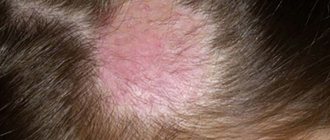
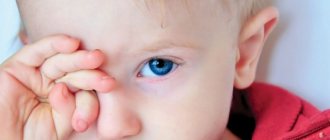
What are the causes of hives in a child?
It is impossible to answer this question in a few words. It can be caused by a huge number of irritants, so the source of the problem must be sought in each specific case. Here are just some of the causes of this disease:1.
- Allergic
A wide range of food products, in particular fish, shellfish, eggs, nuts, tomatoes, strawberries. Various food additives - dyes, preservatives (sulfites, salicylates) and others.
- Toxic
Bites from wasps, bees, mosquitoes, fleas, spiders and other insects. Contact with certain plants, in particular nettles. Contact with jellyfish and other marine inhabitants.
- Physical
Mechanical influences such as pressure or vibration. Exposure to cold, heat, sunlight. High physical activity, stress.
- Pseudo-allergic
Medicines, in particular penicillin drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (for example, aspirin), some antibiotics, insulin, radiocontrast agents and others.
- Autoimmune
Autoimmune reaction.
- Idiopathic
For no apparent reason.
In addition to the direct causes listed in the table, urticaria in a child may be associated, i.e. be a symptom of another disease 1. Sometimes it occurs as one of the manifestations of a bacterial, viral or fungal infection, a deficiency of certain enzymes in the baby’s body, or hereditary diseases.
As you can see, there are a lot of reasons. The only good thing is that it occurs very quickly after exposure to the stimulus, so it is often possible to calculate it “hot on its heels.”
Causes
Any substance can provoke acute urticaria in children. Most often, an allergic reaction develops due to food, household chemicals, medications or insect bites.
Causes of urticaria in children:
- food products - seafood, honey, nuts, chocolate, red berries and fruits, citrus fruits, mushrooms, eggs, products with flavors, flavor enhancers and thickeners;
- household allergens - detergents, dust, wool, pollen;
- medications – vitamins, antibiotics, dietary supplements, analgesics;
- insect bites - bees, mosquitoes, flies, hornets;
- other reasons are thermal factors, sun.
In addition to the causes that directly cause allergies, there are predisposing factors:
- pathologies of the endocrine glands (thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- weakened immune system;
- excessive sterility.
All these factors together increase the risk of developing allergic reactions in childhood. But the main cause of urticaria remains altered reactivity of the body.
What is acute and chronic urticaria?
Despite the name, the acute form can be considered a mild course of the disease. It is characterized by the rapid appearance of blisters or swelling and often their equally rapid disappearance. In children, it can go away in just a few hours without leaving any traces.
The main symptom of chronic urticaria is its duration2. The disease is considered to have become chronic if symptoms persist for more than 6 weeks in a row.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the duration, urticaria in children is classified as follows:
- acute (active symptoms last less than 6 weeks);
- chronic (lasting more than 6 weeks, undulating course with episodes of exacerbations and remissions).
According to the etiological factor:
- allergic or immune-mediated urticaria in children - it is based on immunological mechanisms of activation of mediators of allergic inflammation (including IgE-mediated, immune complex, autoimmune);
- pseudo-, or non-allergic - provoked by the same biologically active substances, but without the participation of immune factors;
- mixed;
- idiopathic – of unknown origin, accounts for up to 25% of all cases of the disease.
Forms of non-allergic urticaria in children:
- cold (acquired and familial, primary and secondary, immediate and delayed, localized and systemic);
- thermal;
- pressure urticaria (immediate or delayed);
- solar;
- vibration;
- dermographic (primary and secondary, follicular, red, white and cold-dependent dermographism);
- aquagenic (provoked by exposure to water);
- cholinergic (in response to increased body temperature or emotional overload);
- contact;
- physical effort.
How common is urticaria in children?
This is a fairly common disease.
According to various estimates, it occurred at least once in 15–25% of the population3. In other words, every sixth - every fourth person in the world has had it. However, it occurs more often in adulthood, and the statistics for this disease among children are not so frightening - only 2.1–6.7%4. Children under two years of age usually suffer only from the acute form. Between the ages of 2 and 12 years, urticaria sometimes becomes chronic, but more often it still occurs in an acute form. In adolescence, the chronic form takes precedence over the acute form.
Types of rashes
A rash on a child’s back may have a specific appearance. There are primary (the rash itself) and secondary (changes in skin color and structure) elements of skin rashes.
There are the following types of rashes on the back of a child:
- Maculae (spots) - located under the skin, invisible to the touch, but have a specific color from white to bright red. They never leave marks on the skin.
- Ulcers are red pimples filled with pus, which can break out and break out, or disappear without a trace. If you open them, there is a high probability that a trace will remain.
- The blisters form reddish spots with clear liquid inside. They do not cause discomfort or pain and pass without a trace.
- The blisters are also filled with liquid, but after it comes out, ulcerations begin to form on the body, which are then successfully treated.
- The small rash is easily felt upon contact and is located in the superficial layer. Often there is no serious cause and goes away quickly.
- The tubercles are formed due to changes in the structure of the subcutaneous layer.
- The nodes have a dense shape, are noticeable to the touch, and also stand out in color.
In a child, a rash on the back may have accompanying symptoms.
Such as:
- dry skin;
- peeling;
- itching and even pain;
- increased temperature locally or throughout the body;
- accompanying signs of the disease (cough, runny nose, lacrimation, photophobia).
All manifestations will depend on what caused these symptoms.
What does urticaria look like in children?
The name of this disease is no coincidence: it really looks like a nettle burn. Characteristic symptoms are pink, sometimes red blisters. Their size can vary widely - from a few millimeters to 10 centimeters, adjacent blisters can merge with each other1. The blisters have a clear border and rise above the surface of the skin. When pressed, they disappear, then appear again. Another common symptom of the disease is itchy skin.
The photo below shows examples of what urticaria can look like. You can find other photos on the Internet.
Why does rash occur in babies?
There are a lot of factors that provoke the appearance of a rash: it can be an allergy, infectious diseases and other diseases. A healthy baby's skin should be pale pink in color, without any rashes.
If a rash is detected on the child’s skin, parents should definitely consult a doctor on this issue. Only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Why is urticaria dangerous?
In most cases it causes discomfort, but nothing more. By itself, it is not capable of causing damage to the child’s organs and systems. However, there are a number of situations in which it can be deadly1:
- Acute urticaria may be accompanied by an anaphylactic reaction. The child quickly develops swelling of the larynx and begins to choke. At the first suspicion of swelling, call an ambulance immediately!
- If the cause of hives is cold, this can lead to suffocation and a drop in blood pressure, which is also deadly. Dial 112 without hesitation if you see that after hypothermia the child breaks out in hives and feels unwell!
Such cases occur infrequently, but it is better to be aware of dangerous symptoms so that they do not take you by surprise.
First aid for hives
The formation of redness and blisters is not as safe as it seems at first glance. In some cases, the situation requires urgent assistance from specialists. Mothers of children prone to allergic reactions should clearly know and adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
Emergency actions for anaphylaxis
- call an ambulance;
- get rid of the allergen;
- provide drinking water;
- take him to the hospital.
With the development of anaphylaxis, antihistamines and hormones, as first aid for urticaria, are of little effectiveness.
If such measures were used, the doctor should be notified. In this case, the emergency medicine is adrenaline (administered only by a medical specialist). Hives on the face of a child deserve special attention, as swelling can block breathing.
First aid for angioedema
If the airways are clear, but angioedema develops, then at home you can give plenty of fluids and use a second-generation antihistamine:
- "Desloratadine";
- "Loratadine."
First generation drugs for the initial manifestations of the disease in children are not prescribed as a start.
Is hives in children contagious?
Urticaria is an allergic disease. Like any other allergy, it is a feature of the body and cannot be transmitted to another person in any way1. The resulting rashes do not contain any “allergy triggers”. You can't infect her!
Theoretically, the following situation is possible: urticaria in a child is not an independent disease, but a sign of infection. If he passes the infection to another baby, who reacts to it with hives, he will also develop rashes. However, even in this case, you can only blame the child’s parents for bringing the infection to the kindergarten or playground.
Drug treatment for urticaria
All parents should remember that urticaria is a serious allergic disease, and therefore, when its first signs appear, you should definitely seek medical help. The doctor will prescribe all the necessary tests and examinations that will determine the cause of the pathology.
Children are prescribed special antihistamines that reduce itching and skin rashes, and also stimulate the removal of the allergen from the body:
- Doratadine,
- Cetirizine,
- Desloratadine.
If such pharmacological agents are ineffective, glucocorticosteroids, that is, hormonal drugs, can be additionally used.
To accelerate the elimination of the allergen, enterosorbents are used - Smecta, Enterosgel. They should be given to the child for 1-2 weeks. Your doctor will advise you on the exact dosage and duration of treatment.
How to treat urticaria in a child?
Treatment always begins with eliminating the causes. If the situation is simple, and it is clear what exactly became the “trigger” of the disease, it is necessary to protect the child from repeated exposure to this factor. For example, if hives developed after a wasp sting, you just need to try to ensure that the baby no longer encounters these insects. If your toddler is blistered after prescribing a certain drug, treatment by elimination will also not take much time.
There are situations, and they are not isolated, when it is not possible to understand what irritant caused the symptoms of urticaria. This happens especially often if the parents did not consult a doctor in time, thinking that the annoying rash would go away on its own, but this did not happen.
If the irritant is unknown, the child is prescribed treatment in the form of a hypoallergenic diet. All foods containing histamine liberators should be excluded from his diet6. The list of risks includes:
- Bright red and orange fruits: orange, pineapple, tomato, strawberry, etc.
- Chocolate, coffee, cocoa.
- Legumes, including soy products.
- Wheat and other grains containing gluten.
- Fermented cheeses and blue cheeses.
- Marinated, salted, fermented foods.
- Fish and seafood.
- Ham and smoked meats.
- Nuts, seeds.
- Spices, herbs and spicy vegetables such as radishes, horseradish, etc.
- Eggs.
- Honey.
- Spinach.
- Food additives - dyes, preservatives, flavors.
The diet is prescribed for a while until the symptoms disappear. After this, you can begin to return foods to your baby’s diet one at a time, monitoring the body’s reaction.
If within 1–2 months the diet does not bring results, it is necessary to move on to drug treatment. It is prescribed by the doctor who is observing the child.
Diet
A nursing mother and artificial babies cannot afford chaotic nutrition.
All products must be healthy and safe, as they are important for the formation of the skeleton, tissues, and organs. Diet for urticaria in children is of paramount importance, since by adjusting the diet, it is possible to smooth out the signs of the disease and speed up the recovery process. List of permitted and unacceptable products
| PRODUCT GROUP | LIST OF PRODUCTS | |
| Acceptable | Prohibited | |
| Cereals, nuts, beans | Buckwheat, rice, corn | Semolina, cereals, peanuts, soybeans |
| Vegetables fruits | Cauliflower, broccoli, zucchini, pumpkin, potatoes, cucumbers, dark fruits | Red apples, fruits, kiwis, citrus fruits, tomatoes, all bright fruits |
| Dairy products | All, without exception, with medium fat content, provided there is no lactose intolerance | Fatty products, with fragrances and synthetic additives, with a long shelf life |
| Meat, fish, eggs | Rabbit, young beef, turkey, quail | Chicken, pork, fish, caviar, seafood, eggs |
| Desserts, sweets | Dried fruits | Chocolate, honey |
Nutrition should be balanced and varied. The consumption of chips, crackers, semi-finished products and food additives is unacceptable. It is also important to control the amount of water consumed. Urticaria in children under one year of age often appears due to a violation of the mother’s diet.
When should you consult a doctor?
Rashes should cause serious concern among parents and immediately call an ambulance if:
- body temperature above 40 degrees, accompanied by chills and fever;
- the second symptom, after fever, is severe itching and the appearance of spots all over the body;
- the spots are shaped like stars and take on the appearance of hemorrhages;
- breathing is difficult, swelling is observed on the face, neck, and other parts of the body.
At the same time, parents cannot:
- allow itching;
- squeeze out accumulations of pus, burst the formed bubbles yourself;
- use ointments with bright pigmentation (this makes diagnosis difficult).
How to suspect?
The distinctive features of urticaria are the following:
- itchy blisters of various sizes;
- when pulled, the blisters turn pale;
- the short duration of the presence of elements of the rash: the blisters disappear without a trace and appear in a different place;
- possible fever, pain in muscles and joints;
- Often, rapidly growing dense swelling of the eyelids, nose, lips, tongue, and hands appears.
Diagnosis and treatment
To find out why unusual elements appeared on your baby’s body, you should visit a pediatrician. He will examine your baby and refer you to a specialist (infectious disease specialist, allergist or dermatologist) if the cause is not heat rash.
Additional tests will need to be carried out:
- general blood analysis;
- analysis for viral infection;
- scraping from the skin, taking biomaterial for research;
- skin tests to identify the allergen.
Having carried out such a diagnosis, you will find out what caused the rash in an infant or older child. The doctor will prescribe specific treatment that will be aimed at eliminating the disease.
It could be:
- Taking antihistamines for allergies.
- Taking antiviral medications and antibacterial agents.
- Antifungal drugs are prescribed for fungal skin lesions.
- Maintenance therapy to eliminate symptoms - ointments, creams, sprays.
If you follow the advice of a specialist, the disease can be cured as soon as possible. It is important to monitor the baby’s well-being. If it worsens, you should immediately make an appointment to rule out an adverse reaction from medications and choose a more gentle treatment.
Folk remedies
Some traditional methods can also be very useful. For example, there are medicinal plants that have anti-allergenic properties, such as raspberries.
Raspberry decoction is used both internally and externally. You can give it to your baby to drink or add it to medicinal baths. Rosehip decoction is also effective.
A popular remedy for external use is chamomile infusion, which can be bought in pharmacies. It is enough to wipe the areas where the rash is observed.
You can add sage infusion to baths, which will help combat rashes resulting from an allergic reaction, especially if it is accompanied by redness of the skin.
Traditional methods also help well in the fight against herpes. If pain occurs, you can apply ice to the affected areas of the skin for a few minutes or make herbal compresses.
In the prevention of herpes, an important role is played by increasing immune defense, which reduces the risk of the disease. Children from an early age need to be taught the rules of personal hygiene, ensure good nutrition, take vitamins in the autumn and spring periods, and harden children.
By following the doctor's instructions and giving your child the necessary medications, you will speed up his recovery and get rid of possible complications.
Source: vysypanie.ru
Viral or bacterial diseases
Chickenpox
photo of a rash on the back with chickenpox
Chickenpox, or chickenpox, is the first thing children often encounter. This happens more often in kindergarten or elementary school, since you can become infected through contact. Chickenpox pimples often turn into blisters, which are then replaced by crusts.
Such crusts should fall off on their own; they cannot be peeled off. The pimples are smeared with brilliant green, firstly, to cauterize them, and secondly, to monitor the disease: after the last fragment appears, the patient ceases to be contagious. Parents should be attentive to this disease.
Rubella
photo of a rash on the back due to chickenpox
Rubella causes rashes on the baby's back and head, and sometimes on other parts of the body. They appear in the form of pink spots that disappear after five days. Along the way, the lymph nodes become inflamed and small signs of acute respiratory viral infection appear. Lifelong immunity to rubella is developed. But if you don’t get it in childhood, then for a pregnant woman the disease can become a big complication and even an indication for termination of pregnancy.
Measles
The spots on the child’s body begin to merge with each other, affecting the entire area of the body.
This phenomenon is preceded by a runny nose and fever, therefore, having started treating the baby with tablets, parents perceive redness as an allergic reaction.
The disease usually goes away after a week, but is dangerous due to its complications (pneumonia, bronchitis, meningoencephalitis).
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is another dangerous disease, which is accompanied by:
- headache;
- persistent increase in temperature;
- signs of sore throat;
- coating on the tongue;
- begins to rash on the back and stomach, as well as arms and legs;
- The skin dries out and peels.
A characteristic symptom of scarlet fever is that the skin on the hands peels off like a glove, but this happens already during the recovery period, so the diagnosis is sometimes made late.
Scarlet fever can cause complications - affecting the kidneys and heart.
Roseola
Roseola is characterized by an increase in temperature, which does not affect the baby’s well-being, and the appearance of a rash on the arms, back and stomach, which goes away on its own without medical intervention.
Vesiculopustulosis
The rashes take the form of pustules, which are dangerous because, when they burst, they affect nearby areas. Therefore, it is important to wipe the surrounding tissues with alcohol, and cauterize the ulcers themselves with a strong solution of potassium permanganate or brilliant green, which should be done from the edge of the fragment inward. The child should not be bathed or dried so as not to spread the disease throughout the body.
Lichen
If your little one loves to cuddle all the street animals, then don’t be surprised by the appearance of pink spots and pustules on your arms, back, and stomach. You will definitely need to visit a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis and get a course of treatment specifically for your type of lichen, since there are a large number of them, and it’s easy to confuse them.
Allergic
Atopic dermatitis is a prolonged allergic skin reaction. Characteristic signs are itching, scratching of the epidermis, blisters and weeping.
When infected, the lesion expands. The current is most often wavy.
With strophulus, the rash is in the form of dense red nodules, with itching. Sometimes pimples develop into a blister, which leaves brown crusts after healing.
Prevention
In order not to encounter such an unpleasant problem in the future, it is worth remembering simple preventive measures.
Do not allow your baby to overheat. The optimal room temperature is 22 degrees, the water for swimming is 37-38 degrees. It is very important to maintain hygiene. The baby needs to be bathed and washed often, and his diapers changed. Air baths are useful. It is worth monitoring the diet of a baby or a breastfeeding mother. Allergens should be excluded from it as much as possible, including red fruits and berries, citrus fruits, smoked foods, and so on.
Complementary foods must be introduced correctly and carefully. Parents should try to eliminate possible allergens from the baby’s environment as much as possible. It is important to regularly clean the room, carefully choose cosmetics and household products, and monitor the child’s reaction to them.
Source: malutka.pro
Therapy
To treat urticaria in children, medications and some traditional medicine recipes are used, and it is recommended to exclude a number of foods.
Use of drugs
Pediatric specialists consider antihistamines to be the drugs of choice for urticaria in children and adults.
After eliminating the pathogenetic factor in the development of the disease, the following are usually used:
- Clemastine, Fenkarol. They effectively suppress the release of mediators, including histamine, and relieve the inflammatory response. In this way, not only acute but also chronic pathology is treated.
- For urticarial rash, the use of Desloratadine is recommended. This is a selective H1 receptor blocker, which, with minimal side effects, allows you to quickly stop the manifestations of the disease.
- To relieve itching, you can take sedatives, calcium gluconate. Zinc ointment helps soothe skin irritation. In some cases, autohemotherapy or immunoglobulin administration provides assistance.
- In the absence of results from desensitizing therapy, treatment continues with glucocorticoids (Prednisolone).
- If infectious complications arise, broad-spectrum antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins) are prescribed.
- If helminthiasis or fungus is present, fungicidal or anthelmintic drugs are used.
To consolidate the positive result, physiotherapy (Ural irradiation, diathermy, acupuncture) should be added to general therapy.
Traditional methods
Treatment at home involves the use of natural remedies. But before use, you should consult a pediatrician or dermatologist, since some plants may in some cases be allergens.
- In order to calm the nervous system and reduce itching, you should take two large spoons of peppermint and steep it in two glasses of boiling water in a thermos for 2 hours. After filtering, the infusion must be filtered and given to the baby 1-3 tablespoons, three times a day.
- Mix nettle, string, oregano, chamomile, valerian and licorice roots in equal proportions. Brew a large spoonful of the mixture with a glass of boiling water and leave in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. Let the product sit for another 45 minutes. Take after filtration, depending on age. Up to 1 year old should drink a teaspoon, up to 3 years old - a dessert spoon, and older children - a tablespoon, three times a day.
- It is useful to combine oral decoctions and infusions with external therapy. Herbal baths help a lot. Mint, chamomile or string are suitable for them. They can be used in a mixture or separately. For this purpose, 100 g of herb is poured with a liter of boiling water and left in a thermos for 5 hours. After straining, you can add one glass of infusion to the bath during water procedures. Store the finished product for no more than two days in the refrigerator.