According to statistics, from 20 to 70% of people encounter aphthous stomatitis in their lives. It is safe to say that this is much more a childhood disease than an adult one. Although aphthous stomatitis can occur at any age in both infants and the elderly.
What is this disease? What are the reasons for its occurrence? Is it possible to avoid the appearance of aphthous stomatitis and is it contagious? How to properly treat the disease? All these questions arise for those who have at least once encountered aphthous stomatitis in their lives.
Description of the disease
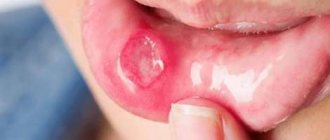
Aphthous stomatitis is a lesion of the oral mucosa, accompanied by the formation of aphthae. They are round, painful neoplasms up to 5 mm in size, covered with a gray coating with a red rim along the contour. At first they appear as ordinary inflammation, but quite soon they turn into blisters or ulcers. Aphthae can be localized on the cheeks, lips, on or under the tongue, as well as on the tonsils. The disease can affect children and adults; it has similar symptoms in representatives of different age groups. This material will tell you about the symptoms and treatment of stomatitis in the throat.
The acute phase of the disease usually passes in humans within 10 days. Most aphthae disappear completely from the mucous membrane, leaving no traces. The largest tumors can leave scars. This link will tell you about chronic recurrent stomatitis.
If a person does not promptly begin treatment for this disease, aphthae can spread to the laryngeal mucosa and then spread through the respiratory tract. This can cause more severe infections.
Main symptoms and duration
The symptoms of the disease directly depend on the form of its course.
Acute form of the disease - everything is unexpected and abrupt
Acute aphthous stomatitis appears unexpectedly. The patient begins to complain of malaise, sometimes a slight increase in temperature is noticeable.
Already at the initial stage, pain is felt in the mouth, which worsens while eating or while talking. Bubbles form on the mucous membrane, quickly developing into erosions, covered with a gray-white coating.
Around the aphthae, the mucous membrane becomes inflamed and becomes loose. You may notice a white coating on the tongue.
As the number of ulcers increases, it becomes difficult to eat solid food; you have to switch to purees and pates.
The duration of this type of disease usually does not exceed two weeks, at the end of which the mucous membrane is restored to its previous state. Very rarely, in the case of a complicated form, minor scars remain.
Chronic form
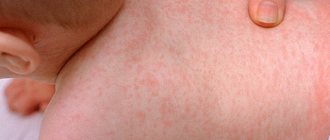
With chronic aphthous stomatitis, as in the photo on the right, the mucous membrane swells and becomes pale.
Ulcers are located on the inside of the lips, cheeks, and under the tongue. Less commonly, aphthae are localized on the palate and gums.
The size of the lesion reaches a centimeter, the halo swells, becomes red, and a dirty gray coating appears. In the case of extensive necrosis, the ulcers become more inflamed and protrude above the surface.
This form of the disease is characterized by an increase in temperature to 38-39 degrees, decreased performance, enlarged lymph nodes, and weakness.
Chronic aphthous stomatitis usually lasts 12-15 days. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, aphthae will begin to grow deeper, affecting the mucous membrane.
At this stage, the sores will begin to bleed, causing even more pain. In addition, this condition is dangerous due to infection. Deep aphthae may leave scars after healing.
There are other types, symptoms and causes of stomatitis, which you can familiarize yourself with in this article.
Read about folk remedies for treating stomatitis here.
Detailed instructions for using Kamistad gel follow the link
Symptoms
Stomatitis has pronounced symptoms. Its manifestations include:
- formation of aphthae in the mouth;
- enlarged lymph nodes, their pain on palpation;
- increased salivation;
- whitish coating on the tongue;
- general weakness, decreased ability to work;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- loss of appetite, irritability.
Infants may also experience deterioration in sleep quality and loss of appetite. They often refuse pacifiers and bottles. Find out about the difference between herpes and stomatitis here.
After a person’s plaque disappears from the canker sores, ulcers appear in their place. These ulcers heal within 10 days, often leaving scars on the mucous membrane.
Forms and varieties of the disease
There are two types of aphthous stomatitis:
- Spicy. It manifests itself in the form of numerous painful ulcers and erosions in the oral cavity, accompanied by severe pain, enlarged lymph nodes, and increased body temperature. With proper treatment, the disease goes away in about a week.
- Chronic. Ulcerative formations in the mouth are less painful (sometimes the pain is not noticeable at all), and are covered with a whitish coating. There is slight swelling of the oral mucosa. It is difficult to cure this type of disease, especially if the patient’s body is weakened by any other diseases.
The disease can be classified into forms, depending on its course:
- Fibrous stomatitis develops as a result of circulatory disorders in the epithelial layer of the oral mucosa. As a result, aphthae appear. They are located, as a rule, on the mucous membrane of the lips and tongue. This form of the disease is prone to relapse. At the initial stage, there are 1-3 relapses per year; later, if appropriate measures are not taken, their number increases. The healing process takes 1-2 weeks.
- Necrotizing stomatitis usually occurs against the background of other serious diseases (somatic diseases, blood diseases). Necrosis of the epithelium of the oral mucosa is noted, followed by the formation of aphthae. At the initial stage of the disease, aphthae are painless, but later, as they grow, they can cause pain. Healing time is up to 2 months.
- to the occurrence of granular stomatitis. Aphthae in this disease are localized in the area of these glands. Hypothermia and the addition of viral diseases lead to faster progression of the disease. Healing time is 1-3 weeks.
- Cicatricial stomatitis also manifests itself due to damage to the salivary glands, however, over time, the inflammatory process spreads to other areas. Aphthae can appear both near the salivary glands and on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and the front part of the palate. As the disease develops, aphthae turn into deep, painful aphthae of a fairly large size (up to 1.5 cm in diameter). Healing time is about 3 months.
- The deforming form of the disease is considered the most severe, since during the course of the disease the connective tissue, area of the palate, and lips are deformed. Canker sores are deep, painful ulcers that take a long time to heal.
Kinds
There are three main classifications of this type of stomatitis. The first takes into account the nature of the disease and distinguishes its two types:
- spicy. This type of disease is characterized by severe symptoms, including the appearance of painful ulcers in the mouth, sometimes on the palate, and increased body temperature. The duration of this form of the disease is up to 2 weeks (for severe bacterial or viral infection - up to 3 weeks);
- chronic (most often a complication of the first type). It is characterized by an undulating course with long-term remissions and rare exacerbations. During the period of remission, the disease is asymptomatic; at the acute stage, fresh aphthae appear. The duration of this disease ranges from a month to 2-3 years.
There are also several forms of stomatitis based on the type of causative agent of the disease:
- viral. It can be caused by the herpes virus on the lip. With this form of the disease, blisters filled with a clear liquid form in the patient’s mouth, which burst over time, and small ulcers form in their place;
- ray. Occurs as a result of irradiation of the mucous membrane with ionizing radiation. Characterized by the appearance of erosions, as well as compactions on the mucous membrane;
- fungal. Develops against the background of decreased immunity or taking antibiotics. With this form of the disease, a white coating forms on the sores. If the patient tries to remove them, erosions appear in his mouth;
- bacterial. It can be caused by streptococci or staphylococci. Characterized by the rapid formation of pustules and healing of ulcers;
- chemical. Appears as a result of burns of the oral cavity with acids or alkalis. Accompanied by the formation of deep ulcers, which subsequently scar and lead to tissue deformation.
Find out about candidal glossitis on the tongue here.
The third classification provides for the division of types of disease according to the nature of the damage to the mucosa. Within its framework, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- necrotic. With this form of the disease, tissue death occurs on which aphthae form;
Necrotizing aphthous stomatitis can have mild, moderate and severe forms.
- scarring. It is characterized by deep tissue damage, in which the size of the ulcers can reach 1 cm. In this clinical case, after the aphthae converge, patients are left with scars on the mucosa;
- granular. With this form of the disease, aphthae form near the salivary ducts, some of which become blocked. The disease has a pronounced pain syndrome, the treatment period is from a week to three.
The scarring form of the disease is considered one of the most severe. It can lead not only to scarring, but also to tissue deformation.
What is aphthous stomatitis
The name of the disease comes from the word “aft,” or ulcer. A characteristic sign of the problem is damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth with the formation of ulcers of various shapes and sizes. Formations occur in the mouth separately or in groups, affecting large areas of mucous structures.
Aphthae are most often localized in the front of the mouth, on the inside of the lips and cheeks. These areas are more susceptible to damage, friction, and accidental bites. Less commonly, stomatitis on the tongue is noted. The disease may be accompanied by a slight increase in temperature and general weakness. Aphthous stomatitis lasts on average 8-12 days.
Aphthae in the mouth are round in shape and resemble erosions with a white or gray coating, surrounded by a bright red membrane. The size of the wounds does not exceed 1 cm in diameter. With a mild course of the disease, 1 ulcer appears in the mouth, with a severe one - from 3. Touching the affected areas gives the person acute pain and discomfort, so eating with the problem is very difficult.
Causes
The disease can develop against the background of a viral or bacterial infection. Less commonly, it appears as a result of an allergic reaction of the body to a particular irritant. There are also a number of factors that increase the risk of developing stomatitis. Among them:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- viral infections in the body;
- severe stress;
- hormonal changes in the body;
- allergic reactions to various pathogens;
- genetic predisposition to the disease;
- mechanical damage to the mucosa;
- lack of a number of substances in the body: vitamins C and B, as well as minerals - zinc, iron;
- rheumatism.
The most important factor determining the appearance of aphthous stomatitis in a person is the state of his immune system. The worse it is, the higher the risk of developing this disease in a person.
Who is at risk
Predisposition to this disease is often inherited.
Any forum on the Internet containing reviews on how to quickly and effectively cope with the disease cites cases like “I myself have always had this problem, but now I had to treat my child for aphthous stomatitis.”
Women are the first at risk; they are diagnosed with this disease more often than men. If we talk about the age preferences of stomatitis, it prefers teenagers, although both children and the elderly can get sick.
Who else is at risk of getting an unpleasant diagnosis? Anyone who does not care about oral hygiene abuses alcohol and smokes.
The etiology of aphthous stomatitis does not exclude allergies to a number of foods as one of the common causes.
Treatment
Aphthous stomatitis is treated conservatively. The following groups of drugs are used to combat the disease:
- antiseptics, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs, including Cholisal. Helps stop the spread of infection in the oral cavity. In the most difficult cases, the patient may be prescribed glucocorticosteroids;
- decoctions of medicinal herbs and sea buckthorn oil. Used for rinsing the mouth, promoting healing of the mucous membrane;
- antipyretic drugs. They are usually used in the first days of treatment to alleviate the general condition of the patient;
- means aimed at eliminating the cause of stomatitis: antiviral medications, antibiotics or antiallergic drugs;
- medications with a hemostatic effect. Prescribed mainly to those patients who suffer from bleeding gums. If the patient does not have this symptom, they may not be included in the main treatment regimen.
Also, during the treatment of this type of stomatitis, a person needs to limit himself to spicy and rough foods. Hot drinks should also be avoided. These products can lead to injury to the mucous membrane and exacerbation of the disease.
The duration of taking medications, their type and dosage in each specific case are determined by the attending physician. The patient is strictly prohibited from arbitrarily changing the list of recommended medications, replacing them with drugs of similar action, or adjusting the dosage. All this can lead to a worsening of the patient's condition.
Features of treatment
By and large, medicine cannot do anything about this common disease. A distinctive feature of all stomatitis is that in most cases treatment comes down to eliminating the symptoms, not the cause. There is no way to treat the cause yet, as it remains unknown.
Which doctor should you contact?
Initial treatment of the acute form of aphthous stomatitis at the first manifestation or in case of relapse of the chronic form is subject to:
- family doctor,
- therapist,
- pediatrician
You should contact a dentist only if stomatitis occurs after his intervention (installation of braces, dentures, etc.). In this case, it is quite reasonable to immediately contact the person who caused the ulcers.
Advice! After contacting your family doctor, general practitioner or pediatrician, it would be a good idea to consult with a dentist, as he is more knowledgeable in matters of oral cavity treatment.
Rules for symptomatic treatment
Medicines for stomatitis are primarily medicines to reduce the severity of symptoms. Pharmacology and traditional medicine have in its arsenal many means to get rid of the painful manifestations of the disease.
The influence of popular folk remedies
Many people of the older generation are convinced that chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis must be treated with such dyes as:
- blue,
- brilliant green,
- potassium permanganate.
Contrary to popular belief, these remedies not only do not help the sick person, but can also aggravate the situation. Their application requires direct contact of a finger or bandage with the resulting ulcers. This can injure these already painful formations and prolong their healing time.
Advice! Until the mouth ulcers have healed, it is better not to brush your teeth with a toothbrush, as this can cause injury to the mucous membrane.
The influence of some other folk remedies:
- Products containing alcohol especially aggravate the situation, delaying the healing process.
- A two percent soda solution, which is popular in the treatment of stomatitis of various natures, will also not bring much relief.
Pharmacological agents
In order to eliminate severe symptoms of aphthous stomatitis, the following are actively used:
- gels containing local anesthetics,
- antiseptic compounds,
- solutions with anesthetics (ledocaine, benzocaine).
Fighting symptoms will not speed up recovery, which in any case will occur in 7 to 14 days. It is carried out in order to avoid ending up in the hospital with problems such as:
- dehydration,
- exhaustion,
- heat.
Painful mouth sores can make it difficult for a person to eat and drink and can be emotionally draining. And if an adult understands the need to take food and water, although this may cause him great discomfort, then it will be extremely difficult to force a child to endure pain.
The importance of rinsing
Gargling is an excellent way to treat the symptoms that recurrent canker sores create. To carry out this procedure you can use:
- saline solution (1 teaspoon of regular or sea salt per liter of water);
- soda solution (in the same ratio);
- special medications for rinsing.
Medical science considers the very fact of rinsing to be effective. By and large, there is no fundamental difference in what to rinse the mouth with stomatitis. The main task is to remove food debris.
Treatment of dangerous cases
Basically, stomatitis should not be perceived as a big problem, but as a small temporary difficulty. But in some cases the situation can become truly threatening.
- If the herpes virus has entered the aphthae, you should not do with just rinsing and treating the symptoms. You should consult a doctor who will prescribe an antiviral drug.
- Infection with staphylococcus also poses a serious danger and requires specific treatment.
- In cases where severe chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis is observed, it is necessary to use antiviral drugs. Which ones the doctor decides depending on the patient’s concomitant diseases.
Complications
If the patient does not cure this disease in a timely manner, he may face its main complication - the transition of aphthous stomatitis to a chronic form. This form has a wave-like flow. During remissions, the patient may not experience any symptoms of the disease. During the period of relapses, which most often occur against the background of a general decrease in immunity, the main symptoms of the disease manifest themselves intensively.
In the chronic form of the disease, each subsequent episode of stomatitis will have more intense manifestations than the previous one. Thus, the number of aphthae in a person will increase each time, as well as the healing time of wounds in the mouth. This article will tell you about the reasons for the appearance of red spots in the mouth.
Diagnostics
A quick cure for the disease is possible only as a result of a competent diagnosis. As a rule, this is done by a dentist.
The necessary information is given to him by a visual examination (what the affected mucous membrane looks like), a questioning of the patient (how long ago did the symptoms of the disease appear, whether they were accompanied by an increase in temperature).
In difficult cases, as well as if it is necessary to decide what to do next, if the healing process is delayed, laboratory blood tests, biopsy, and bacteriological culture are performed.
Prevention
In the vast majority of cases, the occurrence of this disease can be avoided. To do this, you need to follow simple preventive rules:
- Follow oral hygiene recommendations.
- Avoid using hard toothbrushes, which can damage your cheeks or gums.
- Do not eat excessively hot food, as it can injure the mucous membranes.
- Watch your diet. Be sure to regularly eat foods that contain vitamins C and B, as well as microelements.
- Treat existing chronic diseases in a timely manner.
Also, a person who wants to avoid aphthous stomatitis needs to monitor the state of his immune system. It is recommended to undergo a medical examination twice a year in order to promptly identify existing diseases, as well as take vitamin complexes. The latter should be selected for each person by a doctor.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults and children
Depending on the form and stage of the disease, therapy can be local or general.
The main goal of treatment is to achieve complete recovery, or, if this is not possible, stable remission. (For treatment of stomatitis in the tongue, see the link)
- First of all, it is necessary to disinfect the oral cavity, and, directly, treat the aphthae with an antiseptic agent (hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine).
- Periodically rinse your mouth with the indicated antiseptic agents.
- If symptoms are severe, such as pain, high temperature, the doctor may prescribe painkillers and antipyretics.
- Taking vitamin preparations, which include vitamins C and P, will help speed up the healing of ulcers.
- If the cause of aphthous stomatitis is an infection, the doctor will prescribe medications to treat the disease (antiviral therapy). If there are allergic reactions, take antihistamines.
- For successful treatment, the patient must strictly monitor his diet and adhere to a special diet. First of all, it is necessary to exclude foods that irritate the mucous membrane (rough, hot, spicy or sour foods).
- In order to prevent relapses, the doctor may prescribe medications - immunostimulants.
- You should refrain from smoking and alcohol.
In combination with drug treatment, folk remedies for the treatment of stomatitis are widely used:
- Infusion of pharmaceutical chamomile with the addition of honey. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with this product several times a day.
- Crushed burdock seeds must be mixed with a small amount of salt, heated over moderate heat, and interior fat added. Treat the damaged area of the mucous membrane with the resulting ointment.
- Oak bark decoction . This product is intended for rinsing the mouth. Helps relieve inflammation, accelerates the healing process of aphthae.
- Yarrow infusion will help relieve pain and swelling in the mouth, therefore, the healing process will be faster.
As you know, children are also susceptible to aphthous stomatitis (Here are methods for treating stomatitis in infants). One of the most common causes of the development of the disease is an allergic reaction to food. Thus, treatment consists, first of all, in correcting the baby’s diet.
Food should have a delicate consistency, contain the necessary vitamins and microelements, and not cause allergies.
The diet should also include fermented milk products containing probiotics. It is recommended to additionally give the child medications containing vitamin C and zinc.
Strong medications are contraindicated for young children, so to treat aphthous stomatitis at home, it is best to use folk remedies:
- Aloe juice. You can chew a freshly cut and thoroughly washed aloe leaf for a few minutes.
- Periodic rinsing of the mouth with carrot or cabbage juice (the juice must first be diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio) will help relieve the inflammatory process.
- For severe pain, this recipe will help: mix honey and vegetable oil (1 tsp each) with the white of 1 egg, add novocaine (1 ampoule). Mix everything thoroughly and periodically treat the aphthae with the mixture.
Risk factors
The reasons that provoke the development of aphthous ulcers of the oral cavity are the following:
- The presence of deficiency of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12.
- Presence of bacterial infections, such as stomach ulcers caused by Helicobacter.
- Some inflammatory bowel pathologies such as Crohn's disease along with ulcerative colitis.
- Infection of the body with the AIDS virus.
- Presence of Behçet's disease.
The most painful stage
Some patients get canker sores up to three times a year. For others, these ulcers occur constantly. Usually the first three or four days are considered the most painful stage, and then they begin to heal on their own. Small formations are the most common form. They are less than one centimeter in diameter and disappear in seven to fourteen days, usually healing without scarring. As for large ulcers, they are one centimeter or more in diameter and may not heal for several weeks or even months. After the formations disappear, scars remain.
How to treat aphthous ulcers is of interest to many. Next we will talk about diagnostics.
Manifestations of the disease
In this condition, signs of the disease in a person may appear spontaneously. The patient will complain of malaise, weakness and soreness in the mouth when eating. There may also be an increase in body temperature (typical of the acute form of the disease).
Gradually, small ulcers form on the mucous membrane of the tongue, which are subsequently covered with a whitish coating. The skin itself in such an affected area will become red and slightly loose. There will be clear signs of an inflammatory process.
Aphthae bring discomfort when chewing and talking.
In the chronic form of the pathology, the so-called aphthae (ulcers) can be localized under the tongue and on the inside of the cheeks. In this state, their size can be significantly larger. In this case, a person may lose ability to work, lose appetite and suffer from severe weakness.
Important! In the absence of treatment for chronic damage to the mucous membrane, the disease will begin to progress and further spread through the esophagus.
Additional Research
To clarify the nature of the process and find out its cause, it is necessary to use additional methods. The doctor may refer the patient to the following procedures:
- Complete blood count (leukocyte count, ESR).
- Immunogram (activity of the cellular and humoral components).
- Serological tests (antibodies to infections and own tissues).
- Allergy tests (skin tests, scarification tests, injection tests).
- A smear from the surface of aphthae (microscopy, culture, PCR).
It is necessary to differentiate aphthae in the oral cavity from other diseases with a similar clinical picture. First of all, we are talking about herpetic infection, ulcerative necrotic stomatitis.
What does the doctor do?
The diagnosis is made by a doctor based on examination and clinical picture. Specific laboratory tests are not available for canker sores. As a rule, the doctor recognizes canker sores by their typical appearance. If canker sores recur frequently or are particularly large, a doctor should check to see if the disease is causing it. He can then, for example, perform additional blood tests.
If an aphthous condition such as Behçet's disease is detected, you should see a doctor.
In the absence of disease, doctors may prescribe glucocorticoid gels, pastes, rinses, or medications containing drugs such as prednisolone, triamcinolone, or betamethasone, or cortisone ointment in severe cases.
What you need to know about disease therapy
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis should be comprehensive and under the supervision of a doctor. Even after visible signs disappear, you should not stop taking the prescribed medications. This is due to the fact that the disease can return and subsequently develop into a chronic disease.
Local treatment of aphthae
For local treatment in adults, antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gels are prescribed. Drugs may vary depending on the type and duration of the disease; an otolaryngologist or dentist will be able to give recommendations on the choice of drugs:
- Most often, Miramistin in the form of a solution or spray, which is used to irrigate the oral cavity. It has antiseptic properties, fights primarily against the herpes virus, but is nevertheless suitable for normalizing healthy microflora of the oral cavity.
- Also at the initial stage, Cholisal-gel . It is applied to the dried affected areas after rinsing. Procedures must be carried out at least four times a day.
- Dentists often prescribe anti-inflammatory ointments with an anesthetic effect, due to the pain inherent in aphthous stomatitis. Among the popular remedies are Kamistad , Clobetasol , Trasylol .
- Also popular anti-inflammatory and analgesic ointments are Xicaine and Benzocaine . Treatment with such ointments should not be long-term, as there are significant side effects. When using them, you must strictly adhere to the course.
- For rinsing in case of predisposition to allergies, use Diphenhydramine suspension .
- If signs of secondary infection appear, the use of antibacterial agents is recommended: Hexoral , Tantum Verde , Orasept .
- An effective remedy for combating canker sores is the balm Stomatofit-A , which consists of medicinal plants and an anesthetic. It is applied with a cotton swab directly to the sores. The action of the drug is aimed at reducing pain and inflammation.
- As soon as the ulcers resolve, it is worth continuing treatment with epithelializing agents that will restore the mucous membrane. Solcoseryl gel is prescribed as such a drug .
Antiallergic drugs
Treatment of allergic stomatitis is accompanied by the use of antihistamines. These include Diazolin, Claritin, Suprastin, Tavegil.
You can also use other medications to relieve allergy symptoms. Typically, the course of treatment with desensitizing drugs lasts 10-12 days.
Sanitation of the oral cavity
Aphthous stomatitis develops against the background of diseases of the gums and teeth, for this reason, during the treatment of ulcers, it is necessary to carry out complete sanitation of the oral cavity.
Eliminating foci of possible erosion on the mucous membrane will reduce the duration of stomatitis, and will also reduce the likelihood of its secondary occurrence.
It is especially important to carry out sanitation of the oral cavity, if this has not been done previously, in case of chronic stomatitis. The presence of tartar, caries, and pulpitis has a beneficial effect on the formation and development of aphthae.
Increasing local immunity
Fermented toothpastes are prescribed as local immunostimulating drugs. They should contain the following substances: lactoperoxidase, lactoferrin, lysozyme or glucose oxidase. These enzymes help increase the resistance of the mucous membrane and destroy bacteria and viruses.
You can buy Imudon lozenges. They are used six times a day, following a course of 10 days.
Good immunomodulators are: ginseng, echinacea, propolis, thymogen, immunofan. Don't forget about vitamins.
Signs
During an exacerbation, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- The appearance of severe pain in the epigastric region or in the area above the navel.
- The appearance of a discomforting sensation is characteristic mainly on an empty stomach, as well as at night, which occurs due to an increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. The pain usually decreases after eating.
- Unpleasant sensations radiate under the shoulder blades, to the area of the heart and back.
- Characteristic is the appearance of heartburn along with belching, bloating, nausea, vomiting, constipation, irritability, sleep disturbance, weight loss (even despite the patient’s good appetite).
During non-drug treatment, the patient needs to eat rationally. You should eat vegetables and fruits, as well as greens, and completely exclude fried, spicy and canned foods. As a rule, they recommend diet No. 5, steamed and boiled food in semi-liquid form. You need to eat often, in five small portions, excluding alcohol.
During drug therapy, medications are prescribed that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. Antisecretory medications may also be prescribed, and if Helicobacter pylori is detected, antibacterial medications are used. In some situations, due to the development of complications, surgical treatment may be necessary.
As part of prevention, you should pay attention to the nature of your diet; it should be balanced and nutritious; it is important to consume foods that are high in fiber, avoiding spicy, fatty and fried foods. Any intestinal diseases should be treated promptly.
Folk remedies
An ulcer has appeared on the side of the tongue - how to treat it if it is not possible to see a specialist? Traditional recipes are very effective in the treatment and prevention of sores on the tongue, regardless of their location.
And doctors themselves recommend treatment with folk remedies at the initial stage of the disease.
For example, for young patients aged 5 to 12 years, constant rinsing of the mouth with soda solution is recommended. It should be diluted in the following proportions: 1 teaspoon of soda should be diluted with 150 ml of warm water.
For an adult, it is also recommended to rinse using the following medicinal plants: chamomile, calendula, oak bark, sage, St. John's wort.
These decoctions are prepared as follows: add 1 tablespoon of medicinal herb to one glass of boiling water.
After which the infusion should stand for about half an hour. Next, you need to drain it using a strainer.
Then start rinsing. Do not store the decoction for more than 12 hours.
An ulcer has appeared. Also, cauterizing the wound site with ordinary brilliant green has an excellent healing effect. ulcer on the side of the tongue: how to treat it
To do this, generously moisten a piece of cotton wool with a solution of brilliant green and press firmly onto the ulcer.
It will help relieve pain and speed up the healing process of ulcers on the tongue by rinsing with freshly squeezed cabbage juice. To do this, squeeze fresh cabbage leaves in a juicer, then dilute it a little with boiled water, and then start rinsing at intervals of every four hours.
Treatment methods
Only a dentist can say for sure how to treat aphthous stomatitis. It is necessary to confirm the diagnosis; usually an external examination and collection of complaints are sufficient. Perhaps pimples on the mucous membrane are not aphthae; what they are will become clear after instrumental and laboratory examination.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with leukoplakia, cancerous tumors, soft tissue abscess - these pathologies even look similar in the photo. Blood tests and x-rays help confirm or refute the diagnosis; a biopsy is rarely prescribed.
Treatment begins immediately after the doctor is sure that pimples and erosions are really aphthae in the mouth; the causes of the pathology are determined at the initial consultation. To ensure that the patient does not have to re-treat with the same problem and regularly treat erosions, it is necessary to carry out sanitation and, if possible, eliminate somatic diseases of a chronic nature.
The general treatment plan for oral aphthae is as follows:
- In order to remove plaque from erosions, antiseptic solutions and rinsing with decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs are prescribed. The procedure should be repeated after each meal, in the morning and before bed.
- Quick and effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis involves the use of local therapy. Anti-inflammatory creams are applied to the affected mucosa; the products eliminate pain and swelling, increasing the patient’s quality of life. Anesthetic patches are a good alternative.
- If the causes of aphthous stomatitis are associated with a general infection, flu or cold, antiviral drugs in tablet form are indicated.
During the period of therapy, solid foods, as well as spices and other components that irritate the mucous membranes, are excluded from the diet. Hygienic procedures are difficult to carry out due to pain, but refusing to brush your teeth and mucous membranes is strictly prohibited. Patients are allowed to switch to soft-bristled toothbrushes; after recovery, they need to be replaced with new ones.
Dietary recommendations
The disorder is manifested by severe pain when touching the ulcers. For this reason, preference should be given to liquid and mushy foods.
Pastes, soups, purees, porridges are dishes with which you can create a completely balanced diet. You need to eat right, saturating the body with proteins, fats and carbohydrates, so that the immune system can provide full resistance to the disease.
During treatment, it is recommended to reduce the intake of salty, sweet, spicy foods. The surface of the oral cavity is already very inflamed; you should not overload your taste buds with work. Naturally, there can be no talk of alcohol.
Cabbage, carrots, potatoes, peaches, parsley, olives, sea buckthorn juice - all these are desirable foods that help improve immunity, restore healthy microflora and have an antibacterial effect.
Aphthous gastric ulcers
An ulcer in the stomach is said to occur when a deep defect forms on the inner lining of this organ, affecting the mucous and muscle tissues. The pathology can spread to the entire thickness of the wall. Such an ulcer can form in any part of the organ. Factors that lead to the disease:
- The influence of severe stress.
- The appearance of depression.
- Abuse of drugs or their use in large quantities (we are talking about glucocorticosteroids, antacids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, cytostatics, antihypertensive drugs).
- Immunodeficiency state (AIDS along with taking immunosuppressants).
- The influence of improper diet or eating habits (consumption of too hot or cold food in combination with irregular meals).
- Impact of hereditary factors.
- The presence of severe somatic diseases (in the form of tuberculosis, hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, pancreatitis, Crohn's disease).
- Stomach injury.
- The effect of any other organs on the stomach.
The main symptom of a stomach ulcer is pain, which is severe or can also be relatively mild. The occurrence of discomfort is usually associated with the intake of products. The time of onset of symptoms directly depends on the position of the ulcer. If it is located near the esophageal sphincter, then discomfort occurs almost immediately after eating, thirty minutes later.
Therapy
Until recently, the main method of treatment in this case was surgery. True, numerous progressive drugs have now been developed, and the disease is often treated in a conservative way. Since in most situations the development of pathology occurs in conditions of increased acidity, the basic task for any gastroenterologist is to reduce its level to an acceptable value. This function can be performed by antacids along with histamine receptor blockers and proton pump inhibitors.
More modern medications for the treatment of the disease are histamine H2 receptor blockers in combination with inhibitors. For example, Ranitidine acts on special cells located in the gastric mucosa, which stimulate acid production.