of curvature, changes in posture and movements are immediately noticeable. First of all, the smoothed lordosis of the transverse section attracts attention.
To determine the stage of the disorder and possible causes, the doctor conducts a number of studies: General blood test (CBC), General urine test (UCA), biochemical analysis, x-ray of the spine in frontal and lateral projections, ultrasound examination, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), spiral computed tomography (CT), densitometry. To diagnose complications, it is advisable to use spirometry for thoracic kyphosis (diagnosis of respiratory failure), ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver enlargement, nephroptosis, cholelithiasis).
Causes
There are actually quite a lot of reasons under the influence of which thoracic kyphosis develops. The congenital disease is explained by intrauterine developmental defects and the influence of unfavorable heredity. Acquired kyphosis occurs under the influence of:
- Iatrogenic diseases. This could be tuberculosis, rickets suffered in childhood.
- Injury Fractures of the vertebral bodies lead to their improper fusion, and as a consequence of this, a pathological curvature is formed.
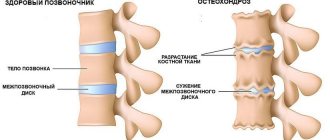
- Degenerative disc diseases. Osteochondrosis belongs to this group of pathologies.
- After surgical complications on the spine.
- Incorrect posture. Weakness of the ligaments and muscles of the back leads to the fact that a constantly slouching person becomes the owner of kyphosis.
Causes and types of spinal curvature
Lordosis and kyphosis are considered normal depending on the region. Kyphosis, or backward curvature of the spine, is considered normal in the thoracic and sacral regions. It is worth noting that when the bending angle increases to more than 45°, a pathological disorder also occurs in these sections - the so-called hyperkyphosis. In the remaining sections (cervical, transverse, coccygeal), the norm is lordosis - forward bending of the spine. It is this mixed arrangement of lordosis and kyphosis that evenly distributes the load on the spine during movements, preventing bone fractures and injuries to internal organs.
Chest
Posterior curvature of the vertebral arch in the chest area is not only an external deformity. The chest anatomically changes and this leads to a decrease in lung volume, which in turn reduces the supply of oxygen to the main organs. As the degree of inclination increases, disturbances in the functioning of organs progress. Patients note:
- The development of frequent colds, bronchitis, pneumonia with a long course.
- Changes in the functioning of the stomach, manifested by poor appetite, belching, and discomfort.
- Rapid heartbeat, blood pressure instability.
- Urinary disorders.
Physiological thoracic kyphosis is a position of the spine in which the angle of inclination is not less than 15 degrees and does not exceed 30 degrees.
The photo shows an x-ray of kyphosis of the thoracic spine, before and after surgery
Kyphosis is intensified when a deformation angle of more than 45 degrees is determined on the x-ray, while the person has an outwardly noticeable, well-defined stoop. Kyphosis is said to be straightening when the angle of inclination is less than 15 degrees. Thoracic lordosis is also a pathology in which the spine curves in the opposite direction.
Treatment begins with identifying the underlying cause of the pathological deformity. If possible, then with the help of drug therapy or surgical intervention they try to eliminate the negative impact of the causes or reduce them to a minimum. In the first stages of abnormal curvature, physical exercises, massages, and, if necessary, traction are necessary.
Treatment
An orthopedic surgeon can answer how to treat kyphosis. The attending physician should first of all explain to you what kyphosis is and how to cure the disease. The therapy itself will depend on the degree of curvature of the spine. It is not uncommon for kyphosis to develop compensatory lordosis in the underlying part of the spine.
Basically, spinal correction consists of:
- Drug therapy;
- Formation of back muscles;
- The use of formative elements - corsets, bandages;
- Vertebral column traction;
- Surgical operations.
Drug therapy
Drug therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms - increasing blood circulation and nerve impulses - this improves the general condition, partially relieves pain and strengthens the back muscles. Glucocorticoids are also often prescribed to relieve pain from tissue entrapment, but they can cause negative consequences for the immune system. An effective technique is to set blockades, which are an injection of lidocaine or novocaine into the affected area.
Formation of back muscles
The formation of correct muscle development leads to alignment of the direction of the back, which improves the prognosis for correction with the help of corsets. Methods of muscle training include physical therapy, massage and physiotherapy. Methods of self-control of posture and improving the position of the back while sleeping and sitting can especially help correct kyphosis.
Exercise therapy is a method of exercise that will lead to increased muscle mass. Sometimes spasmodic drugs are used together with them, which cause muscle tension and displacement of the vertebrae. Massages are aimed at creating “relaxed” zones. Such zones lead to tension in other groups, which begin to pull the vertebrae in the right direction and improve the overall position.
Formative elements such as corsets are designed to maintain correct posture at all times - while walking, sitting and sleeping. Corsets are divided according to their rigidity. Moreover, the stiffer the corset, the harder it is to wear, but the greater the therapeutic effect will be.
The effect of the corset itself is achieved by maintaining posture, tension of individual muscles that straighten the spine and constant deformation of the spinal column. The more such exposure occurs, the better the effect. Treatment of kyphosis in adults is only possible with the help of similar methods, since the muscles are no longer strong enough to independently deform the spine.
Pillar traction and operations
Traction occurs using special devices that slowly stretch the spine. With the correct pulling force and securing the healthy part, it is possible to quickly straighten it. This technique is associated with rather painful consequences - spraining the ligaments causes pain.
Surgical operations are aimed at correcting the shape of damaged vertebrae. Spondylotomy and spondyloplasty change the shape of the vertebra and ligaments. This method is not applicable in all cases and is used only in cases of severe deformation of an individual vertebra.
Remember that whether kyphosis can be cured and how to correct such a curvature - only a specialist can answer. Do not try to resort to traditional methods, as the curvature can affect internal organs and cause serious consequences. Be aware of your actions and do not rely on TV and the Internet.
| Please rate the article |
I RECOMMEND ON
Cervical
Kyphotic anomaly of the spine in the neck area is a rather rare pathology. The cause is injury, degenerative changes, and infectious diseases. Regardless of the degree of kyphosis in this area, a person has quite serious health problems. Patients complain about:
- Headache.
- Hearing and vision impairment, periodic dizziness.
- Loss of sensitivity in the elbow and fingers.
- The appearance of restrictions when moving the neck.
The most dangerous manifestation of cervical kyphosis is compression myelopathy, which consists of compression of the spinal cord. This leads to peripheral paralysis, impaired urination, pathological changes in pain and tactile sensations, and muscle wasting.
The photo shows an x-ray of kyphosis of the cervical spine of an arched shape
Treatment consists of using medications aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. As with other problems with the spine, complexes of physical exercises and manual therapy are prescribed. Doctors often recommend wearing special neck corsets. When kyphosis is complicated by myelopathy, surgical intervention is indicated.
Types of kyphosis by section of the spinal column
Pathological kyphosis can affect any part of the spine, regardless of age and the cause that provokes it. The appearance of symptoms depends on the location of the pathological process. The greater the deformation, the more extensive the symptoms will be.
Cervical kyphosis
Normally, the cervical spine is characterized by lordosis. When straightening of this bend is observed, pathology occurs - smoothed kyphosis of the cervical spine.
The occurrence of kyphosis of the cervical segment is a fairly rare occurrence. Injuries, spinal diseases, infectious diseases, heredity, rickets, etc. contribute to its development. Symptoms of cervical kyphosis include:
- frequent dizziness;
- blood pressure surges;
- neck pain;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- restrictions in neck movement;
- numbness or impaired tactile reflex in the neck or arm (fingers, elbow bend).
The most dangerous consequence of cervical kyphosis is compression myelopathy, which damages the spinal cord.
Myelopathy can lead to severe complications: paralysis, hypotension, atrophy and fascicular twitching.
Thoracic kyphosis
Kyphosis of the thoracic spine is a physiologically correct bending of the thoracic region of the spine. When the convexity of the bend is too pronounced, that is, there is an excessive stoop or hump, pathological kyphosis occurs.
With pathological thoracic kyphosis, the back initially looks stooped, but over time it becomes hunchbacked. The line of the shoulders is bent in an arc with the acromion forward, and the chest is concave. Such deformations of the bones of the thoracic part of the skeleton, in addition to their unaesthetic appearance, also carry negative changes in the internal health system:
- Compression of the spinal cord and nerve roots, which can cause problems in the functioning of the pelvic organs, paralysis, paresis, etc.
- Disruption of the cardiac and respiratory systems as a result of reduction in chest volume.
- Destruction of intervertebral fibrocartilaginous formations.
People suffering from thoracic pathology note changes in their well-being:
- pain, tingling, numbness in the back (usually between the shoulder blades) and in the limbs;
- lack of appetite, belching, nausea;
- blood pressure surges;
- tachycardia;
- pulmonary shortness of breath;
- uncontrolled urination.
Boys aged 9–16 years are most often susceptible to the development of pathological kyphosis of the thoracic spine. It is during this time period that their intensive growth occurs. It also occurs in older people.
Lumbar kyphosis
Kyphosis of the lumbar spine occurs at the site of physiological lordosis. The natural lordotic arch of the lumbar spine is replaced by a rounded lower back. As a result, the spine loses flexibility, becomes stiff and less elastic. The depreciation of the lumbar region is completely impaired, which is why every shock when walking or running is not absorbed, but is reflected in pain.
Lumbar kyphosis occurs as a result of failed surgery, injury or degenerative changes in the lower back. Based on the clinical picture of the disease, the main symptoms of lumbar kyphosis were identified:
- pain in the “center”, radiating to the limbs;
- numbness and decreased tactile reflex in the legs;
- sexual dysfunction;
- uncontrolled bowel movements and urination;
- formation of a lumbar hump.
Classification of kyphosis
Depending on the provoking factor in medicine, the following types of kyphosis are distinguished:
- A congenital kyphotic defect occurs against the background of abnormalities in the intrauterine development of the fetus or during childbirth. As a result of problems with the spine: underdevelopment of the muscle corset, fusion or incomplete formation of the vertebrae, anomalies in the development of the anterior spine. This form of kyphosis often causes congenital paralysis of the lower extremities. In addition, in 20–30% of cases, problems with the genitourinary system, and specifically with urination, may appear.
- Physiological – normal state of the spine.
- Pathological is a condition of the spine in which a physiologically normal curve develops into an excessively convex posterior curvature. Many factors contribute to its development: oncology of the spine or soft tissues, infections and inflammations, hyperthyroidism, degenerative and dystrophic processes, tuberculosis, Cushing's disease, Paget's disease. Kyphosis in children can be provoked as a result of incorrectly formed posture.
- Osteochondropathic (dorsal juvenile, Scheuermann-Mau disease). This disease is characterized by pathological changes in the shape of several vertebral bodies. The vertebrae damaged by the disease take on a wedge shape. There is no specific reason for the development of Scheuermann-Mau disease, however, there is a presumable opinion that the culprit is poor circulation in the supporting column and, as a consequence, deformation of the growth of the vertebrae.
- Genotypic. The appearance of this type of kyphotic deformity is due to a hereditary factor of the dominant type.
- Compression. This type of disease can develop as a result of a decrease in the total height of the thoracic vertebrae obtained after their compression fracture. Excessive physical stress on the spinal column during sports can provoke the development of the disease. Under their influence, the vertebral bodies are deformed and, as a result, their anterior sections are shortened.
- Mobile. Weakening of the muscle corset is the cause of the development of mobile deformity. It is the paraspinal muscles that hold the spine in the correct position. Its weakening or improper development leads to disturbances in the “depreciation” organization. Another reason is prolonged exposure to improper standing, sitting or lying positions. As a rule, in bed the muscles and bones are completely relaxed and take on completely different forms. Everything except the form necessary to keep the spine in good shape.
- Senile (senile) kyphosis develops as a result of degenerative and dystrophic changes in the spine and weakening of the muscles of the supporting column. The main impetus for the development of senile changes is the age factor.
- Paralytic. The impetus for the formation of this type of deformation is diseases against which paralysis develops: poliomyelitis, botulism, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spina bifida, cerebral palsy, acute polyradiculitis, etc. The development of paralytic kyphotic changes occurs gradually.
- Postoperative kyphosis occurs due to the patient’s negligent attitude to the recommendations of doctors after surgery. Another reason is errors in wearing or fixing the postoperative bandage during rehabilitation.
- Degenerative. Develops as a result of degenerative, dystrophic and inflammatory diseases affecting the spinal column (osteochondropathy, osteoporosis, osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthritis).
- Rachitic. The name itself indicates the main reason for its appearance - rickets suffered in infancy.
- Total (arched). The disease is expressed by a uniform bending of the entire spinal column. Its development is accompanied by ankylosing spondylosis, spondylosis, etc.
- Tuberculous. The disease develops as a result of tuberculous spondylitis, which destroys the vertebral body and intervertebral cartilage.
- Angular kyphosis is expressed by an increased convexity with a sharp apex in the thoracic spine. In appearance, the convexity resembles an angle. The culprit of this pathology is tuberculous spondylitis or trauma to the thoracic region.
- Postural (postural, “round back”). The development of a “round back” is accompanied by incorrect posture. The reason for its development is an incorrect position when reading, working at the computer, when walking, as well as a psychological component. Kyphosis in children often develops against a background of self-dissatisfaction. Some guys begin to stoop, feeling embarrassed about their height. Girls who consider their breasts small and not attractive enough try to “hide” them by slouching. Women whose breasts are large and mothers who carry their baby in their arms or in a sling for a long time are also at risk for developing kyphosis.
- Post-traumatic. The cause is a spinal injury. A fracture in the body of the spine creates all the conditions for improper fusion of bones and cartilage, which provokes kyphosis.
Lumbar
Normally, there is lordosis in the lower back. Lumbar kyphosis is a reverse position of the spinal arch. This pathology occurs in an adult after injury, unsuccessful surgery, with prolonged osteochondrosis and hernias of this part of the spinal column. In young people, a kyphotic arch in the lumbar region can be formed due to muscle weakness, leading to poor posture.
In addition to pain, numbness, and sensory disturbances during kyphosis due to compression of the spinal cord, pathological changes occur in the functioning of the pelvic organs. Sexual dysfunction is possible. This pathology is almost always treated with surgery.
Surgical intervention
Surgery for kyphosis is a very risky undertaking, which is prescribed only if all other treatments have failed.
Surgical intervention has several objectives:
- Correction of the arch of the spinal column;
- “Freezing” stages of deformation;
- Reducing pressure on nerve endings;
- Protection of spinal cord substances.
The operation is carried out in two stages:
- Correction of the spinal column;
- Fixation of the spinal column.
For fixation, special systems made of non-magnetic alloys are used.
Operations become possible only after the processes of bone tissue formation are completed, that is, only for adults.
Skeletal spine traction
Surgery is divided into two types:
- Osteotomy is a standard operation to change the vertebra and fix the spinal compartments. The deformed vertebra is cut, placed in its place in the correct position and fixed with a special system. With this type of operation, one or several tissue incisions are made, depending on the degree and location of the curvature of the spine.
- Kyphoplasty. Through a small incision, a special air cushion is inserted into the destroyed vertebra, which allows you to return the vertebra to the desired position, after which it is cemented. This procedure is carried out to fix it and prevent further destruction. This operation is possible only before the vertebral fusion begins.
Diagnostics
Determination of pathological kyphosis begins with an external examination. When bending forward with your back bare, thoracic kyphosis will be noticeable. With a pronounced degree of curvature, a person will not be able to reach his feet. Of the instrumental examinations used:
- X-ray.
- Computer examination.
Kyphosis of any part is treated by an orthopedist; additional examinations by a neurologist or therapist are required.
Classification
Although the thoracic region is most commonly affected, cervical and lumbar kyphosis also occurs. Depending on the type of deformation, the curvature can be arcuate or angular. In the first case, the bulge looks like an arc. With an angular shape, the top of the hump is directed upward. Depending on the curvature index, there is normal, straightened and increased kyphosis.
By severity
Let's talk in more detail about how kyphosis is classified depending on the severity:
Back hump and how to get rid of it
- Stage 1. It is asymptomatic. External signs of pathology are almost invisible. MRI and radiography can detect structural changes in the spinal column. Kyphosis at this stage is easily amenable to conservative treatment.
- Stage 2. Externally, the stoop is clearly visible. When the torso is tilted forward, a hump is visible. Pain usually occurs after physical activity. At this stage, you can do without surgery.
- Stage 3. There is excessive stooping. The pain bothers you regardless of physical activity. Pathological changes affect the lungs and heart. The treatment process at this stage is long and labor-intensive. In some cases, surgery is indicated.
- Stage 4. This is the most severe and advanced degree of kyphosis. The deformity causes significant limitation of mobility. Conservative treatment methods are unsuccessful at this stage.
1st degree
The angle of inclination is small, so the stoop is weakly expressed. There is a complaint about rapid back fatigue, as well as pain that occurs after physical activity.
Many people perceive slouching as a temporary disadvantage. Parents may feel that the problem will go away on its own as the child grows.
2nd degree
It occurs as a result of untreated grade 1 kyphosis. It can also occur against the background of injuries and surgical interventions.
Shoulders are down. In a sitting position, the back takes on an arched shape. This happens because the paravertebral muscles quickly get tired. The patient begins to look for a comfortable position, but all efforts are in vain.
If proper treatment is not carried out at this stage, back curvature will lead to the following serious consequences:
- hernia;
- paralysis;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- inflammation of the spinal cord;
- loss of ability to work;
- myocardial infarction, ISH (coronary heart disease).
3-4 degree
External changes are accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. The spine takes on an S-shape. Height is reduced due to back deformation. At the same time, the legs appear longer.
The pain syndrome becomes permanent. Teenagers lag behind their peers in physical development. Disturbances in the functioning of internal organs progress, leading to deep disability.
With grade 3 kyphosis, a huge hump appears
Kyphosis at this stage of development is accompanied by severe pain. This indicates displacement of the vertebrae and compression of the spinal cords. Among other things, the sensitivity of the lower body is impaired. This causes the development of diseases of the pelvic organs.
If the angle of curvature of the spine exceeds 50 degrees, it causes compression of the abdominal organs. This creates ideal conditions for the development of diseases such as gastroduodenitis, ulcers, cholecystitis, and intestinal obstruction.
By origin
Let's look at some types of kyphosis, which are classified depending on their origin.
Congenital
Kyphosis is caused by abnormalities of intrauterine development. The disorder is accompanied by neurological symptoms. As a rule, it requires surgical intervention.
Paralytic
The main reason for this curvature is paralysis of the paravertebral muscles. Diseases such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, and polio can provoke the disorder.
Paralytic kyphosis is accompanied by a decrease in muscle size, as well as an increase or, conversely, a decrease in their tone. This leads to spinal instability. It manifests itself especially clearly when bending and turning. As a result, even the slightest load can cause displacement of the bones of the spinal column.
Juvenile (Scheuermann-Mau disease)
Juvenile kyphosis develops during puberty. The pathology is discovered completely by accident, when parents notice that their child is slouching a lot. As the pathology develops, the spinal column becomes deformed and becomes flexible. The child becomes hunchbacked.
On a note! The disease develops in adolescence, mainly in boys, and is characterized by rapid progression and severe course.
The exact causes of the development of Scheuermann-Mau disease are still unknown. It is believed that the leading role is played by a genetic predisposition to vertebrogenic (from the word “vertex” - spine) diseases. Scientists have been able to establish a connection between juvenile kyphosis and the following congenital anomalies:
- underdevelopment of back muscles;
- osteoporosis;
- necrosis of the cartilage layer of the vertebrae;
- excessive bone growth.
Back pain appears in a child after physical activity. The teenager will not be able to reach his feet with his hands.
Can juvenile kyphosis be cured? Yes, but it is a long process! Treatment includes special exercises, massage treatments, and physiotherapy. Disability for this disease is not assigned, but young people are exempt from military service.
Post-traumatic
Back deformity occurs as a result of a compression fracture. A decrease in the height of the vertebrae creates the preconditions for an increase in the angle of curvature.
Positional
Positional kyphosis usually occurs in school-aged children. The curvature is caused by weakening of the ligaments and muscles of the spine, as well as poor posture. When detected late, the deformity becomes permanent.
Postural
Most often it develops in people under 30 years of age. It is diagnosed mainly in women. The reason for this is stretched spinal ligaments. When standing or sitting on the back, the deformity is visible. If a person lies on his stomach, the spine will be absolutely straight. No structural changes are detected on the x-ray.
How to correct pathology at home?
To prescribe a course of treatment for kyphosis at any stage of deformation, you must consult a doctor. At home you will need to perform special gymnastics; corsets are recommended.
The use of corsets in the first stages of development of the anomaly in combination with exercise, massage, and specially selected medications will either correct posture or prevent further deformation.
Corsets can be therapeutic or preventive. The latter do not require special selection. Therapeutic corsets have special stiffening ribs and are made only according to individual parameters. In order to achieve positive changes, you will have to wear corsets for most of the day at first.
Diagnosis and treatment
If you suspect problems with the spine, you should contact an orthopedic doctor or vertebrologist. A specialist will determine kyphosis of degree 2 and higher when examining the patient, but to confirm the diagnosis and identify all existing disorders, a hardware examination will be required. The simplest method is radiography, during which the doctor takes pictures of the spine in several projections.
Diagnosis of kyphosis is carried out using radiography
At an early stage, as well as in the case of severe deformities, it is recommended to undergo tomography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. These methods give a more accurate idea of the extent of tissue damage and allow even the most minor changes to be detected. The condition of muscle and nerve tissues is checked using electromyography, and the functions of internal organs are checked using ultrasound. Based on the results obtained during the examination, the doctor selects the optimal type of treatment, taking into account contraindications and the general condition of the body.
MRI is an absolutely safe and painless research method. With its help, any pathologies of the spine, soft tissues, and internal organs are identified. You can learn about the indications and contraindications of this technique, as well as what exactly MRI demonstrates and how the procedure itself is performed on our website.
Drug therapy
Medicines are used in cases where a person experiences severe pain attacks caused by compression of the nerve roots, swelling and inflammation. To relieve pain, drugs of several groups are used:
- analgesics and NSAIDs - Pentalgin, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ketolorac;
Ketolorac tablets
- local anesthetics (for very severe pain) - novocaine and lidocaine blockades;
- antispasmodics – “Drotaverine”, “No-shpa”;
- muscle relaxants - “Tizanidine”, “Mydocalm”, “Sirdalud”.
Instructions for use of tizanidine
If the pain syndrome is moderate, to eliminate it in most cases it is enough to take medications containing B vitamins - Milgamma, Combilipen Tabs, Neurobex. They normalize metabolism, restore the functioning of nerve endings, improve blood supply, due to which pain symptoms decrease and then disappear altogether.
"Kombilipen tabs": instructions for use
Important! Each drug has its own contraindications, and you cannot select medications on your own, so as not to provoke even greater complications. While taking medications, you should strictly adhere to the dosages and duration of treatment prescribed by your doctor.
Physiotherapy
The most important part of treatment is physical exercise. They are aimed at strengthening the muscles and ligaments that support the spine, resulting in alignment. In addition, with the help of exercise therapy, it is possible to restore blood supply to the affected area, the passage of nerve impulses, and improve tissue metabolism. For each part of the spine, its own set of exercises has been developed, affecting the necessary muscle groups.
Video - Exercises for the treatment of thoracic kyphosis
If you want to learn in more detail how to strengthen your back muscles at home, and also consider effective methods, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Positive results can only be achieved with regular exercise over several months. In the future, you shouldn’t give up exercises either, but you can no longer do them every day, but twice a week - for preventive purposes, this is quite enough. Before starting classes, you should make sure that there are no contraindications, the list of which includes:
- acute pain syndrome, exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the body;
- oncological diseases;
- postoperative period;
- serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart and lungs.
You can engage in physical therapy only if there are no contraindications.
Important! Hypertensive patients, as well as people who have recently recovered from a heart attack or stroke, need to exercise under the supervision of a specialist; everyone else can do the exercises at home.
Massage
By massaging the affected area, muscle tone is restored and blood flow improves, due to which the patient’s condition gradually normalizes. Therapeutic massage must be combined with gymnastic complexes, since as monotherapy it gives too little effect. Usually the doctor prescribes 2 courses of massage per year, 10-15 sessions each, with breaks between courses of up to six months. The massage must be performed by a qualified specialist, since deformed vertebrae and affected discs are very vulnerable to external influences, and one careless effort can lead to injury.
Massage for spinal kyphosis helps normalize muscle tone and improve blood flow
Physiotherapy
Like massage, physiotherapeutic treatment is an auxiliary technique and gives good results only in combination with other methods. Physiotherapy helps strengthen muscles, relieve inflammation in tissues and muscle spasms, and eliminate muscular dystrophy of the back and abdomen. The list of standard procedures includes electrophoresis, electromyostimulation, ultrasound therapy, and magnetic therapy. To activate lymphatic drainage and blood circulation, paraffin and ozokerite applications and hot wrapping can be prescribed. Hydrotherapy, which includes sea and sodium chloride baths, as well as therapeutic mud, helps to increase the overall tone of the body.
Sodium chloride baths provide an excellent therapeutic effect in the treatment of spinal pathologies
Additionally, orthotics are often used in the treatment of kyphosis: correct wearing of corrective devices (bandages, corsets, reclinators) until bone growth is complete helps to significantly reduce spinal deformity. Swimming, spinal traction (including underwater), acupuncture, and stone therapy also have a good therapeutic effect.
Acupuncture uses active points, thereby increasing the body’s immune properties
The main condition is that all procedures should be carried out only in medical centers by appropriate specialists, and not in dubious establishments or at home. Kyphosis is a serious pathology, and therefore the approach to treatment should be as responsible as possible, because illiterate actions can cause great harm to a person.
Video - Spinal kyphosis
Exercise therapy against kyphosis
Exercises should be performed daily; the doctor examining and treating the person should select a set of exercises. The most commonly used exercises for chest kyphosis include:
- In a standing position, you need to place a straight stick behind your back and arms, pressing it to your shoulder blades. Then they do squats, exhale when lowering down, and inhale while rising.
- Standing on all fours, you need to rest on your knees and hands. In this position, the head is raised, the elbows are moved to the sides, and the chest should be lowered as far down as possible.
- Lying on a hard, flat surface, you need to extend your arms along your body. Leaning on them, it is necessary to raise the pelvic region and chest.
Exercises used for neck kyphosis include:
- From a sitting position, you need to lower your shoulder girdle down and pull your head up. From the same position, stretch the neck and turn the head in different directions.
- While sitting, you need to make smooth tilts with your head in different directions.
Each exercise needs to be done on average 5 times. It is necessary to increase the load gradually; there should be no sharp pain.
Treatment of kyphosis
Treatment of kyphosis disease is a long process and requires a lot of patience and effort. To cure it, doctors in most cases prescribe conservative treatment, which consists of the following:
- use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- manual therapy;
- reflexology;
- therapeutic acupressure and general massage;
- physiotherapy: electrophoresis, electrical stimulation, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, etc.;
- swimming;
- passive treatment by position: sleeping on an orthopedic mattress, maintaining correct posture;
- use of corrective bandages and corsets.
In particularly severe cases (severe curvature, severe pain, neuralgia, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs), massage for kyphosis or gymnastics will be powerless - surgery is prescribed. Doctors prescribe surgery when the skeletal system is already fully formed. However, not every doctor will offer this treatment option, since spinal surgery involves a lot of risk.
Treatment of pathology at home
Before you begin treating your back at home, you should discuss it with your doctor. Typically, “at-home” therapy methods include enhanced physical therapy, bandages and massage for kyphosis.
The use of corrective bandages in combination with gymnastics, massages and drug therapy makes it possible to almost completely correct deformed posture or stop its pathological development.
Physiotherapy
In the treatment of any spinal disease, physical therapy (PT) is of particular importance. Exercises for kyphosis should be selected by the attending physician, taking into account the localization of the pathology and concentrated on strengthening the corresponding muscle groups.
To correct the existing problem, use the following set of exercises. While performing them, it is important to monitor your breathing rhythm. An approximate set of exercises:
- Exercise No. 1. For this exercise you need to equip yourself with a gymnastic cane. Take it with both hands by the ends and put it behind your shoulders, pressing it downwards towards your shoulder blades. In this case, your feet should be shoulder-width apart. At this stage, you should feel that the back muscles are “playing” and tension has appeared in them. Next, in the same position, we begin to perform squats. Sit down - exhale, stand up - inhale. You shouldn’t torture your body with deep squats right away. Squat as much as you can, increasing the depth of your squat every day.
- Exercise No. 2. Absolutely everyone did this popular exercise as a warm-up in the garden or school. Slowly stand on your toes and simultaneously raise your arms up like a bird (through the sides), while taking a deep breath. Lower your limbs along the same path as you exhale.
- Exercise No. 3. Let's return to the stick. We throw it back over our shoulders, as in the first exercise, with our legs spread apart. We raise our hands and lower our heads back, inhaling the air. We return to the starting position - exhale.
- Exercise No. 4. Here you will need to crawl on all fours. To do this, stand on your knees and hands, and begin to bend your back down, raising your head and taking one step with the same hand and knee. You should feel tension in the muscles. Return to the starting position and step onto the next hand and knee, arching and lifting the head. In total you need to take 40–50 steps.
- Exercise No. 5. We continue to practice in the “four-point” position. We bend our elbows, lowering the front part of the body to the floor and bending forward. Then we slowly return to the original position.
- Exercise No. 6. Lie on the floor and stretch your arms and legs along your torso. Imagine that you just woke up and stretch your hands, placing them behind your head and inhaling. Then come back and exhale.
- Exercise No. 7. We take a “lying” position, preferably on the floor. The arms are bent at the elbows and the legs are extended along the body. We take a breath - “puff out” our chest, leaning on our elbows and the back of our head. We come back - exhale.
- Exercise No. 8. Lying on the floor with your stomach down, you need to bend your elbows and press them to your shoulders. Then, inhaling air, we raise our head, shoulders and chest as high as possible, stretching upward. Lie back down - exhale.
- Exercise No. 9. Let's go back to the stick. We take a lying position on our stomach and throw the stick over our shoulders (as in the first exercise). Then we begin to lift and pull our head and shoulders as high as possible, while inhaling air, thus stretching the spine. Gently lie down in the starting position and exhale.
- Exercise No. 10. Stand up straight and put your hands behind your head. Slowly rise onto your toes, inhaling air, and spread your arms to the sides. Lower yourself, hands on the back of your head – exhale.
Agree, these exercises can be safely performed at home. You just need to stock up on the necessary attribute - a gymnastics stick - and consult a doctor. Exercise therapy for kyphosis does not contain difficult exercises to perform, and even older people can do it.
Symptoms
With all the variety of causes, pathological cervical kyphosis manifests itself in approximately the same way in everyone. First of all, it is severe pain in the neck , radiating to the arms and torso. Neck mobility decreases and a crunching sound appears when moving .
If the vertebrae are located in such a way that they pinch the vertebral artery, severe headaches will be experienced, mainly in the back of the head , aggravated by head movements. As a result, fainting and dizziness may occur .
Other symptoms, less noticeable:
- More or less pronounced cervical hump;
- Reduced sensitivity of the skin on the face;
- Impaired vision, hearing and other senses;
- Deterioration in overall performance, thinking and memory;
- Sudden changes in blood pressure;
- Sensation of tingling and numbness in the lower jaw.
Usually after such symptoms a diagnosis is made. However, to be completely sure an X-ray examination , which accurately shows the curvature.
We recommend reading about the symptoms and degrees of kyphosis, as well as treatment methods for both adults and children that can be done at home.
Risk factors, causes and consequences
All causes of kyphosis are conventionally divided into congenital and acquired . The main risk factor for the appearance of deformity is genetic predisposition. If several generations in the family have had kyphosis, then with a high degree of probability it can be assumed that the genes that are responsible for abnormalities in the development of the spine will be passed on to the child.
With rickets in childhood, the likelihood of developing kyphosis increases. It usually occurs in the first year of life. Experts classify such kyphosis as congenital. In some children, kyphosis appears during fetal development or as a result of birth injuries.
Acquired causes of cervical kyphosis include:
- various diseases of the spine (spondylosis, osteoporosis, osteochondrosis);
- age-related changes that provoke changes in the structure of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs;
- spinal injuries, damage to ligaments and back muscles;
- insufficient physical activity, excessive exercise;
- incorrect posture (scoliosis);
- inflammatory and infectious diseases that provoke the appearance of problems with the spine (for example, with tuberculosis, the structure of the vertebrae themselves changes);
- tumors (benign and malignant) that are in contact with the spine;
- herniated intervertebral discs.
Also, kyphosis of the cervical spine can be one of the manifestations of Scheuermann-Mau disease. It develops mainly in young men during adolescence.
In the absence of treatment or its ineffectiveness, pinching of the spinal cord roots may begin . This leads to disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory and cardiac organs. Patients with cervical kyphosis suffer from frequent pneumonia and bronchitis. Even at rest they experience shortness of breath. But this is not the only negative consequence of kyphosis. Patients also begin to experience arrhythmia and problems with blood pressure.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
It is almost impossible to independently identify kyphosis in the early stages. Therefore, patients need to know what signs of progression of this disease exist. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult your doctor. He will conduct a diagnosis and, if cervical kyphosis is confirmed, prescribe appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of cervical kyphosis include:
- the appearance of headaches;
- numbness of the limbs;
- development of hypertension or, conversely, hypotension;
- slouch;
- tingling sensation in the lower jaw;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- weakness, fatigue.
Doctors divide all signs of kyphosis into 2 groups : vertebral; extravertebral.
The first group includes impaired neck mobility and the appearance of a crunching sound when turning the head.
The second group includes weakness of the eye muscles and decreased skin sensitivity. If the nerve roots are excessively compressed, the condition may worsen. Peripheral and central paralysis occurs, some even experience urinary disorders.
After interviewing the patient and clarifying the main symptoms, the doctor prescribes an x-ray of the cervical spine in two projections. This study allows you to identify the curvature and determine the degree of kyphosis. You can check whether blood vessels and nerve endings are pinched using MRI and CT.
If kyphosis is confirmed, then it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the internal organs that most often suffer from kyphosis: the lungs and heart.
Consequences of kyphosis 1 and 2 degrees
In cases of significant progression of kyphosis, there is a risk of developing concomitant pathologies:
- breathing problems;
- instability of the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Often people with kyphosis may complain of pain in the back and between the shoulder blades.
Dangerous complications of kyphosis are:
- paresis;
- urinary incontinence;
- damage to internal organs and systems;
- intervertebral hernia;
- secondary meningitis;
- disability, loss of ability to move;
- myocardial infarction.
Kinds
Kyphosis manifests itself in different ways - from a barely noticeable stoop to a pronounced hump. Curvatures can be observed in various parts of the thoracic region - cervicothoracic, upper thoracic, thoracolumbar.
By form:
- Angular kyphosis (kyphosis angularis), or hump. Characterized by an angular convexity of the back, with the apex backwards.
- Arc-shaped kyphosis. It is characterized by a convexity of the back in the form of a short or long arc.
- Physiological kyphosis (kyphosis physiologica). Typically a stage of spinal development. It is characterized by a slight tilt of the spine - up to 30 degrees. It can be present in the thoracic region up to 7 years, in the lumbar region (sacrum) - until puberty.
Functional thoracic kyphosis
This type of pathology is also called common stoop. Most often it occurs due to weak back muscles, constant stooping, excessive physical exertion, and improper body position while working at a desk. If you place such a patient on a flat surface, the bend will disappear on its own.
When performing fluoroscopy, no changes in the vertebrae will be noted in the images. To treat this type of disease, conservative treatment, primarily aimed at strengthening the muscles, is sufficient.
Dorsal juvenile kyphosis (Scheuermann-Mau disease)
Scheuermann-Mau disease - develops in adolescence mainly in boys, and is expressed in the formation of wedge-shaped vertebrae in the lower thoracic or upper lumbar spine and changes in the ligamentous apparatus
Congenital kyphosis
This is a defect in the development of the vertebral bodies (anterior sections) caused by a genetic mutation and inherited.
Paralytic kyphosis
Paralytic kyphosis is caused by diseases accompanied by paresis and paralysis of the back muscles (cerebral palsy, poliomyelitis, etc.). With cerebral palsy, there is an increase in thoracic kyphosis and an increase in its length (the curve extends to the upper part of the lumbar region). Kyphosis can be combined with scoliosis. Characteristic is a gradual progression of the deformity. Treatment is usually conservative, complex, and long-term.
Rachitic
Develops in children with rickets starting from the sixth month of life. However, rachitic kyphosis often develops in older children or adolescents who suffered from rickets in early childhood.
Post-traumatic kyphosis
The cause of the development of the disease is previous injury to the spine. The progression of the disease further causes compression of the nerve structures in the spinal column. When the spine is fractured in the thoracic or lumbar region, kyphosis of one degree or another develops; based on the severity of the injury, the appropriate treatment is determined, which, in turn, can be either conservative or surgical.
Postoperative
It develops infrequently after operations on the spinal column due to trauma, anterior displacement of the vertebra due to congenital non-fusion of the vertebral arch with its body (spondylolisthesis), replacement of the intervertebral disc, and others.
Senile (degenerative) kyphosis
This type of curvature is caused by degenerative changes in the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs, which are accompanied by the so-called “subsidence of the spine”, as well as weakening of its ligamentous apparatus
Occupational classification
In addition to the classical classification of this deviation, there is also a special classification used by doctors in this field:
Hyperkyphosis
- hyperkyphosis is when the level of bending exceeds 50 degrees;
- normokyphosis - a level of curvature that is normal for ordinary people is less than 50 degrees;
- hypokyphosis is when the angle of curvature of the spine does not reach even 15 degrees.
In general, in the presence of such an illness of any degree, there is no need to panic and rush to extremes in order to find treatment. Modern medicine is capable of many things, including straightening the spine in ways that are minimally painful for the patient and in the shortest possible time.
How to treat kyphosis and lordosis of the spine
If there is any suspicion of lordosis or kyphosis, the doctor first conducts a visual examination of the patient. Then an x-ray is ordered.
A prerequisite for the treatment of these diseases is the organization of regular physical activity. In this case, all loads must be carefully selected by the doctor according to the individual characteristics of the patient in order to avoid danger and injury to the damaged body.
It is important to adhere to certain rules when performing physical activity.:
- breathe deeply to ensure oxygenation of muscle fibers and a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system;
- adhere to a specific exercise plan recommended by your doctor;
- make only smooth movements to avoid injury;
- perform a feasible load, avoiding intense exercise;
- avoid the occurrence of painful sensations.
In addition to physical therapy, the following methods will bring noticeable benefits.
Massage to restore blood circulation in the tissues where the curvature has occurred. It will allow muscles to relax, restore metabolic processes and reduce various unwanted side effects.
Drug treatment according to an individual regimen to relieve pain and relieve spasms. In some cases, antidepressants are prescribed.
Corrective corsets that will help align the spine and maintain the back muscles in the correct position.
Practicing auxiliary sports , except for physical therapy.
In this case, swimming and yoga are considered the most effective for correcting the spine.
Causes of kyphosis
In children, kyphosis occurs due to the inability to maintain posture, constant stooping, hereditary or congenital pathology of the spine. There are many more reasons for the development of the disease in an adult:
- Infectious diseases that destroy the structure of the joints (for example, tuberculosis);
- Osteoporosis or vertebral fractures;
- Bekhterov's disease;
- Arthritis of the spine of a degenerative nature (fraught with deformation of disc and bone structures);
- Marfan syndrome (connective tissues lose some of their functionality and cannot support the joints in their positions);
- Congenital anomalies that appear with age;
- Tumors of malignant and benign types;
- Paralysis and its causes;
- Lack of spine flexibility;
- Back and spine injuries (bruises, fractures);
- Complications after operations.
Functional type kyphosis is considered less problematic. Its reasons include:
- Incorrect posture;
- Psychological disorders;
- Incorrect positions while sitting;
- Muscle weakness in the back area.
Functional kyphosis deforms the spinal arch slightly. You can get rid of the pathology with the help of physical therapy and constant monitoring of posture.
Prevention
It is possible to prevent the development of the disease! To do this, just follow some recommendations:
- Treat infectious diseases in a timely manner, treat chronic diseases, and pay attention to the spine.
- Sleep on a hard mattress and a comfortable pillow.
- Properly organize your workspace to ensure correct posture throughout the day.
- Fight excess weight, avoid overeating.
- Lead a healthy and active lifestyle. During sports activities, take care of your back and neck and prevent injuries.
- Regularly carry out a gymnastic complex for correct posture.
- Elderly people need to think about the health of their spine as early as possible. Taking vitamins and chondroprotectors, as well as daily exercise therapy will help you stay in shape for a long time and forget about problems with the spine.
Prevention of kyphosis
It is quite possible to prevent the occurrence of curvature of the cervical spine . To do this you need:
- constantly monitor your posture and neck position;
- monitor your physical fitness: regular physical activity helps strengthen the muscle frame;
- If visual acuity is reduced, use glasses or contact lenses.
When the first symptoms of kyphosis appear, you should consult a doctor. Curvature can be corrected in the initial stages of the disease even in adulthood.
Symptoms of kyphosis of the thoracic spine
In the vast majority of cases, kyphosis is diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, during the formation of the spine. The following external symptoms are noteworthy:
- bent back,
- sunken chest
- protruding belly
- retracted shoulders and separated shoulder blades.
But the problems are not limited to just the aesthetic side. Although the deterioration of appearance in itself is a serious psychological trauma, especially for children and adolescents.
Due to the formation of a hump, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- pain in the heart (a person may mistake such pain for a manifestation of cardiovascular pathologies);
- breathing problems, shortness of breath with little physical exertion and even at rest;
- various manifestations of disorders of the digestive tract.
Pain with kyphosis is observed in most cases. The pain syndrome is caused by severe tension in the back muscles, as well as compression of internal organs and partial destruction of the intervertebral discs.
With kyphosis, the vertical axis of the body shifts, and with it the center of gravity. An excessive load is created on the feet, and as a result, flat feet are formed.
In young children, the culprits of kyphosis of the thoracic spine are bone tuberculosis and rickets. The risk of developing the disease increases during adolescence, and boys are especially susceptible to it. In young people under 30 years of age, disorders can develop as a result of engaging in heavy types of work and often being in the wrong position. In old age, it most often affects women.
How to Diagnose Kyphosis
As a rule, in order to find out for sure whether he has this or that disease, a person turns to a specialist. Kyphosis is no exception here, although a preliminary diagnosis here can be made independently. To do this, one of two very simple tests is performed at home. In particular, you should stand straight, leaning your back against the wall, and then try to touch the back of your head to it. If this exercise is difficult, then there is cause for concern.
The second test is even simpler - you just need to lean forward and look at your side reflection in the mirror. In this position, the pathology will be quite noticeable. If a person is suffering from back pain or some other unpleasant sensation, then he needs to contact a specialist, and the sooner the better.
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must conduct a complete examination of the patient. In particular, it should be determined whether the person has any nervous diseases. In addition, the chest and its space are necessarily examined - the emphasis is on checking the functioning of the lungs and heart. Prescribing effective therapy is only possible with a correct diagnosis. In this case, the doctor, before deciding on a treatment option, refers the patient to a tomography to determine the degree of curvature of the spine. This study also allows us to determine the condition of its nerve endings.
What is cervical kyphosis
Normally, the spine has slight curves, which provide shock absorption during movement and evenly distribute the load. In the cervical region, the curve is convex forward, and it is called lordosis. The same lordosis, only with a slightly larger angle of inclination, is present in the lumbar region. Under the influence of certain reasons, pathological changes begin in the vertebrae: their front part is flattened, and the back part, on the contrary, grows beyond the norm. Even if only 2-3 vertebrae are affected, the shape of the entire cervical spine changes.
The affected vertebrae acquire a wedge-shaped shape, the longitudinal ligament thickens
What are the dangers of this condition? First of all, the intervertebral discs are affected. Uneven load leads to disruption of the disc structure, destruction of the fibrous ring and the formation of hernias. In turn, hernias compress the nerve endings and blood vessels passing through the spine, which causes pain, oxygen starvation of tissues and disruption of metabolic processes. This affects not only the spine, but also the brain, problems with blood pressure and the respiratory system arise, and hearing and vision deteriorate.
The progression of kyphosis threatens pinching of nerve endings and the development of other complications
Treatment methods
It is most effective to use several methods of treating kyphosis at once. The set of measures involves the use of kinesiology techniques, manual therapy, reflexology, osteopathy, and massage. An integrated approach allows you to correct disorders in the structure of the spine, relieve pain, and stabilize the functioning of internal organs. The last point is very important, since the pathological curvature of the spine affects the state of the respiratory, cardiovascular and nervous systems.
The hardware methods for treating kyphosis that we recommend are individual physical therapy sessions under the guidance of an experienced doctor and training courses using the Huber Motion Lab hardware complex.
These measures will strengthen the musculoskeletal system, muscle tissue, ligaments and neuromuscular connections, normalize cardiovascular rhythm and improve immune status.
The Integritas Clinic uses the most effective methods for correcting incorrect posture and combating disorders that have arisen secondary. Before visiting a doctor, make an appointment using the feedback form or by phone.
Our clinic uses the most promising methods for correcting spinal curvatures and combating the disruption of internal organs caused by them.
You can ask questions by phone +7 (495) 726-54-14
DOCTORS
Klimov Leonid Vladimirovich Neurologist, reflexologist, chiropractor, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category
Full list of medical team
Second degree scoliosis
With this degree of scoliosis, the deformation of the spinal column is already noticeable visually and does not disappear when X-rayed in a supine position. Unfixed scoliosis is characterized by the presence of a small rib hump and a compensatory arch formed by the spinal muscles. At the same time, for unfixed scoliosis, in contrast to fixed scoliosis, different data on the angle of deformation are characteristic, depending on the position of the patient. The angle of C-shaped scoliosis according to the Chaklin method is 11 – 30; The angle of the scoliotic arc varies from 150 to 169; The angle of scoliosis, according to the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, ranges from 11 to 25.
Exercise therapy for scoliosis: a set of therapeutic exercises
Treatment of
second-degree scoliosis
At this stage of scoliosis, exercise therapy and massage are no longer enough; it is advisable to use medicinal methods of therapy.
Physiotherapeutic methods include:
- Exercise therapy, exercises can be done at home;
- back massage;
- the use of corsets that correct the deformity of the spinal column;
- electrical stimulation of the spinal muscles.
Drug therapy includes:
- Taking medications containing calcium and vitamin D. Doctors usually prescribe 1 tablet once a day.
Forecast
If left untreated, kyphosis will progress . This provokes a deterioration in blood supply to the brain. As a result, the patient experiences severe pain. They are localized mainly in the occipital part. In addition, problems arise with the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
When kyphosis is detected in childhood, it is possible to get rid of the disease using a conservative method in more than 90% of cases. In patients over 16 years of age, it is much more difficult to remove the deformity. Treatment is aimed at stopping the progression of the disease.
Kyphosis: forms
In general, we can distinguish two main forms of kyphosis: pathological kyphosis and physiological kyphosis. The diagnosis of “physiological kyphosis” is established when the angle of inclination of the spine is within 15-30 degrees. As for pathological kyphosis, it, in turn, can be congenital or acquired, corresponding to a certain degree of severity (degree of kyphosis, we will consider them a little below). As for the numbers, pathological kyphosis, in comparison with physiological kyphosis, can be considered changes in which the angle of inclination of the spine corresponds to an indicator of 30 degrees, and the limits of the numbers of such an inclination can reach 71 degrees or more (which determines the extreme degree of this disease).
Kyphosis may correspond to the following types of manifestation:
- Type I kyphosis - this type of manifestation of the disease is characterized by the fact that the vertebral bodies develop abnormally;
- Type II kyphosis – the vertebral bodies are subject to abnormal segmentation;
- Type III kyphosis - this type is mixed and, accordingly, is characterized by a combination of anomalies indicated in the previous degrees.
In accordance with the area of localization of the extreme apex of the deforming process, the following forms of kyphosis are distinguished:
- cervicothoracic kyphosis;
- upper thoracic kyphosis;
- midthoracic kyphosis;
- lower thoracic kyphosis;
- thoracolumbar kyphosis;
- lumbar kyphosis.
Kyphosis of the thoracic region: photo
Let's return to the degrees of spinal deformation with kyphosis; the following main variants are distinguished:
- I degree of deformation - within 30 degrees (this figure, as we have already determined, indicates a physiological deformation, then, accordingly, the degrees of pathological deformation of the spine follow);
- II degree of deformation - here the angle of inclination ranges from 31 to 60 degrees;
- III degree of deformation - the angle of inclination of the spine is in the range of 61-90 degrees (mainly considered as an extreme degree of manifestation of the disease);
- IV degree of deformation - from 90 degrees or more (a rare and much more severe form of kyphosis).
Kyphosis may also differ in the progression of the deforming process. Thus, when the inclination increases to 7 degrees per year, they speak of a slowly progressive form of kyphosis. Accordingly, with rapidly progressing kyphosis, the pathological change in the angle of inclination ranges from 7 degrees or more per year. Depending on the initial detection of the disease, the following variants are distinguished:
- infantile kyphosis (or rachitic kyphosis) - with this form of the disease, the curvature of the back (angle of inclination) is not in a fixed position, and therefore if the child is laid on his tummy, it disappears;
- kyphosis of young children - in this case we are talking about fixed infantile kyphosis;
- kyphosis of adolescents/young men – here we are talking about Scheuermann-Mau disease, which we have already noted earlier;
- adult kyphosis - in this case, the disease is considered in its advanced form (this is either congenital or adolescent kyphosis), as well as a disease that is the result of a certain impact (acquired kyphosis, which arose as a result of trauma, surgery, etc.).
Complications
It is a mistake to think that such a disease is not dangerous. If left untreated, pressure on the spine increases, causing osteochondrosis and intervertebral disc herniation. In addition, a hump gradually forms.
Due to excessive pathological curvature of the spine, there is a negative impact on the spine itself, as well as on all nearby organs. This reduces the volume of the chest and, as a result, the maximum capacity of the lungs. As a result of such changes, blood circulation and oxygen saturation of tissues are impaired. It also negatively affects the heart and leads to disruption of the cardiovascular system.
With severe curvature of the spine, the following diseases develop:
- gastritis, stomach ulcer;
- liver inflammation;
- inflammation of the large and small intestines, sometimes obstruction;
- cholecystitis;
- cardiovascular failure;
- cerebral circulatory disorders.
Main thoughts
Kyphosis is an excessive arched curvature of the spine in the anteroposterior direction. Externally, the disease manifests itself as a hump on the back. Curvature most often occurs in the thoracic region. Kyphosis occurs in 4 stages. You can do without surgery in the initial stages of the disease. It is possible to detect kyphosis even at home. To do this, you need to tilt your body forward. In this position, the curvature is clearly visible. The disease is accompanied by pain that reduces the quality of life. Over time, sensitivity and motor activity are impaired. Advanced forms of kyphosis cause serious problems with the heart, lungs, digestive tract, and excretory system. If you experience discomfort in your back, consult an orthopedist. In the early stages, the problem can be corrected with the help of exercise therapy, physiotherapy, and massage procedures. Treatment of kyphosis in adults in advanced cases is a long and labor-intensive process. In this case, you cannot do without surgery.
Preventive measures
To avoid the appearance of kyphosis, you should monitor your posture. You should always sit up straight and choose flat surfaces for this. If possible, it is better to sleep on an orthopedic mattress.
For work, choose the most comfortable table and chair that will suit your height. If you spend a long time in a sitting position, then you need to do a little exercise every hour, or just walk around the office.
Try to avoid carrying a lot of extra pounds on yourself. Eat foods that are rich in vitamins and microelements. Drink enough water per day.
This disease requires appropriate treatment. If a person begins to engage in spinal restoration at an early stage, then there is a greater chance of a positive result.