The human body contains a large number of different systems. In addition to the digestive, respiratory and circulatory systems, there are many others that are less known to the common man. The lymphatic system, which is an integral part of the cardiovascular system, falls into this category. Let's find out what lymph nodes are on the human body and what they are needed for.
Lymph nodes are one of the most important organs of the lymphatic system
What are lymph nodes
The lymphatic system contains a huge number of lymph nodes, which are located in different parts of the body. The lymph nodes themselves are organs that are small in size and round in shape. The diameter of these organs varies from five millimeters to five centimeters, depending on the location.
Inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes may be associated with an increase in their diameter.
Lymph nodes are located in various parts of the body and in most cases are located close to blood vessels . They are quite easy to palpate, as they are literally on the surface of the subcutaneous tissue. The easiest places to feel are the lymph nodes located in the neck and armpit.
The structure and functions of the lymph nodes in the neck
The lymph nodes are assigned a whole list of functions. The list includes:
- barrier This is one of the important functions of lymph nodes. They are the first to react to contact with a damaging agent;
- filtration Lymph nodes do not allow pathogenic microorganisms to enter the human blood and continue their journey to other internal organs. Here, foreign particles, microbes and tumor cells are retained;
- immune. It is associated with the production of lymphocytes and immunoglobulins;
- synthetic. In the lymph nodes, a special leukocyte factor is synthesized, which has a stimulating effect on the reproduction of blood cells;
- exchange. Lymph nodes are involved in the metabolism of fats, vitamins, proteins and carbohydrates, as well as in digestion processes.
Lymph passes through the sinuses of the medulla, where it is cleansed of foreign antigens. The human immune system responds to all inflammation by enlarging the lymph nodes. Each group is used to protect a specific part of the human body. The function of immune defense is assigned to lymphocytes. They fight viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms. Lymphocytes are located inside the capsule of each node.
Lymph passes through the sinuses of the medulla, where it is cleared of infections, tumor lesions and other foreign antigens. The immune response to certain inflammations in the body is enlargement of the lymph nodes. Each group is needed to protect a specific part of the human body. The function of immune defense is performed by lymphocytes, i.e. protective cells. They actively fight viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. Lymphocytes are located inside the capsule of each node.
Properties of lymph nodes
Each individual element of the lymphatic system is a kind of biological filter. Thanks to the lymph nodes, the lymphatic system is cleansed, which helps prevent the development of dangerous diseases . In addition, each individual element takes a direct part in the fight against various pathogenic organisms that negatively affect the body.
The primary purpose of lymph nodes is the production of lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a kind of protectors of the body and are an integral part of the immune system. Below in the article you can see the location of lymph nodes on the human body in pictures.
Let's look at the main functions of this system. Experts say that this system is responsible for constantly monitoring the effects of various foreign bodies in the human body. When pathogens are detected, the lymph nodes become a kind of barrier to bacteria, viruses and cancer cells. These elements are also responsible for the synthesis of lymphocytes and antibodies.
Certain elements of the lymphatic system are responsible for distributing nutrients throughout the body, as well as removing toxins through the urethra. Based on this, we can say that the lymphatic system is one of the most important components for the human body.
Lymph nodes in the human body
Lymph node is a peripheral organ of the lymphatic system that acts as a biological filter through which lymph flows.
Lymph nodes are located in small groups (on average 7-12 pieces) near all large veins and vital organs. There are more than 500 lymph nodes in the human body, and their exact number is a physiological feature of each organism.
Lymph nodes ensure the cleansing of lymph. This is an important organ of the immune system, which serves as a kind of repository for immune cells and antibodies produced by the body to fight various infections. Lymph (intercellular fluid) moves through the lymphatic vessels from bottom to top and passes through the lymph nodes. In them, it is freed from toxins and infections, and is also saturated with immune cells. The purified lymph then enters the general bloodstream, saturating the blood with immune cells and a number of nutrients.
Lymph nodes are located in groups, such groups are called regional.
Thus, the lymph nodes perform a vital function, providing immune support and protecting the body from various diseases. At the same time, the lymph nodes themselves are a very vulnerable organ, the work of which directly depends on the immune system. Lymph nodes react acutely to any pathological processes accompanied by a decrease in immunity, which manifests itself in diseases of the lymph nodes - lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis.
Anatomy of lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are small formations, predominantly round, bean-shaped or oval. The structure is represented by two elements - the capsule and the internal space of the lymph node. The capsule of the node is formed from connective tissue. The structural basis of the node, hidden in the capsule, is called stroma. The internal part of the node is a complex structure of lymphoid tissue, consisting of two layers: cortical and medulla. Inside the lymph node are lymphocytes - immune cells. These cells saturate the purified lymph and then penetrate the circulatory system, providing complete immune protection for the body.
Each node is connected to afferent lymphatic vessels on one side and efferent vessels on the other. On the convex side of the node there is a valve that prevents the reverse outflow of incoming lymph, and on the concave side there is a node gate that passes into the efferent vessels.
The normal size of lymph nodes is from 5 to 10 mm. Some nodes can reach 50 mm in size, which is not a deviation from the norm. There are no exact standards, since the size of the lymph nodes is individual for everyone and is a physiological feature. The dimensions of the smallest node are less than 1 mm, the largest are more than 5 cm. On average, the size of lymph nodes in children ranges from 3 to 10 mm. Superficial lymph nodes in children and adults are large enough to be palpated; internal ones, located in the chest or abdominal cavity, rarely exceed 5-7 mm in diameter.
The lymph node has a complex structure
Functions
Lymph nodes are the filter of the human body. Lymphocytes mature in them and special antibodies are released to fight infections.
Intercellular fluid from tissues and organs is collected through the lymphatic capillaries and then enters the lymphatic vessels connected to the lymph nodes. Lymph is supplied to the node through the afferent vessels, then cleared in the node, and then exits through the efferent vessels, through which it is then supplied to the bloodstream.
Directly in the lymph nodes, this fluid is cleared of toxins and infections, saturated with lymphocytes and antibodies, and then carried into the circulatory system, supplying immune cells to the blood.
Thus, the lymph nodes perform an important barrier function, protecting the body from various infections. In addition, the protective function of lymph nodes also manifests itself against cancer cells. When cancer cells are “detected” in the lymph nodes, the body’s immune response to the pathological process is triggered.
Lymph node location map
Experts classify these elements of the lymphatic system into two main categories, internal and external lymph nodes. Below is a diagram of the location of these elements in the body.
Lymph nodes play the role of filters, preventing various microorganisms from entering the blood
External lymph nodes
These elements of the lymphatic system are located in various parts of the body. When diagnosing various diseases that are accompanied by inflammatory processes, specialists pay special attention to examining nodes located in the neck, armpit and groin area.
Neck area
Lymph nodes located in this area of the body protect the head from various infections. Pain and increased lymph size may indicate the development of an infection. With a disease such as tonsillitis, the lymph nodes in the neck become so enlarged that they can easily be seen with the naked eye.
Location of lymph nodes on the face:
- under the chin;
- behind the ears.
Light pressure on the above areas will help determine the location of the lymph nodes. Palpation of this important component of the body is part of the mandatory measures when examining patients with colds.
Let's start studying these elements that are located in the neck area. The main part of the lymph nodes is concentrated under the lower jaw in the chin area. The second group of nodes is located in the occipital region. This group includes nodes located behind the ears.
The most important elements are considered to be the pharyngeal lymph nodes. According to the anatomical diagram of the human body, more than a hundred individual elements of the lymphatic system are concentrated in the cervical region.
Each of these elements takes an active part in protecting the body from the negative effects of various pathogenic microorganisms. Lymph nodes act as a kind of barrier that prevents the spread of infection. With a high degree of severity of the disease, the lymph nodes may not cope with their role. This leads to the spread of infection throughout the body. In this situation, in order to speed up recovery, experts recommend starting to use drugs with antibacterial action.
Armpit
Lymph nodes in the armpit area are located on both sides under the limbs. In the absence of pathological processes in this area, it is impossible to palpate these elements. Inflammatory processes in this area in women indicate the development of diseases associated with disruption of the mammary glands. However, inflammation of the lymph nodes is often observed during the development of cancer.
In order to identify the factor that acted as the main cause of enlarged lymph nodes in a given area of the body, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnostic examination. Among the reasons leading to the appearance of this pathological condition, the effect of viruses and the development of colds should be highlighted as the most common factors for enlarged lymph nodes. Lymph nodes on the arm also play an important role during diagnosis. Their condition can tell an experienced specialist about various disorders present in the body.
The location of the lymph nodes is designed by nature to be very rational, so that they serve as a barrier to bacteria, viruses, and malignant cells
Groin area
Lymph nodes located in the groin area are also easily palpable. These elements are located on the inner surface of the thigh. The task of these elements of the lymphatic system is to protect the genital organs from various infections. In addition, the lymph nodes located in this area take an active part in creating barriers against the spread of viruses into internal organs.
When these elements become inflamed, a person feels discomfort when walking. Such symptoms may be a consequence of the development of oncology, and in order to exclude this factor, a thorough medical examination is required.
Among the less important external elements of the lymphatic system, the ulnar, supraclavicular, popliteal and subclavian lymph nodes should be highlighted. Their location on the body is indicated by their name.
Internal lymph nodes
Let's look at where the lymph nodes are located on the human body, a diagram and description of the elements that belong to the internal group of elements. Among the internal lymph nodes, the following should be highlighted:
- Mesenteric - located in the area of the peritoneal fold, at the site of attachment of the intestine to the peritoneum.
- Iliac - located in the pelvis, next to the mesenteric lymph nodes.
- Intrathoracic - this category of elements is called the term “mediastinal lymph nodes”. This type of lymph node is located near the lungs.
- Bronchopulmonary - located near the bronchi, next to the mediastinal lymph nodes.
- Para-aortic - located in the upper abdomen, near the heart.
- Splenic - in accordance with their name, located in the area of the spleen. Since these elements are located deep in the tissues, their condition can only be assessed using ultrasound.
In addition to the above-described groups of internal lymph nodes, there is such an element as the lymphoepithelial ring. This element is better known as the tonsils, and is located on the borders of the pharynx and oral cavity. Each of the above elements takes an important part in protecting internal organs from the negative effects of various types of infection.
Like all body systems, lymph nodes are susceptible to various diseases. Let's find out more about them.
The lymphatic system is not closed in a circle; fluid (lymph) moves through it only in one direction
What to do if a child’s lymph node is inflamed
In 2019, scientists from North Carolina Southeastern Regional Medical Center published data showing that lymphadenopathy (a condition characterized by changes in the lymph nodes) is much more common in the pediatric population. In addition, in more than 75% of cases, enlargement of lymph nodes is local in nature.
Many parents do not know what to do if their child has an inflamed lymph node. Clinically this manifests itself:
- Palpable lumps under the jaw, on the sides of the neck, in the armpit, in the groin or abdominal area;
- Pain or increased sensitivity in the area of the enlarged lymph node;
- Redness and increased warmth in the area.
However, lymph node enlargement rarely occurs in isolation. So, even if the child is small and cannot tell his parents what is bothering him, parents should pay attention to the following symptoms of the disease:
- Runny nose, cough, sore throat (most often manifested when swallowing);
- Decreased appetite;
- Signs of intoxication;
- Fatigue, increased drowsiness;
- Weight loss;
- Rash on the body and mucous membranes.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in children is most often associated with:
- Infection of the body with viruses or bacteria;
- Reactions to medications (some antibiotics and anticonvulsants);
- Juvenile arthritis and joint diseases affecting children;
- Allergic reactions.
There may be other reasons for changes in lymph nodes, but in such cases other symptoms most often come to the fore.
In 2019, scientists from the Medical Academy of Ankara, Turkey, published data according to which inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck in children is more common than in other areas of the body. This is due to the high activity of lymphoid tissue located at the entrance to the upper respiratory tract and digestive tract. Otherwise, this accumulation of lymphoid tissue is called the lymphatic pharyngeal ring.
Thus, if a child has an inflamed lymph node in the neck or in another area, you should consult a pediatrician. It is the specialist who will be able to assess the patient’s condition and prescribe correct and timely treatment, because do not forget that lymphadenopathy is only one of the nonspecific manifestations of the pathological process.
Lymphadenitis
From the above, we learned what lymph nodes are on the human body, the location and purpose of these elements of the lymphatic system. In a calm state, the diameter of the lymph nodes ranges from five to fifty millimeters. An increase in diameter, pain symptoms and other unpleasant sensations may indicate inflammatory processes, which are designated by the term “lymphadenitis”.
This disease is often accompanied by pain on palpation, fever, migraine attacks and increased weakness. Experts divide this disease into two main categories and destructive. In the simple form of the disease, individual elements of the lymphatic system become inflamed. Less commonly, a simple form of the disease is accompanied by purulent processes. With destructive pathology, inflammatory processes spread not only to the lymph nodes, but also to the tissues surrounding them. In addition, lymphadenitis is divided into the following forms:
- Purulent - this pathology has an acute form of development and is accompanied by severe pain in the area of fixed lymph nodes.
- Non-purulent - a less serious form of the disease, which is manifested by a feeling of discomfort when touched.
- Acute - accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature, weakness and pain symptoms when touched.
- Chronic - with this form of pathological condition, a painless enlargement of the lymph nodes is observed. The disease manifests itself in the absence of treatment for the acute form of the pathology.
The appearance of lymphadenitis is most often associated with various inflammatory processes occurring in the body. In order to identify the root cause of the pathology, you will need to undergo a full diagnostic examination.
Treatment
An inflamed lymph node on the face is a serious reason to visit a qualified surgeon to prescribe treatment.
Don't self-medicate!
Follow your doctor's orders
Take prescribed medications and procedures on time
Inflamed lymph nodes on the face are the area of treatment for the surgeon. Based on the results of the examination and tests, he can prescribe treatment:
- Simple relief of inflammation symptoms (symptomatic therapy)
- Resolution of the main problem (disease) is etiotropic treatment
- Restoring all the capabilities of the immune system
Etiotropic treatment
After identifying the underlying disease, the side symptoms of which are lymphadenitis, comprehensive treatment must be carried out.
- If the cause of inflammation of the nodes lies in dental diseases, you need to visit a dentist. Treat all problem teeth and gums. And don’t forget about further dental hygiene.
- Did the nodes become noticeable after suffering from a cold or flu? Then the doctor will prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Allergic manifestations of lymphadenitis on the face can be treated with antihistamines and minimizing exposure to the allergen.
- The cause of inflammation of the nodes on the face is sore throat, rubella, then the doctor will prescribe antibacterial drugs.
Symptomatic therapy
Many doctors, with purulent or painful inflammation of the lymph nodes, try to relieve the symptoms in order to alleviate the patient’s condition.
- Painkillers, antipyretics, anti-inflammatory drugs
- Detoxification medications are prescribed
This approach allows you to relieve acute manifestations of lymphadenitis:
- Painful sensations
- Itching
- Normalizes body temperature
After the symptoms of the disease have subsided, the doctor begins a full examination of the body.
Surgical methods
In most cases, purulent, inflamed lymph nodes on the face are treated with surgery. The operation takes place under local anesthesia, if the purulent capsule inside the node remains intact. The surgeon makes a small incision and, using special instruments, removes the capsule.
But it is not uncommon for the abscess to rupture. It is very good if the contents come out. It happens that pus gets inside. Then surgical intervention is simply necessary with a more thorough approach. General anesthesia and a lengthy process of cleaning the affected area of the face are required.
Lymphadenopathy
A more serious pathological condition accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes. The development of this pathology indicates the presence of infectious diseases accompanied by a severe decrease in immunity.
Also, enlargement of the lymph nodes may be a consequence of developing oncological processes. There are forms of the disease when the processes of tumor formation directly affect the lymph nodes. This pathological condition is called lymphosarcoma.
Each lymph node is responsible for the health of the organs located near it.
Diagnostics
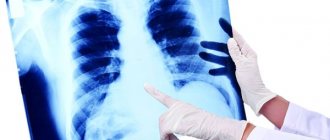
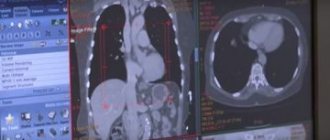
The most accessible method is palpation, but it can only check superficial lymph nodes. The doctor pays attention to the size, presence of redness, skin temperature, adhesion to surrounding tissues. The nodes of the lymphatic system inside the body are studied using x-rays, ultrasound, computed tomography and lymphography. Additionally, the therapist can prescribe consultations with specialized specialists (depending on the location of the inflammation).
If a person comes to the doctor with a complaint of enlarged lymph nodes, palpation is performed first. However, the method allows checking only surface nodes. The following are taken into account:
- size;
- presence of redness;
- local temperature;
- adhesion to surrounding tissues.
If pathological processes occur in deep lymph nodes, an ultrasound examination or x-ray will be taken. Additionally, tomography and lymphography may be prescribed. The patient must also undergo general blood and urine tests. If there are indications, the therapist can refer the patient to specialists.
The condition of the lymph nodes is determined by examination, palpation or ultrasound diagnosis. The method depends on which group of nodes is examined. Check hardness and mobility to see if there is any pain.
Lymph nodes on the head and neck are examined using the fingertips. This should be done easily, smoothly, avoiding strong pressure. In the neck, supraclavicular and superficial lymph nodes can be palpated. More details in the review Palpation of lymph nodes
Supraclavicular lymph nodes are palpated when the following cancers develop:
- prostate cancer in men;
- ovarian cancer in women;
- stomach cancer;
- Bladder;
- pancreas;
- neoplasms in the breast.
The axillary lymph nodes are checked by sliding the hand in the armpit. Determine the abundance and density of lymph nodes, whether there is swelling, redness or pain when touched. For good access, during palpation, the patient moves his arms slightly to the sides, after which palpation is repeated with his arms down.
The inguinal nodes are examined with the patient in a supine position. Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin indicate an inflammatory process in the pelvic area or the presence of a tumor. When the nodes in the groin are inflamed, the patient experiences severe sweating, weight loss, increased body temperature, and men may have difficulty with potency. Purulent processes may even begin. In women, the inflammatory process often affects several organs.
Ultrasound diagnostics is used to determine the inflammatory process in the pelvic organs, the presence of cancer, syphilis or HIV infections. If necessary, MRI, CT or radiography is done.
Lymph nodes under the knees are palpated during examination. The examination is carried out with the patient lying down and the leg bent at the knee. When there are no external signs of inflammation, but the patient complains of pain under the knee when bending the leg, this often means that the lymph nodes are inflamed.
When there is damage to the skin on the lower leg or foot, and there is already an infection there, then the lymphatic vessels delegate the infection directly to the popliteal glands. The nodes become large and painful - inflammation appears.
To diagnose the disease, your doctor may need to:
- Medical history
- Body check
- Blood analysis
- Chest X-ray and CT scan
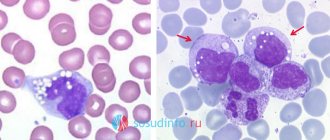
- Lymph node biopsy (as a last resort).
To determine the type of inflammation of the lymph nodes and find out the causes of its occurrence, you will need to carry out the following diagnostic procedures:
- Study the patient's medical record, conduct an examination and interview.
- Check the condition of the lymph nodes by palpation.
- Take general and biochemical blood tests.
- Conduct an ultrasound of the lymph nodes, CT and MRI of the neck.
- Take a puncture for a biopsy of the affected organ.
One of the ways to diagnose the condition is to perform an ultrasound of the lymph nodes.
Hardware diagnostics are used for damage to the deep cervical lymph nodes. A biopsy is performed in rare cases, if a specific type of inflammation is suspected.
Diagnostic methods
Knowing where the lymph nodes are located in a person, photos of which are presented in this article, you can make an assessment of the condition. The following criteria are used for this:
- painful sensations when pressing;
- degree of mobility of elements;
- lymph node density.
During the examination, the doctor measures the diameter of the nodes. The obtained figures will be used for further monitoring, in order to exclude the development of various diseases. When malignant tumors form, lymph nodes constantly increase in size. Unlike oncology, with infectious lesions the size of the lymph nodes either increases or decreases. In the presence of diseases such as tuberculosis, inflammatory processes are observed in the neck and armpits. That is why it is very important to know the location of the most important external elements of the lymphatic system.
If you experience discomfort and pain in the area where the lymph nodes are located, it is recommended to consult a specialist. Self-medication, self-diagnosis and negligent attitude towards one’s health can contribute to the development of severe complications that will require more serious treatment.
After a visual examination, the doctor refers the patient for a diagnostic examination. For this purpose, X-ray examination, computed tomography and microscopic examination of the blood composition are performed. In more complex cases, a biopsy may be required to make a diagnosis.
The lymphatic system is one of the most important in the human body. Each element in this system acts as a kind of indicator of health level. The correct approach to diagnosis allows for timely identification of pathological processes, which significantly increases the effectiveness of therapy.
Increase in size: causes, symptoms
An increase in the size of the lymph node is a sign of an ongoing inflammatory process. Enlargement of several nodes or their groups is a sign of a serious pathological process or disease.
Superficial ones are large; normally in adults they can be up to 1.5 cm in diameter. The internal norm is defined as 3-10 mm. The size of the capsules in young children is considered normal: 2-5 mm, depending on the location. Sometimes due to peculiarities of physiological development. Compliance with the standard is determined by the attending physician, based on the individual characteristics of the person, based on the results of medical research. Selected cases allow dimensions up to 5 cm in a non-inflamed state.
Tumors in the lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are the most vulnerable organ according to their purpose. By blocking infections and pathogenic organisms, they themselves are susceptible to inflammation. Minor changes in capsule size during filtration of an aggressive environment do not cause concern. Often the lesion turns into an independent disease and requires local treatment. Inflammation of the lymph nodes is called lymphadenitis. According to the degree of damage and severity of the course, lymphadenitis can be simple (local), destructive, accompanied by the development of the inflammatory process beyond the capsule itself through the lymph flow, and chronic.
Simple lymphadenitis shows symptoms:
- increase in size;
- change in skin color;
- pain is caused by palpation and movement;
- temperature increase;
- general malaise.
Simple lymphadenitis often takes on a purulent form and requires opening and local antibacterial treatment.
Destructive lymphadenitis complements the above symptoms with a number of signs:
- the number of nodes of one group has been increased;
- change in color and density of the skin;
- edema.
Requires immediate extensive antibacterial treatment, since suppuration and effusion of pus can lead to sepsis.
Self-medication in acute cases of lymphadenitis is unacceptable; you must immediately contact a medical facility immediately after the first signs of inflammation appear.
Chronic lymphadenitis occurs without acute symptoms; apart from an increase in the size of the lymph nodes, the person has no complaints about other manifestations. The absence of acute pain, temperature, and other signs of inflammation indicates the presence of a chronic disease that does not manifest itself in acute form. This pathology occurs unnoticed, but has serious consequences. Tuberculosis, AIDS, hepatitis C, hepatitis B can go unnoticed for a long time.
Lymphadenopathy is damage to the lymph nodes without an underlying disease. Occurs without the course of another disease. The nature of lymphadenopathy can be viral, infectious, or oncological.
Classification of the disease
Enlargement of the ear lymph node can occur in different ways. Experts identify the following types of pathological process:
- Catarrhal. In this case, there is no suppuration, severe pain appears, and no external changes in the skin are observed.
- Purulent. Accompanied by an increase in body temperature, sharp pain, symptoms of intoxication of the body, hyperemia and swelling. The lymph node in this case greatly increases in size.
- Hemorrhagic. The cavity of the node is saturated with blood content, which is associated with capillary dysfunction. This form of the disease is typical mainly for such serious cases as anthrax and plague.
A chronic inflammatory process occurs only when lymphadenopathy continues for 1-2 months and the patient does not receive the necessary treatment. If the contents of the lymph node penetrate into the soft tissues that are located next to it, then we are talking about adenophlegmon. In this case, it is impossible to determine clear boundaries of the infiltrate. The lymph node quickly reaches enormous sizes, and general manifestations of intoxication of the body appear.
Drug therapy
On the one hand, inflammation of the lymphatic structures is a consequence of infectious diseases. First, the doctor takes measures to eliminate the underlying cause of lymphadenitis or lymphadenopathy. For this purpose, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, which is carried out using broad-spectrum drugs: sulfonamides or cephalosporins.
The following are prescribed as additional agents that relieve symptoms and normalize the immune response:
- Antihistamines. Designed to relieve the inflammatory reaction and eliminate chronic inflammation. The drugs reduce swelling, relieve pain, and reduce the severity of hyperemia.
- Vitamin complexes. Necessary for restoring the body's protective functions. It is imperative to normalize vitamin C levels.
- Immunomodulators. Means whose effectiveness is aimed at normalizing the body’s immune response. Can only be used after a doctor's prescription.
After the causes have been eliminated or during the main treatment, physiotherapy is carried out in order to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and eliminate the likelihood of complications. Among the most effective procedures, electrophoresis and helium-neon laser irradiation should be highlighted.
Clinical manifestations
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory reaction that develops against the background of destruction of the lymph nodes. If a similar reaction occurs behind the ear, then the following symptoms occur:
- Swelling. Behind the ears, the skin is thin and taut because it contains hard structures such as the skull bones and tendons. The swelling is limited on almost all sides, so the capsule itself stretches and increases in size quite strongly.
- Hyperemia. In the area of the inflammatory process, dilation of blood vessels occurs, which is fraught with stagnation of arterial blood. Externally, this process is expressed by redness of the skin.
- Increase in local temperature. Excessive blood flow caused by active cellular processes leads to a feeling of heat in the area of inflammation.
- Pain syndrome. When nerve endings are compressed in the area of tendons and skin, a pain syndrome appears. In this case, there is an active release of biologically active substances released by collapsing cellular structures. In this case, the pain is bursting and throbbing. After the acute period passes, the pain syndrome is clearly noticeable only upon palpation.
Lymph nodes of the parotid region
Two groups of lymph nodes are usually called ear:
- behind the ear, which are located directly behind the ears;
- parotid, located in front of the auricle.
Normally, the nodes are not palpable, and the size does not exceed 1 centimeter. They collect lymph from the hearing aid, forehead, parietal and temporal zones. Therefore, when the nodes of the parotid region become inflamed, this is a signal that the foci of pathology are localized in organs nearby.
Cause of inflammation
Parotid and parotid lymphadenitis occurs due to diseases of various etiologies. The nodes react to the entry of pathogenic fungi, viruses and bacteria into the body. Physical and mechanical factors can also cause the development of local inflammatory processes. Among the etiological factors of ear lymphadenitis are:
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, syphilis);
- pathologies of the ENT organs (otitis media, mastoiditis);
- oncological diseases;
- advanced dental and eye diseases;
- physical and mechanical factors (shock, frostbite);
- unhealthy lifestyle (alcoholism, smoking);
- infections acquired after injury.
The cause of inflammation of the posterior ear lymph nodes is often cold weather when people neglect to wear hats. An allergic reaction can also trigger lymphadenitis. Therefore, the root cause does not always lie in the presence of an infectious factor.
Risk group
Lymphatic structures most often become enlarged in people suffering from autoimmune disorders such as HIV and AIDS. More susceptible to the development of lymphadenitis and lymphadenopathy are those people who have a genetic predisposition, and also suffer from systemic endocrine disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus.
Adults are much easier to diagnose than children. This is due to the fact that in childhood, patients may have enlarged nodes in the ear area even against the background of such minor factors as a common cold. In this case, the symptoms go away on their own within 1-2 weeks and do not require additional drug correction.
Where are they located?
A detailed classification describes the specific location of the lymph nodes (shoulder, bend of a limb, for example). They are located in important parts of the body one or several pieces. The following types of nodes are distinguished:
- popliteal on the back of the knee joints;
- axillary, adjacent to the axillary region and the inside of the pectoral muscles;
- superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes located in the inguinal folds;
- submental, several centimeters distant from the chin;
- cervical lymph nodes scattered along the side and front of the neck;
- occipital, which are located at the junction of the neck with the skull;
- submandibular, located in the center of the branches of the lower jaw;
- elbows, located on the front of the joint of the same name;
- parotid and postauricular, which are easy to feel near the auricle;
- iliac, located along the internal iliac artery.
The outer part of the organ is covered with a membrane of connective tissue. Parenchyma of the node, i.e. its main elements are reticular tissue. It contains the cortex (located closer to the peripheral part) and the medulla (located in the center of the capsule). The first part is divided into two more components:
- Superficial zone. It is formed by lymph nodes - follicles.
- Zone of the deep cortex (paracortical). Located on the border of the cortical and medulla layers. Here antigen-dependent division occurs, i.e. proliferation of T-lymphocytes that fight diseases.
Trabeculae, which are bundles of connective tissue, extend from the capsule into the parenchyma into the node. They look like plates, septa and cords that form the skeleton of the organ. There, lymph seeps through special spaces - the lymphatic sinuses of the cortex and medulla. They play the role of a special network that removes foreign particles. The sinuses themselves are located between the capsule and trabeculae.
Under the jaw
In case of purulent processes, in case of infection penetration into the ENT organs, among potential complications, doctors do not exclude inflammation of the lymph nodes under the jaw, which is prone to the formation of malignant tumors. Other causes are systemic lupus erythematosus, serum sickness. To increase the patient’s chances of recovery, it is important to promptly determine the pathogenesis of the disease and find out the etiology of inflammation. The symptoms are:
- lump on the jaw, redness of the skin;
- pain when chewing or while talking;
- difficulty working facial muscles;
- heat.
Purpose
The lymphatic system, consisting of blood vessels and capillaries, permeates the entire body like a network. The viscous living liquid, as it flows, captures nuclides, toxins, cell waste products, microorganisms, bacteria and other harmful substances from them, as well as from connective tissues. On the path of lymph there are “sanitary” points - lymph nodes, including the parotid lymph nodes, the lymph node behind the ear, near the ear, under the urine of the ear, etc., where lymph is filtered. All lymph nodes have 2-4 inputs for lymph and 1-2 outputs. Having entered the gland, the fluid does not flow directly into the exits. It flows through curving corridors (sines), which allows it to better free itself, to cleanse itself of what it has collected. This is facilitated by lymphocytes that produce nodes. The path of the lymphatic system passes mainly along the veins.
The parotid glands clear lymph, which flows into the posterior auricular vein. They cleanse the lymph of the neck and salivary glands. The postauricular lymph nodes protect the parietal and temporal regions. In addition, the lymph nodes behind the ears protect the areas of the eyes, ears, throat, and jaw. The lymph node under the ear protects the corner of the jaw, which is located just below the ear. It is called tonsillar.
Treatment measures
Lymph nodes enlarge in response to certain disorders in the body. Treatment should be aimed, first of all, at eliminating them. After the main problem is relieved, the seals, as a rule, decrease on their own.
Basic therapy is developed individually for each patient and includes the use of the following drugs:
- Antibacterial.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
If there is a purulent process, the doctor may prescribe local compresses or ointments. Under no circumstances should you heat enlarged lymph nodes. This can cause the development of serious complications caused by the progression of the pathological process.
In cases where the lymph nodes are enlarged due to cancer, a course of chemotherapy is prescribed. If necessary, surgical intervention is performed. The earlier a malignant tumor is diagnosed, the greater the chance of a positive outcome.
If the lymph nodes are enlarged over a long period and the drug treatment does not give the desired result, then the doctor may prescribe physical therapy. It is mandatory to take measures to strengthen the immune system, for example, using echinacea tincture and hardening.
The disease, which causes enlarged lymph nodes, should be treated comprehensively. It is unacceptable to interrupt the course of treatment even after the symptoms disappear. If the doctor has prescribed you to take medications for 1.5-2 weeks, then you should follow through. Otherwise, there are risks of relapse. The specific form of lymphadenitis requires long-term therapy, which in some cases takes more than 1 year.
Conclusion
Enlarged lymph nodes are a sign of the body’s fight against harmful microorganisms or atypical cells. The lump can be single or multiple, when compactions are observed throughout the body: in all groups of lymph nodes. This indicates the presence of serious dysfunctions in the body. Both adults and children can suffer from lymphadenitis. The age of the patient does not matter. This is not a primary disease - but a symptom of another disease, the treatment of which requires maximum effort. After eliminating the underlying pathology, the lymph nodes, as a rule, decrease in size and suppuration does not occur.
Causes of inflammation of the behind-the-ear lymph nodes
A disease in which only the lymph node becomes inflamed - lymphadenitis - is rare. This pathology occurs due to the fact that pathogenic bacteria infect the lymphatic tissue. Infection of the lymph node may be primary. That is, such a pathology is independent, and not a complication of another disease.
Lymphadenitis develops as an independent disease, or as a complication of another pathology. Most often, the infection enters the tissue through the hair follicle or sebaceous gland. Most patients have a history of complaints of such problems.
The lymph node hurts due to the fact that its enlargement leads to overstretching of the capsule, which causes pain.
Most often, the lymph node behind the ear is enlarged because another disease is developing nearby. The reasons why the lymph nodes behind the ears become inflamed may be:
- otitis;
- rhinitis and sinusitis;
- diseases of the membranes of the eyeball;
- meningitis and encephalitis;
- pulpitis, periodontal abscesses, osteomyelitis of the lower jaw;
- malignant tumors;
- systemic connective tissue lesions;
- autoimmune diseases;
- lymphomas.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that an enlarged lymph node requires a full examination. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based on this symptom alone. It is necessary to pay attention to the symptoms that develop against the background of the primary disease.
Causes of the disease
Inflammation of the lymph nodes behind the ears in most cases is a sign of a pathological process in the parietal, occipital region, mastoid process and occasionally in the ear. Microorganisms and various toxins enter the node with the lymph and if there is any weakening of the immune system, they damage the structures of the lymph node itself. Most often, lymphadenitis is caused by opportunistic bacteria, anaerobes and intracellular parasites:
- Staphylococcus;
- Streptococci;
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis);
- Chlamydia;
- Aspergillus;
- Francisella (the causative agent of tularemia);
- Escherichia coli;
- Clostridia.
Conditions that can cause isolated lymphadenitis behind the ears:
- Cat scratches in the parietal and temporal region of the head;
- Wounds, abrasions, boils, infected scratches in the same area;
- External and otitis media;
- Mastoiditis;
- Tularemia;
- Tick-borne encephalitis (with a bite in the temporal or parietal region);
- Tumor metastases;
- Lymphogranulomatosis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Actinomycosis of the scalp;
- Syphilis (extremely rare).
Much more often, the lymph nodes near the ear increase in size with systemic damage to the lymphatic system, which occurs when:
- Rubella;
- Corey;
- HIV infections;
- Tumors of the lymphatic system (lymphoma);
- Adenovirus infection;
- Infectious mononucleosis.
For what diseases does it increase?
Many diseases are accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes. They can become inflamed in different ways in certain pathologies:
- Lymphadenitis due to purulent inflammation. The first symptom is pain when pressing on the node, redness of the skin over it.
- Tuberculosis. Regional nodes enlarge in the chest cavity, in the upper back, in the supraclavicular region, at the throat and under the jaw. As the disease develops, they fuse with adjacent superficial tissues, which leads to compaction, expansion, suppuration and even the formation of a fistula.
- HIV infection. An increase in the size of nodes occurs in the armpits, abdomen, chest, lower back and neck.
- ARVI. The lymph nodes enlarge slightly and become slightly painful when palpated.
- Venereal diseases. Lead to inguinal lymphadenitis against the background of ulcers on the genitals. With syphilis, the nodules may be painless, but their size increases to the size of a nut.
- Oncological diseases. Enlarged nodes are often a sign of spread of tumor cells from the primary site.
How to treat lymphadenitis using physiotherapeutic procedures
In the treatment of lymphadenopathy, physiotherapy methods are of great importance.
Their use has the following effect:
- decongestant;
- anti-inflammatory;
- absorbable;
- pain reliever;
- stimulation of regenerative processes;
- improving blood and lymph circulation.
The following procedures are prescribed:
- UHF therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- fluctuarization (electrotherapy);
- ultrasound therapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis (with enzymes);
- galvanization (exposure to weak direct current using electrodes).
Physiotherapy is carried out when the acute inflammatory process subsides.