Cyst on the kidney - is it dangerous, and what treatment is necessary? Urologists usually hear this question from patients whose diagnostic results have revealed a benign neoplasm. The doctor’s answer: “Depends on the size of the cyst, its type, location, concomitant diseases and the degree of dysfunction of the organ.”
What does it represent?
Over the past few years, cases of diagnosis of cystic forms in the kidneys have increased significantly.
The renal cyst on the left side is formed from connective tissue, includes fluid and is a cavity formation in the form of a capsule. Cystic forms located near the surface have the densest walls. Depending on the cause of the formation, formations may include one or more cavities. The exudate that each kidney cyst contains can be of a different nature; as a rule, it is pus, blood or other liquid. Among all patients with cysts of the right and left kidney, the contents in them are most often yellow in color with one chamber.
Symptoms of a kidney cyst - characteristic signs
multiple small cysts
Signs of the presence of cyst cavities in the structure of the kidney, in more than half of the cases, do not make themselves felt for a very long time - occurring in an asymptomatic form. This is especially true for small and insignificant formations. Nonspecific symptoms of a renal cyst appear only when it grows significantly, putting pressure on the surrounding vascular and tissue structure. Or if the formation interferes with the outflow of urine.
Symptoms of a kidney cyst appear:
- Various types of pain symptoms (dull, pulling, aching) or similar to renal colic. In the case of a left-sided formation, pain radiates to the left area of the abdomen and left hypochondrium. It is typical for the pain syndrome to intensify under heavy loads, regardless of what position the person is in.
- A predominant increase in diastolic blood pressure, which is caused by a failure in the secretion of the proteolytic enzyme (renin), which functions to control blood pressure in humans.
- Urodynamic disorders caused by obstructed urine outflow.
- The appearance of bloody inclusions in the urine, which may indicate vascular pathologies in the organ.
- A feverish state, cloudy urine and the development of leukocyturia, which indicates the formation of purulent processes.
- Pain syndrome, combined with sudden weight loss, can mean cystic malignancy - the development of cancer cells.
- Intoxication symptoms, indicating renal dysfunction and insufficiency.
- Areas of compaction in the abdomen, indicating enlarged kidneys.
Depending on what caused the kidney cyst, the disease can develop on the left/right or with bilateral localization, manifest as single or multiple cavities in the form of various pathological processes:
- Renal multicystic disease (unilateral lesion and polycystic disease - bilateral localization), manifested by the development of multiple small cavities in the renal structure. The organ takes on the appearance of one large cyst. The functional abilities of the kidney are completely lost. There is a high mortality rate with polycystic manifestations.
- A simple (solitary) cyst, in the form of a single cavity cystic formation, with unilateral left-sided localization. May be asymptomatic for a long time. Large formations can provoke the development of hydronephrosis, renal dysfunction and infectious processes.
- Parapelvic renal cystic formation with predominant localization in the “gate” - the sinus and pelvis of the right nephron.
- Parenchymatous kidney cyst localized in the tissues of the outer lining of the kidneys (parenchyma). Capable of long-term asymptomatic existence.
- Development of sinus cysts, directly localized to the renal sinus area.
- Complex cysts - multilocular (multi-chamber), having a special structure - dense walls and a non-smooth surface, the presence of several cavity chambers in one connective tissue capsule. There is a high tendency to cancerous degeneration.
- Subcapsular neoplasms - develop in the form of small cavities localized under a dense cover of connective tissue covering the nephrons. Rarely cause complicated processes.
What are the etiology and pathogenesis?
Several factors are involved in the process of cyst formation. A cyst in the left kidney begins with the fact that as a result of some changes in the layers between the tissues, a space is formed, which is subsequently filled with fluid.
Then collagen production is started, and after several biochemical reactions the protein ceases to be soluble. Subsequently, the tissues begin to be torn away from the cavity and form into a capsule.
The subsequent fate in the formation of a cyst is determined by numerous external factors that determine the future size of the formation, content and location.
Why is it dangerous?
Although small in size, the cyst of the left kidney does not pose a risk to human health. However, if the doctor notes that the tumor is rapidly increasing in size and poses a threat to nearby organs, then such cysts must be removed immediately. If the formation is large enough, there is a risk of damage and compression of the kidney vessels, which can negatively affect their function, even leading to the development of renal failure. Cysts with pus and blood pose a great danger, since when they rupture, the contents leak into the body, thereby provoking infection. Such situations require immediate surgical intervention. The most serious complication of cystic formations on the left kidney is a cancer predisposition.
Causes of kidney cysts in women
Parenchymal cyst
A left kidney cyst mainly develops as a result of genetic changes in the fetus while still in the womb. As a rule, this is facilitated by an abnormal development of the fetus in the second trimester of pregnancy. Most often, a cyst in the left kidney is located in the parenchyma and is called parenchymal. The causes of failure in the development of fetal kidneys are:
- Genetic predisposition (that is, the pathology is transmitted along the family line);
- Intrauterine kidney dysplasia (underdevelopment and uneven development of kidney tissue).
Parenchymal formation in the kidneys has the following symptoms:
- Drawing, dull or aching pain in the left hypochondrium or lumbar region;
- Constantly high blood pressure;
- Presence of blood in the patient's urine.
As a rule, parenchymal formation is diagnosed using ultrasound examination of the kidneys and CT/MRI. It is interesting that in patients who are too thin, a large kidney capsule can even be felt with your hands. But it is still better to diagnose the formation using hardware methods.
A cyst forms when epithelial cells begin to grow rapidly in the kidney tubules.
There are the following categories of cysts:
- Multicystic dysplasia, which appears during a person’s lifetime;
- Formed when there is a hereditary predisposition. For adult and childhood polycystic disease, polycystic disease, juvenile nephronophthisis;
- Cysts develop against the background of genetic diseases;
- Acquired cysts;
- Malignant cysts.
Diagnosis of kidney cyst
If a benign renal tumor is suspected, the doctor collects an anamnesis, conducts an examination, and prescribes a number of laboratory and instrumental research methods:
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and abdominal organs.
- Excretory urography.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Biopsy.
- Tests for tumor markers.
The results of the examinations will allow the doctor to make the correct diagnosis, determine the size and location of the formation, prescribe adequate treatment for the kidney cyst, and give useful recommendations on nutrition and lifestyle.
Kidney cyst on ultrasound examination
If there are cysts in the kidneys, treatment is carried out inpatiently or outpatiently. It all depends on the course of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
Classification
Simple cyst
This type of cystic formation does not pose a big threat to health, and is most often diagnosed among patients. Requires conservative treatment.
In appearance, the tumor is a small bubble with liquid inside, the norm is up to 2 mm. The parenchymal cyst of the left kidney is formed precisely in these epithelial-active cells.
It is precisely because the pathology develops in the parenchyma that it received such a name. A separate variant of pathological formation is considered to be a cortical tumor, which forms in the cortical layer of an organ.
A left kidney cyst can be of the following types:
- Simple and single-chamber type. This type of formation is detected quite often. They have a size of up to 2 mm. In appearance they look like a small vial with liquid contents. These formations can be located in different areas of the kidney, but most often in almost 65% of cases they are found in the parenchyma;
- Multi-chamber. This type of formation is similar to single-chamber ones. But they have one characteristic difference - the presence of partitions in the capsule itself. Partitions divide the cavity into several parts, the functioning of which is carried out separately from each other;
- With a complicated character. Single-chamber and multi-chamber cysts can be complicated. In appearance, they are the same as ordinary formations, but inside them there is purulent content with admixtures of blood;
- Tumor pseudocysts. The presence of these formations can only be detected by biopsy. Until an accurate diagnosis is made, these tumors are classified as simple cysts.
Surgical treatment involves complete removal of the cyst. The operation can be performed in three ways:
- Puncture surgery. A small conduction is carried out through the skin, with the help of which puncture is carried out. During this method, the contents of the cavity are only removed;
- Use of laparoscopic surgery. During this removal method, two procedures are used simultaneously. During laparoscopy, both the contents of the cavity are removed and the formation is completely removed;
- Strip operation. Access to the kidney is carried out using a layer-by-layer tissue incision and isolation of the organ with the cyst. This method can use a large number of manipulations - from removing the cyst to completely cutting out the entire organ.
Important! Complete removal of the kidney is performed only in rare cases. The indication for this operation is usually the presence of polycystic disease, which is accompanied by increased insufficiency and arterial hypertension.
In any case, no matter what type of cyst it is, it is worth promptly identifying its presence and eliminating it. If this process is delayed, serious complications may arise in the future, including complete loss of the entire organ and damage to other healthy tissues and organs.
All types of cysts are divided into simple and complex.
Simple types of cysts are classified into:
- Congenital and acquired nature;
- Single and multiple;
- Double-sided and single-sided;
- Cysts can be hemorrhagic, serous or infected according to their filling;
- Cortical, subcapsular, multilocular and peripelvic.
Complex cysts have their own differences:
- It has a non-smooth, rounded shape;
- Its walls are thickened;
- Quite often, these types of cysts degenerate into malignant tumors.
What is a kidney cyst?
A kidney cyst is a pathological condition in which an abnormal growth of a hollow formation occurs. The tumor is a connective tissue capsule filled with fluid. As practice and observations of neurologists show, cysts on the kidneys occupy a leading position among all neoplasms of renal tissue. The size of the band formation can be small from 1 cm to large - 10 cm in diameter, be single or multiple, have different localization, affect one or both lobes of the organ. Considering the tendency of a kidney cyst to degenerate into a malignant process, after its diagnosis the patient requires immediate treatment and constant monitoring, which will allow monitoring the dynamics of the disease.
In the overwhelming majority, the clinical picture of cystic formations does not bother a person, but only until the tumor increases in size or an inflammatory process appears in the tissues of the organ.
Clinical signs of the disease also depend on the location of the formation, size and quantity. Most often, a cyst in the kidney is located at the bottom or top of the internal organ. But there are cases when the growth of a pathological formation is present in the cortical layer of the organ. After reading the information about what a kidney cyst is, you need to consider the main causes of the disease.
Traditional medicine and kidney cysts in women
The following aspects play a role in the process of cyst formation:
- For some reason, space forms between the layers of fabric;
- Instantly this space is filled with intercellular fluid;
- Collagen begins to form around this cavity. This protein becomes insoluble under the influence of biochemical reactions. In the process of such exposure, the tissues are fenced off, and the cyst takes on the appearance of a capsule.
Treatment using the recipes of our grandmothers cannot be perceived as an alternative to conservative therapy or surgery. Herbal medicine should be used only as a supplement to the main course of treatment, and you must first consult with your doctor. Below we list the most common advice from traditional medicine.
Treatment of pathology
What medications are needed?
Kidney cysts can be treated using several methods. Drug therapy cannot ensure complete removal of the tumor from the body, but if the formation does not pose a threat, the patient is prescribed drugs that eliminate unpleasant symptoms in the form of pain, as well as diuretics to normalize the process of urination. If an infection occurs in the body against the background of a neoplasm, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics.
Surgery
There is no more effective means of combating tumors than surgery. It is possible to treat a left kidney cyst without minimal damage to the human body. Popular methods for removing renal parenchyma cysts are laparoscopy and puncture. Using these methods, formations in the organ up to 10 cm are excised. If there is a risk of complications, ruptures or a malignant form of the disease, a complete open operation with a long period of rehabilitation, including drug treatment, is prescribed.
How important is nutrition in diagnosis?
You should avoid coffee during cyst treatment.
For successful treatment, you must strictly adhere to the following diet:
- Eliminate harmful foods from the menu.
- The patient's drinking regime is at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day.
- It is recommended to eliminate or reduce salt intake to a minimum.
- Eat protein foods, meat and seafood in small quantities.
- Drinking coffee and eating chocolate products is prohibited.
- It is recommended to include herbal infusions and decoctions in the treatment.
Symptoms
A cyst does not form immediately, but over a certain number of stages. First, a void forms between the tissue layers of the kidney.
The formed cavity immediately begins to fill with serous fluid. Those tissues that surround the cavity produce insoluble collagen.
As a result, the cyst separates from the tissue and turns into a capsule. At subsequent stages, the neoplasm may be complicated by hemorrhage or suppuration.
This depends on several factors: the size of the cavity, how close it is to the surface of the organ, whether there are other kidney diseases, and the causes of the cyst.
- past ailments of the kidneys and some other organs: among such diseases, most of them are urolithiasis and pyelonephritis; - external factors (injuries, bruises, blows, radiation).
For a long period of time, cystic manifestations do not make themselves felt. Often, due to the presence of a cyst, the patient’s immunity decreases, which entails the risk of contracting infectious diseases.
If this happens, the symptoms become more pronounced, the patient’s temperature rises, weakness and nausea appear. In many cases, tumors are diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound diagnostic session.
The first symptoms of cysts are considered to be pain in the hypochondrium and on the left side of the back. Afterwards, similar symptoms may be observed:
- problematic urination;
- disruptions in blood flow in the left organ;
- the presence of blood and purulent discharge in the urine;
- rapid increase in blood pressure.
Ignoring the symptoms often leads to neglect of the disease and subsequently the cyst on the left side stimulates the development of acute renal failure.
- past illnesses of the kidneys and some other organs: among such diseases, most of them belong to urolithiasis and pyelonephritis;
- external factors (injuries, bruises, blows, radiation).
Cysts of the left and right kidneys form for two main reasons:
- Genetic predisposition - formation appears as a result of tumor growth.
- Acquired cyst – bruises, injuries, various kidney diseases.
Statistics show that neoplasms with different etiologies of development are equally common. It is impossible to trace the original cause for congenital anomalies. Then, acquired ones are easy to track due to the high risk of occurrence after or during urolithiasis, pyelonephritis or impacts (falls) in the lumbar area.
Neoplasms have their own characteristics and properties:
- multilayered – contains many layers of collagen with ectoderm cells. If there are pieces of skin or hair in the cyst analysis, it is called dermoid;
- possibility of growth - a cyst, unlike cancer cells, grows very slowly, over decades;
- malignancy is the growth of cystic tissue into a tumor neoplasm.
The formation of a cyst goes through several stages:
- The void formed in any part of the kidney begins to fill with serous fluid.
- Cells of neighboring tissues produce collagen, thus creating a capsule.
- Further development is determined by the presence of diseases in the body.
In most cases, the development of cystic tissue is asymptomatic. Only in exceptional cases may symptoms not be clearly expressed:
- pain syndrome when the tumor reaches a large size. Often discomfort is felt in the lumbar region, occasionally a mirror image occurs and pain will be felt in other internal organs;
- hypertension occurs with strong pressure on the parenchyma;
- an increase in temperature is caused by the presence of complications, accompanied by purulent filling of the cavity and infection;
- blood in the urine also indicates the development of an infectious process.
More than a third of patients do not even suspect that they have a cyst in the left kidney.
In most cases, the cyst is manifested by the following factors:
- Frequent infectious diseases of the urinary system;
- Blood streaks appear in the urine. In the affected kidney, the pressure increases and this can lead to rupture of the vessel;
- Pain in the lumbar region, radiating to the side, from the side of the affected kidney. The kidney is large in size and compresses neighboring organs. Occasionally, fluid may accumulate in the left kidney and this leads to an increase in its weight;
- Blood pressure increases;
- Protein appears in the urine;
- On palpation, the kidneys in most patients are enlarged in size;
- Patients turn to the doctor when they feel a lump in the abdominal cavity.
- past ailments of the kidneys and some other organs: among such diseases, most of them belong to urolithiasis and pyelonephritis; - external factors (injuries, bruises, blows, radiation).
Possible complications
Cysts are initially considered benign formations, but they cannot be classified as harmless. The danger of their appearance is the high probability of developing complications. The most common of them:
- Infection leading to suppuration of the internal contents and rupture of the membrane. The result is peritonitis;
- Hydronephrosis;
- Persistent increase in blood pressure;
- Purulent form of pyelonephritis;
- Chronic renal failure.
Malignancy of the existing cyst cannot be ruled out. Patients with such kidney tumors should be examined regularly.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of congenital cysts
Thanks to modern technologies, a cyst of the left kidney can be diagnosed already at the 15th week of gestation. This examination is carried out using an ultrasound machine.
This allows you to see the following pathology:
- Number of cysts;
- Location;
- Size;
- Renal dysfunction.
After birth, the newborn undergoes a second ultrasound to clarify the diagnosis 4 weeks after birth.
Diagnosis of hereditary cysts
How is a cyst in the left kidney treated?
With a small pathological formation (up to 1–2 centimeters in diameter) and single tumors, doctors choose a wait-and-see approach. If the cyst does not grow and does not cause discomfort to the patient (it was discovered by chance), there is no need for its treatment. When clinical symptoms of varying severity appear, the patient is sent to the urology or nephrology department, and a certificate of incapacity is opened. At the initial stage, doctors limit themselves to prescribing a gentle diet with control of the level of fluid intake and a minimum amount of salt. Drug therapy is aimed at maintaining the patient’s general condition and eliminating the symptoms of the disease, and the cyst itself can only be removed surgically.
Main goals of treatment:
- normalization of blood pressure;
- pain relief;
- strengthening the immune system;
- prevention of the development of secondary complications;
- stabilization of water-salt balance and protection against intoxication.
Video: doctor talks about therapy for kidney cysts
Table: pharmaceuticals to combat the disease
| Name of the medication group | Main active ingredients | Mechanism of action of the drug | Possible side effects |
| Narcotic analgesics |
| Relieves pain by stopping the flow of nerve impulses from sensory endings to the brain |
|
| Antihypertensive drugs |
| Normalize blood pressure levels, protecting the body from the development of a hypertensive crisis |
|
| Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Relieves swelling of soft tissues and prevents stretching of the renal capsule |
|
| Immunostimulants |
| Promote the formation of protective cells in the bone marrow |
|
Photo gallery: the main drugs to combat the disease
Celebrex relieves inflammatory swelling
Polyoxidonium strengthens the immune system
Furosemide removes excess fluid from the body and normalizes blood pressure
Surgical correction of the problem
Surgery is the only reliable way to get rid of a renal cyst. Indications for its implementation are:
- large tumor size (more than 5 centimeters);
- severe discomfort in the lumbar region;
- difficulty urinating;
- multiple formations.
Depending on the consistency of the cyst (liquid, dense or jelly-like), there are 2 methods of surgical treatment:
- Traditional removal of pathological formation. While the patient is under general or spinal anesthesia, the doctor makes a wide incision in the lumbar region. The skin, fatty tissue and muscle bundles are sequentially cut. A clamp is placed on the renal artery and vein to prevent blood loss. After this, the doctor cuts off the altered tissue along with the cyst, sending it for examination to a histology laboratory. The wound is sequentially sutured and a rubber tube is installed for the drainage of lymph and blood. This technique is used to remove dense or jelly-like tumors.
With traditional cyst removal, recovery takes longer
- Puncture of the contents of the neoplasm. Using ultrasound, the exact location of the cyst is determined, after which a thin needle with a large syringe is inserted into this area. In this way, the liquid contents are removed, as a result of which the walls of the tumor collapse and it stops growing and increasing in size. It is not advisable to use this method to eliminate jelly-like formations, since there is a possibility of clogging the syringe.
Puncture of a kidney cyst allows you to remove its contents
Folk remedies for the treatment of renal cysts on the left
If you cannot visit a doctor in the near future, it is permissible to use natural recipes to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Most of the ingredients for them can be purchased at the grocery store or assembled yourself.
If you are prone to developing allergic reactions, you should start taking any drug with a small dosage, and also keep an antihistamine (Loratadine, Tavegil) on hand.
Do not forget that decoctions and tinctures based on diuretic plants and herbs should be used with extreme caution. In my practice, I have encountered elderly patients who abused the use of bearberry. One of these women took medications to stabilize blood pressure, as she had long suffered from hypertension. At the same time, she drank an infusion of bearberry leaves, which, in addition to its diuretic effect, also had a hypotensive effect. The combination of pharmaceutical and folk remedies led to a sharp decrease in blood pressure and the patient fainted. As a result of the fall, the woman hit her head hard on the corner of the table and had to receive several stitches. To avoid such consequences, doctors recommend consulting with your doctor before starting home treatment.
Folk remedies to combat the disease:
- Mix 50 grams of blackberries with the same amount of orange peels and place in a saucepan with 2 liters of water. Cook over low heat for half an hour, once ready, add sugar or honey to taste, cool. Drink 1-2 glasses every 4 hours (on this day it is better to stay at home). Blackberries in combination with orange peels have an anti-inflammatory effect, and this decoction also contains a large amount of vitamins. It is recommended to use the product once a week for 3 months.
- Brew one teaspoon of chamomile in a glass of boiling water and cover with a saucer or plate. After cooling, drink the resulting product before any meal. Chamomile helps remove toxins from the body and also reduces pain. Chamomile infusion should be used daily for 3-4 weeks.
- Place 20 rose hips and 30 grams of calendula in a saucepan with 1 liter of warm water and cook for 20 minutes. After cooling, use a sieve to remove the remaining raw materials and drink 1 glass before each meal. Rosehip and calendula strengthen the immune system and kill harmful microbes, protecting the human body from the development of bacterial infections.
Photo gallery: folk remedies used for left kidney cyst
Blackberries are a source of vitamins and minerals
Chamomile relieves inflammation
Rosehip strengthens the immune system
Physiotherapy to relieve symptoms of illness
At the recovery stage, it is extremely important to use the body’s internal reserves and direct them to fight the residual effects of the disease. After surgery, the patients' condition improves, but for complete rehabilitation it is necessary to normalize kidney function. For this purpose, doctors prescribe various physical procedures for patients. The duration of such treatment is determined based on the patient’s complaints and his state of health (average periods range from 2 to 6 months).
What procedures are used in the treatment of renal cysts and residual postoperative effects:
- Acupuncture is an ancient oriental technique that is based on pinpoint stimulation of various areas of the body. This effect helps awaken sleeping cells and improve the functioning of the immune system.
- Medicinal electrophoresis. Using a drip system, a pharmaceutical drug enters the patient's body, and in parallel with this, an electric field is connected. This technique ensures deeper penetration of the active substance into the tissue, increasing the effectiveness of treatment.
- Ultrasound therapy promotes rapid healing of the postoperative scar, and also relieves swelling and inflammation. Its use is allowed even in pregnant women and children.
Photo gallery: physiotherapy to combat illness
Acupuncture is used to stimulate reflexogenic points in the body
Electrophoresis is carried out on the basis of an anesthetic or anti-inflammatory drug
Ultrasound therapy has an anti-inflammatory effect
Treatment
As soon as a patient finds out that he has a left kidney cyst, a lot of questions immediately arise. Among them are the possibilities and methods of treating the disease.
What medications are needed?
Unfortunately, a cyst on the left or right kidney cannot be eliminated with drug therapy. Treatment with drugs can only be prescribed to relieve inflammation and suppuration, but the tumor can only be removed surgically.
If the size of the whale is small, the patient is regularly monitored for a certain period. At this time, the size and nature of the cyst is monitored.
Drug treatment
To alleviate the patient's condition, the following is prescribed:
- Painkillers;
- Antihypertensive drugs;
- Antibiotics;
- Vitamins.
For genetic cysts:
- Drink more than 2 liters of water;
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors;
- Antibacterial therapy with a wide range of effects;
- In severe cases, hemodialysis is prescribed;
- Antihypertensive drugs.
Acquired cysts:
- Bed rest;
- Painkillers;
- Surgery;
- Antimicrobial therapy.
Outpatient therapy
Therapy proceeds as follows:
- If the cysts are small, they are drained and then sclerosed;
- The most gentle method of treating cysts and after a couple of days patients are discharged from the hospital;
- Retrograde intrarenal surgery. The cyst can be accessed using a catheter. To prevent scars from forming after the operation, a thin tube is inserted into the kidney after 14 days.
Laparoscopy
Large cysts are removed surgically. The technique depends on the location of the cyst.
One of the progressive operations is laparoscopy. This is the safest and most gentle method. It is performed for large and multiple cysts. A laparoscope and other instruments are inserted through a small hole in the abdominal cavity. The patient remains hospitalized for several days until his condition returns to normal.
Drug therapy is prescribed only to reduce the unpleasant symptoms of kidney cysts in women (pain, high blood pressure). Drugs are recommended to destroy the infection and normalize the salt balance in the body. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are used to lower blood pressure. Long-term courses of antibiotics are prescribed (Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline, Levomycetin).
For a pathology such as a kidney cyst in women, in addition to conservative therapy and surgical intervention, a special diet is also recommended. It implies special nutritional principles, including:
- Limiting the amount of salt consumed. This principle is recommended for those patients whose disease provokes renal dysfunction.
- Control the amount of fluid you drink. This rule applies to those representatives of the fair sex whose pathology is accompanied by the appearance of edema, symptoms of heart failure, and high blood pressure. If the neoplasm is not supported by such signs, the amount of fluid should not be limited.
- Refusal of junk food. This category includes fried and fatty foods, smoked foods, baked goods, and alcoholic drinks.
- Limiting protein intake. If these substances enter the body in large quantities along with food, the likelihood of releasing nitrogen metabolic products is very high. They are very toxic and have a negative effect on a weakened body.
Kidney cysts in women require adherence to the diet described above. However, dietary restriction is not the only sure way to combat pathology. Comprehensive health care and compliance with all recommendations from the attending physician is the key to a quick recovery.
Treatment of kidney cysts - drugs and surgery
The treatment tactics for a kidney cyst are determined by its characteristics: size, type, growth rate, tendency to malignancy. Asymptomatic, small (up to 5 cm) cystic formations that do not have a negative effect on the functions of the organ are not treated, but are observed over time.
Unfortunately, it is useless to do anything to make the cyst on the kidney resolve. There are no dosage forms for self-resorption of cystic formations.
Sometimes this does happen, but spontaneous resorption is typical only for inflammatory cysts. Which speaks for itself about the advisability of wait-and-see tactics. The causes of kidney cysts and treatment are closely interrelated, and therefore, all patients are prescribed therapeutic treatment for the pathology that caused the formation of cystic blisters, and medications to relieve complications and relieve symptoms.
- To stabilize blood pressure, drugs from the ACE inhibitor group are prescribed - Enalapril, Copoten, Monopril or Enapa.
- Pain syndrome is relieved with painkillers - “Papaverine”, “Baralgin”, “Spazmalgon”, etc.
- For inflammatory processes in the urethra - Nitroxoline, Ceftriaxone, Levofloxacin, Fosfomycin.
- Drugs that improve blood flow in the kidneys - Trental or Pentoxifylline
- Non-steroidal drugs in the form of "Drotaverine", "Diclofenac", "Ketorolac" and "Lornoxicam"
To prevent complications, according to indications, a puncture of the cystic cavity may be prescribed with further sclerosis with a special substance that causes gluing of the cavity walls.
An important factor in therapeutic therapy is an organized diet. The principles of the diet for kidney cysts introduce the following prohibitions and restrictions on food products and methods of preparing dishes:
- Ban on fried, fatty and smoked foods;
- Limiting salt in food;
- Complete exclusion of hot herbs and spices, sparkling water, and alcoholic beverages;
- Saturation of the diet with baked, boiled and steamed dishes;
- Limiting protein-rich foods in your diet.
Surgery for kidney cysts - techniques
In some cases, the main method of treating a kidney cyst is surgery (sometimes urgent):
- With the active growth of formations and an increase in their number;
- The appearance of signs of suppuration and hemorrhagic processes;
- In cases of cystic rupture and obstruction of the urethral canal;
- With compression and atrophy of renal tissue.
Based on the scope of pathological disorders, appropriate techniques are selected that can successfully excise the kidney cyst, perform partial or complete nephrectomy.
If there is a likelihood of an oncological process in the organ, surgical intervention should not violate the integrity of the cystic bladder.
The most popular techniques for surgical removal of a kidney cyst include:
1) Laparoscopic method - belongs to the class of minimally invasive surgery. It is used for operations on multicystic neoplasms localized on the anterior or lateral side of the nephron. Cyst removal surgery is performed using a laparoscope.
During the operation, 4 small incisions are made on the anterior and lateral wall of the peritoneum, through which surgical instruments and a laparoscope with a camera are inserted into the peritoneal cavity. The ability to track the progress of the operation on the monitor allows you to remove a cyst on the kidney very delicately and safely for the patient.
2) Method of percutaneous (percutaneous) surgery. It is used for operations on large cysts located on the back side of the affected kidney. During back surgery, a small incision is made in the projection of the organ, through which a special sleeve is inserted, connecting the organ with the skin, and endoscopic instruments are inserted to open the walls of the capsule and excise it.
3) Open surgical approach is used mainly for nephrectomy (complete removal of an organ). The advantage of open surgery is due to direct visualization of the surgical field. The disadvantages are the high likelihood of complications, both during the operation and after it. Today, this method has almost been replaced by minimally invasive techniques.
The selection of a specific surgical method is carried out on an individual basis, taking into account the wishes of the patient and eliminating possible risk options.
Probable forecast
With timely detection and treatment of simple renal cysts, regardless of the treatment methods, the prognosis is always favorable.
Congenital multiple bilateral multiform formations and cysts caused by a genetic mutation are incompatible with life. Rarely do babies survive beyond two months of age.
Tags: cyst, kidneys
- Kidney prolapse - causes, symptoms and treatment,…
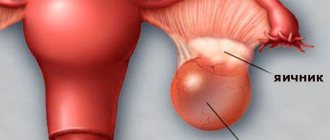
- Follicular ovarian cyst - symptoms and treatment,…
- Causes of pain under the left shoulder blade from the back, what to do?
- Endometrioid ovarian cyst - treatment and pregnancy
- Incomplete right bundle branch block - what is it...
- Male infertility - types, causes and treatment, drugs
Surgery
For simple cysts, that is, of an uncomplicated nature, experts most often recommend drainage with subsequent emptying of the contents of the formation. The procedure is carried out under constant monitoring of an ultrasound machine. A needle is very slowly inserted into the cyst itself, through which all the fluid is pumped out of the formation. Then the cavity is treated with a special sclerosing substance, with the help of which its walls gradually stick together.
In some cases, when the cyst is large or oncological in nature, nephrectomy (removal of the organ) is performed.
Treatment through laparoscopic surgery is currently the most minimally traumatic way to remove a tumor. Initially, the surgeon introduces a gas substance into the operated field to expand it and increase the space for subsequent manipulations. Then the laparoscope and trocars are connected to the work. After removing the cystic formation, the doctor removes all the instruments and applies sutures.
Features of the clinical picture and treatment of left-sided renal cysts in children
In young patients, this pathology is congenital. During the first 5–10 years of a child’s life, the condition of the urinary system is compensated by the activity of the second kidney, as a result of which clinical manifestations are irregular. Children often complain of fatigue, weakness and general weakness, sleep a lot and refuse to eat. They are not characterized by attacks of high blood pressure and pain when urinating.
In thin children and adolescents with a small layer of fat, a pathological formation on the left can be felt through the anterior abdominal wall. It has uneven contours and a bumpy surface.
Treatment of left-sided renal cysts in children is carried out according to the same principles as in adults. Doctors prescribe a gentle diet for the child, limiting fried, fatty, salty foods, as well as carbonated drinks, so as not to burden the urinary system. Surgery to remove a cyst in children is performed only if absolutely necessary (if the tumor causes discomfort), since anesthetics have a bad effect on the development of the nervous system.
The main medications used in pediatric practice:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesic effect: Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Nise;
- antispasmodics: No-shpa, Baralgin, Pentalgin-N, Drotaverine;
- detoxification solutions: Reamberin, Glucosolan, Glucose, Trisol, Acesol.
Photo gallery: pharmaceuticals for the treatment of benign neoplasms in children
Pentalgin relaxes spasmodic muscles
Glucose has detoxifying properties
Nurofen relieves inflammation
Possible complications due to kidney cysts
Most often, cysts in the kidney are asymptomatic and do not bother a person. However, if growth of the formation is noted, it can severely impair the functions of the affected kidney, leading to renal failure.
So, if a growing formation puts pressure on the soft tissue of the kidney, compression of the kidney vessels will occur. In this case, the patient will experience pain on the left side, which usually increases with physical activity.
- If the cyst is not dealt with (not observed and not treated), it can provoke negative consequences for the patient. Thus, due to constantly rising blood pressure, the cardiovascular system and brain will suffer. In the end, at one moment the patient may have a heart attack, stroke or hypertensive crisis.
- Also, if the patient’s urine outflow is impaired due to a capsule in the kidney, a pathology such as hydronephrosis may develop - overflow of the kidney with urine and its subsequent rupture. In addition, against the background of impaired urine evacuation, intoxication of the patient’s body can be clearly visible. In this case, immediate surgery is indicated, since it will be difficult to restore kidney function if there is a cyst in it.
- In addition, a formation in the left urinary organ is fraught with infection of internal organs with possible rupture of the cyst or the kidney itself. A situation that gets out of control can even turn into sepsis.
In the absence of timely treatment, a kidney cyst in women can lead to the development of very unpleasant consequences, the main one of which is its rupture. In this case, its contents begin to pour into the abdominal cavity, which inevitably leads to its inflammation.
Suppuration is diagnosed much less frequently. In this kind of situation, patients note weakness throughout the body, increased pain in the lumbar area and a sudden increase in temperature. This condition absolutely always requires immediate surgical intervention.
Another complication of the disease is the degeneration of the neoplasm into a malignant tumor.
Characteristic symptoms
Small cysts are almost always detected by chance during medical examination, or during an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs for other diseases. Such neoplasms do not lead to pain or other symptoms. But as their growth progresses, the patient may experience:
- Pain in the lower back or under the ribs of a pulling and aching nature.
- Unpleasant sensations in the kidney area during significant physical activity.
- Periodic increase in blood pressure.
- A change in the color of urine to pinkish, which indicates an admixture of blood in the urine.
The addition of an inflammatory process or suppuration of a cyst leads to an increase in body temperature, chills, and increased pain. A large lesion can be palpated (feel with your fingers).
A rapidly growing cyst and its suppuration threatens to rupture the capsule, which leads to the release of serous secretions or purulent masses into the abdominal cavity. This causes peritonitis, with the development of which surgical care should be provided to the patient in the first hours.
What to do for prevention?
Many people think about what preventive measures to take to avoid deviations, how to treat a parenchymal cyst of the right kidney, how to protect the left organ. Among the measures are: timely therapeutic procedures for renal inflammatory processes, maintaining health and, if the slightest signs appear, consult a doctor.
It is necessary to stop smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs, it is recommended to eat properly and strengthen the immune system with vitamins.
prourinu.ru
Treatment of a tumor in the left kidney involves surgery. This is the only way to completely get rid of the tumor. The conservative method eliminates exclusively external signs and symptoms.
Doctors often decide to monitor the dynamic development of cystic tissue. If there is no growth and the size of the formation is not large, then there are no indications for surgery.
How to prevent the development of kidney cysts in women? In order not to encounter this rather serious disease, experts strongly recommend promptly treating all ailments, including those of an inflammatory nature. It is important to avoid hypothermia whenever possible and regularly undergo a full diagnostic examination.
Causes of pathology
The term “cyst” in medicine refers to a formation that has a cavity and is surrounded on top by a capsule. Serous fluid accumulates inside this cavity. Kidney cysts are congenital in 5% of cases, acquired in the rest.
Congenital pathology is the result of infectious diseases of the mother.
Acquired may result from:
- infectious and inflammatory kidney pathologies:
- lumbar region injuries;
- urolithiasis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- tuberculosis of renal tissue;
- aging of the body;
- reduced immunity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- diseases occurring with renal failure.
In men, cysts on the kidneys form more often than in women; this can be caused by prostate adenoma and smoking.
Cyst sizes range from the smallest 1–2 cm to 10 cm or more. Large formations are dangerous to health, but small ones in rare cases also cause complications that are difficult to treat.
What diet is recommended for a left kidney cyst?
Kidney cyst is one of those diseases for which not only treatment is indicated, but also adherence to a certain diet. Its principles are as follows:
- Consuming a minimum amount of salt. A cyst can disrupt the functioning of the entire kidney, causing, for example, kidney failure. In this case, it is better to completely avoid salty foods. If kidney failure is not observed, then such strict restrictions are not necessary.
- The amount of liquid you drink should be controlled. It is necessary to limit fluid intake to those patients who have edema, signs of heart failure, or high blood pressure. Without such manifestations, the level of fluid you drink may not be limited.
- Patients must give up many foods. For example, spicy foods (in particular, all chili seasonings), fried and smoked foods. You cannot drink alcoholic beverages, beer is specially prohibited. Chocolate, seafood, and coffee irritate the kidneys. You should quit smoking completely, including passive smoking.
- Protein foods are harmful for patients with cysts. When consuming large amounts of protein, many toxic substances are released, which is very undesirable in case of kidney failure.
Diet is very important for urinary tract diseases, and especially for kidney cysts. But diet alone will not help you heal. This is just an aid to traditional treatment.
— Consuming a minimum amount of salt. A cyst can disrupt the functioning of the entire kidney, causing, for example, kidney failure.
In this case, it is better to completely avoid salty foods. If kidney failure is not observed, then such strict restrictions are not necessary.
— The volume of liquid you drink should be controlled. It is necessary to limit fluid intake to those patients who have edema, signs of heart failure, or high blood pressure.
Without such manifestations, the level of fluid you drink may not be limited. — Patients must give up many foods.
For example, spicy foods (in particular, all chili seasonings), fried and smoked foods. You cannot drink alcoholic beverages, beer is specially prohibited.
Chocolate, seafood, and coffee irritate the kidneys. You should quit smoking completely, including passive smoking.
- Protein foods are harmful for patients with cysts. When consuming large amounts of protein, many toxic substances are released, which is very undesirable in case of kidney failure.
Diet is very important for diseases of the urinary tract, and especially for kidney cysts. But diet alone will not help you heal. This is just an aid to traditional treatment.
Prevention of kidney cysts
Cystic kidney formations are a multi-cause disease, so there are no clear preventive measures. People who are at risk should know what symptoms are caused by kidney cysts, what they are, how to reduce the risk of complications and tumor degeneration into cancer.
- Proper and healthy nutrition.
- Timely treatment of all concomitant pathologies of the genitourinary system.
- Avoid injuries to the pelvic organs and spine.
- Periodically boost your immunity.
- Maintain weight control.
- Undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal organs once a year.
- Do not self-medicate.
Persons who have a hereditary predisposition to diseases of the urinary system should be regularly observed by a doctor.
Timely diagnosed pathology is the first step on the path to recovery.
Video on the topic:
Classification of the disease
Depending on the causes and mechanism of development, the following types of pathology are distinguished:
- Polycystic kidney disease. This is a disease of hereditary nature, characterized by the formation of numerous small tumors.
- Solitary (simple) cyst. The pathology is a single cavity formation. The disease develops predominantly unilaterally. A cyst of the left kidney is more often diagnosed. In women, the disease may not show clinical signs for a long time, but once it reaches a large size, the likelihood of developing complications increases.
- Parenchymal cyst. The neoplasm is localized in the thickness of the kidney tissue. Symptoms may not appear for a long time. If the tumor size exceeds 5 cm, surgical treatment is required.
- Sinus cyst. It is a cavity formation localized in the sinus of the organ.
- Complex cyst. In this case, under one connecting capsule there is a small multi-chamber cavity with liquid inside. Treatment is exclusively surgical.
- Subcapsular cyst. The size of the formation is usually small. Complications occur extremely rarely and are treated by puncture using an ultrasound machine.
- Parapelvic cyst. The most common cyst is the right kidney. In women, this disease is diagnosed very rarely, mainly after the age of 50 years.
Classification of neoplasms
Types of formations.
Increase. Types of kidney cysts and their classification depend on the origin, location and quantity. A cyst, like a kidney pathology, can be congenital. It occurs as a result of improper development of the organ in the prenatal period. It is also caused by a genetic predisposition and is a hereditary disease. In this case, the onset of the disease occurs in childhood.
Congenital kidney tumors
Congenital neoplasms include:
- Solitary - filled with serous fluid, which may contain impurities of blood and pus. Usually located in the right or left kidney, they have one cavity.
- Multicystic disease affects one of the organs. In severe forms, it spreads to almost an entire organ, which loses its function. In some cases, unaffected healthy areas are preserved.
- Polycystic cysts are cysts that affect the tissues of both kidneys, causing them to take on the appearance of bunches of grapes. It is often a congenital disease caused by a genetic predisposition.
- Multicystic medulla - the formation of many cysts with expansion of the collecting ducts of the organ. It is a congenital disease.
- Dermoid is a congenital disease in which a neoplasm on the right or left kidney is filled with ectoderm elements (teeth, fat, hair, bone inclusions).
- Renal cystic formations - their appearance occurs in hereditary diseases (tuberculosis syndrome, Hippel-Lindau syndrome, Zellweger syndrome, Meckel syndrome).
Causes of acquired tumors
Acquired kidney cystosis occurs due to pathologies of this organ present in the body:
- tuberculosis;
- heart attack;
- pyelonephritis;
- cystic kidney dysplasia;
- parasitic infections (echinococcus);
- tumors;
- glomerulonephritis;
- medullary necrosis.
Localization, structure, contents of cysts
When classifying neoplasms by number, the following are distinguished:
- Single - there may be one cyst in one of the organs, or one formation in each organ.
- Multiple – several neoplasms can be located in one or both organs without interfering with their functioning. Multiple cysts can cause kidney failure in the case of polycystic disease.
According to their location in the tissues of the organ, they are distinguished:
- Subcapsular cysts are located under the renal capsule.
- Intraparenchymal kidney cyst - located in the parenchyma.
- Peripelvic cyst - located near the renal sinus. The most common are peripelvic cysts of the left kidneys.
- Cortical cyst - affects the cortex.
According to its structure, the neoplasm can be:
- Unicameral - a simple kidney cyst, has one cavity. Simple kidney cysts have a low tendency to malignancy.
- Multi-chamber - a complex kidney cyst, has several cavities separated by septa, and thus forming several neoplasms. A multilocular renal cyst may have calcifications, and there is a risk of it becoming malignant.
Single-chamber Multi-chamber
One example of a multilocular cyst is an atypical renal cyst. It has a broken structure and multiple partitions. It is often caused by injuries, infectious and parasitic diseases.
Based on the nature of the contents, cysts in the kidneys are divided into:
- serous - filled with a transparent green-yellow liquid;
- hemorrhagic – filled with blood, occurring after a traumatic impact, or as a consequence of a heart attack;
- purulent - suppurated formations that arise due to infection;
- calcified – formations containing calcifications.
We invite you to watch an informational video on the topic of our article:
Complications and prognosis for kidney cysts
Complications of a kidney cyst may occur if medical care is not provided in a timely manner. Pathology can manifest itself with the following consequences and complications:
- chronic renal failure;
- hydronephrosis (hydrosis of organs);
- purulent pyelonephritis;
- peritonitis due to cyst rupture;
- suppuration of the liquid contents of the neoplasm;
- high blood pressure;
- the appearance of stones in this area;
- high risk of tumor rupture, which can be triggered by even a minor injury in the lumbar region.
The prognosis for a kidney cyst depends on a number of factors, for example, the size of the cyst, its nature and location. Single-chamber cysts of small size and slow growth have fairly favorable prospects. The presence of such a neoplasm does not have pronounced symptoms and does not have a significant impact on the patient’s quality of life.
The prognosis for neoplasms in this area may worsen as a result of relapses or genetic pathologies, although such cases are extremely rare.
An unfavorable prognosis is observed in cases of the development of neoplasms on both organs due to congenital anomalies. The prognosis for multiple congenital formations is especially serious; this type of cyst is not compatible with life.
Cysts in the right kidney lead to unpleasant consequences that directly depend on the size of the growth. A large neoplasm compresses the ureters and vessels, resulting in:
- reverse flow of urine with further infection by toxic substances;
- necrosis of the organ or deterioration of its function, leading to renal failure.
A cyst in the right kidney can rupture and cause a condition that requires immediate surgery.
Surgical intervention is also necessary in a situation where suppuration forms in the growth with the appearance of an abscess. It often leads to infection of the entire body.
In the absence of timely treatment, multiple complications can develop against the background of a renal cyst. The most common of them are:
- renal failure, becoming chronic;
- death of kidney cells;
- disruption of the flow of urinary fluid, which results in infection of the body with harmful toxic compounds; pathology can manifest itself in the presence of cysts in both kidneys;
- dropsy of the kidney;
- pyelonephritis, accompanied by a purulent course;
- rupture of the cyst with subsequent development of peritonitis;
- anemia;
- increased blood pressure.
It is possible to avoid the consequences of tumor rupture through surgery. Intervention is also advisable if suppuration is detected in the cyst. Untimely treatment of the pathology threatens the development of a renal abscess.
Most often, the disease is complicated by the development of suppuration, which occurs as severe pyelonephritis or an abscess. In this case, the patient develops the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in body temperature to 39-40 ° C;
- tremendous chills;
- severe headache and pain in the lumbar region;
- nausea, vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- severe weakness.
When the capsule ruptures, the liquid contents of the formation are poured into the retroperitoneal space or the collecting system. This condition is quite dangerous, as it threatens to develop:
- urinary tract infections;
- bleeding;
- hemorrhagic or infectious-toxic shock.
In the long term, cavity formations can transform into a malignant tumor or cause chronic renal failure.
Causes
The causes of this pathology in the kidneys are not fully understood, and in most cases they are congenital.
Also, urologists still cannot answer the question of why the disease more often occurs in the left kidney; according to one version, this is due to the anatomical structure of the human body, that is, the fact that the left paired organ is located higher than the right.
It is usually believed that pathology can also arise as a consequence of traumatic damage to an organ or previous infectious diseases.
The difficulty of identifying the causes that led to the formation of pathologies is explained by the asymptomatic nature of the disease.
The risk of benign kidney tumors increases due to several factors:
- age over 45 years;
- hypertension;
- VSD;
- traumatic kidney damage;
- tuberculosis;
- heart attack;
- surgical interventions in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- ICD;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.
During its formation, the neoplasm goes through several stages; first, a cavity space is formed, which is then filled with liquid.
These processes trigger the production of collagen by nearby tissues; moreover, due to biochemical reactions, the protein does not dissolve, as a result of which a capsule is formed, and the tissues are separated from the formation.
As a result of this, the neoplasm, having separated from the tissues of the organ, becomes an independent cavity. The further fate of the neoplasm depends on the reasons for its appearance, type and concomitant diseases.
Basic diagnostic methods
The level of development of modern Russian medicine makes it possible not only to promptly identify a kidney cyst, but also to carry out a differential diagnosis. Various methods are used.
First, the doctor will talk to you. At this stage, you can not only suspect the presence of a kidney cyst, but also determine whether it is acquired or congenital. After collecting anamnesis, the doctor will perform palpation, percussion and other diagnostic methods. At the same time, the qualifications of a medical specialist are important: the conclusions at the end of this examination are subjective, and an inexperienced physician may make mistakes. Therefore, further examination is necessary.
General blood and urine tests are indispensable “helpers” in identifying cysts. True, if there are no pathological complications, the results will be indistinguishable from normal ones. In some cases, an increase in the number of red blood cells may be detected. If complications arise, tests will reveal them. The number of leukocytes in the blood and urine will be increased.
To confirm the diagnosis and exclude other diseases, modern diagnostic tools are used:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys can detect most types of cysts even at the initial stage. If the results are questionable, another study may be required.
- Computed tomography is a series of x-rays taken from different angles and planes. For a more accurate result, a special contrast agent is injected into the patient’s vein.
- MRI is a study based on the use of a magnetic field. Compared to ultrasound in combination with CT, it does not provide more accurate results, so it is used if the patient has an individual intolerance to the contrast agent injected into the vein.
- Cyst biopsy. It is used if the tumor has reached stage 3 and there is a suspicion of cancer. In this case, all of the methods listed above will not give a clear result, and differential diagnosis can only be performed by biopsy.
In some cases, the doctor may use other techniques, for example, nephroscintigraphy.
Folk remedies
When fighting the disease, use folk remedies approved by the attending physician. This therapy is used only in combination with drug or surgical treatment. Traditional medicine alone is not able to cope with the disease. Patients are advised to take one tablespoon of burdock juice before eating. An infusion prepared from burdock leaves, knotweed and aspen bark is often used. If you have painful sensations, it is recommended to drink a decoction that includes chamomile, yarrow and St. John's wort.
Symptoms
Manifestations are observed with enlargement of the capsule, as well as with multi-chamber kidney cysts that disrupt the functioning of organs. Pain appears in the pelvic or back area. Physical activity increases its intensity. There may be flakes and blood in the urine, and blood pressure rises.
Pain appears in the pelvic or back area.
When the capsule is enlarged by more than 3 cm or in patients with an asthenic build, the tumor is easily palpable. Stones cause colic.
Conservative treatment
Drug therapy is prescribed only to reduce the unpleasant symptoms of kidney cysts in women (pain, high blood pressure). Drugs are recommended to destroy the infection and normalize the salt balance in the body. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are used to lower blood pressure. Long-term courses of antibiotics are prescribed (Ciprofloxacin, Tetracycline, Levomycetin).
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
With timely treatment, benign tumors of the left kidney can be completely removed. The average duration of therapy along with the recovery period ranges from 4 to 12 months, after which the functions of the urinary system return to normal. The intensity of soft tissue regeneration is influenced by the patient’s age, the presence of hereditary pathologies, various infections, lifestyle and diet.
The body of a teenager or child recovers best. Doctors attribute this to the intensive growth and development of new cellular elements at the site of the removed cyst.
The likelihood of a successful treatment outcome is largely influenced by the state of the person’s immune system. I had a patient diagnosed with a left kidney cyst who also suffered from HIV infection. The peculiarity of this disease is that bone marrow cells are affected, as a result of which the body becomes extremely vulnerable to external influences. The man did not take specific antiretroviral therapy, which led to a disruption of the protective function of the immune system. A common bacterial infection caused his previously healthy kidney to develop a purulent disease, resulting in its having to be resected. Now the patient requires constant visits to hemodialysis - a procedure for artificially removing harmful impurities from the blood in order to feel at least a little better.
Possible complications and undesirable consequences of the development of the disease:
- Formation of renal failure. Against the background of the formation of a foreign body, the urinary system begins to filter the blood worse: toxic substances and breakdown products of proteins, fats and carbohydrates remain in it. This contributes to damage to various organs (heart, brain, liver) and requires correction using hemodialysis or donor kidney transplantation.
- Cyst rupture. During intense physical activity, stress, injury, and neuropsychic shock, the pressure in the abdominal cavity may increase. This is one of the factors that increases the likelihood of cyst rupture. The contents of a benign tumor leak into the surrounding tissues, causing inflammation. The rupture itself is accompanied by severe pain and massive internal bleeding, which can cause the death of the patient. Treatment of such a complication is carried out immediately in the operating room.
- Attachment of a secondary infection. Against the background of weakened immunity, the human body becomes extremely vulnerable to the effects of various bacteria, viruses and fungi. By multiplying in the kidney tissue, they contribute to the formation of abscesses, carbuncles and phlegmons. Purulent-inflammatory processes are accompanied by a rise in body temperature and a sharp deterioration in general well-being. To treat this disease, patients are prescribed antibacterial agents.
Purulent kidney damage occurs due to infection of a small cyst
- Transition of a benign tumor into a malignant one (malignancy). This phenomenon occurs extremely rarely under the influence of ionizing radiation, radiation or chemical pollution of the environment. Malignant neoplasms are characterized by the ability to metastasize and a faster, uncontrolled course. Removal is carried out using surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.
Kidney cancer is characterized by a tendency to form metastases
- During pregnancy, a renal cyst can provoke an earlier onset of labor. Children are born with an underdeveloped respiratory system and underweight, as a result of which they spend a lot of time in intensive care.
How to treat
A patient with cystosis is most interested in how to treat such a disease and whether it is even possible to cure a cyst. If the tumor is small and does not cause discomfort, a wait-and-see approach is most often chosen. In very rare cases, when the development of a neoplasm is provoked by inflammation in the organ, after their elimination the cyst can resolve on its own.
If the tumor begins to progress, a puncture is performed and fluid is pumped out of it, and additional drug treatment is prescribed. If these methods are contraindicated, the cyst and, in more severe cases, the entire kidney should be removed.
Only a doctor can tell you exactly what to do with the tumor after a thorough examination. Self-diagnosis and self-medication are strictly prohibited.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment cannot cure the cyst, but is aimed at eliminating negative symptoms. Antibiotics are prescribed, but only in cases where bacterial infection has occurred. In other situations, there is no need to take drugs of this type.
If you have severe pain in the lumbar region, you may need to take painkillers. When high blood pressure is detected, it is necessary to take a drug that reduces its value. Additionally, medications are prescribed to relieve inflammation and normalize urine output.
Outpatient
Drainage is installed in small-volume cysts, and subsequently they are sclerotized. During this manipulation, a thin needle is inserted into the cyst under the supervision of an ultrasound machine, which sucks out all the liquid contents from the formation, and a special sclerosant (alcohol) is poured inside, gluing the walls of the formation. This is the most gentle and very effective method, after using which the patient goes home almost immediately.
Another minimally invasive method is retrograde intrarenal surgery, during which an endoscope with a laser is inserted through the urinary tract into the kidney, cutting the walls of the cyst. To prevent the formation of sutures, a stent is installed at the incision site for 2 weeks, which is then removed in an outpatient setting.
Indications and contraindications for surgery
If the formation is less than 50 mm, it does not interfere with blood circulation and urine output, there is no need for surgical intervention, such a cyst is simply controlled. We list the main indications for surgical removal of a cyst:
- the cyst causes severe pain,
- the tumor grows and puts pressure on nearby organs,
- the patient has hypertension,
- there is kidney bleeding,
- formation blocks the normal output of urine,
- there is a high risk of cyst apoplexy,
- the tumor is affected by infection,
- there is a suspicion of the presence of oncological processes.
There are also a number of contraindications for kidney cyst surgery:
- cystosis does not cause discomfort to the patient,
- there is no disturbance in urine output,
- problems with blood clotting and pathologies of the circulatory system,
- the presence of severe concomitant illnesses in the patient.
A contraindication for laparoscopic surgery is the patient’s serious condition, concomitant ailments, which increase the risk of complications and impaired blood clotting. Also, this method is not used if the size of the cyst in the kidney exceeds 30 mm and it is located inside the tissues of the organ.
Types of operations on renal cysts
There are several types of cyst removal operations:
- cyst biopsy,
- husking cyst,
- excision of the tumor with partial excision of organ tissue,
- excision of formation,
- nephrectomy.
Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopy is the most progressive and gentle method of removing cystic formations in the kidney. All manipulations during laparoscopic surgery are performed through small punctures in the abdominal wall. The laparoscope and other necessary instruments are inserted through these punctures. To prevent the development of complications after the intervention, you need to stay in the hospital for some time under the supervision of medical staff.
ICD code - 10
In medical science, there is a registry of diseases called the International Classification of Diseases, or ICD for short. Formations on the kidneys in the form of cysts are listed in the ICD under the number 10.
Further, each disease has its own code, depending on the group it belongs to. Thus, the occurrence of cysts is included in the section devoted to congenital anomalies of the urinary system (code Q60-Q64). Cystic formations of the kidneys have the number Q61 , which is then subdivided into Q61.0, Q61.1, ..., Q61.9, which respectively includes a single cyst, polycystic 3 types (children's, adult, unspecified), dysplasia, medullary cystosis, others types of cysts, unspecified cystic diseases.
Acquired cysts are coded N28. 1 in the ICD - 10 and they are included in the group of other diseases associated with the genitourinary system.
Formation mechanism
The formation of pathology begins in the renal tubules. Here, primary urine is concentrated: water with useful substances is absorbed back into the blood, and everything unnecessary is excreted in the form of final urine.
A cyst on the kidney appears in those places where primary urine stagnates in the tubules, as a result of which they increase in size up to 2 mm.
The immune system reacts to this pathology: the growth of epithelial cells of the dilated tubule begins, it is isolated from other structures by a capsule of connective tissue.
Experts identify three groups of factors for the appearance of pathological formations.
Prognosis and outcome of the disease
You can live with a small cyst, if it does not manifest itself in any way, for the rest of your life. At the same time, there are cases when congenital formations have turned into oncology over time. Therefore, in any case, you cannot do without surgical intervention; the main thing is to choose the right time.
If the cyst removal process is neglected, it can lead to serious complications in the patient, such as: decreased kidney function, which can ultimately lead to renal failure; development of peritonitis, with infection of the cyst and its subsequent rupture.
Why do cysts develop?
A kidney cyst in women can be a congenital or acquired disease. The cause of the first may be a difficult pregnancy, during which pathologies and anomalies in the structure of internal organs develop. Congenital cysts are diagnosed in infants due to genetic diseases.
The process of formation of kidneys and their tubules is negatively affected by bad habits of the mother and infectious diseases during pregnancy. Congenital pathology can be hereditary. The risk of developing a neoplasm increases if close relatives have been diagnosed with cases of a similar disease.
The acquired disease develops against the background of chronic inflammatory and infectious processes in the kidneys. Women with high blood and kidney pressure, as well as patients with tuberculosis, which leads to the proliferation of fibrous tissue, are at risk.
The risk of cyst formation increases with urolithiasis, which disrupts the normal process of urination. Stagnation of urine leads to its accumulation in the kidneys, which gradually fills the cavities of the connective tissue. Damage to the connective tissue of the organ as a result of injury also leads to disruption of the process of accumulation and discharge of urine and the formation of a cyst.
Phytotherapy
If the size of the benign neoplasm is small and the symptoms do not cause discomfort, after consultation with a doctor, you can use traditional medicine recipes. A decoction of cedar shells will help get rid of the cyst: 30 g of shells per 200 ml of water, brew and leave. Take a decoction of 50 ml three times a day before meals.
An effective remedy is a gruel made from burdock leaves. To prepare, simply grind the leaves in a blender or pass through a meat grinder. Take 1 tsp. in the morning and in the evening. You can store burdock pulp for no more than 30 days.
A well-known method of treatment is an infusion of elecampane with yeast. To prepare, you will need 20 g of crushed root and sugar, 10 g of yeast, 3 liters of water. Mix and place in a dark place to ferment. Take kidney infusion twice a day, 100 ml. The course of treatment with the listed methods is no more than one month.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely detection of pathology and implementation of preventive measures, the prognosis is favorable. In the case of multicystic disease that occurs in both kidneys, the chances of survival are low. It is difficult to make a favorable prognosis for congenital polycystic disease. It is recommended to consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease and begin treatment on time to increase the chances of a successful recovery.
A patient with an acquired disease is recommended to regularly undergo examinations of the internal organ and monitor the development of pathology. A patient with a cyst should avoid infectious diseases and the penetration of bacteria into the kidney and genitourinary system. It is recommended to eat properly and not drink alcohol. The organs of the genitourinary system should be protected from hypothermia.
Classification and types
Taking into account the type of growth, etiology and degree of damage, certain types of neoplasms are distinguished.
Based on the origin of the cyst in the right kidney, there are acquired and congenital growths. The first has a secondary etiology. Associated with the disease that caused the cyst to appear. Congenital are divided into:
- Solitary cyst. Appearing predominantly in males.
- Multicystic. Characterized by the appearance of more than 2 growths at once on the right kidney.
- Polycystic. Characteristic of injury to both kidneys.
- Multicystic formation of the medulla, during which there is an expansion of the renal canals and a large number of minor formations.
- A dermoid cyst that contains fat, hair, or skin.
The location of the growth will be important. According to this criterion, there is also a certain classification.
Nutrition
In case of a cyst in the kidneys, nutrition is prescribed according to diet No. 7; we list its basic rules:
- fried, spicy and smoked foods are removed from the diet,
- salt is limited or completely removed,
- you need to avoid alcohol and cigarettes,
- tea is limited and coffee is removed,
- drink at least 2 liters of water per day,
- steam dishes,
- limit the consumption of animal proteins, which additionally burden the kidneys,
- enrich the diet with dairy and cereal products.
Methods for detecting tumors
An algorithm of measures to identify a cyst, determine its type, and the degree of impact on kidney function is developed individually by a urologist. In some cases, the tumor is found by chance during examination of the patient for another reason. Another scenario involves a complete diagnosis of the female body to explain nonspecific symptoms or changes in tests.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following measures are used:
- examination by a urologist. Allows you to suspect the presence of a cyst if a round formation is felt in the abdomen. However, such a picture of the disease is rarely observed. In addition, with a kidney cyst, the doctor can detect high blood pressure even in young women;
- general blood analysis. It records a decrease in the number of red erythrocytes and their main component, hemoglobin protein. However, the exact opposite changes also occur - an increase in red blood cells and hemoglobin (polycythemia). The only sign of a kidney cyst is often accelerated sedimentation of red blood cells to the bottom of the tube (ESR);
An increase in ESR may be the only sign of a kidney cyst
- blood chemistry. The activity of the kidney to cleanse the body of toxins is recorded by indicators such as urea and creatinine. Exceeding the norm indicates inadequate urine formation in the kidneys;
- general urine analysis. A typical abnormality for a cyst is the presence of red blood cells (hematuria) in the urine. The degree of hematuria differs in different cases. A reddish tint to urine with a large number of red blood cells is visible to the naked eye. In addition, high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria) are typical for kidney cysts;
Red blood cells in the urine are the main sign of a kidney cyst
- analysis of large volumes of urine (Nechiporenko, Amburge, Addis-Kakovsky test). Such studies help determine more accurately the degree of hematuria and proteinuria. The material is collected within a day or several hours;
- Zimnitsky's test. Allows you to indirectly judge the ability of the kidneys to cleanse the blood. Urine is collected during the day in 8 containers. Low density of urine and the predominance of its excretion at night are unfavorable prognostic signs;
- ultrasonography. It is one of the main criteria for diagnosing a kidney cyst. The picture obtained on the screen of the device allows you to determine its size, the degree of relationship with other structures of the kidney and neighboring organs. In addition, an important indicator is the number of individual cavities and the thickness of their walls;
Ultrasound can detect large and small cysts
- X-ray examination of the kidney. Allows you to identify structural anomalies, as well as the relationship of the cyst to the pelvis and vessels. To obtain a more informative picture, before taking an image, a specific X-ray contrast agent is injected into the patient’s vein, which is quickly filtered by the kidneys from the vascular bed and enters the urine;
- CT scan. Currently, it is the most informative method for studying the anatomy of internal organs and their vessels. Images after processing allow you to obtain a three-dimensional model of the kidney, accurately assess the size of the cyst, its relationship to the glomeruli and pelvis, as well as to the artery, vein and ureter. CT scans are also used to study the effect of the cyst on nearby organs. In addition, examination of the kidney with the preliminary administration of an X-ray contrast agent makes it possible to fairly accurately judge the ability of the organs to cleanse the blood of waste and toxins.
CT allows you to obtain a three-dimensional model of the cyst
- angiography. Allows you to study the structure of large and small vessels of the kidney. To obtain information, an X-ray contrast agent is injected into the femoral artery through a puncture, after which photographs are taken. In this study, the cyst has the appearance of a shadow that does not contain vessels;
- study of a woman’s genes for the presence of defective ones. It is performed for polycystic and multicystic kidney disease.
A kidney cyst must be distinguished from the following urological diseases:
- hydronephrosis - enlarged renal cups and pelvis due to impaired urine outflow through the ureter;
- kidney tumors - malignant or benign neoplasms from various parts of the kidney - glomeruli, tubules, pelvis;
A kidney cyst must be distinguished from a tumor
- kidney tuberculosis - a specific inflammation of the kidney tissue caused by the tuberculosis bacterium;
- kidney abscess - an area of purulent inflammation of the kidney tissue, surrounded on the outside by a membrane (capsule);
- malformations - duplication, fusion, horseshoe kidney.
Hydronephrosis - video
Causes of formation of cysts in the kidneys
Kidney cysts form in women for various reasons. Multiple pathological formations, localized in one or both organs, arise as a result of the influence of incorrect genes. With bilateral multicystic disease, the cause lies in two defective genes received from both parents. This type of inheritance is called autosomal recessive. The defective gene leads to the formation of a large number of cysts in the kidneys.
Their source is tubular tubule cells that have grown to large sizes. Such kidneys cannot both form urine and remove it. Cystic cells of the renal tubules are a significant obstacle to the absorption of necessary substances into the vascular bed. Already formed urine cannot pass through the tubules and enter the renal calyces. In such kidneys, normal activity of the glomeruli, tubules and pelvis is impossible. Often, poisoning of the body begins long before the child is born. Such women very rarely survive to adulthood. The formation of cysts does not only occur in the kidneys. The process affects the liver, esophagus, uterus, ovaries, and cerebral vessels.
Polycystic and multicystic kidney disease are inherited
Polycystic kidney is another type of influence of defective genes. They are already located on another chromosome. For the disease to manifest, it is enough to receive such a gene from only one of the parents (autosomal dominant inheritance). In this case, polycystic disease makes itself felt after the age of 40. Changes occur in the kidneys, similar to those with multicystic disease. However, the process more often affects one organ, giving the opportunity to another to take care of cleansing the blood of waste and toxins.
A cyst in the kidney can appear during a woman's life. However, the process does not happen out of the blue. It is necessarily preceded by changes in the kidney tissue. Most often, a cyst replaces an inflammatory process. The confrontation between bacteria and immunity leads to the formation of cavities filled with pus. This process is no longer called pyelonephritis. The terms abscess and renal carbuncle are used to refer to it. However, over time, immunity begins to take over. Cavities form in place of the pus. The kidney tissue that once filled the area has died. The vacated cavity is often closed with a scar. However, in some cases it fills with fluid, closes, and a cyst forms.
Pyelonephritis often results in the formation of scar tissue
The contents of the cyst, transparent at first, may change in nature. Blood can flow into it from damaged kidney vessels. A liquid containing so many nutrients in a confined space is an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. The contents of the cyst often fester, increasing the risk of infection spreading to healthy kidney tissue.
A single cyst may not have a significant effect on kidney function. The most dangerous consequence of the disease is poisoning of the body with waste, toxins and waste substances - chronic renal failure. If the disease damages both kidneys, the situation worsens significantly. Even more toxins accumulate in the body, affecting other organs and tissues.
Polycystic kidney disease - video
Lifestyle of a patient with a cyst
The appearance of a pathological formation in 90% of cases affects the patient’s health. Even with a minimal size of the cyst, minor trauma to it can lead to undesirable consequences. That is why, immediately after diagnosis, the patient needs to reconsider his usual lifestyle, giving up some activities.
During my internship in the urology department, I had to participate in the treatment of a man with a left-sided renal cyst. He was a professional athlete and regularly trained in martial arts. Almost every training session ended with injury to the lumbar region. When doctors first discovered a cyst in the left kidney, its size did not exceed 1.5 centimeters in diameter. The man was offered surgery, which he refused due to the proximity of the next competition. After six months, during the next battle, the enemy put our patient on his shoulder blades, as a result of which the renal cyst spontaneously ruptured. Since it touched arteries and veins, the victim developed serious bleeding, which doctors were able to eliminate only after surgery.
Lifestyle changes in the presence of a cyst in the left kidney:
- Avoid strenuous physical activity. If your job involves lifting and moving massive objects, you might want to change your focus. Injury-prone sports (hockey, rhythmic gymnastics, wrestling, football, volleyball, basketball, biathlon) should also be suspended. Be sure to inform your trainer about the disease: then he will be able to choose the optimal load regimen for you, which will not provoke an exacerbation of the disease.
- Give up bad habits. Nicotine, alcohol and narcotic drugs significantly slow down metabolic processes in the body. This leads to the progression of the cyst and the development of complications in the blood coagulation system (thrombosis, embolism).
- Do not visit baths or saunas, and do not take too hot baths. High temperature improves blood circulation in the lumbar region, as a result of which the pathological neoplasm receives more nutrients that accelerate its growth and development. Doctors believe that this may also be one of the reasons for the formation of relapses of the disease in the future.
Establishing diagnosis
The disease is detected and subsequently confirmed exclusively by instrumental and laboratory examination. The latest diagnostic option includes:
- Analysis of urine.
- Blood test (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate is a clear sign of the onset of an inflammatory process in the body).
- Biochemical blood test (changes in creatinine levels indicate the development of renal failure).
Instrumental diagnosis of kidney cysts in women implies:
- Ultrasound (allows you to detect the presence of a cavity formation).
- CT and MRI (the study helps to accurately recognize the location of the cyst and its size).
- Excretory urography (x-ray examination using a contrast agent).