Causes of stuffy ear(s)
Hearing loss can be caused by various factors. The most common cause is a pressure difference at depth or height. This is also possible with inflammation directly in the ear or organs adjacent to it. But the feeling of discomfort sometimes manifests itself in different ways, so it is worth studying separately the most common causes that provoke it.
Ear congestion due to wax plug
In the external passage of the organ of hearing there are glands that produce sulfur. It dries quickly and turns into crusts under normal conditions. In the future, they are eliminated independently during chewing.
When this natural process fails, the wax is not removed from the ear canal, but becomes compacted and hardened. This prevents the passage of sound to the membrane, which negatively affects hearing. The feeling of discomfort may be on one or both sides.
Ear congestion due to otitis externa
This infectious disease is characterized by damage to the external canal of the hearing organ as a result of the penetration of pathogens into the upper layer of the skin during the formation of microtraumas. As a result, an inflammatory process develops, accompanied by swelling that blocks the lumen of the auditory canal, which disrupts sound perception.
In the absence of timely treatment, otitis media acquires a purulent form, and exudate pours out, which also reduces hearing.
Ear congestion due to otitis media
Inflammation develops in the area of the eardrum. The provoking factor is dysfunction of the auditory tube. It is responsible for the coherence of the structural components of the organ and the ventilation of the canal, which prevents the proliferation of pathogens.
There are 3 forms of pathology:
- Spicy. Inflammation develops with infection of the upper respiratory tract. The eardrum is significantly strained, so it loses the ability to perceive sound waves, and this negatively affects hearing.
- Exudative. It is characterized by a large accumulation of mucus inside the ear, which fills the tympanic cavity and disrupts the functionality of the auditory ossicles.
- Purulent. It develops when pathogens enter the tympanic cavity and rapidly multiply there. The immune system activates the production of leukocytes to fight them. This provokes the formation of pus, which fills the tympanic cavity.
Ear congestion due to colds and runny nose
Inflammation in this case is characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. This causes blockage of the ear canal, which impairs ventilation. But in this case, there is a temporary feeling of congestion, which goes away after the main cause of inflammation - the cold - is eliminated.
Ear congestion due to sinusitis
Impaired sound perception can be felt in advanced forms of the disease, when purulent exudate extends beyond the maxillary sinuses. This provokes further spread of the infection, which affects the nasopharynx and hearing organs. To eliminate congestion, you need to cure the underlying disease.
Ear congestion due to acute pharyngitis
The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the pharynx. The provoking factor is an infection, a chemical agent.
Their negative effect leads to swelling of the mucous membrane, which blocks the lumen of the auditory tubes, and in both at the same time. In addition to impaired sensitivity to sound, the patient develops hoarseness and pain when swallowing.
Stuffy ears due to sore throat
The pathology is characterized by an infectious lesion of the palatine tonsils. The main pathogens are staphylococci and streptococci. This causes a response from the immune system, which leads to active production of leukocytes, and is expressed by increased swelling of the glands and the formation of purulent exudate.
A high degree of severity of the immune response during angina provokes further spread of inflammation to adjacent organs. This leads to congestion, hoarseness, and pain.
Ear congestion due to allergies
The body's response to an allergen can also interfere with the perception of sound, which is often one of many symptoms. The irritant is pollen, smell or food. The discomfort is felt temporarily and disappears on its own after the allergen is neutralized.
Congestion in the ear with cervical osteochondrosis
The development of the disease occurs against the background of thinning of the vertebral discs in the neck area. This provokes compression of the nerve endings of the spinal cord and disrupts nutritional processes.
The relationship between the appearance of congestion and the development of cervical osteochondrosis has not been thoroughly established, but in patients suffering from this disorder, the pathological condition is diagnosed much more often. This occurs against the background of a malnutrition of the vessels of the auditory organ. Sound perception is fully restored after the underlying disease is eliminated.
Ear congestion after swimming
This reason is common and not dangerous. During immersion, the liquid enters the auditory canal and is retained due to its structural features. As a result, the eardrum is temporarily unable to respond to sound waves.
You can remove water using a simple method. To do this, you need to hop on your leg, tilting your head towards the stuffy ear. These simple manipulations will help quickly restore lost hearing.
Clogged ears on an airplane
The disruption is caused by changes in atmospheric pressure as the plane climbs or descends. For some, congestion disappears immediately after takeoff, while for others it continues until landing. Recent illnesses in which inflammation spreads to the hearing organs can affect its duration.
Sound perception is restored independently and no medical procedures are required.
Ear congestion due to high blood pressure
Discomfort in this case is felt when there is a significant difference between atmospheric and ear pressure. This type of congestion occurs during diving. Diving every 10 m increases the pressure level by 1 atmosphere. The feeling of discomfort is felt at 2-3 m depth and continues to intensify.
After surfacing, the difference between atmospheric and ear pressure remains for another 2-3 minutes, and then hearing is completely restored.
Ear congestion after a blow (trauma)
When injured, congestion can cause hemorrhage in the area of the eardrum. This disrupts the functionality of the auditory ossicles and significantly reduces sound perception. In case of a fracture of the head bones, cerebrospinal fluid may also leak. This condition is life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Increased sound load also provokes congestion. This triggers a protective mechanism that reduces the sensitivity of the middle ear. After eliminating the stimulus, the functionality of the hearing organ is restored.
Ear congestion in a child
The auditory tube in a baby at an early age is short and wide, which leads to the regular development of otitis media. The child’s immune system also develops as it grows, so it is not able to fully resist infections.
This also provokes the development of diseases such as:
- angina;
- allergy;
- sinusitis;
- cold.
At an early age, babies also often stick various small objects into their ears. Therefore, if hearing loss occurs, you should initially examine the ear canal and, if necessary, consult an otolaryngologist.
Ear congestion during pregnancy
Often, a woman feels a decrease in sound sensitivity during pregnancy. This symptom is not characteristic of pregnancy, but appears against the background of the development of concomitant diseases.
Its regular occurrence is explained by decreased immunity, which increases the body’s susceptibility to the effects of pathogens. Eliminating congestion requires eliminating the underlying cause.
Stuffy ears in the morning
Morning discomfort can be caused by excessive wax build-up in the ear canal. Against the background of immobility at night, it partially blocks its lumen, which prevents the passage of auditory waves. Carrying out morning procedures helps remove sulfur reserves, which helps restore hearing.
The appearance of congestion in the morning can be caused by a sluggish infectious process. This contributes to swelling of the nasopharynx, which intensifies at night and blocks the auditory canal. Morning yawning and swallowing help restore the patency of the auditory canal.
What to do if your ear is blocked after a flight or elevator
Usually you don't need to do anything. It is best to prevent such congestion. For example, during takeoff and landing, chew gum or hold a lollipop in your mouth, or at least yawn. Such actions force the muscles that open the Eustachian tube to work, air enters it, and the pressure is equalized.
If your ear is still blocked, try squeezing the wings of your nose as if you were going to blow your nose, and exhale - this is called the Airplane ear Valsalva maneuver. Be careful, it should not be used for infections, so as not to make it worse.
If it doesn’t help, just wait: after a while the pressure inside and outside will come into balance and the unpleasant sensations will disappear.
But there are cases in which you need to see a doctor because barotrauma (damage caused by pressure) can be serious:
- The pain lasts longer than several hours and is very severe.
- There is a ringing in the ears.
- You feel dizzy, sometimes so strong that it leads to vomiting.
- Blood is leaking from the ear.
By the way, any ear infection, runny nose or allergies are additional risk factors that lead to congestion due to pressure changes. Before the flight, put vasoconstrictor drops into your nose and use antiallergic medications.
Symptoms, signs of ear congestion
Ear congestion, the causes and treatment of which may vary in severity, is only a symptom of other, more serious diseases. Therefore, it is worth considering additional signs, the presence of which helps in establishing a diagnosis.
Ear congestion without pain
Sound disturbance, not accompanied by pain, occurs during flights and after swimming. Also, this symptom is possible at the initial stage of the formation of cerumen plug , but subsequently a slight tingling sensation is felt inside the ear.
A mild form of a cold can also be characterized by the absence of pain, despite congestion. Timely treatment is required so that the inflammation does not progress further.
Pain from stuffy ears
Congestion in the ears, the causes and treatment of which may vary depending on the triggering factor. most often occurs against the background of an infectious lesion. When the external canal is inflamed, which provokes otitis media, pain is felt when trying to clean the ear. When the middle section is affected, pain appears 2-3 days after hearing loss.
This accompanying symptom is also possible due to injury to the ear or the presence of a foreign object in it. The pain is felt instantly.
Ear congestion and noise (ringing) in the ears
The presence of an additional symptom indicates increased sound load on the ear. This may cause a loud noise that can cause irritation. That's why a person hears a ringing. This condition disappears on its own, but if the process is prolonged, it requires the help of an otolaryngologist.
Sometimes noise is a sign of otitis media of the auditory canal, which disrupts the functionality of the eardrum, inner ear, and auditory ossicles. Periodically appearing ringing is a sign of cervical osteochondrosis.
Clogged ears and sore throat
The combination of symptoms is a sign of an infectious lesion of the upper respiratory tract - sore throat, pharyngitis, colds. Pain is felt when swallowing, because swelling of the mucous membrane increases sensitivity.
Cough with stuffy ears
The simultaneous appearance of these symptoms is a sign of the initial stage of colds, when cough receptors are affected as a result of inflammation of the respiratory mucosa.
This additional symptom may indicate the formation of sulfur plug at the initial stage. A dry cough occurs as a result of irritation of nerve fibers. It may intensify during ear canal cleaning.
Ear and nose congestion
The cause of the combination of these symptoms is rhinitis. Its development can be triggered by an infection, virus or allergen. Congestion in this case appears against the background of increased swelling of the nasopharynx, which blocks the lumen of the auditory tube.
Ear congestion without runny nose
A decrease in sound perception indicates that the provoking factor lies in the organ of hearing.
Main reasons:
- flight;
- immersion;
- otitis;
- injury;
- cervical osteochondrosis.
A runny nose does not appear with otitis media, but may appear as a result of further spread of inflammation to adjacent organs.
Ear congestion and headache
The combination of these symptoms indicates various pathologies of an infectious nature. As they progress, the immune system activates the production of biologically active components with vasodilating properties. This affects pain receptors in the brain.
Increases discomfort - bright light, loud sound, sudden movement. In case of an infectious lesion, the localization of pain occurs near the temples and the back of the head.
Ear congestion and dizziness
These signs appear when there is a malnutrition of the brain, injury to the ear or vestibular system. Disruption of metabolic processes causes cervical osteochondrosis, accompanied by damage to the arteries of the spine. Dizziness is felt when standing up suddenly.
In the second case, spatial disorientation is felt. Moreover, a sound signal can also provoke injury. Against this background, the person feels dizzy with imbalance.
Ear congestion and nausea
Most often, these symptoms appear during flights, but the mechanisms of their development are not related to each other. The deterioration in health in this case is temporary and goes away on its own after landing.
Ear congestion, nausea, dizziness are symptoms characteristic of dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus. Also, these signs may be accompanied by vomiting when a person tries to change the position of the body or head.
Ear congestion and temperature
The simultaneous appearance of these symptoms indicates an infectious lesion.
Common diseases:
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- tonsillitis.
This combination of pathological signs can also be caused by the penetration of an allergen, which provokes excessive activity of the immune system.
Ear congestion and itching
The accumulation of sulfur secretions can cause itching. To eliminate it, you need to clean the ear canal with a sterile cotton swab. But the combination of these symptoms is not always so harmless.
The following diseases can provoke both itching and congestion:
- otitis externa
- chronic form of otitis media;
- fungal infection;
- foreign object.
Discharge from ear congestion
Under normal conditions, only wax is released from the ear canal. The appearance of another type of discharge indicates a purulent process in the organ of hearing.
The reason for this may be:
- advanced stage of external canal otitis;
- acute form of otitis media;
- injury.
Any of the listed pathologies requires medical attention, since if left untreated it can lead to partial or complete hearing loss.
Prevention
When cleaning your ears, trying to get rid of wax or other objects, do not use pointed instruments. One wrong move can lead to disruption of the integrity of the membrane, otitis media and serious pathologies.
Sometimes, when your ears are blocked for no known reason, a regular diet can help. Eliminate fatty, fried, sweet, spicy foods from your diet and you will be surprised at the results.
To prevent unpleasant sensations from ear congestion, drop almond oil into it. It helps destroy bacteria and prevents the formation of sulfur plugs.
In the absence of heart or vascular diseases, as well as doctor prohibitions, take hot baths. This procedure strengthens the body, tones, softens sulfur deposits.
Diagnostic methods
Congestion in the ears (the causes and treatment are related, since therapy directly depends on the type of concomitant disease), which is felt for several days, is treated under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. This will avoid serious complications.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Visual inspection. Helps identify signs of inflammation in the outer ear.
- Palpation. The sensation of pain when pressing on the posterior region, as well as when pulling back the auricle, indicates a problem in the outer region.
- Otoscopy. The study is carried out using a metal funnel. After inserting it into the ear, the doctor examines the organ from the inside, while turning the device. This helps to identify the presence of swelling, suppuration and perforation.
- Study of the functionality of the auditory tube. For this purpose, a special tube is used, at the ends of which there are funnels. It is used to analyze the sounds released when the patient swallows and takes a deep breath.
- Determination of the level of sound perception. This study is carried out using a tuning fork.
If necessary, the doctor uses the audiometry method, which includes a set of studies using electronic and computer devices. Based on the data obtained, a diagnosis is made and therapy is prescribed.
What to do if your ear is blocked due to illness
When not only the ear, but also the nose is blocked, the throat hurts, or when there is a shooting in the ear, discharge appears and the temperature rises, these are signs of Ear Infection. In this case, you need to see a doctor. The otolaryngologist will understand where the infection is concentrated, what microbes attacked you and how to treat it.
The doctor will prescribe antibiotics, if needed, painkillers, and even tell you what traditional methods can be used.
Why shouldn’t you get treatment without consulting a specialist? Because we can't even see what's happening in the ear. If it suddenly turns out that there is pus or discharge inside the auditory tube, then many home treatment methods are strictly contraindicated.
You cannot warm up your ears yourself if you have an infection: this can lead to a rupture of the eardrum and even deafness.
The same applies to the “bury something” method. This something may be ineffective (at best), or it may cause allergic reactions and, as a result, even more severe swelling.
The maximum we can do before visiting a specialist is to put vasoconstrictor drops into the nose or take antihistamines that will help relieve swelling.
How to treat ear congestion
Treatment of this symptom is carried out as part of a complex treatment, the action of which is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. To do this, you can use several types of drugs prescribed by your doctor. It is also permissible to use massage, physiotherapy and folk remedies if the otolaryngologist recommends their use.
Ear drops
This treatment method is effective for the formation of sulfur plugs, mycoses, otitis media and changes in atmospheric pressure. The duration of use of the drops is discussed with a specialist.
Main types of drugs:
| Name | Indications | Mode of application |
| "Otipax" | Colds, otitis media | 2-3 times a day, 3-4 drops for 10 days |
| Peroxide | Sulfur plug | 1.Introduce 3 drops into each channel. 2.After 2 hours, rinse the ear with a syringe without a needle |
| Boric acid | Inflammation of the middle section | Cotton pads are moistened and placed in the ear canal for 1 hour. Use is allowed from 12 years of age. |
| "Otinum" | External or otitis media, cerumen plug | The medicine is administered 2 drops 2 times a day. Prohibited for use if the eardrum is damaged |
| "Naphthyzin" | Atmospheric pressure surges | Duration of use: 5 days. Use 2 drops in the ear and nose, which relieves swelling |
| "A-Cerumen" | Sulfur plug | 1.Pour the solution into the ear. 2.After 1 min. tilt your head so that the sulfur flows out. 3.Rinse with water |
Vitamins
Treatment for ear congestion may include B vitamins and zinc supplements, regardless of the cause. It is worth taking the medications regularly until their deficiency in the body is eliminated. Vitamins have a strengthening overall effect, which reduces the likelihood of relapses.
Homeopathy
This type of treatment is used as an adjunct to the main therapy. It is effective if hearing loss is caused by colds.
The drugs can be purchased at any pharmacy, but their choice is made by the doctor, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient and the form of the pathology.
Massage
This treatment method is very effective for otitis media of various etiologies, as well as congestion due to a cold. A daily morning massage will help quickly restore lost hearing.
Technique:
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Heat them by rubbing them with your palms.
- Squeeze your ear with both hands.
- Massage in a circular motion, warming it up.
- Place your index finger in the middle and pull the upper edge of the auricle.
- Gradually change the vector of movement, moving towards the lobe.
Massage is recommended to be used not only for treatment, but also as a preventive measure.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
It is acceptable to prescribe physiotherapy for otitis, although according to international standards it is not included in the list of mandatory treatment procedures. Its use is especially effective for frequent sensations of congestion.
Types of physiotherapy:
- UHF;
- electrophoresis;
- microwave treatment;
- ultraviolet irradiation.
The attending physician decides which of the listed methods to use.
Traditional methods of treatment
Acute and chronic forms of inflammation in the outer and middle sections of the ear can be treated using folk remedies. They help significantly reduce symptoms and speed up recovery.
Common types of home remedies:
- Propolis. Tincture is used as a therapeutic agent. To prepare it, you need to pour 15 g of the component into 100 ml of alcohol with a strength of 70%. Pour the mixture into a glass container and keep in the dark for 10 days, shaking occasionally. Place cotton wool in the resulting medicine and insert it into the ear canal for 5 minutes. twice a day.
- Aloe. Cut a leaf from the plant, wash it and put it in the refrigerator for 24 hours. After a while, chop it and squeeze out the juice. Instill 2 drops of it into the ear canal, or insert moistened turundas for upper lesions.
Herbs
Medicinal herbs can be used as an auxiliary treatment. Their use is possible after consultation with an otolaryngologist.
Effective types:
- Chamomile. Pour 50 g of collection into 1 liter of boiling water. Leave for 2.5 hours, clean. Use for rinsing 3 times a day.
- Sage, lemon balm. This recipe is used for a combination of congestion and ringing in the ears. Pour 15 g of dried ingredients into a glass container. Pour 500 ml of boiling water over the mixture and leave for 40 minutes. Take orally 4 times a day in equal portions.
Treatment
Let's look at specific examples of treatment, depending on the cause of congestion:
- In case of a runny nose that causes swelling, drops with a vasoconstrictor effect are used. After drops get inside, it is recommended to take a horizontal position.
- If there is a sudden change in pressure, open your mouth and try to forcefully yawn. Follow the blowing procedure. To do this, cover your nose with your hand and try to exhale with it. With the help of such operations, the Eustachian tube is opened and the pressure is balanced.
- Ear plugs can be removed by rinsing with water or peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide can be instilled using a pipette, a syringe without a needle, or a pre-soaked cotton swab placed in the ear. There are special drops to combat traffic jams Remo-Vax and the like.
- Water that gets into the ear canal can be removed by simply placing a dry cotton wool there. Or use ear sticks; perform all manipulations carefully to avoid mechanical damage.
- If the ears are clogged in the presence of otitis, a set of therapeutic measures is used, depending on the form and stage of the disease. In some cases, antibiotics and painkillers are prescribed, in others - antifungal agents. Additionally, drops and vitamins are prescribed. Before starting treatment, please read the possible contraindications; some medications are prohibited during pregnancy, damaged eardrum, allergies, and for children under 3 years of age.
- If blood pressure is high, medications are prescribed to lower it.
- Foreign objects can be removed by washing. This requires certain knowledge; it is better to seek the help of a qualified specialist.
- Nasal septum defects are corrected by a surgeon.
- For other reasons, blowing, massage and electrophoresis are used.
Preparation for intervention, progress of the operation
Before the operation, preliminary preparation of the patient is carried out. If necessary, sanitation of the nasal sinuses is applied, and adenoids blocking the lumen are removed. Anticoagulants should be discontinued 7 days before surgery. And 3-4 days in advance, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, which reduces the likelihood of complications developing after surgery.
Otitis media can cause ear congestion. Acute otitis media causes suppuration in the area of the eardrum. Treatment is ear shunting
Progress of the operation:
- The upper layer of the epidermis of the anterior layer of the eardrum is incised using a curved needle.
- An oval hole is formed along the diameter of the ventilation tube.
- An attempt is made to suction the exudate from the cavity of the middle ear.
- An incision is made on the posterior wall of the ear canal, not reaching the tympanic ring, the flap is separated and moved to the side.
- Suction removes pathological contents from hard-to-reach places.
- The flap is returned to its place and secured with a glove rubber band.
Why are my ears clogged?
As a rule, painless ear congestion occurs in hypertensive patients, in women during pregnancy, or in people suffering from cervical osteochondrosis. The symptom, in addition, can appear during prolonged exposure to high altitude (after an airplane) or as a result of diving to depth. Congestion without pain often occurs in children with measles, scarlet fever, whooping cough, and diphtheria. The reasons that provoked this symptom may be different. The most common ones are described below.
Ringing in the ear and congestion is called Meniere's syndrome, and it is still not fully understood. The symptom, as a rule, accompanies any pathological processes occurring in the body. These include: allergies, hormonal imbalance, low or high blood pressure, hormonal fluctuations during menopause, dystonia, poisoning. How this syndrome develops is unknown, but it is believed that it is stimulated by changes in metabolism in the tissue of the inner ear.
Data from studies prove that 50% of people who have ringing and noise in their ears have certain impairments in the mobility and functionality of the maxillotemporal joint. Such cases are treated by an osteopath. If you have congestion without pain with characteristic tinnitus, it is recommended to visit a doctor who will diagnose and prescribe adequate treatment.
A decrease in a person’s hearing function can occur abruptly or occur gradually. Moreover, in the second case, a person, as a rule, does not realize for a long time that his hearing has become worse. The causes of hearing loss without pain can vary, depending on the patient's age and other factors. Often a person begins to go deaf if there is a mechanical obstruction (wax plug) in the ear or diseases of the ear canals. Other factors that lead to ear congestion without pain include:
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- age-related changes in the body;
- overuse of medications;
- presence of fluid in the ear canal or wax plug;
- harmful occupational conditions (constant humming noise, working with chemicals);
- atherosclerosis.
My head is spinning
If loss of balance is accompanied by ear congestion, this can be caused by various infectious diseases or traumatic brain injuries. In addition, the cause of such symptoms is sometimes otitis media - it has a general negative effect on the body, including loss of balance.
- spots before the eyes;
- nausea;
- darkening of the eyes;
- tinnitus.
When these symptoms occur simultaneously, they indicate hypertension (high blood pressure). Additional signs may include nausea, weakness, and a feeling of pressure on the temples. If you experience ear congestion without pain with a characteristic migraine, try to sleep or at least take a break from work. If there is a strong jump in pressure, you need to take a pill, and if it is ineffective, call an ambulance.
This condition can develop under the influence of many internal and external factors. Congestion in one or both ears often indicates the development of a pathological process in the sound analyzer or neighboring organs, for example, the throat or nose. Syndromes of this kind are usually accompanied by pain and other negative manifestations.
Among other things, we should separately address the issue of what can cause blocked ears in infants. Due to their anatomical features, children in the first year of life are especially susceptible to the spread of infection from the nose and throat to the ear canal area. For this reason, it is extremely important to provide timely and adequate treatment for respiratory diseases in the smallest children. Meanwhile, among other reasons why ears are blocked, we can highlight:
- high pressure;
- inflammation of the outer ear;
- otitis media;
- wax plugs (due to the accumulation of earwax in the ear canal);
- changes in atmospheric pressure;
- ear infections;
- ingress of foreign objects;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx;
- serious pathologies of the nervous system.
Episodic manifestations of this kind of unpleasant symptoms, as a rule, do not cause concern for the patient’s health. In this situation, doctors recommend regularly cleaning the ear canal with ear sticks and promptly treating diseases of the upper respiratory tract. In case signs of congestion appear after swimming, tilt your head several times in the appropriate direction. Due to the pressure difference, the remaining liquid will come out and the unpleasant symptoms will disappear.
If there is severe itching due to the presence of wax plugs, experts advise dripping a few drops of peroxide or warm olive oil into the ear canal. Remember that introducing any substances into the ear canal in order to eliminate pathological (purulent) discharge is strictly prohibited. Conditions of this kind require immediate contact with a specialist who will examine the ears and prescribe adequate treatment for the resulting syndrome.
Folk remedies
Elimination of ear canal congestion is possible only after getting rid of the problem that led to the development of this unpleasant symptom. However, you can speed up the process using folk remedies. Remember that the use of any recommendations from healers should be discussed with your doctor first.
- Warming compresses. Any such procedures should be carried out only if you are completely sure that there are no purulent or inflammatory processes in the ear. It is recommended to warm up with camphor alcohol. For this purpose, gauze or a cotton swab is moistened in the specified composition, wrung out a little and applied to the auricle. The duration of one session is about 20 minutes. It is recommended to carry out warming three times a day until the condition improves.
- Inhalation with decoctions of medicinal herbs. 2 tbsp. l. pour dry raw materials with cold water and bring to a boil. Then, covered with a towel, breathe in the steam emanating from the container with the medicinal decoction. Carry out inhalations twice a day for a week until the buzzing (ringing) in your ears stops.
- Washing with saline solution. This popular advice is used if your ears periodically become blocked due to a runny nose. The procedure is carried out by intranasal administration of a hypertonic solution. The latter is prepared at the rate of 2 tsp. salt per glass of water. The procedure for washing the nasal passages is carried out using a pipette several times a day.
Recovery and prognosis
In most cases, the prognosis is positive, but the effectiveness of surgical intervention depends on the professionalism of doctors, the neglect of the pathology and the patient’s compliance with the specialist’s recommendations.
The recovery period ranges from 4 to 30 days. During this time, the patient should refrain from blowing his nose, strong coughing, or sneezing. Swimming and bathing should also be avoided. When washing your hair, you should avoid getting water into the ear canal so as not to provoke the development of complications.
Cotton swabs located in the ear cannot be removed independently, so regular examination by an otolaryngologist is required, who will monitor the patency of the auditory tube and replace it as necessary.
Ear congestion is only a symptom and can be harmless or dangerous. Feeling discomfort for a long time should be a reason to consult a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the underlying cause and prescribe appropriate treatment, which will help restore sound perception.
Article design: Mila Friedan
What to do if your ear is blocked after swimming
Water in the ear is one of the simplest cases. As a rule, it flows out by itself or dries out over time without causing any inconvenience. Try to speed up the process:
- Stick a cotton pad into your ear, but not too deep.
- Just lie with your ear on the pillow, placing a towel under it, and wait.
Usually, water in the ear does not lead to serious consequences, but infections can develop and intensify in water. Therefore, if after a few days the sensation does not go away or pain is added to it, consult a specialist.
Folk advice for a stuffy ear
You need to follow folk tips with great caution, and it is better to consult a doctor about the safety of the methods.
1. Douching the ear with warm water helps remove a foreign object.
2. You can try to remove an insect that has gotten into your ear by dropping heated vegetable oil into it.
3. In a composition of solid propolis and alcohol infused for a week, moisten a cotton swab and insert it into the sore ear. The procedure is performed to relieve ear congestion.
4. A swab soaked in honey is inserted into the ear overnight. Helps with ear problems during colds.
5. You can relieve ear congestion by instilling almond oil.
Unilateral and bilateral congestion of the ear canal
Often a person may feel stuffy in both ears in the morning if there are untreated colds in the nasopharynx, when mucus accumulates on the back wall of the throat during sleep. Then the mucus enters the auditory tubes, blocking the passage of air.
Two ears can become blocked at once due to a sharp jump in blood or atmospheric pressure. But the cause can also be bilateral otitis media. Children under three years of age often suffer from otitis media.
Pregnant women often complain of a feeling of fullness in the right ear. This symptom goes away after the baby is born.
A feeling of stuffiness can occur when a foreign body enters the auditory canal. This could be an insect that could crawl into the ear at night, especially if the overnight stay was outdoors.
There may also be wax in the ear or residual water from swimming. Often, two ears become clogged at once during an airplane flight or during normal travel in an elevator or even in the subway.
Ear congestion may be a symptom of increased intracranial pressure.
Diagnostics
If the problem of ear congestion lasts more than a day, then consultation with a specialist is necessary. The doctor will determine why the pathology occurred and establish ways to get rid of its consequences. Diagnostic methods used in medical institutions:
- Visual inspection;
- Taking anamnesis;
- Clinical and instrumental studies.
During a visual examination, the doctor examines and palpates the auricle. This is done in order to identify possible inflammation of the middle ear or swelling. The presence of pain syndrome is also checked. Hearing acuity is determined.
The specialist analyzes the patient’s complaints and asks about chronic diseases. It is also important to identify the conditions and situations under which symptoms appeared. If an inflammatory process is suspected, laboratory tests are prescribed. Elevated levels of ESR and leukocytes, for example, will indicate a pathology such as inflammation of the middle ear.
For painless ear congestion, an otoscopy procedure is usually performed. This diagnosis allows you to examine the ear canal and eardrum. Upon examination, the presence of redness, swelling, and fluid discharge is revealed. In addition to this, the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound and tomography examination.
What causes symptoms
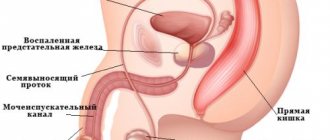
The mechanism for the occurrence of such a nuisance as congestion in the ear is explained by its structure. The ear consists of three compartments (outer, middle and inner). Each of them has its own characteristics. But all together they form one complex system that is responsible for hearing in the body.
The outer ear includes the pinna and auditory canal and borders the eardrum. Its function is to direct sound waves. The middle section includes several auditory ossicles. Its purpose is to receive sound vibrations, amplify them and transmit them further to the inner ear for conversion into nerve impulses going to the brain.
The causes of hearing impairment are varied. Most often this is: an obstruction in the ear canal or the presence of a pathological process there. The response of the ear mucosa is the occurrence of edema. The tissues of the ear canal increase in volume, blocking the space and preventing the passage of air from the middle part of the ear. The pressure balance in the tympanic cavity changes, causing a feeling of fullness in the ear, ringing or noise.
Such symptoms are difficult to miss. The condition is not accompanied by pain, but causes a lot of trouble. Decreased hearing and a feeling of ear congestion interfere with normal life and communication. Timely recognition of symptoms will help identify the causes of the emerging pathology.
Stuffy ears due to cold
If a person has a cold and suffers from a runny nose, then his breathing becomes impaired, he begins to breathe through his mouth and blow his nose profusely, as a result of which the pressure in the middle ear increases. The result of this phenomenon is congestion and discomfort.
It is not recommended to ignore such symptoms. If your ears are blocked due to a cold, this may be a harbinger of incipient otitis media. The most characteristic signs of the development of inflammation are headaches, a shooting sensation in the ear, and later purulent discharge from the ear canal.
If your throat hurts and your ears are blocked, then acute pharyngitis is most likely the cause.
Probable causes and symptoms
In addition to the congestion itself, other symptoms may be present that indicate a particular disease.
- Dizziness.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Noise or ringing in the ears.
- Your own voice and other sounds seem muffled. It feels as if the head is in some kind of vessel.
- There is a feeling of heaviness in the head.
There are no painful sensations. There may be temporary relief of symptoms when swallowing or yawning. If pain is present and pus appears, then this is already a sign of purulent otitis.
Congestion in the ear is accompanied by a significant decrease in hearing acuity. Sounds are not perceived as clearly as before and seem muffled. After swallowing, the ear does not unfold. The disease is often accompanied
which leads to headaches. In some cases, a person may experience dizziness.
When the ear is blocked, the pain may manifest itself as a slight tingling sensation inside the ear. Hyperthermia (increased body temperature) is often observed.
With otitis media, a disease caused by inflammatory processes, ear congestion is accompanied by severe pain and high fever. The treatment of this disease must be taken very seriously. Otitis media is quite common among young children.
Often, congestion and ear noises begin as a result of ENT disorders. They can be associated with both physiological problems and developing diseases.
Physiological problems arise when water, a foreign body, a small insect, etc. gets into the ear canal. Symptoms of this kind go away on their own, without requiring drug treatment. For example, you can remove water with a cotton swab, jump on one leg, turning your head so that the liquid flows out.
Noise is also caused by sudden changes in atmospheric pressure and staying in rooms with loud music. Often people whose work involves noise (traffic controllers, pilots, builders, lathe and milling machine workers) complain about congestion. For the problem to go away, it is enough for a person to get a good night's sleep and relax in a quiet environment.
Among the ENT diseases that cause the patient a feeling that the ears are blocked and the tinnitus does not stop, we can highlight:
- Tubootitis (eustachitis).
- Exacerbated otitis media.
- Complicated rhinitis.
- Sinusitis, sinusitis.
- Purulent sore throat.
- Ear injuries.
Ear ringing may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Throbbing, pressing, piercing pain in the head.
- A feeling that something is stabbing deep in the ear and interfering.
- Increased body temperature.
- Head spinning.
- Pain in the ear when swallowing.
- Hearing impairment.
- Itching in the ear canal.
Such symptoms are characteristic of inflammatory diseases, the treatment of which requires a serious approach, especially when it comes to young children. The disease can be triggered by hypothermia, fungal infection, eczema, or injury to the ear canal.
When a car or plane begins to accelerate, pressure builds up and puts pressure on the eardrum. Drivers and racing drivers often experience noise in their heads and blocked ears. Helps them overcome illness:
- Gum.
- Lollipop.
- SIP of water.
- Mint tablet.
Passengers who experience an unpleasant feeling in transport can also escape using these methods. If the ringing does not leave a person for a long time after he has made a trip, it is necessary to consult an ENT doctor.
Sulfur plug
It is known that clots of wax in the ear canals can cause a sharp deterioration in hearing, coughing, nausea and tinnitus. The causes of sulfur seals may be hidden in:
- Frequent and rough use of cotton swabs (some people use pins or knitting needles to clean the ear canal).
- Physiological structure of the auditory canal.
- Tendency to increased sulfur production.
- Inflammatory diseases of the ear.
- Excessive use of headphones, which injure the skin of the auricle.
- Excess hair growing inside the ear (this problem is more common in older people).
- Working in dusty rooms and being in places with low humidity.
Often a person feels that his head is ringing in the morning or after taking a bath (shower). When drops of water enter the auricle, the plug enlarges and blocks the passage, causing the ears to become blocked, and the tinnitus is constant. It is dangerous to remove wax plugs yourself using cotton swabs, matches or other objects. With one awkward movement, the clot can be pushed deeper and worsen the condition.
If you do not see a doctor, the wax plug can descend into the bones and put pressure on the eardrum, irritating the nerves. This is fraught not only with severe pain, but also with serious consequences, in particular, paralysis of the facial nerve, tachycardia, and seizures.
Otosclerosis
Sometimes the cause of this phenomenon is a pathology of the bone tissue of the auditory canal, in which the metabolic process is disrupted. The healthy bone structure is replaced by spongy, newly formed bone, entangled with many vessels. Typically the damage is located in the internal auditory canal. The first symptoms are observed in young people and middle age. Describing their sensations, patients note a strong noise comparable to:
- The splash of a wave.
- The rustle of leaves.
- The noise of wires.
Patients develop hearing loss, dizziness, and balance disorders. Most often, both ears are affected. A person experiences pain, tingling in the depths of the ears, memory decreases, and sleep is disturbed.
— ringing in the head; — discomfort when swallowing; — dizziness; — “gurgling” and itching in the sore ear.
In the presence of a cold, inflammation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa is noted. But at the same time, significant changes in the mucous membrane are not observed (as with catarrhal otitis media). In this case, ear congestion is temporary and goes away after a cold, body temperature does not change. In the case when both ears are blocked, this indicates a disease such as acute otitis media. To make an accurate diagnosis, an appointment with an otolaryngologist is required.
- a common cold; - congestion after swimming; - acute form of otitis; - foreign bodies or insects entering the ear canal; - presence of cerumen plug; - curvature of the nasal septum.
What happens to the ear when there is congestion?
If the body is functioning normally, there should be no problems with ear congestion. The mechanism for the development of congestion is of two types:
- Differences in pressure inside and outside the ear. The eardrum performs a protective function and protects our ear from the negative effects of the environment, thanks to the air chamber. Complete tightness sometimes leads to barotrauma, which is accompanied by severe pain in the ears due to pressure changes. The negative impact can be reduced by using a special valve that equalizes the pressure. This role is played by the Eustachian tube. The pressure is normalized when swallowing, since at this moment it opens slightly.
- Failure in the formation of a sound sensation and its subsequent transmission. This occurs in various diseases that have nothing to do with this organ.
Medicines
Before using this or that medicine, it is extremely important to understand why your ears are clogged. Thus, a decrease in hearing acuity can be a symptom of serious diseases (hypertension, VSD attack). As a rule, such conditions, among other things, are accompanied by dizziness, nausea, severe pain and other syndromes.
- Otipax. The components of this drug successfully cope with inflammatory processes. Therefore, Otipax is widely used to combat otitis media and ear congestion. The drug does not have a dissolving effect on sulfur plugs.
- Garazon. Antibacterial ear drops used to treat otitis media and eczema of the mucous membrane of the ear canal. Not used for defects of the eardrum.
- Otinum. Has antimicrobial and analgesic effects. Can be used to soften wax plugs. The drug should not be used if the integrity of the eardrum is suspected.
Basic treatment regimens for ear pathology*
| Pathology | Basic treatment methods |
| Sulfur plug | Removal by rinsing or instrumental removal. |
| Otitis externa | Toilet of the external auditory canal, treatment with medications, ear drops, vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, systemic antibacterial or antifungal therapy, FTL**. |
| Tubootitis | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, blowing of the eustachian tubes according to Politzer, pneumomassage of the eardrum, FTL**, catheterization of the auditory tubes if necessary. |
| Otitis media | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, systemic antibacterial therapy, ear drops, Politzer ear blowing, pneumomassage of the eardrum, FTL**, if necessary, catheterization of the auditory tubes, lavage of the nasal cavity using the moving method. If necessary, surgical treatment - eardrum bypass or paracentesis. Complemented by the treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. |
| Suppurative otitis media | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, systemic antibacterial therapy, ear drops, Politzer blowing, if necessary, transtympanic injection of drugs, catheterization of auditory tubes, nasal lavage using the displacement method. If necessary, surgical treatment - eardrum bypass or paracentesis and other operations, FTL**. It is supplemented by treatment of pathologies of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses, if indicated. |
| Exudative otitis media | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, mucolytics, Politzer blowing, catheterization of auditory tubes. If necessary, surgical treatment - eardrum bypass or paracentesis, FTL**. It is complemented by the treatment of pathologies of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses. |
| Sensorineural hearing loss | Catheterization of auditory tubes, systemic vascular and vitamin therapy. |
*These treatment regimens are not a recommendation for self-treatment and serve to familiarize patients with basic treatment methods. The final decision on treatment and examination methods is made by the doctor after the examination!
** FTL – physiotherapeutic treatment.
Possible complications
If your ear periodically gets blocked, but it doesn’t hurt, this doesn’t mean you should ignore this problem.
You should definitely see a doctor and undergo the recommended course of treatment, otherwise the following complications may occur:
- complete or partial hearing loss;
- decreased hearing acuity;
- spread of the inflammatory process to other adjacent organs.
What diseases can occur with such symptoms?
Otitis - inflammation of the outer and middle parts of the hearing organ is a common cause of these unpleasant symptoms. Another characteristic symptom of otitis media is acute shooting pain during inflammation. The disease may also be accompanied by fever and purulent discharge from the ear canal.
A feeling of congestion can appear with a disease of the hearing organ such as labyrinthitis - an inflammatory process that affects the structures of the inner ear. Another internal disease is Meniere's disease. With Meniere's disease, in addition to congestion, the following symptoms appear: headaches, nausea, problems with balance (at times of exacerbation, the patient cannot even sit).
With neuritis of the auditory nerve, in addition to ear noise and a feeling of fullness, the patient complains of frequent dizziness.
Older adults are often diagnosed with otosclerosis, a condition in which the bone in the middle portion of the ear becomes enlarged, leading to hearing problems.
But not only ear diseases lead to such symptoms.
Only an otolaryngologist can determine the exact cause of ear congestion after a comprehensive diagnosis. First of all, you need to eliminate the underlying problem, which in this case becomes a viral or bacterial infection.
How to help your ear when it hits?
A severe bruise causes deformation of the cartilage, the occurrence of a hematoma and the accumulation of cartilage clots. The help of a specialist is inevitable. With a minor impact, when only congestion is felt, it can be eliminated independently.
A common cause is a deformed eardrum. There are some methods that can quickly cope with discomfort:
- Valsalva maneuver. Carried out to equalize external and internal pressure. To perform this, you need to pinch your mouth and nose, close your vocal cords and exhale forcefully.
- Toynbee's method. To perform it, you need to press the wings of your nose and make swallowing movements. With good passability, a characteristic cracking sound should be felt in the ears.
- Frenzel method. Initially, you need to tense your throat muscles, pushing your lower jaw forward. The nose should be pinched. Imitate swallowing movements.
- Pain relief with medications. Paracetamol-based products are popular. They are on free sale.
The following actions are prohibited:
- Clean the ear canals yourself using a match or a cotton swab.
- Use homemade plugs made from cotton wool and bandages.
- Instill medications or other compounds into the ears, following folk recipes.
Causes
To clarify the situation, it is necessary to understand the anatomical structure. The ear is a complex organ with several parts, as can be seen in the figure below. Discomfort occurs if the membrane is blocked from the outside or from the inside.
The main causes of ear congestion:
- When flying, the pressure on both sides of the eardrum is different, so the ears often become blocked.
- Cork. During normal functioning of the organ, the sulfur that is formed is removed outside. If this process is disrupted, it accumulates and forms a dense plug that clogs the ear canal. The result is a sharp decrease in hearing.
- Otitis is an inflammatory process that affects the outer ear. Viruses, bacteria, and fungi are the causative agents of the disease. If inflammation is accompanied by the formation of pus, then the person feels the presence of fluid in the ear. Otitis often appears as a consequence of a disease of the throat and nose.
- If, in addition to discomfort, itching occurs, which is accompanied by uncharacteristic discharge, this indicates the development of an infectious process in the external auditory canal. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the water while swimming at the beach. Small wounds and scratches give rise to infection.
- The volume of sounds may change when water gets into the ear while taking a shower. A person feels the presence of water in the ear, which flows in time with the movements.
- A strong blow to the ear can lead to stuffiness.
- Sometimes an increase and decrease in pressure leads to ear congestion.
- Penetration of a foreign object. Very often observed in young children. A child under three years old should not be left unattended with small objects.