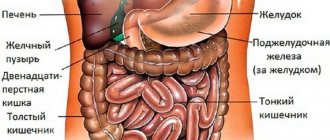
Intestinal diseases are quite common and require careful examination of the organ along its entire length. There are several ways to examine the condition of the intestines, for example, colonoscopy, MRI. The doctor determines and prescribes one or another research method. But patients are wondering: MRI of the intestine or colonoscopy, which is more effective and better? An important aspect is the safety and harmlessness of the diagnosis.
Features of the methods
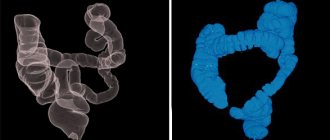
The main difference between CT and MSCT is the technical capabilities of the equipment. MSCT equipment captures X-rays using several rows of detectors. In one diagnostic session, you can obtain information about the condition of the intestine in the form of hundreds of images in sections and various projections. The images are distinguished by good clarity even with natural mobility of organs.
The examination takes place at high speed, which allows you to thoroughly study the anatomical features and life processes of internal organs. The advantage of colonoscopy is the power of the equipment, which guarantees high quality computer images of the intestine, while the patient receives minimal radiation doses. And during a CT colonoscopy, radiation exposure increases 4-5 times.
MSCT differs from MRI examination by its operating principle. As mentioned above, multislice CT uses X-rays, but magnetic resonance imaging uses electromagnetic fields.
Similarities
Comparing colonoscopy and its alternatives, represented by CT and MRI, is pointless. Endoscopy is prescribed to patients visiting a doctor for the first time with intestinal problems, while for re-diagnosis and monitoring the progress of treatment, a tomograph scan is better suited. Traditional colonoscopy is invasive, so it also allows for some procedures in the intestine, while CT and MRI only visualize the organ, albeit in great detail.
But understanding an MRI of the intestine or a colonoscopy, which is better, is much more interesting. This question is often asked to doctors by patients who have already experienced the “charm” of traditional endoscopy and are trying to find an alternative to this rather unpleasant examination method. It is quite difficult to give an exhaustive answer, since both types of scanning are:
MRI of the intestine has a significant list of positive aspects. It does not involve surgical intervention, during its implementation the patient is not exposed to radiation, and the contrast agent has no contraindications for use
- accurate;
- fast;
- painless;
- non-invasive.
The methodology for both CT colonoscopy and MRI of the intestine is approximately the same: a preliminary diet and cleansing of the body, the need to fill the organ with air or water before the examination, a quick scan with quick results.
What virtual colonoscopy and MRI also have in common is that their results relate to the general condition of the intestine, but do not affect its internal surface (internal mucous membranes). In addition, CT and MRI are similar in that they are diagnostic tools and do not allow for the removal of samples for detailed further study, nor for minimal interventions such as removing a polyp or stopping bleeding.
Which is better: CT or colonoscopy?
The painlessness and non-invasiveness of the CT colonoscopy method of the intestine compares favorably with the classical study. But when choosing a diagnostic method, not only the patient’s desire to avoid unpleasant sensations is taken into account. Before prescribing one of the intestinal examination methods, the doctor must take into account the patient's age, medical history, and the severity of the disease.
How to do an MRI of the intestines
Magnetic resonance imaging is a non-invasive procedure that allows diagnostics to be made without harm or X-ray exposure. After it is carried out, the doctor receives layer-by-layer images with a 3D image. As a result of studying these materials, treatment is prescribed.
The procedure session takes place in the following order:
- The patient lies on a table and his limbs are secured using a fixation device to prevent accidental movements. At the same time, when placing the patient in a special tomograph tunnel, the abdominal area should be in the middle.
- Contrast helps visualize the presence of bleeding in the intestinal area. If pathologies are present, he will help identify them.
- The research continues for 15 minutes, and the person does not suffer from discomfort or unpleasant sensations. The only inconvenience is the stiffness of movement, since the patient lies completely motionless.
Features of CT examination
The main advantages of CT colonography are:
- high-quality images of minimal sections;
- the risk of intestinal perforation is eliminated;
- no age restrictions;
- no pain;
- no anesthesia required;
- high probability of detecting polyps, tumors, intestinal stenosis.
But this method of intestinal diagnostics also has some disadvantages. For example, with CT it is impossible to perform a biopsy and histological examination, as with classic colonoscopy. It will also not be possible to fully assess the condition of the intestinal mucous membranes. In addition, CT is not informative in the case of an overweight patient and when examining pregnant women, due to minimal, but still, radiation exposure.
Advantages and disadvantages of MRI
MRI has a number of advantages when used correctly according to its indications. These include:
- No invasion that could cause damage to mucous membranes or skin.
- Quite fast implementation.
- There is no ionizing radiation, unlike radiographic research techniques.
- High-quality visualization of even small formations and structural changes.
Disadvantages of this research methodology:
- the impossibility of performing an MRI if there are metal implants in the body;
- lack of possibility of histological examination, which is very important for diagnosing tumor pathology.
Also, during such a study, it is not possible to carry out therapeutic procedures in parallel.
Features of traditional colonoscopy
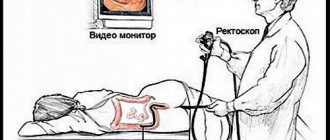
Despite the introduction of high-tech and non-invasive diagnostic methods into medicine, classical studies are still used. Classic colonoscopy involves inserting a probe into the intestine. The probe tip consists of a light fixture and a camera.
The manipulation can be performed under general anesthesia, local anesthesia or under the influence of sedatives. The advantages of the method are:
- the information received is reliable;
- the ability to detect the smallest foci of pathology;
- the doctor can immediately remove detected polyps on the mucous membrane and stop the bleeding;
- To complete the diagnosis, it is fashionable to do a biopsy.
There are a number of complications and contraindications to colonoscopy, which force the use of other diagnostic methods:
- Painful sensations of distension in the abdomen.
- Risks of bleeding and intestinal perforation.
- Allergic reactions to narcotic drugs during anesthesia.
- Residual pain in the abdominal cavity.
Virtual diagnostics excludes the development of complications, but if physiological pathologies (polyps) are detected, it will still be necessary to perform a traditional colonoscopy or surgery.
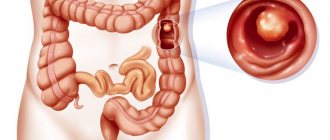
Pathologies diagnosed using CT colonography
CT scan for intestinal diagnostics shows many diseases in the early stages of development:
- Inflammatory diseases of the small and large intestines.
- Benign and malignant tumors located in the wall of the organ and beyond.
- Polyps.
- Erosion of the walls of the organ.
The virtual colonography method eliminates complications that arise during and after colonoscopy:
- Damage to the intestinal walls by the probe is excluded.
- Reduced likelihood of bleeding.
- After the end of the study, the patient does not require a recovery period - there is no abdominal pain, and the person being examined can begin their usual activities on the same day.
Pros and cons of procedures in comparison
Although there is a risk of some complications (bleeding, perforation) during this procedure, it is very small. To provide timely medical care, the patient is offered to stay in the hospital for some time.
Computer colonoscopy is quite effective, but it only detects elements larger than 5 mm. The traditional method of examining the intestines is inexpensive and a specialist can recognize the slightest deviations from the norm in the structure of the walls and tissues of the organ, without particularly risking the patient’s health.
After a classic colonoscopy with taking a biopsy or removing a palip, the risk of acute appendicitis, dehydration, infection, and stimulation of diarrhea increases.
Why is irrigoscopy performed?
X-ray of the large or small intestine with barium is one of the most effective x-ray diagnostic methods. The introduction of contrast is necessary for clear visualization of the contours of the intestine.
When performing a plain radiography of the abdominal cavity, it is impossible to see pathological formations. The study is carried out to identify free liquid and gas. X-rays easily penetrate hollow organs and therefore do not form a clear image on an x-ray.
If you treat the walls of the gastrointestinal tract with a contrast agent, they will “become illuminated.”
The procedure allows you to study the entire ascending and descending colon, rectum and cecum, and appendix. Also, if the bauginian valve (between the large and small intestine) is weak, part of the small intestine can be traced in the image. Diagnostic colonoscopy does not reach this level because the length of the probe is limited.
The irrigoscopy procedure involves administering contrast through the rectum using a Bobrov apparatus. Through a special tube inserted into the anus, contrast is pumped into the colon using a bulb. The radiologist studies its progress under a special X-ray television screen and takes several targeted photographs. The method is characterized by high radiation exposure to the patient, but there is no alternative.
https://youtu.be/AEvIhf0Txvw
Tips for choosing
Colonoscopy is considered the best option for diagnosing bowel diseases. But in some cases, MRI may be a more convenient method. If additional examination is necessary, the doctor will explain the principles of the computed tomograph and the progress of the traditional colonoscopy procedure.
The choice of diagnostic method depends on the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient, susceptibility to anesthesia and other associated factors. But in any case, the choice of research method remains with the doctor.
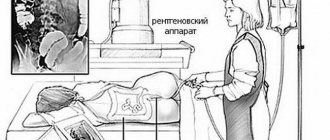
How is the procedure done?
CO2 supply through the anus
The patient undresses from the waist down and lies on the couch on his side. A thin rubber tube is inserted into the anus to a shallow depth, through which carbon dioxide is pumped under slight pressure - this is necessary to straighten the intestinal loops and improve visibility during scanning. The patient may feel slight discomfort and tension in the abdomen. After this, the couch moves into the body of the tomograph, where the scan takes place - during the procedure, the patient will be asked to turn over on his stomach. Colonography does not take much time - the study will take the patient no more than an hour.