What's happened
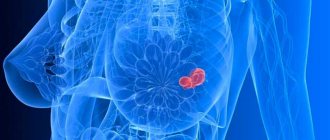
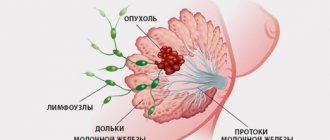
Intraductal papillomas are benign formations in the milk ducts of the gland. Outwardly, they look like papillae filled with liquid. They develop on the inner surface of the ducts and are usually formed in places where they expand.
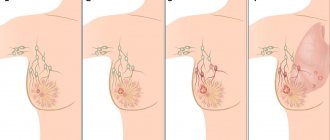
Such growths can appear in one breast or in both at once. Epithelial cell proliferation can begin at any age. The size of the cyst-like growth can range from several millimeters to several centimeters.
There may be several of them in one chest area. The disease requires rapid diagnosis, since there is a high probability of a benign formation becoming malignant.
Description of the disease
Intraductal papilloma has other names - Mintz disease, cystadenopapilloma, cystadenoma, intraductal papillary tumor. This is a benign neoplasm that can be treated if diagnosed in a timely manner. Papillomas cannot resolve on their own: they must be removed. In advanced cases, a benign neoplasm can become malignant, so removal of polyps is vital for every woman.
What do papillomas look like? Outwardly, they resemble warts or papillae, inside of which there is liquid. Polyps are located inside the milk ducts, their size ranges from several millimeters to several centimeters. The tumor can affect both breasts at once or be localized in only one. Growths of epithelial cells form at any age.
Depending on the location of cystadenoma, there are:
- central;
- peripheral;
- areolar;
- atypical.
Central polyps are located in the area of the nipple, peripheral polyps affect the tissue inside the mammary gland, and areolar polyps are localized in the areola area. Atypical papillomas are localized outside the lobules and ducts.
Central papillary cystadenomas rarely take a malignant form and develop into cancer.
The most dangerous are peripheral cystadenomas, since they affect a large area of the mammary gland and most often mutate into a malignant tumor.
According to the form of formation, growths are:
- single;
- multiple.
Single papillomas are localized near the nipples, and multiple papillomas are located inside the mammary gland and form papillomatosis. A single (solitary) papilloma forms a large growth, the size of which reaches two centimeters. Multiple papillomas are not characterized by a specific localization; they are located in the lateral zone of the mammary gland.
Atypical cells with a different structure and shape can form in the growths. This phenomenon can trigger the development of papillary breast cancer.
Single papillomas are diagnosed in women after forty years, and multiple papillomas are diagnosed in younger patients. Papillomatosis (multiple growths) affects both breasts at once. Many doctors consider papillomatosis to be an increased risk factor for cancer.
Papillary cystadenomas do not hurt; this makes timely diagnosis of the pathology difficult. Women pay attention to their breasts only in connection with the appearance of discharge of an unknown nature from the nipple.
https://youtu.be/kAg5auVvobE
Classification
Cystadenomas or cystadenopapilloma are divided into groups, depending on the place of their formation, as follows:
- central - in the area of the nipple;
- peripheral - in the deep tissues of the lobules;
- areolar - in the area of the areola of the gland;
- atypical - outside the ducts and lobules of the gland.
There are certain statistics that confirm that the central type is less likely to develop into malignant formations. Peripheral - more often, papillomas with this type are numerous and affect a large area of tissue.
The atypical type of disease is characterized by growths of unusual shape and structure.
Papillomas are also divided into:
- single or solitary - most often located in the alveolar zone (near the nipple);
- multiple or papillomatosis are the most dangerous growths in the peripheral zone.
What is the disease
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland (cystadenopapilloma, papillary cystadenoma) is a benign tumor that appears as a result of pathological proliferation of epithelial cells. Such growth is benign. The tumor can occur at absolutely any age.
Intraductal papilloma is a benign tumor
In shape and structure, the intraductal formation resembles a cyst. At the same time, she often gets injured.
Malignant degeneration occurs more often with multiple tumors.
Causes
The main reason for the appearance and development of intraductal papillomas of the mammary gland is hormonal disorders in the body. The disease affects both adolescent girls and women during menopause.
On this topic
- Breast
Can fibroadenoma hurt?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 5, 2020
In both cases, a hormonal imbalance occurs in the female body, which can trigger the formation of papillomas. Hormonal imbalances can be caused by:
- operations;
- infection;
- metabolic disease;
- other chronic diseases;
- disorders of the thyroid gland and disruptions of the endocrine system;
- excessive or chaotic use of medications;
- bad habits;
- overwork and stress.
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland can occur as a consequence of other diseases of the reproductive system: mycoplasmosis, gardnerellosis (vaginosis), candidiasis (thrush), ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and others.
The causative agents of the disease can be: gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, myco- and ureaplasmas, herpes viruses and human papillomaviruses.
An important factor in the development of the disease is heredity. Thus, changes in the genes BRCA1/2, PTEN, NBS1, CHEK2 may indicate the possibility of breast cancer, the harbinger of which may well be mammary papilloma.
Diagnosis in the early stages is carried out by a mammologist, who can involve other specialists - an endocrinologist, geneticist, gynecologist, etc. - to ensure accurate predictions.
Doctors recommend that women undergo preventive breast examinations annually to prevent the development of cancer. To do this, you don’t have to wait for symptoms, you just need to contact a mammologist.
Causes of cystadenomas
The dominant factor provoking the development of internal formations in the breast is hormonal imbalances in the body. The pathological condition does not depend on age criteria and can occur in young girls during puberty and in mature women during menopause. Hormonal disorders can be hereditary. In most cases, the pathology is observed in sexually mature nulliparous women. The risk of internal formations increases in women, regardless of category, after the age of 40.
The reasons contributing to the occurrence of hormonal imbalances are:
- Diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes, pathologies of the endocrine glands, obesity)
- Taking oral contraceptives, hormone therapy. Incorrect selection of contraceptives can cause disruption of the hormonal system;
- Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs (ovaries and uterine appendages);
- Artificial termination of pregnancy;
- Dietary disorders that cause excess or excessively low weight;
- Adverse habits: excessive smoking, drinking alcohol;
- Psycho-emotional disorders: stress, nervous breakdowns, severe depression play a beneficial role for hormonal imbalance.
Symptoms
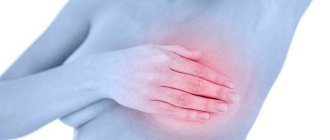
With the development of papillomas in the mammary gland, a woman may not experience any discomfort at all for a long time. Symptoms begin to appear when cystadenopapilloma reaches a decent size and begins to be felt in the breast tissue.
The first dangerous sign is discharge from the nipple, which can be of different colors and consistency. Often the discharge is colorless or has a milky tint, but at different stages of the disease and its types, the color of the secreted secretion can be either bloody or yellow.
These are dangerous signals that the inflammatory process is progressing in the chest, which leads to purulent detachments and tissue necrosis. This is dangerous, as benign cells can develop into malignant tissues and formations.
On this topic
- Breast
Do lymph nodes enlarge with mastopathy?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- November 29, 2020
During primary inflammation, pressing on the nodes and seals does not cause pain. If this causes pain, then the stage of the disease is far from primary, and consultation with a doctor is urgently necessary.
As the disease develops, it acquires other symptoms:
- dizziness;
- increased temperature;
- chills;
- weakness, etc.
If the occurrence of polyps in the ducts is associated with gynecological problems, then additional symptoms arise:
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- spotting ;
- severe pain during menstruation;
- impossibility of conceiving a child and others.
If there are problems with the endocrine system, metabolism is disrupted, a person becomes fat, gains weight, sweating increases, shortness of breath, rapid pulse and palpitations appear.
Symptoms of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland
How to detect intraductal breast papilloma?
Its symptoms are:
- Discharge from the nipple
(it can vary in volume and color; discharge from the nipple that is bloody in color should be especially alarming). - Consolidation in the mammary gland
- only central solitary tumors can be palpated, located close to the skin of the mammary gland and having a size of 7-8 mm and above. They are palpated in the form of an elastic-elastic round formation, with a clear, even, smooth contour, not connected to the skin. - In rare cases inflammation of cystadenopapilloma
- the process is an infiltrate without clear, even contours, with swelling and redness on the skin.
If you have these symptoms, immediately contact a qualified
oncologist-mammologist at our clinic
, who in the vast majority of cases can make this diagnosis after the first examination of the patient, using instrumental diagnostic methods.
A diagnosis of “intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland”
can be suspected even on the basis of palpation of the mammary gland, but for differential diagnosis with other benign or malignant neoplasms of the breast, we use the following methods:
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- Mammography;
- MRI of the mammary glands;
- Ductography or galactography is an X-ray examination of the mammary gland after introducing an X-ray contrast liquid into the gland duct. With ductography, the intraductal papilloma is clearly identified, and its size and location can be clarified in detail, which is important when planning the operation;
- Cytological examination of nipple discharge.
Diagnostics
After an external examination and palpation of the mammary glands, the doctor will prescribe laboratory tests - blood tests:
- general analysis;
- hormone analysis.
These studies will help determine the etiology - the main causes of the disease. So, if the level of glucose in the blood is high and insulin is low, we can talk about the endocrine nature of the appearance of polyps.
The doctor also immediately takes a swab of discharge from the nipple. If an atypical form is detected, a referral is given to study the tumor marker CA 15-3 (breast cancer). If they are detected, the patient is then treated by a mammologist-oncologist.
Clinical instrumental research methods are also used in diagnosis:
- Ultrasound - using ultrasound.
- MRI - magnetic resonance imaging.
- CT - computed tomography.
- Ductography is an X-ray using contrast agents.
- Mammography.
The doctor determines diagnostic methods to make an accurate diagnosis. Sometimes one ultrasound is enough to see all new formations and begin treatment. For more complex stages, several differential diagnostic methods are used.
Reasons for the development of intraductal papilloma
Pathophysiological basis of carcinogenesis Human genes are very important in the pathogenesis of tumors.
Several types of hereditary gene mutations have been described, which lead to the development of intraductal papilloma, which subsequently quickly becomes malignant.
Now there are methods for detecting these changes even in healthy patients, which makes it possible to predict the risk of developing pathology in them in the future.
Such mutations can also occur sporadically under the influence of environmental factors:
- Exposure to chemicals (heterocyclic aromatic carbons, amines);
- Smoking;
- Ionizing radiation;
- The influence of viruses.
The human body has developed mechanisms for searching and correcting these violations. This occurs both at the genetic level (DNA repair) and at the cellular level.
In the latter case, the main role is played by the immune system, which is able to recognize “mutated” cells as foreign and quickly destroy them. Therefore, the degree of its functional usefulness plays an important role.
In the presence of immunodeficiencies caused by both congenital defects and acquired pathologies, the risk of developing tumors, including intraductal papilloma, increases.
Endogenous causes of the development of intraductal papilloma Since breast tissue is regulated by a number of hormones, sudden changes in their concentration in the blood can lead to the changes described above in the genetic material of cells.
Often in women who have been diagnosed with intraductal papilloma, the following pathologies or conditions are then found:
- oophoritis;
- adnexitis;
- obesity;
- disorders of ovarian function of various etiologies;
- long-term uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives;
- abortions.
- Typically, papillomas develop against the background of fibrocystic mastopathy in patients. It is manifested by expansion and deformation of the ducts.
Is it necessary to delete
It is imperative to remove papillomas in the mammary gland. The papillomas themselves will not be able to resolve, but they may very well turn into a cancerous tumor.
Today, surgical interventions are performed under general anesthesia and the affected tissue is removed using a scalpel quickly and painlessly for the patient.
In some clinics, operations to remove formations are carried out by punctures and insertion of an endoscope with a video camera. The doctor himself will determine the method of surgical intervention:
- sectoral resection - excision of a specific area;
- electrocoagulation - using current, performed only on the areola;
- laser - only on the nipple.
On this topic
- Breast
What breast fibroadenoma looks like on ultrasound
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- November 29, 2020
After the operation, the patient’s treatment will begin, which may include:
- medicines;
- diet therapy;
- herbal medicine;
- physiotherapy, etc.
Recovery after surgery and further prevention
Regular self-examination is the key to health
After surgery to remove intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland, the patient is prescribed drug treatment, which is aimed at:
- restoration of the body;
- preventing the development of the inflammatory process;
- normalization of hormonal levels and elimination of imbalance.
Surgery and removal of the tumor increases the chances of avoiding relapse, but does not provide a 100% guarantee that in a few years the patient will not encounter problems again. Therefore, prevention is needed, which is aimed at identifying the causes of pathology and eliminating them.
Preventive measures should include:
- regular self-examination;
- annual visit to the mammologist, even if there are no complaints;
- control of hormonal levels (once a year, if the body is prone to such changes, you need to take a blood test for hormones);
- to give up smoking;
- choice of alternative methods of contraception (refusal of hormonal drugs);
- annual examinations by a gynecologist.
It is very important to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously, walk in the fresh air and get proper rest, avoid stressful situations and try to be as nervous as possible. A healthy body and a strong immune system will prevent the recurrence of the pathology.
Possible complications
A piece of tissue excised during surgery is necessarily sent for histology. If malignant cells are detected, the patient is referred to an oncologist for further treatment - radiation and chemotherapy.
To avoid postoperative complications, daily dressings are done in the hospital until the stitches are removed.
In order to prevent complications, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs that will help the patient recover faster after surgery. The following may also be prescribed:
- vitamins - to maintain immunity;
- painkillers - to relieve pain during wound healing;
- homeopathic medicines to prevent relapses;
- hormonal medications - to normalize hormonal levels.
On this topic
- Breast
The role of breast puncture in fibroadenoma
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 15, 2020
All these methods of rehabilitation and postoperative recovery prevent the risks of complications:
- infection in the wound;
- the appearance of hematomas;
- bleeding.
In a hospital setting, these types of complications are extremely rare.
Reasons for the growth of papillomas in the mammary ducts
Why can such a nasty thing grow in the duct, you ask? The cause of the development of papillary formation is considered to be an imbalance in the hormonal sphere:
- ovarian pathology;
- adnexitis;
- oophoritis;
- numerous abortions;
- excess body weight.
Stressors, ecology, occupational hazards, lack of pregnancy and childbirth, and other factors affecting hormonal homeostasis are secondary causes of the disease. In patients with Mintz disease, a hereditary line can be traced for this disease and for the development of malignant tumors.
Usually papillary formations grow against the background of mastopathy. With fibrocystic disease, the ducts of the gland locally expand, where papillomas grow. Very convenient for a papilloma, right?