| Prescription drug | |
| Release form | Solution for injection, 2000 anti-Xa IU/0.2 ml; 4000 anti-Xa IU/0.4 ml; 6000 anti-Xa IU/0.6 ml; 8000 anti-HaME/0.8 ml; 10,000 anti-Xa IU/1 ml. |
| Manufacturer | Sanofi Winthrop Industrie (France) |
| Active substance | Enoxaparin sodium |
To learn more
Consultations are conducted by professional doctors who have significant experience in solving infertility problems.
Clexane is a low molecular weight heparin. It is used to prevent and also to treat thrombosis and thromboembolism. Prescribed before and after surgery to avoid the formation of blood clots. Prescribed for myocardial infarction, deep venous thrombosis, thromboembolic damage to the branches of the pulmonary artery.
Release form and composition
The drug Clexan is available in the form of a solution for injection of a transparent pale yellow color in glass syringes of 0.2; 0.4; 0.6; 0.8 and 1 ml depending on the content of the main active ingredient in the solution.
The box includes a syringe pre-filled with medicine, which is completely ready for use. Preliminary release of the air bubble is not required, which allows you to avoid wasting the medicine. The contents of the syringe are sterile.
The main active ingredient of the drug is enoxaparin sodium, 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 mg per syringe.
Which is better for IVF: Clexane or Fraxiparine?
The active ingredient in Clexane is enoxaparin sodium. This is a modern low molecular weight heparin that affects blood clotting factors. But its effect does not extend to the ability of platelets to stop bleeding.
An analogue of the drug is Fraxiparine, but it differs in composition and some pharmacodynamic features. The active ingredient is calcium nadroparin. It also reduces blood clotting, but with prolonged use it affects the APTT (activated partial thromboplastin time). This means that if bleeding occurs, the blood will clot worse, which is dangerous for a pregnant woman.
But if the question arises of how to replace Clexane 0.4 during IVF, doctors prefer Fraxiparine, as it is safer among other anticoagulants.
pharmachologic effect
Clexane exhibits antithrombotic properties and is used for subcutaneous injections in the treatment of acute coronary syndrome, deep vein thrombosis, as well as their prevention.
Enoxaparin sodium, the active ingredient of Clexane, is obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of heparin (in the form of benzyl ether), produced from the mucous membrane of the small intestine of pigs. Enoxaparin sodium belongs to the group of low molecular weight heparins, exhibiting high anti-Xa activity; this substance has a slight negative effect on thrombin.
Side effects
Adverse reactions during the treatment of Clexane are observed from various body systems:
- On the part of the circulatory and lymphatic system . Bleeding most often occurs, including large ones, when the patient needs a blood transfusion. In severe cases, retroperitoneal bleeding or intracranial hemorrhage is observed. All this is fraught with death. In addition, it is possible to develop thrombocytosis, and less often - thrombocytopenia and immunoallergic thrombocytopenia with thrombosis, which is sometimes complicated by the development of organ infarction or ischemia of the limbs.
- From the immune system . Allergic reactions are observed.
- From the liver and biliary tract . The activity of liver enzymes, especially transaminases, increases. The upper limit of normal is exceeded by more than 3 times.
- From the skin and subcutaneous tissues . Urticaria, itching and redness often appear, and less commonly, bullous dermatitis, in which the epithelium becomes inflamed and blisters filled with fluid form on the skin. In addition, the following reactions may be observed at the injection site after the injection: hematoma;
- edema;
- bleeding;
- inflammation;
- compaction;
- increased sensitivity;
- skin irritation or necrosis.
If hard inflammatory nodules appear, there is no need to worry, since they disappear within a few days and do not require discontinuation of the drug.
Patients undergoing treatment with Clexane also note a number of side effects:
- from the nervous system – headache;
- on the part of the immune system - sometimes anaphylactic reactions occur, including anaphylactic shock;
- from the vascular system - when using the drug against the background of spinal, epidural anesthesia or spinal puncture, spinal or neuraxial hematomas rarely occur, which lead to various neurological disorders of any severity, including persistent or irreversible paralysis;
- from the circulatory and lymphatic system - hemorrhagic anemia is often observed, and less often - eosinophilia;
- from the skin and subcutaneous tissues - in rare cases, pathological hair loss occurs, leading to its partial or complete disappearance in certain areas of the head or torso;
- at the injection site - cutaneous vasculitis or skin necrosis may develop (the precursor to these diseases is the appearance of purpura or erythematous papules);
- from the liver and biliary tract – cases of hepatocellular and cholestatic liver damage have been recorded.
With long-term use of the drug (more than 3 months), osteoporosis may develop.
Indications for use
What does Clexane help with? Injections are indicated for use in the following cases:
- therapy for angina and heart attack without a Q wave;
- prevention of thrombosis and venous embolism in people who are on bed rest for a long time due to acute therapeutic pathology (chronic and acute heart failure, severe infection, respiratory failure, acute rheumatic diseases);
- therapy for deep vein thrombosis, complicated or uncomplicated by pulmonary embolism;
- therapy of acute infarction with ST segment elevation in individuals requiring drug treatment;
- prevention of thrombosis in the extracorporeal blood flow system during hemodialysis;
- prevention of thrombosis and venous embolism after surgery.
Indications and contraindications for Clexane injections during pregnancy
Clexane belongs to the pharmaceutical group of anticoagulant drugs. It affects blood parameters, in particular, contributes to its dilution. During gestation, blood clotting increases and antithrombic indicators worsen. Injections of Clexane into the abdomen during pregnancy help dissolve blood clots, normalize blood circulation and prevent miscarriage.
The instructions for the drug state that its use during pregnancy is undesirable. Clexane injections are prescribed in extreme cases when it is not possible to do without treatment. Typically, therapy is carried out from the 2nd trimester, for preventive purposes - from the 3rd. Main indications for use of the drug:
- excessive platelet coagulation;
- increased thrombus formation;
- acute heart failure;
- myocardial infarction;
- angina pectoris.
There is no reliable information about the negative effects of Clexane on the body of the mother and child, since research in this direction is not conducted. However, according to clinical observations, the injection is well tolerated by patients and does not have any effect on the intrauterine development of the fetus.
The drug should not be administered if:
- allergies to the active substance;
- lactation;
- high risk of miscarriage;
- diseases with a threat of bleeding: aneurysm of a large vessel, hemorrhagic stroke, complicated abortion, etc.;
- the presence of artificial valves in the heart.
There is also a list of relative contraindications in which you should be careful when using Clexane:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- severe hypertension;
- diabetes;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- postoperative rehabilitation period;
- pathology of the kidneys, liver;
- open wounds;
- open tuberculosis;
- pathologies of the respiratory system;
- hemostasis disorders;
- oncology.
The compatibility of the drug with other medications, especially those that affect blood clotting, is questionable. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor, weighing the pros and cons.
Instructions for use
According to the instructions, Clexane is administered only subcutaneously; intramuscular injections of the drug are prohibited. The medication is administered deeply subcutaneously in a lying position, alternately into the right and left zones of the abdominal wall.
When using Clexane 0.4 and 0.2 ml, air bubbles are not removed from the syringe before injection to avoid loss of the medicine. The syringe needle must be inserted to its full length into the skin fold, vertically, and not from the side. The fold must be held during the injection and released only after the injection is completed; it is not recommended to massage the injection site.
To prevent thrombosis and embolism in acute therapeutic diseases, patients on bed rest are prescribed Clexane 0.4 ml once a day. According to reviews of Clexane, therapy can last an average of 1-2 weeks and be extended if necessary.
Before surgery for operations in general surgery, the drug, for prophylactic purposes, is prescribed in a dosage of 20 ml and administered 2 hours before they are performed once a day.
If a patient is diagnosed with a high risk of thrombus formation and embolism, Clexane 0.4 ml is administered once 12 hours before surgery. The course of treatment is usually 7-10 days, but is sometimes extended according to the doctor’s decision.
After orthopedic operations, the duration of therapy with Clexane 0.4 can reach 5 weeks when administered once a day. When carrying out hemodialysis, the medication is prescribed for prophylactic purposes in a dosage of 1 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
By
How to inject Clexane
Clexane can only be injected correctly if the patient is lying down. The drug is injected subcutaneously into the abdominal muscle. Syringes are prepared in advance, using 20 mg or 40 mg for use. The medicine is injected into the muscle of the anterior abdominal wall. The needle is injected perpendicular to the skin fold, which is not straightened after the injection.
How to administer Clexane before surgery to prevent venous thrombosis and embolism is decided by the attending physician, because The injection of the drug is given 2 hours before the start of the operation. The dose of the medicine is 20 mg or 40 mg, Clexane injections into the stomach are given subcutaneously once a day.
If the patient is at risk, the medication is used according to the instructions, 40 mg is administered once a day.
Sometimes it is better to inject the medication at a dose of 30 mg 2 times a day, starting the medication 24 hours after surgery. After surgery to install a prosthesis, the patient needs to determine the dose of the administered medication Clexane; how to calculate it correctly is indicated in the instructions for the drug.
The patient should know the rules for using the medication to prevent venous embolism if he is on bed rest.
In the morning, the patient is administered 40 mg of the drug subcutaneously. The course of therapy is 6 days. The maximum duration of treatment is 2 weeks.
To treat thrombosis of deep venous vessels, the injection is given in the evening subcutaneously at a dose of 1.5 mg/kg of the patient’s weight once a day.
What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical facility?
What are the dosages and side effects?
The instructions for the drug indicate in what doses Clexane is administered to the patient:
- Prevention of blood clot formation - dosage 40 mg 1 time per day s.c.
- For blockage of the pulmonary artery - 1 mg/kg 2 times a day.
- To prevent the appearance of blood clots during the hemodialysis procedure, a dose of 1 mg/kg of the patient’s weight is prescribed. Medicine is injected into the shunt at the beginning of the procedure.
- For the treatment of myocardial infarction, Clexane is injected into the abdominal muscle at a dose of 1 mg/kg of weight of an adult patient. The patient simultaneously takes an Aspirin tablet at a dose of 350 mg.
- A course of therapy with oral anticoagulants is prescribed simultaneously with injections of the drug Clexane.
The medication may cause the following side effects:
- bleeding;
- thrombocytopenia;
- decreased immunity;
- allergic reactions;
- anaphylactic shock.
The medicine, even after a single dose, can cause the development of bullous dermatitis. Hematoma, swelling, and bleeding sometimes occur at the injection site.
How much to inject after childbirth
The medication is administered to monitor the dynamics of thrombus formation after childbirth, and, taking into account the anti-Xa activity of the drug, it is prescribed to the mother in labor in a prophylactic dose.
After a cesarean section, Clexane, an injection solution, is administered in an amount of 40 mg subcutaneously over 6-8 hours.
To prevent bleeding, 40 mg of the drug is prescribed subcutaneously once a day.
Enoxaparin sodium in the amount of 0.4 ml s.c. is injected into the patient daily until 9 am. Before the operation, the medication is injected 3 hours before the operation.
Contraindications
- Age less than 18 years (safety and effectiveness have not been established).
- Allergy to the components of the drug and other low molecular weight heparins.
- Diseases with an increased risk of bleeding, such as aneurysm, threatened abortion, bleeding, hemorrhagic stroke.
The use of Clexane during pregnancy in women with artificial heart valves is prohibited.
Use with caution in the following cases:
- bacterial endocarditis;
- recent ischemic stroke;
- combined use with drugs affecting the hemostasis system;
- hemorrhagic or diabetic retinopathy;
- recent birth;
- performing epidural or spinal anesthesia, spinal puncture;
- recent neurological or ophthalmological intervention;
- pericarditis;
- severe injury, extensive open wounds;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract;
- kidney or liver damage;
- diabetes mellitus in severe forms;
- severe arterial hypertension;
- intrauterine contraception;
- diseases accompanied by hemostasis disorders (hemophilia, hypocoagulation, thrombocytopenia, von Willebrand disease), severe vasculitis.
special instructions
Clexane should not be mixed with other drugs, with the exception of a solution of 5% glucose or 0.9% sodium chloride.
Clexane should not be combined with other low molecular weight heparins.
It should be borne in mind that if enoxaparin is used in conjunction with acetylsalicylic acid, other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, clopidogrel, dextran, glucocorticoids or thrombolytics, the risk of hemorrhagic complications increases.
When using the drug for prophylactic purposes, a tendency to bleeding is usually not observed. When Clexane is prescribed in therapeutic doses, bleeding is possible. At risk are elderly patients over 80 years of age. In this case, careful monitoring of the patient's condition is required.
It is advisable to suspend the use of any drugs that affect hemostasis before initiating enoxaparin therapy. The exception is life-saving medications. If their use is necessary, careful monitoring of the patient's condition and the state of the blood coagulation system is carried out.
In patients with significant renal impairment, dose adjustment of the drug is required. This is not necessary for mild or moderate renal failure.
The risk of platelets is always reduced when using Clexane. But the decrease in their amount in the blood should not be too strong. Determination of platelet levels is carried out before the start of treatment, and then during therapy. A decrease in the number of platelets in the blood by 30% or more is a reason to discontinue enoxaparin.
Side effects
During treatment with the drug, the patient may develop negative reactions, the most common of which is bleeding. If bleeding develops, the medication should be stopped immediately.
Other side effects from using Clexane include:
- Increased activity of hepatic transminases in rare cases;
- Paresis and paralysis (if the drug was administered after recent epidural anesthesia or puncture);
- Hemorrhages in organ cavities, including the brain;
- Vasculitis in rare cases;
- Thrombocytopenia;
- Local allergic reactions to the administration of the solution - skin itching, burning, redness, inflammation, swelling, rashes, hematoma;
- Hemorrhagic conditions.
Side effects
The most dangerous side effect of taking Clexane is massive bleeding.
The risk of its occurrence increases when using large doses of the drug. Also, therapy with Clexane can contribute to changes in the number of platelets in peripheral blood. The drug quite often causes allergic reactions. They usually manifest themselves as skin changes - itching, rashes, swelling of the tissue. Less commonly, the drug contributes to systemic damage to the body - anaphylactic shock and vasospasm.
Also, after injection of Clexane, many patients note the appearance of a bruise at the site of use of the syringe. From the central nervous system, headaches and nausea may occur. Long-term use of the drug causes damage to liver tissue and disruption of bone structure. Rarely, taking the drug contributes to the development of subcutaneous infiltrates and nodules.
Children, pregnancy and breastfeeding
Clexane should not be used during pregnancy unless the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. There is no information that enoxaparin sodium crosses the placental barrier in the 2nd trimester; there is no information regarding the 1st and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy.
The use of the drug in pregnant women with artificial heart valves is not recommended. When using Clexane during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindicated in children and adolescents under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety have not been established).
Overdose
If an overdose occurs during intravenous, subcutaneous or extracorporeal use of Clexane, this can lead to hemorrhagic complications. The likelihood of drug absorption is low even when large doses are taken orally.
To neutralize anticoagulant reactions, it is necessary to slowly administer protamine sulfate intravenously, taking into account that 1 mg of protamine negates the activity of 1 mg of Clexane if the drug is administered no more than 8 hours before the administration of protamine. If 12 hours or more have passed since the administration of enoxaparin sodium, protamine is not required.
Even with the timely administration of the correct doses of protamine, the effect of Clexane will not be completely neutralized (maximum 60%).
Analogues of the drug Clexane
Analogues are determined by structure:
- Enoxaparin sodium.
- Hemapaxan.
- Anfiber.
The group of anticoagulants includes analogues:
- Angiox.
- Troxevasin Neo.
- Antithrombin 3 human.
- Gepalpan.
- Pradaxa.
- Skinlight.
- Thrombogel.
- Arixtra.
- Pelentan.
- Seprotin.
- Tsibor.
- Fragmin.
- Hemapaxan.
- Marevan.
- Angioflux.
- Venolife.
- Heparin ointment.
- Emeran.
- Heparoid.
- Enoxaparin sodium.
- Warfarex.
- Lavenum.
- Exanta.
- Leeching.
- Nigepan.
- Fraxiparine.
- Ellon gel.
- Hepatrombin.
- Thrombophobe.
- Eliquis.
- Sinkumar.
- Klivarin.
- Trombless.
- Dolobene.
- Fenilin.
- Troparin.
- Viatromb.
- Xarelto.
- Lyoton 1000.
- Venabos.
- Heparin.
- Calciparin.
- Warfarin.
- Essaven.
- Fraxiparine Forte.
Analogs
Among the substitutes, one can distinguish those drugs that have an identical composition, but are produced by other pharmaceutical companies, and those that have a different composition, but have an effect on the body similar to Clexane.
A replacement may be necessary if the patient shows signs of individual intolerance to the medication, or any side effects or complications. Also, the selection of a cheaper analogue is required when the patient cannot financially afford the prescribed medication.
Clexane or Fraxiparine: which is better?
Fraxiparine is an anticoagulant agent. However, it contains Nadroparin calcium, which is a low molecular weight heparin. This medication is also available in the form of syringes filled with a ready-to-use solution. The undoubted advantage of Fraxiparine is its lower cost, which makes it accessible to a larger group of patients. Indications for use for both drugs compared are practically
Hemapaxan or Clexane: what to choose
Both of these drugs are very similar to each other, since they are based on the same active ingredient (enoxaparin). The list of indications and contraindications for the described products is the same. Gemapaksan is much cheaper, even though it is produced abroad (Italy). There is no reliable data on which of these medications is more effective and safe. Doctors who often work with these medications claim that their effects are exactly the same. Complications occur with approximately the same frequency in both the first and second drugs.
Comparative characteristics of Pradaxa and Clexane
Pradaxa contains the active substance dabigatran etexilate, which belongs to the group of direct thrombin antagonists. Pradaxa enters the human body in an inactive form. After absorption from the gastrointestinal tract into the systemic bloodstream, it is activated in hepatocytes, thanks to the enzymatic complexes and compounds they contain.
Accordingly, patients prescribed Pradaxa should not have functional liver failure, as this will have an additional damaging effect on the liver.
Important! The advantage of Pradaxa is the possibility of non-invasive administration (available in tablet form).
Heparin or Clexane: which is better?
The active substance Clexane is a derivative of Heparin. Thus, Heparin is listed as a high molecular weight compound, and Clexane is listed as a low molecular weight compound. The Clexane formula was developed much later, so this drug is safer and more effective, and also less likely to cause unwanted effects.
It must be remembered that the risk of developing such a complication from the use of heparin, such as autoimmune thrombocytopenia, remains even when prescribing its low-molecular derivatives.
Tsibor as an analogue
The active compound of Cibor is the sodium salt of low molecular weight heparin (bemiparin sodium). This medication is widely used in surgical practice and in nephrology (prescribed to patients undergoing extracorporeal hemodialysis using an artificial kidney machine). The mechanism of action of Tsibor is completely similar, since this drug inhibits thrombus formation by interrupting the coagulation cascade. Cibor cannot be used in childhood due to the fact that not enough research has been conducted on the effect of this drug on the children's body.
Enixum and Clexane: comparison of drugs
The drugs being compared contain the same chemical compound, which determines the great similarity of these drugs. Enixum, like Clexane, is available in injection form intended for subcutaneous administration. The drug is available in eight different dosages, which will allow the doctor to choose the most rational and safe concentration of the solution for the patient.
Most often, Enixum is prescribed as a prophylaxis to patients in surgical hospitals who have undergone major operations (especially surgical interventions on the musculoskeletal system).
Enoxaparin sodium as an analogue of Clexane
The composition of both drugs is identical, so all the indications and contraindications for their use are the same. Both Enoxaparin sodium and Clexane are administered into the body via subcutaneous injection, which is not a very pleasant procedure for many patients.
In cases where it is not possible to administer the drug parenterally, Enoxaparin sodium cannot become a substitute. There have been no studies that could accurately say which drug is more effective, but in practice their effectiveness and efficiency are almost equal.
Table comparing drug analogues by cost. The last data update was 10/21/2019 00:00.
Other cheaper substitutes
Clexane is a fairly expensive drug, especially considering that it needs to be injected in entire courses. Below we provide a list of medicines that can replace this medicine, but have a lower cost:
- Sulodexide;
- Fragmin;
- Flenox;
- Novoparin;
- Anfiber;
- Fenilin.
Table comparing drug analogues by cost. The last data update was 10/21/2019 00:00.
Vacation conditions and price
The average cost of Clexane (syringes 20 mg, 0.2 ml, 2 pcs.) in Moscow is 235 rubles. The solution is dispensed from pharmacies with a doctor's prescription.
If the integrity of the syringe is damaged or if there are flakes/turbidity in the solution, the medicine must absolutely not be administered subcutaneously! Freezing or heating the medicine is not allowed.
The instructions for use recommend storing the medicine Clexane at room temperature, out of the reach of children, for no more than 3 years from the date of manufacture.
Post Views: 273
What kind of drug is this?
Clexane is a direct anticoagulant, the active substance of which acts directly on thrombin and reduces its activity to a minimum, thereby thinning the blood flow.
According to the classifier of drugs of the ATP system (anatomical-therapeutic-chemical classification), Clexane has the code B01AB05. It decrypts this way:
- B – drugs affecting hematopoiesis and blood;
- B01 and B01A – anticoagulants;
- B01AB – heparins;
- B01AB05 – enoxaparin.
This drug is produced by the French company Sanofi Winthrop Industrie. It is sold in pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription.
Store Clexane out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. The drug should not be frozen. The shelf life is 3 years. After its expiration, the medicine is disposed of.
Dosage of the drug
The amount of the drug for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes is different. To properly inject Clexane into the stomach during pregnancy, you need to calculate the appropriate dosage. Only a qualified doctor can do this.
Syringe ampoules with Clexane are available in different volumes: from 0.2 ml to 1 ml. The daily dose of Clexane for pregnant women is 0.2-0.4 ml. When determining the volume, the individual characteristics of the patient’s body are taken into account. Exceeding the dosage is fraught with complications and side effects from the medicine.
To prevent blockage of blood vessels, it is recommended to administer 20 mg of the substance for 10-14 days. In practice, a positive result is achieved in 7-10 days.
The duration of the therapeutic course depends on the degree of illness of the expectant mother, but does not exceed 14 days. The daily dose of the drug is calculated using the formula: 1.5 mg per 1 kg of weight. In severe thrombosis, 40 mg of the substance is administered once a day, and when treating deep veins, the frequency of injections is increased to twice a day.
For the treatment of deep vein thrombosis, oral anticoagulants are prescribed in combination with Clexane injections.
What is Clexane?
Clexane is a direct-acting anticoagulant. It is widely used in the field of surgery, orthopedics and traumatology. It is used to prevent and treat deep vein thrombosis. The active substance of Clexane is enoxaparin sodium. This component is a derivative of heparin and has an antithrombic effect, as well as the ability to thin viscous blood. The drug is well tolerated by patients and is recognized as one of the best among low molecular weight heparins. Despite the fact that Clexane has substitute drugs, doctors prefer it.
Clexane is sold in pharmacies in the form of a solution for subcutaneous injection. It is a colorless liquid placed in a disposable syringe. The volume of the syringe can vary from 0.2 to 1 ml depending on the dosage of the drug. There are no other forms of this medication other than injection.
It is important to understand that Clexane is a fairly serious drug, so you need to be careful when using it during pregnancy. Of course, self-medication in this case is out of the question. "Clexane" during pregnancy (reviews from doctors and patients about the drug are positive) are prescribed if treatment is unavoidable and when the benefit to the mother is higher than the potential risk for the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Indications for use
In obstetric practice, this drug is prescribed for the treatment and prevention of blood clots in the placenta. Normally, during pregnancy, the expectant mother’s body experiences activation of the blood coagulation system. The purpose of this process is to prevent heavy bleeding during labor.
Sometimes disruptions occur in platelet activation processes, leading to excessive stimulation of the blood coagulation system. This phenomenon is facilitated by a woman’s hereditary predisposition, carrying twins, high blood pressure, as well as other conditions and concomitant diseases.
Increased platelet activity is a risk factor for the formation of blood clots in blood vessels. Blood clots clog arteries and veins, reducing the rate of metabolism in tissues.
If a blood clot gets into the arteries of the placenta, there is a risk of premature detachment and spontaneous termination of pregnancy. Also, the formation of blood clots causes premature aging of the organ and a strong increase in blood pressure.
If a blood clot forms in a vein, the outflow of fluid from the organ is disrupted. This process leads to the development of edema and decreased nutrition of the affected tissue. The danger of venous clots lies in the risk of their rupture and the occurrence of pulmonary thromboembolism.
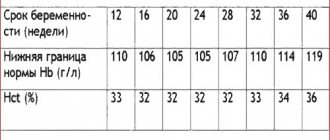
Clexane during pregnancy is prescribed if there are the following abnormalities in the coagulogram (blood test for clotting indicators):
- reduction of blood clotting time;
- increased prothrombin index;
- decrease in the amount of antithrombin III;
- increase in the amount of d-dimer;
- increase in platelet count.
In addition to obstetric indications, Clexane can be used for other diseases. The drug is used to treat and prevent thrombosis in severe heart pathologies - congenital and acquired defects, chronic failure in the decompensation stage.
The drug can also be used for the treatment of thrombus formation in the deep veins of the lower extremities and the treatment of pulmonary embolism. The drug is used for coronary heart disease and the presence of myocardial infarction.
Reviews
Until the 20th week I took blood thinning pills, then I was prescribed Clexane twice a day 0.4. Good drug. I inject it into the stomach myself, they showed me how to do it correctly, at an angle of 45 degrees, however, when my stomach has grown, I don’t want to insert the whole needle there, I’m somehow scared, and all the assurances that I still have a lot there muscle, fat and skin, it's still scary. We got good tests, the baby was born a bit difficult, but there were no problems.
Inject the medicine not quickly, but not slowly either, find a speed that is good for you, find fatter places on your tummy, then you won’t feel anything at all, I once injected above the navel, where the abs used to be, it hurt a little, but not that much . The main thing is not to rub, otherwise you will bruise, I learned this from my own experience.
Drug interactions
During treatment with Clexane, one should take into account not only its characteristics, but also its compatibility with other drugs. If you neglect this, you can reduce or increase the intensity of the action of the medication, as well as create any complications.
Main combinations and their consequences for the human body:
- The simultaneous use of Clexane with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants and systemic glucocorticosteroids may lead to an increased risk of various bleedings.
- The active ingredient of the drug does not combine well with low molecular weight heparins.
- Clexane can cause side effects if used in combination with Ketorolac, Ticlopidine, Dextran, Clopidogrel.
- It is not recommended to inject Clexane during therapy with systemic thrombolytics and salicylates.
Indications
The main indications for prescribing Clexane during pregnancy are:
- deep vein thrombosis;
- development of hypercoagulation syndrome (increased blood clotting);
- unstable angina;
- heart failure;
- predisposition to thrombosis.
A pregnant woman is prescribed the drug only in the second and third trimesters. It has not yet been studied how the medicine affects the development of the embryo, therefore in the first 12 weeks, when the baby’s organs and systems are formed, it is not prescribed.
The American Food and Drug Administration has classified Clexane as category B. This means that experiments conducted on animals did not reveal any negative effects on the fetus. However, adequate and complete studies have not been conducted in pregnant women. Therefore, a doctor can prescribe a drug only if there is a real need for its use.
Rules for injections
- Wash your hands and the abdominal area where the injection will be given thoroughly.
- Lie down on a flat surface with your stomach up.
- To avoid losing the medicinal solution, do not try to squeeze out excess air from the syringe.
- The injections are given in one of the lower parts of the abdomen. In this case, it is taken into account that the injection should be made at a distance exceeding 5 cm from the navel towards the side. It is necessary to avoid injecting into a place where a bruise has formed after a previous injection.
- Disinfect the injection site with alcohol.
- Gather the skin on your abdomen into a fold using your thumb and forefinger and do not let go until you have given the injection. Hold the syringe with the medicine in a strictly perpendicular direction.
- Insert the needle into the skin fold along its entire length.
- Begin to gradually inject the solution by pressing the plunger with your finger.
- Carefully remove the needle, being careful not to tilt the syringe to the side.
- It is not recommended to massage or rub the injection site, so as not to provoke the appearance of a bruise or bruise.
- To avoid complications, injections should be given alternately to the right and left half of the abdomen.
Pharmaceutical properties
The active substance is rapidly absorbed when administered subcutaneously.
The maximum concentration of the active principle in the blood is observed 3-5 hours after injection. It is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. The half-life is 4 hours. In patients with impaired renal function, elderly and obese people, this time increases and varies from 5 to 7 hours.
Formula of the substance Enoxaparin sodium
Pharmacological properties and pharmacodynamics
Clexane has antithrombotic properties. It is used as an injection under the skin during the treatment of acute coronary syndrome, deep vein thrombosis, and also as a preventive treatment for various venous pathologies.
The second international nonproprietary name for this drug is enoxaparin. The drug is a low molecular weight heparin with a molecular weight of approximately 4500 daltons.
During the use of the drug for prophylactic treatment, he experiences a slight change in activated partial thromboplastin time. It also has almost no effect on platelet status and fibrogen binding. Also, during the treatment of various diseases with this drug, the aPTT increases almost 1.5-2 times.
After prolonged subcutaneous injections of a systematic nature in a volume of 1.5 mg per 1 kilogram of body weight, the maximum level of enoxaparin sodium in the body is reached after two days. Bioavailability during subcutaneous administration is 100%.
Metabolization of enoxaparin in the liver is achieved through desulfation and depolymerization. The metabolites that are formed during this process have low activity.
The half-life of the drug lasts from 4 hours to 5 hours during a single dose. If the medicine is taken repeatedly – 7 hours. About 40% of the drug is excreted through the kidneys. The elimination of the active substance enexoparin in older people occurs more slowly, this is due to deterioration of kidney function.
Why are injections prescribed?
Clexane is a medication that has an antithrombotic effect. The active element of the drug is enoxaparin sodium. It is a low molecular weight heparin. The drug is released in the form of a solution. It is used for injection administration.
The drug is administered subcutaneously into the abdominal area. There are several dosage options:
- 1 ml;
- 0.8 ml;
- 0.6 ml;
- 0.4 ml;
- 0.2 ml.
Treatment with the drug is prescribed by a doctor taking into account clinical symptoms. The scope of use is quite wide. Clexane is used in surgery, traumatology and orthopedics. Indications for use are the following:
- heart attack and angina pectoris;
- prevention of thrombosis during hemodialysis;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- preventive measures in the postoperative period.
The active component undergoes transformation in liver cells. The process of removing the drug from the body is monophasic. 10% of the total volume of the drug is excreted unchanged. About 40% is excreted by the urinary system.
Reference. 1 ml of the drug contains anti-Xa ME.