If you think about it, all people on the planet have had or have digestive problems. Many people don’t even realize that a bomb is “ripening” in their body. Poor nutrition, non-compliance with the diet and regime, negligence in cooking or too eccentric taste preferences may not manifest themselves in the best way in the future.
Congestive gastropathy: what is it? How to treat?
All results of the inflammatory process in the stomach can be divided into two categories. These are gastritis and gastropathy familiar to everyone. With gastritis, the gastric mucosa is affected; erosions and minor ulcerations are visible on it. In this case, a person experiences discomfort after eating too spicy, hot or cold food. Everyone has encountered it at least once in their life, especially when they were young and lived separately from their parents.
With gastropathy, no significant changes occur in the gastric mucosa. Small areas of inflammation are visible on it - and that’s all. However, this prosperity is deceptive. There is still damage at the cellular level. Epithelial cells are destroyed, and their recovery is slow compared to normal.
Congestive gastropathy is a disorder of gastric motility and its passage through the digestive canal up to the small intestine.
Treatment of pathology includes drug therapy, taking vitamins, a certain diet and giving up bad habits. It is also recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, including walks in the fresh air.
Kinds
Erythematous gastroduodenopathy varies in forms of manifestation and in the degree of the inflammatory process. The first criterion evaluates the territorial distribution of the area of redness; they are of two types:
- the focal form implies local lesions occupying separate small parts of the upper layers of the stomach. This is the safest type of phenomenon. It occurs with minor deviations in the diet, and rarely results in an independent diagnosis of gastritis. May be caused by a reaction to medications;
- diffuse type (common) is characterized by damage to large areas of the stomach. Redness and swelling can simultaneously affect several parts of the organ. The advanced form progresses to gastritis and can cause additional stomach problems. There is a possibility that the resulting lesions appeared after consuming heavy irritating food or alcohol on the eve of the examination.
Treatment of focal erythematous gastropathy is much faster and does not pose any danger. The common form transforms when symptoms are ignored.
The disease is classified into two degrees of inflammation. The characteristic is determined by monitoring the condition of the surface layer of the mucosa and the stage of impact on the lining of the stomach. The first degree of inflammation is the primary manifestation of deformation of the integument of the organ under study. The second stage indicates the development of the process. This means that the stomach continues to be influenced by external, provoking factors.
Prevalence
Doctors around the world record diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and then compile the information into general statistics so that they know what measures to take to limit the disease.
Congestive gastropathy is a fairly common pathological process, even against the background of other nosologies. It occurs not only against the background of poor nutrition, but also when taking certain medications, after prolonged stress, as well as due to accidents and as a complication of other somatic diseases.
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
More than a quarter of patients taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs report stomach pain; the percentage of gastropathy after burns, injuries and surgical interventions already reaches eighty. Liver cirrhosis and hypertension also contribute to the general “cauldron”. And given that patients either do not pay attention to the symptoms or hide them from their doctor, the statistics are greatly underestimated.
Folk remedies
For erythematous gastroduodenopathy, it is allowed to be treated with traditional methods. Herbal infusions gently relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane and help restore damaged mucous membranes. We offer you several simple herbal medicine options for the stomach.
The main component of this collection is yarrow. 50 grams of dried crushed yarrow flowers and herbs are poured into 400 ml of water and boiled over low heat for 40 minutes. After the broth has cooled, it is filtered and taken warm, a third of a glass, before main meals.
To prepare this decoction, prepare a mixture of the following components:
- centaury;
- yellow gentian;
- chicory flowers;
- fumaria officinalis;
- yarrow;
- St. John's wort.
Do not be alarmed by such variety - the raw materials for preparing the decoction are sold in any pharmacy. Mix the ingredients in equal quantities, take 3 tablespoons of the prepared mixture and pour 400 ml of boiling water. Seal tightly and leave for 4 hours. Strain the broth and take it warm before your main meals - breakfast, lunch and dinner.
These recipes are given in the “Newest Therapist's Handbook”, written by the famous Russian doctor, E. A. Nikolaev.
Etiology
Congestive gastropathy is caused by frequent and uncontrolled use of non-selective NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). They are often prescribed because they have several positive effects at once: they reduce inflammation, reduce temperature and swelling, and relieve pain. But patients must adhere to certain conditions that they often ignore or consider unimportant.
The second cause of gastropathy can be called diseases of other systems and organs:
- pancreatic tumor;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- portal hypertension.
Next in the ranking are accidents associated with the use of chemically active substances. In fourth place are permanent stress and head injuries. And only at the end of the list do gastrointestinal diseases appear, such as reflux of bile or intestinal contents back into the stomach, antiperistalsis.
Risk factors
Congestive gastropathy does not occur out of nowhere. It is always accompanied by actions or conditions that aggravate or provoke the action of the etiological factor.
These include:
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- long smoking history;
- age over sixty years;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach (a microorganism that causes one of the types of gastritis);
- ulcer;
- long-term uncontrolled medication use.
Some of these factors are beyond a person's control, but for the disease to develop, a combination of two or three items from the list must be present.
Causes of the disease
Erythematous gastropathy can be caused by the following reasons:
- Disruption of the circulatory process.
- Presence of pathogenic microorganisms or fungal infection. More often, the cause of the disease is the active activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. In this case, treatment is aimed at getting rid of the provoking factor.
- Chemical burns.
- Infectious diseases.
- Medicinal (medicinal gastritis). The causes of this type of gastropathy include taking aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Heredity.
- Poor nutrition.
- Excessive drinking and smoking.
- Daily routine and stress resistance are of no small importance. Under the influence of psychotraumatic factors, the synthesis of adrenaline increases. It affects the growth of hydrochloric acid production, and its prolonged exposure leads to irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ, provokes redness, inflammation, and in some cases causes the formation of ulcers and erosions.
Pathogenesis
Rough, hot or spicy food in large quantities enters the stomach, which is not able to cope with such a volume of work. Because of this, the area of the mucous layer increases, more folds appear, they become taller and thicker. Microcirculation and vascular permeability increase, more mucus and hydrochloric acid are produced. The body is trying to cope with overloads.
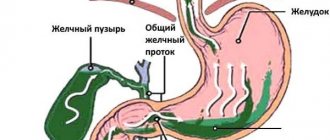
The antrum of the stomach is overstretched, which leads to loose closure of the sphincter between the stomach and duodenum. Because of this, the contents of the small intestine, along with bile and pancreatic enzymes, flow back into the stomach, causing burns and atrophy of the mucosa. This further complicates the digestion process.
How to recognize an inflammatory process in the stomach?
Having contacted a gastroenterologist, the patient is offered to undergo an endoscopic examination to clarify the diagnosis. To do this, a thin elastic tube is passed into the stomach cavity through the esophagus. Thanks to this device, the doctor determines redness and the degree of damage to the organ with 100% accuracy. If gastritis is detected, then swelling of the mucous membrane and excessive mucus production are added to the existing redness. Minor touches with the endoscope can cause small wounds and hyperemia due to the increased vulnerability of the upper layer of the stomach.
Based on the results of this study, erythematous gastropathy can be identified - focal or diffuse inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Usually this problem is accompanied by already diagnosed chronic or acute gastritis, but in some cases it is a primary disease.
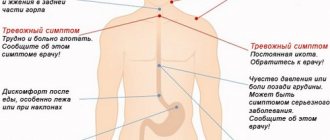
Symptoms
How does congestive gastropathy manifest itself? Symptoms may appear much later than the onset of the disease itself. This is due to the fact that it takes time for gastropathy to form, and at first a person does not notice any uncomfortable changes in the body.
In a later period, the whole range of dyspeptic phenomena appears:
- nausea with vomiting, heartburn;
- decreased or lack of appetite;
- weakness;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach, pain when pressing;
- belching and the appearance of a yellow coating on the tongue.
In advanced cases, when the patient stubbornly ignores the symptoms, gastropathy can manifest itself as gastric bleeding.
Change in general condition
In addition to gastric disorders, pathology may have signs of a change in the patient’s condition as a whole, for example:
- rapid feeling of fatigue and lethargy;
- weakness;
- periodic headaches along with intestinal pathologies;
- pallor of the skin;
- decreased immune reactivity;
- jumps in blood pressure;
- sophistication of appetite and taste preferences.
Now it is clear what it is - erythematous gastropathy. We will find out how to treat the disease below.
Forms
Morphologically, there are two forms of congestive gastropathy - mild and severe. In mild cases, a mosaic pattern of folds and pathologically dilated vessels is found on the mucosa. In severe cases, there are also hemorrhages and inflammatory spots.
There is also gastropathy, which affects only the antrum of the stomach. It is located on the border with the duodenum, and the first is affected by chyme reflux. When stagnation occurs in the stomach, the passage of food through the antrum slows down, which leads to souring or fermentation of food. This increases the acidity of the environment and damages the mucous membrane. A person experiences pain at night, heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
Focal gastropathy is manifested by areas of redness against the background of gastric changes in the gastric mucosa. Ulcers may appear in these areas over time.
Classification
According to some authors, the disease is divided into degrees. The classification is based on the endoscopic sign of mucosal damage. It is customary to distinguish grades 1, 2 and 3 of erythematous gastropathy.
But in recent years, scientists have come to the conclusion that this classification is not entirely correct. The first degree is characterized by local redness.
But the second and third degrees, according to endoscopic signs, are already manifestations of a more severe pathology - gastritis, only in its different forms - superficial and erosive.
Diagnostics
Gastropathy of the stomach does not have specific symptoms. It imitates several gastrointestinal diseases at once, so even the most experienced doctor is unable to understand at first glance what exactly the problem is.
It all starts with a survey, establishing the time of onset of the first symptoms and collecting complaints. Then comes an examination and laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. First of all, the doctor prescribes a general and detailed blood test, biochemical tests, and bacteriological examination of the gastric environment to detect Helicobacter pylori. Characteristic signs are a decrease in hemoglobin and platelet levels.
Fibrogastroscopy is the gold standard in the diagnosis of gastropathy. It allows not only to examine the mucous membrane, but also to collect material for histological examination. A biopsy is taken from pathologically changed areas of the stomach.
If required, the patient undergoes abdominal sonography, radiography, CT or MRI.
Complications
Congestive gastropathy in the antrum is prone to complications. The most common of them include bleeding from pathologically altered vessels of the stomach. Sometimes, this is a late and only symptom of the disease. In more than half of patients diagnosed with gastropathy, fibrogastroscopy reveals ulcers, erosions and perforations.
The most dangerous complication is the development of a tumor process in the gastric mucosa. Since the process of restoration of the mucous membrane is disrupted, and the organ’s protective system works “to wear out,” uncontrolled cell growth may occur against the background of inflammation.
The essence of pathology
Many people are interested in: erythematous gastropathy - what is it? In essence, the pathology is redness of the mucous tissues of the stomach, which is diagnosed during fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This anomaly may be accompanied by swelling of the epithelium, increased sensitivity, and excessive mucus production.
This endoscopic syndrome is caused by the influence of various damaging factors on the mucous membranes of the digestive organs. As a result, this leads to the formation of erythema - redness caused by blood flow to the affected area. These defects are localized on the surface and do not lead to damage to deep structures.
This condition cannot be called a disease, but it often occurs with superficial erythematous gastritis. In this situation, gastropathy has been present for a long time. If treatment is not started in time, there is a risk of developing quite serious pathologies. One of them is peptic ulcer disease.
If redness of the epithelium is detected, there may be a need for additional diagnostic procedures that can be used to identify a bacterial infection and determine acidity. In some situations, there may be a need for a biopsy of the affected areas.
Differential diagnosis
Congestive gastropathy is an extremely difficult diagnosis, despite the apparent abundance of symptoms. Since it mimics other nosological forms found in the gastrointestinal tract. The most common among them are gastritis, gastric or duodenal ulcers, pyloric stenosis, antral sphincter insufficiency, reflux disease and other, more exotic diseases.
In order to make the right choice, the doctor prescribes fibrogastroduodenoscopy, bacterial examination, biopsy and other tests. Having excluded all other options, only congestive gastropathy remains.
Prognosis and prevention
The most extreme measure for advanced erythematous gastropathy is surgical treatment, the so-called gastric resection. With the right treatment tactics with medications and folk remedies at an early stage of inflammation, the prognosis is always favorable. Therapeutic prevention of erythematous gastropathy consists of a balanced diet and timely treatment. If you neglect the doctor’s advice, there is a possible chain reaction: gastritis – ulcer – cancer. Take care of yourself and always be healthy!
Treatment
What can be done for a patient diagnosed with “congestive gastropathy”? Treatment begins with identifying the etiological factor and eliminating it. If the damage to the intestinal tube is secondary, then it is advisable to direct all efforts to cure the primary pathology.
To directly relieve the symptoms of gastropathy, proton pump inhibitors, histamine receptor blockers, antacids, antibiotics and drugs that improve microcirculation are used. The doctor’s main task is to select a combination of drugs that would multiply their positive effects and neutralize each other’s side effects.
The role of supportive therapy should not be underestimated. The patient must be prescribed B vitamins, especially B12, since if the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, its amount decreases sharply. In addition, it is advisable to take vitamins C and K. In addition, the patient is advised to walk more in the fresh air, do gymnastics and strengthen the abdominal muscles and diaphragm.