Causes
Many doctors, when asked what breast fibroadenomatosis is, answer that this disease is a benign tumor. Predisposing factors for the development of fibroadenomatosis are hormonal disorders. Such reasons include:
- Thyroid dysfunction: hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
- Long-term constant stress.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Burdened hereditary history.
- Ovarian dysfunction.
- Diabetes
- Obesity.
- Irregular sexual relations.
- Late birth (over 40 years).
- Start of menstruation too early.
- Late menopause.
- Premature puberty.
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives.
Various liver diseases also contribute to the occurrence of fibroadenomatosis. A decrease in its intoxication and excretory functions leads to the accumulation of breakdown products in the body and hormonal imbalance.
Causes of the disease
The main causes of diffuse adenomatosis of the mammary glands are a sharp increase in estrogen levels, progesterone deficiency and disruption of regulatory processes in the body (neurohumoral regulation). Factors that increase the likelihood of pathology include:
- unfavorable heredity (history of breast diseases in maternal relatives);
- a state of frustration caused by stress, conflicts with others, dissatisfaction with family or intimate life, social status;
- refusal to have children, abortion, late pregnancy;
- diseases of the uterine appendages;
- refusal to breastfeed the child or a sharp reduction in the lactation period;
- injury to the mammary gland or its inflammatory lesion (mastitis);
early onset of menstruation or late cessation;- endocrine disruptions (hypothyroidism, diabetes, underweight, obesity);
- high blood pressure;
- inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder and ducts;
- adrenal diseases;
- increased background radiation;
- habit of sunbathing topless;
- living in regions with unfavorable ecology;
- unbalanced diet high in fat.
It has also been established that the risk of developing diffuse cystofibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands increases in women who smoke and abuse alcohol.
https://youtu.be/4NctA8FBfSU
Clinical manifestations
The main symptom of this disease is pain in the mammary glands. Discomfort increases during the premenstrual period. After the end of menstruation, the discomfort decreases.
The pain is pressing or bursting in nature. The chest becomes more sensitive. Mastalgia can occur when wearing a bra or touching the fabric of clothing.
The woman also exhibits the following symptoms:
- Discharge when pressing on the nipple.
- Dense and swollen mammary gland.
- Enlarged axillary lymph nodes.
- Irritability, nervousness.
- Emotional lability, sleep disturbances.
Chest pain is a symptom of fibroadenomatosis.
Discharge from the nipples with this disease is white or beige. The presence of blood and the green or brown color of this discharge should alert the patient. Such symptoms are not typical for fibroadenomatosis and may be a manifestation of the oncological process.
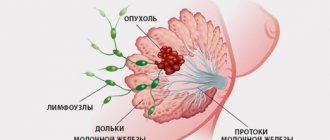
Forms of pathology
There are nodular and diffuse forms of mastopathy. Diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands is divided into several types:
- Adenosis. With this pathology, the glandular component predominates in the mammary gland. The prevalence of this type of disease is 60–70%. Normally, glandular cells (alveolocytes) predominate in breast tissue. With adenosis, there is an increased production of estrogen and a deficiency of progesterone. Estrogens cause excessive proliferation of glandular epithelium by activating fibroblasts. As a result, swelling of intralobular tissue and proliferation of alveolocytes in the milk ducts is observed.
- Fibrosis. The fibrous component predominates. The neoplasm develops from connective tissue. In this case, the mammary gland upon palpation has a fine-grained character. Severe fibrosis is characterized by a significant proliferation of pathological tissue and can lead to organ deformation.
- Multiple cysts. The cystic component predominates. This disease is also called polycystic disease. In this case, bilateral cavities filled with liquid appear in the mammary gland. Cysts are located in small groups and measure up to 5 mm. Localized in the upper - outer quadrant of one or both glands. It is believed that nulliparous and non-breastfeeding women suffer from cystic fibroadenomatosis more often than others.
- Mixed form. It is accompanied by excessive growth of glandular and connective tissue and the formation of cystic cavities. The milk canals are also involved in the pathological process.
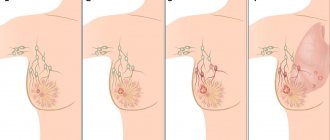
Nodular or localized fibroadenomatosis is characterized by the rapid formation of compactions in the gland. This disrupts blood circulation inside the tumor. The size of the knot can reach the size of a walnut. Diffuse fibroadenomatosis, if left untreated, can lead to nodular mastopathy.
Leading clinics in Israel
Mixed type breast fibroadenomatosis – combines the symptoms of several types of fibroadenomas. With this type of disease, the seal grows inside and outside the duct.
In medicine, there is such a thing as SUSP fibroadenoma. This means suspicion of fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland. Fibroadenomatosis is also divided into types such as clearly expressed, slightly expressed and moderately expressed. But there are no exact characteristics for these types of fibroadenomatosis.
Proliferation is the growth of tissues through cell division. With fibroadenoma in a proliferating form, the septa merge, separating the individual cysts. In this case, the entire cavity is filled with large growths that arise. A large number of small growths can form in the gaps between cysts and ducts. These growths, lined in layers, fill the cyst from the inside or completely block the dilated duct.
Fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland can also occur in a diffuse form, i.e. Many cysts are scattered in the gland. Local fibrosis is characterized by a group arrangement of affected areas, making it easier to detect lumps in the breast. In the nodular form of fibroadenomatosis, several cysts merge to form a painful nodule.
This process can be two-way. Nodes resembling cakes can simultaneously develop in the left mammary gland (LMG) and right (RMG). This disease is most often observed in women aged 35 to 40 years.
Adenofibrosis comes in nodular and leaf (diffuse) forms. Diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands is more common and is divided into:
- adenosis – a tumor with a predominance of the glandular component;
- fibroadenosis (fibrous fibroadenomatosis) – a neoplasm with most of the fibrous tissue;
- fibrocystic – cystic fibroadenoma of the breast.
There is also a mixed form of pathology, in which all the above-mentioned tissues are present in equal parts, or two of them, for example, when a fibrocystic neoplasm occurs. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland can be insignificant, moderate or severe. Depending on the location, number of tumors and nature of the disease, there may be:
- Focal fibroadenomatosis - a large number of nodules form throughout the breast. Neoplasms do not have clear boundaries and are accompanied by constant painful sensations.
- Localized fibroadenomatosis – one or several tumors appear in the breast, but in one quadrant or segment. The size of the formation varies from one to six centimeters. This is a compaction that has clear boundaries and a heterogeneous bumpy or granular surface.
Women encounter localized fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland much more often, and tumors can affect both breasts at the same time. The superior outer quadrant is affected more often because this VNK contains more fibrous and adipose tissue.
Diagnostics
If fibroadenomatosis is suspected, the following types of diagnostic studies are performed:
- Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. Allows you to identify the presence of cystic, fibrous or glandular changes in organ tissue. Using this method, the size and nature of cysts and the structure of their wall are determined. Ultrasound is usually performed in the first phase of the menstrual cycle.
- Mammography. There are X-ray, magnetic resonance, optical and microwave methods for this research. The picture is taken in two projections: frontal and lateral. A mammogram can detect cysts, fibrous nodes, and macrocalcifications.
- Aspiration biopsy. Using a thin needle, fluid is taken from the cavity (cyst), which is then sent for histological analysis. It confirms the benignity or malignancy of the pathological process.
- Color Doppler sonography. Allows you to identify any minute structural changes in the soft tissues of the gland and determine the blood supply to existing neoplasms.
Ultrasound is a method for diagnosing fibroadenomatosis.
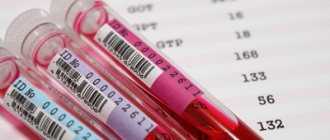
Additional diagnostic methods include taking a general blood test, determining the level of sex hormones and thyroid hormones. Every woman must have a consultation with a gynecologist to identify gynecological pathologies.
Treatment options
The treatment tactics for fibroadenomatosis depend on the form of the disease, the severity of clinical manifestations, the age of the patient and concomitant pathologies. There are surgical and conservative treatment options.
The patient is also prescribed a diet excluding chocolate, alcoholic beverages, strong tea and coffee. It is allowed to eat vegetables, fruits, meat, and dairy products.
It is not advisable to use traditional methods for treatment. This can lead to loss of time and contribute to tumor malignancy.
Drug treatment
Diffuse fibroadenomatosis is treated with medication. In order to cure this disease, hormone replacement therapy is necessary. It consists of using the following medications:
- Thyroid hormones. They are used in the presence of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- Gestagens. These include progesterone drugs. They ensure the normal functioning of the genital organs and mammary glands and eliminate hyperestrogenemia. Tablets, vaginal suppositories or gels are used.
- Combined oral contraceptives. These medications reduce the proliferation of glandular epithelium, prevent the formation of cysts and the development of fibroadenoma.
- Gonadotropic hormone agonists. They are used to suppress the synthesis of estrogen by the ovaries and reduce the production of estradiol. This normalizes a woman’s hormonal levels and reduces the likelihood of fibroadenoma.
Painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, hepatoprotectors, and antioxidants are used as additional drugs. Vitamins A, B, E, adaptogens, and mild sedatives are also prescribed.
Surgery
The nodular form of fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands cannot be treated with conservative methods and requires surgical intervention. Indications for surgery are rapid growth of cystic formations, large sizes, and a high risk of malignancy.
For localized fibroadenomatosis, there are two types of operations:
- Sectoral resection. In this case, the node is excised along with healthy tissue. If the cyst is large, its contents are pumped out, and sclerosing substances are injected into the empty cavity.
- Enucleation of the node. It represents the desquamation of only a separate fibroadenoma nodule. In this case, an incision is made along the border of the areola and a small suture is applied.
Surgery is a method of treating fibroadenomatosis.
In the postoperative period, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed: ketorol, ketonal, Flamax. Sometimes broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are prescribed for prevention.
Treatment of mastopathy
To prescribe treatment for localized fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland, the doctor determines the type and stage of the disease. The principle of treatment of the disease is directly affected by the age of the patient.
Breast disease is proposed to be treated in two ways:
- conservative treatment - carried out with the aim of restoring tissue, normalizing hormonal levels, getting rid of symptoms
- surgical treatment - the lesion is removed
Conservative treatment
In addition to taking medications aimed directly at treating mastopathy and balancing hormonal levels, maintenance therapy is necessary. The doctor also prescribes vitamins. In particular, B vitamins, the action of which is aimed at improving metabolism. Vitamins A, C, P help strengthen the vascular wall and reduce swelling, vitamin E affects hormonal and fat metabolism.
To relieve swelling and reduce pain in the mammary glands, diuretic and anti-inflammatory drugs have a therapeutic effect. The nervous system can be brought back to normal by taking sedatives.
Conservative treatment of fibroadenomatosis involves following a diet. It is important to limit the consumption of hot drinks such as tea, coffee and cocoa. It is necessary to add variety to the diet, including fresh vegetables and fruits.
In what cases is surgery necessary?
The decision on radical measures is taken in the following cases:
- large size of the pathological formation
- rapid growth of nodes
- suspicion of a malignant tumor
- severe course of the disease
Preferably, a separate part of the mammary gland is removed. If there is localization of multiple local fibroadenomas located throughout the breast, the gland is completely removed. Upon completion of the operation, the removed part is sent for analysis. Radical excision guarantees a complete cure.
Traditional medicine recipes for fibroadenoma
The traditional way of treating localized fibroadenomatosis includes the use of means aimed at establishing hormonal levels and metabolic processes in the body. At the same time, natural ingredients do not cause side effects. In this case, it is proposed to treat with herbs such as valerian, birch buds, nettle, burdock root, and corn silk. For external use, cabbage leaves are used, which must be applied to the sore spot.
Timely treatment gives a positive prognosis for local fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland.
https://youtu.be/s9GCEesIOxw
Fibroadenoma and IVF
During the IVF procedure, a woman is prescribed stimulating therapy, which increases the release of estrogen. This method promotes the rapid development of eggs in the ovaries. However, this also leads to an increase in the existing benign tumor in the mammary gland.
Today, the treatment tactics for mastopathy before IVF are determined strictly individually. In case of diffuse fibroadenomatomal mammary gland, conservative treatment is sufficient.
In case of nodular fibroadennoma, removal of cystic formations is recommended before artificial insemination.
Diagnosis of the disease
Note! All symptoms of the disease are conditional and may well indicate other health problems. Therefore, to make a correct diagnosis, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
There are several methods to diagnose this disease. The very first thing is to consult a specialist. By palpation, he can identify the quantity and quality of tumors. Having found out the history of the disease, the doctor can send for an ultrasound (usually performed on women under 35 years old) to determine the degree of infection and to determine the structure of the tumors. Mammography may also be prescribed (taking into account the use of radioactive radiation, this method is used to diagnose the disease in women over 35 years of age, since sensitivity to x-rays decreases with age), and an analysis of hormone levels in the blood. And to diagnose pathologies, a biopsy is prescribed; for this, a piece of the tumor is removed from the mammary gland. To identify all kinds of complications, MRI and various blood tests may be prescribed, including tumor markers to determine the presence or absence of cancer cells. As a rule, to make laboratory tests more informative and accurate, they are carried out in the first days of the menstrual cycle.
Important! It is possible to detect diseases of the mammary glands in the early stages of the disease using the self-examination method.
Prevention of breast fibroadenomatosis
Preventive measures include:
- Regular examination by a mammologist.
- Monthly breast self-examination.
- Wearing a comfortable, non-squeezing bra.
- Quitting drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Use of oral contraceptives.
- Breastfeeding after childbirth for at least 3 months.
- Maintaining a full sex life.
Regular examination by a mammologist is included in the measures to prevent fibroadenomatosis.
Diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland is a common disease of women of childbearing age. If you notice a lump in the chest, or pressing or bursting pain, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment will help avoid unpleasant complications and tumor malignancy.
https://youtu.be/_TFg7vFsJco