Cold weather and damp weather lead to an increase in the number of various infections. The respiratory system suffers the most. Tracheitis, sinusitis and bronchitis are common complications of colds. The question of how to treat laryngitis also becomes important. The disease cannot be neglected, because it can become a source of more serious health problems. Timely treatment is the key to a quick recovery and absence of complications.
Symptoms of laryngitis
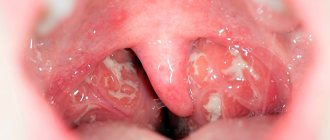
The clinical picture of the disease is specific - redness and even swelling of the throat membrane, the addition of a hoarse and dry cough. Laryngitis in an adult is accompanied by severe soreness and pain, hoarseness - in some cases, even loss of voice.
General intoxication can be identified. It is expressed by an increase in temperature and headaches. The combination of two or more symptoms indicates that an adult with laryngitis needs to begin treatment as soon as possible.
Symptoms
Inflammation develops due to the penetration of a pathogenic microorganism into the cell. Then inflammatory mediators are produced in the affected area, macrophages and other protective cells of the body are activated. Inflammation develops.
Doctor's advice
Inhalations have worked well for laryngitis. This can be a simple way - inhale steam from hot water, or using a nebulizer. In the first case, use an alkaline solution (a pinch of soda per glass of water), a decoction of chamomile and sage (1 tsp per 200 ml of water) or thyme (1 tsp per 1 glass of water). In the second case, you can use ambroxol, saline solution. In case of severe swelling, hormonal drugs (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) can be used; they are prescribed by a doctor. Any inhalations are performed at a body temperature not higher than 37.0 in children and adolescents and 37.2 in adults.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
The body begins to respond to these processes by increasing blood flow to the affected area - hence the swelling. Swelling leads to a narrowing of the glottis. In addition to hoarseness, this is also manifested by poor ventilation of the larynx. Less moisture begins to flow into it. It dries out and becomes even less protected.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Itching, pain, soreness or burning in the throat.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the larynx.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Hoarseness and hoarseness of voice. In advanced or acute forms of laryngitis, this symptom can lead to complete loss of voice in an adult.
- Barking cough. As the disease progresses, the nature of the cough will change. Initially it will be dry, irritating the inflamed mucous membrane. When the treatment enters the active phase, the cough will become moist and the sputum will be easily expectorated.
- Temperature. If it is a virus, the temperature will rise to 38-38.5 almost from the first hours of illness and will last no more than three days. But a sign of bacterial laryngitis is a long-term inflammatory process, during which the temperature remains around 37.5 degrees.
- General malaise and weakness.
- Headache
- Loss of appetite, fatigue.
First aid
The following measures will help you smoothly enter the recovery course for laryngitis:
- stopping smoking and eating spicy foods or dishes throughout the recovery course;
- absolute speech rest - for at least five to six days;
- drinking alkaline drinks in significant quantities - this could be teas with herbs, milk with the addition of honey.
In the first hours and days of illness, you cannot do without regular ventilation of the room or the entire apartment. An important aspect of the treatment of laryngitis in an adult is maintaining a special microclimate - temperature from 19 to 21 degrees, air humidity - from 55 to 65. This will help prevent drying out of the mucous membranes and minimize the severity of painful coughing attacks.
How to treat laryngitis during pregnancy?
Treatment of laryngitis during pregnancy should begin with the first symptoms of the disease. Sore throat, hoarseness, fever - all these are signs that indicate the onset of the disease and the need for treatment. In pregnant women, laryngitis may be more severe in the presence of rhinitis during pregnancy. Swelling of the mucous membrane leads to difficulty breathing and increased stress on the heart. Doctors may recommend treatment for expectant mothers with the following drugs:
- antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs: Cetrizin, Claritin, Zyrtec;
- topical anti-inflammatory drugs: Ingalipt, Lisobakt, Miramistin, Faringosept;
- expectorants: Sinekod, preparations based on thermopsis and marshmallow root;
- antiviral drugs: Aflubin, Viferon, Oscillococinum.
Essential Medicines
In the treatment of laryngitis in adults, one cannot do without the use of medications. I would like to dwell on their forms of release, influence and specific names in more detail.
| Type of drug | Effect on the body | Name |
| Lollipops | Reduce inflammation in the larynx, soften the mucous surface of the throat and accelerate the recovery process | Strepsils, Travisil |
| Sprays | Provide disinfection and suppression of the activity of infectious agents | Ingalipt, Kameton |
| Antitussives | Stops an exhausting dry cough by suppressing the corresponding reaction | Intussin, Tusuprex |
| Mucolytics | Reduce the viscosity of sputum | Solvin, ACC |
| Expectorants | Promote faster and more complete removal of mucus from the respiratory system | Alteika, Prospan |
| Anti-inflammatory, antipyretic | Allows you to get rid of signs of fever and inflammation - chills, increased sweating | Paracetamol, Ibuprofen |
Additionally, antibiotics, antiviral and antihistamine names are used. Without the former, it will not be possible to destroy microbes in inflammatory foci (Ceforal, Panclave), without the latter, it will not be possible to cope with various agents and reduce their number in the body (Tamiflu, Ingavirin). With the help of antihistamines it is possible to eliminate swelling, itching and other unpleasant symptoms in the larynx. Suprastin, Loratadine and other names previously prescribed by a pulmonologist are used.
Causes of laryngitis
In most cases, acute laryngitis does not develop as an independent disease, but in parallel with inflammation of other parts of the respiratory tract (nose, throat, trachea, bronchi and lungs) - the cause of this is acute respiratory viral infections (influenza, parainfluenza, adenoviral infection). The larynx is also involved in the pathological process in measles, diphtheria and whooping cough, and can be a complication of syphilis and tuberculosis.
Less commonly, acute laryngitis is caused by a bacterial infection, in particular strepto- and staphylococcal - usually this occurs due to secondary infection of the pharyngeal mucosa when the body’s immune system is weakened due to acute respiratory viral infections or chronic infections.
In addition to infectious agents, the causes of acute laryngitis are:
- particles of steam, gases and dust contained in the air;
- external allergens (plant, food, chemical);
- thermal effects on the laryngeal mucosa (hot or cold food and drink);
- increased load on the vocal apparatus;
- smoking.
Less commonly, acute laryngitis can occur against the background of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), when the acidic contents of the stomach enter the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, in particular the larynx, and irritate them.
The development of chronic laryngitis is promoted by:
- frequent acute laryngitis, especially without adequate treatment;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract;
- hypothermia;
- regular increased load on the vocal apparatus (more common among teachers - the so-called lecturer's laryngitis);
- active smoking (occurs in almost 100% of smokers - “smoker’s laryngitis”) and passive smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- inhalation of air contaminated with chemicals and dust.
Therapy by type of disease
Separately, treatment measures for acute and chronic forms of laryngitis in adults should be considered. This will speed up the healing process and prevent the development of complications.
Acute form
To combat this form of the disease, a whole range of means is used. First of all, these are antibacterial names - lozenges, sprays and aerosols, for example, Hexoral or Strepsils.
In case of severe pain, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are prescribed - Nurofen, Nimesil. Their advantage is the elimination of all signs of deterioration of the condition: pain, voice disorders.
Adaptogens are used in recovery to increase immune activity. In this case, it is better to ask a specialist how to treat laryngitis in adults. But most often several types of tinctures are used: ginseng, eleutherococcus.
An excellent remedy that has a positive effect on the healing process is Lugoli's solution. It is used to lubricate the throat to provide reliable protection to the mucous membrane of the larynx. After approximately the third or fourth day of illness, the composition can be replaced with sea buckthorn oil. This component will also have a restorative and protective effect on the mucous surface.
Chronic form
The goal of therapy in this case is to achieve remission and reduce critical manifestations to a minimum. There is no talk of complete relief from laryngitis in adults in the chronic stage. It should be understood that patients with the presented diagnosis are at risk due to the likelihood of developing laryngeal cancer. That is why treatment of the disease must be comprehensive and complete.
For an adult, therapy for chronic laryngitis should consist of:
- The use of medications and, as an additional measure of influence, vitamins.
- Carrying out alkaline inhalations. Similar procedures using antibiotics can be carried out.
- Physiotherapy. Patients undergo magnetic therapy (the effect of magnetic fields on the mucous membrane of the throat), electrophoresis (the introduction of drug solutions into the problem area). Pulmonologists prescribe CUV irradiation (the use of ultraviolet irradiation), as well as amplipulse therapy (the influence of sinusoidal currents).
- Traditional medicine recipes. They are used only after agreement with the pulmonologist and achievement of positive results as part of the treatment.
The recovery course in this case is long. It can last from two to four months. Depending on the age of the patient and the severity of the general condition, treatment of laryngitis in an adult can be carried out at certain intervals – once every year to a year and a half.
Diagnostic methods
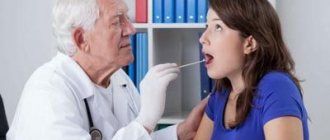
If you suspect that you are suffering from laryngitis, you should immediately consult a doctor, because an advanced disease can leave you bedridden for a couple of weeks or deprive you of your voice.
Diagnostics occurs in several stages:
- Taking an anamnesis, during which the doctor asks you about the time the first symptoms appeared; about whether you have had laryngitis before, whether there were additional factors against which inflammation of the larynx could develop.
- Examination of the larynx and laryngoscopy. The specialist examines the mucous membrane for the presence of edema, enlarged ligaments, infiltration, white plaque, and microcracks.
- In the acute form, a laboratory smear test is usually performed. Additionally, blood and urine collection may be required.
Laryngitis has common symptoms with a number of serious diseases - syphilis of the larynx, tuberculosis and even cancer. Therefore, sometimes a doctor can prescribe a differential diagnosis to accurately identify the pathology.
Surgery
A similar approach to recovery for laryngitis in an adult is permissible only in a limited number of cases. We are talking about an abscess form of the disease, the development of phlegmon of the neck (this is an acute purulent inflammation of cellular structures). You cannot do without surgery if there is a rapid formation of stenosis in the area of the larynx - narrowing of its lumen, as well as the lack of results from long-term complex therapy.
Due to such intervention, it is even possible to degenerate tissue structures if their malignant degeneration occurs. Also, surgery for laryngitis in an adult helps to partially or completely eliminate the main signs of pathology, minimizing exacerbations during chronic disease.
Medicines for laryngitis in adults
For local and general therapy, the following groups of drugs are used:
- expectorants - Mukaltin, Gerbion, Prospan, Eucabal;
- antihistamines - Zodak, Loratadine or Suprastin;
- antiviral agents - Fenspiride or Fusafungin;
- immune-strengthening agents - compositions containing Eleutherococcus or Radiola;
- absorbable tablets (Isla, Neo-Angin) and aerosols (Tera-Flu, Camphomen).
Antibiotics for laryngitis are prescribed only in cases where, during a diagnostic examination of the patient, it was confirmed that the disease is of bacterial origin. The following drugs are most often used to treat this pathology:
- Amosin;
- Flemoxin;
- Augmentin;
- Amoxiclav.
Inhalations for laryngitis
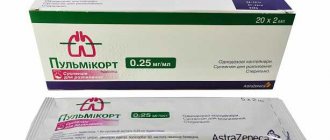
To combat this disease, nebulizer therapy is prescribed. If laryngitis is diagnosed (symptoms and signs are appropriate), this treatment in adults and children is considered the safest and most effective. A nebulizer is used for inhalation. This device is a special chamber into which a drug is injected, which during the procedure turns into an aerosol. Pulmicort can be used for laryngitis. However, this is not the only drug prescribed to combat the disease. The following groups of drugs are most often used:
- antibiotics – Miramistin, Dioxidin;
- mucolytics – ACC, Chymotrypsin;
- mineral alkaline water (it speeds up the process of sputum discharge);
- emollient solutions (for example, Citral oil solution).
Before treating laryngitis with inhalations, you need to carefully study the contraindications to these procedures. These include the following phenomena:
- allergic reaction to the drug used;
- increased body temperature;
- high blood pressure;
- purulent sore throat;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
Folk remedies
For restoration purposes, it is recommended to resort to additional measures of influence. It is acceptable to carry out home inhalations, for example, breathing over boiled potatoes, to which chamomile flowers or eucalyptus are added.
Treatment of laryngitis in an adult will be accelerated if:
- use an infusion of ginger root with the addition of linden or acacia honey;
- chew spruce or pine resin - a universal disinfectant composition;
- use oil as nasal drops: olive, sea buckthorn, sunflower;
- prepare a mixture of honey and aloe juice to dissolve throughout the day.
It will be useful to use an infusion of onion peels to rinse the larynx. In addition, it is acceptable to use simple warm compresses. It is recommended not to affect the area of the endocrine gland.
Helping a sick person
Otolaryngologists advise that at the first manifestations of the disease, consult a doctor who, after examining the patient, will confirm or deny the possibility of laryngitis and prescribe the correct course of treatment. But if this is not possible, then in the first hours of laryngitis it is necessary to put the patient to bed, providing the most comfortable conditions for him. This will ensure a quick recovery process.
- Ventilation. Provide cool air in the room where the child is, so ventilate the room.
- Optimal humidity levels. Purchase a hygrometer that measures indoor humidity. This is especially true in winter, when the heating is on and the indicators are rapidly falling down. Low air humidity leads to dryness of the nasopharyngeal mucosa. This changes her work and aggravates the existing disease. Increase humidity by placing containers of water in the room or hanging wet towels on radiators.
- Breathing through the nose. It is important to breathe not through your mouth when you have laryngitis. This closes the gate for additional infection to enter the inflammation site. If nasal breathing is complicated, use vasoconstrictor drops, which will relieve swelling of the mucous passages and allow nasal breathing to normalize.
- Walks in the open air. If there is no high temperature and the patient feels well, the inflammatory process has subsided, quiet time in the air is allowed. Children with laryngitis can go for a walk, but games should not be active. Just walking is the best option. A child with laryngitis can swim provided there is no fever. Add a few drops of essential oil to the bath, which will give an inhalation effect.
- Treatment of laryngitis in adults and children also involves adjusting the patient’s diet. All products that are considered allergenic are excluded from the menu (honey, chocolate, citrus fruits, fish, etc.), which, if the immune system is weakened by infection, can worsen the course of the disease due to allergies. Don't eat spicy food.
- Take care of your vocal cords. Reduce tension on this part of the nasopharynx to a minimum: try to talk less, but do not whisper. This can also be explained to a child at an older age. And the baby needs to be distracted, play calm games with him or read a book.
- Provide the patient with plenty of fluids. To do this, use warm herbal infusions, compote, tea, and fruit drinks. Folk remedies include warm milk diluted with alkaline mineral water, to which butter, previously melted, is added.
- LiveJournal
- Blogger
Before going to bed, it is recommended to steam your feet in water with mustard
These are the main methods of helping and alleviating the patient’s condition if laryngitis is suspected. By adhering to them, it is possible to stop the rapid development of the disease until examination and prescription of drug treatment by a doctor.
Special food
If the condition is not severe, and therapy was carried out on time, a special diet will help to quickly cure laryngitis in an adult. So, you need to remember the list of prohibited products. We are talking about all alcoholic drinks, sparkling water, seeds or nuts. Products with a pronounced taste such as horseradish, mustard, garlic and the like are unacceptable for consumption. It is recommended to avoid herbs, spices and seasonings.
In general, it is desirable that the food be ground or liquid, but not very hot and, especially, cold. It is necessary to avoid fried or fatty foods. The same products as meat and fish are cooked exclusively by steaming.
In a long-term fight against laryngitis in adults, vegetable oils will be an excellent help. They are dropped into the nose or applied to the throat. Fresh fruits or vegetables and juices from them will be useful. However, using the former as a puree is undesirable.
Drinking for this disease, as in the case of food, should be warm and sufficiently plentiful. All formulations are consumed in small sips. Borjomi, natural milk and sage will help to cope with the pathological condition in an adult much faster.
Treatment regimen
Otolaryngologists advise adhering to the above rules of conduct. This will ensure rapid recovery of the affected mucosa and mild laryngitis.
Particular attention is paid to treatment if laryngitis affects the patient’s speech. You can quickly restore the vocal cords in case of illness and not aggravate the situation by reducing the load on them. Do not be silent. Speak, but do it without straining or screaming. Whispering will cause even more harm, since it requires a lot of strain on the vocal cords. Therefore, you should not talk to them if you have laryngitis.
If you want to quickly get rid of the disease, then give up smoking and alcohol. Remove too hot drinks and dishes from the menu. Make sure you drink enough fluids.
You can reduce irritation of the larynx, which causes a dry, painful cough, by inhalation using a pharmaceutical saline solution or mineral water. These procedures using herbal infusions moisturize the mucous membrane and help quickly restore the voice in case of laryngitis.
By providing the patient with bed rest, warm drinks and a special diet, you help the body cope with the inflammatory process.
Prevention of laryngitis
In order to exclude the development of this pathology, it is necessary to follow some recommendations. It is important to ensure prompt treatment of infections, colds and chronic conditions.
If an adult develops an acute respiratory viral infection or acute respiratory infection, a special regime cannot be avoided. So, the patient needs to be treated at home, drink warm drinks in sufficient quantities and, if possible, spare his voice - speak in a whisper or quietly, and refuse physical activity.
An obligatory step in the prevention of laryngitis in an adult is the elimination of bad habits - smoking, alcohol addiction. You should not neglect simpler recommendations, for example, wet cleaning in the apartment. Moderate daily exercise and walking will be a huge plus.
Laryngitis - types and forms
Laryngitis is a disease in which a person’s ligaments are inflamed and cannot fully perform the function of producing sounds. Laryngitis has two forms:
- Acute laryngitis.
A common complication of colds. It begins abruptly with a sore and painful sensation in the throat, followed by a cough and hoarseness. - Chronic laryngitis.
Its causes are the following factors: improper treatment, increased load on the vocal cords and chemical exposure.
Each form of laryngitis has several types. Acute laryngitis is like this:
- Catarrhal.
The mildest form of laryngitis. It occurs with a slight increase in temperature, redness of the throat and hoarseness. - Lining.
Occurs in children. Characterized by severe swelling and narrowing of the larynx. Needs urgent treatment. - Hemorrhagic.
Characterized by hemorrhage in the laryngeal mucosa. - Phlegmonous.
Purulent formations appear on the mucous membrane. The treatment is antibacterial in nature and lasts 7-10 days.
Chronic laryngitis occurs with mild symptoms and can have the following types:
- Catarrhal laryngitis.
The patient feels a sore throat, coughing, and the throat is slightly red. - Hypertrophic laryngitis.
Symptoms of this disease are: blueness of the throat, hoarse voice, severe swelling. Lack of proper treatment leads to the formation of nodules on the ligaments. - Atrophic laryngitis.
It is characterized by loss of functionality of the tissues of the nasopharynx. - Allergic laryngitis.
A sore throat and swelling of the mucous membrane are observed when exposed to an allergen. Often combined with allergic rhinitis and pharyngitis. - Occupational laryngitis.
Constant straining of the voice leads to the formation of thickenings on the ligaments that cannot be cured with medications.
Diagnostics
Determination of symptoms and treatment of laryngitis in adults should be under the supervision of a physician.
During the diagnostic process, the doctor initially examines the medical history, conducts a physical examination and interviews the patient about the nature of the onset and development of the disease. A thorough examination of the sound of the voice, as well as the vocal cords, helps to select the right approach to treating the disease.
In addition to a general medical examination, the doctor may also use additional research methods, especially in case of chronic laryngitis or protracted acute laryngitis:
- laryngoscopy;
- blood analysis;
- fluorography of a difficult cell;
- bacteriological examination of swabs, smears from the larynx, etc.
A person who does not have a medical education can diagnose laryngitis on his own, but the likelihood of an error is very high. Although the pathology has characteristic symptoms, in some cases it can take a “blurred” course. Some signs may be completely absent.
You should contact an otolaryngologist if:
- Your symptoms do not improve within 2 weeks;
- You have sudden severe pain (especially radiating to the ear), difficulty swallowing, or coughing up blood;
- Suspect another disease;
- There is a suspicion that laryngitis may become chronic.
Preventive measures
Prevention of inflammation involves avoiding risk factors. Persons exposed to adverse effects at work should not underestimate the use of protective equipment (respirator masks in the construction industry, dusty industries, etc.). Otherwise, there is a risk of chronic damage as an occupational disease.
- It is necessary to observe moderation in alcohol and smoking; it is important for singers to pay sufficient attention to the hygiene of the vocal system.
- During the period of increased incidence (autumn and early spring), it is advisable to increase the consumption of vitamin-rich foods.
- In frosty weather, it is recommended to avoid mouth breathing through a coat collar or scarf and drink hot drinks more often.
It is necessary to pay attention to all the symptoms of inflammation of the airways and treat them correctly (today people usually deliberately skip the most important part of the therapeutic process - rest), otherwise they can threaten other parts of the airways along the descending or ascending path.
Etiology
The cause of acute inflammation of the pharynx is infection:
- Rhinovirus,
- Coronavirus,
- Adenoviral,
- Flu,
- Parainfluenza,
- Herpetic,
- Enteroviral,
- Cytomegalovirus.
In more rare cases, the causative agents of pharyngitis are respiratory syncytial virus, Coxsackie virus, Epstein–Barr virus, and human immunodeficiency virus.
- The cause of nonspecific bacterial pharyngitis is usually streptococcal, mycoplasma, chlamydial, or staphylococcal infections.
- Specific forms of pharyngitis are associated with a specific pathogen: gonococcal pharyngitis is caused by gonococcus, leptotrichosis of the pharynx is caused by Leptotrix buccalis.
- The causative agent of fungal pharyngitis is a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida.
- Protozoal lesions of the pharynx are rare and indicate dysfunction of the immune system.
- Allergic pharyngitis is associated with the penetration of allergens into the body along with inhaled air. Often the cause of the disease is food allergy.
Irritating factors contributing to the development of the disease include:
- Cold,
- Smoking,
- Chemicals - alcohol,
- Rough, spicy and hot food,
- Infectious foci in the body - caries, sinusitis, rhinitis,
- Long conversation
- Industrial emissions,
- Predisposition to allergies
- Discharge flowing down the back wall of the pharynx, with chronic sinusitis.
The main factors provoking the disease include the following:
- Features of the anatomical structure of the pharynx and digestive tract,
- Infection - bacteria, viruses,
- Bad habits,
- Hypo- and vitamin deficiency,
- Allergy,
- Impaired breathing through the nose,
- Menopause,
- Endocrine diseases - diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism,
- Condition after tonsillectomy,
- Irritants - chemicals, smoke, dust,
- Chronic pathology of the digestive organs,
- Weakening of the immune system
- Cardiovascular and hepatic-renal pathology.
Causes
Before choosing a home remedy for a sore throat, you need to find out the etiology of the pathological process and eliminate the main provoking factor and its destructive influence. It is not easy to differentiate the diagnosis, since an acute process in the larynx is characteristic of many diseases of the respiratory system of a viral, infectious nature. The reasons for relapse may be:
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- the result of smoking and systematic abuse of alcoholic beverages;
- prolonged overstrain of the vocal cords;
- chronic throat diseases;
- congenital anomalies;
- allergic reactions to external allergens;
- mechanical damage to the larynx.
Laryngitis: loss of voice
If your voice has lost its sonority and disappeared, then the following remedies will help you get it back:
1. Boiled peanuts should be dried a little, fried and eaten.
2. Soak half a glass of anise seeds in a glass of boiling water. Place the mixture on the fire for 15 minutes of boiling. Then strengthen the drink with a spoon of honey and cognac. Drink a large sip after 1 hour.
3. Mix lemon pulp with honey and keep in the mouth for 5 minutes.
4. A mixture of mineral water and warm milk will help restore the sonority of your voice. For greater effect, you need to stir a spoonful of honey, butter and cognac into the drink. Drink in small sips when warm.
5. You can take a sip of warm milk, first with 2 cloves of garlic boiled there. You need to drink 40 minutes in the morning and evening.
6. Before treatment with folk remedies, you should consult a certified specialist.
Treatment methods
There is no universal remedy for treating a sore throat. The effectiveness of therapy can be manifested in the targeted and simultaneous elimination of acute signs and causes of the pathology.
The general therapeutic regimen for inflammation is based on the use of medications to stabilize the immune system, heal tissue and relieve pain. These remedies can be combined with other over-the-counter medications, physiotherapy and traditional medicine recipes. Take them as long as symptoms persist.
Drug treatment for throat
Various lozenges and sprays help not only to quickly relieve discomfort, but also to stop the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Anti-inflammatory medications of non-steroidal origin in the form of sprays are intended for the throat: “Tantum Verde” and “Tantum Verde Forte” (with an increased concentration of active substances), “Hexoral”, “Cameton”, “Anti-Angin”.
See also
What to do to avoid getting sick if your throat starts to hurt at home
Read
Antibacterial and analgesic components are included in medicines in the form of lozenges, lozenges and lozenges: Strepsils, Lizobakt, Faringosept, Grammidin Neo.
For dryness and itching, in addition to sprays, you can choose pharmaceutical solutions for irrigation and rinsing: Lugol, antiseptics Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
If the body’s resistance to the pathogenic environment is weak, vitamins containing ascorbic acid, as well as immunomodulators: “Bronchomunal”, “Immunal” are included in the complex of therapy.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed by a doctor for severe intoxication and to avoid the development of complications of infectious diseases. They cannot be universal.
Important! The selection of an antibiotic is carried out on an individual basis, but first the doctor must obtain laboratory confirmation of the bacterial environment in the body. For diseases caused by viruses, antibiotics are ineffective.
ethnoscience
In most cases, in case of an infectious disease, doctors allow treating the throat with folk remedies. There is no doubt about the effectiveness of many traditional medicine recipes in eliminating foci of inflammation in the throat. You can prepare them at home. However, they are not suitable for monotherapy; the order of administration and dosage should be agreed with your doctor.
When choosing herbs for the throat, you should also take into account that many plants can cause allergic reactions. Decoctions of oak bark and chamomile for gargling are considered safe; mint tea relieves inflammatory processes; ginger tea with honey and cranberry juice are suitable for restoring the mucous membrane.
Rinse
Comprehensive treatment of the throat must necessarily include rinsing the larynx, oral mucosa and tonsils. For rinsing, decoctions and solutions of active substances are used, which can have an antimicrobial and wound-healing effect. Washing out purulent accumulations will provide good support to the body and reduce the severity of intoxication.
For the procedures, salt solutions are used (a mixture of sea and food with iodine), essential oils (eucalyptus, tea tree, juniper), infusions of medicinal herbs (sage, calendula, coltsfoot). Plaque from tonsils can be removed with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
Prevention and prognosis
If we are not talking about severe oncological diseases of the throat, then in most cases simple preventive measures help prevent the development of the inflammatory process:
- Humidify the air in the room. When the microclimate is disturbed, the mucous membranes dry out and cause inflammation even without an infectious agent.
- Strengthen the immune system. Good sleep, daily exercise, and a balanced diet will contribute to this.
- To refuse from bad habits. First of all, from smoking, because even staying in a place for smokers can cause a sore throat.
- Observe sanitation and hygiene rules. Hands should be washed as often as possible, and protective masks for the mouth and nose should be used when in contact with a sick person and during periods of epidemics in crowded places.
For any discomfort in the throat, it is important to carry out a timely diagnosis so that the treatment is effective.
Complications
The most common complication of laryngitis is chronic bronchitis and tonsillitis. Often in the acute phase there is a danger of developing laryngeal edema and the occurrence of false croup. In this condition, the person begins to choke, the skin turns pale, and the nasolabial triangle becomes blue. If a person in this condition is not given immediate assistance, he may die.
Chronic laryngitis can also lead to complications such as:
- benign tumor formation in the larynx;
- proliferation of polyps, formation of cysts or granulomas;
- development of laryngeal cancer;
- laryngeal stenosis;
- impaired mobility of the larynx.
Treatment of acute laryngitis
Modern medicine knows how to treat acute or chronic laryngitis. Mild forms of laryngitis are amenable to complex treatment, and even prevention can bring positive results. Comprehensive treatment means a combination of drug treatment, following doctor’s recommendations for lifestyle changes and therapeutic measures. A severe case may require immediate surgical intervention and it is definitely not worth delaying such surgical treatment.
Most likely, after visiting a therapist and otolaryngologist, the patient will receive a lot of recommendations, including4:
- Drinking plenty of fluids , especially with laryngitis against the background of ARVI;
- Gentle vocal mode - try to speak less and not overstrain the vocal cords;
- Ventilating and humidifying the air in the room will have a positive effect not only on the prevention of laryngitis, but also on general well-being;
- Help for local and general immunity - a healthy lifestyle, high-quality nutrition, hardening (except for moments of exacerbation of the disease), special medications;
- 100% cessation of smoking and alcohol during illness.
Treatment of laryngitis with medications is determined exclusively by a doctor. The selection of medications against laryngitis depends on its form and complications4:
- The common catarrhal form is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and astringents. Inhalations have proven themselves well. In rare cases, when a bacterial infection occurs, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- If a person is struck by phlegmonous laryngitis, then hospitalization and rapid surgical intervention are often required, which will allow one to get rid of the enlarged abscess without consequences. In most cases, treatment is supplemented with antibiotics.
- Infiltrative laryngitis is treated inpatiently, using antibiotics and various expectorants that provoke sputum production.
- Hemorrhagic laryngitis requires increased attention from a doctor. The patient is prescribed rest, therapeutic diets, calcium chloride and antitussives, since attacks can be too painful.
For subglottic laryngitis (false croup), first of all, measures are taken to relieve swelling and restore free breathing.
Treatment of chronic variants of laryngitis is based on similar principles. It is necessary to eliminate the root cause and allow the body to restore the inflamed mucous membrane of the larynx. The main emphasis should be on maintaining the strength of the immune system, because it is the one that resists the main causes in the form of viruses and bacteria.
For infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx, the drug Imudon® has proven itself to be effective, the mechanism of its operation is based on the activation of the body's defenses. Imudon® is an immunostimulating drug of bacterial origin for topical use in otorhinolaryngology and dentistry. Indications for its use include diseases such as pharyngitis and chronic tonsillitis6.
Instructions
Learn more
Developed with support from Abbott to improve patient health awareness. The information in the material is not a substitute for healthcare advice. Contact your doctor. 1. Pavlikhin, O. Acute laryngitis and its complications / O.G. Pavlikhin // Directory of a polyclinic doctor - 2006 - No. 7 - P. 7-13. 2. Soldier's. Yu Diseases of the larynx / Yu.L. Soldatsky // Pediatric pharmacology - 2008 - No. 2(5) - P. 20-25. 3. Kolesnikova, O. Integrated approach to the treatment of chronic laryngitis / O.M. Kolesnikova, M.E. Malkova // Pharmateka - 2019 - No. 2 - pp. 22-25. 4. Kunelskaya, N. Rational antibacterial therapy of acute edematous-infiltrative laryngitis / N.L. Kunelskaya, G.N. Izotova, S.G. Romanenko // Medical Council - 2013 - No. 7 - pp. 18-20. 5. Chernikov, V. Use of a topical immunomodulator for the prevention and treatment of acute respiratory infections in children / V.V. Chernikov // Issues of modern pediatrics - 2012 - No. 4 (VOLUME 11) - P. 15-20. 6. Instructions for medical use of the drug Imudon® dated 07/01/2013 RUIMD181930 dated 05/23/2018
Why is my throat sore?
An acute process in the throat begins with an unpleasant soreness and internal discomfort of the larynx, while the mucous membrane becomes deeply red, the tonsils become purple in color, and swells greatly.
With inflammation of the tonsils, the appearance of a white coating, characteristic of follicular tonsillitis, cannot be ruled out. Upon visual examination, the doctor identifies a reddened throat, which requires timely treatment with medications. Pathogens can enter the body in several ways:
- Through the air. Infectious diseases affecting the respiratory tract are often transmitted through airborne droplets. The increased risk is due to mouth breathing due to the lack of natural defense mechanisms. In this case, the mucous membrane is susceptible to pathogenic microorganisms that settle on its surface. The next stage is active reproduction. Some infections develop quickly. Infection can occur after a couple of minutes of interaction with an infected person.
- Oral route. Certain intracellular pathogens that inflame the throat enter the body in this way. Such microorganisms include chlamydia.
- Contact. You can become infected by touching personal belongings that belonged to the patient. The throat also becomes inflamed with physical contact.
//youtu.be/RTOopIukAuI
Inflammation of the larynx: treatment and symptoms
The main clinical sign of acute pharyngitis is a sore throat that gets worse with coughing. Often the onset of pain is preceded by dryness and soreness that persist for several days. The more pronounced the swelling of the mucous membrane, the more intense the pain. Severe pain radiates to the ears and causes patients to refuse to eat. After the formation of a persistent pain syndrome, a painful, dry, “scratching” cough appears in the throat.
Common symptoms of pharyngitis are: deterioration of general condition, weakness, malaise, fatigue, fever. These signs of intoxication persist for three days and gradually disappear.
When examining a patient, an ENT doctor discovers hyperemia of the posterior wall of the pharynx with areas of mucopurulent plaque, as well as swelling of the palate, tonsils and uvula. The submandibular and cervical lymph nodes are painful and enlarged in most patients.
Pharyngoscopy allows you to detect the inflamed mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall with characteristic manifestations - hyperemia, edema, lymphoid granules on the mucous membrane.
Gonococcal pharyngitis is a symptom of urogenital gonorrhea, and in some cases it is an independent pathology. Gonorrheal pharyngitis develops after unprotected orogenital intercourse with an infected person. In most cases, the pathology is asymptomatic and is discovered accidentally during microbiological examination.
Some patients develop classic symptoms of pharyngitis. On the hyperemic and edematous mucous membrane of the oropharynx, areas with a yellow-gray coating and individual follicles in the form of red grains appear. Inflammation often spreads from the pharynx to the tonsils, gums, palate, and larynx with the development of corresponding pathologies.
Allergic pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharynx that develops after an allergen enters the mucous membrane. Allergens can include: dust, pollen, pet hair, feathers, medications, food, chemicals used in everyday life and at work. All symptoms of allergic pharyngitis are associated with swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa.
The disease manifests itself with local symptoms - dryness, sharp pain when swallowing, increased mucus production. In addition to the symptoms of inflammation of the pharynx, nasal congestion, hoarseness and other signs associated with exposure to the allergen on the upper respiratory tract occur. If it is not eliminated in time, acute pharyngitis can become chronic.
Local signs of catarrhal inflammation:
- Dry throat mucosa,
- Sore throat,
- Painful and dry cough,
- A constant desire to cough, associated with the irritating effect of accumulated secretions on the pharyngeal mucosa.
Patients become irritable, their sleep and normal rhythm of life are disrupted.
In adults, some forms of chronic pharyngitis may differ in morphological changes and clinical signs.
- Granular pharyngitis often complicates the course of inflammatory diseases of the nose, paranasal sinuses, tonsils, and caries. In the absence of adequate and timely therapy, red nodules form on the pharyngeal mucosa, causing paroxysmal coughing. The pathology manifests itself as painful sensations and sore throat, paroxysmal cough with copious sputum.
- Subatrophic pharyngitis is a consequence of regular exposure to substances that irritate the pharynx. This form of the disease often complicates the course of chronic pathologies of the digestive organs - pancreas, gallbladder, stomach. Treatment consists of eliminating the main etiological factor.
- Hypertrophic pharyngitis is manifested by thickening and hyperemia of the pharyngeal mucosa, as well as the formation of purulent secretion. This pathology is characterized by the formation of lymphoid accumulations in the pharynx and the release of viscous sputum.
DETAILS: Good for periodontitis
Pharyngitis is a pathology that quite often affects the children's body, occurs in various forms and is often a manifestation of another disease - adenoiditis, scarlet fever, tonsillitis. Children who do not walk much and sleep in a room with dry and warm air are at risk.
To avoid severe complications and the transition of the disease to an atrophic or subatrophic form, sick children are prohibited from going outside in wet weather and soaring their throats for a week. Soda rinses are also not recommended for children with chronic pharyngitis, since soda dries out the mucous membranes, which can provoke the development of severe complications.
It is quite difficult to identify pathology in children. This is due to mild clinical manifestations that do not allow the disease to be detected by eye. After listening to the complaints, the specialist examines the child’s pharynx. The oropharynx in this disease is red, swollen, swollen with the presence of mucous or purulent discharge, the posterior wall is granular with pinpoint hemorrhages or blisters filled with blood.
The child's main complaints:
- A sore throat,
- Soreness or itching
- Slight cough
- Pain and itching in the ears,
- Runny nose,
- Conjunctivitis.
Local signs persist for a couple of days and gradually disappear. Body temperature is subfebrile or normal. Children usually find it more painful to swallow saliva than to swallow food.
When a secondary infection occurs and complications develop (angina or adenoiditis), general symptoms with severe intoxication begin to increase.
Pharyngitis, like any other disease, is dangerous for a pregnant woman’s body and creates many inconveniences associated with the inability to use conventional treatment methods.
The disease manifests itself in pregnant women with classic local symptoms, low-grade fever, lymphadenitis, hoarseness, and hacking cough.
Pharyngitis often complicates pregnancy. In the absence of adequate treatment in the early stages, it can lead to miscarriage, and in the later stages - to premature birth.
If your throat is inflamed, there is no pain at first. However, the patient complains of internal discomfort, the presence of a foreign body in the larynx. Symptoms are rapidly increasing, the sick person’s temperature even rises, there is general weakness, which confines one to bed and provokes aches throughout the body. In addition, dangerous inflammation of the larynx is accompanied by:
- persistent runny nose;
- dry strong cough;
- muscle and joint pain;
- depressed state;
- swelling of the mucous membranes;
- other symptoms of respiratory diseases.
If the disease remains without attention and medical attention for a long time, damage to the respiratory tract becomes chronic and incurable. In this condition, a sore throat attacks in periodic attacks, and the patient’s main task is to prolong the period of remission. Here are the unpleasant symptoms characteristic of chronic tonsillitis:
- pain with enlarged lymph nodes;
- occasional throat irritation;
- tendency to chronic rhinitis;
- moderate increase in body temperature (in the range of 37-37.5 degrees);
- nasal congestion;
- weakened immunity.
Diseases that provoke inflammation in the throat have similar symptoms:
- Fever.
- Sore throat.
- Painful sensations when moving, a feeling of aching.
- Attacks of dry cough.
- Apathy, decreased ability to work, poor health.
Once the inflammatory process affects the uvula and tonsils, the patient suffers unbearable pain when speaking, swallowing or coughing. There is a sharp deterioration in appetite. Often, against the background of inflammation, the lymph nodes in the larynx become enlarged.
- To get rid of swelling and redness. You can resort to rinsing procedures using medicinal herbs. A decoction can be made using sage, calendula or eucalyptus as plants that have effective anti-inflammatory as well as antibacterial effects. At home, if there are no herbs from the list, you can resort to a regular solution of water and soda. The patient needs to drink a lot. It is advisable to add lemon or raspberries to tea, and at night add honey to milk to soften your throat.
- If the patient has contracted a sore throat, the use of products like propolis and royal jelly will be effective. The medicine has an analgesic effect, suppresses pathogenic microflora, and restores tissue. It is necessary to chew propolis thoroughly and, an hour later, anoint the larynx with bee milk mixed with honey. They resort to medicine to soften the larynx.
- In case of pharyngitis, rinsing procedures will not be superfluous. Using beet juice has a quick and positive effect on the body. Peeled beets are rubbed, squeezing out the juice. After this, the mixture is poured with warm water. The solution is perfect for gargling about six times a day. It is better not to say a certain period of time after rinsing.
There are several recipes used for recovery. How to treat a sore throat:
- Yogurt, coffee, garlic and honey are mixed in a ratio of 3:2:1:10, after which corn flour is added so that the resulting sour cream takes on the desired consistency. The medicine is perfect for external use. Application of the product should be repeated several times a day with an interval of four hours. To achieve the desired effect, it is necessary to carry out the procedure for at least a week.
- Chopped garlic must be stuffed into walnut shells. The inner sides of the palms are treated with filling, when the shell is fixed using a breathable bandage. The procedure should be repeated regularly for the first five days. The use of the drug is justified at the onset of a sore throat. If the patient's condition is advanced, there is a decrease in effectiveness.
When should you see a doctor? Which one do you need?
If the inflammation is mild, it can be treated at home. But, if the symptoms of the disease do not go away within two weeks after their onset, you should definitely seek medical help. Treatment of laryngeal disease is carried out by an otolaryngologist. In children, this disease is treated by a pediatrician.
Medical attention is required immediately if the patient has severe difficulty breathing, there is bloody discharge in the mucus, and the body temperature is significantly increased.
Inhalations
During laryngitis, inhalation is effective. They significantly improve breathing, relieve inflammation and dry mucous membranes. The manipulation is carried out using a nebulizer, inhaler or home remedies. Inhalations include the following medications:
- Ambrobene. This medication during laryngitis gives good results due to the rapid mitigation of cough and liquefaction of sputum. The product is diluted in a ratio of 1 to 1 with physiological solution, and the dose is indicated by a specialist in accordance with age indicators.
- Adrenaline, Epinephrine. Basically, these types of medications are prescribed by an otolaryngologist only if there is a predisposition of the disease to develop into bronchitis or pneumonia. The drugs are diluted with saline in a ratio of 1 to 6. It is prohibited to use the drugs yourself without the consent of a specialist.
- Saline solution or mineral water (Essentuki, Narzan). The use of such remedies is also effective in the presence of a disease. The therapy helps to moisturize and soften the throat, which eliminates the symptoms of the disease in the shortest possible time. Procedures are carried out up to 5 times a day, taking into account the severity of laryngitis.
- Fluimucil. This remedy effectively copes with the viral form of laryngitis or laryngotracheitis without the use of systemic antibacterial drugs. It affects the larynx and trachea, so it works faster than tablets. The drug and dose are prescribed exclusively by a specialist.
Recipes for solutions for inhalation.
Medicines
Inhalation of medications involves the use of a nebulizer without heating the solution. The patient pours the solution inside according to the instructions and breathes over the vapor. For these purposes the following are used:
- Berodual;
- Lazolvan;
- Dr. Theiss Syrup;
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Rokotan.
It is necessary to take time intervals between taking medications. So, for example, they initially take tablets, then inhale, and after a quarter of an hour they use a spray.
Herbs
It is also permissible to carry out procedures with herbs. For these purposes, 2 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with boiling water and infused for 30 minutes. Afterwards it is filtered and poured into the inhaler. It is optimal to carry out inhalations with steam. The following medicinal plants are used:
- Chamomile;
- Calendula;
- Sage;
- Eucalyptus.
Perhaps make a mixture of the above plants and brew it.
Oils
Oil inhalations are done only when there is no allergic reaction to the components used. Essential oils are mainly used:
- Eucalyptus;
- Fir trees;
- Cedar;
- Lavender;
- Mint.
For 1 tbsp. add 4 drops of oil to water, then mix the solution and pour it into the inhaler or nebulizer.