What is breast fibrosis
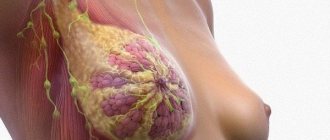
Anatomically, the mammary gland is glandular and adipose tissue, which is supported by Cooper's ligaments (connective tissue structures that act as a framework).
Fibrosis of the mammary glands is a natural involutive process during which glandular tissue in the form of milk lobules is replaced by connective tissue cords and fibrous structures. Normally, every woman experiences moderate involution, which does not have a negative effect on the mammary glands.
Severe fibrosis in women can cause pain and discomfort, so in each specific case it is necessary to seek help and perform tests prescribed by a doctor. Depending on the diagnostic results and identified problems, the following 2 main pathology options are distinguished:
- Local (focal);
- Diffuse fibrosis.
When performing a mammogram, the doctor can determine the following types of disease:
- linear;
- periductal;
- perivascular;
- stromal;
- ponderous.
Symptoms may be absent - manifestations of involutive processes do not always bother a woman. Often, breast fibrosis is discovered accidentally during preventive mammography, which must be done at least once every 2 years.
What is fibrofatty involution of the mammary glands?
The female body is a complex system that must work like a clock. Any deviation must be noticed and treated promptly. Therefore, upon learning their diagnosis - fibrofatty involution of the mammary glands - ladies begin to panic. What is it, what are the symptoms of the mysterious disease and how to treat it? This review will help you understand this burning topic.
A complex process, as a result of which glandular elements are gradually transformed from other types of tissue (fibrous or fatty) - this is the involution of the mammary glands. This is not a disease, so there is no need to worry too much. Change occurs as a result of aging. The female body loses its reproductive function, so the organ is no longer needed to feed the child.
If you are concerned about fibrous changes in the mammary glands, what it is is easy to understand. The breast decreases in size, and the gland is divided into small lobes, which are surrounded by a layer of fat and connective tissue. Sometimes benign cavitary neoplasms can be observed, which can be easily palpated during self-examination. Small signs of involution are found in young mothers who breastfeed their babies for a long time.
Fibrous tissue, what is it? It is often mistakenly confused with oncology. No need to worry - this is a connective substance that performs a protective function for the body. The female breast consists of glands, which are gradually replaced with auxiliary components with age. Disorder of fibrous tissue is a loss of elasticity of body fibers and sagging skin and muscles, which is characteristic of aging.
Involutive changes in the mammary glands are caused by hormonal changes in a woman’s body. This occurs after the birth of a child or in old age. If transformations are noticed in a nulliparous woman, then it is necessary to conduct examinations to exclude the appearance of endocrine pathologies. If a transformation is detected, the doctor prescribes therapy.
The state of a woman’s health is judged by the condition of the mammary glands. With a normal hormonal background, correct development of the breast is ascertained. In case of any violation, tissue replacement begins with adipose or connective tissue. Often, a nulliparous woman at 50 years old has excellent breast indicators. Age stages of development:
- childbearing – from the beginning of reproductive age to 45 years;
- menopausal – from 45 to 55 years;
- senile – over 55 years old.
For a forty-year-old woman, changes are considered normal, but if signs are found in a young lady who has not given birth, then you should consult a specialist. These could be complications after illness or hormonal imbalance. The doctor must determine what is the cause of involution and how to deal with it. At the very first signs, you need to contact a specialist.
There are no symptoms of this process as such. Sometimes patients complain of slight pain in the mammary gland when pressed, which is mistakenly attributed to spinal osteochondrosis. Self-examination of the glands reveals a lack of elasticity and sagging skin. It is possible to confirm or refute the diagnosis only with hardware examination. All changes are clearly visible on x-rays.
Local (focal) fibrosis of the mammary gland - what is it?
Any dense formation in the breast indicates a high risk of cancer. The focus of fibrosis is a nodular neoplasm of a benign nature, but this can only be clarified after a complete examination.
Localized fibrosis is a limited local process in the mammary gland, which can become the basis for malignant degeneration: the doctor knows what the tumor looks like, why the node is dangerous, and what the differences are between fibrosis and cancer. You should contact a specialist if you notice the following symptoms:
- detection of a dense nodule of any size in the chest;
- painless education;
- node mobility;
- breast deformation.
After the examination, the doctor may identify the following types of pathology:
- fibrosis;
- single cyst;
- polycystic node;
The real danger of fibrotic changes is unpredictability - it is extremely difficult to guarantee a woman the absence of breast cancer without ultrasound, mammography and biopsy.
Symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the pathology characterized by fibrosclerosis. If the disease affects the mammary gland, the patient feels pain that intensifies in the second half of the menstrual cycle, tissue swelling and a change in the shape of the organ are visible. Gradually, as dysplasia progresses, the patient may experience increased anxiety, depression, and fear of dying from breast cancer.
Multifocal sclerosis is a consequence of genetic changes. Symptoms increase slowly, gradually over several years. Mainly localized in the liver, gall bladder, and its ducts. A person suffers from digestive disorders, nausea, periodic vomiting, pain in the right hypochondrium, skin itching, icteric staining of the mucous membranes and epidermis. In a third of cases, concomitant pathologies include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Pulp fibrosis is characterized by tissue compaction against the background of chronic inflammation, discomfort, a feeling of heaviness in the jaw area, pain that increases with the consumption of hot or very cold food and radiates along the maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve. Sometimes it is asymptomatic and is discovered completely by accident when examining the oral cavity by a specialist.
Diffuse fibrosis of the breast
The most favorable option for age-related changes is a diffuse distribution of connective tissue structures throughout the mammary gland. The absence of nodes and tumor-like formations ensures a low risk of oncology: diffuse fibrosis extremely rarely causes malignancy, but can provoke the following unpleasant symptoms:
- pulling sensations in the chest;
- diffuse pain in the mammary glands (without specifying a specific location);
- engorgement of tissues before critical days;
- unevenness of tissue upon palpation;
- change in breast shape.
It is important, after examination and exclusion of oncology, to continue monitoring with a doctor, visiting a specialist at least once a year.
Linear breast fibrosis
Examination for breast pathology includes the following studies:
- Ultrasound scanning;
- Aspiration biopsy;
- Tomography (MRI according to indications).
Using mammography, you can identify a linear version of fibrosis, which looks like various thin lines on the pictures and affects the following:
- interlobular spaces;
- intralobular spaces;
- intraductal structures.
Linear fibrosis of the mammary glands is a favorable type of changes in the breast that requires observation and symptomatic therapy.
From prevention
The development of fibrosclerosis can be prevented under the following conditions:
- avoiding abortions, and, accordingly, the development of mammary gland pathologies
- clear monitoring of the menstrual cycle - if it is irregular, a trip to the gynecologist is recommended, who will determine the reason for the change in the schedule
- quitting smoking and alcohol abuse
- Regular examinations with a mammologist are very important, this is especially important for women who have a genetic predisposition to breast cancer
- control and timely treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory and infectious pathologies, disorders of the endocrine system.
- Nervous breakdowns and stressful situations should be avoided in every possible way.
Medical assistance may not be needed if you live correctly and monitor the condition of the mammary glands.
The prognosis for timely diagnosis of breast fibrosclerosis is quite positive; it is not a dangerous disease. But, like any other disease, it cannot be ignored. Treatment is preceded by strict control of the hormonal state, a balanced diet, regular visits to the gynecologist, mammologist, and regular self-examination of the mammary glands.
Periductal and perivascular fibrosis - what is it?
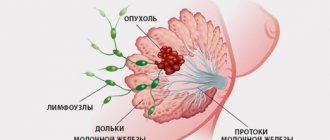
In addition to the adipose tissue and connective tissue framework, the basis of the breast is the milk lobules, fibrosis of the tissue around which leads to a periductal type of fibrosis. The vascular network in the mammary glands provides nutrition to the tissue: the deposition of fibrous tissue around the arteries and veins leads to the formation of perivascular fibrosis of the mammary glands.
Both options refer to a relatively safe type of involutive changes that do not require surgery or the use of aggressive treatment methods.
Severe fibrosis of the mammary gland
A rare variant of the distribution of fibrous structures is stellate or stranded fibrosis. With this type of change in the mammary glands, the doctor sees radially diverging rays of fibrous tissue on mammographic images. Provoking factors for the formation of cords include:
- Medical or cosmetic surgeries;
- Radiotherapy (after radiation therapy);
- Post-traumatic changes;
Pronounced and rough connective tissue cords are a protective reaction of breast tissue to any type of damage.
There is no need to treat or operate on severe fibrosis: it is quite enough to visit a doctor regularly for preventive purposes.
Breast fibrosis - ultrasound
Using an ultrasound scan, you can assess the condition of the mammary glands and make a preliminary diagnosis. Standard signs of fibrosis on ultrasound include:
- Reducing the amount of glandular tissue and fat lobules;
- Thickening of Cooper's ligaments with the formation of fibrous cords;
- Detection of interlobular linear structures.
Ultrasound will help identify the first signs of involutive changes, but an accurate diagnosis can be made on the basis of x-rays and biopsy. In difficult cases and according to indications, the doctor will prescribe magnetic resonance imaging, with which you can confidently exclude or confirm breast cancer.
Treatment of the disease
Fibrocystic formations of the connective tissue of the mammary gland do not degenerate into breast cancer, but areas of pathology can complicate the diagnosis of pathological changes in the mammary glands and cause severe discomfort to patients. Treatment of the pathology is aimed at preventing tumor enlargement, normalizing hormonal levels, treating concomitant pathologies, and stabilizing the patient’s neuropsychic state. It is impossible to get rid of the tumor with medications, but you can stop its growth and also remove it surgically.
The most effective way to treat fibrosclerosis is surgery. It is carried out in several ways:
- Enucleation. Used to remove single small tumors.
- Sectoral resection is the removal of a section (sector) of the mammary gland with multiple tumors during a recurrent course of the disease.
If signs of tumor development appear or for a qualitative diagnosis of the condition of the mammary glands, contact a medical professional. We see highly qualified specialists in the field of oncology and mammology, specializing in the treatment of breast tumors. At any convenient time in the clinic you can undergo the full range of mammary gland examinations - ultrasound, mammography, biopsy of altered tissues, and conduct histological and cytological studies. Based on the results of the examination in the clinic, you can receive qualified advice on the nature of the existing disorders.
You can make an appointment by phone: + 7 (812) 407-10-17, +.
How often do you visit a gynecologist (not during pregnancy)?
Please choose 1 correct answer
The medical term “breast fibrosis” refers to thickening of the connective tissue in the breast. It should be noted that this disease can affect not only the chest, but also any organ - liver, lungs, etc.
general characteristics
Breast fibrosis begins with increased production of collagen in the body. In general, this substance is intended to create a foundation for connective tissues. However, gradually its amount exceeds the norm - this provokes the displacement of normal cells of the body. This diagnosis is most often made to women aged forty to fifty years.
Pathologies
The disease is dangerous mainly because it entails many consequences. For example, lens fibrosis in most cases ends in cataracts. In women, fibrosis often leads to infertility. It should be noted that at the moment there is no method in medicine for the regeneration of connective tissue, so there is no need to talk about a complete recovery. However, constant monitoring by a doctor and proper therapy allow the patient to lead a normal life.
Possible reasons
Breast fibrosis can develop as a result of injury, radiation, infection, or even an allergic reaction. However, most often it occurs against a background which, in turn, is caused by hormonal imbalance.
Symptoms
Breast fibrosis is also dangerous because at an early stage it is completely asymptomatic. As the disease progresses, a small formation (or several formations) begins to be felt in a woman’s breast. As a rule, its growth is not accompanied by pain. Therefore, many patients find out about its presence quite by accident - during a routine examination by a mammologist.
Diagnostics
Local breast fibrosis is diagnosed after mammography and breast ultrasound. In addition, cytological and histological examinations may be required.
If your suspicions are confirmed and the doctor says that you really need to start immediately. Of course, it is not as dangerous as cancer, but you should not neglect your health. Therapy usually depends on the cause of the disease. Most likely, hormonal balance adjustments will be required. You will have to take a course of immunomodulatory drugs and antihomotoxicological medications. Following medical recommendations will improve within a few days. As a preventative measure, it would be advisable to be regularly examined by a gynecologist and endocrinologist, and not to get carried away with taking hormonal drugs (it is better not to use them at all without a specialist’s prescription).
Is surgery necessary?
This question concerns almost all women faced with fibrosis. There is no definite answer to this and there cannot be one. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and her indicators. In general, we can say that if the nodule does not increase in size, surgery is not indicated.
Fibrosis of the mammary glands (breasts) is an inflammatory pathology. It is as a result of fibrosis of the mammary glands that cysts and nodes develop. For a long time, mammologists have been urging women not to ignore the symptoms of fibrosis, as this disease can lead to dangerous consequences for health and life. Every woman should have an idea of what this disease is, know its symptoms, complications and methods of treatment.
At its core, fibrosis, both in the mammary gland and in other tissues, is an increased proliferation of elastin and collagen fibers, as well as fibroblasts, fibrocytes and other cells. As a result of this pathological process, various changes occur in the tissues, which are similar to scarring, and this, naturally, affects the functioning of the organ.
In the female breast, two components predominate - stromal and glandular. The first is a kind of frame, and the function of the second is to produce milk during the lactation period. Fibrosis of the mammary glands is a violation of the ratio of these two components; the stromal component becomes larger. This leads to tissue compaction, that is, fibrosclerosis develops.
Why does fibrosis develop? Pathological processes in the mammary gland are triggered as a result of an imbalance of sex hormones. This mainly concerns progesterone and estrogen. Since these two hormones can lead to hormonal imbalance. Many women experience this phenomenon during natural monthly bleeding. The balance of these hormones is of great importance during pregnancy, menopause, and after abortion. It is always difficult to balance these hormones, so it is necessary to closely monitor their levels and take appropriate measures if there are deviations.
The following factors can provoke breast fibrosis:
- Prolonged stress and overwork, especially if these conditions turn into depression.
- Various pathological processes in the functioning of the endocrine glands and pancreas - hypothyroidism or diabetes mellitus.
- Toxic poisoning of the body by certain substances.
- Inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs that are ignored and not treated in a timely manner.
Breast fibrosis can occur with a hereditary predisposition to this disease; this phenomenon is usually observed in women after 40 years of age. However, if provoking factors occur, the disease can begin at an earlier age.
There is another reason why fibrosis can develop (in the mammary gland) - radiation, for example, during radiotherapy. But solariums can also provoke violations, so women are contraindicated to sunbathe topless.
If fibrosis occurs due to radiation exposure, then mammologists classify it as radiation fibrosis; treatment of this type of disease is carried out according to a special scheme. Women should understand that the radiation form of fibrosis can give impetus to the onset of pathological fibrotic processes in other tissues that are not related to the mammary gland.
Reasons for development
The pituitary gland influences the thyroid gland, which controls the amount of estrogen
Fibrosis develops when the structures in the mammary glands change, which can be triggered by hormonal imbalances and high levels of estrogen. These disruptions are caused by the following disorders in the body:
- pathologies of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland;
- long-term use of drugs with estrogens;
- tumors and inflammatory processes in the organs of the reproductive system;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity and other metabolic pathologies;
- consumption of estrogen-containing products;
- excessive emotional and physical stress;
- pregnancy after 35 years;
- Puberty too early.
The diagnosis is most often made in women aged 35 to 50 years, but some forms are detected later, after menopause.
Pathological growths of fibrous tissue occur against the background of hormonal imbalances. An increased amount of estrogen accumulates in the body, which contributes to the development of breast fibrosis.
Deviations occur under the influence of predisposing factors:
- dysfunction of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland,
- uncontrolled long-term use of estrogen-based medications,
- metabolic disorders and associated obesity, diabetes mellitus,
- inflammation and tumors in the organs of the reproductive system,
- premature puberty,
- first pregnancy after 35 years,
- excessive physical and emotional stress,
- Excessive consumption of estrogen-containing products.
Most often, fibrosis is diagnosed in women aged 35-50 years. Physiological aging of the ovaries occurs; normally, estrogen levels drop. But the risks of hyperestrogenism increase, which is facilitated by many factors.
The condition of the mammary glands is directly dependent on the balance of 16–30 hormones. In most cases, changes in the breasts develop due to hormonal imbalance, which can be normal or pathological.
Thus, the development of fibrofatty degeneration begins in women when they reach approximately 35 years of age. During the process of involution of the mammary glands, glandular tissues are replaced by fat due to a lack of sex hormones and the decline of reproductive function, which is not a disease.
Involution in the postlactation period is also natural.
In other cases, hyperplasia is a consequence of:
- hereditary predisposition;
- early onset of menstruation and late menopause;
- neuroendocrine disorders;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- metabolic disorders, including diabetes and obesity;
- late first pregnancy and childbirth;
- excessively long, short or complete absence of lactation period;
- inflammatory and hyperplastic processes of the internal organs of the reproductive system of a chronic nature;
- multiple artificial terminations of pregnancy;
- prolonged neuropsychic fatigue and frequent stressful situations;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- traumatic injuries;
- medical or cosmetic operations;
- radiotherapy;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs.
One of the reasons leading to tissue transformation is an unbalanced diet, which lacks vitamins A, E, B6 and fiber, and also contains a predominance of foods containing methylxanthines (tea, coffee, chocolate) and fats.
With the development of an inflammatory process or mechanical damage, fibroblasts are activated to isolate healthy membranes from infection or hemorrhage. They accelerate the production of collagen, elastin and glycoprotein cells, which are the basis of connective tissue. This process can occur in all internal organs of a person.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Face masks for expression wrinkles: homemade mask around the eyes, for wrinkles on the forehead
More often, stromal fibrosis develops in women of childbearing and menopausal age in the mammary glands and uterus (myometrium). As a result of the pathological proliferation of connective tissue, the formation of compactions and scars, an inevitable disruption of the organ’s functioning occurs. Thus, fibrosis of the myometrial stroma is the cause of missed abortion and infertility.
General factors leading to the replacement of organ cells with connective tissue include:
- genetic predisposition;
- diseases of the thyroid and pancreas;
- use of hormonal contraceptives (pills, intrauterine device);
- inflammatory processes in the uterus and ovaries;
- completing a training course (radiotherapy), hormonal therapy;
- early puberty;
- late pregnancy;
- mechanical damage to tissues;
- allergic reactions;
- bad habits;
- obesity;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- stressful situations.
In addition to the above reasons, the disease can occur due to refusal of breastfeeding.
Types of pathology
Changes in the tissues of the mammary gland can develop in several directions; this is explained by the unequal sensitivity of areas of the mammary gland to the effects of hormones. Therefore, there are different forms of fibrosis:
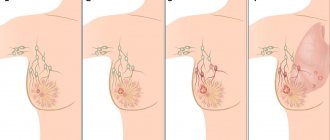
- Focal fibrosis develops when connective tissue begins to grow pathologically somewhere in one place. That is, there is a focus of pathology, as a rule, it is located in the upper region of the mammary gland and looks like a dense nodular formation. The size of this formation can be from one to several centimeters.
- Nodular fibrosis develops in the same way as focal fibrosis.
- Cystic fibrosis (CF) is characterized by the appearance of cavities (cysts) that are filled with liquid contents. This pathology is called fibrous cyst of the mammary gland.
- Periductal fibrosis is the growth of collagen fibers directly around the glandular ducts. This process is often observed in patients who have entered menopause.
- Linear fibrosis. Connective tissue looks like a large number of strands.
- Stromal fibrosis. From the name it is clear that in this case the pathological process affected the stromal component of the organ.
Diffuse FAM and fibrous adenoma of the mammary gland are distinguished by mammologists separately, since in these pathologies fibroadenomas are formed - a large number of benign tumors. Fibroadenoma is diagnosed and examined not only by mammologists, but also by oncologists.
How does fibrosis develop?
In its pure form, breast fibrosis is extremely rare. As a rule, it is one of the components of fibrocystic mastopathy.
With the development of fibrocystic mastopathy, part of the glandular tissue is transformed into cysts (cavities), and the stroma grows, thickens, displacing the glandular tissue. If stroma predominates in the composition of breast tissue, fibrosis develops.
Fibrous tissue can be isolated or form a knot. The nodular (local) form of fibrosis can be determined by palpation of the gland. With a local form of fibrosis, the node has a smooth surface, round or oval shape, is mobile, and is not fused to the skin.
Diffuse fibrosis sometimes occurs. Diffuse (widespread) fibrosis does not have clear boundaries and is not always determined by normal palpation of the gland.
With widespread fibrosis, connective tissue can form in excess around the milk ducts, inside them, as well as in the area of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and capillaries.
If fibrous tissue grows inside the ducts or in the area of the septa between the lobules of the mammary gland, then these ducts or septa turn into dense elongated cords. In such cases, stranded or linear fibrosis occurs.
With any form of breast fibrosis, there are no changes in the skin of the gland over these formations. Lymph nodes in the axillary, supraclavicular and subclavian areas do not enlarge.
Clinical picture
While the change in the mammary gland is mild, the woman may not experience any symptoms, but as the disease progresses, the following signs appear:
- The mammary glands become engorged and increase in size (mastodynia).
- In the middle of the menstrual cycle or just before menstruation, discomfort appears in the chest.
- On palpation, increased sensitivity and soreness of the mammary gland is noted.
- Pain (mastalgia) can be temporary (premenstrual) or permanent.
- The skin on the breasts may change color, and there may also be discharge from the nipples.
- A woman can feel the lumps themselves a few days before the start of her period.
All of these symptoms are a reason to consult a mammologist, especially since the symptoms of fibrosis are quite similar to other pathologies of the mammary gland.
How is fibrosclerosis different from other breast tumors?
0
The problem of breast anomalies is currently considered very relevant, since there is a tendency towards a constant increase in incidence. Quite often, neuroendocrine pathology manifests itself, a disease called fibrosclerosis appears (part of the group of benign mammary dysplasia).
The peculiarity of this disease is the non-specificity of the signs, the diversity in the manifestations of sonographic, radiological, and pathomorphological forms. This sometimes makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. However, today the most modern diagnostic technologies have been developed that can improve the quality of preoperative diagnosis of benign breast dysplasia.
How do benign mammary dysplasias manifest?
The main manifestations of the disease are:
- tenderness in one or both mammary glands;
- pain is observed in the second half of the menstrual cycle;
- pain may intensify several days before the start of menstruation;
- pain of varying nature and intensity;
- engorgement (mastodynia) of the mammary glands;
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- increase in breast volume;
- pain disappears with the onset of menstruation - in its first days;
- sometimes the soreness of the mammary glands is constant, regardless of the phase of the menstrual cycle.
Some patients may not experience any discomfort in the mammary glands; they do not experience pain. They can see a doctor if they feel lumps in the glands or for a routine examination. Patients with severe pain in the mammary glands often experience:
- anxiety;
- depressive syndrome;
- cancerophobia (obsessive fear of getting cancer).
Sometimes women may complain of various types of discharge from the nipples. Fibrosclerosis clinically manifests itself as a local nodular formation of the mammary gland, but can also take the form of diffuse nodular changes. The main clinical sign that distinguishes fibrosclerosis from other tumor diseases of the mammary glands is painlessness and immobility of the formation. The disease most often appears in patients aged thirty-five to fifty-five years.
Why does fibrosclerosis appear?
The cause of this disease may be an imbalance between the content of connective and glandular tissues, which normally should form mammary gland tissue. Most often, fibrosclerosis appears when connective tissue cells dominate the glandular cells and displace them towards the armpits. As a result, areas of tissue compaction with typical uneven edges are formed.
udoktora.net
Diagnostic measures
It is impossible to diagnose fibrosis on your own. This can only be done by a mammologist, and only after a diagnostic examination. Therefore, you should not start looking for drugs to treat breast fibrosis, much less take them, until the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
It is not possible to determine the problem by symptoms alone; as mentioned above, the symptoms of fibrosis are quite similar to the signs and manifestations of other breast ailments. Therefore, the doctor, after a conversation with the patient (during which symptoms and complaints, heredity, background diseases, etc. are clarified), palpates and refers her to the following diagnostics:
- mammography;
- general blood analysis;
- blood test for hormones;
- Ultrasound, CT;
- study of the nature of blood flow in the chest and determination of the condition of blood vessels - dopper sonography;
- X-ray examination of the mammary gland ducts using a contrast agent - chromoductography;
- biopsy and histology of the obtained material.
Treatment of fibrosis
If the diagnosis of fibrosis is confirmed, therapy should begin as soon as possible; timely treatment of this disease is very important, since if you delay, you may encounter more serious diseases.
Don't think that your doctor will immediately prescribe a mastectomy for you. No, with fibrosis, the breast is not removed in all cases; most often, only nodes and cystic formations are removed. It is also worth saying that surgical intervention is prescribed only in difficult situations and in acute cases of the disease. In all other cases, fibrosis is treated with conservative methods.
Drug treatment of fibrosis is based on an integrated approach, which includes eliminating the cause of the disease. As a rule, doctors prescribe medications to eliminate premenstrual syndrome, hormone therapy, and dietary nutrition.
The regimen and tactics of therapy are determined by the doctor based on the form of the disease and the reasons that provoked it. In addition, the patient’s age, the presence of underlying diseases and other points must be taken into account.
If focal fibrosis is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed Duphaston, a hormonal drug containing progesterone (prescribed only if this hormone is insufficient). This will neutralize the effect of estrogen.
Cytophene or Zitazonium also reduces estrogen levels. These drugs block the receptors that are responsible for their quantity.
They also use an external remedy - Progestogel, which relieves breast swelling well and also contains progesterone.
In rare cases, Abergin is prescribed, however, it cannot be used for benign tumors, or if a woman has premenstrual syndrome. For diffuse fibrosis, Mastadion is prescribed. This is a homeopathic remedy that has a herbal composition.
If a woman has hypothyroidism, she is prescribed Iodomarin and other iodine-containing drugs. And if there are liver problems, then it is mandatory to take hepatoprotectors - Karsil, Essentiale. If breast swelling is severe, herbal diuretics may be required. Vitamin complexes and sedatives are also prescribed.
It is very important to maintain normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract during therapy; the fact is that estrogens are excreted by the liver during treatment, and if there is constipation, they are very quickly reabsorbed from the intestines into the blood. Therefore, you need to eat more vegetables and fruits to ensure regular bowel movements.
As for traditional medicine, in this case it cannot cope with the disease. The only way traditional medicine can help with fibrosis is to normalize stools and relieve pain. Therefore, it is not worth wasting time on herbal treatment.
In severe and complicated cases (fibroadenomatosis, cyst), surgical intervention is possible.
Fibrosis of the breast and mammary glands in women and how to treat them
Fibrosis of the mammary glands (breasts) is an inflammatory pathology. It is as a result of fibrosis of the mammary glands that cysts and nodes develop. For a long time, mammologists have been urging women not to ignore the symptoms of fibrosis, as this disease can lead to dangerous consequences for health and life. Every woman should have an idea of what this disease is, know its symptoms, complications and methods of treatment.
At its core, fibrosis, both in the mammary gland and in other tissues, is an increased proliferation of elastin and collagen fibers, as well as fibroblasts, fibrocytes and other cells. As a result of this pathological process, various changes occur in the tissues, which are similar to scarring, and this, naturally, affects the functioning of the organ.
Reasons for development
In the female breast, two components predominate - stromal and glandular. The first is a kind of frame, and the function of the second is to produce milk during the lactation period. Fibrosis of the mammary glands is a violation of the ratio of these two components; the stromal component becomes larger. This leads to tissue compaction, that is, fibrosclerosis develops.
Why does fibrosis develop? Pathological processes in the mammary gland are triggered as a result of an imbalance of sex hormones. This mainly concerns progesterone and estrogen. Since these two hormones can lead to hormonal imbalance. Many women experience this phenomenon during natural monthly bleeding. The balance of these hormones is of great importance during pregnancy, menopause, and after abortion. It is always difficult to balance these hormones, so it is necessary to closely monitor their levels and take appropriate measures if there are deviations.
The following factors can provoke breast fibrosis:
- Prolonged stress and overwork, especially if these conditions turn into depression.
- Various pathological processes in the functioning of the endocrine glands and pancreas - hypothyroidism or diabetes mellitus.
- Toxic poisoning of the body by certain substances.
- Inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs that are ignored and not treated in a timely manner.
Breast fibrosis can occur with a hereditary predisposition to this disease; this phenomenon is usually observed in women after 40 years of age. However, if provoking factors occur, the disease can begin at an earlier age.
There is another reason why fibrosis can develop (in the mammary gland) - radiation, for example, during radiotherapy. But solariums can also provoke violations, so women are contraindicated to sunbathe topless.
If fibrosis occurs due to radiation exposure, then mammologists classify it as radiation fibrosis; treatment of this type of disease is carried out according to a special scheme. Women should understand that the radiation form of fibrosis can give impetus to the onset of pathological fibrotic processes in other tissues that are not related to the mammary gland.
Types of pathology
Changes in the tissues of the mammary gland can develop in several directions; this is explained by the unequal sensitivity of areas of the mammary gland to the effects of hormones. Therefore, there are different forms of fibrosis:
- Focal fibrosis develops when connective tissue begins to grow pathologically somewhere in one place. That is, there is a focus of pathology, as a rule, it is located in the upper region of the mammary gland and looks like a dense nodular formation. The size of this formation can be from one to several centimeters.
- Nodular fibrosis develops in the same way as focal fibrosis.
- Cystic fibrosis (CF) is characterized by the appearance of cavities (cysts) that are filled with liquid contents. This pathology is called fibrous cyst of the mammary gland.
- Periductal fibrosis is the growth of collagen fibers directly around the glandular ducts. This process is often observed in patients who have entered menopause.
- Linear fibrosis. Connective tissue looks like a large number of strands.
- Stromal fibrosis. From the name it is clear that in this case the pathological process affected the stromal component of the organ.
Diffuse FAM and fibrous adenoma of the mammary gland are distinguished by mammologists separately, since in these pathologies fibroadenomas are formed - a large number of benign tumors. Fibroadenoma is diagnosed and examined not only by mammologists, but also by oncologists.
Clinical picture
While the change in the mammary gland is mild, the woman may not experience any symptoms, but as the disease progresses, the following signs appear:
- The mammary glands become engorged and increase in size (mastodynia).
- In the middle of the menstrual cycle or just before menstruation, discomfort appears in the chest.
- On palpation, increased sensitivity and soreness of the mammary gland is noted.
- Pain (mastalgia) can be temporary (premenstrual) or permanent.
- The skin on the breasts may change color, and there may also be discharge from the nipples.
- A woman can feel the lumps themselves a few days before the start of her period.
All of these symptoms are a reason to consult a mammologist, especially since the symptoms of fibrosis are quite similar to other pathologies of the mammary gland.
Diagnostic measures
It is impossible to diagnose fibrosis on your own. This can only be done by a mammologist, and only after a diagnostic examination. Therefore, you should not start looking for drugs to treat breast fibrosis, much less take them, until the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis.
It is not possible to determine the problem by symptoms alone; as mentioned above, the symptoms of fibrosis are quite similar to the signs and manifestations of other breast ailments. Therefore, the doctor, after a conversation with the patient (during which symptoms and complaints, heredity, background diseases, etc. are clarified), palpates and refers her to the following diagnostics:
- mammography;
- general blood analysis;
- blood test for hormones;
- Ultrasound, CT;
- study of the nature of blood flow in the chest and determination of the condition of blood vessels - dopper sonography;
- X-ray examination of the mammary gland ducts using a contrast agent - chromoductography;
- biopsy and histology of the obtained material.
Treatment of fibrosis
If the diagnosis of fibrosis is confirmed, therapy should begin as soon as possible; timely treatment of this disease is very important, since if you delay, you may encounter more serious diseases.
Don't think that your doctor will immediately prescribe a mastectomy for you. No, with fibrosis, the breast is not removed in all cases; most often, only nodes and cystic formations are removed. It is also worth saying that surgical intervention is prescribed only in difficult situations and in acute cases of the disease. In all other cases, fibrosis is treated with conservative methods.
Drug treatment of fibrosis is based on an integrated approach, which includes eliminating the cause of the disease. As a rule, doctors prescribe medications to eliminate premenstrual syndrome, hormone therapy, and dietary nutrition.
The regimen and tactics of therapy are determined by the doctor based on the form of the disease and the reasons that provoked it. In addition, the patient’s age, the presence of underlying diseases and other points must be taken into account.
If focal fibrosis is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed Duphaston, a hormonal drug containing progesterone (prescribed only if this hormone is insufficient). This will neutralize the effect of estrogen.
Cytophene or Zitazonium also reduces estrogen levels. These drugs block the receptors that are responsible for their quantity.
They also use an external remedy - Progestogel, which relieves breast swelling well and also contains progesterone.
In rare cases, Abergin is prescribed, however, it cannot be used for benign tumors, or if a woman has premenstrual syndrome. For diffuse fibrosis, Mastadion is prescribed. This is a homeopathic remedy that has a herbal composition.
If a woman has hypothyroidism, she is prescribed Iodomarin and other iodine-containing drugs. And if there are liver problems, then it is mandatory to take hepatoprotectors - Karsil, Essentiale. If breast swelling is severe, herbal diuretics may be required. Vitamin complexes and sedatives are also prescribed.
It is very important to maintain normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract during therapy; the fact is that estrogens are excreted by the liver during treatment, and if there is constipation, they are very quickly reabsorbed from the intestines into the blood. Therefore, you need to eat more vegetables and fruits to ensure regular bowel movements.
As for traditional medicine, in this case it cannot cope with the disease. The only way traditional medicine can help with fibrosis is to normalize stools and relieve pain. Therefore, it is not worth wasting time on herbal treatment.
In severe and complicated cases (fibroadenomatosis, cyst), surgical intervention is possible.
Predictions and prevention
As for the prognosis, it is favorable; doctors are confident that this pathology, with proper and timely treatment, cannot cause oncological processes.
There is currently no specific prevention of the disease. The only thing that can be recommended is regular breast self-examination for early detection of the disease.
The risk of developing the described disease is lower in women who gave birth to a child before the age of 30, who did not terminate the pregnancy, were not addicted to hormonal contraceptives, and breastfed the child for up to a year. In addition, it is recommended to give up bad habits and visit a mammologist once a year for preventive purposes.
Fibrocystic mastopathy, causes. Treatment of the breast – Jozef Krinicki CHEST PAIN! MASTOPATHY! The best remedy for chest pain and mastopathy! Biopsy of breast tumors under ultrasound control. Mastopathy (fibrous, diffuse, cystic). Treatment of the mammary gland - Jozef Krinitsky Benign tumors of the mammary gland Fibroadenoma of the mammary gland - symptoms and treatment Breast cyst. Breast cyst - treatment without surgery or medication. Nikolay Peychev. Breast fibroadenoma: don’t miss the threat! How to treat fibrous mastopathy of the mammary glands How to treat fibrous mastopathy of the mammary glands? Menopause in women, symptoms and treatment Elena Malysheva. Fibrocystic mastopathy Elena Malysheva. Fibrocystic mastopathy Symptoms of fibrocystic mastopathy Complications after mammoplasty. Capsular fibrosis. — Vasily Khrapach
medistoriya.ru
Predictions and prevention
As for the prognosis, it is favorable; doctors are confident that this pathology, with proper and timely treatment, cannot cause oncological processes.
There is currently no specific prevention of the disease. The only thing that can be recommended is regular breast self-examination for early detection of the disease.
The risk of developing the described disease is lower in women who gave birth to a child before the age of 30, who did not terminate the pregnancy, were not addicted to hormonal contraceptives, and breastfed the child for up to a year. In addition, it is recommended to give up bad habits and visit a mammologist once a year for preventive purposes.
More and more women in recent years are faced with the development of tumor formations in the mammary glands. A very common phenomenon is benign growths of the connective tissue of an organ, as a result of which seals are formed. Almost 80% of women aged 30-45 experience fibrous changes in the tissues of the glands.
Breast fibrosis eventually leads to scarring neoplasia and impaired breast functionality. Although the disease is benign and does not pose a threat to life, it must be treated as quickly as possible after detection. The proliferation of fibrous tissue in some cases can develop into a malignant process, and also lead to external cosmetic defects of the breast and psychological discomfort for the woman. The disease code according to ICD-10 is N63.
Forms and symptoms
The breast is composed of fatty, glandular and fibrous tissue. With age, as reproductive function declines, fat cells are replaced by glandular ones. The main function of the stroma is to support their location, form the walls of the milk ducts and septa between the lobules of the parenchyma.
- With the development of mastopathy, the stroma grows and displaces glandular cells, which transform into cavities (cysts). If connective tissue predominates in the breast, fibrosis develops, the nature of which depends on the form of the pathology.
- At the initial stage of the disease, local fibrosis appears. This type is characterized by the formation of mobile (not fused to the skin) nodes (cysts) with clear contours and a smooth surface. They have a round shape and range in size from 0.2 cm to 3 cm. The lesions are easy to detect by palpation.
- If left untreated, connective tissue grows, displacing parenchyma and fat cells. Complete damage to the mammary gland is called extensive (diffuse) fibrosis. It does not have clear boundaries when palpated.
- Women of menopausal age often develop periductal fibrosis (plasmacytic). It is characterized by the growth of stroma around the milk ducts.
- In ductal fibrosis, excessive formation of connective tissue occurs inside the milk ducts, while adjacent tissues are not affected. It is a type of periductal form.
- Periductal perivascular fibrosis involves areas around the milk ducts, lymphatics and blood vessels.
- Excessive growth (proliferation) of interlobular connective and intraductal tissues is called linear (interlobular) fibrosis. When palpating the breast, dense cords are felt, the contours of which are clearly visible on the mammographic image.
Symptoms of breast fibrosis:
- the presence of moving nodes or compacted areas of different localization that do not cause pain upon palpation;
- change in skin pigmentation over the site of the gland lesion (not always found);
- liquid discharge from the nipple mixed with blood or clear;
- discomfort in the chest (pain, heaviness, pressure from inside);
- severe nagging pain during menstruation, radiating to the armpit and shoulder;
- swelling and engorgement of the mammary glands in the premenstrual period.
If cysts form during the growth of fibrous tissue, then when they are palpated, a feeling of pain appears; before the onset of menstruation, the lymph nodes may enlarge. As the disease progresses, the size of the nodes increases.
Depending on the strength of the manifestation of characteristic symptoms, the disease can be moderate or severe.
Types and forms of pathology
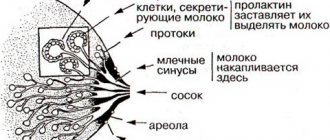
The mammary gland consists of glandular and stromal components. The glandular tissue is the alveolar glands, from which the breast lobules are formed. There are many small milk ducts in the gland, which turn into larger ones that go to the nipple. The inside of the duct is lined with epithelial tissue.
The stroma consists of adipose tissue, fibrous structures of fibrous tissues consisting of fibroblasts, collagens and elastin. Stromal elements surround the gland lobules and ducts and represent a kind of breast frame. It is the proliferation of stromal components that leads to an imbalance of glandular and fibrous tissue, and subsequently to the development of fibrosis.
An imbalance between stroma and glandular tissue can be physiological or pathological. Physiological changes are associated with the phases of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and the woman’s age. Pathological fibrosis develops against the background of abnormal disruptions in the body.
There is no single recognized classification of breast fibrosis. The disease is divided into different forms based on the symptomatic, histomorphological characteristics of the changes.
Based on the structure and distribution of the formation, breast fibrosis is divided into several types:
- Focal (local)
- a limited oval or round formation, which is a dense node that can reach several centimeters in diameter. - Diffuse (widespread)
- the distribution of fibrous tissue does not have clear boundaries. It forms near or inside the milk ducts. - Traumatic (linear)
- tissue proliferation inside the ducts and in the interlobular septa, as a result of which elongated cords appear. - Perivascular
- fibrous tissue grows around both ducts and blood vessels.
What pathologies do they mean when they say “breast fibrosis”?
One of the most common causes (or, one might say, varieties) of breast fibrosis is the fibrous form of mastopathy. It is believed that the growth of connective tissue in the mammary gland in this case is caused by a hormonal imbalance, namely, the excessive effect of estrogen hormones.
Fibrous mastopathy
With fibrous mastopathy, lumps appear in the breasts on both sides, increase in size before menstruation and decrease after them. Similarly, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, the intensity of symptoms changes: chest pain, discharge from the nipples. These signs distinguish mastopathy from cancer: in cancer, the tumor, as a rule, appears only on one side and does not change depending on menstruation.
Fibroadenoma of the breast
Sometimes fibrosis is called breast fibroadenoma - a benign neoplasm that consists of glandular and connective tissue. Its occurrence, like mastopathy, is associated with hormonal changes in a woman’s body.
Radiation therapy for cancer can damage not only tumor tissue, but also healthy tissue. Subsequently, scars remain at the site of damage. This complication is called radiation fibrosis; it can develop in the mammary gland and other organs.
One of the possible complications after breast augmentation with implants is capsular contracture. The body reacts to the implant as if it were a foreign body and forms a capsule of connective tissue around it. This condition can also be called fibrosis. The capsule compresses the implant, resulting in breast deformation and a feeling of discomfort.
Fibrosis can also be called any formation of connective tissue in the mammary gland that is not a malignant tumor. For such cases, the International Classification of Diseases provides a separate diagnosis - “unspecified formation in the mammary gland.”
Causes
Pathological growths of fibrous tissue occur against the background. An increased amount of estrogen accumulates in the body, which contributes to the development of breast fibrosis.
Deviations occur under the influence of predisposing factors:
- dysfunction of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland;
- uncontrolled long-term use of estrogen-based medications;
- metabolic disorders and associated obesity;
- inflammation and tumors in the organs of the reproductive system;
- premature puberty;
- first pregnancy after 35 years;
- excessive physical and emotional stress;
- Excessive consumption of estrogen-containing products.
Most often, fibrosis is diagnosed in women aged 35-50 years. Physiological aging of the ovaries occurs; normally, estrogen levels drop. But the risks of hyperestrogenism increase, which is facilitated by many factors.
Causes
Among all the predisposing factors, experts put in first place the process when glandular tissue degenerates into connective tissue. The activation of this state is facilitated by an increased concentration of fibrin.
This substance is an insoluble protein produced from fibrinogen. An increase in its quantity occurs against the background of the development of acute inflammatory processes in the body.
In turn, inflammation can be triggered by a number of reasons. Among them are:
- genetic predisposition;
- disorders occurring in necrotic tissues;
- prolonged course of the inflammatory process;
- disturbances at the hormonal level;
- mutations in breast tissue;
- autoimmune diseases ;
- poor blood circulation in the mammary glands;
- long-term use of potent medications that have a number of side effects.
In addition, the cause of the disease can be wearing uncomfortable underwear, which results in compression of the chest and disruption of blood flow in it.
Signs and symptoms
For a long time, clinical manifestations of fibrosis may be absent. The progression of pathological changes in organ tissue leads to the appearance of certain symptoms:
- increase in breast size;
- discomfort and heaviness in the gland on the eve of menstruation;
- pain and increased sensitivity of the glands upon palpation;
- local or diffuse compactions and nodes determined during palpation of the breast;
- in some cases, the color of the skin changes and discharge from the nipples appears.
Signs of pathology
Breast fibrosclerosis may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain on palpation of the mammary glands;
- increase in volume and swelling of the mammary gland, the skin of the gland becomes sensitive and rough;
- increased breast tenderness before menstruation, after menstruation the pain goes away;
- the presence of pathological discharge from the breast - transparent or yellowish.
The disease is often accompanied by a deterioration in mental state - depression, irritability.
Diagnostics
Any changes in the breasts and discomfort should be a reason to contact a gynecologist or mammologist. First, the doctor palpates the organ and asks a series of clarifying questions.
To confirm the diagnosis, diagnostic tests are prescribed:
- (recommended for women over 40 years old);
- general blood analysis;
- blood on the genital hormonal organs;
- examination of the condition of blood vessels;
- chromoductography - study of the state of the milk ducts using contrast;
- histology of breast biomaterial for suspected malignant process.
Effective treatments
Treatment tactics are determined individually and depend on the type of fibrosis, its causes, characteristics of the patient’s body, and the presence of concomitant diseases. Preference in most cases is given to conservative therapy. Surgery is also possible.
For local fibrosis of the mammary gland, hormonal drugs are used that neutralize the activity. One of the effective remedies is a progesterone analogue. It is recommended to take 1 tablet (10 mg) per day for 14 days of each cycle.
On the page, read about what breast puncture is and how the procedure is performed.
The following have antiestrogenic properties:
- Nolvadex;
- Tamoxifen.
Medicines block estrogen receptors and are recommended for women during menopause and for various breast tumors.
Prevention measures
There are no specific measures that prevent the development of fibrosis. No woman can be sure that she will not experience pathological changes in the tissues of the organ. It is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations to promptly detect problems in the chest. 1-2 times a year, women under 40 years of age need to undergo a routine ultrasound of the mammary glands, after 40 years of age - mammography. It is also necessary to monitor the level of sex hormones in the blood.
- do not delay having a child after 30 years of age;
- do not have abortions;
- take hormones only under the supervision of a specialist;
- breastfeed your baby for as long as possible;
- ensure proper sleep;
- eat properly and balanced;
- avoid stress.
Breast fibrosis is a common phenomenon that significantly affects a woman’s health. The breast is very sensitive to the effects of various factors and changes in the body. It is necessary to constantly monitor her condition, undergo timely examinations, and, if necessary, seek medical help.