Do your breasts hurt during menopause?
Women who do not know whether their breasts hurt during menopause worry when they encounter various problems and pain in the chest area. In fact, breast pain during menopause, as during the fertile period, is a commonly diagnosed symptom. In fertile women, painful sensations of varying intensity are observed monthly before menstruation, and in elderly patients, the mammary glands hurt non-cyclically.
The appearance of pain symptoms is observed during menopause during premenopause and menopause. Usually the pain is non-localized, spreading throughout the tissues. It can ebb and flow. The woman feels either a burning or tingling sensation. For many patients, discomfort occurs only in the nipples. Spreading pain is usually not dangerous, but pain localized in a small part of the tissue can signal oncology.
70% of patients experience discomfort in the breast tissue throughout their lives. But most women have mild pain in the mammary gland, and only 10% of patients complain about the intensity of the pain syndrome. In some cases, the symptoms are so strong that they interfere with leading a full life.
Breasts hurt during menopause - what to do?
About 10% of women experience chest pain during menopause, but most often these sensations are caused by age-related involutive changes. Every woman needs to know about the possible risks of oncology or a benign tumor, which include:
- hereditary predisposition (family history of breast cancer in close relatives);
- long-term diffuse mastopathy;
- fibroadenoma diagnosed before menopause;
- any breast surgery;
- endocrine disorders and diseases;
- refusal of childbearing and lactation.
The mammary glands in menopause never hurt for no reason, but it is important to distinguish between pain of an involuting and tumor nature. The doctor knows what to do, how to detect pathology and identify age-related problems: by contacting a specialist as soon as possible from the moment chest pain occurs, you can identify the main causes of unpleasant symptoms using the following research methods:
- mammography;
- ultrasound scanning of the mammary glands;
- blood test for tumor markers;
- microscopy of nipple discharge;
- aspiration biopsy (performed according to indications when a node is detected in the chest).
An accurate and timely diagnosis is the basis for successful therapy. Surgery is not always required; a significant part of diseases during menopause can be treated with pills. In each specific case, the mammologist will select the optimal and effective treatment option that will save the woman from unpleasant problems.
Changes in the mammary glands during menopause
A healthy mammary gland has three types of tissue:
- glandular, which is a lobular formation that secretes a secretion;
- fibrous, which is the supporting basis of the glands;
- fatty tissue that forms the outline of the breast.
With the advent of menopause, when a hormonal imbalance occurs, glandular cells are converted into fatty and fibrous cells. This transformation can cause pain in the mammary gland. This painful condition, although pathological, is not dangerous.
However, during menopause it is important to monitor the condition of the mammary glands. A woman may think that the discomfort is caused by age-related hormonal changes, but in reality she is developing a benign or malignant tumor disease.
Dangerous symptoms
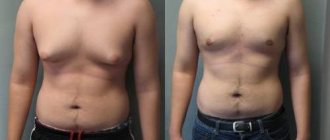
During menopause, the risk of developing tumors in the breast increases significantly. Due to their growth, the breasts also increase. Formations of a benign nature grow slowly, while malignant ones progress quickly, causing deformation of the glands, changes in the skin, and the shape of the nipples.
Symptoms that may indicate dangerous diseases:
- bleeding from the vagina;
- sunken nipples;
- nipple discharge;
- change in skin color on the mammary glands;
- itching, visible swelling of the breasts;
- granularity of the mammary glands to the touch;
- compactions when palpated.
Important! If any lumps appear in the mammary glands, an unusual increase in size, deformation, or changes in the nipples, you should consult a doctor.
Causes of chest pain
If pain in the breasts on the eve of menstruation is caused by cyclic hormonal changes, then pain in the mammary glands during menopause is a consequence of the influence of the following factors:
- age-related transformations in glandular structures;
- fibrous or cystic mastopathy of the mammary gland;
- fibroids, lipomas or other benign tumors;
- breast oncology;
- chest injuries;
- severe stress;
- ischemia, angina and other cardiac pathologies;
- chronic disruption of the pulmonary system;
- diseases of the liver, urinary and other internal organs;
- metabolic disorders, obesity;
- bad habits;
- long-term use of certain medications.
Usually, during menopause, the mammary glands hurt not because of hormonal fluctuations, but because of age-related deformation of the breast tissue or disruption of the vascular system, accompanied by instability of pressure and an abundant rush of blood to the breast.
During menopause, breasts can not only hurt, but also:
- increase;
- swell, as before menstruation;
- itch;
- become covered with knots, become lumpy;
- discharge fluid from the nipples.
In case of the above phenomena, you need to urgently go to a mammologist so that the doctor can promptly identify a dangerous disease if it has developed.
If your chest hurts on the left side during menopause, then you can assume heart pathology or increased blood pressure. In this case, you need to go to a cardiologist. Patients with chronic diseases of the pulmonary system should be examined by a pulmonologist. If you are obese, you should consult an endocrinologist. And if the pain develops against the background of diseases of the kidneys, liver and other internal organs, then the help of a hepatologist, nephrologist and other specialized specialists is required.
Causes of the disease
The standard age for menopause is 45–55 years. During this period of time, numerous metabolic and endocrine changes occur in the female body due to the cessation of ovarian function. The main causative factors of mastopathy after menopause:
- a sharp decrease in the influence of estrogen hormones;
- almost complete cessation of the antiproliferative effects of Progesterone;
- change in the ratio of pituitary hormones (FSH, LH);
- fat deposition in the mammary glands;
- growth of connective tissue in the breast (fibrosis).
The following provoking factors are of great importance for the formation of fibrosis and diffuse changes in the breast:
- female diseases (uterine leiomyoma, endometrioid disease);
- refusal to bear children;
- frequent abortions with complications and inflammatory processes;
- general metabolic and endocrine diseases (diabetes, metabolic syndrome, thyroid diseases);
- prolonged psychological tension or stress.
The risk group for developing mastopathy includes nulliparous women
During menopause, the female body is subject to fluctuating hormone levels. This promotes the proliferation of breast connective tissue. Certain factors can cause such a violation:
- early puberty associated with high levels of hormones in the body;
- venereal diseases, especially their chronic forms;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- disorders during lactation; the risk group often includes women who have not given birth or breastfed;
- abortions that provoke significant hormonal disorders;
- nervous disorders and pathologies, diseases of the central nervous system.
Treatment of mastopathy during menopause should be comprehensive, consisting of different techniques. The main thing in such therapy is constant control of lifestyle. It is necessary to eat right, eliminate bad habits, avoid stress and negative environmental influences. If a woman works in a hazardous industry, she needs to change her field of activity.
Silest is one of the most prescribed drugs
Products based on estrogen and progesterone are widely used in the treatment of mastopathy during menopause. Oral contraceptives are most often prescribed. But only if the cause of the disease is hormonal fluctuations. The most common drugs include: Silest, Diane-35, Ovidon. Other drugs are also used for treatment: Femoston, Janine, Klimonorm, Regulon, Mercilon, Novinet, Triquilar.
Special hormonal therapy with progesterone-based drugs is also used. This may be a product of the same name or Utrozhestan. External agents are also used, including Progestogel. It contains a special form of progesterone, which quickly relieves the symptoms of mastopathy. If a high level of prolactin is diagnosed in a woman’s body, Bromocriptine, Abergin, Parlodel are additionally prescribed.
Mastodinon is used for menopause and mastopathy
In the treatment of mastopathy after 50 years, products based on phytoestrogens are widely used, which do not contain dangerous chemicals and synthetic hormones. Very often, Klimadinon is prescribed for mastopathy - an effective herbal preparation that eliminates pain and tension from the mammary glands. Mastodinon, which belongs to the group of natural medicines, is also indicated for menopause and mastopathy.
Other remedies include: Klimakt-Hel, Gineko-Hel, Cyclodinone. You can use analogues if the woman’s chronic illnesses are on the list of contraindications for these drugs.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Spanish abdominal massage and intestinal lymphatic drainage
Patients are prescribed multivitamin complexes specifically for women during menopause. They contain E, A, C and other useful substances. Constant intake of vitamins helps improve metabolism and other positive processes.
Often, sedatives are prescribed along with taking herbal medicines, such as Climaxan for mastopathy. It is recommended to use natural sedatives: valerian, motherwort, mint, St. John's wort, thyme. If natural substances do not help, the specialist prescribes strong drugs: Efevelon, Rexetine, Paroxetine, Adepress, Velafax.
You can also take folk remedies internally, if the doctor does not prohibit this approach: decoctions based on St. John's wort and nettle, rose hips and celandine. Brew dry herbs in the amount of 1 tsp. for 1-2 cups boiling water. Leave for several hours and then filter. You need to take a glass a day.
During menopause, surgical intervention is prescribed only in case of oncological tension, if there is a risk of developing atypical cells. There are several ways to remove tumors, which initially involve only a small incision. If the tumor is large, partial or complete resection of the mammary gland is performed.
If the pathology is not treated, over time it can lead to malignancy, and this is a direct path to breast cancer. The risks are especially high for mastopathy complicated by infections and nodular forms. Symptoms such as intoxication of the body and high temperature are dangerous for mastopathy.
Age factors have different effects on a woman’s mammary glands. Under the influence of hormones and age-related changes, the following signs and symptoms of mastopathy of the mammary gland during menopause in women are detected:
- aching chest pain that constantly gets worse, may be absent for a long time, appear and disappear suddenly;
- small nodules gradually form in the tissue, which cause pain upon palpation;
- compactions gradually form and can quickly increase in size, reaching the shape of a walnut.
The main danger of mastopathy is its development into malignant tumors. Also, the symptoms of the disease greatly depend on the form of the disorder.
Classification
There are several forms of mastopathy after 50 years:
- diffuse – the initial stage, in which dense nodules and cords appear in the chest;
- nodular - the nodes become large, reach the size of a walnut, and the lymph nodes in the armpits also enlarge;
- fibrocystic - accompanied by the appearance of neoplasms, fluid-filled cysts, and severe pain.
With form 3 of the disease, bloody and watery discharge from the nipples often begins.
Small-grained tumors are often detected by ultrasound
https://youtu.be/U_LTK72S3Co
For diagnosis, mammologists use a standard set of procedures and tests:
- blood donation for hormonal factors;
- blood test for the presence of cancer markers;
- Ultrasound allows you to determine the type of mastopathy and see the shape and boundaries of the tumor;
- mammography is necessary to determine early forms of mastopathy;
- A biopsy is performed when diagnosing tumors and cysts of any form.
After the biopsy, the result is sent for histological examination. This method is recognized as one of the most reliable and accurate. The accuracy of the results reaches 90-95%.
Breast enlargement during menopause
From the age of 25, the mammary glands are fully formed, and during the fertile period, breast enlargement without an increase in body weight is considered a dangerous phenomenon.
But during menopause, there is nothing wrong with engorged breasts; the glands can swell due to the formation of adipose tissue instead of glandular tissue, and breasts also swell as a result of age-related weight gain. With age-related hormonal imbalance, a woman can gain weight by 5 kg or more, become the owner of large breasts, and it is very difficult to lose those extra pounds. Swelling of the mammary glands is observed mainly in premenopause, then this symptom gradually disappears.
Slight swelling of the nipples is also considered normal. But the condition of the nipples should be monitored carefully. Due to swelling of the nipple tissue, Paget's cancer can develop, a fast-acting cancer that requires urgent surgical intervention. Therefore, older women with any changes in the breasts during menopause should be examined by a mammologist.
Swelling of the mammary glands
Breast swelling occurs due to increased levels of progesterone, which stimulates the formation of fatty tissue in the breast. When the mammary gland is deformed, adipose tissue is displaced by connective tissue. At the chemical level, the ratio of estrogen and progesterone changes, which has the scientific name involutive fibrosis. The breasts lose elasticity, become saggy, but with compactions.
Causes
The main reasons for breast swelling during menopause are:
- a sharp decrease in estrogen levels;
- disruption of ovarian function;
- metabolic disorders in all tissues in the body.
It is very important not to be confused, since swelling of the mammary glands is considered a completely natural phenomenon due to atrophy of the glandular tissue and its secretory lobuloalveolar structure. In other words, involution of the breast occurs - the glandular tissue decreases in volume, and fatty tissue fills the connective capsules, which contributes to swelling.
Symptoms
Additional symptoms may include:
- pain;
- burning;
- feeling of discomfort;
- increased sensitivity of the nipples.
Such symptoms indicate that the patient needs to consult a doctor for advice to exclude the development of serious diseases.
Diagnostics
It is extremely important to identify the reason why your breasts swell and hurt. When observing nipple swelling, it is necessary to undergo several examinations to find out whether the cause of such a symptom is serious. The patient should contact a mammologist, who will prescribe instrumental studies for her - ultrasound of the mammary glands, mammography - due to which age-related, natural deformation is distinguished from the development of pathology. In some cases, if cancer is suspected, the doctor may order high-quality thin-section photographs of the nipples.
Treatment methods
There are several effective methods to get rid of breast swelling:
- Drug treatment. The doctor, based on the tests and examination results, may prescribe painkillers - Diclofenac, Nimesil or Ibuprofen, as well as phytoestrogen - Mastodinon or Remens.
- Folk remedies. Decoctions of flax, soybeans, barley, clover, black root, sparrowweed, hemlock, etc. reduce breast swelling.
- The right underwear. If you choose the wrong bra, your breasts may feel uncomfortable, which causes swelling.
- Diet and hygiene. A contrast shower, therapeutic breast massage, following a diet, proper sleep, as well as taking the required amount of vitamins will ensure that the breasts fall to their normal state.
Discharge from nipples during menopause
There should be no discharge from the breast during menopause, because the glandular cells that form the liquid secretion turn into fibrous and fatty cells. If suspicious fluid leaks from the nipples, you should immediately go to the doctor. Most likely, the release of fluid is a consequence of galactorrhea, an unpleasant disease manifested by spontaneous leakage of colostrum from the breast.
Liquid may leak from the nipples:
- whitish (colostrum);
- purulent;
- bloody;
- transparent.
With galactorrhea, pain in the nipples is often noted, the breasts swell, and some pain also occurs in its internal tissues. In this case, pain indicates that galactorrhea has become a provocateur of a benign tumor or oncology.
Nature of pain
The proliferation of adipose tissue and its replacement of glandular cells leads to the appearance of pain of a different nature.
It can be pulling, aching, stabbing, localized in the right or left breast, and even depend on certain conditions (for example, food or nervous tension).
A painful symptom is characteristic of the initial period of menopause, when hormonal activity is unstable. After menopause, pain often goes away, but only if this is not associated with the development of pathology. The mammary glands may hurt during sleep or when walking or exercising. They can begin at any time of the day and also pass suddenly. A common symptom is nipple pain. Normally, they should not change structure, color, and have no discharge. Pain in the mammary glands can greatly affect the normal rhythm of a woman’s life: contribute to a lack of appetite and reduce physical activity.
https://youtu.be/BAOwDZw7pHM
Nipple pain during menopause
During the menopausal period, a woman should regularly conduct self-examination of her breasts so as not to miss the moment when a visit to the doctor is necessary. You should look especially carefully at the condition of the nipples, since it is from them that it is easiest to identify developing pathology.
We can talk about pathological changes if nipples periodically or continuously hurt during menopause, as well as:
- itchy;
- tingling;
- are burning;
- release liquid.
Ignoring such symptoms is unacceptable. A woman should contact a mammologist. The doctor will determine exactly why your nipples hurt and prescribe effective therapy.
Treatment of breasts during menopause
Women who have reached menopausal age need to undergo medical examinations three times a year. And if the patient has any pathologies, the doctor prescribes preventive examinations and tests every 3 months.
To prevent pathologies of the mammary glands, you should periodically visit a mammologist. To identify symptoms of mastopathy and other breast diseases, the doctor sends the patient for an ultrasound of the chest area.
Medical examinations cannot be ignored. Firstly, based on the patient’s complaints, the doctor prescribes medications that eliminate chest pain during menopause and alleviate menopausal syndrome. Secondly, timely medical examination makes it possible to identify oncology and other serious diseases at an early stage, due to which breasts may hurt at the beginning of menopause, which simplifies further treatment.
You should definitely go to the doctor if you suspect a tumor disease if:
- nipples are swollen and discolored;
- dense lumps are felt inside the chest;
- I lost my appetite.
To relieve chest pain during menopause, the doctor prescribes to the patient:
- non-hormonal analgesics – Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Voltaren;
- sedative herbal remedies;
- homeopathy and dietary supplements based on phytohormones to improve well-being.
In some cases, it is necessary to prescribe antitumor drugs or hormonal replacement drugs.
Possible causes of discharge
The root causes of discharge can be both natural and pathological. In most cases, the color of the discharge indicates the main reason for its appearance.
Green discharge
If, when pressed, a secretion of a greenish tint appears from the mammary glands, then in most cases this indicates the presence of mastopathy - tissue proliferation. The discharged substance has a thick consistency with mucus impurities. In addition to discharge, symptoms such as breast hardening and pain appear.
Discharge from the mammary glands when pressed may be a sign of one of the forms of mastopathy
You can get rid of this disease in a short time with a timely visit to a specialist who will identify the form of mastopathy and the stage of its development. Otherwise, when the disease is advanced, the effectiveness of therapy is significantly reduced.
The list of mandatory diagnostic studies for this pathology includes tests for hormones such as progesterone, prolactin and estradiol.
Transparent selections
A clear secretion released from the nipples is not a symptom of a serious disease. It can appear due to trauma to the chest (bruises or blows), constant stress and hormonal changes during menstruation. Usually the fluid comes out on its own, without pressing on the chest area.
The separated substance contains cellular enzymes, lymph transudate and all kinds of microorganisms. The discharge should not have a distinct odor, and should also be accompanied by discomfort in the chest and the appearance of such unpleasant symptoms as pain, lumps and enlarged lymph nodes.
Yellow discharge
Discharge, which has a yellowish tint, is one of the early symptoms of pregnancy. Watery discharge has a sweet odor and is produced by prolactin. Most often, this kind of secretion appears in the first weeks after conception, in the middle of pregnancy or immediately after childbirth.
The color of the discharge varies from yellow to almost clear liquid. The composition of the discharge includes lipids, proteins and minerals.
Prolactin can provoke the appearance of this kind of discharge not only during pregnancy. They can appear in women of any age, even girls. This occurs when the level of this hormone increases. Deviations can be detected using a blood test, and hormonal levels can be normalized by using prolactin inhibitors.
Release of fluid
The appearance of liquid secretion is an alarming signal in cases where it is accompanied by a number of other symptoms:
- pain in the mammary glands;
- itching around the nipple, discoloration of halos and the appearance of spider veins in this area;
- breast asymmetry, changes in the shape and color of the skin in this area.
If any of these signs are present, you should urgently contact a mammologist to examine the mammary glands and analyze the secreted fluid. Until this time, it is forbidden to squeeze out the secretion on your own to avoid injury and provoking the development of infection.
Brown discharge
Brown discharge indicates bleeding in the ducts, which is formed due to damage to the blood vessels. Disturbances occur both with the growth of tumors and with small cysts in the mammary glands.
This is interesting: Epithelium in a smear in women. The norm in the table is by age, during pregnancy. Analysis transcript
Cysts are benign formations, and when they occur, nipple discharge may be brown with a greenish or grayish tint without traces of blood.
The appearance of brown secretion may depend on the age of the woman. For example, at the age of 50, ductal ectasia may occur. With this disease, the discharge has a sticky consistency. When diagnosing, a specialist must check the milk ducts for the absence of a bloody component.
Bloody issues
The appearance of blood discharge indicates the formation of a benign or malignant tumor. Such neoplasms cover the small blood vessels of the mammary gland, so the discharge from the breast becomes mixed with blood.
The danger lies in the fact that even a simple papilloma can degenerate into a malignant tumor. That is why it is important to immediately contact an oncologist if any bloody traces appear to rule out breast cancer.
The following symptoms also indicate the presence of a serious illness:
- secretion from only one mammary gland;
- noticeable breast enlargement;
- pain on palpation;
- the appearance of dense areas on the gland.
Women over 35 years of age, as well as girls who have not yet given birth, are at risk. In rare cases, discharge mixed with blood may appear during pregnancy, which is associated with a sharp change in hormonal levels.
White discharge
White secretion secreted from the mammary glands is the main symptom of galactorrhea. Excessive production of prolactin causes the synthesis of milk, which begins to appear in small quantities when pressed.
Discharge from the mammary glands of this kind, which appears when pressure is applied, is not a sign of pathology during pregnancy. In other cases, immediate assistance from a specialist is needed, especially if the secretion is released several months after the end of lactation.
Discharge from the mammary glands when pressed, which is white in color, also indicates the presence of problems with the urinary, reproductive, endocrine systems, as well as changes in the functioning of the hypothalamus.
Dark discharge
Most often, the dark color of the secretion is caused by traces of blood, which give the discharge a black or dark brown tint. This type of discharge indicates the presence of neoplasms in the mammary gland. A dark secretion with a green tint appears with cystic mastopathy or with inflammatory processes in the chest caused by a pyogenic infection.
In the presence of dark discharge from the chest, it is impossible to speak unambiguously about any pathological changes in the body. When diagnosing, one should take into account the results of laboratory tests, palpation and visual inspection.
Light discharge
If the appearance of light discharge is not associated with bearing a child, then it is called galactorrhea. This secretion is odorless and appears from both mammary glands.
Its appearance is associated with an increase in prolactin levels, which is caused by the following factors:
- use of contraceptives;
- taking medications for the treatment of estradiol without medical supervision;
- thyroid diseases;
- cancer.
If left untreated for a long time, galactorrhea begins to negatively affect the performance of the ovaries, increases the risk of infertility, causes early miscarriages, and in rare cases affects the occurrence of tumors in the brain.
Bloody discharge
Most often, bleeding appears due to intraductal papillomas, which occur due to hormonal imbalances. They compress nearby vessels, causing internal bleeding.
Other causes of blood secretion from the mammary gland include breast trauma. If a hematoma or hemorrhage occurs as a result of a bruise, a small amount of blood may enter the ducts. Therefore, it is important to inform the specialist about any injuries during the examination.
Sticky discharge
Discharge from the mammary glands when pressed, which has a thick and sticky consistency, is the main symptom of lacteal duct ectasia.
This disease is age-related and is associated with channel changes, for example:
- deformation;
- dilation of the ducts;
- narrowing of the milk ducts.
All transformations occur in the ducts located close to the nipples. Such changes provoke blockage of the channels and the development of inflammation. The release of a sticky secretion of any color occurs simultaneously with the appearance of a modification of the nipple and lumps of the mammary gland in this area.
Black discharge
Black discharge from the mammary gland, which appears when pressure is applied, occurs when a cluster of pathogenic bacteria forms in the ducts. The reason for their development is blockage or deformation of the canals. The black tint to the secretion is given by pathogenic microorganisms and traces of their vital activity.
The most common cause of black discharge is the appearance of blood in the milk ducts. It is dead red blood cells that make the color of the discharge mass dark. Blood in the discharge serves as a signal for the occurrence of tumors of any nature. With this pathology, the secretion is released only from the affected mammary gland.
Blood in the milk ducts is a serious signal, so if black discharge appears, you should immediately contact a mammologist for a full diagnosis.
Purulent discharge
Discharge of this type indicates that an inflammatory process with ulcers and abscesses has formed in the ducts. All this is accompanied by pain, swelling of the breasts and the appearance of redness around the nipples.
This is interesting: How, when and why is an ultrasound of the heart done?
To eliminate the abscess, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately, which usually consists of taking antibiotics and applying compresses. In acute cases of the disease, the doctor prescribes an opening of the inflamed area in order to remove pus and clean the ducts.
General recommendations
To successfully treat breasts during menopause, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- lead an active and healthy life, take regular walks;
- wear high-quality underwear that supports the breasts well;
- normalize the diet, introduce more fiber into it;
- eliminate bad habits, including addiction to coffee, because nicotine and caffeine can significantly worsen the state of health during menopause, and chest pain increases because of this;
- take sedative medications and vitamin supplements as recommended by a doctor;
- do not overcool the chest;
- maintain hygiene;
- use breathing exercises as an additional method of therapy.
Manifestation of pathology during menopause
Most often, mastopathy during menopause is manifested by fibrocystic neoplasms of a benign nature. Mastopathy during menopause can be completely asymptomatic, and therefore, with the onset of the first stage of menopause, it is necessary to regularly visit the gynecologist’s office and take all the necessary tests.
However, even with obvious signs of an existing disease, not all women immediately recognize the pathology. During menopause, patients actually experience symptoms similar to fibroadenomatosis, which occur with hormonal changes. This is what distinguishes the insidiousness of the disease, because more than 50% of women simply do not take into account the dangerous symptoms, associating them only with menopausal syndrome.
How do signs of breast fibroadenomatosis manifest during menopause?
In general, the manifestation of signs of fibroadenomatosis in the menopausal stage is not very different from the symptoms of the disease during childbearing age. However, against the background of age-related changes, the symptoms are smoothed out. Mastopathy during menopause symptoms:
- Painful sensations . Pain due to mastopathy during menopause can be severe or limited to a pulling sensation when wearing tight underwear. Discomfort can be either constant or intermittent. When pain occurs, there is usually a feeling of heaviness in the chest.
- The appearance of dense areas . A woman detects this sign by palpation. Lumps can be large or small, nodular or vague. Most often on x-ray they look like a cyst in the breast. Any changes in the condition of the mammary glands require mandatory diagnosis during menopause.
- Discharge from the chest during menopause . Discharge from the mammary glands during menostasis has a yellowish or grayish tint. Their consistency is similar to colostrum. If the pathology is aggravated by purulent inflammation, when pressure is applied, pus streaked with blood is released.
The disease can be identified quite easily. It is important to carefully monitor the condition of your bust, conduct regular self-examinations and regularly visit a gynecologist.
Important! Any of the above symptoms of breast fibroadenomatosis during menopause should be a reason to contact a gynecologist or mammologist! Discharge from the mammary glands during menopause deserves special attention. This symptom may also indicate oncology.
Drug therapy
Taking medications, dietary supplements and anesthetics should be carried out only with the permission of a doctor. The use of medications at your own discretion is unacceptable.
To relieve pain in the mammary glands during menopause, various anesthetics are used. The supervising doctor should know about taking even a mild pain reliever. Medicines based on antibiotics should not be taken for a long time, as they can aggravate the condition of the body.
Among the dietary supplements for breast tenderness during menopause, it is recommended to use:
- tocopherol solution;
- pyridoxine solution;
- Omega fatty acids.
These supplements suppress inflammation and reduce pain.
Also, if your chest hurts during menopause, you can use decoctions and teas based on medicinal plants:
- sage;
- celandine;
- chamomile;
- calendula.
If the patient’s condition is serious, the doctor may send her to a hospital for treatment.
Definition
Breast tenderness (scientific name mastalgia, mastodynia) is a general term used to mean discomfort, tenderness, or pain in one or both breasts when touched or pressed. Some authors use the term more generally to refer to any chest discomfort. In addition to pain in the gland tissue itself, sometimes chest pain can be caused by extra-mammary causes. A common cause of extra-mammary mastalgia during menopause is inflammation of the cartilage at the junction of the ribs with the sternum (Tietze's disease). This cause can usually be successfully treated with rest and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
American doctors recommend keeping a “pain diary”; for many women this is enough to critically evaluate anxiety and stop paying attention to the feeling of fullness in the glands.
Breast tenderness can manifest differently at different times in a woman's life cycle, and can vary depending on the unique physiology and genetics of the fairer sex. However, some symptoms are common to this pathology.
Prevention
Speaking about why breasts hurt during menopause, it is also necessary to note the fact that the provocateur of the pathological phenomenon is a woman’s incorrect lifestyle during her fertile years. To reduce the likelihood of pathologies of the mammary glands in old age, in youth and in adulthood, you need to:
- eat right, do not indulge in fatty and fried foods, sweets;
- give up alcoholic drinks and cigarettes;
- lead an active life, engage in feasible sports (the healthiest thing for a woman is running, fitness, gymnastics, swimming).
A woman entering menopause needs to begin stabilizing her hormonal system. For this, in the initial stages of menopause, herbal remedies with phytohormones and folk recipes are suitable. This therapy normalizes the physical and emotional state and prevents the further development of menopausal syndrome.