Mastalgia
This condition is also called mastodynia, and it describes the entire spectrum of breast pain. There are two types of mastalgia. The first is periodic breast pain that comes with ovulation and continues until the start of a new menstrual cycle. It can manifest itself in one gland, in both, or radiate to the armpits.
The second type of pain is not associated with cycles and comes from the breast itself, from muscle tissue or joints. Non-cyclical pain usually occurs in a specific location due to injury, bruise or arthritis.
Treatment
Warm compresses and pain relievers will help with occasional chest pain. There are other ways to alleviate the condition:
- Reducing caffeine
- Increasing vitamin E in food
- Avoiding junk food
Depending on the source of pain, age and health status, the doctor may suggest oral contraceptives, thyroid hormones, estrogen blockers and other medications.
Causes of pain in the mammary gland
Large breast size
Women with breasts of size 4 or more experience heaviness and soreness of the mammary glands at the end of the day.
Unpleasant sensations occur when there is insufficient support for the breasts, causing them to sag and creating additional stress on the spine. The pain is dull, non-intense, significantly reduced in a horizontal position. The symptom is accompanied by a painful aching sensation in the scapular region. The appearance of pain in the mammary glands is provoked by an incorrectly selected bra, which either does not hold the breasts at all or compresses them too much. Patients complain of bursting pain of moderate intensity in the mammary glands, which is aggravated by accidental careless touch. If such signs are observed daily or the pain increases sharply, you should consult a specialist.
Sports training
Women who exercise intensively and exercise their pectoral muscles often complain of pain in the projection of the mammary glands. Muscle pain is caused by the accumulation of lactic acid in tissues and swelling of myofibrils after overexertion. Symptoms disappear on their own after rest. Prolonged sharp pain after exercise can be caused by pathological causes, so in this case you need to consult a specialist.
Menstrual cycle
Hormonal reasons contribute to the development of mastalgia before menstruation. A sharp decrease in the amount of estrogen provokes swelling and swelling of the mammary gland tissue, and dull pain of moderate intensity occurs. Patients note increased breast sensitivity and increased pain during touching and wearing a bra. In most cases, the symptom disappears 2-3 days after the start of menstrual bleeding.
Some women experience cyclic pain in the middle of the monthly cycle, which corresponds to ovulation. During this period, the mammary glands are prepared for possible fertilization, and the volume of secretory cells increases. Such changes are manifested by discomfort and a feeling of fullness, an increase in the size of the mammary glands. Increased or paroxysmal nature of cyclical pain indicates pathological causes requiring medical attention.
Pregnancy and lactation
Beginning in the first trimester of pregnancy, both mammary glands undergo structural changes necessary for milk production. This is accompanied by constant heaviness and pain, the chest seems to “fill up” and swell. The pain in the mammary glands is moderate and does not cause severe discomfort. As labor approaches, the nipple may release a few drops of yellowish fluid.
Normally, there is no pain during breastfeeding. Discomfort is associated with a violation of the interval between feedings, when a large amount of milk accumulates in the ducts and alveolar tissue, causing bloating and heaviness. Sharp local pain in the areolar area is caused by cracks in the nipple and erosions of the delicate skin, which form when feeding techniques are violated and when the child’s first teeth erupt.
Mastopathy
Fibrocystic changes in glandular tissue are the most common pathological causes of pain. With nodular mastopathy, the pain is localized in one mammary gland. The symptom is observed in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, when unilateral swelling increases and the breasts increase in size. The pain is aching, stabbing, and often radiates to the shoulder or shoulder blade.
Diffuse mastopathy is characterized by painful bursting or stabbing pains that spread throughout the chest. Before menstruation, the breasts swell, their tissue becomes dense, and the pain intensifies at the slightest touch. With the onset of bleeding, the pain gradually subsides. Regular severe pain disrupts sleep and appetite, and some patients develop a fear of cancer.
Mastitis
Infectious causes cause severe pain in the mammary gland in women, caused by a purulent process and the accumulation of pathological inflammatory mediators that irritate the nerve endings. The pain associated with purulent mastitis is sharp, tugging, and unbearable. They are aggravated in an upright position and subside slightly with an elevated position of the mammary gland. A foul-smelling yellow-green liquid is released from the nipples.
Due to severe pain, patients stop sleeping, their condition worsens due to high fever and intoxication. With non-purulent mastitis, the pain is less pronounced, constant dull pain is felt in the chest against the background of an increase in body temperature to 38.5 ° C. Discomfort intensifies when squeezing the areola area or touching the affected part of the mammary gland. Such symptoms are an indication for emergency medical care.
In advanced situations, purulent inflammation turns into a breast abscess, as evidenced by increased and more precise localization of pain in one area. The skin over this area becomes red or purple in color, and touching causes severe pain. There is usually no discharge from the nipple. Against the background of pain, high fever occurs, sometimes of the hectic type.
Nipple diseases
With nipple eczema, itching and discomfort first appear in the areolar area (the darker skin surrounding the nipple), and after a few days polymorphic rashes form, combined with sharp pain. Then the blisters turn into erosions and small ulcers, and an increase in pain is noted. As you recover, the pain gradually subsides and is replaced by intense itching, mainly at night.
Pain in the mammary gland on the affected side is characteristic of inflammation of the nipple of bacterial and viral causes. Symptoms are localized in the areola area, sometimes the pathological process spreads to the surrounding breast tissue. When pressing on the nipple, a purulent or bloody secretion is released. The disease requires examination by a specialist, since without treatment there is a risk of massive purulent inflammation or sepsis.
Injuries
When blows to the chest area, a sharp, severe pain initially occurs, which lasts from hours to several days, depending on the degree of injury to the mammary gland. In uncomplicated cases, a bruise forms on the skin, but the glandular parenchyma remains intact. With strong blows, the pain lasts a week or more, and bloody fluid is released from the nipple.
Pain in the mammary glands occurs not only with direct mechanical influences, but also when wearing a tight bra. Prolonged traumatic compression of the chest leads to microcirculation disorders, which is manifested by bursting painful sensations and heaviness. Symptoms intensify in the evening, when there is severe swelling and increased sensitivity of the skin of the gland.
Benign formations
In the initial stages of breast adenoma and cyst, pain is not always a concern. Discomfort and heaviness that are observed before menstruation are characteristic. As the formation increases in size and hormonal imbalances, a constant pain syndrome develops, the breast becomes denser and swells. Sometimes the patient independently finds a dense node in the mammary gland, upon palpation of which the pain becomes stronger.
Unpleasant sensations remain the only symptom of the disease for a long time, then the pain is accompanied by periodic discharge of a transparent or whitish secretion from the nipple. With intraductal papilloma, pain is accompanied by the flow of a thick greenish secretion that occurs when the contents stagnate in the milky tubules. With a lipoma, slight pain is felt in the area of the mass formation.
Malignant tumors
In advanced stages of breast cancer, tumor causes cause severe excruciating pain, leading to neurasthenia and insomnia. But at the beginning, nonspecific symptoms predominate in the form of discomfort and pain, heaviness in the chest in the evening. These manifestations are similar for many diseases, so it is important to maintain oncological vigilance.
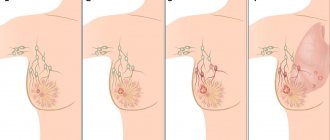
During an independent examination of the mammary gland, the patient discovers a formation of irregular shape and dense consistency, which does not move in relation to the skin, and is very painful. In this area, typical changes in the skin are formed: “lemon peel”, retraction of the skin area. Sometimes the pain spreads to the armpits, which indicates the involvement of the lymph nodes in the process.
Thoracic osteochondrosis
Degenerative changes in the connective tissue of vertebral cartilage lead to damage to nerve fibers. The pain that occurs with thoracic osteochondrosis is localized not only in the back, but also along the anterior surface of the chest in the area of the mammary gland. The pain is strong, paroxysmal, usually aggravated by sudden turns and bending of the body.
This disease is sometimes a provoking factor in the development of intercostal neuralgia, which is characterized by stabbing or burning pain in the ribs and mammary glands. The pain is localized along the anterolateral side of the chest and is aggravated by careless touching and squeezing by tight clothing. The pain often radiates to the area of the shoulder blades and collarbones.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Mastalgia is mainly associated with the use of female sex hormones. Symptoms occur at the stage of selecting oral contraceptives, when prescribing estrogen derivatives during menopause. Pain in the mammary glands is not severe, its character resembles soreness during the premenstrual period. The symptom is also provoked by other medicinal causes: taking antipsychotics, antidepressants, tranquilizers.
Rare causes
- Iatrogenic conditions
: the first days after an abortion, operations in the anterior chest wall. - Placement of breast implants
. - Intercostal myalgia
. - Endocrine diseases
: pathology of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands. - Breast tuberculosis
.
https://youtu.be/dcwubRRQDPY
Pregnancy
Excessive sensitivity, a feeling of “fullness” and heaviness during pregnancy are normal, and symptoms may appear in the first trimester.
Progesterone increases the sensitivity of the breasts, and this cannot be avoided - it is this hormone that maintains pregnancy. Additionally, progesterone "straightens up" in the second half of your menstrual cycle.
Breasts grow as your pregnancy progresses, and this may be accompanied by pain from underwear that is too tight or from a change in the load on your shoulders and back. The beginning of lactation is also associated with unusual, not always pleasant and even painful sensations.
Treatment
The main treatment method in this case is the correct underwear. Maternity bras are designed to distribute weight correctly, relieving painful weight imbalances. Also, according to a 2020 study, cold and hot compresses are quite effective. They need to be applied to the painful area for twenty minutes, alternating temperatures and repeating this procedure twice a day.
Typically, breast pain during pregnancy is not too severe and does not require medication. But if the pain is more intense than just an “unpleasant pulling”, do not put off going to the doctor.
Classification and causes of chest pain
Chest pain can be divided into several types according to different characteristics:
- The period of occurrence is cyclical and non-cyclical.
- The nature of the pain is dull, shooting, sharp, stabbing, throbbing, aching, pulling, burning.
- Strength – intense, weakly expressed.
It can be difficult for a non-specialist to describe, for example, the nature of pain. However, if a woman knows what criteria to look for, she can better explain her problem to the doctor.
Even minor discomfort that bothers you for a long time is considered dangerous. Many dangerous diseases practically do not manifest themselves in the initial stage, while timely treatment helps save the patient’s life.
The following factors increase the likelihood of developing pathologies in the structure or function of the mammary glands:
- Individual anatomical features. Some features of the structure of the breast, including its large size, only increase the likelihood of an inflammatory process after a common injury or minor surgery.
- Taking hormonal drugs.
- Acid imbalance in breast tissue, which affects the degree of their sensitivity to hormones;
- A history of endocrine or gynecological diseases, as well as liver and kidney diseases.
Breast-feeding
Breastfeeding, especially immediately after giving birth, can be quite a painful experience, and the glands themselves can feel like they are filled with stones. Both the young mother and the baby have yet to get used to new experiences.
48 hours after the birth of the baby, a rather sharp and sudden enlargement of the breasts may occur, which “fills up” with milk (which is what happens). The breasts appear larger and feel heavy, tender, and bloated.
Treatment
Although breastfeeding is a natural process, you don't have to endure the discomfort that comes with it. Try the following methods:
- Breastfeeding or pumping every two hours
- Gentle breast massage
- Warm compresses before feeding
- Expressing a small amount of milk to soften the areolas and keep your baby interested
- Cool compress after feeding (frozen vegetables wrapped in a towel will do)
- Warm shower
Let's talk separately about the cabbage leaf: this grandmother's method works great - it helps cool the chest and provides noticeable relief. There are even scientific studies that prove this!
Causes and mechanisms
Only a doctor can understand why breasts become a source of discomfort. A specialist with the necessary qualifications and experience will examine the woman and indicate the origin of the problem. In most cases, worries are in vain, because everything is determined by physiological changes. Most often, breast engorgement and tenderness is a normal phenomenon observed during various periods:
- The onset of puberty in girls.
- In the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
- During pregnancy.
- After childbirth.
This effect is primarily due to increased progesterone and growing prolactin. The latter is especially actively produced by the pituitary gland in the last trimester of pregnancy and after the birth of a child. Similar processes are observed during an abortion, but to a much lesser extent. In addition, pain may occur due to the individual characteristics of the body and the increased sensitivity of the nervous system.
In addition to conditions that can be explained from a physiological standpoint, pathological processes, both general and local, become causes of obvious discomfort in the chest. Most often we are talking about endocrine disorders, inflammatory and tumor disorders. Therefore, doctors may suspect:
- Premenstrual syndrome.
- Mastopathy.
- Mastitis.
- Breast cancer.
Hormonal disorders, which often underlie the symptoms that arise, can occur against the background of the influence of unfavorable factors, which include physical fatigue, poor nutrition, emotional stress, infections and intoxications, bad habits, and gynecological diseases. This is something that can disrupt the natural regulatory balance in the female body and cause breast problems. But each case requires individual consideration and differential diagnosis.
When faced with chest discomfort, you should immediately consult a doctor to find out the nature of the changes.
Infections
It is natural that an infection nestled in the chest will cause pain. Doctors usually talk about the two most common reasons.
Mastitis
It happens when milk “stagnates” and the milk ducts literally become blocked. Symptoms are unpleasant and serious:
- Heat
- Chills
- Warm or swollen breasts
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Vomit
- Yellow discharge from nipples
Mastitis is treated with antibiotics, and discomfort is treated with warm compresses. You can feed and take medications at the same time, but after consulting a doctor about the safety of the drug.
Thrush (aka candidiasis)
In this case, the symptoms look different:
- Nipple pain
- Nipples that are cracked, dry or shiny, itchy, and too pink
- Aching chest pain
- White spots on your baby's cheeks, tongue and gums
After feeding, you may feel a sharp piercing pain in your chest.
Thrush, of course, needs to be treated with medication, not only for yourself, but also for the baby. For specific recommendations, you should consult your doctor.
To prevent thrush from returning, try these steps:
- Replacement and washing of linen every day, and at high temperature with the addition of bleach
- Using only disposable diapers
- Washing the nipples after feeding with water and a small amount of vinegar.
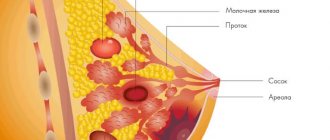
How are breasts constructed?
The structure of the female breast
Before the onset of puberty, the mammary glands of boys and girls do not differ significantly. After 9 years, young representatives of the fair sex have breasts that rapidly develop and grow. This process stops around age 16. The female hormone responsible for it is estrogen, produced by the ovaries. Any disorders that are associated with its production will affect the chest.
A fully developed breast consists of certain structural elements. These include:
- Milk ducts;
- Adipose tissue;
- Nipple with areola;
- Connecting partitions.
In addition, there are cone-shaped lobes inside it. As a rule, their number reaches 18–20 pieces. They are located so that their tops are directed towards the nipple, and the base itself is directed towards the sternum. Each lobe contains ducts through which milk flows and accumulates. The largest area of the chest is occupied by glandular tissue. The milk ducts are located not only inside the lobes, but also extend beyond their boundaries and finally merge with each other and open at the nipple.
Partitions are needed to separate the largest lobes, and also thanks to them, the frame of the mammary glands is formed. The breasts rest on what is called a mat of fatty tissue, which gives them their shape and size.
Breast fibroadenoma
Fibroadenoma is a benign formation in the mammary gland. They can cause a feeling of heaviness. Cysts form when gland tissue thickens and can cause pain or discharge from the nipples.
Treatment
The following methods can be used to relieve symptoms for fibroadenoma:
- Warm or cold compresses (depend on how you feel)
- Changing your bra to a more comfortable one
- Avoiding salt, caffeine and fatty foods
- Taking oral contraceptives
- Taking painkillers
If a cyst is causing you concern or discomfort, your doctor may drain it.
Why does a woman's chest hurt?
Pain in a woman in the area of the mammary glands can be associated with normal life situations. For example, breast tenderness often occurs during menstruation and while breastfeeding. If you experience prolonged pain that bothers you periodically, it is necessary to undergo a breast examination to determine the causes of the discomfort.
One breast hurts
Unpleasant sensations may be the result of blunt trauma to breast tissue (for example, from a fall). At the same time, the chest that has been bruised aches. Damage to the mammary gland is accompanied by pain on palpation, redness, and swollen parts. Other causes include diseases of the internal organs. When they worsen, sharp, stabbing, aching pain may be observed on one side or the other of the sternum.
If the right chest hurts, the following diseases are possible:
- hepatitis;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- diseases of the esophagus;
- diaphragm damage;
- spinal injuries with disc displacement to the right.
When the mammary gland on the left side hurts, it may be due to:
- disorders of the spleen;
- gastritis, pancreatic diseases;
- pancreatitis;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- heart diseases (acute pericarditis, angina pectoris).
It's a dull pain
If the pain is nagging and prolonged, this may indicate mastodynia. This condition occurs as a result of hormonal imbalance. The woman feels cyclical pain, which tends to intensify. The cause may be gynecological diseases, stress, menopause.
A woman may experience discomfort when touching her breasts. Often pain in both mammary glands occurs when feeding a child. This happens with lactostasis (milk stagnation). It occurs due to an excess of milk fluid or when the baby does not suck well. Pressing on the chest can create pain during mastopathy.
Stitching pain
Painful attacks of an acute nature can occur with intercostal neuralgia. A person feels stabbing, piercing pains that can radiate to the chest, shoulder blade, and lower back. The same sensations appear during attacks of angina pectoris, pericarditis, and other acute heart diseases. Sometimes tingling occurs due to mental disorders. Acute pain can occur with pleurisy and pneumonia. They are accompanied by shortness of breath and cough.
Tugging sensations in the chest area may appear due to muscle spasms. This effect can occur when playing sports or exercising. Sometimes breast pain is caused by hormone therapy or a woman taking oral contraceptives. Breast tenderness may indicate pregnancy. This means that the body has begun to rebuild at the hormonal level. The intensity of pain can vary: from mild to strong.
When tilted
If your chest begins to hurt when performing some movements, the cause may be a previous injury. By pressing on the sternum you can locate the painful area. If damaged, it will be painful to touch the injured area. Pain when lowering or turning the body can be observed due to diseases of the esophagus (hernia). The cause of pain that appears after bending the body may be intercostal neuralgia.
Some diseases cause tumors or an increase in breast size. These include:
- fibroadenoma;
- mastopathy;
- mammary cancer;
- cyst formation;
- lactation mastitis.
A cyst can form in healthy women. This is a cavity inside the mammary gland that fills with fluid. In most cases, these formations resolve on their own. Fibroadenoma is a benign tumor. The formation cells grow and put pressure on the milk ducts, which causes pain.
Pain under the nipple
During the feeding procedure, a woman may develop microcracks, which causes inflammation of the nipple. This causes damage to the nerve endings, which causes pain. The cause of these unpleasant sensations may be long-term use of hormonal drugs. Also, pain under the nipple can be caused by the following diseases:
- acute mastitis;
- herpes virus;
- nipple cancer;
- mammalgia;
- some types of lactostasis.
In the middle of the cycle
Slight painful sensations in the breasts in women 8-10 days before the onset of menstruation are considered a normal physiological phenomenon that does not require treatment. Sometimes this can be a sign of pregnancy. Factors such as stress and fatigue can contribute to discomfort. The woman feels fatigue, lethargy, and headaches appear.
If your chest hurts, then you should imagine what is happening to it at this moment. In most cases, the appearance of bruises, and as a result, lumps, is preceded by a malignant proliferation of connective tissue, which covers 70% of the mammary glands in women. In the advanced stage, you will most likely feel discomfort when your nipples come into contact with your underwear.
If your mammary glands hurt and you experience sensations similar to how a bruise hurts, then most likely the reasons are the following:
- benign breast tumor;
- fibrous mastopathy;
- formation and development of cysts (sometimes this disease is called fibrocystic mastopathy).
If, when pressing on the chest, unpleasant sensations occur on the side and throughout the entire area of the chest, then the reasons may be as follows:
- diffuse mastopathy;
- fibrous mastopathy;
- in rare cases of thyroid disease;
- in rare cases, liver disease (possibly chronic);
- hormonal surge, imbalance, which is often caused by constant stress and nervous tension;
- cancerous disease.
As statistics show, of all the above possible diseases that provoke pain when pressing in the chest, the most common are: the development of a benign tumor and various forms of mastopathy.
Therefore, it is their symptoms that we will consider in more detail, so that every woman can notice the lump in time and refer it to a specialist.