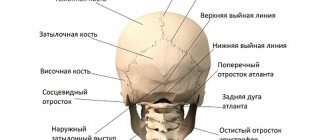
Often this disease develops as a result of brain injury.
In modern society, great attention is paid to the problems of preventing cardiovascular diseases and oncopathology, but the specific growth of injuries continues to grow steadily and is catching up with common diseases by leaps and bounds. In the pursuit of civilization and urbanization, humanity is losing its best representatives - young people, since the number of road accidents is simply in the nature of some kind of epidemic of the twenty-first century. The first place among injuries is occupied by traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Causes of traumatic brain injury
There are various causes of traumatic brain injury. The most common of them are:
- Road traffic accidents. Drivers and passengers in private and public transport, pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists suffer.
- Household
- Production
- Sports
- Criminal
Winter time is characterized by similar injuries resulting from falls due to ice, and a large number of such injuries occur as a result of fights or falls under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Moderate bruise
This injury is characterized by more severe damage to brain tissue. It is almost always combined with a skull fracture, resulting in subarachnoid hemorrhage. The main symptoms of brain contusion of this degree are:
- Underestimation of the severity of one’s own condition, loss of consciousness for 1-3 hours, episodes of psychomotor agitation.
- Amnesia (retrograde, congrade, anterograde).
- Severe headaches, severe dizziness.
- Repeated vomiting, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, increased breathing, nausea, increased temperature.
- Severe focal neurological symptoms (changes in muscle tone, paresis, loss of sensation in the extremities, pathological hand and foot symptoms, strabismus, facial distortion, spontaneous nystagmus, epileptic seizures, speech impairment).
- Meningeal symptoms.
Symptoms of such a bruise last from several weeks to two months. Over time, neurological symptoms gradually disappear. However, a number of changes that occur immediately after injury may be irreversible.
Types of traumatic brain injury
There are many different classifications of traumatic brain injuries based on certain characteristics. So, according to severity, they designate mild, moderate and severe forms. In appearance, this is an open or closed damage. By nature, such injuries are of the following types:
- Shake. Minor damage. Symptoms disappear after some time
- Injury. It varies in severity, occurs as a result of an impact of the brain on the skull, sometimes hemorrhage occurs
- Diffuse axonal brain damage. Often occurs during an accident, the functioning of nerve cells is disrupted
- Compression of the brain or head
There can also be isolated, combined and combined injuries, based on the area of damage. Often the brain is injured not only at the point of contact with the skull, but also at the point of impact from the reverse side.
Causes and consequences of injury
Damage to the skull can occur due to:
- Motor vehicle accident.
- Impact (beating, domestic, sports injury).
- Accidental/deliberate fall from a hill. You can get fatally injured by falling even from a small height, not exceeding your own height.
When physical damage occurs to the bones of the cranial vault, brain structures, nerve roots and blood vessels, brain function is disrupted. Even the slightest changes occurring in neurons significantly affect the function of the damaged area.
With a strong impact, the non-branching processes of neurons are twisted and stretched. The entire force of the damaging impulse falls on the cerebral hemispheres and medulla oblongata. The difference in pressure between intracerebral structures leads to the formation of microhemorrhages associated with the rupture of the smallest capillaries.
Damage to intracranial blood vessels is considered one of the most severe and dangerous head injuries. As a result, hemorrhage occurs in neighboring areas of the brain, which causes acute attacks of headaches, nausea, and episodes of vomiting. The consequences of such conditions can be the most tragic. Often, patients with TBI, even after long rehabilitation, experience limb paresis and cognitive impairment.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a traumatologist primarily relies on clinical symptoms and anamnesis. In addition, a neurological examination is carried out, additional clinical, instrumental and laboratory examinations are carried out. In some cases, they donate blood for analysis, do an electrocardiogram, computed tomography, x-ray, and ultrasound. Consultation with a surgeon or neurosurgeon may be required. Based on the data obtained, the type of traumatic brain injury is determined and appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Types of injury
In modern medicine, the injury in question is divided into 3 degrees:
- Mild brain contusion (consequences are not so significant).
- Moderate bruise (lesions can cause consequences, but not always).
- Severe brain contusion (the consequences can be dire).
All of these forms have their own clinical characteristics and are also characterized by a different prognosis. Let's look at them in more detail.
Symptoms
The duration, intensity and types of symptoms in the case of traumatic brain injury depend directly on the type of injury. However, there are classic signs that indicate such damage. This:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Pale skin
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Weakness, fatigue
- Loss or confusion of consciousness
- Irritability
- Noise in ears
- Insomnia
- Hallucinations
- Rave
- Violation of blood pressure, pulse
- Memory loss
- Bleeding
In severe cases, visual impairment, speech impairment, subarachnoid hemorrhage, increased body temperature, aches, cerebral edema, convulsions, paralysis, and coma may occur. It is important to understand that some symptoms may not appear until some time after the injury itself.
A head injury has occurred - what to do?
First aid consists of activities carried out in relation to the patient:
- the person is placed on his side so that if vomit passes, he does not choke on it;
- Place a towel soaked in cold water on your head, maybe with ice;
- the legs are pressed to the stomach so that the body acquires a fetal position;
- in case of injury, the main task is to stop bleeding, if any;
- medical services are calling: ambulance, Ministry of Emergency Situations.
Taking medications is prohibited, as they can aggravate a person’s condition and make it worse.
Diagnostic measures
Traumatic brain injury requires a number of procedures to be performed and prescribed to help select treatment for the patient:
- Diagnosis consists of laboratory blood tests to determine the amount of electrolytes and components of biological fluid.
- In cases of traumatic brain injury, other examinations are also carried out: x-rays of the skull in several projections.
- If technical equipment is available, the patient undergoes CT and MRI. The decryption of the images is carried out on an emergency basis.
In children, procedures are prescribed to detect damage:
- examination of the face, measurement of head circumference;
- assessment of the degree of development of motor and communication skills.
Babies are checked in a different way; before the fontanel closes, an ultrasound of the brain can be done. The procedure will not cause pain to the child, it is quick and helps to obtain information.
Ultrasound in pediatrics is also necessary when collecting information about the consequences of traumatic brain injuries: the size of cysts, areas of hemorrhage.
Treatment of TBI
In case of cerebral trauma to the skull, treatment is selected by a neurologist after diagnostic procedures. It depends on the degree of damage, symptoms, condition of the patient and his complaints.
After a head injury, therapy is divided into 2 stages:
- Providing first aid to stabilize the patient's condition.
- Carrying out rehabilitation procedures aimed at eliminating the consequences of damage.
When treating TBI, they resort to the help of drugs, they:
- They help normalize pressure in the brain, since its increase will lead to the development of hydrocephalus, and secretions begin to accumulate, which will have to be removed with medications.
- Stabilize blood counts, normalize blood pressure to improve gas exchange.
In case of brain injury, during the recovery period they resort to the help of nootropics. These medications restore speech, communication functions, and speed up thinking. Medicines “accelerate” the human central nervous system.
The patient can be treated with vascular tablets, which normalize the flow of blood and nutrients to the tissues of the brain. Medicines are taken in a hospital setting, the person is hospitalized, and solutions are obtained by drip. Because the victims cannot swallow the pills. When a patient is admitted to the department, his condition is assessed by a neurologist or neurosurgeon. The doctor decides whether the patient needs surgery; if there are no such doctors, then a traumatologist is invited.
In cases of traumatic brain injury, surgical interventions are rarely performed, only when the dynamics are negative: when a cyst is discovered, it increases in size or the hematoma grows, threatening to “degenerate” into a tumor.
If a TBI is diagnosed, restoration of the skull frame is required, this procedure is called repositioning. Trepanation is performed less frequently.
If the MT was open in nature, then after the operation the patient is prescribed antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the risk of secondary infection.
Long-term observation of the patient is not always required. If there is a positive trend, then the person is discharged in the absence of nausea, vomiting and high intracranial pressure.
Treatment of traumatic brain injury with folk remedies
After a traumatic brain injury, a person needs peace; noise, stress and excitement are contraindicated. In this case, soothing baths, infusions or decoctions of medicinal herbs can help. Such therapy will be an effective addition to traditional drug treatment. Folk remedies will help relieve headaches, relax, they promote speedy recovery and recovery after surgery, and strengthen overall immunity.
Bath with peony root decoction
A relaxing, soothing bath is an excellent therapy to help quickly recover from a traumatic brain injury. It is necessary to pour 100 g of crushed peony roots into 1 liter of boiling water, then simmer over low heat until the contents are reduced by half. After this, the finished product is poured into a previously prepared warm bath.
Periwinkle decoction for traumatic brain injuries
You need to pour 1 tablespoon of the above-ground part of the periwinkle with 500 ml of water and put it on low heat for 15 minutes. After simmering, squeeze out the grass and add more water to the solution to make half a liter of liquid. You can drink it a third of a glass before meals. You can also take relaxing baths with this decoction.
Valerian root as a sedative
This remedy helps get rid of headaches after injury, it promotes faster recovery, and helps relieve tension. It is necessary to grind dried valerian roots into powder and take 1-2 g three times a day with a small amount of warm water.
Melissa infusion for headaches
Melissa infusion promotes recovery from injuries, strengthens the immune system, and calms. You need to pour 2 teaspoons of the herb into 175 ml of boiling water and put in a warm place for 1 hour. After this, the product is filtered and drunk before meals. It is recommended to drink this tea no more than 3 times a day.
Collection of herbs with a calming effect
An infusion of medicinal herbs can be used as a sedative and restorative. To do this, mix 2 teaspoons of chopped hop cones, thyme, motherwort and 1 teaspoon of wormwood. The mixture is poured with boiling water and left for about 2 hours, after which it is filtered and drunk 3 times.
Pine cone bath after traumatic brain injury
A bath with pine cones provides a good strengthening and calming effect. Add 3 cups of chopped pine cones to 10 liters of warm water. You can pre-fill the cones with a small amount of boiling water (about 1 liter), let it sit and pour the strained solution into the prepared bath.
Calming infusion of oregano
To get rid of headaches after traumatic brain injuries, you can use oregano infusion. To do this, pour 2 teaspoons of dry herbs into 1 glass of boiling water and leave in a warm place for about 20 minutes. After this, the product is filtered and consumed 4 times a day before meals.
Rowan fruit decoction
For rehabilitation in the postoperative period, it is recommended to use a decoction of rowan berries. It is necessary to pour 30 g of dry fruits with 2 cups of boiling water and simmer over low heat for about 15 minutes. This solution should be infused for at least 1.5 hours, after which it should be drunk 2 tablespoons three times a day.
Infusion of linden flowers for headaches
Linden blossom will help relieve headaches, relieve nervous tension, calm down and relax. For infusion, take 1 tablespoon of linden inflorescences and pour 1 glass of boiling water. This product is kept in a thermos for about 40 minutes. Drink it 1 glass as tea up to 4 times.
First aid
If an episode of loss of consciousness is indicated, the victim needs emergency transportation to a hospital, since syncope is fraught with complications dangerous to the body. When examining the victim, you should pay attention to:
- the presence of bleeding or liquorrhea from the nose or ears (a symptom of a basal skull fracture);
- the position of the eyeballs and the width of the pupils (unilateral mydriasis may result from homolateral intracranial hemorrhage);
- physical parameters (try to record as many indicators as possible): skin color;
- RR (respiratory rate);
- HR (heart rate);
- HELL;
- body temperature.
If the patient is unconscious, to prevent tongue retraction and prevent possible breathing difficulties. If you have the skills, you can push the lower jaw forward, placing your fingers behind its corners, and sew the tongue with thread and tie it to a shirt button.
Complications
After a traumatic brain injury, serious complications can occur, both immediate and long-term. The presence and severity of them depend on the severity and type of injury itself, on the speed of assistance, the age of the patient and rehabilitation measures after treatment. There may be:
- Secondary ischemic strokes
- Post-traumatic encephalopathy
- Epilepsy
- Paralysis or other motor problems
- Swallowing disorder
- Weakness
- Chronic pain syndrome
- Problems related to speech, hearing, writing, reading
- Impaired perception, difficulty processing external information
- Slowness, aggression, fears
- Emotional instability
- Problems with urination or bowel movements
- Sudden mood swings, depression, irritability
- Constant headaches
- Insomnia
If the traumatic brain injury is severe enough or if medical care is not provided, complications can lead to disability.
Severity of concussion
Concussions are divided both by area of impact and severity:
- Easy . Characterized by the absence of loss of consciousness or its temporary loss for several minutes. The victim may have headache, vomiting, pale (or red) face, and sweating. Increased blood pressure is common in elderly patients. With hypotension it can become very low. Similar symptoms are observed within 15 minutes and disappear without consequences. If a person is under the influence of alcohol/drugs at the time of injury, unpleasant symptoms will persist longer.
- Average . Characterized by loss of consciousness for up to five minutes, dizziness, pain in the head, nausea. A pronounced sign of this condition is disturbance, confusion, and tinnitus. When examining the victim, the presence of small bruises in the eye area is revealed. Photo and sound sensitivity and loss of concentration are also recorded. Instrumental diagnostics of brain injury (computer, magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalography) does not reveal abnormalities in brain tissue and other pathologies inherent in cerebral head injury.
- Severe degree . Significant hematomas around the eyes, fainting lasting more than five minutes, intense cephalalgia, vomiting, memory impairment and other neurological signs are noted. In this case, the functioning of the cardiac and pulmonary systems suffers, which requires immediate medical intervention.
Mild and moderate concussions threaten health no less than a severe form of closed skull injury. Therefore, the patient needs appropriate therapy and supervision by specialists.
The consequences of a concussion without proper treatment can occur at any time and lead to:
- Depressive state.
- Sudden mood swings.
- Brain swelling.
- Loss of visual acuity and hearing.
- Memory impairment.
- Neurosis.
- Migraine attacks.
- Meningioma, brain cancer.
Is it possible to eat after a head injury?
Previously, doctors believed that patients with TBI should not eat for a while. However, new research suggests that patients should not fast after a head injury.
Hypermetabolism, hypercabolism, and altered immune function are part of the body's response to TBI. If a person with acute traumatic brain injury develops a hyperdynamic state, this accelerates protein breakdown and leads to starvation. Nutrient deficiencies in these patients are associated with increased morbidity and mortality.
Patients with severe head injury require incomplete parenteral nutrition
Enteral nutrition is the preferred method of food intake but is often not tolerated by patients with head injuries. In case of intolerance, food must be delivered to the body parenterally.
Treatment of brain contusions
Depending on the severity of the brain contusion, treatment can be carried out conservatively or surgically.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is performed in approximately 20% of cases if, as a result of swelling, the brain is compressed or the position of brain structures changes.
Traumatic edema leads to a significant increase in intracranial pressure, which is not regulated with medications, and neurological symptoms increase. This is an indication for urgent surgery.
The patient is also operated on if his internal organs have increased dysfunction or the area of crushed brain tissue is too extensive. Hematomas larger than 4 cm in diameter are surgically removed.
In order to gain access to brain tissue, the neurosurgeon performs a craniotomy (making holes in the bone).
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy is carried out to eliminate secondary brain damage. They are a consequence of injury and significantly increase the risk of death, and also lead to damage to tissues and blood vessels. Conservative treatment uses respiratory therapy. If breathing is impaired and the level of oxygen in the patient’s blood decreases, a machine for artificial ventilation of the lungs is used.
Ceraxon is used to reduce the impact of secondary damage
In order to reduce the consequences of a bruise, drugs are used that restore the volume of lost blood, saturate with oxygen and restore the water-salt balance.
When intracranial pressure increases above 21 mm Hg. Art. An intraventricular catheter is used to drain cerebrospinal fluid. A solution of mannitol is administered intravenously, which reduces intracranial pressure.
If there is no expected effect from these manipulations, the patient is placed in an artificial coma. In this condition, the cerebral cortex is less susceptible to damage.
In order to reduce the impact of secondary damage on nerve cells, neuroprotectors are used: Erythropoietin, Ceraxon, Neuroxon, Gliaton. They begin to be administered immediately after the patient is admitted to the hospital. These medications help restore the white and gray matter of the brain.
Type of damage.
Based on the type of injury, focal, diffuse and combined brain injuries are distinguished.
Focal damage is caused predominantly by impact-impact trauma. In this case, both minor, microstructural damage to the brain substance can occur, and areas of brain destruction with the formation of detritus with varying degrees of hemorrhagic saturation of the brain tissue, pinpoint, small- and large-focal hemorrhages at the site of impact, counter-impact, along the path can be diagnosed. shock wave.
Diffuse injuries are caused by acceleration-deceleration trauma. In this case, damage to the pathways occurs, caused by tension and ruptures in the axons of projection, associative and commissural fibers in the brain stem, center semiovale, subcortical ganglia, and medulla. In addition, there are pinpoint and small focal hemorrhages in the same structures.
Combined damage involves the simultaneous impact of acceleration-deceleration and shock-countershock mechanisms on the brain, which leads to the appearance of signs of both diffuse and focal brain damage.
The main consequences of brain contusion
What can be the consequences of a brain injury? The consequences of such an injury directly depend on the strength of the blow received. With a mild bruise, severe complications are almost never observed.
Moderate brain injuries may also not affect the patient’s future fate. This is especially true in cases where the skull fracture does not occur simultaneously with subarachnoid hemorrhage. However, it should be noted that for a favorable outcome, the victim requires full therapy.
In some cases, such an injury does not go away without a trace. Its consequences can be post-traumatic hydrocephalus, post-traumatic arachnoiditis, post-traumatic epilepsy and encephalopathy, as well as vegetative-vascular dystonia syndrome.
As for severe brain contusion, it has the worst prognosis. Approximately 30-50% of such injuries are fatal.
Principles of providing first aid for severe TBI
When providing assistance to a victim with a traumatic brain injury, you must adhere to the following rules:
- put the person on a horizontal surface and ensure peace;
- the head and cervical region should be fixed. A homemade roller made from clothing or any dressing material is suitable for this. This point is especially important if it is necessary to move the victim.
- to prevent swelling, apply cold (ice, snow, a bottle of water) to the injury site;
- Cover the open wound with clean material. If there is a foreign object in the wound, do not try to pull it out under any circumstances. Cover it with tampons on all sides and bandage it using the crosswise technique.
- if you notice blood from the ear, nose or mouth, cover with a sterile bandage and turn the person to the side where the liquid is flowing;
- monitor the victim’s condition: check pulse, breathing;
- transportation is carried out only in cases of emergency. Definitely with neck and head fixation.
- in the presence of vomiting and any brain damage, pain relief cannot be administered until the ambulance arrives;
- if breathing stops, begin resuscitation measures (indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration).
Thus , before the medical team arrives, you must provide the victim with rest, apply cold, immobilize the head and neck, and monitor the general condition. It is prohibited to give medications to the victim. Given the seriousness of traumatic brain injuries, hospitalization or evaluation by an appropriate specialist is necessary to prevent unwanted health problems.
Symptoms (external signs, how it manifests itself)
Traumatic brain injury is a rather dangerous condition that requires immediate medical examination. There are a number of symptoms that immediately after receiving injury can be used to understand that a person has a TBI (some symptoms appear immediately, while others appear after a certain period of time):
- Loss of consciousness. This is the most obvious sign of TBI. Loss of consciousness usually occurs immediately after injury. A person can remain unconscious from a few seconds to several days and even weeks.
- Headache. They usually appear immediately after a person comes to his senses.
- Nausea and vomiting. However, after the attack the patient does not experience any relief.
- Dizziness and severe sweating.
- Obvious damage to the skin and bones. For example, blood may appear at the site of the injury. A hematoma may also appear (and not necessarily at the site of the impact, but also behind the ear, under the eye and in other places on the head). However, this sign is characteristic only of open injuries.
- The appearance of cerebrospinal fluid from the nasal passages or ears. The cerebrospinal fluid itself is cerebrospinal fluid, which constantly circulates in the ventricles of the brain. It is responsible for nutrition and metabolism in the “gray matter”. In the normal state, the cerebrospinal fluid is located in a slit-like cavity, which is located between the brain itself and the skull. If serious bone damage occurs, the dura mater may rupture, allowing fluid to leak into the ear or nasal passages.
- Cramps. A seizure is an involuntary contraction of the muscles of the limbs. During convulsions, the patient may lose consciousness.
- Amnesia. After a serious concussion, so-called retrograde amnesia can develop. It is characterized by the fact that the patient remembers only what happened to him before the injury. Sometimes memory returns, but there are times when the patient cannot remember anything.
There are also a number of individual conditions under which a certain list of symptoms is observed:
| Type of damage | Symptoms |
| Injuries that lead to damage to the blood vessels of the brain. In some cases, we are talking about subarachnoid hemorrhage (blood enters the space between the brain and the skull) | Severe headaches (appear suddenly in the form of attacks), signs of photophobia (pain in the eyes from bright or even daylight), vomiting, fainting. If you ask the patient to throw his head back, he will experience pain in the suboccipital muscles. |
| Frontal lobe brain injury | Speech impairment (the patient cannot pronounce the simplest phrase, unconsciously changes letters in words), unsteadiness when walking, severe weakness in the arms and legs (usually on one side of the body). |
| Temporal lobe injury | Problems with speech perception (the patient hears what is being said to him, but does not understand anything; his native language may sound like a foreign language to him), loss of vision (not completely, but in any one zone of the visual field), convulsions (can occur throughout body or only in the limbs). |
| Damage to the parietal lobe | The patient may completely lose sensation on one side of the body. In this case, you will not feel touch or pain in this area. |
| Occipital lobe injury | Vision problems (total or partial blindness). |
| Damage to the cerebellum | Problems with coordination (movements become unclear) and gait (the body leans more to the side while walking), the eyes begin to “wander,” muscle hypotonia (severe weakening of muscles). |
| Damage to cranial nerves | Strabismus, hearing problems, the appearance of facial asymmetry (one side of the mouth, cheeks or eye slits may droop). |
Traumatic brain injury is a very complex condition that has many forms and varieties. Therefore, you can only theoretically determine how serious the damage is. It is also worth finding out what most often leads to TBI.
Stages and degrees
There are several forms of TBI depending on various factors.
Based on the damage to the skin, we can say that the patient suffered from:
- Open traumatic brain injury. In such a situation, characteristic damage to the scalp will be visible to the naked eye.
- Closed TBI. A condition in which there are no obvious breaks in the skin tissue, but damage affects the brain itself.
There is also a category of combined injuries. In this case, we are talking about the fact that the damage was not necessarily caused mechanically. Negative effects could be caused by radiation or aggressive chemicals.
Next, the doctor must determine the type of damage to the dura mater of the brain, which separates the bony part of the skull from the gray matter itself.
Based on this, the injury may be:
- Penetrating. In this case, there is damage to the hard part of the shell.
- Non-penetrating. There is no damage to the hard part.
TBI can also be isolated (only the head is damaged) or combined (other parts of the body, such as the pelvis or chest, are also affected).
There are also several forms of TBI, which depend on how severe the damage to the skull is, as well as its contents:
- Concussion. This form of TBI is considered the mildest. In this case, the patient complains of a short-term loss of consciousness (can last up to several minutes), a state of weakness and autonomic disorder (manifested in rapid heartbeat, sweating). No focal (obvious damage to a specific area of the brain) symptoms are observed.
- Mild brain contusion. A person can remain unconscious for a period from 2-3 seconds to several hours. In this case, mild focal symptoms are observed. These include weakness in the arms or legs and nystagmus (characterized by pendulum-like movements of the visual organs, that is, when the pupils begin to “run”).
- Moderate degree of brain contusion. Loss of consciousness in this situation can last several hours. Focal symptoms are also quickly identified. They manifest themselves as severe weakness in the arms and legs, as well as slurred speech. Additionally, the patient is diagnosed with facial asymmetry. The danger is posed by possible intrathecal (subarachnoid) hemorrhages.
- Severe brain contusion. The patient may remain unconscious for up to several weeks. Additionally, muscle tone disorders are clearly expressed. A person cannot bend and straighten his limbs independently. Also shows strabismus, high body temperature lasts a long time. The pupils move slowly. Additional signs of a severe form of bruise include convulsions, during which tongue biting often occurs.
- Diffuse axonal damage. In this case, very severe brain damage is observed. The patient, as a rule, is not just unconscious, but in a coma. This means that it does not show any reaction to external and painful stimuli. Additionally, he may have problems with breathing problems (it becomes intermittent or disappears altogether), a sharp decrease in blood pressure, and a lack of limb flexion. Also, patients often have a high fever and squint.
Healthy! Diffuse damage is most often diagnosed in victims of road accidents.
- Compression of the brain. This is the name for compression of the cerebral tissues of the brain. Intracranial pressure begins to rise sharply. This condition is considered the most dangerous. The fact is that the patient may be in a coma or, conversely, conscious, feeling relatively stable. However, at this time, the intracranial hematoma (strong accumulation of blood) continues to grow.
Brain injury does not always occur in the exact location where the blow occurred. Often lesions are diagnosed on the opposite side of the skull, in the so-called impact zone.
Late period
Treatment in the late post-traumatic period is carried out on an outpatient basis. If necessary, the patient consults the attending physician. The drugs are prescribed in tablet form, which greatly simplifies the treatment process. Treatment in a hospital setting is planned and carried out in courses. Their need is determined by the general condition of the patient and the severity of symptoms that remain after brain damage.
The victim must continue to engage in physical therapy, undergo physiotherapeutic procedures, and massage. To stimulate intellectual activity, it is recommended to read, study foreign languages, solve crosswords, and solve logical puzzles.
Psychological assistance, auto-training sessions and other non-specific treatment are actively used, the main task of which is to help the patient adapt to everyday life and society, to increase his independence and communication skills.
Treatment methods
It all depends on the patient’s condition, research results and the exact classification of the injury. For example, if the patient’s condition was assessed as 8 points on the Glasgow scale, then tracheal intubation is recommended. Thanks to this procedure, doctors will be sure that the normal level of oxygen that the brain receives is maintained.
If the patient has problems with reaction, has photophobia, or even coma, then in this case there are grounds for mechanical ventilation (assisted or controlled type). This will also help maintain normal oxygen levels.
In severe TBI, the level of intracranial pressure is determined. It should not exceed 20 mmHg. To maintain the required level, the drug minnitol is used, hyperventilation is performed, or barbiturates are prescribed.
The basis for the operation is an epidural hematoma, the volume of which exceeds 30 cubic meters. see. To perform the so-called evacuation of the hematoma, transcranial removal is performed. Surgical treatment is also necessary if the hematoma thickness is more than 10 mm.
Typically, treatment for TBI is aimed at preventing possible secondary damage to a person’s brain.
Medications
Only doctors can prescribe the course of treatment and dosage of drugs. In many ways, these data depend on the specific case, the volume of the hematoma and other factors. There are also medications that help alleviate the condition when anxiety symptoms occur. For example, in order to prevent the occurrence of seizures and epileptic seizures, you will need to take anticonvulsant drugs.
Most often, the doctor prescribes:
- Levetiracetam. Tablets for oral administration. Taken twice a day. The dose is determined by the doctor. The drug costs about 300-350 rubles.
- Valproate. For example, Depakine for oral administration. The main component of the product is valproic acid. The dosage is also determined by the doctor. The product costs about 100-250 rubles.
If a patient has frequent headaches, the doctor may prescribe analgesics. When diagnosing autonomic dysfunction, beta blockers may be required.
When the danger has passed and the patient’s condition has stabilized, medications may be required that normalize blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. These drugs include Cortexin, Actovegin and Cerebrolysin.
Traditional methods
Using this type of treatment as the only one to stabilize the condition is very dangerous. If there is a suspicion of a TBI, then you need to take a horizontal position and move as little as possible. While the ambulance is traveling, you can apply a cold compress to the bruise site.
Traditional methods can be used only after discharge from the hospital or if the doctor allows it. As a rule, such drugs are used after the main treatment, during the recovery period.
There are several infusions that have a beneficial effect on the general condition of the patient:
- Creeping thyme tincture. To prepare it, you need to pour one tablespoon of herb into two glasses of water. After this, the liquid must be brought to a boil and left for 1 hour. When everything is ready, all that remains is to strain the infusion and take half a glass of it before each meal.
Tea with wild thyme outdoors.
- Aralia infusion. This plant has a positive effect on the nervous system and brain performance. To prepare a medicinal tincture, you need to pour a tablespoon of herb with 100 g of vodka. After this, the container with the liquid must be wrapped and sent to a dark place for 3 weeks. After this, the composition must be filtered and taken 30 drops once a day before lunch.
Other methods
Once the critical effects of the injury have been resolved, there is still a lot of work left to do. First of all, the patient needs recovery.
In this case, the doctor may prescribe a course of additional treatment in the form of:
- Physiotherapy. Such treatment consists of exercises to change body position. This stimulates motor ability, weakened muscle mass is strengthened. Thanks to this, a person quickly returns to his usual lifestyle.
- Vojta therapy. In this case, treatment is aimed at restoring the connection between brain activity and reflex movements. To do this, different irritants are used on different parts of the patient's body. This encourages the TBI victim to make certain movements.
- Mulligan therapy. It allows you to relieve tension from the muscles. Movements no longer cause pain. For this purpose, a device called “Exarta” is usually used. It is a suspension system that not only relieves pain, but also returns atrophied muscles to work. Melligan therapy also includes exercises on various exercise machines.
- Occupational therapy. This is a type of rehabilitation that involves helping a person who has suffered from a TBI to re-adapt to the world around them. The patient learns to take care of himself and perform simple household manipulations. In the future, the person will be able to fully return to normal social life and get a job.