Classification
There are 3 types of this tumor in the liver:
- Tricky. They consist of several large vascular cavities filled with blood. Over time, the tumors increase in size up to 20 cm and can occupy the entire right lobe of the liver. Pathology requires mandatory treatment. Most often, the cause of this type of liver hemangioma is the pathology of the development of the organ. The tumor is accompanied by mild symptoms.
- Capillary hemangiomas in the liver. Pathology occurs frequently, in 20% of the population. These are tumors no larger than 3 cm in size. They rarely grow, so they do not manifest themselves in any way. Growth is diagnosed in only 15% of patients. Capillary hemangiomas in the liver consist of small vascular cavities filled with venous or arterial blood. The tumor can be fed from one vessel. It is difficult to detect during examination. More often, the appearance of a neoplasm is caused by pregnancy or taking extragenic medications.
- Atypical. This type is rare and often occurs in the absence of treatment. The tumor has a non-standard structure and is covered with keratinized tissue.
To detect the growth of hemangioma in time, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound examination once a year.
The active growth of capillary neoplasms is facilitated by the use of hormonal drugs and contraceptives.
Provoking factors that contribute to the increase in cavernous tumors:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- poisoning;
- hormonal imbalance;
- bruises and liver injuries;
- excessive physical activity;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking medications.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of the occurrence of the choroid plexus is the impact of external negative factors on the process of formation of the vascular system. The formation of capillaries, arteries and veins occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy. However, the exact reasons for this phenomenon have not been established, so scientists have identified provoking factors that can affect the formation of hemangioma. Provoking factors:
Female. It has been established that women are more susceptible to the pathological process. This is due to the level of sex hormones - estrogen.- Direct pregnancy. 80% of newborns have nodular choroid plexuses in the hepatobiliary system. With age, hemangiomas disappear, but about 2-3% remain without causing harm or discomfort. In the early stages of gestation, viral infections (ARVI) can have a detrimental effect on the process of formation of the vascular wall. In this case, nodular formations in the fetal liver are also possible.
- Taking hormonal drugs in the first trimester of pregnancy: steroids, estrogens and gonadotropins are taken to prolong pregnancy, but sometimes a “complication” of hormone therapy affects the condition of the gestating female fetus.
- Genetic predisposition. Despite the fact that the disease is not hereditary, there is a pattern to the development of the pathology. Thus, according to the study, the tumor was identified in children whose mothers have blood group II. In addition, isolated familial cases of benign liver tissue formation have been described.
Mechanical causes cannot be excluded, when an internal hemangioma has formed as a result of injury, blow or bruise.
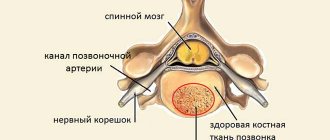
What is liver hemangioma and the causes of its occurrence?
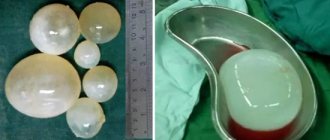
Strictly speaking, a hemangioma is a collection of vessels, which are flattened endotherial tubes separated by fibrous septa. Usually there is only one hemangioma on the liver; cases where there are several of them are quite rare.
The sizes of hemangiomas can vary from small formations on the liver measuring 2 mm to giants more than 20 cm. Upon superficial examination, the surface of a liver hemangioma can be either flat or bumpy due to subcapsular lesions (hematomas). One of the main signs of hemangioma is color; It is reddish-blue and is clearly distinguishable against the background of the surrounding liver tissue. Large tumors may be pedunculated. The right lobe of the liver is more susceptible to the formation of hemangiomas than the left.
Liver hemangiomas can be either cavernous (several large cavities with internal walls made of fibrous tissue) or, in much rarer cases, capillary (many small cavities, each of which contains a vessel). The latter are very difficult to diagnose - they are so small that they are not visible during examination.
The causes of liver hemangioma remain a mystery to doctors, although it is assumed that hormonal contraceptives and steroids can accelerate its growth (it is unclear, however, whether these drugs can contribute to its formation). It is also unknown whether there is a hereditary predisposition to the appearance of liver hemangioma; There is evidence, albeit rare, that several women of different generations in the same family had hemangiomas. Some scientists believe that liver hemangioma is a benign congenital hamartoma (tissue abnormality). Hemangiomas can either start in childhood or arise under the influence of still unknown factors.
Cutaneous hemangiomas are much more common in the liver; however, it is unclear whether they in any way influence the existence of their “sisters” in the liver.
Forecast
Such a pathology as liver hemangioma has a positive treatment prognosis due to the following aspects:
- Until modern times, there is no information about cases of degeneration of hemangiomas into malignant neoplasms.
- In the vast majority of patients, the tumor had absolutely no negative impact on the quality of life, that is, there were no restrictions on playing sports, the ability to bear children, or on choosing a profession.
- Patients who underwent the course of treatment describe the therapy as well tolerated and without complications.
- Health after surgery is restored quickly and fully.
Among the variety of tumors, there are liver hemangiomas - these are formations with which people sometimes live their entire lives, unaware of their presence. Doctors classify the pathology as a rare disease, despite the fact that it occurs in 7% of the world's population.
Article design: Mila Friedan
Symptoms
Typically, liver hemangioma does not have clear symptoms; it does not make itself felt for years and is detected by chance during ultrasound or laparoscopy due to other reasons. Small hemangiomas may never be found during the patient’s lifetime.
If the tumor reaches 4 or more centimeters, then approximately half of the patients may experience complaints. They must be interpreted with extreme caution, and only after a comprehensive examination can it be established whether the tumor really causes symptoms or whether the cause is in other diseases of the digestive system. In a third of patients, after surgery to remove hemangioma, complaints persist, which speaks in favor of the initial asymptomatic nature of the tumor formation.
The most common signs of a tumor are:
- Soreness;
- Feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- Nausea, feeling of fullness in the stomach, vomiting;
- Jaundice.
Usually the most characteristic symptoms are pain and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, associated with an increase in the size of the liver. The pain can be intermittent, usually it is aching and not intense. When hemangioma vessels rupture or thrombosis, the pain becomes acute, and the patient requires emergency medical care.
If the hemangioma is large and compresses neighboring organs of the abdominal cavity, then there are signs of dysfunction of the stomach or intestines (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain). Jaundice is possible if the bile ducts are damaged or the evacuation of bile from the gallbladder is impaired. When large vascular trunks are compressed, heart failure and swelling of the lower extremities develop when the inferior vena cava is compressed.
A long asymptomatic course of a hemangioma can result in its rupture and hemorrhage, then the first signs of the presence of a tumor will be acute abdominal pain and symptoms of shock (a sharp decrease in pressure, impaired consciousness and function of vital organs). Massive blood loss and irritation of the peritoneum from the gushing blood pose a threat to the patient’s life and require immediate medical attention.
In rare cases, with diffuse tumor growth, liver failure may develop, and giant nodes, in which a significant amount of blood accumulates, can provoke a blood clotting disorder, combined with thrombocytopenia, and DIC syndrome with its characteristic thrombosis and bleeding (Kasabach-Merritt syndrome) .
Causes
As we said, experts cannot identify specific causes, but they tend to identify the three most likely factors influencing the process of the occurrence of liver hemangioma. Among them are:
- Heredity The hereditary cause of liver hemangioma stems from the fact that very often this pathology is detected in childhood. Perhaps certain genes are passed from parent to child, or the new human body combines genes that cannot be found together.
- Hormonal background The disease is often detected in pregnant women, which may be evidence that hormonal levels directly affect the occurrence of hemangioma. It may also be that hormones affect not the formation, but an increase in the size of the tumor, which makes it easier to see.
- Mechanical damage Mechanical injuries in the area of the right hypochondrium can harm a person, causing the occurrence of hemangioma.
Recent scientific research suggests that disruption of the development of the human vascular system occurs even during its development in utero, when a person is still in the embryonic stage. Based on this, it can be assumed that the occurrence of hemangioma may be associated with a viral or infectious disease suffered by the child’s mother.
In order to accurately determine the mechanism of the appearance of hemangioma, it is necessary to conduct a more detailed examination, which may shed light on the probable cause of this pathology.
More than 20% of the world's population is susceptible to hemangioma.
Development in children and pregnant women
It is not easy to detect such a tumor in children. Usually, immediately after the birth of a child, he is prescribed an ultrasound scan, which should not be refused. It is during this examination that such a formation can be seen. If we talk about external signs, doctors note the presence of choroid plexuses, this may indicate the same growths in the liver.
It is important to control the growth of the tumor in the first months of the baby’s life, since during this period the hemangioma can quickly increase in size or disappear completely. If the formation has increased significantly, the doctor will even be able to detect it by palpation.
Signs that occur during intensive tumor growth in a child:
- yellowness of the skin;
- hemorrhages inside the body and bleeding;
- liver or kidney failure;
- the patient feels unwell, crying, sleep disturbance;
- Digestive problems.
In such a situation, the disease can threaten the child’s life, so it is urgent to begin a thorough diagnosis and treatment. When the formation becomes large, it will not be possible to save the child’s life without surgery. You should not refuse surgical intervention, since the complications that arise are extremely dangerous.
Complications in children:
- Organ rupture.
- Massive internal bleeding.
- Sepsis.
- Heart failure.
- Hemangioma changes its properties according to the type of malignant tumor.
- Arterial thrombosis and necrotic changes in tissues.
- Death.
When a baby is diagnosed with such a formation in the liver, parents should constantly monitor its size, conduct an ultrasound in a timely manner and consult a doctor. If the hemangioma begins to grow, surgery will be suggested.
For a pregnant woman, such a diagnosis can also become a serious problem. Even if the tumor has not previously manifested itself, during the period of bearing a child its growth may begin, which is triggered by changes in hormonal levels. In such a situation, the expectant mother experiences a large number of unpleasant symptoms, indicating that the woman needs urgent help.
Signs in pregnant women:
- attacks of vomiting and nausea;
- bloating, intense gas formation;
- loss of appetite;
- the appearance of heartburn;
- liver enlargement;
- stool disorder;
- weakness, severe fatigue;
- the color of the stool changes to darker;
- urine takes on a red tint;
- hemoglobin level decreases;
- The eye sclera turns yellow.
The treatment methods used in such cases are not suitable for a pregnant woman, so she is prescribed a strict diet and other lifestyle recommendations.
During this period, doctors closely monitor the growth of the tumor. If the hemangioma increases, then a decision is made on the treatment method most suitable for such patients. Complications of this tumor that occur during pregnancy can be severe, from rupture of the tumor to peritonitis, sepsis, and heart failure.
What it is
Liver hemangioma is a formation in the human gland, which consists of vessels and vascular cavities, intertwined with each other in a loose manner and filled with blood. Typically, such a tumor is quite small in size, but sometimes it can develop, gaining more and more volume.
Such a tumor is often a congenital developmental defect and does not cause the patient virtually any discomfort. Statistics show that liver hemangioma occurs more often in women - this occurs 6-8 times more often than in males. Since this disease has not been fully studied, it is impossible to fully answer the question about the reasons for the appearance of this anomaly; we can only assume possible options, which we will talk about later.
Liver hemangioma according to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) belongs to the class Neoplasms, group Benign neoplasms, with code D18. This code records all hemangiomas and lymphangiomas of any location in the human body.
The detection of such a pathology often occurs by accident, since the symptoms of the disease may be mild or completely absent for many years. This is due to the very slow growth of the tumor.
Diagnostics
How is a liver tumor found? By chance, if the process occurs without symptoms, or with the help of various instrumental methods, if the person begins to complain. So, most likely, the patient's path will be like this:
- First, he will be sent to the laboratory, where he will undergo a general blood test, determine the activity of liver enzymes (AlT, AST), the level of bilirubin and other indicators that will interest the doctor;
- The next step will be a trip to an ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the abdominal organs, where the doctor, having discovered signs of liver hemangioma, will recommend clarifying the diagnosis by conducting additional examination (CT, MRI);
- CT (computed tomography), which has several advantages over ultrasound, and/or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), which has high sensitivity and specificity, usually completes the diagnostic search;
- Angiography is rarely necessary, unless CT and MRI could not give a clear answer to the exciting question.
If a hemangioma is suspected, a liver biopsy is usually not performed: there is no urgent need for it, and, moreover, such a procedure can lead to a life-threatening complication - massive bleeding.
Proper nutrition
Most often, for liver hemangioma, nutrition and diet according to Pevzner are recommended, which in gastroenterological practice is better known as dietary table No. 5. This diet is based on limiting the consumption of fats, salt, purines, coarse fiber, oxalic acid, as well as products that contain extractives that stimulate the production of digestive enzymes. All drinks and dishes are recommended to be consumed warm; the diet should be based on vegetarian and dairy first courses that do not contain tomato and sorrel. The dishes can also be baked and stewed.
Fried foods should be completely excluded from the diet, as well as:
- rich broths;
- semi-finished products;
- red meat;
- sausages and smoked products;
- fatty dairy products;
- canned food;
- fatty fish and caviar;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- radishes, ginger, white cabbage, sorrel, spinach;
- corn grits;
- bread products made from wholemeal flour;
- ice cream;
- chocolate;
- marinades;
- bakery.
As for drinks, it is undesirable to consume concentrated juices, coffee, green tea, alcohol, and sweet carbonated drinks.
Separately, it is necessary to say about restrictions in sports. If there is a hemangioma in the liver, it is not recommended to engage in sports that involve impacts - martial arts, boxing and others. But moderate activity is still required. It is important to maintain normal vascular tone and heart rhythm.
How to treat?
Treatment of liver hemangioma is not required if the tumor is small. When it grows, serious symptoms may occur, which require surgical removal of the tumor to eliminate.
The following criteria serve as indications for surgery:
- hemangioma of the right lobe of the liver, as well as its superficial location;
- the tumor begins to put pressure on the internal organs and continues to grow;
- the neoplasm can infect the main veins of the liver.
When hemangiomas in the liver are localized on both lobes of the organ, but surgery is prohibited.
Effective medicines
The essence of this therapy is to take hormonal drugs. The dosage and duration are determined individually by the attending physician.
The following non-surgical methods can be used to treat hemangiomas on the liver:
- Microwave radiation;
- radiotherapy;
- exposure to a laser beam;
- use of liquid nitrogen.
Forms and symptoms
Liver hemangioma is a disease that, based on its origin, is divided into 2 forms:
- Cavernous they look like several to dozens of large cavities collected together, which are surrounded by a membrane of fibrous tissue. This form is most often diagnosed.
Liver hemangioma can develop into cancer
- Capillary formations consist of a large number of small cavities containing areas of blood vessels. This form is difficult to identify, since the tumors are quite small in size.
Cavernous hemangioma
The signs of neoplasms depend on their size: the larger the benign tumor, the more noticeable the symptoms. When the hemangioma is up to 4 cm in diameter, 40% of patients have complaints.
If a pathology measuring 10 cm is observed, then the number of patients with symptoms increases to 90%. Although, along with benign tumors in such cases, other diseases of the internal organs are diagnosed.
Signs of cavernous hemangioma of the liver can include:
- the appearance of a jaundiced complexion and mucous membranes;
- an increase in the size of the liver gland, which can be determined by palpation;
- digestive disorders in the form of nausea, vomiting, bloating (flatulence);
- aching pain on the right side of the body under the ribs;
- the appearance of a feeling of pressure on internal organs.
Pain in the liver with hemangioma can be caused by thrombosis and hemorrhages when the tumor compresses other organs. All these symptoms indicate the presence of changes in the structure of the liver, which lead to its destruction.
Capillary hemangioma
This form of pathology, as a rule, does not cause any inconvenience to a person and is tolerated without symptoms. Capillary hemangiomas are detected accidentally during routine preventive examinations, and sometimes during autopsies after death.
The fact of accidental detection of a tumor can only cause psychological discomfort. Here you should set yourself up that the education is benign and you can live with it calmly until the end of your days.
Diet for liver hemangioma
For this type of disease, a strict diet is not required, but many doctors recommend eating in accordance with “Table No. 5.”
It is necessary to get rid of “heavy foods” in your daily diet, eat less fatty, fried, smoked, canned and salty foods. In addition, you need to give up ice cream, carbonated drinks and strong coffee. Spicy dishes are completely excluded. Fresh vegetables and fruits should be consumed regularly. Beets, carrots, strawberries, and citrus fruits are especially beneficial for liver health.
Dairy products, fish, and animal liver are also necessary, which are rich in vitamin B12, which plays an important role in the normal functioning of the liver.
Types and stages
Often, the development of hemangioma occurs in the right lobe of the liver. It has a fairly dense but elastic structure, a round or slightly elongated shape, and is also colored red. In accordance with the structural units of the tumor, hemangioma is divided into two types:
- Capillary
Capillary hemangioma is distinguished by the fact that it often forms several small tumors. Each of them is filled with blood inside. That is why each individual neoplasm often feeds one of the organ’s vessels - a vein or artery. The diameter of the capillary formation in rare cases exceeds 20-30 millimeters.
- Cavernous
Cavernous hemangioma is a separate formation connected to each other by a network of vessels. Between them there are small vascular walls that fence off adjacent cavities. All of them are filled with blood and can reach enormous sizes - often they increase to more than 20 centimeters. That is why they can completely replace one of the livers or even go bankrupt. In the early stages, the disease proceeds according to its standard development scenario, but in the later stages the tumor can sometimes turn into an atypical liver hemangioma. Its peculiarity is its non-standard structure, since all cavities with blood, which are part of it, have keratinized particles at their edges. This change can happen for two reasons:
- as a result of a person suffering from a somatic illness;
- due to the formation of scar tissue against the background of inflammation.
To ensure that the hemangioma does not develop into an atypical tumor, it is necessary to periodically monitor its development and growth.
Traditional methods
In combination with the main treatment for hemangioma in the liver, it is allowed to use effective folk remedies. Sometimes with their help it is possible to avoid surgical treatment of hemangioma on the liver. Therapeutic measures using folk remedies involve the use of the following recipes:
- Oat drink. You need to take 250 g of oat seeds and place them in a container. Add a liter of water, bring to a boil and wait 12 hours. Afterwards you need to filter and take 100 ml 3 times a day. This therapy for hemangioma in the liver with folk remedies lasts 1.5 months.
- Herbal collection. Treatment of hemangioma on the liver with the presented folk remedies involves taking 15 g of black root leaves, tansy and yarrow flowers. Add to them 30 g of cat's purse grass, St. John's wort, celandine, cherry, plantain. Place all the herbs in a container and add 45 g of coltsfoot leaves. Take 3 small spoons of the mixture and add 500 liters of water to it. Bring to a boil, strain, strain the broth into 4 parts and use 4 times throughout the day. Therapy for hemangiomas in the liver with the presented folk remedies lasts 21 days.
- Lime tea. Take the infused drink every day for 60 days. Treatment of hemangiomas on the liver with such folk remedies should be carried out once every 60 months.
- Potatoes in the treatment of hemangioma on the liver. It is necessary to remove the skin from two or three potatoes, and then consume 3 times throughout the day in the form of 20 g. Gradually, it is necessary to increase the amount of potatoes consumed to 150 g. This treatment of hemangioma in the liver with folk remedies should be carried out 30 minutes before meals.
- Sagebrush. A tincture prepared from this herb has a positive effect on the body in case of hemangioma in the liver. This product is sold ready-made. Take 12 drops 3 times throughout the day. The therapeutic course usually lasts 2 months. To effectively eliminate the manifestations of hemangioma in the liver, you need to complete 3 such courses.
Why is hemangioma in the liver dangerous?
If the tumor grows rapidly, there is a threat to both the liver and the entire body as a whole. Complications that may occur with hemangioma in the liver may be as follows:
- bleeding due to injury to the affected organ;
- worsening blood clotting;
- vascular thrombosis, leading to organ death;
- jaundice;
- ascites;
- abdominal dropsy;
- inflammatory process;
- liver failure;
- heart failure;
- compression and displacement of internal organs;
- transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant one.
Liver hemangioma during pregnancy can also be accompanied by a number of complications. While carrying a child, a woman's estrogen level increases, which can negatively affect the tumor - it can begin to grow. If the cavity structures of the tumor rupture, then the risk of fetal death is high. If you have this disease, you should approach the issue of childbirth very responsibly; a caesarean section may be required.
Operation
Surgery to remove a hemangioma is dangerous due to the likelihood of bleeding, since intervention in the tangle of blood vessels is required. It is done in the following cases:
- large sizes - over 5 cm;
- compression of neighboring organs;
- the need for hormone therapy;
- high growth rate;
- planned pregnancy;
- feelings of discomfort;
- danger of rupture due to injury.
It is easier to remove a tumor that is located on the outer surface of the liver. This organ has the peculiarity of being completely restored, even after a large part has been cut out. The following operation behavior options are possible:
- the vessels are removed, while the organ tissue can be preserved;
- the lobe of the liver with affected venous formations is excised;
- in case of cavernous form, an incision is made and the vessels located inside are removed.
Treatment
Often, with liver hemangiomas, doctors recommend an observation regime. It consists in the fact that the patient needs to periodically undergo a complete examination to monitor the growth or degeneration of the formation. This tactic is quite correct, since the tumor may not increase in size at all, which is why it may not cause any harm to the patient for years, or even decades. In this case, ultrasound examination is often prescribed once a quarter. Additional diagnostics will also need to be carried out in cases of any injury, since the structure of the hemangioma is quite vulnerable.
If the tumor grows to a size of more than 5 centimeters and also begins to pose a danger to the functioning of other organs, surgical intervention is indicated. This is due to the fact that the larger the volume of the formation, the higher the chances that it can rupture or affect the functionality of the liver itself and neighboring human organs. The essence of the operation is to remove the hemangioma, including all its structural units, if it is multiple.
If the tumor ruptures for certain reasons, the patient must immediately undergo appropriate surgical intervention. This is important because disruption of the hemangioma membrane creates a risk to the patient’s life. This process can be fatal. Irreversible consequences may also be due to the fact that tumor rupture leads to rupture of the liver itself.
Cases of degeneration of liver hemangioma into a malignant formation have not yet been recorded. But theoretically this is possible, as with any other neoplasm in the human body. Therefore, it is extremely important to be extremely careful, especially when there are problems with hormonal levels. The amount of estrogen in the blood can significantly affect the normal development of hemangioma.
Today, this disease is not considered dangerous, since most patients live with it for the rest of their lives for many decades without experiencing any problems with the liver. But due to certain risks, you should always treat hemangioma with caution, carrying out periodic diagnosis and treatment, if required.
Liver hemangioma is not recommended to be treated with folk remedies, however, with constant monitoring and with the permission of a doctor, this is still possible. In this video you will learn several homemade treatment recipes.
How to treat liver hemangioma that cannot be removed?
There are cases in which it is technically difficult to remove the tumor, doubts arise about the degree of risk, and there are concomitant diseases in older people. In such cases, radiation therapy is prescribed.
If radical surgery is not possible, it is recommended:
- sclerosis - administration of a drug that causes the proliferation of fibrous tissue;
- embolization of the artery feeding the tumor is carried out by introducing a catheter with a special preparation of gel consistency made of polyhydroxyl methacrylate, the technique disrupts growth and leads to a decrease in formation.
There is a method of creating a high-frequency electromagnetic field in the hemangioma area, in which the temperature rises, which leads to the death and splitting of tumor tissue. In all cases, you should carefully approach your dietary intake. It is necessary to prevent stress on the liver and disruption of its functioning.
Liver hemangioma on MRI, ultrasound and computed tomography
In this case, consultation with a gastroenterologist without preliminary diagnosis is of little use, since in most cases hemangioma has no visible signs and can only be detected during various types of diagnostic measures. Examinations that allow you to see a hemangioma and determine its diameter are:
- ultrasonography. Liver hemangioma on ultrasound is often noticeable in the liver parenchyma in the form of a round formation with heterogeneous contents and clear contours;
- MSCT of the abdominal cavity;
- hepatoscintigraphy is a method that allows you to examine soft tissues for malignancy. A biopsy for this diagnosis is prohibited, since damage to the tumor can cause massive internal bleeding, since the tumor itself consists of blood vessels;
- MRI and CT scan of the liver and biliary tract. These studies allow us to see the tumor more accurately from different angles. Before these examinations, the patient must be injected into a vein with a special drug - contrast, since liver hemangioma on CT with contrast is outlined more clearly, and the chance of confusing it with another neoplasm is significantly reduced.
Doctors at the Yusupov Clinic are constantly improving their skills, which allows them to stay up to date with the latest methods for studying liver diseases. Our doctors are competent and attentive to drawing up a treatment plan for each patient, because only an individual approach to recovery gives the expected results.
Complications
Without treatment, the pathology can cause serious complications. The risk is highest with multiple processes. Patients develop:
- liver rupture with internal bleeding;
- intestinal bleeding from the biliary tract (hemobilia);
- hepatitis;
- liver cirrhosis with liver failure;
- jaundice;
- severe ascites;
- torsion of the leg of the knot;
- necrosis and abscessation of the tumor;
- chronic heart failure;
- displacement of compressed internal organs;
- thrombosis of the abdominal veins;
- Kasabach Merritt syndrome - a disorder in the coagulation system with a drop in platelet levels, intravascular thrombosis;
- malignant degeneration and metastasis.
Types of removal operations
Removal of liver hemangioma is carried out in the following cases:
- the tumor is more than 5 cm in size;
- there is pressure on neighboring organs;
- the patient has severe pain;
- A blood vessel ruptured, resulting in bleeding.
There may be contraindications for surgical intervention:
- the tumor has grown into the liver vessels;
- the pathology is combined with cirrhosis;
- the tumor is located in two lobes of the organ.
Embolization of liver hemangioma is one of the types of treatment for pathology. The tumor receives nutrition from a large vessel, so if it is blocked, the formation will resolve. The procedure involves introducing a certain substance into the circulatory system. When sclerosing the vessels, polyvinyl alcohol is injected into the tumor, which helps stop the growth of the tumor.
Microsclerotherapy is prescribed for the treatment of formations no more than 2 mm, echosclerotherapy is used for deep veins, the foam method is prescribed for large arteries and veins.
If there are contraindications, the following methods of treating the disease are used:
- Radiotherapy. This is a fairly old method in which the neoplasm is exposed to radio rays, stopping its growth.
- Removal of liver hemangioma with laser. The laser beam heats the vessels, as a result of which they stick together and the tumor loses the ability to feed from the artery.
Prevention
Preventive measures in this case include:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- It is not recommended to use medications containing hormones—estrogens—on your own without a doctor’s prescription;
- prevent liver injury;
- systematic observation by a medical specialist if there is a suspicion or an existing predisposition to the development of hemangiomas.
If you suspect liver disease, you should promptly seek medical advice. The doctor will conduct the necessary examination, prescribe tests and examinations, on the basis of which he can make a diagnosis, prescribe adequate treatment and outline a further plan for monitoring the health condition.
Hepatitis C: first signs and treatment regimen Rectal cancer Lung cancer Fatty liver hepatosis: symptoms and treatment Cirrhosis of the liver Uterine fibroids
Hemangioma on the liver - possible complications
A benign liver tumor, hemangioma, rarely causes serious complications. The only serious complication is rupture of the hemangioma vessels, and subsequent hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity. This only applies to a very narrow group of patients with lesions larger than 10 cm in diameter. To control the bleeding, immediate surgery is required, followed by removal of the liver growth if possible. Symptoms indicating rupture of a hemangioma:
- severe, growing pain that does not go away despite taking painkillers;
- fever;
- disturbance of consciousness;
- sweating and pale skin.
If such symptoms are detected, you should immediately call an ambulance.
A healthy diet is very important for the liver
Morphological types of benign vascular tumors
According to the structure and characteristics of tissue changes in benign vascular nodes, the following options are distinguished:
- Hemangioendotheliomas - arise from the endothelium (inner lining of the vessel);
- Capillary - a cluster of capillaries (sinusoids) separated by partitions;
- Cavernous - a vascular tangle with localization inside the organ;
- Racilic;
- Lymphangiomas - from lymphatic vessels;
- Hemangiomatoses are a complex of vascular changes.
The focal node is morphologically presented in the form of a bluish elevation, soft density, with smooth or lumpy contours. The average size is 1-2 cm. Nodes in the liver sometimes reach 5 cm. Under the influence of hormones during pregnancy, angiomas “grow” up to 10 cm.
Causes of hemangioma
Hemangioma is formed due to impaired formation of blood vessels during human embryonic development. Therefore, doctors and scientists still cannot decide on the question: “What is a hemangioma: is it a tumor or an intrauterine pathology?”
It has also been proven that liver hemangioma in infants can suddenly disappear, and this occurs quite often (in 80% of cases of the disease). Naturally, this fact is recorded if ultrasound monitoring is regularly carried out until the newborn is 3 months old.
By the way, hemangioma often forms in female infants; scientists suggest that this is due to the direct effect of estrogens on tumor growth.
Prevention and prognosis
If the tumor is small, stable, and not prone to enlargement, the prognosis is favorable. After surgical removal, if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations and is not examined regularly, there is a risk of relapse. There are no preventive methods to help prevent pathology in adults. To avoid the intrauterine formation of neoplasms, during pregnancy it is important for a woman to follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, eat right, and not take heavy medications without a doctor’s prescription.
What, where and when
Cavernous hemangioma of the liver is a type of pathological vascular neoplasm, locally located in the main functional tissue of the liver, consisting of cells of the hepatic plates. Tumor cells do not develop into pathological malignancies. The disease has an ICD-10 code – D18. However, not all medical scientists consider this pathology to be a tumor. Some are of the opinion that this is an abnormal proliferation of blood vessels, a pathological vascular tangle. The danger lies in the rapid proliferation of cells, followed by perforation, leading to death. Vascular rupture is caused by dangerous injuries and excessive tension in the abdominal cavity.
Foci of tumor localization
It is located inside the liver, can be localized in the left or right lobe, and can affect the entire organ. A hemangiomatous blood node appears locally followed by proliferation. At the beginning of the disease, the tumor is small, no more than 5 cm. Then, if no treatment is carried out, it reaches gigantic sizes and threatens to rupture when the tumor vessel is damaged and severe internal bleeding occurs. The formation also brings physical discomfort if it compresses nearby tissues, leading to constant aching severe pain.
When and why does the threat arise?
The etiology of hemangiomas is discussed by medical scientists throughout the entire period of observation of the disease. Some scientists suggest that this is an acquired disease. The main group of doctors proves that the etiology of the described type of formation is congenital.
Cavernous hemangioma in the liver
Cavernous hemangioma in the liver can form in the early stages of pregnancy, at the time of formation of blood vessels. Reasons: during formation, a systemic failure of fetal development may occur, expressed in the pathology of liver tissue. The disease is acquired mainly by women under the influence of the hormone estrogen, if it increases compared to the norm. 7% of the population is diagnosed with cavernous hemangioma of the liver. The outcome of the disease can be fatal if the tumor is not detected in time and treatment is not started!
Treatment of cavernous tumor
Doctors have still not decided whether to treat hemangioma and how to do it.
Cavernous neoplasia is benign and practically does not degenerate into oncology. In the absence of disease symptoms and complications, the tumor does not require special treatment or surgery. The only recommendation in this case is to monitor changes in your health, reduce physical activity and constantly visit a doctor. Women should be especially careful about hemangioma. Pregnancy or the use of hormonal drugs can trigger the growth of neoplasia.
If symptoms of hemangioma appear, its rapid development or complications, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
There are no conservative methods of therapy to get rid of hemangioma. The main and most effective remedy is still surgery. Surgical removal is necessary in the following cases:
- the tumor begins to interfere with the work of nearby organs, squeezing and pinching them;
- tumor size exceeds 5 cm;
- neoplasia is constantly increasing, acquiring alarming proportions;
- there is a sharp pain in the abdomen, nausea, loss of consciousness. These signs indicate a possible rupture of the hemangioma.
If alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Treatment with folk remedies is inadmissible and dangerous.
In all these cases, urgent hospitalization is required. In case of extensive bleeding, emergency surgery is very dangerous and can be fatal. In inoperable cases, the bleeding is first stopped by squeezing the hepatic artery. Then, after the patient’s condition has stabilized, surgery is scheduled.
Relative and absolute indications for hemangiomas surgery
Conditions for which surgery is required:
- Formation of blood clots (thrombi) inside the vascular dilation. When migrating through arteries, the likelihood of death increases due to the risk of blockage of the pulmonary artery. The addition of a bacterial infection increases the likelihood of sepsis (spread of microbes through the blood);
- Obstructive jaundice is a violation of the secretion of bile through the ducts due to an obstruction (stone, hemangioma, polyp).
Relative indications for surgery:
- Pain syndrome of the right hypochondrium;
- Localization near the porta hepatis;
- Concomitant changes in nearby organs.
Nodules larger than 8 cm do not cause clinical signs. Surgery is performed only if complications are likely.
Before resection of hepatic segments, the likelihood of additional intervention on the vascular-secretory pedicle is assessed. In some patients, the pathological process spreads to the great vessels and provokes concomitant complications from the gallbladder, intestines, and diaphragm.
Features of conservative treatment of vascular formations
A small liver hemangioma, treated conservatively, does not lead to complications. With hormonal therapy in women, the likelihood of tumor growth increases. Individual therapy is based on the use of laser or microwave radiation, radiofrequency pulses, electrocoagulation, cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen, and electric current.
Conservative procedures require courses of a certain duration. The effectiveness of therapeutic manipulations of a diet with the limitation of irritating foods - coffee, alcohol, spirits, smoked foods, chocolate, soda - increases the effectiveness.
We recommend reading:
Treatment of burns with boiling water at home
Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out at regular intervals over a long period of time.
European specialists are developing adaptive technologies aimed at preventing dangerous complications. Not only pharmaceutical drugs are being developed, but also effective immune stimulants.
Tablets to prevent stimulation of the release of special substances that provoke the growth of the vascular wall were developed by oncologists. They are prescribed only when special compounds are identified near hemangiomatous tissues.
Diagnostic capabilities
Unlike external hemangioma, liver hemangioma may not initially manifest itself and be diagnosed by chance. It is detected during ultrasound or tomography of internal organs. A person can live to adulthood and not suspect that they have the disease.
The presence of cavernous hemangioma of the liver in children can be detected in the maternity hospital. As already mentioned, indications for examination should be a large number of external vascular formations, liver symptoms, and hereditary predisposition.
Ultrasound or tomography allows you to determine what it is, the location and size of the hemangioma, and monitor changes in its size.
As a rule, cavernous hemangioma is a single formation; extremely rarely there can be several of them. Tumor sizes up to 5 cm are considered small.
If necessary, an angiographic examination is prescribed, using X-ray contrast to give a complete picture of the condition of the tumor vessels.
Biopsy is not used as it leads to bleeding.
Treatment of liver angioma
When liver hemangioma is small and asymptomatic, no treatment is required. The doctor's only advice in such situations is to undergo periodic examinations to monitor the size of the benign tumor: this precaution is necessary because usually hepatic angiomas tend to grow in size.
On the other hand, when the liver angioma is large and causes severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, surgery is usually required.
Possible procedures
Liver hemangioma can be treated, depending on where it is located and what structure (one or more), in the following ways:
- Surgical intervention is limited only to removal of the angioma . If diagnostic images show that the tumor mass is not too deep, you can limit yourself to removing only the angioma, without touching a large part of the liver. The surgeon may use laparoscopy , a minimally invasive surgical technique that typically requires 2 or 3 small incisions, or laparotomy , a much more invasive surgical technique than the previous one, in which the patient's abdominal cavity is cut through and "opened up." Both intervention methods require general anesthesia.
- Surgery to remove part of the liver affected by hemangioma . If the angioma is in an awkward and deepened position, the affected part of the liver should also be removed. As in the previous case, the surgeon can perform this operation by laparoscopy or laparotomy.
- Surgery to interrupt blood flow to treat angioma . By interrupting blood circulation in the arterial vessels that supply the tumor mass, the angioma stops growing and undergoes necrosis (note: without receiving blood containing oxygen, the cells that make up the benign tumor die). This operation can be performed in two ways: either by ligating the arteries or by embolization . In both cases the fundamental principle is the same, i.e. blocking blood flow directed to the angioma; the only difference is that during ligation, the surgeon “ties up” the arterial vessel, and during embolization, he introduces coagulants that stimulate the formation of blood clots.
- Liver transplant . This is a surgical operation to replace a diseased liver with another healthy one, taken from a living or dead donor. This intervention is intended for cases of very severe liver angioma, characterized by large and multiple tumor formations.
- Radiation therapy . The operator tries to reduce the size of the tumor mass by exposing it to a certain dose of high-energy X-ray radiation. This therapeutic option is used very rarely, not least because it is not clear what long-term consequences it may cause.
Symptoms and signs
When the tumor is small, there are no symptoms or signs. The neoplasm is most often discovered accidentally. If the tumor grows to five or seven centimeters, then the manifestation of the disease will be the appearance of minor pain in the right hypochondrium. When the tumor size is ten centimeters, vivid symptoms appear.
We recommend reading Intramural uterine fibroids - causes, signs, treatment
The main symptoms of liver hemangioma with which people go to the doctor are the following:
- painful sensations, mainly in the right hypochondrium, which are dull and aching in nature;
- sensations of constriction in the stomach, duodenum and all adjacent structures;
- dyspeptic symptoms - diarrhea, bloating, nausea, vomiting, heaviness in the stomach even after eating a small amount of food;
- jaundice and its signs - discolored stool, concentrated urine, yellowing of the skin and sclera.
Occasionally, sudden intense pain may occur, which may indicate tumor infarction, necrosis, or bleeding. In case of such pain, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible; it is best to call an ambulance. Basically, symptoms and treatment depend on the morphological appearance of the tumor and its size.
Treatment tactics for liver hemangiomas
Surgical treatment is carried out for large lesions that lead to clinical symptoms and pressure on surrounding organs. A contraindication to intervention is cirrhosis of the liver, in which the only solution is an organ transplant.
Due to difficulties in selecting donor livers, the intervention is only available to a limited number of patients who are lucky enough to receive an HLA-matched donor liver.
What surgical interventions are performed for hemangioma:
- Removal of the edge (marginal resection);
- Enucleation (excision of the source of vessel growth);
- Segmental resection – removal of only the affected liver segments (segmentectomy, bisegmentectomy, trisegmentectomy).
A common manipulation is sclerosis of individual areas. The manipulation involves the introduction of a sclerosing agent through a needle directly into the node. At the initial stage, the artery is ligated. Then sclerosing suspensions and ferromagnets are introduced.
Emergency surgery is performed when there is bleeding from a ruptured vessel. Without qualified help, death occurs. It is difficult to diagnose the condition without an ultrasound, so in case of anemia an ultrasound scan is mandatory.
Symptoms of the disease
Detection of hemangioma is complicated by the fact that the organ cannot respond with pain to the appearance of a neoplasm in the organ. The pathology occurs for a long time without any symptoms, and only when the tumor reaches a critical size does the body begin to signal about the existing problem as follows:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea and vomiting;
- enlargement of the liver, which can be detected by palpation of the organ.
If these signs are present, the patient needs urgent hospitalization, since strong pressure inside the organ, which in turn puts pressure on neighboring ones, can lead to rupture of the hemangioma and fatal bleeding.
Classification of cavernous hemangiomas
In medicine, hemangiomas are usually classified depending on their location. Formations can be: skin, musculoskeletal, parenchymal organs.
Cutaneous cavernous hemangiomas (eyes, lips, face) differ in their location on the epidermis. Sometimes the doctor may suggest not to touch them, the only exception being those tumors that have appeared on the neck, face, or genitals.
Cavernous hemangiomas of parenchymal organs are those that form in the organs:
- brain;
- ovaries;
- spleen;
- esophagus;
- uterus.
Formations also appear in the gonads and liver. They can be life-threatening and require immediate initiation of therapy. With hemangioma of the liver, the filtering organ weakens, and there is a threat of developing severe liver diseases, including the appearance of cirrhosis.
Hemangiomas of the musculoskeletal system cause the patient no less problems than other types of similar neoplasms. If we are talking about a child, the neoplasm grows much faster than the skeleton.
In medicine, there is another classification, namely by the type of blood vessels that change during the development of hemangioma: capillary, arterial, venous. Capillary hemangioma appears in 90% of all cases. There are situations where hemangioma resolves over time without medical intervention.
Treatment methods
If a tumor is newly detected and does not exceed five centimeters in size, the patient is recommended to have a repeat ultrasound examination after three months. If the diameter of the formation has not changed, dynamic monitoring is established with ultrasound every six months. If an increase in cavernous hemangioma of the liver is detected, treatment is required.
Medication
Drug therapy is not particularly effective and is symptomatic. Painkillers and hepatoprotectors are used. Women may be prescribed hormonal drugs, since hemangioma increases under the influence of estrogen.
Operational
The need for surgical intervention is observed in 10% of patients. Indications for the operation are:
- intensive growth of hemangioma;
- the size of the neoplasm is more than 7 cm;
- compression of neighboring organs by the tumor;
- severe symptoms that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods;
- pregnancy planning.
There are two types of surgical interventions, differing in the extent of organ removal.
- Palliative. The purpose of this operation is to cut off the blood supply to the tumor so that it decreases in size. It is carried out when it is not possible to remove the hemangioma itself.
- Radical. Aimed at removing the tumor, they are carried out by cutting out part of the liver (resection), or removing the tumor from the capsule (enucleation).
Palliative methods are preferred because they minimize the amount of intervention while preserving the maximum amount of functioning liver tissue. This treatment is carried out using the following methods:
- ligation of blood vessels;
- embolization (blockage) of the vessel feeding the tumor;
- hardening of the arteries, that is, the introduction of a special substance into them that promotes their adhesion;
- laser cauterization;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen.
Attention! Unfortunately, such interventions are not always possible, which is why radical operations are also performed.
Urgent surgery
Urgent surgical intervention is necessary in case of complications, especially when the tumor capsule ruptures and, as a consequence, bleeding occurs. In this case, the bleeding is first stopped with simultaneous infusion therapy to replenish blood loss. Then, if possible, the tumor itself is removed.
Contraindications for surgery
Surgical treatment has some contraindications:
- formed cirrhosis;
- damage by hemangioma of the inferior vena cava;
- severe heart pathology;
- severe jaundice;
- blood clotting disorder.
In such situations, only conservative therapy and constant monitoring by a doctor are possible for timely action if the condition worsens.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies is possible for small tumors and only as an auxiliary treatment.
- Grind coltsfoot and St. John's wort herbs. Mix a tablespoon of raw material and pour 250 ml of boiling water. Let it brew for 60 minutes. Take a glass during the day – treatment course is 21 days.
- Grind wormwood leaves. Place in a glass container and add alcohol in a ratio of 1:10. Infuse the product for 20 days. Then strain and store in a dark place. Take 12 drops before meals. The tincture should be treated for at least 40 days.
- Take 200 g of unpeeled oats. Pour in 1000 ml of water and let stand overnight. Then boil and leave overnight. Strain, add 1000 ml of water. Take 50 ml before meals. The treatment course is 45 days.