The period after childbirth is one of the most dangerous and difficult for the child and his mother. Among the dangers that await a woman, mastitis occurs most often.
Mastitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the mammary glands, which develops in nursing women after childbirth. This disease occurs in about a third of women in the first month after giving birth. In almost all cases, the cause of this disease is Staphylococcus aureus.
Definition
Mastitis is the medical term for inflammation of the breast tissue. Previously, people called it a baby. According to statistics, this disease occurs in about 5% of women during lactation, but it also affects non-pregnant girls, men and newborn children.
The main symptoms of mastitis are pain and tenderness of the breasts.
Mastitis occurs when the breast tissue is affected by an infection, after which the inflammatory process begins.
Treating mastitis at home
Treatment of mastitis can occur at home, but in strict accordance with medical prescriptions. Self-medication of mastitis rarely leads to success, but only takes time and allows the pathological process to become more complicated.
In addition to taking medications and following other recommendations, it is useful to:
- drink a lot of liquid, in particular rosehip decoction, uzvara, warm non-mineral water;
- before feeding - apply warm wet compresses to the chest and dry heat to the neck and shoulders, which helps relieve spasm of the milk ducts and reduce breast swelling;
- after feeding - apply cold dry compresses to the chest.
As part of the prevention of mastitis, it is recommended:
- apply the newborn to the breast correctly;
- breastfeed on demand, not according to a schedule;
- carefully observe personal hygiene and feeding hygiene;
- If cracks form, treat them promptly and correctly.
Strictly contraindicated:
- limit the frequency and duration of feedings;
- express milk unnecessarily, that is, when the baby is sucking well;
- abruptly wean the child off the breast unless the doctor insists on it; For uncomplicated mastitis, feeding promotes recovery.
Causes of mastitis
Mastitis is bacterial in nature. The most common pathogens are Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. When vulnerable spots appear on the skin (cracks, scratches, bleeding wounds), it is very easy for microorganisms to penetrate the mammary glands through their excretory ducts. Less commonly, pathogenic particles are delivered from other foci through the blood or lymph.
In conditions of trauma to the skin of the chest, the following triggers can provoke the development of mastitis:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Prolonged hypothermia;
- Weak immune system;
- Breast injuries and consequences of surgery;
- Cracked nipples;
- Stagnation of milk in nursing women (lactostasis);
- Infectious foci in the body (pulpitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, sore throat, inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- Congenital anomalies of the mammary glands;
- Metabolism problems;
- Primary immunodeficiencies;
- Autoimmune diseases.
Routes of infection:
- Through the affected skin of the mammary glands or nipples, microcracks, wounds;
- Pyoderma and boils on the chest;
- Diseases of the epidermis (dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis);
- Hematogenous;
- Lymphogenic.
Prevention of mastitis
To avoid mastitis, as well as complications - pericarditis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis - it is necessary to monitor your health and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Symptoms of mastopathy appear long before the onset of pain, so it is advisable to check your hormonal levels in advance in order to take measures to correct estrogen/progesterone/prolactin. This will prevent the growth of glandular and fibrous tissue in the mammary gland.
To prevent infection from other organs from entering the chest, it is necessary to promptly treat teeth, infectious diseases of the genital organs and urinary system, tonsillitis and sinusitis.
Maintaining the functions of the thyroid and pancreas will strengthen the immune system during adolescence and menopause. Older women need to be regularly examined by a mammologist so as not to miss the onset of fibrocystic mastopathy. Women need to do the same after breast surgery, since according to statistics, mastitis can begin 2 to 6 years after surgery.
Well-chosen underwear does not compress the breasts and allows lymphatic fluid to circulate freely through the vessels.
Classification and symptoms
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish three types of mastitis, which are also forms of severity.
Serous stage
The disease begins with the penetration of bacteria into the mammary glands. Microbes begin to multiply, thereby causing inflammation. This is where the serous stage occurs.
It is characterized by:
- A sudden strong increase in temperature to 38-38.5 degrees, chills;
- General weakness, malaise;
- Lack of appetite;
- Headache;
- Aching pain in the chest area, gradually increasing in intensity;
- The affected area turns red;
- Hardening and thickening of the breast.
Infiltrative mastitis
If measures are not taken in time, the next phase begins - infiltrative mastitis. The foci of inflammation merge and swelling forms. The temperature persists, the pain becomes more intense, a solid lump is felt in the chest, resembling a small tumor. It is called infiltration. Lymph nodes in the armpit area may become enlarged.
Purulent stage
The purulent stage is considered the most dangerous. The temperature rises to a critical level (39.5 degrees), the affected breast obviously changes: it becomes larger, turns red, and swells. The skin of the affected area becomes hot, and when touched, the person experiences unbearable pain. The pain syndrome is pronounced, the pain is pulsating in nature. The lymph nodes in the armpit are greatly enlarged and painful. The patient's general condition is extremely serious: appetite decreases, nausea and vomiting, headaches and dizziness are present.
Lactational and non-lactational
There is another classification, according to which mastitis can be lactation and non-lactation.
The first occurs in women during breastfeeding. Women are most susceptible to it after the birth of their first child. The most common cause of this type of mastitis is milk stagnation. In addition, risk factors are cracked nipples, improper expression of milk or violation of the feeding regime and other features of lactation.
Lactation mastitis in 90% of cases affects one breast (usually the right).
Inflammation can be passed on to the baby through breast milk. If a child shows signs of illness, he should be seen by a doctor immediately.
Non-lactation mastitis is rare - only 5% of the total number of all clinical cases. The main risk factors are usually called:
- Decreased immunity (as a result of serious viral infections, severe somatic or chronic diseases, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, stress, insomnia, nervous or physical exhaustion);
- Changes in hormonal levels;
- Injury to the breasts and nipples;
- Malignant tumors.
Teenagers, especially girls, are susceptible to non-lactation mastitis. During puberty, there is a hormonal surge or imbalance; the teenager's body is hypersensitive to infections.
It is also customary to subdivide mastitis into acute and chronic recurrent.
Symptoms and signs of mastitis outside the lactation period
Symptoms of mastitis
Symptoms of mastitis in non-lactating women in some cases develop as quickly as during lactation. On average, 4–5 days pass from the onset of the disease to the purulent form, so you need to have time to make a diagnosis and begin treatment so that you do not have to resort to surgery.
The first signs of the disease begin to appear a couple of hours after infection:
- Pain appears in the mammary gland. Most often this is a one-way process. This may cause sleep disturbances.
- The temperature rises initially locally - in the chest, then the woman feels a general malaise.
- Decreased appetite due to intoxication, nausea.
- General weakness, headaches.
If you do not start treating mastitis at an early stage, within the next two days the lymph nodes under the arms may begin to hurt and become enlarged.
Serous mastitis
Mastitis develops in three stages:
- Serous. It is characterized by a general deterioration in health, thickening of the mammary gland and its soreness.
- Infiltrative, in which infiltrate accumulates in the chest - lymphatic fluid mixed with blood. The skin over the sore spot turns red, and the tissue inside thickens.
- Purulent - formation of a capsule. There are three forms of purulent mastitis - abscess, gangrenous and phlegmonous. In the latter case, the abscess is not delimited by a capsule and the pus quickly spreads to all tissues of the mammary gland, including the muscles of the sternum.
Acute non-lactational purulent mastitis
According to the nature of the course, mastitis can be acute, subacute and chronic. The acute form is more common and requires immediate medical attention. In subacute non-lactation mastitis, the clinical picture is blurred - minor pain, slight redness of the skin, body temperature up to 37.5 degrees. Sometimes this is caused by taking antibacterial drugs.
A chronic, sluggish process is manifested by elevated body temperature, but not higher than 38 degrees, as well as mild pain in the chest. The danger of the chronic form is that the diagnosis of non-lactation mastitis may hide the initial stage of breast cancer. In 2% of cases, patients are diagnosed with malignant tumors.
A feature of non-lactation mastitis is its subacute or chronic course. In case of low immunity, the process can increase quickly.
Complications of mastitis
If purulent mastitis is not treated, the disease will become severe.
The most common complications of untreated or undertreated mastitis include lymphangitis or lymphadenitis - inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and nodes. This is fraught with congestion in the upper extremities, their swelling, as well as transfer of the disease to the blood vessels, muscles and joints.
During the inflammatory process in the lymphatic system, painful lumps similar to rosary beads are felt.
The formation of purulent fistulas occurs with improper postoperative care and wearing tight underwear.
In most cases, patients who were operated on due to a purulent form of mastitis experienced relapses during the first year after surgery: in 60 out of 81 cases (statistics taken from the journal “Surgery,” published by the Department of Surgery of Sechenov First Moscow University).
Most often, inflammation occurs in the upper outer and lower quadrants of the breast. Inflammation involving more than one quadrant occurs after breast augmentation surgery. In the period from 2 to 15 years, women who have undergone breast surgery develop non-lactation mastitis or gel fistula after contour plastic surgery. Leakage of the gel can occur not only in the breast tissue, but also in the chest or abdominal cavity, which will lead to extensive inflammation and suppuration. Blood poisoning is possible if you do not go to a medical facility in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures that can be carried out by a mammologist, gynecologist, or surgeon consist of:
- Detailed questioning of the patient and taking an anamnesis;
- Palpation of the affected area;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
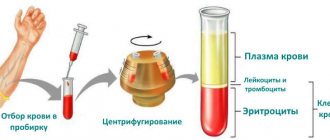
- Blood test to determine the pathogen;
- Bacteriological examination of milk (in nursing mothers) and nipple discharge;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Cytological examination (scraping);
- Puncture of infiltrate (in case of abscess or gangrenous form) with bacteriological examination of the contents;
- Mammography.
How to treat?
Of course, mastitis should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor and taking into account his recommendations. Such issues are dealt with by a mammologist, although you can contact your local gynecologist, or urgently call an ambulance. Remember that self-medication can seriously aggravate the condition of a young mother.
What are the consequences of a negligent attitude towards the problem:
- blood poisoning;
- spread of infection, emergence of new foci of inflammation;
- serious condition caused by severe intoxication;
- formation of fistulas at the site of suppuration.
The specialist will individually determine the stage of the disease and prescribe effective treatment. Often in such cases it is impossible to do without taking antibiotics, however, when mastitis begins, it is enough to simply adjust the correct placement of the child to the breast and try to empty the stagnant areas of the gland. In this case, cracks in the nipples will heal faster, the child will empty the breast better, and accordingly, the risk of “milk lumps” in the breast and inflammatory processes for this reason is significantly reduced.
Treatment of mastitis at home with folk remedies is carried out in order to alleviate the condition of a nursing mother and in the event that it is not possible to see a doctor at the moment. The main principle in using traditional methods is “do no harm,” because in trying to relieve pain and discomfort, women often only worsen their situation.
- Cold compresses
. Yes, it is the cold that will help relieve inflammation during developing mastitis. When the infiltration stage has already arrived, such a compress is, to put it mildly, useless. It is at the very beginning of the development of the disease that cold compresses help alleviate the condition of a nursing mother.
Cold is applied during periods when the baby is not breastfeeding; if necessary, the compress is changed to a new one. Under no circumstances should you HEAT the affected area of the chest, rub it with warming ointments, wrap it up or apply hot lotions. Heat only provokes the development of inflammation, worsening the mother’s condition.
- How to break up lumps in the breast?
Just try to express as much as possible, trying to squeeze the milk out of your overcrowded areolas. You will feel relief as soon as the stagnant milk comes out. If you can’t express yourself, feed your baby and let him help you empty your breasts. Moreover, it is important that the baby’s chin is on the side where the problem area is located. This makes it more likely that the milk will come out of the desired alveoli. You can use a breast pump if you cannot express milk yourself.
- Rice compress.
Starch, contained in rice in large quantities, according to traditional medicine, can help with breastfeeding. The rice is soaked in cold water until it becomes a thick paste. Cold rice is applied to the affected area, the compress is left for a while, and if necessary, changed.
- It is believed that cabbage leaves can cure inflammation and “draw out pus.”
A cabbage leaf is beaten with a hammer so that it becomes soft and gives juice, after which it is applied to the sore breast for a long time, then the procedure is repeated.
- Pumpkin compress
is also used to treat breastfeeding. The pumpkin pulp in the form of a paste is applied to the gland.
- To eliminate the root cause of mastitis - nipple fissures - people use a paste of grated apples and
butter. The mixture is applied to the nipple, wait a while, remove the residue and repeat the procedure until healing.
- Contrast shower for breasts
. This is practiced for both prevention and treatment, alternating cold and moderately hot streams of water directed at the sore breast.
Treatment
To treat mastitis in the initial stages, conservative methods are sufficient. First of all, the root cause of the disease is determined. If it is some kind of infectious disease, therapy is aimed at eliminating the pathogen.
So, the first steps on the path to recovery are as follows:
- Restoration of hormonal levels;
- Elimination of stress;
- Treatment of infectious diseases;
- General strengthening of the immune system.
The serous stage of mastitis is treated by magnetic therapy, laser therapy, light stimulation, ultrasound massage, and electrical neurostimulation.
If a patient self-medicates during the acute course of serous mastitis, the disease becomes chronic.
Conservative treatment is used under certain conditions:
- The patient's general condition is relatively satisfactory;
- The first symptoms appeared no more than 3 days ago;
- Temperature less than 37.5 degrees;
- There are no signs of purulent inflammation;
- The infiltrate occupies no more than 1 quadrant of the mammary gland;
- The blood test revealed no abnormalities.
The basis of conservative treatment is drug therapy. Antibiotics are prescribed. For symptoms of intoxication, special measures are taken intravenously. Be sure to prescribe medications for general immunity strengthening and vitamins.
After 2 days, the patient’s condition should improve noticeably, but if this does not happen, the question of surgical intervention arises. If an abscess is observed in the mammary gland, or the disease has taken purulent, phlegmonous or gangrenous forms, surgery is recommended.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital. When choosing a method, the doctor relies on certain nuances:
- How important is it for the patient to maintain the aesthetics of the breasts and the possibility of breastfeeding? The location where the incision will be made depends on this;
- Surgical treatment must be thorough, i.e. the entire affected cavity must be thoroughly cleaned of pus.
After the operation, a drainage-washing system is installed so that the wound is washed for a certain time (5-12 days).
In complex destructive forms of mastitis, maximum cleansing of the mammary glands is carried out, so the woman may need plastic surgery.
The postoperative period involves taking antibiotics.
Treatment of the disease
Mastitis in women (symptoms and treatment are interrelated) requires therapy. After studying the diagnostic results, treatment is prescribed.
The following is used as therapy:
- medicines;
- traditional therapy;
- surgery;
- proper nutrition.
Depending on the mechanism of development of the disease, there are general recommendations for treatment.
Therapy for lactation disease consists of the following points:
- Breast-feeding . It is not recommended to end lactation. You need to latch on to your baby at least 9-12 times a day. Thanks to regular feeding, you can reduce milk retention in the breast, alleviate the symptoms of the disease and speed up recovery. But the doctor can exclude this item from therapy.
- Massage events . If the doctor has recommended that a woman stop breastfeeding, she should express milk manually or with a device. Additionally, it is necessary to do a massage. Thanks to the procedures, blood circulation improves and pumping becomes easier. Massage activities should be carried out only after consulting a specialist, since in some cases the inflammatory process may intensify.
- Reducing symptoms . The doctor prescribes medications that help cope with the symptoms of the disease.
Non-lactation mastitis requires a different treatment regimen, it depends on the form of the disease. For example, if the condition arose due to changes in hormonal levels, the symptoms are mild, then you need to follow proper nutrition. But most often medications are prescribed for mastitis.
Conservative therapy (without surgery) is carried out in the following cases:
- the woman feels satisfactory;
- the duration of the disease does not exceed 3 days;
- the temperature does not rise above 38 degrees;
- no purulent inflammation;
- When palpating the chest, the discomfort is not severe;
- After a general blood test, the indicators are within normal limits.
If 2 days after using conservative therapy there are no results, this indicates purulent inflammation, and surgery is necessary.
Medicines
Medicines are the basis in the treatment of mastitis. Frequently prescribed groups of medications are listed in the table.
| Drug group name | Action | Medicines |
| Antibacterial | Reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms. | Amoxiclav, Cephalexin |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | The drugs can reduce pain, swelling and inflammation. | Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Ketorol |
| Antispasmodics | Improve milk flow and normalize lactation. | No-shpa, Spazmalgon |
| Antiallergic | Reduce the manifestation of allergies. The drugs are used in conjunction with antibiotics in cases of hypersensitivity to drugs. | Claritin, Zodak, Suprastin |
| Probiotics | Prescribed in combination with antibiotics. The drugs help normalize intestinal microflora and improve digestion. | Linex, Bifiform |
| Sorbents | Removes toxic substances from the body. Prescribed in the presence of clear symptoms of intoxication. | Smecta, Filtrum – STI, Enterosgel |
| Immunomodulators | Stimulate the functioning of the immune system. | Immunal |
| Vitamin complexes | Restores the level of nutrients in the body. | Vitrum, Complivit |
| Anti-inflammatory for topical use | Reduce swelling and heal the skin. The products are intended for external use. That is, they need to be applied to the skin. | Traumeel, Dexpanthenol |
Folk remedies
For mastitis, the use of traditional therapy is allowed. But this should be done only after consulting a specialist. Compared to medications, traditional therapy has a reduced likelihood of side effects.
Popular herbal recipes:
- St. John's wort decoction . To prepare, take 1 tbsp. component, pour 0.3 liters of hot water. Leave for 60 minutes, filter. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
- Chestnut flowers . To prepare the product, you need to take 6 tbsp. component and 1 liter of hot water. Cook over the fire until it boils. Pour the mixture into a thermos and leave for 12 hours. Filter, take 1 sip every hour.
- Compress with chamomile . For cooking you need to take 1 tbsp. component and 1 glass of hot water. Leave for 45 minutes, filter. Moisten gauze with the solution and apply to the inflamed chest for 20 minutes.
- Compress . To prepare, you need to take 1 raw yolk, 1 tbsp. vegetable oil and 1 tsp. honey. You will also need rye flour (1 part). Everything needs to be mixed to form a dough with a thin texture. Apply the mixture to the inflammatory area and wrap with gauze. The number of uses per day is up to 3. But each time the dough must be prepared anew.
- Collection . To prepare the product, you need to take St. John's wort, chamomile and burda in the amount of 2 parts of each component. You will also need 2 parts calendula and 1 part walnut. Mix everything, take 2 tbsp. collection and 0.4 liters of hot water. Leave the mixture for 3 minutes. to a water bath. Pour into a glass and leave for 45 minutes. Filter, take 15 minutes before. before meals, 200 ml 3 – 4 times a day.
Surgical intervention
Surgery is performed in the presence of purulent formations. And also in case of lack of effectiveness from the use of conservative methods of therapy. Most often, anesthesia is used during the intervention. The method of performing the operation is determined by the doctor.
When pus forms, the surgeon does the following:
- An incision from the nipple to the base of the mammary gland (longitudinal). And less often - horizontal, which runs above the chest.
- Removes pus and damaged tissue.
- Cleans the wound with an antiseptic.
- Introduces drainage, which drains the remaining pus. It is left for 3 – 4 days. If the inflammatory process becomes less, the drainage is removed, and the hole that remains after it is sutured.
- Sew up the incision.
After the operation, various medications are prescribed - antibiotics, NSAIDs, immunomodulators.
In some cases, due to surgical intervention, there is a need for plastic surgery of the affected breast. This happens at maximum volumes of the operation. For example, in the case of gangrenous mastitis. If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, you can reduce the likelihood of complications after surgery.
Sometimes the intervention is characterized by the following conditions:
- phlegmon, gangrene of the mammary gland - conditions lead to blood poisoning;
- recurrence of purulent mastitis;
- cosmetic defects due to significant excision of the affected area.
Diet therapy
If you have mastitis, it is recommended to follow proper nutrition.
Diet principles:
- Eat 5-6 times a day every 3-4 hours. Portions should be 200 - 300 g.
- Avoid fried, salted and smoked foods.
- Steam, bake or boil food.
- Avoid sweets.
- Replace high-fat foods with low-calorie ones.
- Add more vegetables and fruits to your diet, they are rich in vitamins.
- Take time to drink regularly. The recommended amount of clean still water per day is at least 1.5 liters. But you should exclude alcohol and soda.
Complications
If the disease has reached the purulent stage, but the patient for some reason ignores its appearance, complex destructive forms of mastitis develop.
Phlegmonous mastitis is a degree of severity in which the purulent-inflammatory process spreads to the subcutaneous fat and other breast tissues (more than 3 quadrants). This stage is characterized by:
- Severe redness of a large area of the chest with a bluish tint;
- Sharp, unbearable pain that makes it difficult to touch, sleep on your stomach, or wear underwear;
- Nipple retraction;
- High body temperature (38-39 degrees);
- General malaise, weakness and dizziness;
- Refusal to eat;
- Convulsions and loss of consciousness.
Gangrenous mastitis is an even more serious condition. There is a total enlargement of the mammary gland and the appearance of areas of dead tissue. Gangrenous mastitis can be fatal.
The activity of bacteria can provoke other serious conditions:
- Bacterial endocarditis, pericarditis;
- Meningitis, meningoencephalitis;
- Sepsis;
- Blood poisoning;
- Pneumonia;
- Osteomyelitis;
- Infectious-toxic shock;
- DIC syndrome (blood clotting disorder).
What to do if you have mastitis?
Before treating mastitis, it is necessary to determine its type and the cause of its development. According to these criteria, an individual treatment plan is drawn up, which is often based on antibacterial drugs. Self-medication for mastitis is unacceptable, therefore, in order not to harm your health, a woman should consult a doctor. As an urgent measure, before contacting a specialist, cold applied to the site of inflammation can be applied.
At the first stage of the pathology, without purulent lesions, it is eliminated using conservative methods. To influence the source of inflammation, antibacterial drugs, penicillins and cephalosporins are used:
- Penicillin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Ampicillin;
- Cefotaxime.
Anti-inflammatory and anesthetic agents are used for pain relief:
- Ibufen;
- Ibuprofen.
If lactation mastitis develops, a woman can independently provide first aid:
- Completely express both breasts.
- Treat cracked nipples with Bepanten and Vaseline oil.
- Wear thick underwear and bandage your chest with a towel.
- Avoid milk stagnation.
Mastitis in a nursing mother
As has been said many times, mastitis most often occurs during lactation. Usually a woman notices that her breasts seem to have become stone, and feeding and, in general, any mechanical impact causes severe discomfort and pain.
A nursing mother usually detects the disease within a month after the birth of the child.
Sometimes the first signs appear in the last months of pregnancy. The woman notes breast tenderness, swelling, redness of the skin, chills, and swelling of the nipple. Sometimes the symptoms resemble lactostasis, but there is one significant difference: with mastitis, the overall body temperature rises, and with lactostasis - only in the armpit on the side of the affected breast.
Causes of mastitis in nursing mothers:
- Stagnation of milk;
- Incorrect feeding technique;
- Improper expression of milk;
- Cracked nipples;
- Improper breast skin care;
- General weakening of the immune system.
During lactation, mastitis develops at a high rate. In just 4-5 days, the serous stage can develop into a purulent stage. In this case, the woman feels severely unwell, and the baby cannot receive milk naturally.
If you have mastitis, you should stop breastfeeding! Lactation is stopped with medication, i.e. with the use of drugs that stop milk production.
Precautionary measures
If a nursing woman suspects the development of mastitis, she should immediately consult a doctor. When for some reason it is not possible to do this immediately, the main thing is to prevent the condition from worsening. Therefore, doctors recommend taking some precautions:
- Do not expose your breasts to strong mechanical stress: do not wear underwear, do not use rough washcloths during hygiene procedures, do not squeeze or squeeze your breasts, try not to sleep on your stomach.
- Wear clothes only made from natural soft fabrics.
- Do not warm the chest: take a hot bath or shower, use heating pads or make warm compresses.
Treatment
Conservatively, mastitis in a nursing mother is treated with medication, as well as by following some simple doctor’s instructions. A woman should remain calm and wear underwear that does not put pressure on the affected breast. Security measures include:
- Mandatory pumping of milk every 3 hours, first from a healthy gland, then from the affected one;
- 20 minutes before pumping, an antispasmodic is injected intramuscularly from the diseased gland;
- Retromammary novocaine blockades are performed daily.
To fight the infection, antibiotics are prescribed, it is mandatory to take new generation antihistamines, and vitamin therapy. When the patient is on the mend, ultrasound and UHF therapy is performed so that the function of the mammary gland is restored faster.
Prevention of postpartum mastitis
Mastitis during lactation mainly occurs in firstborns. This is due to the fact that they do not have enough experience and knowledge to properly care for the breast and feed the baby. The preventive measures are as follows:
- Do not allow milk to linger in the mammary glands. It must be expressed regularly;
- If there are external changes in the breasts, unpleasant or painful sensations, regardless of feeding, you should urgently consult a doctor;
- It is necessary to follow the technique of proper feeding of the baby: make sure that it completely covers the areola, and not just the nipple, feed from both breasts in turn, and take the correct position. Proper feeding prevents the appearance of cracks in the nipples, which, in turn, often provoke mastitis;
- It is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene. You need to wash your breasts daily, carefully, without using detergents or cosmetics. To dry your chest after a shower, you need to prepare a special soft towel, and also be sure to wear underwear made from natural fabrics. If milk leaks, you need to change the napkins frequently;
- A breastfeeding woman should adhere to the rules of a healthy diet and also get enough sleep;
- It is necessary to avoid stress, excessive stress and overexertion, not to overcool or overheat;
- Try to feed your baby at the same time every day.
Planning a pregnancy is also an important preventative measure. If a woman prepares in advance to become a mother, examinations and tests will identify infectious diseases, and they can be eliminated before pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman's immunity is greatly weakened, and the likelihood of infectious diseases increases greatly. In addition, the course of some diseases during pregnancy can worsen and harm not only the mother, but also the baby.
Causes
The causes of this disease can be both external and internal factors. The majority of all mastitis is of infectious origin. But infections can occur both from within and from without. Internal chronic diseases, such as sexually transmitted infections, upper respiratory tract infections, dental infections, etc., give impetus to the development of pathogenic flora in the chest.
The main causes of mastitis in a nursing mother are:
- Lactostasis. The most common reason. After childbirth, the breasts increase in volume, while the baby does not take them too often, so milk stagnation occurs with infrequent breastfeeding. Or, if the amount of milk produced exceeds the volume of outflow.
- Mastitis in a nursing mother occurs when the breasts are not completely emptied during feeding. The baby does not always eat all the milk, so some of it remains and stagnates, forming plugs. To avoid this, a woman needs to pump.
- The appearance of cracks in the nipple, through which infection occurs. The causes of cracks may be a lack of vitamins, improper feeding, or thrush.
- Mom does not follow the simplest rules of hygiene. At the same time, a whole range of concomitant diseases appears, which lead to numerous inflammatory processes in the mother’s body.
- Hypothermia. The temperature regime for mother and child is always maintained at a high level. A decrease in temperature leads to irreversible consequences for the mammary glands, which causes mastitis after childbirth.
- Breast injuries. With strong impacts, hematomas occur. Breast mastitis appears.
- Welts and scars present on the chest. Small cavities with fibrous tissue are formed under them, which are well suited for the development of infectious flora
- Complications after childbirth associated with purulent infections. The causative agents of infectious diseases spread throughout the body and the breast is no exception.
- Incorrect positioning of the baby during latching. This leads to difficulty feeding and injuries. As a result, breast mastitis occurs.
- Breast mastopathy. Pre-existing breast diseases often lead to mastitis.
- Non-standard nipples. Such as elongated, flat or very large nipples lead to injury, difficulty in milk flow and stagnation. Mastitis in women often occurs precisely for these reasons.
The causes of mastitis are very diverse. To accurately determine the cause, it is best to carefully analyze your everyday life and lead a healthy lifestyle, observing general hygiene rules.
Mastitis in men
Many people mistakenly call mastitis a woman’s disease, because sometimes it appears in men. The routes of infection are the same - damage to the skin of the chest or penetration from another inflamed area of the body.
Causes of mastitis in men
Factors that provoke the development of the disease:
- A pathological condition of the mammary glands in men, in which they have an increased size - gynecomastia;
- Diabetes;
- Malignant and benign formations in the genital area;
- Frequent drinking of beer;
- Taking anabolic drugs during intense physical activity;
- Chest injuries;
- Weakened immune system, hypothermia.
The state of the endocrine system is of great importance for men. Inflammation of the mammary gland can occur if the amount of male hormone (testosterone) in the body decreases and estrogen and progesterone increase.
Symptoms
In men, the disease develops in stages. Serous mastitis is characterized by mild symptoms: there may be slight swelling of the gland and discomfort. The end of this stage is accompanied by enlargement of the lymph nodes.
When an infiltrate forms, the swelling increases, pain increases, and the temperature rises. The man feels general weakness of the body, chills, and symptoms of intoxication may occur. Lymph nodes become even larger.
Purulent mastitis is characterized by pronounced symptoms: the temperature rises to 40 degrees, severe intoxication begins, the affected breast becomes greatly enlarged and thickens. Palpation reveals a large, indurated, hot mass surrounded by swollen, reddened skin.
What factors provoke mastitis?
- Lactostasis (stagnation of milk in the ducts of the mammary glands) - milk is an excellent breeding ground for the proliferation of microbes.
- Cracked nipples create a pathway for infection from the outside.
- Poor treatment of nipples before and after feeding.
- Violation of the technique of attaching the child to the breast, when he sucks for too long or the main load falls only on certain areas of the nipple. This may cause cracks to appear.
- The presence of foci of chronic infection in the body.
Mastitis in children
Inflammation of the mammary glands occurs in children under 1 year of age. In children, mastitis is especially acute. The skin of the affected area becomes rough, redness and swelling are visually noticeable, and the temperature rises.
The main factor causing the disease is a sharp decrease in the hormone estrogen. During intrauterine development, the hormone continuously enters the fetus's body, and after birth the supply stops. These changes are accompanied by rashes on the face, breast swelling and nipple discharge and are called physiological mastitis.
Physiological mastitis occurs in 95% of newborn babies.
The disease affects both boys and girls and appears on only one side or both. Most often, the first signs are detected 5-10 days after birth.
Causes of mastitis in children
Mastitis affects infants for several reasons:
- Penetration of bacteria inside due to defects in the skin or cracks in the nipple;
- Improper child care;
- The child was born premature or weakened.
Pathological mastitis often becomes a consequence of physiological mastitis, if parents tried to cure the child themselves: they used external agents, squeezed out the contents of the nipples, or used folk methods.
Diagnosis and treatment
As a rule, childhood mastitis is easily diagnosed. After this, the doctor performs a culture of the nipple discharge to identify the pathogen.
Treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting. First, the doctor determines the stage of the disease - whether a purulent formation has appeared. If it is not there, conservative anti-inflammatory treatment is used: dry heat, warm compresses, antibacterial drugs.
For purulent mastitis, surgical intervention is required. The pus is removed promptly, drainage is installed, and the operated area is covered with a bandage. During the rehabilitation period, antibiotics, vitamins, and physiotherapeutic measures are prescribed.
Complications
Mastitis in newborns can lead to a number of serious health problems. Among them are inflammation of adipose tissue, phlegmon, sepsis and atrophy of the affected tissues. Female babies may have problems with lactation in the future.
Prevention
To avoid inflammation, the child should be protected from people with infectious diseases, protected from injuries and damage to the chest area, and observe the rules of hygiene. The baby needs to be bathed daily, touched only with clean hands, and be sure to keep clothes, diapers and linen clean. During swaddling, do not squeeze the baby's chest or swaddle tightly.
Mastitis is a serious and dangerous disease that develops rapidly and causes complications if left untreated. To prevent the onset of the disease, you need to closely monitor your health, regularly undergo medical examinations, lead a healthy lifestyle and adhere to proper nutrition.
Mastitis can affect a person of any gender and age if the general condition of the immune system is poor or there is a hormonal imbalance. Self-medication or ignoring the disease can worsen the health condition. At the first signs of mastitis, consult a mammologist or local physician.
Drug therapy
To treat simple forms of breastfeeding, conservative therapy methods are used. Serous mastitis is treated as follows:
- For lactating breastfeeding, milk must be expressed from both breasts. The procedure is performed up to 8 times a day.
- To eliminate serous mastitis, No-shpa and Oxytocin are prescribed. The drugs stimulate milk flow and relieve tension in the breasts.
- For intense pain, Novocain and antibiotics are administered.
- Allergic reactions are suppressed with antihistamines.
- When acute mastitis subsides, UHF therapy is used. It promotes the resorption of compactions.
- Purulent mastitis, resulting in a complication, is treated with surgical methods.
- Women are advised to follow a diet: eat foods enriched with vitamins.
Non-lactation mastitis can disappear spontaneously. If the disease does not go away, drug therapy is carried out.
Why does mastitis occur?
The causative agents of mastitis are staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. Infection is possible both inside and outside the hospital. Bacteria can enter through poorly treated linen, care items, or from hidden bacteria carriers (medical personnel, roommates, relatives). Another source of the disease may be the baby. Sometimes he develops inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, nasopharynx, and pustular lesions of the dermis. Once on the skin of the breast, bacteria do not cause disease. For this to happen, certain factors must be present for mastitis to develop:
- structural features of the nipples – inverted flat, lobed;
- mastopathy – proliferation of glandular tissue associated with hormonal imbalance;
- the presence of rough scars after surgery;
- abnormal course of pregnancy - premature birth, threat of miscarriage, toxicosis;
- deviations during childbirth - large blood loss, manual separation of the placenta, large fetus;
- complications after childbirth - exacerbation of chronic diseases, bleeding, fever.
As a result of these phenomena, tissue resistance to the harmful effects of bacteria decreases with reduced immunity after childbirth and the presence of hypovitaminosis. Prosperous soil appears for the development of the disease.
Systematization of mastitis
The classification of the disease has several directions and is very confusing. It causes a lot of controversy among medical representatives. Mastitis - inflammation of the mammary gland - is divided into two types:
- infectious;
- non-infectious.
Next comes the classification, depending on the time of its occurrence depending on the functional activity of the mammary gland; two forms are recognized:
- lactation – after childbirth;
- non-lactational – before birth.
According to the course of the inflammatory process, it is divided into:
- spicy;
- chronic.
According to the nature of the inflammation, mastitis is:
- serous – more common in primiparous women;
- infiltrative;
- purulent – has its own classification;
- abscess;
- phlegmonous;
- gangrenous.
Physiotherapy
When treating the initial form of mastitis, physiotherapeutic methods are used that increase lymph and blood flow in the stagnant area and have an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect. They do not cause pain or create discomfort. Basically, the following procedures are used:
- Ultrasound. It penetrates deeply into the tissue and gently massages the breast tissue. The duration of the session is 3–5 minutes, the course of treatment is up to 10 sessions, improvement occurs after three procedures.
- Pulse magnetic therapy. Inductors are placed on the affected area on both sides of the mammary gland, the impulses from which affect the seal. Sessions are carried out daily, for up to 10 days, for five minutes.
Physiotherapy is carried out in addition to the main course of drug therapy.
Reasons for the development of a painful condition
The main cause of non-lactation mastitis is strong hormonal surges at different periods of a person’s life, for example:
- The onset of menopause.
- Sexual crisis in newborns.
- The period of puberty in adolescents.
Among other provoking factors of the disease in women who have not given birth, experts note:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Nipple piercing.
- Injuries of the mammary glands.
- Weak immune system.
- Cracked nipples.
- Constant lack of sleep.
- Sudden hypothermia of the body.
- Complication after breast surgery.
- Chronic stress.
- Systematic overwork.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Incorrect metabolic processes.
- Unfavorable ecological environment.
- Physical or nervous stress.
- Chronic infectious diseases.
- Malignant tumors in the body, including the breast.
Risk factors for the manifestation of pathology
In mammology, there are three age periods when a woman is most at risk from non-lactational mastitis:
| Age period | Peculiarities |
| Adolescence (14-18 years old) | At this time, an increased amount of estrogen is noted in the body, and the protective capabilities of the immune system are reduced due to rapid restructuring of the body, which is a favorable condition for the development of inflammation in the breast. |
| Reproductive age (19-35 years) | At this stage of life, many women are at risk of developing fibrocystic breast tumors and dyshormonal hyperplasia. As a result of a decrease in the glandular component in the breast due to the active growth of connective tissue, the formation of mastitis can begin. |
| Premenopausal age (45-55 years) | There is a drop in estrogen levels and a weakening of immune abilities, and susceptibility to pathogenic microorganisms increases. |
In addition, representatives of the fairer sex who have:
- Large bust size.
- Nicotine addiction.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Chronic pyelonephritis or tonsillitis.
- Non-standard nipple shape.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Therapy
The process of treating the disease should begin with the appearance of the very first signs - breast distension, slight swelling or the formation of cracks in the nipples. To do this, you must immediately consult a doctor. Depending on the condition of the nursing woman, he will give recommendations, prescribe treatment, and in more advanced cases, write out referrals for examination. In addition to a general blood test, breast milk will need to be examined for the content of pathogenic bacteria. The issue of continuing to breastfeed the baby is immediately decided. During the inflammatory process, breast milk may contain pathogenic microorganisms.
To avoid infection of the baby, doctors recommend switching the baby to artificial feeding until the mother fully recovers, especially since she will be prescribed a course of antibiotics to treat mastitis. Only a doctor can select the necessary medications after receiving the results of tests for the sensitivity of bacteria to the drugs. The drugs are prescribed as droppers, injections or orally. During treatment, the mother must constantly express milk so that stagnation does not form again. Sometimes the doctor prescribes hormonal medications to reduce lactation and make it easier to express milk. Treatment of mastitis at the purulent stage is carried out in a hospital. In some cases, only surgical intervention is indicated for the patient. Maintenance therapy is also carried out. The woman is prescribed medications to boost immunity and reduce general intoxication. After completing the course of treatment, the patient is again tested for breast milk. If there is no infection in it, the baby can be breastfed again. After a course of treatment for mastitis, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the mammary glands.
Therapy with folk remedies
The disease is characterized by the rapid development of inflammation. A woman who notices signs of the disease should immediately consult a doctor. You should not start treatment with traditional methods, although there are a great many of them. In this case, you can simply waste time and aggravate the development of the disease. One should not completely deny the benefits of treating mastitis with folk remedies, but it should be started after consultation with a doctor, using it in conjunction with medications. The following folk remedies have proven themselves to be effective in treating the disease:
- Dill seeds. Their unique chemical composition contains vitamins and microelements: sulfur, zinc, phosphorus, selenium, vitamins B, C, A, which will help recovery. A decoction is prepared from them: a tablespoon of seeds in half a liter of water. Consume three times a day in small portions.
- Honey. On the first day of the appearance of signs of the disease, apply a honey compress to the chest. It will help relieve pain and facilitate the process of expressing milk.
- Cabbage. It has been used for a long time to treat various diseases. Beat the inside of a fresh cabbage leaf with a mallet until the juice comes out. Apply it to the inflamed area and secure it loosely. It will relieve fever and relieve pain.
- Burdock root. Contains many vitamins and microelements. It has an anti-inflammatory and mild analgesic effect. A decoction is made from it: a tablespoon of crushed raw material is poured with a liter of boiling water. The prepared drug is drunk three times a day in small portions.
- Beet. The raw pulp is grated and a compress is made if cracks occur on the nipple. It promotes wound healing and prevents inflammatory processes.
By using natural remedies that have been proven over the years, along with medications and constant consultation with a doctor, the signs of mastitis can be cured quickly.
Measures to eliminate milk stagnation
Some women, feeling the pain associated with stagnation of milk, begin to panic. They are lost and don’t know what to do with mastitis, what to do, who to turn to for help. Inflammation develops very quickly, especially in the evening and at night, so you should immediately consult a doctor. Signs of the disease:
- a lump has appeared, the mammary gland has enlarged;
- there is a sharp throbbing pain in the place where the inflammatory process occurred;
- severe redness of the skin in the area of inflammation;
- The temperature during mastitis rises sharply to forty degrees;
- general weakness, aches and malaise sets in;
- headache.
The same picture of the patient’s condition is also typical when lactostasis occurs, a disease that precedes mastitis. The only difference is the absence of temperature. Due to the seriousness of the pathology, you should contact the hospital emergency room as an emergency in the evening and at night. Which doctor should I contact for mastitis? In the daytime - to the clinic, to the surgeon or obstetrician-gynecologist. There is a misconception that mastitis should be addressed to a mammologist. A doctor with this qualification deals with the problem of neoplasms of malignant and benign origin in the mammary glands.
Antibiotics
When a diagnosis of “lactation mastitis” is made with the manifestation of such signs as a serious condition and high body temperature; the presence of cracked nipples and pain in the mammary glands; milk has been expressed, but the condition has not improved, a course of antibiotics should be started, this is done in order to prevent an abscess. The treatment regimen and the drug itself are selected by the attending doctor individually for each patient. On average, antibiotic treatment for mastitis lasts a week.
For this purpose, drugs of the following groups are used:
- Penicillins are broad-spectrum drugs with rapid absorption. They have side effects: disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, skin reactions. Partially penetrates into mother's milk and is taken with caution during breastfeeding.
- Cephalosporins are characterized by rapid absorption from the stomach and have an effect on the affected tissue. Excreted in urine. May cause an allergic reaction and headache. It passes into mother's milk in small quantities, the risk to the child is minimal.
- Macrolides - after taking drugs by a nursing woman, their high concentration is observed in breast milk. Drugs from this group of antibiotics do not have a negative effect on the baby’s body.
- Aminoglycosides - drugs are not used during breastfeeding and pregnant women. Treatment with antibiotics for mastitis from this group is possible if the baby is temporarily transferred to artificial feeding.
- Fluoroquinolones – It is not recommended to breastfeed your baby while taking these drugs. They are absorbed into milk and have a certain toxicity.
Only a doctor selects the necessary antibiotics for treatment of a nursing woman. He will prescribe a specific course of therapy and give advice on breastfeeding.
Prevention measures
In order to prevent the recurrence of mastitis outside of pregnancy, experts recommend:
- Periodically see a mammologist.
- Correct hormonal imbalances in a timely manner.
- Do not delay treatment of chronic infections.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Stick to a regimen of rest and activity.
- Eat rationally and correctly.
- Get rid of obesity.
- Lead an active lifestyle and play sports.
Breast massage
At the first symptoms of mastitis, massage has a good effect. To carry it out, you need to wash and dry your hands well, and your nails should be cut short. First of all, you need to do the preparatory exercises. To do this, make light movements with the fingertips from the edge of the chest to the center in the form of a spiral. Then they find areas to massage. To do this, feel the breasts and identify lumps and painful areas. Each seal is massaged separately. Movements are made clockwise from the center to the periphery. Then they move on to working on the entire mammary gland. Massage for mastitis begins with the axillary area. The duration of the procedure is no more than five minutes. It should be remembered that all movements must be smooth and not cause pain. It is advisable to do the procedure regularly to obtain the desired effect.