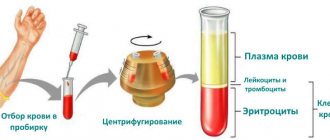
The doctor often looks at C-reactive protein in blood tests together with ESR to determine the possibility of an inflammatory process in the body in the acute phase.
Analysis of the presence of C-reactive protein in the blood began to be used back in the 30s of the twentieth century. A distinctive feature of this protein is its rapid response to the onset of the disease. The level increases within 6 to 12 hours after the onset of the disease, when there are still no symptoms. “Golden marker” is what clinicians call C-reactive protein for its ability to detect the acute phase of the inflammatory process. To the delight of those same clinicians, test results can now be obtained in half an hour (in some cases in an hour) instead of 24 hours due to the introduction of modern techniques. With this speed of blood test processing, in addition to diagnosing the disease, it is also possible to monitor the treatment process.
Functions
The synthesis of C-reactive protein is carried out by liver cells (hepatocytes) under the influence of pro-inflammatory cytokines to perform the protective functions of the body:
- binds substances (polysaccharides, nucleic acids, polyanions) located on the surface of bacteria, fungi and parasites;
- activates the work of immune system enzymes for nonspecific protection against infectious processes;
- promotes phagocytosis - the capture and destruction of foreign cells by macrophages, microphages and monocytes;
- activates the work of platelets during bleeding;
- identifies, neutralizes and removes toxic substances formed during the breakdown of its own cells.
Interpretation of test results
A C-reactive protein level that is slightly or moderately elevated may be difficult to interpret.
A huge range of conditions can raise C-reactive protein levels slightly, and it's difficult to draw any conclusions from just this test.
The following factors may also make it difficult to interpret C-reactive protein levels:
- Medicines that reduce inflammation in the body, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) and specific nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), lower C-reactive protein levels.
- Minor injury or infection may temporarily raise C-reactive protein levels and mask other potential illnesses.
- Chronic diseases that cause constant inflammation, including autoimmune diseases, may mask other possible causes of elevated C-reactive protein, such as a minor infection.
- Estrogen levels. Estrogen-based medications, such as birth control pills and hormone replacement medications, may increase C-reactive protein levels.
- Pregnancy can increase C-reactive protein levels, especially later in pregnancy.
A doctor will usually order a C-reactive protein test along with several other tests to get an overall picture of a person's health. This will allow a number of medical factors to be considered.
The doctor may also repeat the test to see how C-reactive protein levels change over time before making a diagnosis.
However, regardless of any other external factors, C-reactive protein levels above 10 mg/L usually indicate inflammation in the body.
Indications for use
Analysis for C-reactive protein is part of a set of diagnostic measures and is prescribed to identify the following diseases and pathological conditions:
- parasitic, bacterial and viral infections;
- tumors;
- oncological processes;
- assessing the degree of tissue necrosis as a result of injuries, burns, destructive changes in internal organs;
- early detection of postoperative complications;
- diagnosis of transplant rejection;
- assessment of the condition during myocardial infarction;
- tracking the results of therapy for rheumatoid processes;
- determination of cardiovascular risk;
- the effectiveness of antibacterial, anti-inflammatory treatment, immunosuppressive therapy;
- neonatal sepsis.
Reasons for increasing CRP concentrations
A high level of reactive protein is observed during bacterial infection. When the inflammatory process begins, the amount of the substance increases tens and sometimes hundreds of times.
In this case, C-reactive protein in the blood serum may be elevated to 1000 mg/l. This indicator is an indication that it is urgent to begin treatment with antibacterial drugs. An increased CRP level is most often observed in the following cases:
- With viral infection, but in this case the indicator increases slightly.
- For autoimmune diseases, in particular rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, systemic vasculitis. In such cases, the higher the indicator, the more severe the disease.
- With the development of a heart attack. As a rule, the indicator increases 18-32 hours after the attack, then gradually decreases by the twentieth day and completely normalizes by the fortieth day. A very high concentration of CRP in the blood indicates an unfavorable prognosis.
- With tissue necrosis as a result of tumor disintegration.
- In case of tissue damage due to injury, burns or frostbite.
- For chronic muscle pain.
- For oncological diseases.
- For diabetes mellitus.
- For arterial hypertension.
- For hormonal imbalance.
- In the presence of diseases of the digestive system, in particular with acute pancreatitis.
C-reactive protein in the blood is always elevated in the postoperative period, but during the normal recovery process its concentration decreases sharply. If elevated levels persist for a long time, this indicates the development of complications or indicates rejection of the transplanted tissue.
Also, significant upward deviations in CRP are observed in women carrying a child when there is a threat of premature birth. C-reactive protein may be elevated in the blood due to various subjective factors. The main ones:
- Extensive physical activity for several days before donating blood.
- Hormonal contraceptives.
- Excess body weight.
- Maintaining a protein diet, which is often followed by athletes.
- Depression and insomnia.
- Tobacco smoking.
Features of increased CRP in children
C-reactive protein may be elevated in the blood of children, and the reasons for this are the same as in adults. Therefore, for diagnosing the inflammatory process in a child, this analysis is of high value.
You should be aware that protein may not appear in the blood of a newborn even in the presence of sepsis. This pathology is characterized by a strong inflammatory process in one or more organs. Sepsis is always accompanied by high temperature, which becomes the main indicator for taking urgent measures.
The absence of CRP in the blood serum of newborns with obvious symptoms of inflammation is due to the fact that in infants the liver cannot work at full capacity, and therefore does not synthesize protein. But if the analysis shows that the level of C-reactive protein in the blood is increased, then antimicrobial therapy must be carried out urgently.
When children are sick with rubella, chickenpox or measles, a blood test will also definitely show an increase in CRP levels. Moreover, the concentration of the substance begins to increase sharply in the first days of the disease, when fever and increased body temperature are observed. After recovery, the indicators quickly decrease to normal.
An increase in CRP in the blood after any operation is an indicator of infection in the child’s body. If the level of the substance in the blood remains high despite antibiotic therapy, this indicates the development of complications.
Preparing for analysis
C-reactive protein levels can change under the influence of external factors, so before taking the test you should definitely adhere to the following recommendations:
- donate blood only on an empty stomach;
- the day before the study, you must refrain from smoking, drinking alcohol, physical activity, and stress;
- Before the blood collection procedure, you should sit for 20 minutes;
- do not take medications before the test;
- do not donate blood if X-rays, physiotherapeutic procedures or ultrasound were performed before the study.
The results of CRP studies in different laboratories may differ depending on the methods of analysis (radial immunodiffusion, immunoturbidimetry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, nephelometry), units of measurement, and reagents.
When is it sent for analysis?
That’s why CRP testing is often used in the following circumstances:
- search for risk factors for vascular and cardiac abnormalities;
- drug therapy assessment;
- control of therapy in the postoperative period;
- diagnosis of rheumatological diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- clinical examination;
- suspicion of neoplasms.
Tests for CRP, as well as ESR, should be prescribed for acute symptoms of infectious diseases. But these studies can be trusted to diagnose both autoimmune and rheumatic diseases. CRP is also prescribed for symptoms suggestive of cancer.
Indications for the test
So, a blood test for CRP in an adult is used for:
- assessing the level of risk in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), arterial hypertension (AH), and renal failure;
- early detection of pre-stroke conditions, as well as heart attacks in patients suffering from coronary artery disease;
- detection of post-infectious complications;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment with aspirin, statins, corticosteroids;
- diagnosis of tumor metastases;
- assessing the effectiveness of treatment of an infectious disease.
This indicator has a wide range of diagnostics.
How to prepare for analysis
So, venous blood is taken for a biochemical blood test and c-reactive protein. Before submitting, you must follow the following rules:
- the day before, avoid alcoholic beverages, fatty and spicy foods;
- avoid physical and emotional stress;
- eating food 12 hours before the test;
- all drinks except pure water are prohibited;
- smoking no later than half an hour before the test.
Norm of C-reactive protein (table)
Normally, the level of CRP is absent or in small quantities (up to 5 mg/l), regardless of gender and age. The exception is when, due to physiological reasons, there is increased activity of the immune system, for example, during pregnancy.
| Categories | Norm of SRP, mg/l |
| Newborns | 0-10 |
| Adults | 0-5 |
| Pregnant | 0-20 |
| For nicotine addiction | 0-25 |
SRP norm for women, men and children
Throughout the entire life cycle, CRP levels in people who do not have chronic diseases and are healthy at the time of blood sampling remain normal. At the same time, the age criterion, regardless of who donates blood for analysis - a woman, a man or a child - does not have any effect on the final result.
Important! The exception to the general rule is infants. In newborn babies, this blood level should not exceed 1.6 mg/l.
Reference values for all patients, regardless of gender, are 1.00 – 5.00 mg/l. Exceeding the upper limit is a clear signal for doctors about the inflammatory process occurring in the human body.
In order to normalize the level of CRP, the patient is prescribed additional diagnostic tests to identify hidden/overt inflammation. Based only on a blood test, a physician cannot determine the location of the source of infection.
Important! With significant damage to the skin as a result of a burn, the level of CRP rises to a maximum of 300-400 mg/l.
Normal CRP levels in women
Blood CRP levels in women change throughout life and depend on the patient’s age. In medicine, the following indicators are accepted as the norm for c-reactive protein in women:
- newborn babies (regardless of gender) – 1.60 mg/l;
- children under 12 years of age – 1.00-5.00 mg/l;
- teenagers and girls aged 12-20 years – 1.00-5.00 mg/l;
- adult women – 1.00-5.00 mg/l;
- elderly women – 1.00-5.00 mg/l;
- during the period of bearing a child - 3.60-8.60 mg/l.
CRP levels in pregnant women
During pregnancy, the CRP level in the blood increases. This is the physiological norm accepted by doctors. This excess of the norm is explained by the body’s protective reaction, designed to protect not only the health of the mother, but also the unborn child.
At the same time, a very rapid increase in the level of CRP in the blood of a pregnant woman indicates an existing infection. Pathology can develop both in the expectant mother and the pregnant child.
In addition, a rapid increase in protein levels may indicate the onset of premature delivery, placental bruise, or other related problems. In a healthy pregnant woman, the results will be as follows:
- 16-28 weeks – 2.30-3.60 mg/l;
- at week 32 – 2.20-3.20 mg/l.
Just before childbirth, protein levels will increase, and after the birth of the child they again become low and remain so constantly.
Important! In addition to inflammation in a woman’s body, CRP levels can increase as a result of taking hormonal medications, including oral contraception, as well as during menopause and excess weight.
Norm of CRP in men
The permissible norm of SRP for men is 1.00-5.00 mg/l. But, if its level exceeds 1.80 mg/l for a long time, then there is a possibility of developing depression. In addition to infection and inflammation, high levels of protein can provoke:
- alcoholism;
- stressful conditions;
- obesity;
- use of anabolic steroids;
- abuse of tobacco products;
- significant physical and emotional stress.
Acceptable level of CRP in children
The first time a blood test is performed on a child immediately after birth. Blood is drawn from the umbilical cord. The analysis is performed to exclude sepsis. Immediately after birth, the child’s level may increase to 1.60 mg/l.
Important! Deviation from the medical norm can cause chronic benign agranulocytosis. As a rule, the pathology goes away on its own, without drug treatment.
Reference values for children are 1.00-5.00 mg/l. The following diseases can increase CRP levels:
- lupus erythematosus;
- meningitis;
- flu;
- measles;
- chickenpox;
- rubella.
Causes of increased C-reactive protein
The formation of increased levels of CRP in the blood is caused by inflammatory processes due to acute and chronic diseases of various origins.
In cases where the analysis indicators range from 10 to 50 mg/l, this may indicate the development of:
- tuberculosis;
- dermatomyositis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- gout;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- ulcerative colitis;
- myocardial infarction;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
CRP test results of more than 50 ml/liter indicate serious pathologies with possible death:
- acute pancreatitis with tissue necrosis;
- severe bacterial infections (sepsis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis);
- Crohn's disease in the active phase;
- seronegative spondyloarthritis;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- tumor necrosis.
In some cases, the level of C-reactive protein rises to 100-300 mg/l, which is typical in severe inflammatory processes as a result of extensive burns, injuries, as well as sepsis, including postoperative sepsis.
During the diagnostic process and when assessing the effectiveness of drug therapy, approximate CRP indicators are used, which differ depending on the disease.
| Diseases | Features of increasing C-reactive protein |
| Viral infections (influenza, chicken pox, rubella, viral hepatitis) | Increases slightly (up to 20 units) |
| Bacterial infections (streptococcal, staphylococcal, meningitis, salmonellosis, bacterial pneumonia) | The level of CRP reaches 100 mg/l, but after the start of effective treatment it decreases on the third day of therapy |
| Neonatal sepsis | Increase to 12 mg/l |
| Abscess, thrombophlebitis after surgery | Protein levels do not decrease on the fifth day after surgery |
| Oncological diseases (malignant tumors) | An increase in the level of C-reactive protein in the blood to 20-40 mg/l is due to tumor growth, and more than 100 is due to metastasis |
| Diseases accompanied by tissue necrosis (myocardial infarction, intestinal necrosis, lung necrosis) | Malignant tumors are characterized by high levels of CRP (more than 120-150) in the absence of any acute symptoms |
In some cases, the cause of increased CRP is long-term use of hormonal drugs with estrogen, oral contraceptives, anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids.
Treatment methods
Deviation of CRP from the norm, when there are no physiological prerequisites for this, requires treatment. This is because elevated CRP can be a sign of risk for cardiovascular disease.
Of course, the prescription of a specific treatment is carried out only by a specialist after passing all the tests and studies. The level of such a protein can only be reduced if the root cause of the increase has been established. Treatment is prescribed individually for each patient.
To enhance the effectiveness of treatment, it is advisable to include a diet in addition to medications. It is necessary to choose products that will further strengthen the cardiovascular system. In addition, you will need to reduce blood cholesterol. To keep your body in good shape, you will need to exercise regularly and also monitor your weight, especially if you have problems with it.
For those suffering from diabetes, checking your sugar levels and blood pressure is mandatory. It is necessary to stop smoking and completely eliminate alcoholic beverages. Only all these measures taken together will quickly and effectively reduce the level of DRR.
During pregnancy
In cases where during pregnancy a general blood test shows an increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, then in order to further diagnose the causes of inflammation, a test for C-reactive protein is prescribed.
Depending on the trimester, the concentration of CRP in the blood changes several times throughout pregnancy as a result of the mother's immune response to the development of the fetus, which is a natural process.
| Trimester | Norm, mg/l |
| I | 0 |
| II | 0,4-20,3 |
| III | 0,4-8,1 |
High levels of CRP during pregnancy can be caused by the inflammatory, infectious, autoimmune and cardiovascular diseases mentioned above.
In some cases, elevated C-reactive protein indicates pathology of the vascular system (including at the initial stage), which can complicate pregnancy and lead to slower fetal growth, dysfunction of the placenta, low birth weight of the newborn, and also increases the risk of premature birth.
CRP in the blood: what is it?
So, CRP in the blood is a reflection of an acute inflammatory response. What does it mean – there is an increased production of it by the liver when any organ is damaged. In diagnostic activities, it goes hand in hand with ESR, but is more accurate and reliable.
To determine the concentration of CRP, a biochemical analysis is used, which shows the quantitative value of inflammatory proteins. With it, these proteins increase after 6-12 hours. They are great for tracking the effect of the prescribed treatment.
But the risk of laboratories is also great; an increase in CRP alone should not be considered 100% the result of a terrible diagnosis. With inflammation, CRP, in contrast to ESR, approaches normal levels immediately after the patient’s condition improves. But the ESR remains high for months.
CRP blood test
To eliminate errors when studying a biochemical blood test for CRP, you should adhere to simple rules that are observed before going to the laboratory. These are the recommendations:
- the day before taking a biochemical analysis, heavy physical stress, stressful situations, and sex are excluded;
- exclude fatty foods, spicy foods, and alcohol from the diet for 24 hours;
- Do not smoke for at least 2-3 hours;
- Blood is taken from a vein, on an empty stomach, in the first half of the day, preferably in the morning;
- At least 12 hours must pass between the test and the last meal; a little clean water is allowed;
- Warn the laboratory assistant if medications that provoke an increase in protein are taken during this period.
Carrying out the technique
This technique allows you to determine the exact answer in 30 minutes, diagnosing the process in the body. With the help of such a quick study, timely diagnosis occurs, and, in case of a negative answer, immediate medical assistance is provided. The correct tactics of complex treatment measures are also prescribed. C reactive protein during pregnancy sometimes appears due to hormonal changes.
With increased reactive protein causes: this happens when there is an allergic reaction in the body, as well as an active period. When rheumatism, myocardial infarction is also increased with protein.
Reactive protein in the blood: this occurs due to macrophages, which, when performing their main task in areas of inflammation, help capture foreign antigens. At the same time, they enter the lymph node, and there they produce antigen presentations. C reactive protein is positive: the norm for C reactive protein in the blood is when it does not appear during the test. Reactive protein is increased reasons: The factor why the indicator increases is that:
- an oncological disease has formed in the system;
- trauma after surgery;
- consequences of burns;
- sepsis occurs.
C reactive protein norm in women: determined during analysis, it depends on age, internal and external factors. An increase in CRP often occurs in diseases such as tuberculosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, nephritis, and rheumatism. C-reactive protein is a type of compound that allows you to determine if an inflammatory process has formed in the system. The amount of reactive proteins is determined using a cereactive protein detection assay. When the body is in generally normal condition, the protein is not detected during the analysis.
Increased reactive protein in the blood: this occurs due to both external and internal influences on the body. But, when an infectious process has formed in the body, the manifestation of this type of substance is an early sign of a serious illness. Reactive protein in the blood is normal: often, an increased concentration of the substance in the blood of children is the only sign that an infection has formed in the body. The increase in the indicator increases with some childhood diseases, these are: chickenpox, rubella, measles. A test for c reactive protein is prescribed. During the examination, treatment measures are prescribed to eliminate the cause of the disease. A biochemical blood test, SRB, is prescribed for an accurate result.
CRP (CRP) in a biochemical blood test: increased, normal, interpretation of indicators
When you noticeably feel a loss of strength, and the reason is unclear, the doctor prescribes a test to determine CRP standards using a biochemical blood test. CRP is nothing more than C-reactive protein, an elevated level of which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. This method of laboratory diagnostics is widely used in modern medicine, since it is recognized as the most informative. Based on its results, the doctor will be able to build a line of correct therapy.
What is C-reactive protein
Human blood contains a whole group of plasma proteins. One of them is C-reactive protein. This blood component is known for its hypersensitivity - it instantly reacts to the appearance of even the slightest inflammation in the body.
CRP is secreted by the liver. Its main function is to increase the body's immune defense.
Even with slight damage to internal tissues, CRP begins to rise, thereby forcing the entire system to work to increase the level of protection.
C-reactive protein “works” in tandem with pneumococcal polysaccharides. Combining together, they become a barrier to infection and prevent it from spreading throughout the body. These are some kind of protectors. It is no coincidence that the worse a person feels, the higher the level of this protein in the patient’s blood.
CRP actively stimulates the production of leukocytes and phagocytosis of cells. In other words, there is active stimulation of innate immunity.
Why get tested?
Biochemistry to detect the level of CRP in the blood is prescribed to detect foci of inflammation. When present, the level of this protein increases several times.
This study helps determine the nature of the inflammation: viral or bacterial.
Biomaterial collection is mandatory after surgery. In this way, the attending physician monitors the quality of rehabilitation. Nature intended that immediately after surgery, the level of protein “takes off” sharply in order to maximally protect the body from infection. As soon as the patient begins to return to normal, the level of CRP immediately stabilizes.
Thus, the main objectives of the study are:
- Determine the degree of intensity of the inflammatory process
- Monitor whether drug therapy is successful
- Monitoring postoperative complications
- Determine whether the body has begun to reject tissue after transplantation
Today, such diagnostics are carried out using two methods:
- Veltman's test
- alpha - 1 - antitrypsin
Indications for analysis
Laboratory blood diagnostics for elevated c-reactive protein are prescribed in the following cases:
- postoperative period;
- condition after a stroke;
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- cardiac ischemia;
- the appearance of tumors, both benign and malignant;
- latent infections.
- examination before surgery, especially before coronary artery bypass grafting.
Doctors recommend that everyone undergo this examination at least once a year. Men and women aged 60+ are at risk. It is better to prevent a disease than to try to treat it for a long time.
What kind of research is this
Human blood is never left without immune surveillance. This helps the body to constantly be in a protected state. The main role in this process is performed by specific proteins from the complement system. When any pathological changes occur in the body, including inflammatory ones, or massive tissue destruction, the number of immune protein components begins to increase. The part that reacts fastest is called C-reactive protein. It is synthesized by liver cells in response to inflammation in any part of the body. The more active the pathological process, the more C-reactive protein circulates in the blood. Its physiological role is to enhance immune reactions and phagocytic (neutralizing) activity of blood cellular elements.
Its determination in the blood is quantitative in nature and allows one to obtain the result in the form of a certain value, which is compared with established standards. The analysis for C-reactive protein has advantages over other acute-phase blood parameters, since it is an absolute indicator of inflammation of any localization almost from the first hours of its occurrence. Based on the dynamics of the obtained indicator, one can judge the activity of the process and the effectiveness of the ongoing treatment measures.
Indications for analysis
C-reactive protein is a compound that can, within a few hours, indicate the development of pathology even before the onset of its symptoms. The maximum concentration of the marker in the blood is detected 24 hours after harmful bacteria enter the body or cell death in tissues.
Analysis for the level of C-reactive protein is carried out when:
- suspected problems of the cardiovascular system;
- assessing the possible development of a stroke or heart attack;
- development of ischemia of the brain or heart muscle;
- diagnosing coronary syndrome;
- control of prescribed treatment;
- monitoring of body systems in the postoperative period and after illnesses that can cause complications;
- diagnosis of neoplasms;
- identifying bacterial or viral infection of the patient.
Certain patient groups require monthly monitoring of protein levels along with other vital signs.
These groups include people:
- those suffering from diabetes;
- with hypertension;
- elderly;
- athletes;
- alcohol and tobacco abusers.
In some cases, a situation may arise when a person is healthy, but the protein level is high.
Such situations include:
- early gestation;
- breastfeeding period;
- use of hormonal drugs.
Collection of biomaterial for analysis should be submitted in the morning, before 11 o’clock. The procedure must be carried out strictly on an empty stomach.
To avoid analysis errors, it is recommended to adhere to certain rules when preparing to donate blood:
- per day it is necessary to exclude tonic drinks containing caffeine: coffee, tea and energy drinks;
- the last meal should be no later than 15 hours before blood collection;
- do not drink alcohol 24 hours before the test;
- You should stop smoking 4 hours before the procedure;
- exclude active sports 48 hours before the test;
- Avoid visiting the sauna or taking a hot bath 10 hours before the procedure.
If you are forced to take medications or have undergone previous surgical interventions, you should notify your physician before taking the test.
C-reactive protein is a protein compound that is detected even in small concentrations. The material for analysis is blood serum. Protein content is determined using a photometer. This device is capable of measuring protein concentrations below 0.4 mg/l.
Biomaterial is taken from a vein in the elbow:
- The puncture site is treated with an antiseptic.
- The veins above the elbow are clamped with a tourniquet to ensure good flow of blood to the lower part of the arm and slow down its outflow.
- The patient must clench and unclench his fist for several seconds to increase blood flow to the lower veins.
- A specialist, using a conventional syringe or a special vacuum system, inserts a needle into a large vessel and collects the required amount of venous blood.
- After taking the material, the puncture site is treated with an antiseptic.
- The patient bends his arm at the elbow and holds it in this position for several minutes to stop the bleeding.
A blood test takes 30 minutes. up to 1 hour.
What can affect the results of the analysis?
The results of the CRP blood test are influenced not only by the professionalism of the doctor who will decipher the indicators, but also by the patient’s preparedness for the procedure. False data can occur in the following situations:
- Taking oral contraceptives;
- Hormone replacement therapy;
- Taking certain medications (beta blockers, statins, corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- Bad habits;
- Intense physical activity.
Deciphering a blood test for C-reactive protein is the task of a qualified specialist. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors use a comprehensive assessment of indicators. The laboratory, which is located on the territory of the Yusupov Hospital, eliminates differences in units of measurement, as happens in other medical institutions. Doctors take into account the fact that the result of the analysis is influenced by the patient’s gender, age and weight parameters. The Yusupov Hospital has the latest equipment that is used in foreign countries, so you will not have to wait for the results of such important tests for several weeks. The hospital's medical staff will be happy to help if you have any questions. You can find prices for services provided by the Yusupov Hospital on the website or directly from the administrative person. If a disease is detected, our specialists will conduct an effective course of treatment and rehabilitation. The comfortable rooms are equipped with everything you need so that you do not need anything throughout your entire stay in the hospital. During its short period of existence, the Yusupov Hospital can boast of an excellent reputation, as well as an impressive number of grateful patients. You can make an appointment or consultation by phone.
Author
Alexander Vyacheslavovich Averyanov
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Doctor of the Highest Qualification Category
C-reactive protein is elevated: what does this mean, the norm in men, women and children
According to WHO, pathologies of the cardiovascular system (CVS) occupy a leading position among the causes of death in people around the world. This fact makes it important to identify deviations from the norm at an early stage. Laboratory analysis to detect the level of c-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood is necessary to assess the risk of CVD diseases and predict their outcome, as well as to identify the inflammatory process. The study is of particular importance when it is necessary to select adequate antibiotic therapy or when correcting already selected methods.
What is c-reactive protein, and how much should the norm be?
C-reactive protein is a two-component molecule consisting of proteins (peptides) covalently linked to several oligosaccharides. The name is due to its ability to interact with C-polysaccharides of bacteria of the Streptococcaceae family, thereby forming a stable antigen-antibody complex (precipitation reaction). This mechanism refers to the protective reactions of the human body to infectious infection.
When a pathogen penetrates, the immune system is activated, which stimulates the process of synthesis of small peptide molecules - cytokines. They provide signal transmission about the manifestation of the inflammatory process and the need to enhance the production of acute phase proteins, which are CRP. After 1-2 days, there is an increase in CRP by tens and hundreds of times compared to normal values.
It is noted that the maximum level of CRP (more than 150 mg/ml) is recorded in infectious diseases of bacterial etiology. While during viral infection the protein concentration does not exceed 30 mg/l. Tissue death (necrosis) is another cause of elevated C-reactive protein, including heart attack, cancer, and atherosclerosis (deposition of excess cholesterol in blood vessels).
Physiological function of CRP
CRP is classified as an acute phase protein of the inflammatory process; it takes an active part in:
- launching a cascade of enzymatic reactions of the compliment system;
- strengthening the process of production of monocytes - white blood cells capable of implementing the process of phagocytosis of relatively large foreign particles;
- stimulating the synthesis of adhesion molecules, which are necessary for the attachment of immune cells to the surface of the infectious agent;
- the process of binding and converting low-density lipoproteins (“bad” cholesterol), the accumulation of which indirectly increases the risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies.
Thus, the importance of c-reactive protein for the human body is difficult to overestimate, since without it it is impossible to carry out full protection against foreign pathogenic microorganisms.
Blood test with reactive protein
Determining the value of CRP quantitatively is a technique implemented in private and some public laboratories. The execution time, not counting the day of taking the biomaterial, does not exceed 1 day. However, results may be delayed due to laboratory workload.
The analysis is performed using the immunoturbidimetry method, the essence of which is to determine the degree of turbidity of the solution in the presence or absence of the formation of a stable antigen-antibody complex. The advantages of the method include low cost, high degree of reliability and the ability to obtain quantitative results.
The technique is divided into analysis with normal and increased sensitivity. A highly sensitive blood test is necessary to diagnose the presence of not only acute, but also chronic inflammatory processes in blood vessels, as well as early forms of atherosclerosis. The minimum level of SRP detectable by instruments is 0.1 mg/l.
Signs of elevated c-reactive protein
Symptoms of elevated CRP levels correspond to the clinical picture of the disease that caused this pathological condition. Patients often experience a sharp increase in body temperature (fever), joint pain, nausea and vomiting, as well as a general state of weakness and increased drowsiness.
Oncology can proceed for a long time without the manifestation of typical symptoms. The classic clinical picture can develop at stages 3-4 of cancer, when the malignant neoplasm has led to tissue necrosis and the spread of metastases.
The danger of atherosclerosis lies in its long-term asymptomatic course. This disease significantly increases the risk of myocardial infarction, which can be fatal.
Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo an annual scheduled preventive examination, which includes a set of mandatory general clinical and biochemical tests, and often specific laboratory markers (if indicated).
Indications for the test
A test for c-reactive protein in the blood is prescribed for:
- the need to identify inflammatory processes resulting from autoimmune pathologies or infectious invasion;
- assessing the effectiveness of the chosen tactics for treating infectious diseases;
- differentiating a bacterial infection from a viral one;
- determining the severity of an inflammatory or autoimmune disease;
- postoperative control and prevention of infectious complications;
- deciding on the need to prescribe antibiotic therapy, as well as the duration of the course;
- drawing up a prognosis, including a lethal one, against the background of pancreatic necrosis;
- analysis of the extent and extent of damaged tissue by malignant neoplasms;
- differentiation of certain pathological conditions that are similar in symptoms and manifestations. For example: with granulomatous enteritis, c-reactive protein is increased, and with nonspecific ulcerative colitis it is decreased;
- continuous monitoring of the activity of chronic pathologies.
A blood test for C-reactive protein in newborns is performed if sepsis is suspected. It is characterized by infection by pathogenic microorganisms not of individual organs and tissues, but of the entire human body as a whole. The condition is life-threatening.
Normal indicators for adults and children
Important: only the attending physician can decipher the results of a blood test, determine the diagnosis and select treatment methods.
It should be noted that the isolated use of the CRP test when examining a patient is unacceptable. To make a final diagnosis, data from other laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostic methods, as well as the patient’s medical history, are taken into account.
The level of c-reactive protein in women and men varies depending on the degree of sensitivity of the method used and is presented in the table.
| Degree of sensitivity of the technique | Normal values, mg/l |
| Normal | 0 — 5 |
| High | 0 – 1 |
It should be noted that the norm of c-reactive protein in children is similar to adults and should not exceed the specified reference (normal) values.
The norm of reactive protein in women after 50 years also corresponds to standard values, while even a slight increase in reference indicators is a sufficient reason for conducting a comprehensive examination.
Assessing the risk of heart attack using CRP
Important: in order to assess the risk of a heart attack, it is permissible to use only highly sensitive techniques. A test with normal sensitivity does not determine the likelihood of developing a heart attack or other cardiovascular diseases.
A direct relationship has been established between the level of CRP and the degree of risk of CV pathologies, as well as their complications. Thus, normal values not exceeding 1 mg/l are characteristic of a low probability of developing cardiovascular diseases. The concentration of the considered laboratory criterion from 1 to 3 mg/l correlates with the average risk of developing atherosclerosis and, as a consequence, myocardial infarction. An increase in value to 3 mg/l or more indicates a high probability of vascular and cardiac pathologies.
An increase in CRP to 10 mg/l or more is a sufficient reason to conduct additional examination to identify infectious diseases, viral or bacterial etiology.
It should be noted that, in comparative terms, patients with increased levels of CRP and normal levels of “bad” cholesterol are characterized by a higher risk of developing CV pathologies than people with normal levels of CRP and elevated cholesterol.
If a person with coronary heart disease has high values of the criterion under consideration, then we can talk about a dangerous risk of recurrent heart attack or stroke, as well as a high probability of developing complications after coronary artery bypass grafting.
What does it mean if an adult has elevated C-reactive protein?
The reasons for the increase in c-reactive protein in children and adult patients may be different, which allows us to classify the study as low specific. List of possible reasons:
- acute form of infectious infection with viruses (increase in the range of 10 - 30 g/l) or bacteria (from 40 to 100 mg/ml, and with severe infection - up to 200 mg/l);
- autoimmune pathologies (arthritis, vasculitis, polyarthritis);
- some lymphadenopathy;
- extensive damage to the integrity of tissues and organs: surgery, trauma, acute pancreatitis, necrosis of pancreatic tissue, heart attack, stroke (up to 100 mg/l);
- penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the tissues of the heart valve;
- cancer accompanied by the spread of metastases;
- extensive burns and sepsis (more than 300 mg/l);
- excess production of female sex hormones (estrogens and progesterone). What explains the increased CRP in the blood of women during pregnancy, as well as when taking oral contraceptives. However, it should be taken into account that a significant deviation from the norm (2 times or more) indicates the development of the disease and requires immediate further examination.
It is noted that a slight excess of the norm is recorded in diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure and in the presence of excess weight in a person.
Preparation for delivery of biomaterial
The biomaterial for the test is venous blood serum taken by a specialist from the cubital vein on the elbow. More than 70% of errors are made at the preanalytical stage: at the stage of preparing the patient and during incorrect implementation of the blood collection procedure. Therefore, the reliability of the results obtained depends not only on the accurate implementation of the test in the laboratory, but also on the correct preparation of the patient himself.
It is necessary to donate blood in the morning strictly on an empty stomach, the minimum time interval after the last meal should be 12 hours. In addition, half an hour before donating the biomaterial, the patient is prohibited from smoking, as well as from experiencing physical and emotional stress. Sports training in the evening before the morning visit to the laboratory should also be canceled.
You should avoid taking any medications for 2 days, after consulting with your doctor. This rule is of particular importance for people who use the following medications:
- aspirin ® ;
- ibuprofen ® ;
- steroids;
- lipid-lowering drugs;
- beta blockers.
This fact is due to the ability of the above drugs to temporarily reduce the concentration of the laboratory criterion in question. Failure to comply with this rule may result in false negative results and, as a consequence, delay in the administration of necessary treatment.
It is extremely important to take a responsible approach to your health and be aware of the fact that the earlier the disease is detected, the easier it will be to cure it and the more favorable the outcome prognosis for the patient.
Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova)
Certified specialist, in 2019 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiology. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University.
In 2019 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”.
Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the “Biological Sciences” category 2019.
Thanks to the developments of scientists, doctors have a unique opportunity to determine the development of inflammation at the very beginning of their formation. A blood test for CRP instantly gives a conclusion that pathologies have appeared in the body. This helps to start timely treatment and avoid dangerous complications. It is useful to understand this important indicator in the analyzes.
C-reactive protein - what is it?
In extremely low concentrations, this substance is invariably produced by the liver. Of all the proteins found in the body, this protein is the most highly sensitive. When several hours pass from the moment of inflammation, a sharp increase in its quantitative composition occurs tens of times. This shows the beginning of an acute process. Even a disease that has just begun will be reflected in the results of blood plasma tests by increased levels of CRP protein. With treatment and progression of the disease into the chronic phase, the values decrease.
C-reactive protein is a substance that:
- reacts with polysaccharides, binds and precipitates them;
- removes fatty acids formed when cell membranes are damaged with the onset of inflammation;
- recognizes and destroys microbes;
- stimulates defensive reactions;
- helps wound healing;
- promotes the production of leukocytes that create a barrier to infection;
- activates the immune system.
DRR analysis
Laboratory testing is carried out by collecting venous blood on an empty stomach. The assay is performed using protein-sensitive reagents. The correctness of the results is affected by the use of hormonal drugs, contraceptives, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To take the test, you need to prepare:
- stop taking medications, alcohol, fatty, spicy foods one day before;
- do not eat 12 hours before the procedure;
- exclude physical activity;
- to be in a complacent state;
- no smoking in an hour.
When is it prescribed to determine CRP parameters in a biochemical blood test? This is done if necessary:
- examinations of hypertensive patients;
- performing diagnostics;
- assessing the effect of treatment;
- prognosis of tumor development;
- control over the progress of treatment;
- prognosis of cardiovascular system anomalies;
- performing a tumor test;
- assessing the severity of infection;
- identifying postoperative problems;
- monitoring the survival rate of transplanted organs;
- analysis of the use of antimicrobial drugs.
The values of the indicators reflect the course of inflammatory processes in association with diseases:
- maximum 30 mg/l – tumor metastases, viral diseases, rheumatic pathologies;
- from 40 to 95 – operations, bacterial infections, acute myocardial infarction, worsening chronic processes;
- over 295 mg/l – sepsis, major burns, severe infections, cancer.
A very important role is given to analysis as a means of preventing atherosclerosis and the development of thromboembolism. If indicators change, treatment is promptly prescribed to save the patient’s life. The diseases are inflammatory in nature and have deadly consequences - stroke, heart attack. If a vessel is destroyed:
- cholesterol attaches to the crack;
- a loose plaque appears;
- it can come off;
- the blood clot will block the vessel.
C-reactive protein is normal
Throughout a person’s life, CRP levels in a healthy body remain normal. Whether it is a woman, a man or a child, young or old, does not matter. The only exception is newborn babies, in whom the indicator should not show a value higher than 1.6 mg/l. The normal level of C-reactive protein in the blood is considered to be no more than 0.49 mg/l. Increased values are a signal of the onset of acute inflammation. To reduce them, it is necessary to carry out additional diagnostics and treatment - the analysis does not indicate the exact location of the anomaly.
C-reactive protein is normal in women
Researchers have discovered a pattern: an adult woman will have lower CRP levels if her mother breastfed her as a child. In addition to inflammation, test results are affected by taking hormonal medications, including oral contraceptives, menopause, and excess weight. When a biochemical analysis reveals that a woman’s CRP is elevated, this may mean thyroid disease or toxicosis of pregnancy. The normal level of C-reactive protein in women, when they are healthy, cannot exceed 0.49 mg/l. High values can be reduced with timely treatment.
C-reactive protein is normal in men
There is a peculiarity in the male body. If C-reactive protein remains above 1.8 mg/l for a long time, then there is a high probability of developing a depressive state. The normal level of C-reactive protein in men cannot exceed 0.49 mg/l. The deviation of indicators to large numbers is influenced by:
- alcohol abuse;
- stress;
- excess weight;
- taking anabolic steroids;
- smoking;
- increased stress – physical and emotional.
C-reactive protein is normal in children
The first determination of CRP indicators is carried out in the child in the maternity hospital, blood for laboratory testing is taken from the umbilical cord. This is necessary to exclude sepsis. In a newborn child, the values of indicators are increased to 1.6 mg/l. Fluctuations from the standards are caused by chronic benign agranulocytosis, which goes away without treatment by three years. The normal level of C-reactive protein in children is similar to that of adults. Elevated values may indicate the presence of diseases:
- meningitis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- chickenpox;
- flu;
- rubella;
- measles.
C-reactive protein is elevated - reasons
The following diseases are the basis for abnormal values of CRP protein:
- tumors – melanoma, carcinoma, leukemia;
- autoimmune – rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatism;
- infection with parasites – toxoplasmosis, giardiasis;
- bacterial infections – meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis, chlamydia;
- tissue death - myocardial infarction, transplant rejection, pancreatic necrosis.
The analysis is interpreted by the attending physician, who determines the reasons for the increase in C-reactive protein in the blood. These include violations of tissue integrity observed as a result of:
- getting injured;
- significant burns;
- carrying out surgical intervention;
- organ transplants;
- bypass operations;
- rupture of the amniotic sac - a threat to premature birth.
The reasons for the increase in CRP results in the analysis include low-grade inflammation, which provokes the risk of an increase in cardiovascular pathologies. An important role is played by the exacerbation of chronic infectious diseases. Indicators are increased if:
- Cushing's disease - pathology of the pituitary gland;
- thromboembolism;
- tuberculosis;
- jade;
- diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- atherosclerosis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- gynecological pathologies;
- apoplexy;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- viral infections;
- allergies.
C-reactive protein in oncology
A test for possible cancer development is a CRP test. To specify the diagnosis, special studies using tumor markers, ultrasound, and computed tomography are required. The appearance of metastases is characterized by CRP readings in the range of 10-31 mg/l. This analysis helps monitor the progression of the tumor and the dynamics of its growth. With its help, the doctor gives a prognosis of the condition and life expectancy. If C-reactive protein is elevated in oncology, this is characteristic of cancer:
C-reactive protein in rheumatoid arthritis
This blood test method is very sensitive to inflammatory processes that begin in joints and bones. This helps to make an early diagnosis and begin treatment, which is effective at this stage. C-reactive protein in rheumatoid arthritis rises tenfold if the cause of inflammation is bacterial. The viral source of the disease does not give high readings. When the process develops into the chronic phase, the normal level of CRP in the blood is observed. This means that during this period the analysis is not relevant.
C-reactive protein during pregnancy
For a woman expecting a baby, elevated CRP levels are not dangerous if other tests are normal. Otherwise, it is necessary to look for the cause of the inflammatory process. Indications may increase to 115 mg/l with toxicosis. When they increase to 8 mg/l from 5 to 19 weeks, there is a risk of miscarriage. C-reactive protein in pregnant women is checked regularly, because diseases of the mother can affect the development of the unborn child. The reasons for the increase are:
- viral infections, if the level is up to 19 mg/l;
- bacterial causes when it is more than 180 mg/l.
Sources: https://sovets.net/8861-s-reaktivnyiy-belok.html https://studopedia.ru/6_107853_svertivanie-krovi.html
Conclusion
Since C-reactive protein is synthesized in response to necrotic changes in tissues and the occurrence of an infectious disease, its determination is necessary for accurate early diagnosis. They also study it to monitor how successful the therapy is. It is better not to independently diagnose an increase in the level of C-reactive protein in the blood, but to entrust this to specialists - a rheumatologist, cardiologist, oncologist, surgeon. Indeed, to determine the cause of the disease, accompanied by an increase in the concentration of CRP, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination of the patient.
Video version of the article
Rating: (votes - 7 , average: 3.86 out of 5)
Reasons for deviation from the norm
What is SRB in children? Normally, CRP, when the result is positive, the protein is not detected in the analysis. When protein levels increase, this is affected by the presence of indirect symptoms such as high fever, chills, and shortness of breath. This happens with increased general sweating, when the analysis recorded the fact of an increase, as well as an increase in leukocytes in the blood. Previously, tests for the determination of reactive protein were used to identify the latent formation of the inflammatory process. If CRP is positive, then this means the development of the disease.
As a rule, this is necessary for older people. The main symptom for a thorough examination is when coronary heart disease develops, especially with atherosclerosis. With timely fixation, when an exacerbation occurred after surgery (during bypass surgery or after an angioplasty process). When the level is assessed, whether treatment with an antibacterial drug is effective. And also when there is a bacterial infection in the body. All this affects the deviation of the indicator from the norm.
When therapeutic treatment of a cardiovascular disease occurs, especially if it is suspected that a neoplasm has occurred in the body. When symptoms appear that lupus erythematosus is developing, as well as with ulcerative colitis. To ensure a reliable result, testing must be carried out in the morning. CRP is increased: 12 hours before this technique you should not eat food, and you should also avoid physical activity. You should also avoid stressful situations. All this is necessary for the result to be accurate.
Spermogram analysis10497
Revealing the result
If the body has an infection or contamination with a parasitic microorganism, as well as an injury or wound that results in an inflammatory process, then the cells in the liver will begin to produce this substance. This will stimulate the immune system. SRP in a biochemical blood test, when this type of protein compounds is detected, is the earliest sign of diagnosis in a system of processes with an infectious nature. C reactive protein is increased: when an inflammatory process occurs, the reactive protein begins to increase with proper treatment and use of the right medicinal substance, then the level of these compounds will quickly decrease. The manifestation of a substance often means a failure in the system.
Reactive protein in the blood, when a change in the amount of protein occurs, it is necessary to change the course of drug therapy. They also changed the medications that were originally prescribed. If reactive protein is detected in a newborn, this often means that the child is developing sepsis. Blood test for CRP: in order to correctly establish the diagnosis, as well as evaluate the process of eliminating the disease until complete recovery, it is necessary to compile all the data about the amount of CRP with a different indicator. The norm of CRP in the blood: the result without identifying the protein, which was obtained during the examination, as well as a blood test for the substance.
This indicator is used for ESR. When the ESR indicator is high, it follows that the CRP indicators are also high. The most common reasons for elevated substance c are factors such as viral infection. When it is discovered that there is an increase in protein in the body, then the correct selection of a method of complex effects is necessary to eliminate the disease. SRB blood test: a study is prescribed to identify the disease that provoked an increase in levels in human blood serum. The high sensitivity of CRP manifests itself in the various forms of events as well as changes that occur.
The norm for ESR in children is 20645
Protein is also affected by the effects of therapeutic measures; this requires the use and monitoring of the course of the disease. Elimination of various types of pathology that provokes an increase in the substance’s normal levels. Reactive protein is also detected using latex tests. SRP analysis: the basis of such analyzes is the effect of latex agglutination, using qualitative and semi-qualitative analysis. After a thorough study, the exact result for the indicator of the substance is revealed, meaning that protein is increased in the body.
Causes of high CRP levels
This blood marker is a complex compound consisting of carbohydrates and proteins. C-reactive protein is synthesized in liver cells; it is a highly sensitive compound in the human body and responds to any pathological changes in it.
In the blood of a healthy person, protein can also be contained in small quantities. This blood marker is a necessary element for maintaining immunity, which activates immediately after birth.
C-reactive protein has a number of important functions for humans. He:
- binds saccharides and removes them from the body in the form of sediment;
- removes the resulting fatty acids that are formed during traumatic cell breakdown;
- promotes rapid tissue regeneration;
- activates the production of substances that destroy microbes and viruses;
- stimulates the synthesis of leukocytes, creating an immune barrier;
- strengthens the body's defenses;
- connects innate immunity with acquired immunity, preserving immune memory for the production of the required antibodies;
- stimulates the immune system.
C-reactive protein has several types:
- Polymer protein: consists of 5 different components and is synthesized by the liver when necessary.
- Monomeric protein: consists of only 1 protein unit and has greater mobility and speed of activation of the immune system, as well as the synthesis of biological compounds.
In the acute course of the inflammatory process, the multidimensional protein disintegrates and becomes monomeric, exerting a more effective effect on the site of pathology.
At elevated values, the C-reactive marker has a negative effect on the condition of blood vessels, as it disrupts lipid metabolism and promotes the accumulation of harmful cholesterol on the walls of the arteries.
C-reactive protein synthesis can be affected by:
- bacteria;
- viruses;
- yeast and mushrooms;
- various injuries;
- operations performed;
- allergens;
- chemical substances;
- inflammation of internal organs due to damage to their tissues;
- malignant formations;
- diseases of the vascular system and heart;
- autoimmune diseases.
C-reactive protein is a biological substance that is produced by the liver not only when a person is injured or infected, but also during long-term chronic inflammation, when the body experiences physiological stress.
A number of diseases in the initial stage occur without obvious symptoms:
- pre-stroke condition;
- obesity;
- prehypertension;
- diabetes;
- hypotension;
- thrombophlebitis;
- tuberculosis;
- periodontal disease;
but an increased protein concentration in the blood indicates their presence.
Also, a high content of C-reactive protein in the body provokes an increase in the amount of high-density lipoproteins, which attach to the walls of blood vessels and form cholesterol plaques.
With minor inflammation, protein can weaken the action of insulin in the muscles, which leads to a lack of oxygen and nutrients in them. In this case, the muscle fibers atrophy.
The content of C-reactive protein varies depending on the type and severity of the disease. The decision about the need to reduce its level should be made only by the therapist.
SRP for infections
Protein plays an important role in human infection. It is able to activate the body's natural protective barriers, stimulate the immune system and suppress the proliferation of bacterial or viral organisms.
Protein levels differ when infected with different antigens:
- Viruses: from 10 to 45 mg/l.
- Bacteria: from 50 to 210 mg/l.
When infected with macrobacteria, the level of C-reactive protein can reach 300-500 mg/l.
This blood marker at elevated values provokes the development of atherosclerosis and a decrease in the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels. The level of values in this case ranges from 7 to 15 mg/l.
The protein concentration is used to estimate the risk of death from a heart attack or stroke. To do this, you need to undergo a highly sensitive protein detection test.
Protein at high levels in the blood reduces the lumen of blood vessels, changing the elasticity of their walls. This leads to increased blood pressure. With its systematic increase, the level of C-reactive protein remains within 10-100 mg/l.
Metabolic syndrome is directly related to increased protein levels.
The marker increases its values with increasing:
- fat deposits;
- number of triglyceride particles;
- blood glucose.
CRP for obesity
If there are disorders of fat metabolism in the body, the level of C-reactive protein increases. A person begins to suffer from excess weight, and then he is diagnosed with obesity.
Based on protein fluctuations in the blood, nutritionists calculate a diet with a certain calorie content, and also select a treatment regimen to normalize metabolic processes in the body.
SRP for stroke
A high concentration of this protein occurs with the development of pre-stroke conditions or stroke. The level of protein is associated with the stage of the disease and its severity.
When the protein concentration is from 1 to 3 mg/l, it is worth monitoring the condition of the heart and blood vessels, as it indicates possible problems in the future.
CRP for sleep apnea
With chronic respiratory arrest during sleep, the concentration of C-reactive protein increases. And it persists until oxygen starvation is completely eliminated by medicinal methods.
The blood marker has jumps in values during the development of autoimmune diseases. It is able to remove accumulated dead cells from the body and reduce autoimmune reactions. After this, the protein level drops significantly and does not exceed 10 mg/l. In this case, the acute stage of inflammation of tissues and organs occurs with obvious symptoms.
To normalize the patient's condition, it is necessary to increase the level of C-reactive protein to a concentration of 50 mg/l.
The highest concentration of protein is observed in inflamed areas of the joints. The protein level can remain in the range of 100-300 mg/l, which indicates the development of acute inflammation.
As bone tissue in the oral cavity is destroyed, protein levels increase. As the disease progresses, the protein concentration also increases. With adequate treatment of periodontal disease, the level of C-reactive protein decreases by 1 mg/l.
The protein content in the blood increases slightly with intestinal diseases. The protein level is maintained at a certain level and does not depend on the severity of the disease.
Suspicion of intestinal inflammation appears when C-reactive protein values in the range of 1-5 mg/l are obtained for a long time.
SRP for fatigue
C-reactive protein is a substance that is produced by the liver even under minor stress loads on the body. If fatigue or weakness occurs in the limbs, the value of C-reactive protein will be slightly increased within the range of 2-7 mg/l.
CRP for depression
Depressive syndrome causes the body to produce “harmful” hormones and slow down the synthesis of the hormone of happiness. This condition activates increased protein production to block the negative effects of these substances.
Macular degeneration refers to problems in recognizing objects in the center of the visual field, in which the blood supply to the eye is disrupted. In this case, the marker level becomes more than 3 mg/l.
CRP in dementia
Elevated levels of C-reactive protein are closely associated with the development of dementia in people over 50 years of age. This phenomenon occurs due to the destruction of nerve connections in the brain and oxygen starvation of cells as a result of vasoconstriction.
CRP for cancer
Long-term inflammation of organ tissues keeps protein concentrations at critical levels for the body. This provokes the proliferation of cells and their transformation into malignant formations.
High levels of C-reactive protein promote the development of cancer at the site of inflammation:
- stomach;
- lungs;
- leather;
- ovaries;
- colon.
When tumor lesions appear, the protein concentration exceeds 10 mg/l for a long time.
Eating certain substances reduces the concentration of an inflammatory marker.
Such connections include:
- Vitamin D;
- vitamin A;
- vitamin K;
- vitamin E;
- a nicotinic acid;
- folic acid;
- beta-carotene;
- selenium;
- magnesium;
- calcium;
- chromium;
- acetylsalicylic acid;
- Omega-3 acids;
- cellulose;
- probiotics.
Protein concentration can be reduced by:
- coffee;
- green tea;
- sea fish;
- eggs;
- cocoa;
- avocado;
- carrot;
- citrus;
- nuts;
- bell pepper;
- broccoli;
- sorrel;
- watermelon;
- garlic;
- lentils;
- buckwheat;
- olive oil;
- cherry;
- honey.
The blood plasma protein responsible for diagnosing inflammatory processes is called C-reactive protein or CRP.
Its concentration in the blood is directly related to the activity of the immune system.
After all, every day a person is attacked by bacteria, viruses, sometimes minor injuries occur, which means that the body’s defense system has to work constantly.
In simple words, the process can be described as follows: during inflammation or infection in an organ, cell membranes are damaged. As a result, biochemical processes are disrupted, red blood cells die, and toxins enter the blood.
CRP is produced in the liver during moments of acute inflammation or worsening chronic diseases.
C-reactive protein is one of the most sensitive markers, since its increase in the blood is observed within 6-12 hours after the onset of inflammation. And although the presence of protein does not indicate a specific disease, it does mean that a destructive process has begun in the body.
This indicator is considered the so-called indicator of problems that have arisen in the body, since its elevated level is observed in various pathological conditions. The causes of elevated reactive protein are the same in both children and adults. The exception is newborn babies. It may not appear in them even with sepsis.
For example, when children suffer from measles, chickenpox or rubella, the level of this protein is significantly higher than the permissible levels. The decrease occurs immediately after recovery. Elevated C-reactive protein in the blood after surgery indicates that the child is infected. The development of complications is indicated by high CRP numbers in tests, despite antibacterial treatment.
- tuberculosis;
- inflammatory processes in the acute and chronic stages;
- injuries: burns, wounds, fractures;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- myocardial infarction;
- IHD;
- hypertension;
- parasitic infections;
- autoimmune diseases - Crohn's disease, lupus erythematosus and others;
- pathologies of the endocrine system, for example, obesity, diabetes;
- cancer diseases;
- necrosis;
- arthritis;
- meningitis;
- hormonal disbalance;
- taking certain medications (hormones, NSAIDs).
Traditional recipes for normalizing CRP levels
800 g of dry wormwood are boiled in 3 liters of water, after which the resulting solution is added to a bath of warm water. You need to take this bath for about 20 minutes.
Young nettle leaves are poured with 300 ml of boiling water and left for 1 hour. The resulting solution must be drunk within 24 hours.
The crushed root is poured into 250 ml of boiling water and infused for 10-12 hours. The resulting infusion must be consumed during the day.
An increase in the concentration of C-reactive protein in the blood signals the onset of an inflammatory process or infection of the body. Monitoring of such an inflammatory marker and examination of the body must be carried out at least once a year. These manipulations will eliminate the risk of developing many diseases and prevent them in a timely manner.
Interpretation of the obtained analysis data
The standards for the concentration of C-reactive protein in the blood are set by each laboratory that conducts the study. This is due to the presence of reagents with different sensitivities for its detection. Therefore, next to the number with the result, the norm is usually indicated. The generally accepted standard for C-reactive protein in the blood is values that are less than 3 mg/l.
Only cases of detection of an increase in the content of C-reactive protein above standard values are considered pathological. Based on the value of the obtained indicator, the activity of inflammatory and immune reactions in the body can be assessed. The increase can be within a few units of measurement, or a hundred times compared to the norm.
Some laboratories use simplified options for determining C-reactive protein using a qualitative method. In this case, a minus sign or a certain number of pluses (from one to four) is indicated in the column of the result obtained. The greater the number of pluses, the more active the inflammatory changes in the body.
Scientists have found that C-reactive protein is a reliable prognostic sign for diseases of the heart and blood vessels, such as heart attack and atherosclerosis. If it is elevated in the range from 3 mg/l to 10 mg/l, this may indicate an increased risk of their occurrence or progression of the existing process.
We advise you to read: Why is the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation reaction increased?
In some diseases, C-reactive protein increases several times compared to normal. This may indicate:
- Autoimmune diseases;
- Rheumatoid and other types of arthritis;
- Malignant neoplasms and their metastases;
- Amyloidosis of internal organs;
- Tuberculosis process;
- Myocardial infarction in the acute period;
- Purulent diseases and septic condition;
- Infections of different localization (intestinal infections, hepatitis, meningitis, pneumonia, etc.);
- Burn disease and injuries;
- 1Diseases of the blood system.