Frequent ailments from the digestive tract, such as heartburn, belching, heaviness in the stomach after eating or nausea, may indicate the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the body. The activity of the pathogenic agent in the stomach and duodenum causes serious diseases that require long-term and expensive treatment.
In order to avoid undesirable consequences, it is necessary to promptly identify and neutralize a dangerous enemy. In medical institutions, you can do a stool test for Helicobacter pylori and thus verify the presence or absence of infection.
What is Helicobacter
The body of the gram-negative bacterium has the shape of a spiral with four or six flagella, which help it move in a thick medium - a mucous gel that covers the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. It parasitizes the stomach and duodenum, which are anatomically connected. Most of the colonies of Helicobacter pylori are located in the area of the pylorus, connecting these two organs. Based on these characteristics, the microorganism was called a spiral-shaped bacterium (helicobacte) that lives in the pylorus (pylori).
Microbes cannot live and multiply in the acidic environment of the stomach, since their bodies are not protected from the action of hydrochloric acid. Helicobacter pylori is an exception to the rule. The bacterium requires an acidic environment to function, so it does not live in the intestines, like most types of gram-negative pathogens. Moreover, the intestinal tract has little oxygen and a lot of destructive pancreatic enzymes and bile, which adversely affects the viability of the microorganism.
The bacterium secretes a special enzyme - urease. The presence of this enzyme in the stomach, and accordingly Helicobacter, can be quickly detected using a urease test. It is performed at the time of gastroscopy and allows you to obtain reliable results within a few minutes. Feces for Helicobacter pylori have been studied for a longer time, but such an analysis has its advantages.
The insidiousness of the pathogen lies in the fact that it quietly destroys organs from the inside. Once the body is infected, there are no symptoms indicating infection. All negative phenomena arise only when diseases develop in the stomach or duodenum - gastritis, duodenitis, ulcers.
Another unpleasant feature of the microorganism is its ability to transform into a coccal (spherical) form, reminiscent of spores. This occurs if the pathogen enters an unfavorable environment, for example, during antibiotic therapy. In this state, the bacteria becomes less vulnerable and is able to hide in the body for a long time.
Who is it recommended for?
Helicobacter Pylori is considered one of the most common infections in humans. Most often it is diagnosed in patients over forty years of age. People can be carriers of the bacteria and not even know it because they have no symptoms. Carriage does not always pose a serious threat to health, however, for any gastroenterological disease, stool or blood tests are done to detect Helicobacter pylori.
You should undergo a medical examination if you have the following symptoms:
- frequent heartburn, belching;
- regular bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation);
- nausea, feeling of heaviness after eating;
- aversion to protein foods (meat, poultry);
- increased gas formation;
- pain in the projection of the stomach;
- sustainable weight loss;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing).
Since the pathogen is transmitted through mucus or saliva, the infection quickly spreads within the family through the use of shared utensils and personal hygiene items. If one family member is diagnosed with Helicobacter, then other close relatives are also recommended to undergo appropriate testing.
How to prepare for the test
Before you donate stool for Helicobacter pylori, you need to familiarize yourself with the rules for preparing for analysis and collecting material. These may be verbal instructions from a doctor, or printed instructions, which are usually issued by private clinics.
General recommendations are as follows:
- one month before the study, you should avoid taking antibiotics, and three days before the study - laxatives;
- for three days before the analysis, you should not eat coarse fiber and coloring foods;
- you need to collect stool in a special container (you can take it at the clinic or buy it at the pharmacy);
- material should be taken from three points where there is no blood, mucus, pus or urine;
- it is necessary to deliver stool to the laboratory within two hours after defecation;
- A repeat test for the effectiveness of treatment should be taken a month after taking antibacterial drugs.
Stool analysis for Helicobacter pylori: review of methods and evaluation of results
There are a variety of ways to identify a pathogen. They differ in the material studied, laboratory research method, accuracy, and information content. The price factor is also important, because not every person can pay the required amount for the analysis. Some techniques are used only in expensive clinics, but this does not mean that patients with low incomes will not be able to receive the necessary medical care in this matter.
The least expensive, and at the same time quite informative, is a stool test for Helicobacter pylori. The patient does not need to personally come to the laboratory; it is only necessary to deliver the material for research there in a timely manner. This point is especially important for parents of young children, as children often feel anxious when visiting unfamiliar institutions.
Another advantage of this analysis is the simplicity and painlessness of the material collection procedure. After defecation, you just need to put the feces in a clean container and take it to the clinic. In other studies, the patient may have a vein pierced or a duodenal tube inserted into the digestive tract.
There are three methods for analyzing stool for Helicobacter pylori:
- bacteriological culture;
- immunological research;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Bacteriological culture method
The classic way to identify pathogenic microorganisms is by culturing on a nutrient medium. Analysis of stool for Helicobacter Pylori using this method is considered the most difficult for a number of reasons:
- when sowing, it is necessary to exclude access of oxygen to the nutrient medium;
- active spiral-shaped bacteria are rarely present in feces, and coccal forms are not recognized;
- antibiotic sensitivity testing may be inaccurate;
- the analysis is done for at least a week.
What methods of detecting Helicobacter Pylori exist?
Suspecting the presence of a pathogen, the doctor prescribes tests to detect Helicobacter. Doctors have the following methods to confirm the presence of a pathogen:
- Respiratory analysis. Its advantages are the speed of obtaining results, simplicity, low cost, lack of lengthy preparation, feasibility in any conditions, painlessness and non-invasiveness. The disadvantage of the method is that it is not highly efficient. This is due to the fact that during a breath test it is not the pathogen itself that is detected, but the conversion of urea into ammonia. Since such cleavages are produced by Helicobacter pylori, when the amount of NH3 increases above the threshold values, the result is regarded as positive.
- Blood test for antibodies to Helicobacter Pylori. This method is indirect, that is, it does not detect the pathogen itself. It is aimed at identifying substances in the blood that the body produces in response to their introduction. The protective antibodies produced - immunoglobulins - can be detected in the laboratory. They indicate that after the bacteria enters the body, the immune system has developed antibodies to it in sufficient quantities. The method is also not highly sensitive, since it depends not only on the presence of the pathogen and the sensitivity of the reagents, but also on the properties of the organism itself. For example, in immunodeficiency states it will be negative.
- Stool analysis. With its help, DNA sections of the pathogen are detected. Stool testing using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is convenient for patients. It does not require personal presence in the hospital, is not traumatic, and identifies the pathogen itself. The disadvantages of the method include the fact that PCR detects both viable and killed bacteria.
- Biopsy examination. When performing an endoscopy, a small section of the mucous membrane is taken. The resulting material can be studied using cytological, cultural methods and tested for urease. Triple control, in which each method complements each other, gives maximum results. The disadvantages of endoscopic examination are the high cost, complexity, duration of manipulations, and their unpleasantness for patients.
Tests for Helicobacter pylori: types, norm and interpretation
Helicobacter pylori is a pathogenic spiral-shaped bacterium that is resistant to gastric juice. Once in the body, it settles in the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, leading to its inflammation, the development of erosions, gastritis, and peptic ulcers.
Timely detection of Helicobacter pylori infection is the key to successful treatment of these and other pathologies, including cancer.
In what cases is an analysis for H. pylori necessary?
An analysis is needed when a person complains of discomfort and pain in the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms that require testing for this bacterium include:
- regular heartburn;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- painful sensations, in particular those that disappear after eating;
- the body's rejection of meat food, up to nausea and vomiting.
A laboratory examination is carried out if there is a suspicion of peptic ulcer disease, inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, gastritis, or malignant tumors.
It includes four methods:
- ELISA – enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori;
- UBT (urea breath tests) – urease breath test;
- PCR – stool test;
- mucosal biopsy with cytology.
What do the tests show?
blood test for Hilobacter pylori
Shows the presence and concentration of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori in the blood. Their appearance is a signal that the immune system has detected the pathogen and has begun to fight it.
Each type of pathogenic microorganism produces its own immunoglobulins. Antibodies to H. pylori appear in the blood from a week to a month after infection and come in three types: IgA, IgG and IgM. They indicate the presence and stage of development of the infection.
This method is the most reliable; with its help, the DNA of the pathogen is detected in the patient’s stool.
PCR finds even a negligible amount of bacteria, which helps predict the disease and reveals a tendency to develop gastritis, stomach cancer, intestinal cancer and other pathologies associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
To protect against gastric acid, H. pylori bacteria secrete an enzyme called urease. It has the property of splitting urea into two substances - ammonia and carbon dioxide CO2, which is released during respiration and is detected by the urease test.
A breath test for Helicobacter pylori is carried out using a urea solution labeled with carbon isotopes. For children and pregnant women, a less accurate but safe helic test with urea is used.
This type of study shows the presence of Helicobacter pylori in gastric mucus. The test is considered positive when at least one bacterium is detected, and depending on the amount of H. pylori, the degree of contamination is determined:
How to get tested for Helicobacter pylori?
To test for antibodies to H. pylori, blood taken from a vein is used. In a test tube, it is folded using a special gel, which separates the plasma from the formed elements (platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes).
If the H. pylori bacterium is present in the body, the required immunoglobulins are found in the plasma. A blood test for Helicobacter pylori is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach. The day before, you should not eat fatty foods.
Stool analysis requires preparation - for 3 days before it is taken, you should not eat food with a large amount of fiber (vegetables, fruits, grains), with dyes and salt.
During this period, it is also prohibited to give an enema, take antibiotics, drugs to enhance peristalsis, and use rectal suppositories.
A breath test for Helicobacter pylori is performed as follows:
- The patient breathes twice into a tube placed deep in the mouth.
- Next, he drinks a test solution of urea labeled with carbon isotopes.
- After 15 minutes, he delivers another 4 portions of exhaled air.
- If the second test shows the appearance of a carbon isotope in the samples, then the result is considered positive.
It is important that no saliva gets into the tube, otherwise the procedure will have to be repeated. 3 days before the urease test, it is forbidden to drink alcohol and foods that provoke gas formation in the intestines (legumes, cabbage, rye bread, apples, etc.).
From 10 pm until the test itself, you should not eat; on the day of the test, you should avoid factors that increase salivation (chewing gum, smoking). You should not drink anything an hour before the test.
Cytological analysis examines smears of gastric mucus taken during fibrogastroduodenoscopy (this is a method of examining the gastrointestinal tract using a probe).
Interpretation of test results for Hilobacter pylori
Deciphering the blood test
When testing blood for Helicobacter pylori, the results depend on the presence or absence of immunoglobulins to the bacterium, as shown in the table below.
Three types of H. pylori antibodies (A, G and M) appear at different stages of infection and help determine how much time has passed since infection.
What to do if the test is positive?
Visit a gastroenterologist as soon as possible to find out whether the bacteria need to be eradicated (removed from the body). This is an ambiguous process, there are contraindications, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
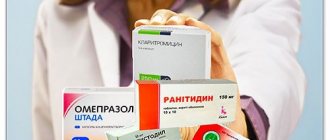
After assessing the level of health, the doctor selects one of the regimens approved by the international community. Depending on the characteristics of the pathological process, drug combinations of drugs from the following groups are used:
- proton pump inhibitors - Omeprazole, Rabeprazole and others;
- Clarithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic;
- amoxicillin – semi-synthetic penicillin;
- Metronidazole is an antiprotozoal drug with antibacterial activity;
- bismuth preparations are anti-ulcer drugs that have a protective effect on the gastric mucosa;
- tetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
We recommend reading:
How to take a stool test for intestinal microflora?
Helicobacter tests may be repeated during treatment to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
After the bacteria are detected and removed, ulcers and other mucosal lesions heal completely, and all secondary disorders stop - microflora, synthesis of vitamins and hormones, digestion are restored, and the risk of developing stomach cancer is reduced.
In continuation of the topic, be sure to read:
- Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori: antibodies, breath test and biopsy
- Helic test for the detection of Helicobacter pylori: preparation, implementation and interpretation
- Blood test for Helicobacter: normal and pathological indicators, interpretation
- Breath test for Helicobacter pylori: types of tests, reliability, preparation and conduct
- pH-metry of the stomach: preparation, implementation and interpretation of diagnostic results
- Duodenal erosion: symptoms, treatment and prognosis for life
- Antisecretory agents: list and types of drugs, application features
- Gastroduodenitis: how is the pathology manifested and treated?
- Erosive gastroduodenitis: symptoms and methods of treating pathology
- H2-histamine blocking drugs and their use in gastroenterology
How to get tested for Helicobacter pylori? Interpretation of results and norm
Analysis for Helicobacter pylori is the only reliable way to detect the pathogen. Up to 90% of those infected with this spiral-shaped bacterium do not show any complaints. Carriage is asymptomatic. The prevalence of damage by this pathogen reaches 70–75% among people over 40–45 years of age. When a disease appears (gastritis, peptic ulcer, etc.), the presence of the pathogen will be detected only using laboratory diagnostic methods. There are no other clinical methods of diagnosis.
How to properly collect stool for analysis for helminth eggs
https://youtu.be/PinqkgyG7wU
In fact, there should be no specific preparations before taking a stool test for helminth eggs.
Rules for preparing for analysis:
- urinate before collecting material to prevent urine from getting into the stool;
- it is necessary to take a clean, dry container where defecation will be carried out;
- from the resulting material you need to take 8-10 cm3 (~2 teaspoons). Feces are collected using a special “spoon” that is built into the lid of a special container that you should be given to collect feces;
- feces for analysis are collected from different parts of the feces (top, sides, inside);
- the material (feces) is placed in the container given to you and closed tightly;
- you must sign the container (your first and last name, date of collection of the analysis).
To obtain the most accurate data, it is strongly recommended to submit stool for analysis for helminth eggs within 30-45 minutes after defecation. You can store feces for 5-8 hours in the refrigerator, in a tightly closed container at a temperature of +4ºС-+8ºС. However, storage may adversely affect test results.
For analysis, it is necessary to collect 8-10 cm3 (~ 2 teaspoons) of feces. It is recommended to take the resulting material to the laboratory as soon as possible, this will allow the analysis to be carried out with the highest quality and will allow you to obtain the most reliable results.
However, if you do not have the opportunity to take the material to the laboratory in the near future, you can store the material in the refrigerator at a temperature of +4ºС / +8ºС for 8 hours. The longer the material remains in the refrigerator, the less accurate the results will be.
Helicobacter pylori (helicobacteriosis), antigen, feces
Preparing for the study:
It is not recommended to take proton pump inhibitors, bismuth preparations, antacids and antibacterial drugs 14 days before the test.
Material tested:
Feces
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium that attacks the wall of the stomach and duodenum, causing atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcers and malignancies. About 50-60% of the population is infected with Helicobacter pylori, infection usually occurs in childhood.
Due to its form, Helicobacter pylori is capable of damaging the protective layer of the gastric mucosa. The bacterium produces the enzyme urease, which is capable of neutralizing hydrochloric acid in the stomach. Thus, the stomach wall becomes susceptible to the damaging effects of hydrochloric acid and pepsin, which leads to gastric or duodenal ulcers.
Helicobacter pylori can act directly on stomach cells, weakening the protective mechanism and causing inflammation of the mucosa. Helicobacter pylori is capable of increasing the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, although the mechanism of this process has not been studied. The route of transmission of infection is oral-fecal and household. Infection usually occurs from person to person through close contact (kissing). The source of infection can be saliva or water.
Often the infection can be latent without causing any symptoms.
Duodenal ulcer is associated with Helicobacter pylori in almost 100% of cases. Antibacterial therapy, which is aimed at destroying bacteria, leads to a complete cure for peptic ulcer disease.
Helicobacter pylori is found in 90% of people suffering from gastric ulcers. Antibacterial treatment leads to scarring of the ulcer in 70-90% of cases. Severe gastric disease - adenocarcinoma - in 70-90% of cases is caused by infection with Helicobacter pylori.
In what situations is it prescribed?
It is required to submit stool for analysis in case of various pathological disorders in the digestive system. The bacteria Helicobacter pylori is determined by several methods, each of which is used for different disorders. A PCR stool antigen test should be taken in the following cases:
- stomach ulcer;
- the formation of erosions in the duodenum and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- atrophic process in the mucous membrane;
- polyps and neoplasms;
- gastroesophageal reflux, characterized by the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus;
- genetic predisposition to various pathologies of the abdominal organs.
PCR testing of stool is the most accurate method for monitoring the state of gastric microflora during treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Pathogenic microflora provokes stool disorders.
You can also take an immunological test, carried out in the following cases:
- broken stools, heartburn, discomfort and other pathological manifestations of digestive tract dysfunction;
- before taking a course of antibiotics;
- iron deficiency anemia or thrombocytopenia of unknown origin;
- genetic factor;
- the presence of infection in the immediate environment.
How to take the test correctly?
The result depends on the correct preparation and collection of material. No human presence is required; it is enough to deliver the correctly collected material on time.
Preparing for the test
When preparing, you must strictly follow the following rules:
- donate stool for analysis no earlier than 1 month after the last dose of antibiotics;
- during the 3 days preceding the collection of material, you should not consume coloring products (tea, coffee, red and orange fruits and vegetables, turmeric, curry, soy sauce),
- exclude coarse fiber - cabbage, radish, radish, pearl barley, bran, beets;
- You should not take medications that enhance intestinal motor function - Lactulose, Motilium and the like;
- give up alcohol;
- do not take antacids (Almagel and the like);
- collect material during the first week after the onset of symptoms of the disease (then the concentration of Helicobacter in feces decreases).
3 days are enough for preparation. At this time, it is advisable to stop taking all medications (if this is not possible, tell your doctor the names and dosage). You need to reduce your consumption of fish and meat, steam or boil them. The best food for this time is porridge and fermented milk products, vegetable and fruit purees, weak soups, neutral natural juices (apple, white grape), compotes, fruit drinks, weak tea, rosehip decoction.
Preparing containers
Some laboratories provide containers for analysis, including their cost in the total price. This is the best variant. A container for feces can be purchased at a pharmacy, it costs a few rubles. The container is sold sterile and must not be opened, wiped or washed. A plastic spoon is attached to the lid, which is used to scoop up the material.
As a last resort, you can use a glass jar with a well-fitting lid (baby food). The jar needs to be washed well and then boiled along with a lid and a spoon or other object that will be used to collect feces. If bacteria remains on the dishes, the analysis will be incorrect.
Collection of material
You cannot collect material from the toilet or diaper. The toilet should be covered with a clean plastic bag, and instead of a diaper (for a child or a bedridden patient), an oilcloth should be laid. It is allowed to take material from a clean pot.
The container is filled no more than one third, close the lid tightly. Attach the directions to the container or write on the label (legibly) the patient's first and last name, year of birth.
How and for how long can the material be stored?
The container with the material is delivered to the laboratory as early as possible, optimally on the day of collection. If there is no possibility of urgent delivery, storage in the refrigerator for no more than 2 days at a temperature not exceeding +4 ° C is allowed. If longer storage is necessary, the material is frozen once at a temperature of -20 ° C.
What is a coptogram
https://youtu.be/-3YcioW_-kk
A coprogram (sometimes called a general stool analysis) is one of the laboratory methods for studying stool, widely used in medicine to assess the function and diagnose diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
This analysis is very informative; it helps to assess the motor and enzymatic function of the intestine, the state of the microflora, suspect an inflammatory process and cancer, and detect helminths.
The main advantages of this analysis are its high information content, ease of execution, and most importantly, accessibility. Due to the immaturity of the digestive system, coprogram in children has its own characteristics, therefore the patient’s age must be indicated on the container with the research material.
Using the coprogram you can evaluate:
- the presence of bile pigments in the stool. Normally, stercobilin should be present;
- how well the digestive glands work is determined by the number of crosses opposite muscle fibers, starch, neutral fat, fatty acids, and digestible fiber. The more pluses next to each of these names, the worse the food is digested;
- whether or not there is inflammation in the intestines. Indicators that there is inflammation are the presence of pathological impurities in the stool: mucus, blood, pus - they are indicated with pluses if they are present. Normally, they are not present in the stool. The presence of a large number of leukocytes in the stool analysis (normally they are single); the presence of red blood cells in the stool analysis. Normally, they are absent. Intestinal epithelium should not be normal.
- Whether there are parasites and their eggs in the intestines or not, normally there should be no one or the other in the feces.
Medicines can affect the coprogram: enzyme preparations and antibiotics. The doctor who orders the test and then evaluates the result must know that you are taking these medications.
It is not always necessary to discontinue the medication to get tested; sometimes it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment based on the results of a stool test.
You should not stop taking medications on your own before taking this test; you should consult your doctor about this. The analysis is usually ready the next day.
Methods for analyzing and deciphering indicators
Biological material can be studied in different ways.
| Method | Dates | Decoding the results |
| PCR | 1 working day |
|
| Bakposev | from 6 to 12 days |
|
| ELISA | Material – venous blood, during the working day, urgently within 2 hours |
|
Preparing for the test
It is very important that the patient properly prepares for the diagnostic examination, since preliminary preparation can significantly reduce the risk of diagnostically incorrect data, which can complicate the further treatment process. Before taking the test, you will need to exclude all spicy, fatty and overly spicy foods from your diet. You should also stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking tobacco products. The consumption of the above foods and alcohol should be excluded from the diet 2-3 days before the test, and smoking should not be done until just an hour before the procedure. All this will increase the accuracy of the results of a serological blood test.
Other ways to identify Helicobacter
During the examination, several methods are usually used to finally verify the presence or absence of Helicobacter:
- Breath test. You exhale into the prepared bag, then give medical radioactive carbon to drink, after 10 or 30 minutes you need to exhale into another bag. Detects the presence of Helicobacter in very small quantities.
- Rapid urease test of gastric biopsy. It is based on the fact that the bacterium secretes urease, which breaks down urea into ammonia and CO 2. During an endoscopic examination, 4 biopsies are taken from different parts of the stomach and placed in the cells of the CLO test. The more Helicobacter, the faster the color of the cell changes.
- Helicobacter antigen in feces. Particles of the bacterial wall react with the monoclonal antibody, which changes the color of the indicator. Test cassettes are available for home use. According to the instructions, feces are mixed with a solvent (a test tube with it is included), a few drops are applied to the cassette window. Two stripes are positive, one is negative. Additionally, you can find out from the marking whether the test is valid.
- Histological examination of the biopsy specimen. The biopsy obtained during FGDS (5 samples) is stained using various methods, the sensitivity of the analysis reaches 99%.
- Western blot. It is carried out in those who have antibodies to Helicobacter using the ELISA method (described above). The number of antibodies of each class (A, G, M) is determined.
The range of diagnostic tests depends on the equipment of the medical institution. Histological examination is considered the “gold standard”. However, a positive result from at least two different tests is considered sufficient to confirm the presence of the bacterium.
How to properly collect stool for rotavirus
Popularly known as “stomach flu,” rotavirus infection is a very common, extremely contagious and quite dangerous disease. At risk are all those who have a weakened immune system - children, pregnant women, the elderly.
Even if you are not one of them, do not think that the virus is not dangerous for you. The fact is that such universal disinfectants as bleach, for example, pose no threat to it at all.
Therefore, it is transmitted by airborne droplets, water, and poorly washed fruits and vegetables. Therefore, timely detection of infection by taking a stool test for rotavirus and treatment is the key not only to your health, but also to the well-being of others.
Remember that the disease manifests itself almost instantly after the infection enters the body - after 12 hours. And it manifests itself very violently: loose and frequent stools, vomiting, elevated body temperature. To exclude other diseases and prescribe the correct treatment, you need to take a stool test for rotavirus as early as possible.
Since the analysis is often prescribed when all the signs of a disease or, at least, illness are present, no special preparation is required. The rules are simple: the biomaterial must be collected in a sterile container, a few grams will be enough, after which it must be delivered to the laboratory within 3 hours.
Normally, rotavirus should not be detected. Otherwise, the doctor will immediately prescribe you treatment in order to start the healing process as quickly as possible, fight infection and prevent dehydration, which poses the greatest danger, due to fever and frequent bowel movements or vomiting.
If you or your healthcare provider suspects that you or your child may have rotavirus infection, try to have a stool test tested for rotavirus as soon as possible. This can be done by bringing the material to any convenient department of the Health clinic. The result and its transcript will be ready the next day.
What is Helicobacter pylori?
Helicobacter pylori is a type of bacterial infection that lives in the pyloric area, between the stomach and duodenum. This bacterial species is equipped with rope-like processes, with the help of which the bacterial form moves through thick mucus. The bacterium is well adapted to acidic environments. Such an organism is powered by hydrogen molecules produced by intestinal bacteria.
Helicobacter produces enzymes: oxidase, urease, catalase.
Helicobacter pylori is considered one of the most dangerous types of infection, since when infected there are no symptoms for a long time, and in a situation that threatens its existence, it can become covered with a spherical protective shell.
With the help of thin tentacles, Helicobacter clings to the walls of the stomach. Being in a calm state, it initially does not make itself felt. If a person infected with a bacterium has a weakened immune system, then this bacterium penetrates deep into the duodenum, after which it begins to multiply and generates the onset of inflammatory processes and a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
Helicobacter infection occurs through poorly washed dishes, kissing, and poor hygiene. You should monitor personal hygiene, household cleanliness and limit personal contact with Helicobacter carriers.
It is impossible to detect an adult in feces, since it does not live in the intestinal environment. The intestines do not have the necessary acidity or sufficient oxygen. The bacterium will not survive under the strong influence of bile and pancreatic enzymes. In this regard, only the coccal form of the bacterium can be found in feces.
Many carriers of the bacteria do not notice symptoms such as malaise and gastrointestinal discomfort, because Helicobacter is dormant. Poor nutrition, prolonged stress, and failure to comply with hygiene rules reduce immunity and trigger bacterial activity.
The appearance of ailments and malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract is a reason to consult a doctor. The appearance of gastritis, heartburn and stomach pain is the main indication for checking for the presence of Helicobacter in the body. Despite the fact that these pathologies can be observed regardless of the presence of bacteria, a complex of such disorders is a reason to consult a doctor.
It is not recommended to ignore the appearance of gastrointestinal disorders and diseases such as heartburn, gastritis and stomach ulcers. The lack of treatment for such pathologies provokes further degenerative processes, including cancer.