Bleeding in the middle of the menstrual cycle can be a consequence of normal physiological processes or a sign of disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system and serious gynecological diseases. Moderate, light bleeding on days 14-16 of the cycle (during ovulation) is considered normal. This condition can last another 1-3 days after ovulation and is accompanied by minor pulling sensations in the lower abdomen. In some cases, a woman’s basal temperature may rise - this is also considered normal and is associated with increased production of progesterone, which is necessary for the successful attachment of the zygote (fertilized egg) to the walls of the uterus.
Bleeding in the middle of the cycle: causes
If the bleeding is profuse, accompanied by a rise in temperature, severe pain, or deterioration in health, you should see a local gynecologist, since such a picture is not typical for a healthy woman. It is very important to describe not only the time of appearance of the discharge and its quantity, but also its appearance. Abnormal discharge may be brown or brown in color, look like blood, or appear as clear (cloudy) mucus streaked with blood. All this is of great importance for diagnosis and allows you to more accurately determine a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe the necessary examination.
What is intermenstrual bleeding?
Intermenstrual bleeding is moderate or heavy bleeding from the genital tract, which can occur in the first half or middle of the cycle. The menstrual cycle in a healthy woman usually lasts 28-30 days, but in individual cases shifts up or down are possible. If the cycle lasts 24 days or 35 days, there is no cause for concern if this cyclicity occurs constantly. The beginning of the cycle is considered the day the menstrual bleeding begins, therefore, the middle of the cycle is the period from 9 to 13 days after the end of menstruation.
Menstrual cycle
There are two types of intermenstrual bleeding:
- metrorrhagia – dysfunctional uterine bleeding resulting from pathological disorders in the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system;
- physiological bleeding - bleeding that is the result of physiological processes in a woman’s body and appears strictly on days 10-16 of the cycle.
They may differ in the amount of blood released, accompanying symptoms, duration of discharge and other symptoms, by which an experienced doctor can immediately classify the pathology.
Diagnostics
Finding out the cause of the possible occurrence of bleeding in the middle of the menstrual cycle is a rather complex question:
- Initially, the doctor needs to talk to the woman and find out from her the possible causes, clarify the history and state of reproductive function, and the conditions under which bleeding occurred.
- Afterwards, an examination is carried out on a gynecological chair.
- Of the laboratory methods, it is mandatory to take a smear for flora and infections , conduct a general clinical blood test, as well as a hormonal profile.
- Of the hormones, the doctor is most interested in the level of progesterone, FSH, prolactin, as well as human chorionic gonadotropin, the pregnancy hormone. The assessment is carried out depending on the day of the menstrual cycle.
- Of the instrumental ones, the main one is ultrasound examination. It can be done at any time during bleeding. It allows you to identify a possible cause determined by the condition of the ovaries, endometrium, as well as the uterus itself and surrounding tissues.
- If necessary, separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is performed , followed by histological examination.
When should you not worry?
If a woman's cycle is irregular, bleeding 7-10 days before her expected period may be menstrual bleeding. There are many factors that can trigger the occurrence of menstruation ahead of schedule. These include:
- taking certain medications;
- severe stress;
- intense physical activity;
- emotional stress;
- hormonal imbalances.
Severe stress can cause uterine bleeding mid-cycle
Even dietary errors can cause early menstruation. For example, heavy consumption of snacks, crackers, spices, spicy and fatty foods, and alcohol negatively affects the condition of all organs of the female body, including the reproductive system. If a woman abuses harmful products, she is more likely to experience cyclical disturbances between menstruation and diseases of the female genital area.
Consumption of harmful products leads to cyclical disturbances between menstruation and diseases of the female genital area
Moderate bleeding during ovulation and the next 2-3 days is also considered normal. This sign indicates that a mature egg is ready for fertilization. Bloody discharge in this case occurs due to the rupture of the dominant follicle, which “releases” a mature egg into the fallopian tube, where it can unite with a sperm and form a zygote.
Important! Light bleeding during and after ovulation is called “ovulatory syndrome.” During this period, a woman may experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lower back and coccygeal region. Temperature (including basal values) also usually increases by 0.5°-1°. General health may deteriorate: weakness, drowsiness appear, and performance decreases. All these symptoms should completely disappear on the 16-17th day of the cycle. If this does not happen, you should consult a doctor.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
Pathological causes of bloody secretion rejection
Blood discharge between menstruation does not always fall within the physiological norm. A significant role in establishing the root causes of what is happening is played by the symptoms accompanying rejection and the nature of secretion throughout the entire menstrual cycle.
Gynecologists say that there are a number of signs, in combination with any of which the appearance of blood spots is considered as a symptom of pathology. These include:
- bloody or brown dark discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- itching in the groin area;
- burning during urination;
- constant nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- acute pain syndrome in the “groin triangle”;
- irregular indicators in tests for hormone levels;
- increased body temperature;
- the appearance of reddish blisters in the groin area;
- changes in the menstrual cycle.
It is worth noting that with pathological changes in the reproductive system, “neighboring” organs, for example, the rectum, may become ill.
A number of pathologies can cause intermenstrual bleeding, aggravated by the above symptoms. Let's take a closer look at them.
Endometritis
This disease is characterized by a strong inflammatory process in endometrial tissue. Experts say that a similar phenomenon may occur due to complications received during the abortion process. At an early stage, symptoms of the disease include a sharp increase in body temperature and constant nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
The chronic stage of endometritis is manifested by intermenstrual bleeding. Sometimes they are indicated in the middle of the cycle, but more often spotting with a smell in women is observed after menstruation.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Very often, the cause of spotting between periods is infectious diseases transmitted from partner to partner during sexual intercourse. Regardless of the bacteriological type of infection, brown secretion throughout the entire cycle is accompanied by characteristic discomfort. These include:
- The presence of a characteristic nauseating odor in the rejected substance, which many women associate with the aroma of rotten fish.
- The appearance of severe itching in the groin area.
- Presence of blisters or pimples on the labia.
- The presence of yellow or putrid green clots in the rejected secretions;
- Increased body temperature.
- Discharge with blood after sexual intercourse.
- Burning during urination.
For successful treatment of sexually transmitted diseases, parallel therapy of partners is necessary.
The course of treatment very often includes two stages. The first is antibiotic exposure, and the second is maintenance therapy. After prescribing a course of treatment, you must strictly follow the doctor’s instructions and be observed by a specialist throughout the entire period of therapy. The transition of infectious diseases to the chronic stage is fraught not only with acquired infertility, but also with death.
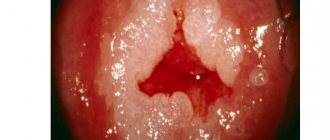
Cervical erosion
This disease is characterized by the appearance of scars and ulcers in the cavities of the organs of the reproductive system. Experts say that erosion is a disease with mild symptoms.
In the early stages, a woman can find out about the presence of the disease only during an examination in a gynecological chair. Moreover, the development of erosion is quite slow and the disease may not manifest itself for many years.
Unidentified erosion that has become chronic can cause brown discharge between periods. One of the complications accompanying this disease is the development of acquired infertility.
Pregnancy
A positive test indicating pregnancy brings not only a lot of positive emotions, but also a lot of anxiety and fears associated with worries about the health of the fetus and the woman in labor. In the next nine months, it is necessary to carefully monitor the woman’s health and the discharge that signals the condition of the fetus and reproductive system.
An alarming symptom indicating abnormalities during pregnancy is mucous discharge mixed with blood that appears during the calendar cycle. Their reasons can be varied. Gynecologists admit the presence of blood secretion in the usual cycle in the early stages of gestation.
This phenomenon may indicate the attachment of a fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus or hormonal changes characteristic of the perinatal period.
Systematic mucous rejection with blood, which can be constantly discharged for several days, depending on the period, is a symptom of frozen pregnancy, premature placental abruption or miscarriage. Study the characteristics of vaginal discharge after a miscarriage using the link.
Experts recommend undergoing timely examinations and taking supportive therapy so that the development of the fetus occurs organically.
If disturbing symptoms appear, accompanied by blood secretion and pain in the lower abdomen, both in the first and last months of pregnancy, you must immediately contact the gynecologist who is observing the woman!
Tumors and neoplasms
Discharge of blood between periods and disruptions in the calendar menstrual cycle may indicate the presence of tumors in the organs of the woman’s reproductive system.
Based on statistical data, experts say that the most common reasons that provoke the occurrence of neoplasms are hormonal imbalances during menopause or complications resulting from an abortion.
One of the most common types of tumors are polyps. Diagnosing the disease at an early stage is very simple; all you need is a series of examinations.
Read the article at the link on how to avoid surgery and whether a polyp can come out with menstruation.
The situation is complicated by the fact that tumors do not have pronounced symptoms at an early stage. Women who are faced with this pathology can identify several signs indicating the presence of a tumor:
- Constant feeling of fatigue.
- Discomfort during gastric emptying.
- Blood secretion at any period of the cycle.
- Low hemoglobin.
- Changes in the calendar menstruation cycle.
If a woman experiences the above symptoms, aggravated by spotting, especially during menopause, she should immediately consult a specialist!
Hormonal imbalances
The causes of intermenstrual spotting may lie in a hormonal imbalance that occurs against the background of thyroid dysfunction or disruption of the adrenal glands. In this case, spotting secretion may be bleeding in the middle of the cycle or a “shift” in the calendar menstruation.
Women who are faced with this disease claim that if there is a hormonal imbalance, menstruation can begin at any time, but always before the onset of the critical days, the lower abdomen begins to ache strongly.
The reasons that trigger the processes leading to hormonal disorders are extremely diverse. But, from the general mass, a number of the most common ones stand out:
- Eating disorders.
- Physical exercise.
- Change of climatic zones.
- Presence of stressful situations.
- Lack of daily routine.
Hormonal imbalances occur “spontaneously”, but without proper treatment, such a pathology can cause irreparable harm to the female body. To monitor hormone levels, it is necessary to take appropriate tests at least once every few months.
Intermenstrual mucous bleeding, in most cases, is a physiological norm. But the presence of aggravating symptoms may indicate a possible pathological process affecting the reproductive system. To diagnose the disease, you must immediately contact a specialist and undergo a series of tests that will help you create a correct medical history and find out the root cause of what is happening!
Early pregnancy symptom
Brown spotting may be a sign of pregnancy. In this case, they are usually accompanied by painful sensations in the lower abdomen, where the uterus is located, and other general symptoms, which include:
- dizziness;
- poor appetite;
- nausea upon waking (some women may feel nauseous throughout the day);
- weakness and drowsiness;
- forgetfulness;
- swelling of the mammary glands.
Signs of pregnancy
To check whether a woman is pregnant or not, you can use a test to determine the level of hCG in morning urine or do an ultrasound with a transvaginal sensor (but it should be borne in mind that in very short periods such an ultrasound may not be informative).
Important! At the slightest suspicion of pregnancy, you should consult a doctor to rule out an ectopic position of the fertilized egg. Brown discharge during early pregnancy can also indicate a miscarriage, so consultation with a gynecologist for these symptoms is necessary.
Danger of bleeding
Seeing a doctor after brown discharge appears is especially important when it is a sign of tumors. Just one timely visit to the gynecologist will give you a chance to stop the progression of the disease. If bleeding suddenly begins, and your period is still far away, you should immediately call an ambulance.
It is not always possible to predict with certainty whether the cause of bleeding is ovulation or a cancerous tumor. Therefore, you should not postpone a visit to a specialist until more alarming symptoms appear or wait until it goes away on its own. Health requires careful attention.
Oral contraceptives
Oral contraceptives are contraceptives for women in the form of tablets or capsules (for oral administration) containing hormones. Most often, women are prescribed medications based on estrogen or progesterone. It can be:
- "Diana-35";
- "Yarina";
- "Janine", etc.
Mechanism of action of hormonal contraceptives
Drugs in this group can be used to protect against unwanted pregnancy or treat gynecological diseases, for example, endometriosis of the uterus. In case of uterine bleeding, women can also be prescribed increased doses of hormones, but this method of stopping bleeding cannot be used independently, especially if the woman has a history of benign or malignant formations.
You need to start taking oral contraceptives from the 1st day of the cycle (in some cases, the doctor may prescribe an appointment from 3-5 days from the start of menstruation). If a woman stops taking the drug before the end of the course (21 days), “withdrawal bleeding” may begin. This is profuse, breakthrough uterine bleeding, which in most cases can only be stopped using a curettage procedure or vacuum aspiration.
Oral contraceptives may cause bleeding mid-cycle
Important ! Emergency contraceptive medications (" Postinor ", " Escapelle " or " Ginepriston ") can also cause heavy bleeding, so after taking them, a woman must be under medical supervision for 10-14 days.
Types of spotting
To understand the reasons for the occurrence of the phenomenon, you need to understand what kind of spotting it is in the middle of the cycle. This is what is called scanty mucous blood discharge from the vagina.
The basis of such secretions contains a mucous secretion produced by the glands of the female genital organs. For various reasons, a certain amount of blood enters it, which, when released, mixes with mucus and oxygen, acquiring a certain shade. It all depends on where exactly the blood has clotted, what its composition is, the content of the mucous secretion, and the characteristics of the body.
This mucus is produced in moderate quantities and has such a consistency that when it gets on a panty liner or underwear, it quickly spreads and is absorbed, creating the effect of unevenly smeared stains. You can see their photos below.
Pink discharge with blood
Brown discharge
Light red discharge
Spotting creamy discharge
They occur at the end of the follicular, throughout the ovulatory and early luteal phases of the menstrual cycle. It can be thick white, cream, liquid pink, dark brown, brown, light brown vaginal discharge. Normally there are few of them, they are odorless and are not accompanied by unpleasant sensations.
Creamy, yellow, curdled, stretchy, bloody, profuse, dark, watery, unpleasant-smelling discharge, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, itching, weakness and other inconvenient symptoms, indicate the pathological etymology of such bleeding.
Learn what the nature of your menstrual discharge should be when taking Jess or Jess Plus by following the link.
What factors can trigger bleeding in the middle of the cycle?
Very often, women who have an intrauterine device installed, a local hormonal agent that prevents fertilization, complain about mucous discharge streaked with blood. The spiral (as well as the rings) must be changed after a certain period of time. If this is not done, an inflammatory process may begin, accompanied by an increase in temperature and moderate bleeding. Improper installation of the spiral can also cause injury to the mucous membranes and minor bleeding.
Inflammation of the uterus and fallopian tubes causes bleeding
Other factors that can cause mid-cycle bleeding include:
- chronic state of stress (divorce, hard work, scandalous atmosphere at home);
- lifting heavy objects (rearranging furniture, lifting heavy bags up stairs);
- injuries to the genitals and vagina (for example, when using sex toys);
- lack of vitamins C, A and E, involved in the functioning of the hematopoietic system;
- active or rough sexual intercourse.
Important! If bleeding begins 1-2 days after visiting a gynecologist, it may be caused by medical procedures and the use of gynecological instruments. Such discharge should not last more than 24-48 hours. If the bleeding does not stop, you should consult a doctor.
Video - Intermenstrual discharge
Additional reasons
The functioning of the reproductive system is affected by even a slight deviation of the hormone level from the norm. A similar phenomenon can occur as a result of:
- Metabolic disorders or development of obesity.
- Use of hormonal drugs. They may be prescribed to treat infertility or menopause. The use of such medications leads to menstrual irregularities. One of them may be the appearance of spotting in the middle of the cycle.
- Lack of vitamins. This phenomenon develops due to poor nutrition. If a woman has vitamin deficiency, there is a disruption in the production of hormones. This occurs due to a lack of substances that are required to carry out the process. Additionally, there is difficulty in cell regeneration. As a result, pathological processes begin to develop in the tissues of the genital organs. There is a change in the structure of blood vessels. All this leads to the appearance of blood in the leucorrhoea.
- Stress. This condition can occur as a result of severe emotional overload, fatigue or anxiety. Stress affects the production of hormones in the body. As a result of changes in hormonal levels, the body malfunctions.
Bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle can occur in women with reduced blood clotting. Similar phenomena can be observed if the patient takes medications that have a decisive effect on the blood.
Possible diseases
If bleeding from the genital tract, which began in the middle of the menstrual cycle, is profuse, accompanied by other pathological symptoms, pain, or deterioration in health, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a gynecologist to exclude possible diseases of the genitourinary and reproductive systems.
Pathologies of the mucous membrane of the uterus
The most common cause of bleeding on days 10-14 of the cycle is pathology of the mucous membrane of the uterus (endometrium). Heavy, breakthrough uterine bleeding is often observed with excessive growth of the epithelial layer - endometrial hyperplasia. The disease is caused by an excess of sex hormones - progesterone and estrogen - and requires correction using hormonal medications. Often a woman is prescribed diagnostic curettage, during which the doctor uses a special surgical knife (curette) to remove the entire endometrium and send it for histological examination.
Endometriosis of the uterus
Other common endometrial pathologies are endometriosis and endometritis. Endometriosis is the pathological growth of mucosal tissue beyond this layer. If inflammation joins the process, the woman is diagnosed with endometritis. All disturbances in the functioning of the endometrium are accompanied by characteristic symptoms, including:
- pulling sensations in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- menstrual irregularities;
- bloody spot between periods;
- problems with conception;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- insufficient production of vaginal secretion (lubrication).
Description of endometritis
Note ! Endometrial pathologies increase the risk of malignant processes several times, so you should not delay consulting a doctor.
Tumor processes
With various types of tumors, bleeding is chronic and appears in almost every cycle. The discharge may have a red or brown color (less often a light pink tint), is not accompanied by painful sensations and is usually of moderate intensity.
Types of tumors in the uterus, ovaries and other organs of the reproductive system
| Type of education | Image | What it is? | Characteristics of intermenstrual bleeding in this type of tumor |
| Myoma | Benign tumor of the myometrium - the muscle layer that makes up the walls of the uterus | Streamly, profuse bleeding. Blood surges and blood clots may occur. It is difficult to stop with the help of medicinal methods - in most cases, surgical intervention is required (if we are talking about the diffuse form) | |
| Polyp | Proliferation of the epithelial layer (its glandular structure) against the background of inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system. 94% of polyps are benign tumors | Rare, light discharge of blood (a few drops) in the middle or second half of the cycle. Not accompanied by any other symptoms | |
| Fibroma | Benign nodular tumor of the muscular layer of the uterus | Breakthrough bleeding accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, headache, dizziness and other symptoms of deterioration of health | |
| Sarcoma | A malignant tumor that can occur in the muscle layer, connective fibers, embryonic rudiments | Bleeding can take any form, but most often it is brown spotting from days 10 to 18 of the cycle |
Important! It is impossible to determine the signs of a malignant process on your own. This will require an examination by a doctor, consultation with an oncologist, a biopsy of damaged tissue, colposcopy and other instrumental examination methods. Uterine cancer is curable only in 8-9% of cases and only if diagnosed in a timely manner, so if there is any bleeding (especially if it recurs frequently), you should consult a doctor.
Intermenstrual bleeding in most cases is normal, but sometimes such symptoms can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the most important organs of the reproductive system and even malignant processes. Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of the pathology after examination, collecting an anamnesis and studying the examination results. In some cases, differential diagnosis with other female diseases may be required, so it is better not to delay contacting a gynecologist.
Video - Bloody discharge between periods
Physiological causes of bloody secretion rejection
Gynecologists say that the rejection of discharge containing blood in the middle of the cycle does not always indicate the presence of pathological processes affecting the reproductive organs. Depending on the external factors affecting the body and the physiological characteristics of the woman, this phenomenon may be completely normal and does not require medical intervention. Gynecology identifies a number of conditions in which brown spotting released in the middle of the cycle does not pose a threat to health.
Find out why you experience spotting a week before your period.
Juvenile bleeding
The arrival of the first menstruation, menarche, indicates the girl’s puberty and the final stage in the process of formation of the organs of the reproductive system. This period is characterized by the absence of a clearly formed, monthly cycle of critical days.
Gynecologists say that the process of forming temporary periodization can last up to six months. In this interval, the appearance of red discharge in the middle of the expected cycle is a physiological norm and does not require contacting a specialist. But the observation of uncharacteristic discharge mixed with blood for longer than the established period indicates the need to contact a specialist.
The root cause of juvenile bleeding may lie in an imbalance of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones.
Ovulation
Ovulation refers to the period of the female cycle during which the formed egg leaves the follicle. In this case, intermenstrual bleeding can be caused by several reasons:
- A sharp hormonal surge. This phenomenon does not indicate the presence of pathology. Experts say that an increase in estrogen levels during ovulation is a physiological norm. Hormonal levels stabilize on their own a few days after the end of this period of the menstrual cycle.
- Injury to the endometrium during the movement of the fertilized egg or its attachment to the surface of the uterus.
These phenomena lie within the physiological norm only in the absence of accompanying discomfort and stability in the periodization of the calendar cycle.
Doctors say that normal secretion during ovulation should be different:
- Scarcity. Discharge during this period of the menstrual cycle should be barely noticeable and have a spotting character.
- No unpleasant odor. Please note that ovulation secretion should not have a strong, nauseating odor. The mucous fluid secreted during this period has a light, slightly perceptible odor of iron.
- No discomfort. During ovulation, rejection of bloody secretion should not be accompanied by girdle pain affecting the lower abdomen and lower back, burning during urination or itching in the groin area.
If the described spotting during ovulation is intense or accompanied by acute pain, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Such symptoms may indicate a malfunction of the reproductive organs or the onset of uterine bleeding.
Sexual intercourse
The appearance of bleeding not during menstruation, but after sexual intercourse in any phase of the cycle, may indicate excessive intensity of sex or slight damage to the vagina associated with an inappropriate position for a woman or too large a size of the sexual partner’s dignity.
Some women noted the appearance of ichor after sexual intercourse due to insufficient hydration of the genitals during intercourse. Such secretion should be rejected painlessly and, visually, resemble ichor.
The average time interval allowing for the presence of non-pathological spotting is no more than 3 days from the moment of sexual intercourse.
The process of rejection of secretions, caused by the occurrence of microtraumas in the genital organs during sex, most often ends on its own and does not require medical intervention. But if a woman notices an increase in the volume of rejected bloody secretion or the presence of clots in it, it is necessary to consult a specialist. In this case, we may be talking about a rupture of a blood vessel in the endometrial tissue.
Oral contraception
Bleeding from the middle of the cycle may be a response of the female body to a change or the introduction of a new means of oral contraception. Experts say that if spotting appears or scanty periods begin while taking birth control pills for three months after starting to take the drug, then this is not a side effect and is quite physiological. The presence of discharge when taking birth control pills for a long time and in large volumes throughout all phases of the cycle indicates the need to stop using this contraceptive.
Emergency contraceptive drugs such as Postinor, Escapelle or Gynepristone deserve special attention. Such medications can not only provoke bleeding from the uterus in the middle of the cycle, but also make adjustments to the established cyclicity of menstruation. After Escapel and Postinor, periods do not come regularly, long delays occur. Many women, while taking emergency contraception, noted mild pain in the lower abdomen and a pulling sensation in the lower back. The use of these contraceptives is permissible only under the supervision of a gynecologist! Read more about bloody discharge after Postinor and brown discharge after Escapel.
Climax
Premenopause and menopause itself are characterized by the appearance of bloody discharge after menstruation. It is worth noting that some women noted spotting before menstruation. This daub is scanty in nature and is rejected against the background of accompanying symptoms. These include:
- increased sweating;
- fatigue;
- a sharp change in psycho-emotional state.
The average age of menopause and menopause is 40–45 years.
It is worth noting that spotting during this period of the cycle should be painless and not very abundant. An increase in the volume of rejected secretion and the appearance of a pronounced scarlet tint may indicate the presence of a malignant tumor. The designation of such symptoms requires immediate contact with a gynecologist!
To eliminate the discomfort caused by menopause and menopause, a specialist may advise the woman on hormone therapy. Medicines in this spectrum will help not only reduce the “blow” caused to the body by hormonal changes, but also neutralize the accompanying symptoms.
Postpartum period
Regardless of the method of delivery, whether natural childbirth or cesarean section, a woman’s body endures serious stress. This has a particularly acute effect on the genitals and hormonal levels. Gynecologists claim that the menstrual cycle after childbirth, in fact, forms anew, as before menarche.
Many women recovering from childbirth have noted the appearance of dark discharge between periods. The secretion of this type is completely physiological. The reason for its appearance, in addition to “tuning” the cyclicity of the menstrual cycle, can be breastfeeding or jumps in estrogen levels. The amount of brown secretion rejected during the intermenstrual postpartum period should not be large. Visually, it resembles blood ichor present in white clots of mucus.
It is necessary to take into account that an increase in the volume of constantly rejected secretions during this period may be a symptom of uterine or vaginal bleeding. Diagnosing yourself with such symptoms is a serious reason to contact a gynecologist. Elimination of this problem, in most cases, is carried out surgically and involves cleaning.
Intrauterine device
Experts say that the use of this method of contraception, most often, can cause bleeding in the middle of the menstrual cycle. This phenomenon is associated with injury to the mucous membrane of the reproductive organs. Discharge of this kind should be insignificant and its duration should not exceed several days after the introduction of the spiral.
It is worth remembering that if the secretion does not decrease, but rather increases in volume and is accompanied by discomfort in the genital area, you should consult a doctor. In this case, it is advisable to remove this contraceptive and select a medicinal analogue.
Diagnosis and treatment of disorders
Diagnosis and treatment of any menstrual irregularities should be carried out only by a medical specialist. Intermenstrual bleeding is no exception. Self-diagnosis and therapy are unacceptable. Also, the causes of this phenomenon cannot be attributed solely to any nervous shocks or consequences of changes in diet or medication. Only a gynecologist, after conducting an examination, can determine the true cause of the discharge and, if necessary, prescribe the correct treatment. After all, not only physiological processes cause intermenstrual bleeding, but also a serious pathology, which is impossible to establish and treat on your own.
When discharge is a result of ovulation
The course of pathologies should not be ruled out.
In diseases, the discharge has an uncharacteristic odor and an unpleasant odor. The consistency may also differ significantly. The main root causes of spotting:
- bacterial vaginosis;
- colpitis;
- candidiasis.
When pathogenic microorganisms enter the body, an inflammatory process occurs. This is facilitated by hypothermia, hormonal imbalances and weakened immunity. Usually the disease is accompanied by itching and burning in the genitals. Urination becomes painful. There is discomfort in the abdominal cavity.
If discharge occurs between menstruation, it is important to pay attention to its nature. Color plays a significant role. Dark spotting usually indicates that a woman is taking birth control medications.
- If bloody, brown discharge appears in the middle of the cycle, between menstruation and the woman is not taking hormonal contraceptives
- If at the same time there is pain in the lower abdomen, itching, burning and dryness in the vagina, increased body temperature, painful sexual intercourse
- If a woman has been in menopause for a long time and has not had a period for more than a year
- If you regularly experience spotting after sex
Drops of blood give the brown, dark color to discharge in women. In absolutely healthy women, this can be observed in the following situations:
- A few days or hours before your period - a sign of approaching menstruation
- After your period, a few days are normal, as the uterus gets rid of unnecessary drops of blood.
- In the middle of the cycle for those taking birth control pills
- Violent sex - if a woman does not have full arousal and does not develop a sufficient amount of lubrication, this damages the vaginal mucosa and creates microtraumas
During the first sex and 2-3 subsequent sexual intercourses, when a girl is just starting to have sex.
Vaginal discharge serves to clean the genital tract, as well as protect it from various infections. But this is normal, since there are also pathological bleeding in the middle of the cycle. Since they appear not during menstruation, which is normal, but at other times, this indicates the presence of a certain problem that must be clarified.
Mucus, blood clots, liquid bleeding - all this accompanies a woman throughout the entire menstrual cycle. These substances are produced by the genitals or represent remnants of unclaimed biological material. The intensity of discharge is very different - during menstruation it increases significantly, while at other times it decreases noticeably.
Their number and composition changes after the red days of the calendar have ended, as well as upon the onset of ovulation. Normally, they should not stain underwear (except during menstruation). The color of normal non-menstrual discharge is white or yellowish.
Accordingly, bleeding in the middle of the cycle indicates that certain pathological or specific processes have arisen in the body. This is mainly true for those cases when they are very abundant and cause a lot of discomfort.
Very often, intermenstrual discharge indicates that some kind of disease is developing in the body.
The structure of a woman’s genital organs is quite specific, which is why they are susceptible to many diseases, both dangerous and not so dangerous. In any case, they will definitely need to be diagnosed and treated.
Medicine has a sufficient level of knowledge about ailments that may cause bleeding in the middle of the cycle:
- Endometriosis is a complex disease characterized by pathological growth of the upper layer of the uterine lining - the endometrium. Characteristic symptoms are significant pain in the lower abdomen, constant bleeding, and in some cases, infertility develops. Lack of proper treatment leads to the fact that endometrial cells invade not only the outer part of the uterus, but also other genital organs. Moreover, once they enter the bloodstream, they spread throughout the body. There have been cases when they were placed in the eyes, which caused such a specific syndrome as “bloody tears”;
- endometritis is a classic inflammation of the uterus. Red discharge in the middle of the cycle is very often associated with this particular problem. The inflammatory process can develop against the background of an infection or an abortion. This disease is also characterized by severe pain in the abdomen. An important symptom is an increase in temperature;
- infectious diseases. Any infection, regardless of its etiology, always leads to inflammation. This is especially true for the chronic stages of development of infectious diseases;
- early miscarriage - this extremely unpleasant situation can be triggered by various factors. In this case, bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle will contain the embryo, as well as all kinds of auxiliary biological material, accordingly, they are very abundant and painful;
- polycystic ovary syndrome is a very serious pathology that requires immediate treatment. The disease provokes a lack of progesterone in the blood, which disrupts the normal functioning of the entire reproductive system, as well as the menstrual cycle. In advanced cases, the disease leads to incurable infertility;
- Uterine fibroids - this very common disease is characterized by irregular scarlet discharge in the middle of the cycle. The situation requires immediate resolution, as it threatens serious complications;
- fibroids and uterine polyps;
- oncological diseases, primarily of the uterus. There is no need to say anything here - such a pathology directly threatens not only the health, but also the life of a woman;
- therapeutic or diagnostic procedures that caused injury to the uterus. For example, this could be a biopsy or cauterization;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland. It is responsible for the production of hormones, so if it does not work as it should, then it will be impossible to avoid hormonal balance;
- rupture of the ovary - this problem is characterized not only by bloody discharge with mucus in the middle of the cycle, but also by sharp pain on one side of the abdomen. Heavy bleeding threatens significant blood loss, so it is very important to seek professional help in a timely manner.
Diagnosing most of the above diseases using modern techniques is not difficult. But for this, of course, you need to go to the hospital in a timely manner. Delay can have a significant impact on a woman's reproductive function, as well as her overall health.
Pathological discharge that appears outside the menstrual period may indicate the presence of any diseases that are transmitted as a result of intimacy. If this is so, then specific symptoms should be noted:
- constant or recurrent pain in the lower pelvis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- chronic candidiasis;
- low-grade body temperature;
- fertilization of the egg is impossible, even if healthy sperm enter the uterus.
Infection with infections such as chlamydia, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, etc. occurs through direct sexual contact between a healthy person and a sick person. Their characteristic feature is that they may not manifest themselves for a long time, which makes their diagnosis more difficult.
However, they are very dangerous, as they lead to chronic inflammation of the reproductive system, infertility, impotence, liver disease and many other problems.
If in the middle of the cycle there is blood discharge with mucus, light and spotting, then this is almost guaranteed to indicate that an STI is present in the body.
Treatment of sexually transmitted diseases is complex. Antibiotics, antiprotozoal drugs, antiviral agents, vaginal suppositories, and immunomodulators are prescribed. You need to understand that against the background of such ailments, the immune system deteriorates, which means you will need to worry about protection from other bacteria and viruses.
- Hormonal contraceptives
The essence of hormonal drugs is that they literally block the release of the egg from the follicle, as a result of which fertilization is excluded.
However, there is also a negative side to the coin - such drugs directly affect the production of hormones, which can lead to hormonal imbalances.
As a result, discharge may not occur at all when expected.
The same applies to the intrauterine device. It does not affect hormones, but can damage the rather delicate lining of the uterus, which will cause bleeding. Why do I have bleeding in the middle of my cycle? It is quite possible that the reason lies in incorrectly selected vaginal and oral contraceptives.
Already during the first days of pregnancy, literally immediately after the sperm enters the egg, colossal changes occur in the female body. This is especially true for hormonal levels.
Migration of a fertilized egg through the tubes and uterus is a natural process that may be accompanied by minor vaginal discharge of a bloody nature. The reason is that the fetus needs to attach to one of the walls of the uterus - this process is relatively traumatic, as it leads to slight damage to the endometrial layer.
It is important that such processes should in no case be accompanied by painful sensations. If they are, it means something is going wrong, and therefore it’s time to contact a gynecologist.
For some reason, bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle frightens many women. However, they can be completely harmless. Ovulation is the process of the release of a mature egg from the follicle.
It usually occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, accompanied by significant hormonal fluctuations, changes in the condition of the endometrium and the uterus itself, as well as a slight increase in basal body temperature.
Ovulation lasts no more than a few days. It is believed that this is the most optimal period for conceiving a child.
Causes of pathological discharge
Brown discharge at the beginning, middle or end of the cycle in some cases is a symptom of concomitant diseases in the body.
In this case, pathological leucorrhoea can be recognized by the presence of the following signs:
- impurities in the form of blood clots and fragments of the uterine mucosa;
- unpleasant odor;
- pus;
- intense discharge;
- the color changes over time to a bright red hue;
- pain syndrome in the lower abdomen;
- general malaise of the body.
The most common diseases that are characterized by the appearance of brown discharge:
- infectious and inflammatory pathologies;
- cervical erosion;
- malignant tumors;
- myoma;
- endometriosis;
- oncology;
- hormonal imbalances;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Endometriosis
Regular brown discharge in the middle of the cycle, characterized by a darker shade, is the main symptom of the development of endometriosis. With this disease, the cells of the lining of the uterus actively divide and extend far beyond the organ. But at the same time, they still react to the established hormonal cycle and therefore provoke the formation of the endometrium in a new place.
In this regard, regular bleeding occurs, accompanied by inflammation of adjacent tissues. If left untreated, endometriosis can cause infertility.
The development of the disease is caused by a mutation of cells in the muscles of the uterus. As a result, a benign neoplasm is formed, which, with further growth, injures the blood vessels and mucous membrane of the organ. The peculiarity of fibroids is that they do not grow into further tissues.
Small growths can develop asymptomatically, without causing any discomfort to the woman. Large specimens often cause brown secretion to appear in the middle of the cycle. Therefore, it is important to control their growth and further development, since sometimes they provoke uterine bleeding, which can only be stopped with surgery.
Cervical erosion
Brown discharge with this pathology occurs not only in the middle of the cycle. As the disease develops, characteristic ulcers appear on the mucous membrane directly near the cervix. The danger of the disease is that it can provoke the development of cancer.
The disease can be detected by blood secretion after each sexual intercourse or after a medical examination, that is, when there is direct contact with the cervix. The final diagnosis is determined by a specialist after additional examination using a colposcope.
The appearance of brown discharge in a woman who is sexually active, ignoring the rules of contraception, should be an alarming signal that she should be examined by a specialist.
If the secretion is accompanied by the smell of rotten fish and there is a general malaise of the body, then most likely this is a sign of a sexually transmitted disease (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis). Therefore, it is recommended to undergo an examination and a prescribed course of treatment to avoid irreversible consequences. Sometimes the cause of discharge is genital herpes and papillomavirus.
When pathological secretion is accompanied by a general malaise of the whole body, as well as aching pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back, and at the same time the body temperature rises noticeably, then most likely the cause of its occurrence is inflammation of the genital organs, bladder or rectum.
To prevent the disease from subsequently becoming chronic, you should contact an experienced specialist and undergo a course of therapy.
Doctors' recommendations
Depending on the intensity, duration of bleeding and the presence of accompanying symptoms, gynecologists' recommendations will vary. If vaginal bleeding occurs, immediate hospitalization is necessary.
If the discharge is not abundant, then it is necessary to understand the reasons for its appearance. If infectious and inflammatory diseases, hormonal disorders or other pathologies are detected, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Patients with ovulatory bleeding are advised to reduce physical activity in the middle of the cycle and avoid stress. To restore health, vitamin complexes are selected. With prolonged bleeding, anemia may develop, so special attention is paid to the intake of iron in the body.
Types of brown discharge between periods
Just by the appearance of the discharge you can understand its approximate cause. The secretion from the genitals can be dark or light brown, scanty or abundant. It may be accompanied by nagging pain or be completely painless. In certain diseases, brown spotting in the middle of the cycle contains blood impurities. Sometimes a girl is bothered by itching.
Dark brown discharge mid-cycle
Brown spotting mid-cycle may occur in women taking combined oral contraceptives. The secretion is not abundant, it can be light or darker. The lighter the shade, the less blood is released. This symptom is more favorable.
A dark brown secretion when taking birth control is a reason to contact a gynecologist. He will order tests to check the woman’s hormonal levels and decide on the advisability of replacing the contraceptive.
The appearance of secretion clearly in the middle of menstruation indicates a connection between the symptom and ovulation. One of the diseases that leads to the formation of a dark brown secretion at the time of ovulation is an ovarian cyst. The disease is characterized by the presence of a cavity in one or two uterine appendages. This is manifested by disruption of the ovary, in particular, failure of ovulation.
Light brown discharge mid-cycle
As noted above, a light brown secretion appears when taking oral contraceptives. Normally, spotting goes away after a couple of menstrual cycles as the body adapts to the pills.
Light vaginal secretions are the first sign of pregnancy for many women. It appears when the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. As a rule, this occurs on the 9th day after conception. But the time frame can vary from a week to 23 days.
Scanty brown discharge mid-cycle
The cause of spotting between periods can be inflammatory diseases of the uterus and its appendages. Such pathologies include:
- endometritis - inflammation of the inner layer of the uterine wall;
- salpingitis - an inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes;
- colpitis – pathology of the cervix;
- adnexitis - inflammation of the ovaries.
Diseases develop due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the uterus and appendage: staphylococci, E. coli, streptococci.
Thrush with bleeding
Attention! If the discharge is white without blood, but resembles egg white, this may be a symptom of a disease such as thrush. Today it is being successfully treated. Thrush with blood can be dangerous, you should consult a doctor. A woman’s body, at the very beginning after childbirth, is very vulnerable. The reproductive system is especially sensitive to any change. It is at this time that candida can begin to develop rapidly. During this period, women in labor experience peculiar separations after delivery - lochia.
They include:
- rejected tissues,
- mucous fluid,
- Blood.
It is against this background that a woman who has given birth can detect liquid discharge with blood due to thrush in the first month after delivery.
Treatment of pathological causes of discharge: drugs, suppositories
Spotting in the middle of the cycle can be effectively treated with tablets and suppositories. But only when the bleeding is not caused by pathology.
List of drugs:
- if the discharge is accompanied by severe pain, then anti-inflammatory suppositories with an analgesic effect are prescribed; oral administration is also possible. Candles are more effective;
- be sure to take hormonal medications to even out the cycle (if there was a failure);
- for infectious diseases, antibiotics are prescribed (can be in the form of tablets or suppositories);
- a complex of vitamins and agents that strengthen the immune system;
- hemostatic agents, if it is necessary to stop bleeding and there is a problem with blood clotting;
- Douching with herbal decoctions may be prescribed.
If no significant deviations are detected during the examination, then treatment may last no more than a week (although you will need to drink the vitamin complex for a month). If time was lost, then treatment will last from 3 weeks to several months.
When to worry
If there are some manifestations, contacting a doctor should be mandatory. The following symptoms accompanying intermenstrual discharge require contacting a doctor:
- increased abundance of discharge;
- the presence of an unpleasant odor from the daub;
- itching and burning;
- severe pain during sexual intercourse;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness;
- constant drowsiness;
You should be concerned if pain or itching begins
- excessively prolonged discharge;
- the presence of clots in the daub;
- constant appearance of intermenstrual bloody secretion.
The listed signs, as a rule, cannot be physiological. A comprehensive diagnosis will help to establish the true cause of the disorder.
Symptoms of uterine bleeding: when do you need to see a doctor urgently?
Uterine bleeding can be very dangerous to a woman’s health and life, and therefore requires urgent medical attention. Alarming symptoms cannot be ignored.
Symptoms of uterine bleeding (if pathologies are present):
- menstruation is usually long, about 7-8 days, unscheduled heavy discharge occurs;
- severe nagging pain in the lower abdomen that radiates to the lower back;
- heavy periods with bloody clots;
- general weakness, headache, dizziness, pale skin;
- rapid pulse;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- possible loss of consciousness;
- nausea or vomiting.
These signs are dangerous to your health and indicate a problem. Symptoms indicating surges in blood pressure are especially dangerous, as they may indicate internal bleeding.
Etiology of the disease
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause after a thorough examination of the patient.
There are several reasons why brown discharge may appear in the middle of the menstrual cycle:
- Ovulation. During the maturation of the egg and when the follicle is released, slight bleeding may appear. This is a signal from the body that a woman is ready to become pregnant. If the smudge is light brown or dark brown in color and does not cause discomfort or pain, then there should be no panic, this is the norm.
- Early conception. When the egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, endometrial detachment may occur with the appearance of occasional dark-colored bleeding. However, after a month, menstruation will not come, and the woman will realize that she is pregnant. If bearing a child goes without problems, then such brown discharge should not appear during pregnancy.
- Tumor in the uterus. Some women are at risk of developing a tumor as they age. An ultrasound can confirm or refute the presence of a tumor in the uterus, on the basis of which the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. If it is not a cancerous tumor, but a small fibroid and it is not growing, then it is not removed. In this case, spotting may appear from time to time. It is important to monitor the dynamics and growth of fibroids and be systematically examined by an experienced specialist.
- Presence of endometriosis. Endometriosis is a disease characterized by the growth of tissue in the uterus. Pain may appear in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. Colposcopy will help diagnose this disease. Only after a detailed examination and necessary research can a doctor diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment.
- Erosion of the uterus. In this case, spotting appears due to a hormonal imbalance.
- Using vaginal and oral medications or a special vaginal ring as contraception.
Seeing a doctor and getting the correct diagnosis
In addition to the above reasons, bleeding or light brown discharge in the middle of the cycle, as already mentioned, can be a sign of the onset of ovulation - a period when you can plan for procreation. It is important to understand that during the period of ovulation, minor discharge is acceptable; the blood may only be slightly smeared. Scanty discharge is normal and does not need to be treated.
If the discharge is dark in color - black, brown, then this may be a sign of diseases of the genital organs, polyps on the uterus or detachment of the uterine epithelium due to the effects of estrogen.
Typically, these pathological conditions are accompanied by fever and pain. You can understand the cause of ailments by passing a series of tests and undergoing special examinations. It was said above that contraceptives in tablets can provoke discharge in the middle of the cycle, but it is important to know that such a symptom is possible only in the first 60 days after starting to take the tablets. When brown discharge appears later, you should consult a doctor.
Natural discharge and its causes
Brown discharge in the middle of your cycle is not always a serious cause for concern. In some cases, a spotting, light-brown secretion that does not have an unpleasant odor is considered normal.
The main causes of natural physiological secretions are:
- ovulation;
- attachment of the egg to the uterus after maturation;
- miscarriage of the fetus in the early stages;
- puberty of girls;
- premenopause;
- use of contraceptives;
- physical exercise;
- postpartum period.
Ovulation
The process of maturation of the egg and its release from the follicle is sometimes accompanied in the woman’s body by characteristic scanty blood discharge, which, when interacting with oxygen, oxidizes and turns brown. This is a kind of signal from the body that the woman is ready to conceive a child.
Brown discharge in the middle of the cycle during ovulation, not accompanied by pain or unpleasant odor, is considered normal.
Pregnancy
The appearance of scanty brown leucorrhoea in the first trimester of pregnancy may occur during the period when menstruation would normally occur. This is a sign of hormonal changes in the body due to a lack of progesterone. After the placenta is formed, the hormone level returns to normal and the discharge stops.
But in any case, if there is brown secretion during pregnancy, a woman should consult a doctor. Since with a significant lack of progesterone, the risk of miscarriage increases, which can be signaled by such discharge during this period.
This type of discharge is observed in teenage girls aged 12-18 years in case of menstrual irregularities. Most often, this pathology is observed within 2-3 years after the onset of menstruation. One of the reasons for discharge is a lack of vitamins during the winter-spring period of the year.
In addition, the following factors can provoke secretion of this type:
- mental injuries;
- physical and psychological stress;
- infectious diseases;
- unbalanced diet.
Uterine bleeding in a teenage girl is a symptom of reproductive failure and is often a sign of hemorrhagic syndrome. In this regard, when leucorrhoea appears, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gynecologist and carry out timely treatment, which will help normalize the menstrual cycle.
When using contraceptives to prevent pregnancy, secretion may occur as a characteristic primary reaction of the body to hormonal drugs. It is acceptable to have brown leucorrhoea for the first 3 months after starting to take the medication.
Brown discharge in the middle of the cycle is most often observed when using an intrauterine device.
After childbirth, a woman also faces a difficult period, as the body readjusts to its previous state. This is due to the fact that hormonal balance is restored and menstruation begins.
The appearance of a brown shade of secretion during breastfeeding, especially after the first pregnancy, is the norm, but the discharge is not accompanied by pain in the abdominal area. In addition, they must have a meager character and resemble daubs.
Otherwise, this pathology, accompanied by elevated body temperature and cramping pain, indicates an acute inflammatory process in the reproductive organs or the development of a tumor. Therefore, you should immediately call an ambulance for further hospitalization of the woman.
Climax
Hormonal imbalance in the body is the main cause of brown discharge. Therefore, the onset of menopause is also characterized by the presence of secretion, which is associated with a reduction in hormone production. All these changes lead to thinning of the vaginal lining and therefore any microcracks can provoke the appearance of light brown leucorrhoea.
If they are not accompanied by itching, burning and an unpleasant odor, then there is no particular cause for alarm. Otherwise, the discharge may signal the development of infection or inflammation, so it is necessary to undergo examination by a specialist.
Loads
Brown discharge in the middle of the cycle after active sports, physical or psychological stress, according to experts, is not considered the norm. Often, the appearance of secretion is caused by chronic inflammation of the reproductive organs, coagulopathy or endometriosis.
Therefore, the regular appearance of brownish leucorrhoea after exercise should be a reason to consult a doctor to identify the main cause of the pathology and prescribe adequate treatment.
What to do?
Therapy depends on the cause of intermenstrual discharge and the diagnosis and age of the patient. There are 2 types of treatment: conservative (medication) and surgical to eliminate the source of bleeding. In early adolescence, operations are resorted to only as a last resort.
Drug therapy usually consists of taking hormonal drugs. They should normalize the menstrual cycle and hormonal levels. If there is heavy bleeding, it is recommended to take iron-based medications to stop the bleeding.
Spotting due to pathology
Pathological spotting in the middle of the cycle is accompanied by certain symptoms. This may include thick white discharge, yellow discharge with heterogeneous consistency, runny leucorrhoea, spotting that develops into heavy bleeding. They are complemented by: a specific smell, burning and vaginal itching, pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the side radiating to the lower back, fever, nausea, and in advanced cases, vomiting. Such discharges can be conditionally divided into two groups depending on the reason for their appearance.
The first group - caused by uterine pathology
- Erosion of the uterine cervix is an inflammatory process of tissue, the main symptom of which is periodic bleeding, from spotting to heavy. They are often indicated after sexual intercourse and between menstruation. For many, the pathology is asymptomatic. Erosive destruction of tissue increases the risk of infection. Therapy uses medications, laser, radio waves, cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation, chemical coagulation, and electrical excision. Small affected areas are most often left untreated and monitored periodically.
- Endometriosis is a pathological benign process of tissue growth outside the uterine lining. It manifests itself as spotting and heavy bleeding, prolonged critical days at the beginning, middle, and end of the cycle, pain in the lower abdomen, shifts in menstruation, and painful sexual intercourse. It can be eliminated by electrotherapy, laser, ultrasound, surgical curettage, and combined treatment with medications.
- Endometritis is inflammation of the surface layer of the endometrium. Spotting brown, pink, purulent discharge in women, including in the middle of the cycle, is the main designation of pathology. It is characterized by increased temperature, nagging pain in the lower part of the peritoneum, radiating to the side, and painful sexual contact. For treatment, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial tablets or broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
- Polyps and neoplasms of various etymologies are characterized by bleeding after menstruation (in the first half of the cycle). Like any pathological changes in uterine tissue, they lead to periodic heavy bleeding. These symptoms are accompanied by pain, general weakness, and nausea. Treatment depends on the etymology and stage of the disease.
- During pregnancy, brown spotting along with pain and cramps indicate fetal fading, threatened miscarriage, as well as ectopic pregnancy. If a sign is detected, you should immediately consult a doctor to remove the dead embryo to avoid infection of adjacent tissues. Sometimes a fetus with blood leakage can be saved. An ectopic pregnancy must be removed urgently, as it threatens to rupture the fallopian tube.
The second group - provoked by inflammatory processes, urological and infectious diseases
Inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system occur for a number of reasons: complications after a cold, hypothermia, weakened immunity, infection, proliferation of opportunistic bacteria, improper hygiene.
The appearance of copious leucorrhoea, gray, purulent discharge with itching in the vagina, the unpleasant smell of rotten meat, fish, onions and other stench characterizes bacterial vaginosis. The disease relates to inflammation and is transmitted both sexually and develops against the background of the proliferation of opportunistic bacteria living in the microflora. Such symptoms, supplemented by a curdled leucorrhoea and a sour milk smell, indicate candidiasis. Such diseases can generally be treated locally with suppositories and douches.
Infectious diseases, in particular sexually transmitted ones, are indicated by yellow, green, purulent discharge, they stink and appear at any time, either by spotting or by copious mucus secretion. They can be liquid, stretch like snot, or jelly. With such illnesses, the vagina itches, there is a burning sensation and pain when urinating, and the external genitalia become inflamed. Such diseases are treated with antibiotics in combination with anti-inflammatory and other drugs.
Briefly about the main thing
Our small research showed that the topic of spotting in the middle of the cycle is discussed quite often in reviews on the forum and blogs.
The scant bloody discharge described by women, which is spotting in nature, without any foreign odor or accompanying symptoms, is considered normal. But there are also pathological signs that require medical attention.
There is no need to be afraid of visiting a doctor, since statistics show that in 68% of cases the described symptom has a physiological etymology, 40% of them are associated with hormonal changes, and 32% of the total number of women who apply have signs of a pathological nature. Therefore, we can say that it is more likely that the symptom you discovered is not caused by a disease. The probability of a hormonal shift is slightly higher, but if you are approaching 45 years of age, this process is natural in connection with the approaching menopause. At a young age, such a disorder is extremely rare.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis begins with a full examination by a gynecologist. The doctor visually examines the uterine and vaginal cavity and takes the necessary smears. Hysteroscopy is widely used - an informative and minimally invasive research method.
Diagnostic measures:
- cytological analysis of a sample of the endometrium of the uterus or cervical canal, taken by aspiration or scraping;
- Ultrasound of the reproductive system;
- laboratory analysis for hormone levels;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- MRI, CT, radiography (if absolutely necessary).
What is the danger
Sometimes bloody discharge from the genitals can be a sign of a dangerous disease, so at the first unexpected discharge you should consult a doctor. They may also be the norm. Under certain conditions, brown discharge in the middle of the cycle is not a pathology.
However, if after sexual intercourse severe bloody spotting begins, this cannot be ignored; it may be a sign of a disease of the reproductive system.
What matters in this case is the number of discharges and their duration. If spotting continues for more than 2 days, it is painful and accompanied by a feverish state and weakness, then it is necessary to urgently seek medical help, because these are signs of an inflammatory process.
Severe and prolonged bleeding can also be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy or a threatened miscarriage. Dark brown discharge in the middle of the cycle is classified as metrorrhagia and intermenstrual bleeding. Metrorrhagia can occur at any age and be a symptom of the following diseases:
- adnexal tumor;
- fibroma;
- malignant uterine tumor;
- sarcoma;
- cervical cancer;
- endometriosis;
- uterine erosion;
- endometritis;
- adenomyosis is not external.
All of the above deviations are dangerous to a woman’s health and she should seek help from a doctor. Intermenstrual bleeding can occur for the following reasons:
- hormonal disorders;
- genital injuries;
- using the IUD for contraception;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- vaginal infection;
- contraceptives in the form of tablets containing estrogen;
- a number of gynecological procedures;
- medications taken without a doctor's prescription;
- state of shock, experienced stress.