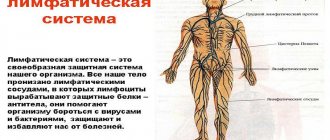
The human body has many lymph glands that protect against various harmful microorganisms and viruses. Inflamed lymph nodes in the neck can indicate either a common cold or a serious illness, one of which is cervical lymphadenitis.
Pathology is not an independent disease. This is only a concomitant illness that accompanies multiple infectious diseases. If the lymph nodes in the neck are enlarged, we can say that the body is affected by some kind of infection or that a pathology of the lymphatic system is developing.
There are isolated cases when lymphadenitis occurs as an independent disease: the infection enters the lymphatic network through mechanical damage to the skin or mucous membrane. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, serious infectious complications such as sepsis or adenophlegmon may develop.
Reasons why lymph nodes in the neck hurt
Pain in the lymph nodes in the neck indicates the presence of infection in the body, lack of immunity, autoimmune diseases, malignant tumors and other hidden pathologies. The exact cause of pain and inflammation of the lymph nodes can be determined by examination by a doctor.
The most common reason why the lymph nodes in the neck hurt are the following diseases of the upper respiratory tract:
- purulent sore throat;
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis.
Colds, ARVI, viral rhinitis, sinusitis, otitis media and other diseases traditionally classified as “ear, nose and throat” are often accompanied by enlargement and pain in the lymph nodes. Depending on the patient’s immune status and the severity of the disease, the condition of the lymph nodes can vary: from slight enlargement to severe inflammation and severe pain.
Causes of lymphadenitis
There are from 500 to 1000 lymph nodes in the body, measuring 2-8 mm. In a healthy person, the nodes are soft and cannot be felt.
Most of them are in places where blood circulation is increased. There are several groups on the neck:
- posterior cervical;
- anterior cervical;
- supraclavicular;
- occipital, parotid;
- preauricular (in front of the tragus of the auricle);
- tonsillar.
When the neck nodes become inflamed, they harden and increase in size. If the enlargement of nodes is caused by oncology, it is extremely dangerous to choose on your own what to treat, whether it is possible to warm up the lymph nodes in the neck.
Inflammation of the lymph node in the neck is caused by:
- infections of the neck, head;
- infections of the nasopharynx (angina, pharyngitis, otitis, sinusitis);
- acute respiratory infections (influenza, adenovirus);
- diseases of the teeth and jaws (caries, periodontitis, stomatitis);
- infectious thyroiditis;
- osteomyelitis;
- allergies;
- autoimmune processes;
- oncology or tumor metastases.
The nodes near the source of infection become inflamed. Treatment of an inflamed lymph node in the neck begins after diagnosis of the disease that caused its enlargement.
If the node becomes inflamed on one side, this means that the inflammation is not systemic in nature.
So, on the one hand, swelling is felt under the lower jaw due to caries, unilateral sore throat, pharyngitis. On one side, a node becomes inflamed behind the ear with unilateral purulent otitis media.
Enlarged nodes on the side of the neck and back may indicate diseases such as:
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- tularemia;
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- herpes;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- tumors, lymphocytic leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis.
Inflammation of the nodes located under the lower jaw is provoked by:
- dental diseases;
- infections (pharyngitis, sore throat);
- rubella;
- cytomegalovirus.
But the appearance of swelling under the jaw can also be explained by dangerous diseases:
- head and neck carcinoma, lymphoma, leukemia;
- rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Wagner's disease, serum sickness.
Enlarged nodes behind the ear can cause otitis media.
Enlargement of nodes behind the ear is caused by:
- otitis media of the middle and external ear;
- abscess of the ear canal;
- mastoiditis;
- rubella;
- neuritis;
- eustachitis;
- mumps.
Some diseases on the list cause severe complications. Thus, mastoiditis can be complicated by a brain abscess. This means that independently diagnosing illnesses and deciding how to treat inflamed lymph nodes in the neck behind the ear is dangerous.
An increase in nodes on the right is observed with infections of the right side of the pharynx and thyroid gland. The appearance of a swelling on the right side of the neck may indicate infection with cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, or inflammation of the abdominal organs.
Signs of lymphadenitis in children
In 70% of cases, the lymph nodes in the neck of children hurt due to inflammatory processes in the ENT organs. Inflammation of the nodes is caused by diseases:
- tonsillitis;
- angina;
- sinusitis;
- otitis.
Along with this, the nodes in children become inflamed with scarlet fever, rubella, diphtheria, and mumps. The cause of childhood lymphadenitis can be skin diseases: dermatitis, eczema.
Lymphadenitis in children is accompanied by inflammation of the submandibular, cervical, and parotid lymph nodes. The disease occurs in acute or chronic form. There are 3 stages of acute lymphadenitis:
- catarrhal;
- hyperplastic;
- purulent.
Unfavorable development of the disease leads to purulent melting of the lymph node. Children tolerate lymphadenitis hard. Additional symptoms of the disease in children:
- high temperature (39 °C);
- fever;
- weakness;
- complete loss of appetite;
- sleep disturbance.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck - causes
The prerequisites for the disorder can be different; more often it becomes the result of some kind of disease. The shape, volume and strength of the discomfort will indicate the character. The proliferation occurs due to the stimulation of the production of lymphocytes, which try to cope with the emerging health threat. Cervical lymphadenitis is caused by:
- infections of the respiratory tract and mouth;
- skin infections;
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- syphilis;
- gonorrhea;
- HIV;
- staphylococcus;
- fungal proliferation;
- autoimmune diseases;
- suppressed immunity due to stress and lack of vitamins;
- chronic alcoholism;
- allergies;
- infectious mononucleosis;
- tumors located in the upper half of the body;
- mechanical damage.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck goes through 3 stages, each with its own distinctive characteristics. It is important to notice problems with this system in time and begin treatment. Otherwise, suppuration may occur, threatening sepsis. Recovery from this form of the disease will be much more difficult, because you will have to undergo surgery to remove the node.
Catarrhal lymphadenitis
It starts with increasing the size of one or a number of nodes, gradually losing mobility. The compaction is accompanied by pain, which becomes noticeable at rest or when pressed. Serous lymphadenitis continues with the development of edema and redness of the skin. If you ignore therapy, suppuration will begin. It can only be eliminated surgically.
Lymphadenitis in the neck in adults often goes away without noticeable deterioration of the condition; it is more difficult to tolerate in young children under 3 years of age. They face the classic results of intoxication:
- temperature rise;
- weakness;
- suppression of appetite.
Hyperplastic lymphadenitis
This is the second stage of formation, characterized by pronounced swelling of the lymph node, which acquires density but does not lose mobility. The pain is mild or absent. For treatment, it is necessary to establish the cause, that is, to identify specific or nonspecific lymphadenitis. This is not always easy to do; due to the sluggish process, a person does not feel a significant deterioration in health and does not go to the doctor.
Purulent lymphadenitis
The final stage, during which the node is destroyed. Purulent lymphadenitis, the causes of which are incorrect or delayed treatment in previous stages, is expressed by a rise in temperature to 38 degrees. Flickering pain in the area of inflammation at rest and when pressed, redness, density and immobility of the node, weakness. Children have a harder time, the temperature reaches 39.5 degrees.
How do they hurt?
The nature of pain in the lymph nodes, their size and structure vary depending on the type and course of the disease.
- The lymph nodes in the neck hurt, but are not enlarged, the discomfort is of medium intensity, the pain intensifies only with palpation.
- The nodes are significantly enlarged, protrude above the surface of the skin and are visible even without palpation. Pain is felt when chewing and swallowing food, talking and turning the head. The consistency of the node is dense and hard, less often soft.
- The lymph node on the neck on the right, left or both sides hurts severely. The enlarged node protrudes significantly above the surface of the skin and is clearly visible. The area around the LU is red.
How to treat yourself at home
After identifying the causes of inflammation, they choose how to treat inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck. You can warm it up with such a proven home remedy as an alcohol solution of iodine.
A similar warming and anti-inflammatory effect can be obtained by lubricating the unit with Ichthyol ointment, Dimexide, and “Asterisk”.
But before smearing the lymph nodes in the neck, you need to attend a doctor’s appointment to find out whether it is possible to heat the inflamed lymph nodes.
Iodine mesh is contraindicated for purulent lymphadenitis, hyperthyroidism, allergies to iodine and children under one year old.
For purulent lymphadenitis, Levomekol is used. This ointment contains an antibiotic that exhibits antimicrobial activity even in the presence of pus.
For purulent lymphadenitis, Levomekol is used.
The doctor may recommend treating the lymph nodes in the neck with folk remedies as an additional way to speed up recovery.
Having chosen how to treat the inflamed lymph nodes, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and treatment with ointments and compresses.
Skin infections
Skin infections, which include boils, carbuncles, cellulitis, and erysipelas, cause lymphadenitis, accompanied by an enlarged node and an increase in temperature.
How to treat lymph nodes for bacterial infections of the scalp and neck:
- Take antibiotics (Augmentin, Ceftriaxone).
- Lubricate the sore spot with Tetracycline ointment.
If the skin disease is caused by a virus, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck should be treated with antiviral drugs in tablets and ointments. Zovirax, Acyclovir, Herpevir, Citivir act against herpes infection.
All medications are prescribed by the doctor based on the results of the examination and tests. The doctor will identify the nature of the inflammation and also explain whether it is possible to warm the lymph node in the neck, when it is better to refrain from heating.
Self-treatment for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is dangerous. With purulent lymphadenitis, surgery may be required to remove the festering node.
Diseases of the nasopharynx
How to treat lymph nodes in the neck for oral infections:
- Antimicrobial, antifungal or antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- Painkillers (Nimesil) are used.
- The mouth is rinsed with Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, infusion of calendula, chamomile, and sage.
- They resort to surgery (removal of a carious tooth, opening of a gum or tongue abscess).
Lymphadenitis often accompanies sore throat, pharyngitis, runny nose and other bacterial diseases of the ear, nose and throat or ENT organs.
How to treat lymph nodes in the neck for diseases of the nasopharynx:
- Antibacterial drugs (Augmentin, Meropenem, Cefotaxime).
- Rinse with Miramistin, Rotokan.
- For a runny nose - drops into the nose, saline solutions (Dolphin) to rinse the nasal cavity.
Non-communicable diseases
Lymphadenitis is diagnosed in allergies, sarcoidosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Allergies are a common cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck; treatment in this case is aimed not at the node itself, but at suppressing the allergic reaction.
It is useless to smear the lymph nodes that have arisen as a result of an allergic reaction. With allergies, one node may become inflamed, but all cervical nodes may become enlarged at the same time.
How to cure a lymph node in the neck from allergies:
- take antihistamines, anti-inflammatory steroid drugs as prescribed by a doctor;
- eliminate contact with the allergen.
Treatment of lymph nodes in the neck at home for inflammation caused by allergies is impossible without the use of hormonal drugs, antihistamines, and is carried out only under medical supervision.
Treatment of specific infections
Tuberculosis, syphilis, HIV infection, and rubella can cause damage to the cervical nodes.
How to treat an inflamed node in the neck due to tuberculosis:
- Take anti-tuberculosis drugs (isoniazid, rifampicin).
- Do not smoke, observe work and rest schedule.
For lymphadenitis caused by tuberculosis, a balanced diet and strengthening the immune system are crucial. To strengthen the immune system, take ascorbic acid in the amount of 750-150 mg per day.
Preventive measures
To ensure that the lymph glands never become inflamed, you must treat your body carefully and with care. There is no specific prescribed prevention program, since lymph nodes in adults, like in children, are a complication of other inflammatory diseases.
We can only recommend a number of strict rules that must be followed to prevent lymphadenitis.
1. Treat in a timely manner and prevent infectious and viral diseases from spreading.
2. Protect the body as much as possible from any hypothermia or drafts.
3. Keep your immune system at a high level of protection by consuming vitamins.
4. Maintain hygiene and cleanliness (especially during colds).
Preventive actions
As a rule, it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it later. Therefore, one should not neglect the prevention of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck.
In order to prevent pathology, you just need to follow simple recommendations:
- monitor the state of the immune system;
- carry out procedures to harden the body;
- treat acute diseases caused by infections in a timely manner;
- avoid hypothermia;
- Maintain personal hygiene and, if necessary, use a gauze bandage during the epidemic.
Thus, inflammation of the lymph node in the neck is a sign of a malfunction of the immune system. If you suspect a pathology, you should immediately seek medical help. At any stage of development of the disease, its treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
What does pain in the cervical lymph nodes indicate?
Painful sensations vary in intensity and nature. In respiratory and dental infections of moderate severity, the pain of the nodes is insignificant and is felt only upon palpation. The more serious the disease, the more painful the lymph nodes may be. By the way the lymph nodes in the neck hurt and other symptoms accompanying the pain, one can tell about the type and nature of the pathology.
- If when swallowing, moving the head, talking, the cervical lymph node on the right under the ear hurts a little and is enlarged, this may indicate unilateral otitis media or ARVI with damage to the auditory canal.
- Severe pain in the submandibular node will indicate pulpitis, caries, stomatitis, impacted or dystopic wisdom teeth.
- Pain in the supraclavicular nodes on both sides or when the left cervical lymph node is painful and inflamed indicates an infection of the upper respiratory tract, trachea or lungs.
- If the lymph node on the neck on the left, right or on both sides in the area of the angle of the lower jaw hurts, this may indicate purulent tonsillitis or inflammation of the tonsils.
Respiratory infections are a common, but not the only group of diseases that cause pain in the lymph nodes in the neck: the causes may lie in pathologies of the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis, autoimmune thyroiditis, diffuse goiter). Autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiency conditions (including HIV and AIDS) can cause pain.
With malignant tumors, enlargement and pain in the lymph nodes are often observed. The focus of malignant cells can be either in the node itself (lymphosarcoma, lymphogranulomatosis, lymphocytic leukemia) or in metastases.
If pain is observed in one place in the area of the carotid artery, collarbone or lower jaw (for example, the right cervical lymph node near the clavicular cavity hurts or aches), this may mean pathology in the node itself. Lymphadenitis is an inflammation of the lymph node caused by infection through a wound or scratch.
If the cervical lymph node on the back right side is painful and enlarged, especially in a child, the doctor may suspect infectious mononucleosis. Other diseases accompanied by pain in the posterior cervical nodes may be associated with the presence of cytomegalovirus, meningitis, and tuberculosis.
Algorithm of action when one/several enlarged lymph nodes are detected in the neck
If you feel (or your child complains to you) local pain in the neck or under the jaw:
- Examine this area. There you can find a soft tissue injury or an abscess.
- Gently, with two fingers, feel and “roll” the tissue in the painful area: with lymphadenitis, you will feel a “ball”. If it is myositis, no local formation will be palpable.
- If you feel a “ball”, note the following facts for yourself: pain when pressed, displacement of this formation relative to the skin above and muscles on the sides, skin temperature above it. If the lymph nodes are small, painless, “roll” with your fingers, there are many of them at once, this indicates pathologies of the immune system. The consultant who will help you understand the pathology is an infectious disease specialist.
- An uneven contour, palpable “bumps”, poor mobility of the formation and its painlessness are serious signs. You need to visit an oncologist who will prescribe the necessary examinations.
- If we are talking about the purulent process of the lymph node itself, it can become very painful and hot. Your specialist is a surgeon.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the throat, oral cavity and neck will be characterized by increased pain on palpation and slight “rolling” under the fingers. Here you need to visit an ENT doctor, a therapist (for children - a pediatrician), and sometimes a dentist.
The lymph nodes are clearly divided into groups for a reason: each one collects lymph from a designated area of the head and neck, so the focus of infection or atypical cells can be found. But there is a “but”: with a pronounced inflammatory process, as well as systemic (they affect many organs at once) diseases or damage to the immune system, several groups are affected at once, which makes diagnosis much more difficult.
Diagnostics
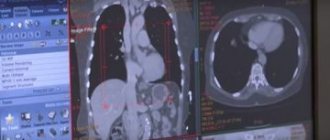
The most accessible and informative method for diagnosing cervical lymph nodes is ultrasound examination (ultrasound), it allows you to determine the size and shape of the lymph nodes, evaluate their structure, and in some cases the nature of the lesions of the formations
After taking the history, a physical examination is performed. The doctor evaluates the consistency, tenderness, color, mobility and size of the lymph nodes. For more accurate visualization of the tumor, ultrasound and computed tomography are used. If a specific disease is suspected, additional special examinations may be carried out.
Lymphadenectomy is performed for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. If necessary, medications that reduce blood clotting, such as Marcumar or aspirin, should be stopped in advance. Before the operation under local anesthesia, it is forbidden to eat or smoke for four hours. It is also forbidden to drink two hours before surgery. If the examination is carried out on an outpatient basis, the patient must stop driving for 1 day. Likewise, important decisions should be postponed for 1-2 days.
Malignant head tumors often form metastases. In approximately 5-10% of cases, the primary tumor cannot be identified. To confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy of the affected lymph node is often performed. Often, only a certain section of tissue is cut out from a lymph node. If several lymph nodes are enlarged, it is recommended to remove the one closest to the primary tumor. The resulting tissue is sent to the laboratory for histological examination.
A pathologist can differentiate between malignant and benign lesions. If leukemia is suspected, further diagnosis and therapy will be carried out by an oncologist.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck - treatment
The problem is often caused by other diseases, so treating the underlying cause will help eliminate lymphadenitis. Gradually, the nodes will decrease in size and their condition will return to normal. Help is provided with antibiotics, antihistamines, antifungals and drugs that relieve symptoms. Physiotherapeutic procedures are sometimes used. This is true for all forms except purulent, when surgical intervention is required.
What to do if the lymph nodes in the neck are inflamed?
Sometimes the problem goes away after a good rest, if the source was stress. In case of infection, it is necessary to eliminate the pathogen. To do this, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and recommends physical rest. It is recommended to adjust the diet during the recovery period, giving preference to warm drinks and soft foods that will not injure the throat. The following should be completely excluded:
- sauces and marinades;
- hard and dry foods;
- spicy food;
- spices;
- fatty and fried foods;
- soda;
- alcohol.
In the case of the development of a purulent form, treatment of lymphadenitis in the neck consists of opening and drainage, after which antibacterial therapy is carried out. To reduce compaction, relieve swelling and pain, physiotherapeutic procedures can be prescribed, which are carried out only under the supervision of a specialist. Patients are often kept in the hospital for monitoring.
It is important to know what not to do with lymphadenitis; incorrect actions can aggravate the disease. Therefore, if it is impossible to immediately consult a doctor, you must carefully choose folk remedies. Any of them that can warm up the site of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck are prohibited. If there is an infectious cause, this will help the infection spread faster to neighboring organs. If the problem is a malignant tumor, then thermal exposure will increase the risk of growth and metastasis. Warming up should be prescribed by a doctor after a thorough analysis of the problem.
Ointments for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
- Heparin.
Relieves inflammation, helps to quickly remove negative manifestations. Can be used for children. It produces a warming effect, so consultation with a doctor is required. - Vishnevsky.
This answer to the question of how to relieve inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck has been known for more than 100 years. The ointment also has antibacterial and antiseptic activity. It is used in the form of compresses, the effect is noticeable on the third day. Do not apply during pregnancy and lactation. - Ichthyol.
Helps regenerate and eliminate inflammation, stimulates microcirculation. Use it twice a day. - Dimexide.
Reduces pain, has an antimicrobial effect, relieves inflammation and makes the microflora more sensitive to the action of antibiotics. Dimexide for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck can be used in the form of an ointment, gel or solution. In the latter case, apply compresses. - Diclofenac or Ketoprofen.
Relieves pain and has a quick effect. Reduce swelling.
Use ointments for no more than 7 days, following the recommendations of a specialist. The affected area is treated 1-3 times a day. This treatment is contraindicated if:
- allergies to components;
- ulcers or purulent processes;
- open wounds at the site of application;
- deep venous thrombosis.
Tablets for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
The duration of admission depends on the severity of symptoms, which is determined by the doctor. He also tells how to treat lymphadenitis - conservatively or surgically. If the choice fell on tablets, then the following groups of drugs can be prescribed.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesil, Ketorolac).
Help reduce inflammation, pain and temperature. - Antihistamines (Cetirizine, Lorano).
They constrict blood vessels, reduce capillary permeability and the intensity of leukocyte migration. - Antibiotics (Amoxiclav, Clindamycin, Ceftriaxone).
They are selected according to the type of bacteria and prevent their proliferation. After eliminating the pathogen, the inflammation goes away. - Antiviral (Remantadine, Acyclovir).
Suppress the reproduction of viruses, eliminating the inflammatory response. - Antituberculosis (Rifampicin, Ethambutol).
It has a targeted effect, reducing the production of protein in tuberculosis bacteria. - Antifungals (Amphotericin B, Fluconazole).
Used if inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is caused by a fungal infection. They increase the permeability of fungal membranes, helping to suppress its reproduction.
Injections for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
In this way, drugs are administered at the beginning of treatment. If antibiotics are prescribed for lymphadenitis, it is important to ensure their rapid delivery to the lymphatic system. Only the injection method can do this. The maximum concentration of the active substance is reached 90 minutes after the injection. Therefore, in the first days of therapy they do them, and then switch to the tablet version of the same drug. This scheme is not mandatory; sometimes injections are not prescribed.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck - treatment with folk remedies
You should use home methods for no longer than a week. It is advisable to obtain a doctor's recommendation; in case of high fever and purulent form, an urgent visit to the hospital is required.
- Warming up.
This method helps the seals dissolve faster, but is only suitable for mild cases or during the recovery period. A doctor should tell you how to treat inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck; if he does not establish any contraindications, then you can warm up the sore spot using hot bags of sand or coarse salt. The procedure is performed 2-3 times a day. - Echinacea tincture.
The finished drug is sold in pharmacies and helps improve the functioning of the immune system. Take 20-40 drops dissolved in 100 ml of warm water. For compresses, you need to dilute the drug with water in a ratio of 1:2, wet gauze and apply it to the inflamed area overnight.
If the lymph nodes hurt but are not enlarged
Pain that is not accompanied by enlargement or inflammation may indicate various conditions of the body. Most often this is a residual phenomenon after ARVI, purulent tonsillitis and other respiratory infections.
By how long the cervical lymph nodes hurt after recovery, one can indirectly judge the patient’s immune status: the longer pain in the nodes is observed after a cold or flu, the weaker the body’s protective function.
Another common cause of pain without lymph node enlargement is local infection and mild hemorrhagic inflammation that does not affect the general condition.
Why are the nodes on the neck enlarged?
People without medical education know much less about the lymphatic system than, for example, about the circulatory system. Not everyone knows that lymph is formed from intercellular fluid, therefore it is part of the internal environment of the body. Tonsils, follicles, and spleen are also part of the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes are filters for lymph coming from organs and parts of the body.
What to do if your lymph nodes are inflamed and painful? Why do they increase in size? There are more than 100 diseases that can affect the lymphatic system. The causes of enlarged lymph nodes in children in nine out of ten cases are infectious diseases. If the doctor confirms that there is no reason for concern, warm compresses on the neck will be enough (but it is dangerous to treat this on your own, because the cause may be, for example, suppuration).
In older people, the most common cause is tumors, including benign ones. In general, lymph reacts to any “invasion” into the body: if the fight against bacteria or viruses does not bring positive results, the lymph nodes enlarge. The filters are, one might say, overcrowded and overstressed as they try to remove the by-products of the infection from the body.
If the enlarged node also hurts, it is most likely due to inflammation. If the lump is painless, a tumor may be suspected.
The lymph node hurts, but is it the only one that is enlarged? Most often, the cause must be looked for locally. For example, after an animal was scratched, cat scratch disease developed, the throat or lungs were affected (tuberculosis), the oral cavity (there is a bad tooth, a wisdom tooth is erupting, etc.), facial tissue (boil, abscess due to improperly squeezed out eel or pimple).
If several lymph nodes in the neck have enlarged at once or, in addition to the cervical one, they have changed in size in other parts of the body, you should especially quickly consult a doctor: this is a sign of a viral or bacterial infection that has spread throughout the body, and can also be a symptom of blood cancer.
If the skin over the swollen lymph node turns red, most likely it is about suppuration. In acute cases, pus can break through and spread to surrounding tissues, in which case urgent surgical intervention is required.
What to do?
No qualified doctor has the right to give general recommendations on what to do if a lymph node in the neck hurts or is enlarged. Pain, increase in size and inflammation can be associated with various pathologies. The main task of the patient is to visit the doctor in a timely manner.
An infection accompanied by severe inflammation and the formation of pus, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications: sepsis (blood poisoning) and other acute conditions.
If the lymph node in the neck hurts for a long time and the pain becomes chronic, you should not let the condition take its course. It is important to see a doctor and get examined. The specialist who can solve the problem works in the field of surgery, infectology, hematology or oncology. The doctor will conduct an examination and questioning, and, if necessary, prescribe an ultrasound of the inflamed/painful node. A biopsy is sometimes prescribed to determine the quality of cells in the lymphatic system.
Why is inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck dangerous?
Without proper therapy, severe pathologies develop against the background of cervical lymphadenitis, which require long-term hospital treatment and can cause disability or death. Due to the proximity of inflammation to the head, brain diseases can occur - meningitis, encephalitis.
Possible complications of lymphadenitis:
- abscess;
- osteomyelitis;
- rapid development of oncological processes;
- thrombophlebitis;
- mediastinitis;
- elephantiasis of the limbs.
Lymphadenitis is dangerous due to the development of thrombophlebitis
Against the background of a chronic inflammatory process, lymphoid tissue begins to be replaced by connective tissue, which leads to a deterioration in lymph flow and severe swelling of the face.
Important!
The most dangerous complication of inflammation of the lymph nodes is sepsis; blood poisoning develops rapidly, often the patient cannot be saved.
Classification of the main forms of the disease by etiology
The disease is divided into the following categories based on the method of entry into the lymphatic system:
- Hematogenous. Intervention of foreign elements through the bloodstream.
- Contact. Transfer of infectious components from organs located close to the nodule.
- Mechanical. The contractor enters the lymph node through skin lesions.
Based on its origin, pathology is divided into 2 types:
- Non-specific. It develops against the background of infection of the body by various types of bacterial, fungal and infectious microbes. As a rule, these are streptococci and staphylococci.
- Specific. It occurs due to infection of the patient with special microorganisms that appear in autoimmune diseases of complex etiology (HIV, AIDS, tuberculosis).
In addition to this, there are also:
- Primary lymphadenitis. Characterized by the absence of an initial infectious source, and implies 5% of the total number of diseases. Pathogenic microbes enter the lymph system through damaged mucous membranes or skin.
- Secondary lymphadenitis. It is assessed as a complication due to inflammation at the original source, and is common in 95% of cases of the disease. It is found anywhere, but the ENT system, genitals, mammary gland and skin are most often affected.
Causes of inflammation
The causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes can be different depending on which nodes are inflamed.
Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes are most often a consequence of diseases such as:
- tuberculosis;
- bacterial infection;
- herpes;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- lymphadenitis.
Inflammation of the occipital nodes, if the infection penetrates directly into the lymph nodes, mainly occurs due to the following diseases:
- syphilis;
- HIV;
- AIDS;
- tuberculosis;
- measles.
When the infection does not affect the node itself, but the organs located near it, the causes may be diseases such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other infectious diseases affecting the eye and mouth area.
An advanced form of caries can lead to inflammation of the lymph node in the neck on the right or left side under the jaw. Untreated caries penetrates the root and causes inflammation. In addition, inflammation of the node under the jaw can be caused by infection of diseases:
- tonsillitis, sinusitis, mumps;
- atheroma - a tumor in the throat;
- cancer.
Causes of inflammation in children at the back of the head:
- measles;
- rubella;
- toxoplasmosis;
- Infectious mononucleosis.
These are usually chronic diseases. Non-chronic diseases include diseases of the ENT organs.
There are many causes of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes, the most common of which are the following:
- mesotympanitis;
- furuncle;
- epimesotympanitis;
- otitis media and external otitis.
Ear disease can be caused by diseases such as:
- acute leukemia;
- oral disease;
- Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Some of the reasons for the formation of a lump on the neck may be:
- lipomas;
- skin cysts;
- atheromas;
- folliculitis;
- follicles (inflammation of hair follicles).
By location
Based on the positioning of foci of inflammation, doctors determine the following types of illness:
- Submandibular, located under the jaw in the area of the tonsils.
- Lymphadenitis of the cervical type is the most common. It is typical for children, as well as for people who often suffer from colds.
- Axillary.
- Parotid form of the disease.
- Mesentral, in which the mesenteric lymph nodes located in the navel area become inflamed.
- The inguinal type is typical for older people and is not typical for children and adolescents.
Lymphadenitis and pregnancy
During pregnancy, lymphadenitis under the jaw or in the neck is not uncommon. This is due to changes occurring in the body.
After conception, the so-called fetal protection is activated in the female body, in which the immune system weakens its effect by 2 times so that the egg attached to the wall of the uterus is not rejected.
Such changes cause the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the body, which the lymph nodes continue to fight.
That is why pregnant women are not recommended to visit public places and come into contact with people sick with colds and infectious diseases.
Clinical manifestations
Treatment tactics are determined taking into account the type of infection, as well as the type of pathology - serous or purulent.
With purulent lymphadenitis, pronounced local swelling and tissue hyperemia appears in the projection of the problem area. An infiltrate forms in the node, which in some cases can spontaneously open. With the non-purulent variety, there is no redness of the skin, and the purulent focus is localized deep inside the structures of the lymph node.
The first symptom of the pathology is severe pain. The patient has to periodically change position and take the so-called. "forced position" In the projection of the affected lymph node, swelling and hyperemia are visible. As the pathological process increases, symptoms of general intoxication appear - poor health and hyperthermia. The contours of the lymph node often lose clarity. When you try to palpate the problem area, the pain increases.
Drug treatment of the disease
First of all, it is important to establish the main cause of lymphadenitis, since the treatment method directly depends on the form and stage of the disease.
Treatment of inflammation is carried out conservatively,
however, if a purulent process occurs, surgical intervention is indicated .
- Treatment of cervical lymphadenitis is based on antibacterial drugs that effectively fight purulent and bacterial processes. I prescribe antibiotics for lymph nodes depending on the age, course of the disease and the patient’s condition.
- Drugs with antibacterial action that are aimed at treating enlarged lymph nodes: Ciprofloxacin, Amoxicillin, Sumamed, Azithromycin, etc., on average the course of treatment is at least 10 days. Antibiotic treatment should not be interrupted, as this may lead to relapse of the disease and the development of immunity.
- If the cause of lymphadenitis is a viral infection, then it can be cured with antiviral drugs: Arbidol , Anaferon, Ergoferon, etc. These drugs significantly suppress the reproduction of viruses and significantly help produce their own interferon.
- For autoimmune diseases, effective immunosuppressants are prescribed: Cyclosporine A, Tacrolimus, etc.
- With the development of tumor processes, neoplasms can be blocked by drugs: Thioguanine, Methotrexate, Decarbazine, etc.
- To eliminate pain from inflamed lymph nodes located on both sides, it is recommended to take painkillers, and if the temperature increases significantly, antipyretics. If the cause of lymphadenitis is ARVI, acute respiratory infections and colds, it can go away on its own without special treatment.
- Physiotherapy has a positive effect in the treatment of lymphadenitis: laser therapy, galvanization and UHF. Such procedures are aimed at improving lymph circulation and cell restoration.
If the lymph nodes in the neck are enlarged, heat treatment in combination with drug treatment promotes a speedy recovery, but heating is prohibited in case of tuberculous lymphadenitis and intoxication.
Axillary area
Lymphadenitis (symptoms are localized in the axillary region) of this type is uncommon and develops due to:
- infected skin lesions on the upper limbs, back and sternum;
- carbuncles and boils, which are located in the armpit area and arise as a result of inaccurate depilation;
- purulent mastitis;
- inflammatory processes in the mammary gland;
- tuberculosis and genital infections.
The signs make themselves known as follows:
- a painful lump forms in the armpits, preventing the arm from moving and sleeping normally on the side;
- the inflammation becomes purulent and the skin above it acquires a red tint;
- sometimes pus comes out through thin patches of skin in the armpit area;
- the purulent form of axillary lymphadenitis can unite all the lymph nodes into a general inflammation, and thus spread the disease throughout the human body.
Tumor nature of unilateral lymphadenitis
If there is unilateral enlargement of the lymph nodes in the back of the neck, it is first necessary to exclude malignant causes. Especially if the patient is over 50 years old, there is no pain or sensitivity when palpating the cervical nodes.
If one lymph node (or group) is enlarged above the collarbones and there are no other symptoms of the disease, this should always be alarming. It is necessary to exclude tumors of the mammary gland, chest cavity, and internal genital organs. The presence of a left-sided enlarged supraclavicular lymph node requires immediate examination of the stomach.
Metastatic damage when malignant tumor cells spread throughout the body on the neck in the right or left (upper and middle) region is possible with tumors of the head, nasopharynx, palatine tonsils (tonsils), and tongue.
On the neck in the lower third, lymph nodes are detected when pathology develops in the underlying organs: the esophagus, lungs, and a number of glands (breast, pancreas, prostate).
The cause of unilateral inflammation of the axillary nodes is not only infections of the extremities, but also neoplasms of the lungs, mammary glands, and kidneys. The side of location of lymphadenitis corresponds to the position of the affected organ.
With malignant processes in the abdominal cavity, a single enlarged node may appear in the right umbilical region or on the left.
Features of lymphadenitis of metastatic nature:
- pronounced density;
- immobility, cohesion with each other and with surrounding tissues;
- absence of pain and presence of sensitivity only upon palpation.
In this case, primary damage to the node by the tumor process is also possible.
Tumor lymphadenitis is characterized by the following features:
- elasticity and painlessness;
- formation of dense conglomerates from several lymph nodes;
- mobility, fusion with soft tissues and skin.
If lymphadenitis is of an infectious nature, inflammation develops quickly, usually against the background of the underlying disease. At the same time, tumor pathology determines gradual development over several weeks.
Diagnostic measures for the development of this pathology
If the lymph nodes are enlarged and painful, it is recommended to consult a physician. This doctor can refer the patient to more specialized specialists: a urologist, gynecologist, dentist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, mammologist or surgeon.
In case of reactive lymphadenitis, the following laboratory tests are necessary to determine the cause of the disease:
- general urine and blood tests;
- blood test for syphilis, viral hepatitis, HIV;
- bacteriological examination of urine and blood;
- tumor markers;
- blood for hormones;
- blood biochemistry;
- cytological analysis of discharge from the urethra and vagina;
- puncture of the lymph node with cytological examination.
The list of instrumental diagnostic methods includes:
- X-ray;
- computed tomogram;
- gastroduodenoscopy;
- bronchoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy.
What to do if you have inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes
At the first suspicion of inflamed lymph nodes, you can conduct an independent diagnosis at home:
- Examine the neck area where inflammation is found. Perhaps it's just a boil or soft tissue damage.
- If point 1 is confirmed, then this area should be diagnosed in more detail. Gently touch this area with your fingers. If a ball can be felt under the skin, it means that this is clearly an enlarged lymph node.
- Next, we examine the discovered “ball”. If there are a lot of these balls, they are painless when pressed, then this indicates a compromised immune system. You should contact an infectious disease specialist.
- If pain occurs during palpation, as well as lumpiness and immobility of the node under the skin, then a serious diagnosis is needed in the clinic. Diseases of the throat and mouth are characterized by soreness of the lymph glands.
- If you suspect diseases of the ENT organs, you should visually examine your oral cavity for the presence of sore throat, as well as stomatitis, caries. A healthy oral cavity has clean mucous membranes without plaque, teeth are white without black spots. If a visual examination reveals problems, this means that this is the cause of lymphadenitis.
Very often, enlarged lymph nodes occur without obvious symptoms. To do this, you need to see a doctor and carry out a competent diagnosis from a specialist.
Based on the diagnostic results, the therapist refers the patient to the appropriate specialist: ENT specialist, dentist, surgeon, oncologist, hematologist. Inflammation of the lymph glands accompanies about a hundred diseases. With timely treatment of the disease, lymphadenitis also returns to normal.
If the patient has undergone treatment, and the nodes do not decrease within 3-4 months, then a full examination of the body should be done: donate blood for tests, do an ultrasound of the main organs, and consult with specialists.
_
An inflamed node for 6 months can signal the presence of a tumor. In this case, you need to take a biopsy and make an appointment with an oncologist as soon as possible.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods are used to treat lymphadenitis.
Echinacea tincture helps relieve inflammation in the node:
- Dilute the pharmaceutical extract with heated water in a ratio of 1 to 2.
- Soak a small piece of bandage in the solution.
- Apply the moistened material to the affected area overnight.
- For internal use 30-40 drops. dilute tinctures in 0.5 tbsp. water.
- Drink 3 r. per day until final recovery.
Pine decoction:
Treatment of lymph nodes at home
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is a secondary form of the disease, so treatment should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of the pathology. And you can get rid of lymphadenitis only by removing the infection and increasing immunity.
As therapeutic measures, it is possible to use both traditional therapy and folk methods.
Traditional medicine
Ultrahigh-frequency therapy has been widely used to treat pathology. This is a technique that affects the body using an ultra-strong frequency electromagnetic field.
Anti-inflammatory drugs can only be taken as prescribed by your doctor, as they have many side effects and contraindications. These drugs include: Deltasone, Medron, Prednisol.
Taking antibiotics is possible if the inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection or with a purulent complication.
Catarrhal and hyperplastic forms of inflammation imply the use of conservative treatment on an outpatient basis.
Key recommendations at these stages:
- Rest the affected area.
- Take broad-spectrum antibiotics – 1-3 generation cephalosporins; anti-inflammatory – Diclofenac, Nimesulide; multivitamins – Vitrum, Duovit; absorbable agents – Serta.
- Use local compresses with Dimexide in the ratio: 1 part of the drug to 4 parts of water.
In the purulent stage of inflammation, the node is opened, the surface of the wound is treated with an antiseptic solution and drained. Subsequent treatment is the same as for a purulent wound. Systemic antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate intoxication.
Folk remedies
It is important to remember that the use of traditional methods can either help in treatment and speed up the healing process, or cause harm.
Various infusions and decoctions are not able to completely get rid of the disease, but they can significantly alleviate the condition.
There are proven recipes that have repeatedly proven their effectiveness:
- Echinacea tincture. It is a good antiseptic and the most effective remedy. 10 drops must be diluted with 50 milliliters of boiled water. Take 4 times during the day.
- Aloe juice. Take one tablespoon of freshly squeezed juice orally daily.
- Chamomile, mint, calendula. A decoction is prepared from these herbs and is intended for gargling. Procedures must be carried out at least four times a day. In addition, tea can be brewed from the collection.
- Dried Canadian goldenseal. To take, one spoon of powder is diluted in a glass of water. It is recommended to drink the drink every day. At the same time, fermented milk products should be present in the diet, since such a drink can provoke an upset stomach.
- Salt and soda. Dilute half a teaspoon of both components in 200 milliliters of hot water. After cooling the solution, gargle several times throughout the day.
- Green jadeite. The stone should be the size of an inflamed lymph node. It is applied to the affected area for 10 minutes. This is done several times a day.
- Massage with the addition of essential oils: eucalyptus, lavender and tea tree. Take one part of each and dissolve in olive oil (20 parts). Perform movements carefully, from top to bottom along the neck.
The main thing is that the use of any folk remedy must be agreed with the attending physician, otherwise you can harm your health and provoke complications.
What is forbidden to do if the lymph nodes in the neck are enlarged?
Self-treatment of cervical lymphadenitis using traditional medicine without consulting a specialist can lead to very sad consequences. Lymph nodes are not to be trifled with. If a lump appears and pain occurs when you touch this area, it is strictly forbidden to expose this area to heat. Heating leads to the growth and rapid spread of infectious pathogens; through the bloodstream they enter neighboring organs, not excluding the brain.
In addition, heat exposure can provoke metastasis of malignant neoplasms, and enlarged lymph nodes sometimes indicate the growth of cancer cells in them.
If treatment of the acute form is not started in time, the inflammation can become chronic, accompanied by generalization, scarring of lymphoid tissue and its replacement with connective elements that are not able to perform protective functions.
You may be interested in an article about the healing properties and harms of Echinacea tincture.
There is also a useful article on treating intestinal inflammation at home.
Here you will learn about the treatment of tracheitis with folk remedies.
Alcoholism and lymphoid tissue
Taking alcohol-containing substances leads to an increase in the number of neutrophils in the peripheral blood and a decrease in the number of lymphocytes. This is regarded as the body's reaction to stress of chemical etiology. Additionally, laboratory parameters characterizing the state of tissue trophism are affected:
- retinol binding protein;
- vitamin B12;
- transferrin;
- magnesium;
- zinc.
Impaired blood supply to tissues and organs, suffering of lymphatic tissue leads to a decrease in immunity due to alcohol abuse, and susceptibility to inflammatory diseases.
What can be confused with enlarged nodes on the neck?
Lymph nodes are easily confused with the salivary gland, muscles, cysts (bumps filled with fluid, most often congenital or enlarged after trauma to the tissues of the neck). Cysts in old age should be monitored using ultrasound, since in rare cases they can degenerate into a malignant neoplasm.
Call your doctor if your swollen lymph nodes:
- Appeared for no apparent reason
- Continue to increase for two weeks
- Solid, don't move when you press on them
- Accompanied by persistent fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss
- Having difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Prevention
In order to avoid the possibility of the formation of lymphadenitis, it is necessary: timely treatment of any skin wounds and chronic infections, compliance with precautions to prevent injury.
Maintain your immunity at the proper level and consult a doctor promptly. When it comes to nutrition, there are certain foods you should avoid that may increase the inflammatory response. This meat is fatty and coarse-fiber (especially lamb and pork), spicy, salted and smoked; dairy products. Foods rich in vitamin C promote recovery. Stomach cancer Tuberculosis Brucellosis in humans Hemorrhoids Tonsillitis Hepatitis C: first signs and treatment regimen
Gang locations
There are 300 units of cervical lymph nodes. The location diagram makes it possible to see where the lymph nodes are located in the neck. The diagrams show that the location of the lymph nodes in the neck in people is in the area of the cervical vertebrae. According to classification, they are divided into groups:
- anterior cervical (anterior) and posterior cervical;
- submandibular and chin;
- supraclavicular;
- ear;
- occipital
The anatomy of the location of the glands in the neck can be seen in the diagrams.
Front
The anterior cervical lymph nodes, which allow the head to tilt and rotate, are located above and below the sternocleidomastoid muscle in front of the internal jugular vein. These are superficial jugular nodes. They are small, but there are many of them. The anterior cervical cleanses the lymph entering the pharynx, throat, tonsils and thyroid gland.
In turn, if you look at the figure, it is clear that among the anterior glands there are groups of preglottic, thyroid, paratracheal and pretracheal. These are deep nodes.
Palpation of the cervical node is difficult, it is impossible to find them, since they are small. In an adult they are smaller than in children.
The lymph node on the left or right side of the neck is inflamed. We need to find out what happened:
- The tonsils are inflamed.
- There was an infection in the oral cavity.
- Bacteria entered the respiratory tract.
The reason could be:
- decreased immunity;
- lack of vitamins;
- freezing of the body;
- long-term stressful situations;
- insect bites;
- inflammation in the ears.
A lump appeared on the front of my neck. Often it is not painful. The anatomy of the appearance of a lump is as follows: depending on the infectious lymph node that first caught the infection, the lump can be in the front, side or under the chin.
The submandibular glands are the first to fight infection of the pharynx, mouth and throat. Changes usually take place at the micro level. The neck remains unchanged. When an infection or viruses enter the gland, the node swells.
The neck can be seen with a lump under the chin. If the lump is on the neck when the glands have returned to normal, then the doctor can answer whether the lymphadenitis has developed into a chronic stage.
Glands at the back of the neck
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the back of the neck is a sign of some kind of disease: an organ or infection in the body. The posterior cervical lymph nodes, located between the clavicle and the mastoid region of the temporal bone, protect the respiratory tract from infection. When the glands in the back of the head become swollen, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the back of the neck can occur.
Lymph nodes in the neck, located at the back, can be seen if you look at the diagram.
Chin
Lymph in this area flows from the chin to the submandibular glands. The mental glands are located below the chin, cleaning the lower lip, tip of the tongue, and central incisors.
Submandibular
Submandibular or submandibular cervical lymph nodes are located under the jaw bone on the sides.
The lymph flow goes from the lower oral cavity through the pharynx to the tonsils. In addition, lymph flows from the lower teeth, excluding the central incisors, to the maxillary molars, including the small anterior teeth.
The draining lymphatic vessels of the skin go to the submandibular and anterior nodes of the neck from the middle part of the face. They pass through the submandibular and from the lower part of the face.
The figure shows the view on the left, showing the drainage lymph from the tongue.
Supraclavicular
If you look at the cross-sectional drawing, you will see the supraclavicular nodes and the subclavian trunk. The supraclavicular glands are located in the pits near the junction of the clavicle with the sternum. They control the flow of lymph from the abdominal and chest area.
The nodes that are responsible for the flow of lymph from the abdominal region are known as Vikhrov's nodes and are considered the main ones. Since these nodes transport incoming lymph back into the venous circulation through the left subclavian vein, they are susceptible to the creation of painful neoplasms such as infection in the arm, lymphadenitis, and breast cancer.
Ear
Are there ear glands? The side view in the figure answers this question. To the left of the group of parotid nodes, there are several ear glands at the base of the neck. With otitis, the lymph nodes on the front of the neck and on the left side become inflamed; inflammation of the nodes on the front surface of the neck and submandibular can occur. The pain will be felt in the neck and radiate to the ear.
Occipital
The occipital nodes are located on the back of the neck. If in children under 5 years of age the occipital nodes have slightly increased in size, but the swelling quickly subsides, there are no symptoms of the disease. There is no need to see a doctor. It is the lymph nodes in the back of the head that work, successfully coping with the infection. This process is considered normal, since at this time the child’s immunity is developing.
Deep
There are also lateral (side) cervical nodes: superficial and deep. The deep ones are more numerous and deserve special attention. The location of the lymph nodes in the neck is responsible for the movement of lymph. The deep cervical glands move lymph along the neck through the carotid vagina, pharynx, esophagus and trachea.
Deep cervical lymph nodes are divided into two groups: primary and secondary:
- The primary ones ensure the movement of lymph flow along the paths of the head, occipital part of the neck, thyroid gland, pharynx, esophagus, trachea, nose, palate and tongue. In this case, lymph is taken from the deep primary nodes in the neck and neck muscles.
- The second group is responsible for lymph flow from the chest, part of the arms and the surface of the liver. Receives lymph from the deep primary glands in the neck and neck muscles.
There is also a group of deep cervical nodes: lateral jugular, anterior jugular; jugular: jugular-digastric and jugular-scapular-hyoid. The jugular-digastric is the deepest. It can only be felt if the tongue, tonsils, or pharynx are inflamed. The jugular-scapular-hyoid is located between the internal jugular vein and the omohyoid muscle.
The figure clearly shows how each location of the gland groups is located.
What is a tonsillar lymph node?
These are glands located in the corners of the jaw. There are several tonsillar nodes; they protect the body from diseases, especially infectious and bacterial ones. Inflammation occurs with respiratory diseases such as tonsillitis, tracheitis and similar infectious diseases.
1) Tonsillar (jugulodigastric) lymph nodes are located in the jugular region of the neck
With chronic tonsillitis, the condition is often similar to the condition during the listed diseases.
Jugular fossa (suprasternal fossa)
Depression at the bottom of the neck. V-shaped depression, limited laterally by the sternocleidomastoid muscles. The outflow of blood from the head and neck to the heart is carried out by several veins located in the jugular fossa.
Delfiano
This is an area in the jugular fossa associated with the mucous membrane in the lower part of the larynx, pharynx and the thymus gland, which regulates the human immune system. Impact on the zone increases the body's resistance to infectious diseases by improving blood circulation in the thymus (thymus gland).
Rubella
An acute infectious disease in which intoxication is moderate, but there is a rash on the skin. The causative agent is a virus, the source of infection is a sick person. A constant sign is the involvement of the lymph nodes of the neck in the pathological process, which become painful when palpated.
Damage to the lymph nodes in the neck is bilateral, develops before the appearance of the rash, and disappears after the skin rash fades.
Additional symptoms:
- General weakness, malaise, pain in joints, muscles, head.
- Temperature 37.3-37.4°C.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Pale pink spots on the soft palate.
- Rhinitis.
- Dry cough.
- A constant sign is a rash on the face, behind the ears, and scalp. The rash quickly spreads to the body and limbs.
If you suspect rubella, you should contact an infectious disease specialist or pediatrician.
With rubella, complications are rare, but they are serious:
- arthritis;
- pneumonia;
- polyneuropathy;
- neuritis;
- sinusitis;
- otitis;
- meningoencephalitis;
- nephritis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- damage to the pancreas with the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture, epidemiology. anamnesis and laboratory data:
- complete blood count – leukocytes and platelets are reduced, the number of plasma cells is increased, ESR does not respond;
- serological analysis is aimed at identifying immunoglobulins of class M, IgG;
- molecular biological method - PCR;
- According to indications, ECG, neurosonography, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, radiography of the paranasal sinuses and lungs are performed.
Treatment
The following drugs and methods are used for treatment:
- interferon alpha;
- clavulonic acid;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for arthritis;
- if there is difficulty in nasal breathing - xylomethine;
- for detoxification, intravenous saline solutions;
- for cough - acetylcysteine;
- for dyspepsia - smecta;
- severe course requires the use of prednisolone;
- for bleeding - etamzilat, vikasol;
- physical methods of cooling when drugs for the treatment of hyperthermia are ineffective.
Signs of cervical lymphadenopathy
The following symptoms indicate that inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck has occurred:
- In the place where the neck hurts, you can feel a “pea” of soft elastic properties, movable relative to the overlying skin and nearby muscles. With severe inflammation, it is no longer a “pea” that is determined, but a formation with a diameter of up to 5 cm (less often, a larger one), which is already visible to the naked eye. This is an inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck, and its treatment is anti-inflammatory. If such a structure is dense, its contours are unclear, lumpy, and cannot be moved to the side, it may be a lymph node, but it contains abnormal cells. This is called lymphadenopathy.
- The structure is painful
- It becomes painful when food passes through the enlarged lymph node.
- There may be redness of the skin above the painful “ball”.
- Symptoms from the whole body also develop: weakness, low-grade fever 37.2 – 37.6°C, fatigue, mild headache.
Often, such symptoms are preceded by signs of the infectious process that served as the trigger for cervical lymphadenitis. This is a sore throat with acute respiratory infections, rashes with measles and rubella, high temperature with scarlet fever or lacunar tonsillitis, intense pain in the jaw with a change in general condition - with phlegmon of its soft tissues or osteomyelitis, etc.
Location
The localization of formations is determined by the protective functions performed. This arrangement makes it possible to most effectively block the path of infection and cancer cells. Mostly lymph nodes are located in front and behind the neck. Clusters are observed near the carotid artery, ears, and under the jaw. Inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes in a specific area can be correlated with signs of certain diseases.
In a healthy person, the cervical lymph nodes should not be palpable. Under pressure, the contours of the formation can be felt, but not accompanied by pain or discomfort. Such manifestations are a sign of inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes and are regarded as pathological symptoms.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis
The main manifestations of inflammation of the lymph nodes are the appearance of small lumps in the neck area. In some cases, they can even be seen with the naked eye, as pronounced swellings appear under the skin.
This is accompanied by pain in the lymph node under the jaw, which increases during palpation and with movement.
Seals and pain in the area of the lymph nodes are accompanied by the appearance of additional symptoms that are characteristic of the acute stage of progression:
- migraine and loss of appetite;
- general malaise and weakness;
- aching joints and difficulty swallowing;
- signs of intoxication and increased body temperature.
In the chronic course of lymphadenitis, the seals are almost invisible. It should be remembered that an exacerbation may occur at any time, which is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in general well-being.
In this case, pain in the lymph node on the left or right side of the neck under the jaw is paroxysmal, in the area of inflammation the skin darkens and swelling increases. When touched, unbearable discomfort occurs, and body temperature rises to 38 degrees.
In advanced cases, pain in the cervical lymph nodes is accompanied by severe proliferation of the area of inflammation and a pronounced migraine. The affected tissues grow noticeably, which is due to the presence of pus.
The condition of the vascular-cardiac system noticeably deteriorates, and adenophlegmons develop. The pathological condition is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39.0-40.0 degrees and above. In this case, the patient needs urgent hospitalization, as emergencies may arise.
general information
The human body contains a huge number of lymph nodes. They perform a protective function and help fight various infections. Accordingly, the lymphatic system is one of the components that are part of the general immune system. Therefore, if the lymph node on the right side of the neck is inflamed, then first of all the suspicion falls on the immune system. However, treatment will directly depend on the specific reasons that caused such symptoms.
Purpose
Lymph begins its journey in the lymphatic system when a person walks. From the feet, when walking, a clear fluid called lymph rises to the head. The system does not have its own engine. Therefore, lymph flows back to the feet by gravity, making a full circle around the body. Lymph nodes are located near vital organs in humans, including the lymph nodes in the neck, which are part of the lymphatic system. In the lymph nodes, the lymph is cleansed of bacteria and infections in order to prevent infection of the areas near the glands, including in the neck.
Inflammation of the cervical nodes: characteristics of the concept
Lymph nodes tend to become inflamed and increase in size. Why is this happening? The problem is the development of lymphadenitis.
Lymphadenitis is a disease associated with a specific or nonspecific inflammatory process in the nodes. An increase in the size of the nodes is accompanied by a feeling of pain in them. In addition, a person develops a headache, general malaise and weakness, low-grade fever or, less commonly, high fever.
Most often, pathology occurs as a secondary complication in the presence of inflammatory processes of any localization. Infectious agents, together with the toxins they secrete, penetrate into the regional lymph nodes along with the lymph flowing from the primary lesion. In some cases, this focus has already disappeared by the time lymphadenitis appears, and it cannot be recognized. Sometimes the disease occurs as a result of infection entering directly into the lymphatic network through damage to the mucous tissue or skin.
The developing inflammatory reaction is a protective function of the lymphatic system: with the help of such a barrier, the body limits the further spread of pathogenic particles through tissues, organs, and blood.
At the same time, along with the development of inflammation in the nodes, a person may begin to develop purulent processes - sepsis and adenophlegmon. The danger of this condition lies in the approach of the infected lymph flow to the brain. If the fluid with the infection it contains enters the brain, it becomes infected, and then serious complications, disability, and sometimes death occur.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck is not an independent disease - it is a signal of the presence of other pathologies and disorders. In addition, inflammation is accompanied by disruption of the entire system of lymph nodes and blood vessels.
Groups of cervical lymph nodes and their location
In the modern classification of lymph nodes of the neck, adopted in 2001, there are 6 groups of lymph nodes, or “levels”.
- Level 1: chin and submandibular;
- Level 2: upper jugular;
- Level 3: middle jugular;
- Level 4: lower jugular;
- Level 5: back group;
- Level 6: front group.
Levels 1, 2 and 5 are divided into sublevels with different locations.
Diagram of the lymphatic cervical system
Level I: mental, submandibular
The mental lymph nodes, included in sublevel 1A, are located in the triangular area created by the anterior belly of Musculus digastricus and Os hyoideum. These include the following nodes:
- chin;
- sublingual;
- suprahyoid;
- Thyroglossofacial.
The submandibular or submandibular lymph nodes, included in sublevel IB, are limited to the anterior portion of the Musculus digastricus, Musculus stylohyoideus, and the mandible. These include the following nodes:
- preglandular;
- postglandular;
- retrovascular;
- post-vascular.
Level II: upper jugular
The superior jugular lymph nodes are located next to the retropharyngeal system
The superior jugular group is located close to the jugular vein and the accessory nerve of the spinal cord. It extends from the base of the skull to the lower part of Os hyoideum. On the right it is bounded by Musculus stylohyoideus, on the left by the posterior margin of Musculus sternocleidomastoideus.
Sublevel IIA is located in front of the spinal nerve, closer to the jaw.
It includes the following types of lymph nodes:
- retropharyngeal;
- tonsillar (angle-maxillary);
- jugular-digastric.
Sublevel IIB is located after the accessory nerve, closer to the neck. It includes the external jugular, or superficial cervical lymph nodes.
Level III: middle jugular
A group of nodes located next to the jugular vein from the lower part of Os hyoideum to the upper part of Cartilago cricoidea. The anterior and posterior borders are similar to the superior jugular lymph nodes.
Location of the middle jugular lymph nodes in the neck
Level 3 lymph nodes include:
- upper thyroid;
- upper deep lateral.
Level IV: lower jugular
The level is located near the jugular vein from the lower part of Cartilago cricoidea to the collarbone. The medial and lateral borders coincide with the upper and middle jugular groups.
The group includes the following types of lymph nodes:
- lower deep lateral;
- jugular-scapular-hyoid;
- Virchow's supraclavicular.
Level V: rear nodes
Neck massage to relieve inflammation of the lymph nodes
The posterior group includes the cervical lymph nodes, fenced in front by the posterior edge of Musculus sternocleidomastoideus, and behind by the anterior edge of Musculus trapezius. The upper border of the region is the connection of these muscles, the lower border is the collarbone.
Sublevel VA is located in front of the cricoid cartilage and includes:
- posterior cervical lateral nodes;
- insertion node.
Sublevel VB is located under the cricoid cartilage and contains the following lymph nodes:
- transverse cervical;
- lower deep lateral;
- supraclavicular, with the exception of Virchow.
Level VI: anterior nodes
The lymph nodes of the anterior group are located under the chin, and are limited on the sides by the common carotid arteries. They are limited above by Os hyoideum, and below by Incisura sterni jugularis.
The front group includes the following nodes:
- pretracheal;
- paratracheal;
- precricoid;
- perithyroid.
Lymph nodes not included in the classification
Location of the postauricular lymph nodes
The following types of cervical lymph nodes are not included in the official classification:
- behind the ear;
- occipital;
- facial nodes;
- parotid, including preauricular;
- retropharyngeal.
During diagnosis and treatment, they are referred to by traditional names.
Types of lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis occurs when one or more lymph nodes become inflamed. Pathology can often be accompanied by the discharge of pus. Today there are several types of the disease, the list of which includes:
- Acute lymphadenitis. The development of the disease begins suddenly. This often happens after surgery or wound suppuration.
- Chronic. Occurs as a result of a prolonged course of infection in the body or progression of the oncological process.
- Recurrent. A type of disease can develop due to chronic inflammation.
Lymphadenitis is also classified according to etiology. There are specific and nonspecific diseases. In the first case, it appears when the pathogens of toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis or syphilis spread throughout the body. In the second case, inflammation is caused by bacteria or fungi.
The nature of inflammation also influences the classification of the disease. A person may experience purulent lymphadenitis. In this case, the topology is accompanied by severe pain and general difficulty. If a person develops serous lymphadenitis, the clinical picture may be blurred. This is possible with viral diseases and oncology.
Reasons for the increase
Soreness indicates the development of an infectious process in humans. The following diseases can provoke lymphadenitis:
- Inflammatory diseases of the neck, head: boil, erysipelas, herpes and fungal inflammation, osteomyelitis and otitis media, hematoma suppuration.
- Dental infections: caries, periodontitis, stomatitis, glossitis.
- Respiratory diseases: tonsillitis, rhinitis, laryngitis, scarlet fever and tuberculosis, tracheitis and influenza.
- Systemic infection: syphilis, AIDS, mononucleosis.
- Non-infectious disease: lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, lymphoma, allergy.
- Blood circulation system: lymphocytic leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis.
- Metastases of oncological tumors of the neck, head and other organs.
A common cause of inflammation in a child is colds. The same effect is exerted by weak immunity against the background of insufficient vitamins and unfavorable ecology.
You should not delay visiting a doctor if the following signs are observed:
- the lymph node has increased sharply;
- soreness to touch;
- in a calm state there is pain;
- the area around the lump turns red;
- purulent foci form on the skin;
- the temperature rises;
- the organ swells.
Timely treatment will help avoid complications. Enlarged nodes can be detected symmetrically.
How to treat lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes themselves cannot be treated. There are no drugs “for lymph nodes”, so symptomatic therapy is carried out for lymphadenitis. Lymphadenopathy (enlargement of nodes) does not need to be treated with special means, since the pathology goes away after the cause of its occurrence is eliminated. In this regard, it is important not to try to treat the lymph nodes yourself without identifying the underlying disease.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is caused by viruses and infections
With lymphadenitis, the cause of the disease lies in infection of the lymph nodes. Contrary to popular belief, various compresses, lotions and dressings with ointments are not able to get rid of the internal inflammatory process, since the components of such a drug cannot properly penetrate the lymph nodes.
Any external means are used to reduce discomfort. For a complete cure, it is necessary to destroy pathogens in the lymph nodes and strengthen the immune system. All this is done with the help of special medications that can only be selected by a doctor.
However, this does not mean that lymph nodes cannot be treated at home. You can make you feel better with simple remedies from your home medicine cabinet, but the effectiveness of such therapy is questionable if the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes is not promptly identified and eliminated.
Before you begin treatment at home, you should be able to distinguish lymphadenitis from lymphadenopathy. This can be done based on the nature of the pain syndrome and accompanying symptoms. If the nodes are enlarged but do not hurt, this is lymphadenopathy. In this case, no specific treatment is required. With lymphadenitis, an inflammatory process begins in the nodes, which is accompanied by pain that intensifies with palpation and sudden movements.
When the lymph nodes are inflamed, the body temperature rises; if suppuration develops, the temperature can reach 40 degrees. As a rule, any inflammatory processes in the body are accompanied by general malaise; symptoms of intoxication may be present - headache, nausea, single vomiting, weakness.
Local therapy (ointments and gels)
How to cure lymph nodes depends on the cause of their inflammation. External agents, gels and ointments, are used as symptomatic therapy for inflammation of the lymph nodes. As a rule, at home they use:
- ichthyol ointment;
- Vishnevsky liniment;
- drug Levomekol;
- heparin ointment.
The effect of each of the listed drugs is due to the active components in the composition. For inflammation of the lymph nodes, the listed medications are applied under a bandage, which should be changed every 6-8 hours. Thus, dressings are done 2-3 times a day.
Ichthyol ointment is used for inflammation of the lymph nodes due to its antiseptic effect. The drug has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, is able to penetrate deep into the epidermis, and has a pronounced antiseptic and disinfectant effect. The medicine has an affordable price - about 50 rubles per tube of ointment. The drug has no contraindications, except for individual intolerance. When using the ointment, it is important to prevent it from coming into contact with mucous membranes and eyes, so after applying the product you should wash your hands thoroughly. Ichthyol ointment helps reduce inflammation of the lymph nodes and eliminates pain. It should be used twice a day. Side effects: allergic rash, skin irritation, itching of the epidermis in the treated area.
The most effective and relatively safe remedy is Vishnevsky ointment for inflammation of the lymph nodes. Vishnevsky's liniment is a thick, viscous mass of dark color with a specific odor. The product is intended for the treatment of abscesses, boils and lymphadenitis. The drug has an antiseptic and antibacterial effect, stimulates tissue regeneration. Vishnevsky ointment is applied to the inflamed lymph nodes once a day. The cost of the medicine is no more than 45 rubles.
The drug has no contraindications, except for intolerance to the main active ingredient. Those who doubt whether Vishnevsky ointment can be applied to inflamed lymph nodes should carefully study the official instructions, in which lymphadenitis is included in the list of indications for the use of the drug. However, if there is no improvement 4-5 days after starting treatment, you should consult your doctor.
Levomikol helps relieve inflammation and swelling of the lymph nodes
Another popular drug with an antibacterial effect is Levomekol ointment for inflammation of the lymph nodes. This is a combination drug that has an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect, while simultaneously promoting rapid wound healing. The medicine is intended for the treatment of trophic ulcers, infected wounds, boils, but can also be used for lymphadenitis. The drug has several contraindications - fungal skin infections, eczema, psoriasis. The medicine should also not be used in case of individual intolerance. The ointment can cause allergic reactions, including angioedema. Before starting use, you should exclude intolerance to the drug. The cost of the ointment is about 100 rubles.
Heparin ointment is a local anticoagulant and is intended for the treatment of varicose veins and the prevention of blood clots. Heparin ointment for inflammation of the lymph nodes is used for symptomatic treatment due to its decongestant, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. The drug can also be used for lymphadenopathy - enlarged lymph nodes without inflammation. Another indication for use is lymphostasis of the extremities. The ointment helps resolve swelling in the area of the affected lymph nodes and reduces pain. The drug has a number of contraindications:
- open infected wounds;
- ulcers;
- necrotic processes;
- thrombocytopenia;
- hemophilia.
Before you start using the medicine, you should consult your doctor. It is not recommended to apply ointment to lymph nodes if a purulent inflammatory process is suspected. The drug can cause an allergic skin reaction, irritation of the epidermis, itching and burning.
The cost of the medicine is 50-80 rubles.
How to use the ointment?
Medicine for inflammation of the lymph nodes in the form of an ointment must be used correctly. Having decided what to apply to the inflamed lymph nodes, you should take a piece of bandage or gauze and fold it 6-7 times. When treating lymph nodes with ointments, gauze is soaked in the drug and then applied to the site of inflammation, secured on top with a clean piece of gauze or an elastic bandage. Such compresses should be changed 1-2 times a day. So, ichthyol ointment can be applied every 6 hours, heparin ointment - in the morning and evening, Vishnevsky ointment - once a day.
In the first two days of treatment, dressings can be done more often.
If inflammation is accompanied by a pronounced enlargement of the lymph nodes, it is recommended to give preference to heparin ointment, as it helps reduce tissue swelling. In general, what to smear the lymph node with is best determined by the doctor after examining the patient.
Preparations for internal use (tablets)
Tablets for inflammation of the lymph nodes should only be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication may be unsafe for the patient's health. For inflammation of the lymph nodes, drugs of four groups are used - painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antiviral drugs and immunostimulants.
Before using medications, you should consult your doctor.
Painkillers for lymph nodes with inflammation:
- Ibuprofen;
- Nimesil;
- Nalgezin et al.
All these drugs belong to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They have a pronounced analgesic effect, reduce inflammation, and normalize body temperature. The most affordable drug for inflammation of the lymph nodes is Ibuprofen. Its cost does not exceed 100 rubles. The drug has a number of contraindications: severe forms of heart, kidney and liver failure, gastric ulcer, pregnancy, intestinal inflammation. The drug is used to reduce pain every 4-6 hours. The drug can cause a number of side effects, including liver and kidney problems, so it should be used with caution.
Note! Anti-inflammatory drugs for inflammation of the lymph nodes can be taken for no more than 5 days in a row.
Nimesil is available in powder form for the preparation of a suspension. A package of 9 sachets costs about 300 rubles. The product has a pronounced antipyretic effect, therefore it is recommended for inflammation of the lymph nodes, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. The maximum daily dosage is 2 sachets at regular intervals.
Nalgesin and Nalgesin Forte are potent anti-inflammatory drugs that are also used for inflammation of the lymph nodes. The drug effectively eliminates pain and reduces fever. The cost of packaging is about 200 rubles. It is important to understand that if the lymph nodes become inflamed, you should act on the cause of the disorder, and not treat the symptoms. At the same time, all of the listed anti-inflammatory drugs refer to drugs for symptomatic therapy.
One of the effective medications prescribed for inflammation of the lymph nodes is the drug Kagocel. This remedy has an antiviral effect and is a powerful immunostimulant. The drug stimulates the release of interferon in the body, thereby tuning the body to fight viruses that provoke inflammation of the lymph nodes. At the same time, the medicine is ineffective against bacterial inflammation. Kagocel has no contraindications, except for individual intolerance and pregnancy. The product should not be given to children under three years of age. Side effects include allergic reactions. The cost of the medicine is about 250 rubles per package.
Antibiotics for lymphadenitis are selected and prescribed only by a doctor.
In addition to the medications listed, for inflammation of the lymph nodes, it is recommended to take vitamin C tablets (ascorbic acid). As practice shows, vitamin C accelerates the recovery of inflamed lymph nodes by stimulating the immune system.
Diagnosis of pathology
Diagnosis of inflamed cervical lymph nodes is carried out by a therapist. For successful treatment it is necessary to determine the causes of the disease. An examination by an ENT specialist, dentist, or dermatologist may be required. To confirm the diagnosis, a laboratory blood test and scraping (for dermatological diseases) are done.
If the cause of lymphadenitis cannot be identified, additional procedures will be required: ultrasound diagnosis of internal organs, chest x-ray, etc. In advanced cases of the disease, an ultrasound examination of the lymph nodes is performed, and if a tumor is suspected, a biopsy is performed.
To diagnose the disease, you should not wait for the intensity of the first symptoms to increase. Only a specialist can correctly determine the reasons.
The main methods for diagnosing pathologies of lymph nodes are:
- Blood analysis;
- Visual inspection, palpation;
- MRI, CT, ultrasound;
- Biopsy of inflamed lymph nodes;
- Carrying out histological analysis.
Treatment of posterior cervical lymph nodes
After eliminating the cause of the disease in the lymph nodes in the back of the neck, their size gradually returns to normal. The choice of drugs is made based on the cause of the pathology. Thus, treatment of fungal infections of the scalp is usually carried out using local remedies. Systemic antibiotics are rarely used (only for severe fungal infections). If the inflammatory process is bacterial or viral in nature, antibiotics or antiviral medications are used.
If a person has inflamed posterior cervical lymph nodes, then medications are usually prescribed that improve the functioning of the immune system and stop the inflammatory process, for example, Prednisolone, Medrol. Sometimes it is recommended to take vitamin C, which helps strengthen the body's defenses. Echinacea tincture, which can be purchased in finished form at a pharmacy, has a similar effect.
If the posterior cervical lymph node has enlarged due to a dental disease, then, first of all, sanitation of the oral cavity is required. Treatment with drugs is not always necessary.
Physiotherapy can be used to normalize size. These methods are indicated for the treatment of certain diseases that cause the development of inflammation in the lymphatic system. In this case, they are used in combination with other measures.
If the posterior cervical lymph nodes have enlarged as a result of a cancerous process, then consultation with an oncologist and treatment using chemical or radiation therapy, or surgery to excise the affected tissue is required.
With timely and correct treatment of the underlying disease, the condition of the posterior lymph nodes gradually normalizes. Purulent tissue damage requires urgent treatment, since otherwise the infection can spread to the brain. It should be remembered that an enlarged cervical lymph node can provoke swelling of the parotid and salivary glands, as well as the tonsils and thyroid gland.
Herbal infusions
Enlarged lymph nodes are returned to a healthy state using the following recipes:
- Add 10 drops of echinacea to ¼ glass of water or juice. Take orally from 4 r/day. If echinacea is in powder, then take ¼ tsp orally. 3 r/day. To prepare the syrup, you need to boil 1.5 cups of water, add 4 tsp. dried root, let simmer for 20 minutes. After removing from heat, add 50 g of fresh peppermint. Let stand for about 5 minutes, then strain and add honey to taste. Drink 3 times a day, 1-2 tsp. until complete recovery.
- 1 tsp. dilute Canadian goldenseal powder in 200 g of boiled water. Take orally 1 time/day. During the course, it is recommended to give preference to fermented milk products to reduce the risk of intestinal disorders.
- Squeeze 1 tbsp from a fresh aloe leaf. l. juice Consume daily on an empty stomach before meals.
- Wash the pine shoots, add water, and put on fire. After boiling, cook over low heat for about 20 minutes, covering with a tight lid. Cool, strain, add 2.5 tbsp. l. honey Take orally on an empty stomach before breakfast and before bed.
- Grind and mix plantain, calendula, birch leaves in equal proportions, put the herb collection on the fire. After boiling, remove from heat and leave for 3 hours. Strain, add 0.5 tsp. lemon juice. Consume on an empty stomach before breakfast for a month.
In addition to the above recipes, herbal decoctions of mint, chamomile, currant leaves, elderberry, horsetail, and calendula effectively restore the activity of the lymphatic system. It is recommended to add lemon and honey to taste to the decoctions to enhance the effect.
Where are they located?
By the names of these peripheral organs one can understand their localization. Lymph nodes are mainly localized in the back of the neck, as well as in the front part of it in the area of the carotid artery.
You can also feel them near the ears, in the area of the connection of the lower jaw and the skull, near the hyoid bone, behind the ears, near the clavicular cavity, near the point of connection of the cervical vertebrae and the skull. Knowing where the lymph node is located in the neck, you can determine the cause of the appearance of lumps and nodules in the soft tissues under the skin.
Neck location diagram
The location of the lymph nodes in this area is easy to describe even without an image. The pattern of lymph nodes in the neck correlates with the location of large blood and lymphatic vessels. They are arranged in the form of connected chain links parallel to the direction of blood and lymph flow. The lymph nodes in the back of the neck, whose location corresponds to the splenius and suboccipital muscles, are also included in this group.
Posterior (posterior cervical)
This group of lymph nodes is located, as its name suggests, on the back of the neck and at the base of the skull. The posterior cervical lymph nodes include:
- retroauricular;
- occipital;
- deep and superficial cervical.
Anterior cervical
The anterior cervical lymph nodes include the deep cervical nodes located above the carotid artery. The anterior cervical lymph nodes include subclavian lymphatic formations.
Submandibular
The group of submandibular lymph nodes includes the submandibular lymph nodes themselves, as well as the mental and tonsillar lymph nodes. Close to them, in the ear area, are the parotid and preauricular lymph nodes, which some doctors classify as a separate subgroup.
Stages of inflammation
Depending on the intensity of inflammation, the process can develop at different speeds. At the initial stages, there is a slight increase and pain on palpation, which, with timely treatment, leads to a rapid recovery from local lymphadenitis. If the causes are deeper, this will lead to the opportunity to diagnose a dangerous disease and begin treatment immediately.
Advanced lymphadenitis develops into a serious form, which is characterized by constant pain. The nodes become denser and enlarge even more.
The extreme stage is acute purulent lymphadenitis, which leads to tissue damage. The person’s condition deteriorates greatly, the temperature rises to a critical level, the skin in the area of the inflamed nodes changes color.
At the stage of purulent formations, urgent hospitalization and medical supervision are required to prevent pus from entering the body.
Classification
There are several types of lymph nodes depending on their location. Cervical lymph nodes, the location of which allows them to be called para-aortic, are divided into several subgroups. The standard classification of neck lymph nodes includes:
- deep and superficial;
- anterior and posterior cervical;
- supraclavicular;
- submandibular;
- chin;
- tonsillar;
- occipital;
- behind the ear and parotid;
- sublingual.
Location and purpose
Lymph nodes are peripheral organs of the lymphatic system that take on the function of a biological filter. Lymph flows through them, which comes from other parts of the body and organs. The main task of the lymph nodes is to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from entering the body. However, the body also performs a whole list of other functions, the list of which includes:
- participation in biological processes;
- formation of blood elements - lymphocytes;
- stimulation of cell proliferation in some organs;
- formation of immune cells.
Lymph nodes are located throughout the human body. However, most of them are located on the neck. Based on the location of the lymph nodes there are:
- retropharyngeal;
- submandibular;
- anterior and posterior cervical;
- anterior and posterior ears;
- chin;
- submandibular
In normal condition, the lymph nodes cannot be palpated, with the exception of the superficial lymph nodes. They are located close to the skin and can be noticeable upon palpation. Healthy lymph nodes are soft to the touch and mobile. Their palpation does not cause pain. In this case, the size of one lymph node should not exceed 1 cm.
If the number of pathogenic microorganisms increases greatly, the lymph nodes cease to cope with their function. This leads to an increase in their size. In medicine, inflammation of the lymph nodes is called lymphadenitis.
What are the cervical lymph nodes responsible for?
The muscles connecting the head and torso are the main area where the lymph nodes in the neck are located. In addition to the neck, the main areas where large lymph nodes are located are the armpits, torso, elbow and knee joints, and groin area.
The concentration of nodes in the neck and groin area is explained by their proximity to natural openings in the human body. Through them, infections most often enter the body - bacteria, viruses, microbes. Based on this, you can understand the purpose that these lymph nodes serve: being located on the neck close to these openings allows the body to more quickly and efficiently cope with the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms.
The main thing that the cervical lymph nodes are responsible for is stopping the spread of infection that enters through the nose, mouth and ears.
The lymph nodes of the neck are designed to fight respiratory infections and microbes that cause inflammation in organs that are commonly called “ENT organs” (influenza, ARVI, tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis, sinusitis). The second thing that the lymph nodes in the neck are responsible for is the fight against infections of the oral cavity and teeth - caries, acute pulpitis, stomatitis, gingivitis. Often, enlarged lymph nodes are observed when the growth of wisdom teeth is activated.
Lymph nodes in the neck, where large blood vessels are located, are designed to stop the spread of infection with the help of increased production of immune cells - lymphocytes and phagocytes during the active phase of the life of a virus or bacteria (streptococcus, staphylococcus).
When a foreign agent invades the body, an active immune response manifests itself in the form of several symptoms. Evidence of the body’s enhanced fight against infection is:
- increased size of lymph nodes;
- soreness and redness of the skin;
- good visibility and easy palpation of formations.
The stronger the immune response, the larger the size of the nodes may be. The normal size of cervical lymph nodes in adults usually does not exceed 5–7 mm. In acute infections, accompanied by high body temperature and the formation of purulent foci, the lymph nodes can increase in size by 5–10 times, sometimes reaching a diameter of 5 cm or more. In this state, they are clearly visible under the skin, their structure becomes denser or, conversely, heterogeneous and glandular. Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck can limit head movement and lower jaw mobility, making chewing, swallowing and speech difficult.
Which doctor should I contact if I have swollen lymph nodes?
| Manifestations of pathology | Specialist |
| The links of immunity are defined as balls to the touch and move under the skin | Infectious disease specialist |
| Lymph nodes have uneven borders, a heterogeneous structure (“lumps”), do not move, and do not cause pain when palpated | Oncologist |
| Suppuration of the formation, in which it becomes hot and painful | Surgeon |
| Inflammation of the throat or oral cavity, accompanied by increased pain when palpating the lymph node and its mobility | ENT, therapist, dentist |
The nodules are collected in groups. If certain lymph nodes in the neck are inflamed, then most likely the problem lies in neighboring organs. Then, when the pathological process is systemic in nature or there are diseases of the immune system, several formations are affected at once.
Ointments
After a compress or massage, it is recommended to smear the lymph nodes with ointment. Ointments that effectively affect inflamed areas include Vishnevsky ointment (relieves inflammation) and Ichthyol ointment (relieves severe pain and swelling). The following recommendations will tell you how to treat lymph nodes in the neck with ointments:
- smear the affected areas with one of the ointments 2-3 times a day;
- use Ichthyol ointment for severe pain. Stop using if an allergic reaction occurs;
- To avoid getting dirty, it is recommended to cover the smeared area with a scarf or gauze.
Homemade recipe:
- Heat 100 g of interior fat in a water bath.
- Add 1 tbsp to melted fat. l. dried norichnik.
- Steam the mixture for about an hour.
- Strain without waiting for it to cool.
- Warm slightly before each use.
- Keep refrigerated.
What are the symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes?
If a node in the lymphatic system becomes inflamed and begins to enlarge, it is a sign that something has gone wrong in your body.
This condition is called lymphadenitis and it can cause discomfort and pain in the lymph nodes, as well as swelling, which can enlarge the node to the size of a pea, bean, and sometimes a walnut.
Depending on the cause of inflammation of the nodes, you may experience other symptoms:
- Common symptoms of a cold: runny nose, sore throat, high fever. In this case, the lymph nodes under the jaw and behind the ears may also be bothersome.
- General enlargement of lymph nodes throughout the body (this symptom may indicate infections such as HIV or mononucleosis, as well as some autoimmune disorders such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis).
- Swelling of the extremities, which may indicate blockage of the vessels through which lymph moves.
- Hard and rapidly growing nodes, which may indicate the possibility of developing a cancerous tumor.
- Fever, without any other cold symptoms.
- Increased sweating at night.
- The appearance of unusual vaginal discharge in women.
The nodes become especially painful when they suppurate. In this case, they can become very dense, lose clear contours and cause many severe symptoms in the patient:
- temperature,
- headache,
- loss of appetite.
Purulent nodes are also very painful, so they can interfere with movement.
Symptoms of the disease
An enlargement of one cervical lymph node in an adult causes a certain discomfort that occurs when turning the head. The sensations are most often pulling, although they can be sharp. The patient can also palpate and identify the enlarged area. His throat hurts and it’s hard to take a sip. When you press on a lymph node, a person experiences quite severe pain.
In addition, other symptoms of pathology can be identified:
- apathy;
- change in temperature indicators;
- general malaise;
- deterioration or lack of appetite;
- pronounced change in the size of the lymph node;
- in the presence of suppuration, the organ becomes either too soft or hardens;
- redness of the skin around the affected lymph node;
- headache;
- discomfort in the muscles.
Unilateral lymphadenitis can become chronic. However, patients do not have acute symptoms. Either one or several lymph nodes may be affected. When you press on them, the pain will not be pronounced. A sick person should consult a family doctor (general practitioner or pediatrician). You may need to consult other specialists: endocrinologist, oncologist, infectious disease specialist, hematologist.
If the enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes on one side is not treated, the tissue of these organs will begin to grow, and the pathological process will be accompanied by the appearance of suppuration.
Possible diseases
If the lymph nodes in the back of the neck are enlarged, but there is no pain, then this anomaly is called lymphadenopathy and is usually a sign of ailments of nearby organs.
Soreness that appears in the posterior lymph node of the neck indicates inflammation that has developed in it. This pathology is called lymphadenitis and occurs in response to too much pressure of microorganisms on the lymph node or due to insufficient filtration of lymph by it.
If the lymph nodes in the back of your neck have become enlarged, you need to see a doctor and get a treatment regimen. To restore the healthy state of an organ, as a rule, it is enough to treat the underlying disease that led to an increase in size.
The posterior lymph nodes in the neck may become enlarged due to the following reasons:
- otitis;
- metabolic disorders;
- rhinitis;
- the presence of a boil;
- pneumonia;
- cancer;
- animal scratches;
- diseases of the oral cavity (for example, caries);
- HIV infections;
- tuberculosis;
- purulent sore throat;
- syphilis;
- allergic pathologies;
- ailments caused by fungi;
- immunodeficiency;
- alcohol abuse;
- rubella, toxoplasmosis and other infectious diseases;
- pharyngitis.
Posterior cervical lymphadenitis on one side is just as dangerous as bilateral lymphadenitis, since the affected areas are located near the brain, which over time can provoke the spread of infection to its tissue. Inflammation on both sides may indicate a serious illness.
Clinical picture
Cervical lymphadenopathy is accompanied not only by dull, aching pain, the intensity of which increases with pressure. When palpated, you can detect a small elastic, elastic and movable seal. If the inflammatory process worsens, the size of the formation increases. Sometimes they exceed 5 cm and the compaction is clearly visible. Unlike malignant tumors, such a formation with unclear contours has a dense, tuberous structure. Lymphadenopathy is also characterized by other signs:
- when swallowing food, painful sensations occur;
- the skin above the seal becomes even and red.
In response to the penetration of foreign proteins into the body, symptoms of general intoxication develop. Body temperature rises to subfebrile levels (37.5°C), headaches, weakness, fatigue, and dyspeptic disorders occur.
Inflammation and pain in the cervical nodes in children should be a signal to immediately consult a doctor. The immune system of babies is just developing, so it is not able to cope with infectious agents. In the absence of medical care, chronic lymphadenitis develops. It is usually detected by chance, when palpating the lymph nodes, which are always slightly enlarged.
The acute inflammatory process in the lymph nodes in children is much more severe than in adults. The temperature rises, the neck swells, and sometimes a fever occurs. The pain when swallowing is so acute that the child refuses not only to eat, but also to drink.