Description of the disease
Infiltrating lobular cancer or lobular carcinoma of the breast is a type of disease, more precisely, its late stage. It is characterized by damage to the lobules, as well as the spread of the process of malignancy of cells and its localization around the ducts. Neoplasms often form special structures in the breast tissue, whose structure and shape resemble a kind of target. This form of cancer is considered advanced and is most often diagnosed in women over 45-50 years of age who are approaching or at the stage of menopause or menopause.
A more rarely found type is invasive lobular breast cancer. This disease is prone to active progression and differs from other forms by the involvement of surrounding tissues in pathological processes, which provokes the formation of some kind of compaction. And since it is not obvious and does not have strictly defined boundaries and rounded shapes, it does not look like a bump found in other varieties.
The infiltrative form of lobular cancer includes several varieties, depending on the structure of the neoplasm and its location. Highlight:
- alveolar tumors with rounded lobules
- lobular
- pleomorphic with different types of malignant cells
- tubular-lobular
- solid with uniform and small cells
- mixed
Treatment
A treatment regimen is selected individually for each patient. Methods may differ depending on the degree of development of the disease, the site of the lesion, the form of pathology, the age of the woman and a number of other conditions.
Therapy is selected comprehensively and can combine the following methods:
- Surgical intervention.
- Hormonal therapy.
- Radiation therapy.
- Chemotherapy.
Each of the methods has its own characteristics; they are often combined to achieve the remission stage.
Surgical intervention
Operations can be performed according to different principles, it all depends on the stage of the disease, the form of cancer, the number of tumors and their location. The possibility of surgical manipulation is also generally considered, since in some cases the tumors may be inoperable.
Surgical intervention can be performed according to the following principles:
- Excisional biopsy. It involves removing the tumor along with some of the tissue in contact with the cancerous tumor. Conducted under local anesthesia, it involves further therapy to prevent new lesions. After an excisional biopsy, the patient should be examined at least once a year to ensure timely detection of possible relapses.
- Mastectomy. It is a necessary measure when the tumor is large, there are many nodes, the process is rapidly spreading to other tissues, the disease has already reached stage 3 and there are multiple metastases. Either one mammary gland or both at once can be removed.
Any surgical intervention does not guarantee an absolute cure, so additional therapy is prescribed, regular visits to the doctor followed by examination.
Hormone therapy
If the form of lobular breast cancer has a hormonal dependence, a rapid increase in metastases is noted, and other indications are present, then a course of hormonal therapy is prescribed. It usually complements other treatments, mainly after surgery.
Radiation therapy
Prescribed mainly after surgery to reduce the risk of re-development of cancerous lesions . Pathogenic cells are destroyed under the influence of dosed radiation. The procedures are carried out systematically.
Chemotherapy
In some cases, chemotherapy replaces surgery, and sometimes complements treatment. It involves the effect of special chemically active solutions on cancer cells. Allows you to reduce tumors to conditions in which surgery is allowed. Chemotherapy is practiced not only as a preparation before surgery, but also in order to maintain positive dynamics after it.
Selecting an effective treatment against cancer is quite difficult and requires special experience from the oncologist. In each case, therapeutic or supportive therapy is prescribed individually.
Possible causes of the disease
Until now, doctors do not know exactly and reliably for what reasons lobular breast carcinoma can develop. But there are several negative factors that can affect the structure of the mammary gland and trigger the mechanism of cell mutation. These include:
- late pregnancies or complete absence of childbirth
- abortions or miscarriages, especially multiple ones
- uncontrolled or excessively prolonged use of oral contraceptives and other hormonal drugs
- early puberty and onset of menstruation
- genetic predisposition
- average age from 40 to 50 years (at this stage menopause or menopause occurs)
- exposure to radiation or undergoing radiation therapy
- some diseases of the endocrine system, kidneys and liver, especially those developing in adulthood or old age
- injury to mammary tissue
- refusal of lactation or its abrupt and brutal cessation
- concomitant gynecological diseases or serious hormonal imbalances
Symptoms
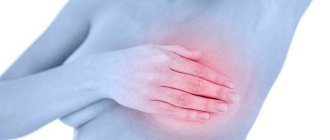
Infiltrative lobular carcinoma is usually practically asymptomatic and therefore extremely difficult to detect, especially during self-examination. Since there are no obvious neoplasms, they cannot be easily palpated. Lobules are involved in the process, but their size and structure remain virtually unchanged. And only as the disease develops and moves into later stages, some signs characteristic of other forms of cancer may appear.
Possible symptoms of infiltrating lobular cancer:
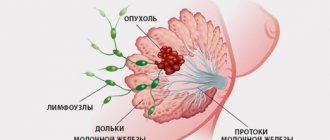
- A palpable lump in the chest, which, as a rule, does not have clear contours and is characterized by the absence of regular shapes.
- The skin over the tumor may change: peel, lighten or, on the contrary, darken and become rough.
- When the milk ducts are compressed or deformed, pathological discharge from the nipples, for example, mixed with blood, is likely to appear.
- Feeling of heaviness and fullness, discomfort.
- With the rapid growth of the tumor and a significant increase in its size, the shape and size of the mammary gland may change.
How quickly does breast cancer develop?
There are many cases where in some patients the duration of development of breast cancer was more than 5 years, and in others it was 1-3 years. Simply put, the rate at which breast cancer develops varies from person to person. The exact reasons that influence the speed and activity of the development of this pathology have not been established to date. However, it has been found that the rate of cancer development primarily depends on:
- The level of sensitivity of the tumor to the effects of hormones.
- Occurrence of Her2neu markers during the development of pathology. These markers indicate rapid and aggressive tumor growth within the body.
The rate of development of the disease is influenced by external factors: bad habits (use of alcohol, tobacco, drugs), radiation contamination, frequent contact with dangerous chemicals that provoke the development of oncology. The rate of development of breast cancer also depends on the general state of the person’s immune system and the presence of a genetic predisposition to the appearance of this disease.
Diagnostics
The only effective and proven method for the timely detection of lobular infiltrating carcinoma is diagnostics. But a method such as mammography, used to assess the structure and condition of the mammary glands, in the early stages turns out to be uninformative and does not allow identifying pathological processes occurring in the lobules.
Therefore, other diagnostic methods are used, for example, magnetic resonance or computed tomography. In addition, blood tests are often prescribed to determine hormone levels and detect tumor markers - special proteins synthesized in the body during malignant neoplasms.
If there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor discovered during the diagnostic process, then to determine its nature and evaluate its composition, a specialist may recommend a puncture or biopsy, which involves removing a fragment of altered tissue and their further microscopic examination.
Therapy and prognosis
If lobular carcinoma is found, different treatment options may be used.
- The first method is the most effective and involves removing the tumor. The operation can be performed in two main ways. During an excisional biopsy, the tumor is removed along with surrounding healthy tissue under local anesthesia. After such an intervention, the patient must undergo routine examinations every six months to a year.
- The second method is mastectomy, which involves complete removal of the breast. In some cases, for example, with the rapid growth of a tumor and damage to large areas, a prophylactic total bilateral mastectomy is recommended.
- If the size of the tumor is small and does not exceed 1-2 centimeters, then the oncologist may first prescribe conservative treatment. Since lobular cancer is considered hormone-dependent, hormonal drugs are recommended in most cases.
- Chemotherapy is also a frequently prescribed and very effective method of treatment, but it is not permitted in all cases and creates a huge burden on all systems of the body.
- Radiation therapy is used less frequently, but sometimes achieves positive results.
- Another relatively new method is hyperthermia. A drug is injected directly into the tumor to promote the breakdown of mutated cells. Next, the mammary gland is placed in hot water, and this thermal effect enhances the effect and increases the activity of the injected substances.
- Taking immunomodulators may also be rational. Such remedies activate the body’s natural forces and help the immune system independently destroy the tumor or stop its growth.
Lobular breast cancer and prognosis are issues of concern to all women faced with such a serious disease. The development of events depends on many factors, including the age and health status of the patient, the individual characteristics of her body, the stage of development of the disease and its form, the chosen methods of therapy, the size and structure of the tumor, the presence or absence of metastases.
Infiltrating lobular breast cancer is a dangerous and serious disease. But if it is detected in a timely manner, this will allow immediate initiation of therapy and stop the growth of the tumor or remove it completely.
Methods of treating the disease
Lobular carcinoma requires complex treatment, which includes multidirectional measures.
Surgery
Surgical treatment involves different types of surgical interventions. A possible option is determined based on:
- stages of the disease;
- localization of the outbreak;
- tumor size;
- number of cancer lesions;
- the presence of a goal of organ preservation.
Surgery cannot be performed if:
- severe cardiovascular diseases;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- liver and kidney failure;
- diabetes mellitus;
- tumor growing into the chest;
- the transition of multiple cancer foci to the lymph nodes.
It is impossible to save an organ if there is:
- large tumor in a small breast;
- cancer is located near the nipple;
- significant spread of the tumor process;
- the presence of several cancerous nodes.
Conservative therapy
After surgery, radiation therapy is prescribed, since surgery does not provide a 100% guarantee that there are no tumor cells left in the organ.
This therapy has a destructive effect on cancer, after which it has no possibility of recovery, and the prognosis of the disease in most cases is favorable.
Lobular breast cancer is a hormone-dependent disease, therefore, after diagnosis, the attending physician prescribes treatment with hormones, the task of which is to eliminate the negative effects of estrogens on tumor cells. To reduce negative interference, antiestrogens are prescribed, which have a blocking effect on hormones. This type of therapy increases the survival rate. Hormone therapy is indicated for:
- a small number of metastases;
- over 55 years of age;
- long-term remission.
Hormonal therapy is not very effective for:
- rapid spread of metastases;
- short period of remission;
- under 35 years of age.
With the help of chemotherapy, it is possible to convert inoperable tumors into operable ones. In addition, this procedure makes it possible to reduce the size of the cancer tumor to a state where it is possible to perform organ-sparing surgery. Chemotherapy can be performed instead of surgery, as well as before and after it.
Immunotherapy is a young and promising area of oncology treatment. This procedure involves the introduction of biological drugs that have antitumor activity into the body, where they begin to fight cancer cells by cutting off nutrition to the tumor (Herceptin, LAC therapy).
With the cessation of tumor growth, the oncological process is blocked. Anti-cancer biological substances are prepared individually for each patient. They are taken by collecting cellular material, after which the substance is processed and introduced into the body, where it begins to work immediately and significantly increases the chance of a favorable prognosis.
Important! The probability of cure after a full course of immunotherapy is over 80%.
https://youtu.be/7qbqUGjFxZI