Medical Consultant Pulmonology Pulmonary pneumosclerosis: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
Protracted pulmonary and bronchial diseases lead to the formation of connective tissue scars. The same changes occur when inhaling dust and toxic substances, congestive pneumonia and heart failure.
This causes sclerosis of the lung tissue and the occurrence of a number of chronic diseases.
- Causes of pulmonary pneumosclerosis
- Symptoms of pulmonary pneumosclerosis
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment of pulmonary pneumosclerosis
Traditional methods of treatment
General information
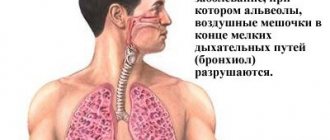
Pulmonary pneumosclerosis is a condition characterized by the proliferation of connective tissue in the lungs, leading to the gradual replacement of pulmonary connective tissue.
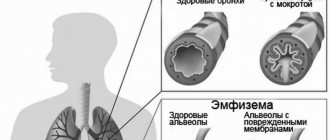
Accompanied by impaired lung function caused by changes in the elasticity of the lung tissue and gas exchange in areas with pathological changes. Replacement and pronounced proliferation of connective tissue leads to compaction of the lung tissue and causes deformation of the bronchial tree. In fact, pneumosclerosis is the outcome of a number of diseases of both the bronchopulmonary system and diseases of other organs and systems. It should be noted that pneumosclerosis is a constantly developing process of restructuring of the lung tissue, in which lesions of the interstitium, alveoli and perialveolar tissue, and pulmonary capillaries gradually increase. Such pathological changes contribute to excessive fibrosis formation and gradually destroy/deform lung tissue, forming pulmonary pneumosclerosis. Some authors believe that there is a genetic predisposition in individuals to the development of diffuse lung diseases, developing as a response to nonspecific damage to the lung epithelium.
The course of the disease, the severity of clinical manifestations and its prognosis are determined by the degree of impairment of respiratory function and gas exchange, which in turn is determined by the prevalence of the pathological process. Changes in the lungs at the level of local lesions occur predominantly without respiratory distress and asymptomatically, and a diffuse process affecting a significant part of the lung tissue is accompanied by impaired ventilation in the lungs of an obstructive/restrictive type with the development of hypertension in the pulmonary circulation or its absence and is manifested by rapid fatigue, chest pain, progressive shortness of breath and cough.
A diffuse process in the lungs, as a rule, leads to a number of disabling complications and a significant deterioration in the patient’s quality of life, and in severe cases, it reduces life expectancy. In the structure of pneumosclerosis, focal and diffuse forms occur in approximately equal proportions. Sometimes patients ask whether pneumosclerosis is contagious or not? The disease itself is not contagious, but some diseases that underlie its development can be contagious, for example, tuberculosis .
Prevention
Pneumosclerosis is dangerous because it can affect a large area of lung tissue. This is fraught with the development of serious complications that can lead to the death of the sick person. If there is a hereditary predisposition or lung diseases already exist, it would be useful to carry out daily prevention of this disease .
What can be done to prevent pneumosclerosis:
- quit smoking, minimize the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- promptly treat lung diseases and colds;
- change jobs that involve inhaling foreign substances (dust, gas, mold, etc.);
- ventilate the room more often, regularly spend time in the fresh air, walk in the forest or at sea, harden the body with rubdowns;
- do not take toxic drugs without a doctor’s prescription.
Any person over 14 years of age is required to undergo a fluorographic examination every year , which helps to identify any changes in the bronchopulmonary structure and begin treatment in a timely manner. X-rays are also indicated if there is persistent shortness of breath or cough.
The condition of the body should not be aggravated by constant exposure to predisposing factors if there are already lung diseases. Such a patient needs to be observed by a pulmonologist once every six months.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of pneumosclerosis depends on its etiology. However, regardless of the etiological forms, the leading pathogenetic mechanisms of the disease are: impaired ventilation of the lungs, decreased drainage function of the bronchi, and blood/lymph circulation disorders. The process of proliferation of connective tissue is directly caused by a violation of the structure and destruction of the morphofunctional elements of the lung parenchyma.
Inflammation is of greatest importance in the development of the disease. The histogenesis of pneumosclerosis of inflammatory origin is based on edema, inflammatory infiltration , carnification , development of granulation tissue, sclerosis of the walls of bronchioles with subsequent fibrosis of foci of interstitial inflammation of the interalveolar septa, promoting the development of a honeycomb lung with the destruction of the interalveolar septa and the formation of multiple cavities.
Under conditions of infectious inflammation, increased production of elastase , which causes destruction of the connective tissue matrix and alveolar walls with the formation of common cavities. fibroblasts are activated , which contributes to the increased development of connective tissue in the lung parenchyma and the formation of fibrosis.
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs - life expectancy
Basal pneumosclerosis refers to diseases that lead to irreversible consequences. Lung tissue changes its structure to a more dense one, after which it cannot be returned to its original state. If the disease is focal in nature and is not complicated by pulmonary emphysema, then the prognosis for pneumosclerosis can be favorable. With proper treatment and constant prevention of complications, the patient can continue his normal life.
Weak immunity, bad habits, extensive lesions or diffuse lesions, concomitant diseases, and improper treatment can cause the patient’s condition to worsen and shorten life to several years. How long a patient with pneumosclerosis can live will depend on the severity of the disease, its rate of progression and general health.
Classification
Based on etiology, they are distinguished:
- Infectious specific (mycotic, tuberculous, parasitic, syphilitic) and nonspecific (post-traumatic, post-aspiration).
- Toxic (reaction to exposure to toxic substances).
- Pneumoconiotic (occupational pathology).
- Dysplastic (developing as a result of congenital enzymopathies or malformations of the lung).
- Dystrophic (due to ossification, radiation pneumonitis, amyloidosis).
- Allergic (exogenous - from inhalation of fungal spores, medicinal) and endogenous (for collagen diseases, Hamman-Rich syndrome, for idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis, for allergic granulomatosis).
- Cardiovascular (for congenital/acquired heart defects, accompanied by hypertension of the pulmonary circulation, embolism/thrombosis of the pulmonary circulation).
According to pathomorphological characteristics:
- Local (limited) small- and large-focal - characterized by the formation of individual foci of sclerosis . Macroscopically it represents a limited area of compacted pulmonary parenchyma with a reduced lung volume in this part. The local focus of pneumosclerosis does not have a significant effect on the elasticity/gas exchange function of the lungs.
- Diffuse pneumosclerosis. What it is? This form of the disease is characterized by extensive perivascular/peribronchial growths of connective tissue in the form of a mesh with large cells (reticular pneumosclerosis) or diffuse sclerosis of predominantly interalveolar septa (interstitial pneumosclerosis). The diffuse process is characterized by a picture of a rigid lung with reduced ventilation.
Pathogenetically, inflammatory , atelectatic , lymphogenic and immune pneumosclerosis .
Depending on the prevalence of the affected structural elements of the lungs alveolar , interstitial , perivascular , perilobular and peribronchial in the mediastinal zone are distinguished ( hilar pneumosclerosis ). Based on the affected segments, hilar pneumosclerosis of the lungs is distinguished, this is when the pathological process is concentrated in the hilar areas of the lung and basal pneumosclerosis, when any basal segment of the lungs is involved in the pathological process (anterior, medial, lateral and posterior basal segments).
Description
Fibrosing idiopathic alveolitis (synonyms: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, Hamman-Rich syndrome) is a progressive diffuse bilateral lesion of the alveoli and interstitial lung tissue, accompanied by the development of diffuse fibrosis and increasing respiratory failure.
Fibrosing alveolitis has an exclusively pulmonary localization, is difficult to treat, and is often fatal. Fibrosing alveolitis is a relatively rare disease of unknown etiology, but tends to increase. Fibrosing alveolitis more often affects men over 50 years of age (20 cases out of 100 thousand) than women (13 cases out of 100 thousand). Mortality with fibrosing alveolitis reaches 3.3 cases per 100 thousand population.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:tv.youtube.com
shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, cyanotic coloration of the skin, fatigue. Diagnosis includes radiography and tomography of the lungs, as well as pulmonary function test. Therapy for diffuse pneumosclerosis consists of medication (glucocorticoids, bronchodilators, cardiac glycosides) and non-drug support (oxygen therapy, massage, exercise therapy).
Causes
Pneumosclerosis can be the outcome of a number of inflammatory/destructive lung diseases (chronic pneumonia, abscesses, pleurisy), specific diseases ( tuberculosis ), fibrosing alveolitis, occupational diseases ( pneumoconiosis ), radiation injury, traumatic damage to lung tissue, etc.
Lung diseases:
- Pneumonia . Among infectious lung diseases, the leading role belongs to chronic pneumonia of various origins (bacterial, mycotic, tuberculous etiology, Legionnaires' disease, cytomegalovirus infection, chlamydial pneumonia), which are often complicated by pleural empyema , lung abscess , resolving with the formation of pneumosclerosis.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, including bronchial asthma , in which the inflammatory process is accompanied by a pronounced change in the structure of the bronchial wall with the development of pneumosclerosis.
- Dust occupational lung diseases ( pneumoconiosis ). Caused by prolonged inhalation of various types of aggressive dust: silicon/coal dust ( silicosis ); cement, asbestos, talc, kaolin dust ( silicates ); dust of aluminum, beryllium, iron ( metalloconiosis ), etc. Occurs in the initial stages of the disease as chronic bronchiolitis/progressive alveolitis, turning into pneumosclerosis .
- The pulmonary form of sarcoidosis is accompanied by gross disturbances in the structure of the lungs, the formation of bronchiectasis and bronchial stenosis with the gradual development of widespread pneumosclerosis with severe respiratory failure.
- Allergic lung diseases (allergic exogenous alveolitis , hypersensitive pneumonitis ). Diseases of an immunopathological nature that develop when inhaling an antigen, often organic dust or vapors - heavy metal salts, polyurethane, dyes, fungicides.
- Idiopathic fibrosing alveolitis . It is characterized by a progressive disruption of the structure of the pulmonary structures, diffuse thickening of the interalveolar septa, and the formation of cystic cavities leading to the development of diffuse pneumosclerosis .
- Lung operations, the complication of which is excessive diffuse sclerosis of the interalveolar septa.
Diseases of other systems and organs:
- Active chronic hepatitis .
- Systemic autoimmune diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus , scleroderma , ankylosing spondylitis , rheumatoid arthritis . Systemic diseases are, in principle, characterized by fibrotic changes due to an increase in the function of fibroblasts in the tissues of various organs, including the lungs.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels (congenital/acquired heart defects, accompanied by pulmonary hypertension) - they are characterized by diffuse pneumosclerosis of cardiovascular origin.
Common reasons:
- Radiation therapy , one of the complications of which is post-radiation pulmonary pneumosclerosis. It develops more often in breast cancer/lymphogranulomatosis after irradiation of the mediastinal area. The frequency of complications is determined by the total focal dose. Persons aged 65-70 years have complications 1.5 times more often than patients aged 40-60 years.
- Toxic damage (inhalation of toxic substances). Toxic diffuse pneumosclerosis often develops when exposed to toxic warfare gases, oxygen and ozone in high concentrations, smog, industrial pollutants, and prolonged inhalation of cigarette smoke. At the same time, not only the inhalation of toxic substances matters, but also their exposure and individual sensitivity to them.
- Taking medications: Methysergide , Methotrexate , Proctolol , Amiodarone , Propranolol . Pneumosclerosis can develop as a long-term complication.
Etiology
There are a number of pathologies that, without timely and competent treatment, can lead to the progression of pneumosclerosis in humans:
- aspiration, infectious and viral pneumonia;
- pulmonary sarcoidosis;
- mycosis;
- tuberculous lesions of the lungs and pleura;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels;
- chronic bronchitis;
- allergic and fibrosing alveolitis;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels;
- exudative pleurisy;
- gastroesophageal reflux with a chronic course;
- injuries of the sternum or lung parenchyma.
In addition, it is worth highlighting the following etiological factors:
- inhalation of industrial gases;
- conducting radiation therapy in the treatment of malignant tumors;
- genetic predisposition to the progression of lung pathologies;
- entry of a foreign object into the bronchi;
- taking certain groups of synthetic medications;
- smoking;
- living in environmentally unfavorable areas.
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs
Symptoms of pneumosclerosis
Pneumosclerosis has no characteristic clinical signs. More often in the clinic, the symptoms of diseases that caused the development of the disease ( chronic pneumonia , bronchiectasis , tuberculosis , etc.) come to the fore. With focal damage to the lungs, symptoms are mild or may be absent altogether. The main manifestation of diffuse forms of the disease is a violation of the ventilation function of the lungs, which can manifest itself in an obstructive or restrictive type, which is manifested first by shortness of breath during exercise, and later at rest and cyanosis. General symptoms of pulmonary sclerosis are manifested mainly by fatigue, weakness, dry cough, low-grade fever, and weight loss. Auscultation at the height of inspiration reveals crepitus in the posterior lower regions.
When large fibrous nodes form against the background of pleurisy, there may be complaints of chest pain and tingling between the shoulder blades. In chronic bronchitis - cough with sputum. Subsequently, as pneumosclerosis progresses, the phenomena of pulmonary hypertension , hypoxia , respiratory and right ventricular heart failure increase.
Treatment of pneumosclerosis
Treatment of pneumosclerosis should begin with the elimination of the inflammatory process and the primary disease that led to the development of pneumosclerosis.
If the disease is caused by pneumonia or bronchitis, then treatment is medicinal, with the prescription of anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and expectorant drugs. Additionally, therapeutic breathing exercises with stress on the muscles of the lungs and heart are indicated.
Patients are advised to swim more, condition the body, and do breathing exercises.
In severe cases, when the symptoms are fully manifested, surgery may be performed to remove the affected part of the lung.
The main goal of treatment is to relieve the causes and factors that led to the disease, as well as the existing unpleasant symptoms. If there is a severe cough, expectorants and bronchodilators are prescribed. In case of congestion in the lungs, drainage is performed.
Treatment is complex, with the prescription of diuretics, glucocorticoids, cardiac glycosides during the course of the cardiomyopathic form of the disease.
If pulmonary insufficiency is detected, then the following are indicated:
- iontophoresis;
- ultrasound;
- inductothermy by affecting the chest;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- oxygen therapy to saturate the lungs with oxygen.
If suppuration is observed in the lung parenchyma, then it is possible to use a radical surgical method to excise fibrous tissue together with nearby affected areas.
When treating pneumosclerosis, folk remedies cannot be used. They can only aggravate the course of the disease and provoke serious complications.
Patients are recommended to eat boiled onions, aloe, honey, dried fruits on an empty stomach in order to reduce congestion in the lungs, drink red wine, and take tincture of eucalyptus and thyme.
Tests and diagnostics
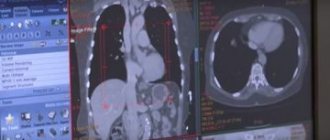
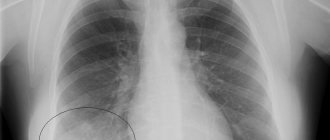
The main diagnostic methods are radiography, fluorography and computed tomography of the lungs.
In pneumosclerosis, the X-ray data of the lungs are variable and reflect changes in the lungs characteristic of the underlying disease, against the background of which, in addition, signs of diffuse pneumosclerosis are determined: fine mesh deformation of the pulmonary pattern, a decrease in the size of the lung, emphysema, less often - changes in the “honeycomb lung” type.
High-resolution computed tomography allows you to more clearly determine the nature, severity, extent and dynamics of changes.
If necessary, a pulmonary function test and transbronchial cryobiopsy are performed.
Pneumosclerosis - diagnosis
The results of diagnostic data will depend on the extent of lung damage. When listening over the area of localization of pneumosclerosis, weakened breathing and wheezing are detected. Externally, a receding chest may be detected. The following methods are used to diagnose pneumosclerosis:
- Radiography.
Pneumosclerosis is detected on x-ray even at the asymptomatic stage. Using the image, you can determine the extent of the lesion and the nature of the disease. - Bronchoscopy.
In this type of diagnosis, pneumosclerosis is defined as chronic bronchitis. Helps to identify the strength of pathological processes. - Peak flowmetry, spirometry.
In the presence of pneumosclerosis, this type of examination will indicate a decrease in the vital capacity of the lungs and a decrease in bronchial patency. - MRI and CT scan of the lungs.
These types of diagnostics help to obtain detailed information about the pathology of the respiratory system and identify difficult-to-detect hilar pneumosclerosis.
Forecast
The prognosis of diffuse pneumosclerosis is determined by the course of the underlying disease and the rate of progression of sclerotic changes in the lung tissues. An unfavorable prognostic sign is the formation of a “honeycomb lung”, pulmonary heart and the addition of a secondary infection. It is impossible to say exactly whether life expectancy changes with pulmonary pneumosclerosis or not, since everything is individual. With the local form of the disease, patients live their usual lives without any restrictions, while significant deterioration in the patient’s quality of life accompanies diffuse pneumosclerosis . It is also difficult to answer how many people live with this. Some patients live to a ripe old age, others live with disabling complications, and some patients die due to bacterial infection , tuberculosis , or pneumomycosis .
Symptoms of the disease
If the lesion is focal, the patient may not feel signs of the disease. They develop only with diffuse changes in lung tissue .
Symptoms of pulmonary pneumosclerosis:
- Cough. Initially, mild coughing is a concern, which intensifies over time. The cough becomes productive, viscous, purulent sputum begins to separate.
- Dyspnea. At the initial stage of the disease, it appears only during physical exertion. However, as it progresses, it is also observed in the resting stage.
- Cyanosis and pallor of the skin. Impaired microcirculation of blood in tissues develops due to impaired gas exchange, due to which the skin on the face becomes pale, the nasolabial triangle has a bluish color.
- The inability to carry out full breathing movements causes swelling of the neck veins.
As the disease progresses, the patient may experience a general deterioration in health, which is associated with impaired ventilation . In severe forms of pulmonary pneumosclerosis, a displacement of the mediastinum is visually observed, the chest partially collapses inward.
List of sources
- Kogan E.A., Korenev B.M., Popova E.N. and others / ed. ON THE. Mukhina. Interstitial lung diseases. Practical guide. - M.: Litterra, 2007. - 432 p.
- Shmelev E.I. Differential diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases // Handbook of a practical physician. - 2005; 5:6: 3-16.
- Aisanov Z.R., Kokosov A.N., Ovcharenko S.I., Khmelkova N.G., Tsoi A.N., Chuchalin A.G., Shmelev E.I. Chronic lung diseases. Federal program. RMJ, 2001; No. 1: p. 9 – 33.
- Ivanova A. S. Fibrosing processes / A. S. Ivanova, E. A. Yuryeva, V. V. Dlin. M.: Overlay, 2008. 196 p.
- Avdeeva O.E., Avdeev S.N. Idiopathic fibrosing alveolitis: modern approaches to diagnosis and therapy // Consilium medicum. 2002; 4 (4): 195-201.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of pathology appear, you should immediately contact a medical institution for an accurate diagnosis and diagnosis. After examination and history collection, the patient is prescribed instrumental and laboratory examination techniques.
Instrumental techniques:
- radiography;
- bronchoscopy;
- spirography;
- CT scan of the lungs;
- MRI;
- ECG;
- echocardiography;
- Dopplerography.
Laboratory techniques:
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood chemistry;
- immunological blood test.
Treatment
Treatment of pneumosclerosis should begin as soon as the diagnosis has been confirmed. In this case, the prognosis will be most favorable. The disease should be treated only in a hospital setting.
The treatment plan is based on the use of the following techniques:
A set of exercises for pneumosclerosis
- oxygen therapy. Gas is supplied using a tube, a mask, and oxygen tents. The technique allows you to restore cellular metabolism;
- drug therapy. It is necessary to treat pneumosclerosis with the help of synthetic medications only as prescribed by a doctor. Self-prescription of drugs is unacceptable! Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, expectorant, bronchodilator and mucolytic agents are prescribed. If the process is very severe and the symptoms are pronounced, then pneumosclerosis is treated with glucocorticosteroids;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- surgical intervention. This method of treating pneumosclerosis is used in case of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, as well as if the patient is diagnosed with a local form of the pathology.
Pneumofibrosis of the lungs - treatment
If you notice any alarming symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help.
Before prescribing therapy, the doctor will recommend the patient to undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
- MRI;
- radiography;
- bronchoscopy;
- CT;
- general laboratory tests;
- spirometry.
Based on the results of the diagnostic study, the doctor can conclude whether the patient has pulmonary fibrosis or not. In addition, when prescribing therapy, the specialist takes into account the degree of development of the disease. He knows how to treat pulmonary fibrosis, so he will select the most effective regimen. More often, an integrated approach is used to combat such pathology.
It includes the following therapy methods:
- drug treatment;
- use of folk remedies;
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- oxygen therapy;
- special diet.
Drug treatment of pneumofibrosis
The treatment regimen directly depends on the cause of the disease and its degree.
Treatment for pneumofibrosis includes the following:
- To improve the drainage function of the bronchi, Fenoterol or Norepinephrine is prescribed.
- In advanced forms of pathology, steroid hormones are used. Prednisolone and Cortisone are most often used.
- NSAIDs will help remove the inflammatory process and relieve pain. In this case, Nimesil, Diclofenac and Ibuprofen will come to the rescue.
- To normalize bronchial patency, ACC or Bromhexine is prescribed.
- In addition, diffuse pulmonary fibrosis requires the use of expectorants. More often prescribed are Salbutamol or Ambroxol.
- To support the heart muscle, glycosides are prescribed. Strophanthin and Panangin are often prescribed.
- To prevent the proliferation of connective tissue, use Cyclophosphamide or Azathioprine.
- For any form of pulmonary fibrosis, angioprotectors are prescribed. These include Bilobil, Actovegin.
How to treat pneumofibrosis with folk remedies?
Alternative medicine “drugs” are prescribed as auxiliary methods of complex therapy. Since pulmonary fibrosis is a dangerous disease, the use of folk remedies should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
When treating, it is important to follow the following rules:
- To prepare infusions and decoctions, use medicinal herbs sold in pharmacies. Such raw materials are collected in ecologically clean areas and dried using technology.
- Strictly observe the dosage.
- During the treatment period, give up bad habits.
- During therapy, be regularly monitored by your doctor.
How to treat pulmonary fibrosis with infusion of rose hips and elecampane?
Ingredients:
- rose hips - 1 tablespoon;
- chopped elecampane rhizome – 1 tablespoon;
- drinking water.
Preparation, use
- Take a mixture of medicinal raw materials (1 part) and pour hot water (3 parts).
- This mixture is simmered over low heat for 13-15 minutes.
- Remove the medicine from the stove and leave for 3 hours.
- Take the drug for 2 months in a row. If the acidity is low, the “medicine” is drunk 15 minutes before meals, and if the acidity is high, half an hour after the meal.
Treatment of pneumofibrosis with birch leaves
Ingredients:
- crushed birch leaves – 30 g;
- water – 250 ml.
Preparation, use
- Pour boiling water over the raw materials. Place the mixture on the fire and cook for 10 minutes.
- Infuse the drug for a couple of hours and filter it.
- Take 70 ml three times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor. More often it lasts about 2 weeks.
Exercises for pulmonary fibrosis
Such gymnastics is an effective method of complex therapy. The main goal of such gymnastics is to relieve excessive stress and reduce fatigue. Such exercises help remove congestion, reduce inflammation that provokes the proliferation of connective tissues, and normalize metabolic processes.
If focal pneumofibrosis or another form of pathology is diagnosed, it is recommended to perform the following gymnastics (6 approaches):
- Inhale with the maximum possible inflation of the abdomen and exhale with its full retraction. In this case, the diaphragm must remain motionless.
- Slowly inhale and exhale with your lungs. The stomach should be motionless during this exercise.
- Inhale with maximum protrusion of the abdomen. Exhalation is performed through the chest.
Risk factors
Factors that can cause the development of pneumosclerosis are:
- Long-term smoking.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Tendency to allergic reactions.
- Regular inhalation of asbestos, coal dust, animal or bird droppings.
- Parasitic diseases.
- Age. Pneumosclerosis of the lungs in older people is caused by an age-related decrease in the elasticity of the lung tissue.
Long-term smoking is a factor that can cause pulmonary pneumosclerosis.
The use of certain drugs for chemotherapy and the treatment of heart disease also increases the risk of this pathology.
What happens if you don't get treatment?
Let's look at how dangerous pulmonary pneumosclerosis is if you don't fight it, and whether it affects life expectancy.
There are two main pathological consequences of the disease - heart or pulmonary failure. This complication is observed in advanced situations, when the damaged lung looks like a porous sponge and does not fulfill its function of absorbing oxygen and saturating the blood with it.
When the disease is controlled and combated, there is no direct effect on life expectancy. But in the opposite situation, after some time the patient will suffer a heart attack or will helplessly suffocate and it will be possible to help him only in emergency resuscitation conditions.
Regime and diet
In severe cases of the disease, fever is prescribed bed rest, when the condition stabilizes - semi-bed rest, and then general rest. In this case, the air temperature in the room must be at least 18-20°C, with mandatory ventilation. Don't forget to spend more time outside.
Nutrition (11 or 15 tables) for a disease such as pneumosclerosis should be comprehensive and include: taking large amounts of vitamins, fruits, and vegetables. This will help increase the body’s defenses, speed up metabolism, and improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The 11th table menu includes foods containing more calcium, B vitamins, potassium salts, folic acid, ascorbic acid and honey. Eat regularly, but in small portions 3 to 5 times a day. It is important to limit yourself in consuming large amounts of table salt so that fluid does not retain in the body.
Traditional methods of treatment
Before treating pulmonary pneumosclerosis with traditional methods, it is better to consult a therapist or pulmonologist.
If approved, the following methods can be used:
- A mixture of aloe and honey. To prepare it, several pieces of the plant are crushed with a knife or blender. Add 2 tablespoons of liquid honey. Mix well, transfer to a glass jar, and store in the refrigerator. Take 1 tbsp. in the morning and in the evening.
- Eucalyptus decoction. Several leaves are poured into 200 ml of water and boiled in a water bath for about half an hour. Then cool and add to the solution for inhalation. Inhaling eucalyptus vapor helps to resolve inflammation and thin mucus.
- Raisins and dried apricots. They are twisted in a meat grinder and poured with a glass of boiling water. Leave for 2-3 hours covered. It is necessary to take 2 tablespoons of the resulting solution every day. It must be shaken before use.
Pneumosclerosis of the lungs is a severe and serious disease. It is obvious that treating this pathology only with folk remedies can lead to adverse consequences. However, combining such treatment options with methods of official medicine can improve the patient’s condition and alleviate the course of the disease.
Forecast and prevention of diffuse pneumosclerosis
The prognosis of the disease is associated with the complexity of its course, that is, the rate of respiratory and heart failure.
Disease manifestations limit the choice of treatment options. How long people live with diffuse pneumosclerosis and what its outcome will be depends on these features. Irreversibility of the process can occur with the formation of a “honeycomb lung” and the presence of recurrent infections. The disease is aggravated by respiratory failure, and cor pulmonale develops.
Tuberculous and mycotic conditions against this background lead to death. The individual resistance of the sick person’s body is of great importance. Timely identification of symptoms and elimination of dangerous causes is of paramount importance.
The disease can last for a long time. Timely consultation with a doctor affects the recovery time. The progression of the disease can be slowed down if active treatment therapy is started. Often the patient becomes disabled.
Low performance, constant deterioration of health and relapses are observed even with constant monitoring by doctors.
It is possible to increase life expectancy in complex cases by 10-15 years.
If the form is advanced or treatment is refused, the countdown begins on months of life.
Timely treatment of any infectious processes in the body serves as an effective obstacle to the development of pneumosclerosis.
Complications in the functioning of the respiratory tract, untimely or poor-quality treatment provoke sclerosis.
Pneumotoxic substances and pneumotoxic drugs affect the lungs without taking precautions. Preventative measures should be observed by those working in mines, glass carvers and grinders.
The negative impact is somewhat weakened by the use of personal protective equipment and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Air pollution and dustiness, living next to industrial enterprises only provokes the appearance of lung problems.
What it is
The concept of pneumosclerosis (literally from the Latin hardening, hardening of the lungs) of the lungs in medicine means a pathological condition characterized by an abnormal degeneration of normal organ tissue into nonspecific connective tissue. Those. in place of the highly functional lung parenchyma, an accumulation of non-functioning tissue is formed, which interferes with gas exchange. Foci of pneumosclerosis most often form at the end of an inflammatory or degenerative process in the lung tissue.
The formation of connective tissue foci in the organ leads to disruption of the configuration of the bronchi, sharp compaction and wrinkling of lung tissue. The organ loses its ability to exchange gases and shrinks. With pneumosclerosis, persistent progression of the pathological process is observed, due to the fact that the tissues are constantly subject to abnormal changes.
Untreated disease leads to severe disability and death.
Attention! According to medical statistics, the disease most often affects men over the age of 50, which is directly related to lifestyle and the presence of bad habits. Smoking is one of the leading causes of pathology.
Useful: Anti-allergy injections
Severity of the disease
There are several types of this disease, depending on the severity of the course:
- Emphysema and pneumosclerosis. With emphysema, there is a noticeable increase in the amount of air in the lung tissues. And pneumosclerosis occurs as a result of inflammation of the respiratory tract. Diseases develop as a result of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
- Moderate. As a result of this form, the altered lung tissue alternates with healthy one. The patient's condition is unchanged.
- Radical. It can appear against the background of dystrophy or inflammation, and causes a disturbance in the exchange of gases in the affected tissue.
- Focal. May appear as a result of destruction of the pulmonary parenchyma or abscess.
- Local. It may not manifest itself for a long time; it can only be detected with the help of an x-ray. Causes compaction in the lungs.
- Age. The reason will be changes in the body due to its aging. More often it may appear due to pulmonary hypertension.
- Apical. Leads to damage to the upper part of the lungs when healthy tissue is replaced by connective tissue. The initial stage resembles bronchitis.
- Basal. Connective tissue replaces pulmonary tissue. This disease can occur due to inflammation of the lung.
- Reticulate. With this form, you can notice changes in the structure of the lungs, they will be reticulated and lose clarity and purity. Tissue compaction increases.
- Interstitial. You can observe how connective tissue grows and appears on the septa, around the bronchi and blood vessels.
- Postpneumonic. Appears as a result of complications of pneumonia. The lung decreases in size and the affected area appears denser.
- Post-tuberculosis. The affected tissues grow due to pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Peribronchial. Around the inflamed bronchi, significant tissue changes can be noticed (normal tissue is replaced by connective tissue).
Basic research methods
- Bronchoscopy - you can observe the development of bronchiectasis and symptoms of long-term bronchitis.
- Functional pulmonary tests - in case of illness, a noticeable deviation from the norm that is not subject to therapeutic correction.
- Spirometry and peak flowmetry show the maximum volume (capacity) of a person's lungs. In this case, a decrease in VC will be visible.
- Bronchography - there is a convergence or deviation of the bronchi, their compression and change, small bronchi are not identified.
- MRI (computed tomography of the lungs).
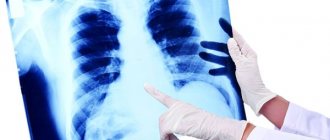
- X-ray. Shows sclerotic changes in the organ and other parallel diseases: emphysema, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis. The image shows a decrease in the volume of the affected lobe of the lung and its deformation. How the procedure is performed: the subject stands between the X-ray tube and the cassette, while his chest is closely located with the cassette. The distance between a person and the device is 60-100 cm. In radiography, two types of projection are used - direct (when the patient is turned either with his face or his back to the film) and lateral. The duration of the procedure is 1-5 minutes, and the result can be found out the next day. Because the film must still be processed in a special darkroom.
- Electrocardiography (ECG) is a well-known method for assessing heart function. It can help the doctor make a diagnosis - stenosis of the aorta or mitral valve, and these are the main causes of the development of pneumosclerosis. The ECG clearly shows all abnormalities in the heart.
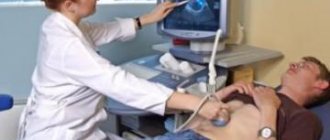
- Echocardiography. Prescribed for obtaining images of the heart using ultrasound. This is necessary to promptly detect right ventricular hypertrophy and the development of cor pulmonale.
- Dopplerography. Measures pulmonary artery pressure, which may be elevated in patients with this disease.
The following pathologies of the respiratory system can be seen on the x-ray.
Various zones of darkening in the lungs. They come in different intensities and sizes. If there is slight darkening, this indicates the likelihood of initial fibrosis, and if total areas of darkening appear, this is a clear signal of the formation of sclerosis. Other options: subtotal - when it is present in only one lobe of the lung and limited - in a specific segment.
Changes in the pulmonary picture. These are the so-called blood vessels that arose against the background of the pulmonary alveoli, bronchi and connective tissue layers. During the inflammatory process, these formations appear due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue along the vessels, bronchi and other structures.
There is a decrease in the size of the organ. If only one part of the lung is affected, it will become smaller in volume than the other. This is due to the fact that less air enters the affected area, while the elasticity of the organ is limited.
Mediastinal shift. The image shows an uneven darkening, which is located in the very center of the X-ray image behind the sternum. When one part of the lung decreases in size due to disease, the mediastinal shadow will correspondingly shift towards the affected side.
Preventive measures
Prevention of this disease includes:
- Timely treatment of colds and infectious diseases.
- Use only medications prescribed by a doctor, avoid self-medication.
- Stop smoking.
- Exercise caution when in contact with pneumotoxic substances: wear a respirator, ensure adequate ventilation.
- Maintaining an active lifestyle.
Measures to prevent pulmonary pneumosclerosis include an active lifestyle.
Pneumosclerosis is an incurable disease; it is impossible to completely get rid of it. To date, there are no drugs that would promote the complete restoration of normal lung tissue and the resorption of scars.
Only compliance with preventive measures and fulfillment of all doctor’s prescriptions will allow you to achieve long-term, sustainable remission and increase life expectancy.
How to treat
There are no sufficiently effective methods for absolute recovery from the disease.
Treatment of diffuse pulmonary pneumosclerosis is carried out in stages. The primary task of doctors is to eliminate the main cause, that is, the underlying disease. https://feedmed.ru/bolezni/organov-dyhaniya/diffuznyj-pnevmoskleroz.html
It is important to prevent the patient from being in a harmful environment filled with toxic substances. A change of profession is required if there are mechanical factors in the development of pneumosclerosis.
Constant alcohol abuse and smoking significantly worsen the patient’s well-being.
Physical activity should be proportional to the degree of respiratory and heart failure.
Restrictions are necessary even with slight shortness of breath. Treatment in an inpatient facility relies on synthetic drugs.
Drug groups:
- Expectorants and mucus thinners,
- Bronchospasmodics to eliminate shortness of breath,
- Cardiac glycosides to eliminate circulatory disorders,
- Glucocorticoids.
Periodically recurring bronchitis and pneumonia are treated in a hospital setting with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Physiotherapy exercises and breathing exercises have no contraindications. You can harden yourself with caution. Don't forget about walks in the fresh air. Health improvement in sanatorium-resort-type institutions allows you to ease your well-being after a long treatment with the help of physiotherapy, chest massage, and oxygen therapy.
Surgical intervention is required when a purulent process develops. Limited pneumosclerosis, cirrhosis and fibrosis of the lungs are also indications for surgery.
Causes of pathology
The main reasons causing the development of pneumosclerosis include:
- Inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, pneumonitis).
- Pathologies caused by specific bacteria or fungi (tuberculosis, aspergillosis).
- Occupational lung diseases (silicosis, pneumoconiosis).
- Allergic or autoimmune lesions (bronchial asthma, Goodpasture syndrome).
- Idiopathic fibrosing alveolitis.
- Lung tissue injury, radiation exposure, or use of pneumotoxic drugs.
- Heart failure due to stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
Regardless of the etiological factor, pneumosclerosis disrupts the ventilation capacity of the lungs, their blood circulation and the drainage function of the bronchi.
Symptoms of the disease
Since pulmonary pneumosclerosis is not an independent disease, but a consequence of many other inflammations, it is difficult to name the exact symptoms of the disease. But still, some of them are more common than others:
- slight shortness of breath, which after a while becomes constant, even at rest;
- unbearable difficult cough with the appearance of a small amount of mucopurulent sputum;
- unrelated fatigue, weakness, regular migraines;
- pain in the chest area;
- change in skin color - cyanosis;
- weight loss;
- changes in the structure of the chest;
- severe pulmonary insufficiency;
- deformation of the upper limbs in the form of drumsticks;
- listening to wheezing during auscultation - from dry to fine bubbles.