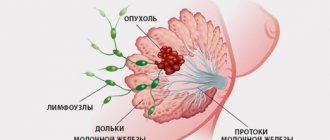
A breast cyst is a fairly common pathology, which is a cavity in the mammary gland with liquid contents.
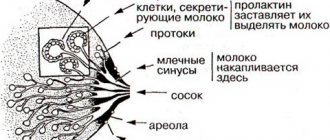
As a rule, a breast cyst lasts for quite a long time and does not bother the woman. Only after a while does discomfort, pain and a burning sensation in the chest area arise. Before and during menstruation, these manifestations tend to intensify. The cavity of a mammary gland cyst is formed due to an increase in the size of the gland duct, in which secretions accumulate. Gradually, the formation of a fibrous capsule occurs. These neoplasms may be round, oval or irregular in shape.
With a breast cyst, inflammation and suppuration of the cystic cavity are noted. Rarely does a breast cyst degenerate into breast cancer, but at the same time it slightly increases the likelihood of developing a malignant neoplasm in the mammary gland. Often a breast cyst is accompanied by disturbances in the hormonal sphere and a woman’s intimate life. Large cysts change the shape of the breast.
Etiology
A cyst is a pathological neoplasm, which can be either single or multiple and consists of a capsule and its liquid contents. A breast cyst appears in its ducts and has the following characteristics:
- The shape of a breast cyst can be different - oval, round, irregular. The size of the cyst can vary from a few millimeters to 5 centimeters, and in some cases more;
- a typical cyst has smooth and even internal walls, while an atypical cyst may have a growth that diffusely penetrates into its own cavity, and thus, difficulties with treatment arise, since puncturing a multi-chamber cyst is much more difficult, since it is difficult to completely empty all the chambers;
- if there are many cysts, this phenomenon is called polycystic breast disease; such formations can merge and transform into multi-chamber clusters. In such cases, cystic tissue can affect more than half of the breast;
- in the thickness of the mammary gland, a cyst is a cavity filled with non-inflammatory fluid;
- Before the formation of a cyst, the milk duct expands, then secretions begin to accumulate in it, and a fibrous capsule appears around the formation. In some cases, a cyst can form in the final section of the duct; such a cyst is isolated in the future and loses connection with the duct;
- the fluid that accumulates in the cyst can have a different color (brown, dark green, yellow), which depends on how long it has existed and the composition of the cyst. Often the contents include dense elements, which, when calcified, form lumps of lime. Such a compaction is not dangerous to health, but indicates that the cyst has existed for a long time;
- if the cyst appeared long enough ago, its capsule becomes denser and, accordingly, in a recent cyst the capsule has thin walls;
- the woman does not experience any symptoms for a long time;
- during the development and growth of the cyst, inflammation and suppuration may occur;
- a breast cyst quite often occurs in combination with the presence of dyshormonal disorders of the female reproductive system;
- if the cyst is large, it can affect the shape of the breast;
- cysts can form either on one breast or on both mammary glands at once;
- in most cases, the capsule of the formation contains benign cells, but malignant cells may also be present;
- the frequency of formation of breast cysts is quite high, the risk of its development is especially high in women 35-60 years of age who do not have children;
- the formation of a breast cyst is a sign of fibrocystic mastopathy;
- In some cases, a fatty cyst may form in the breast, the occurrence of which is not associated with tissue secretion. Such formations arise due to the filling of the sebaceous gland of the skin with fatty secretions. In case of significant growth of a fat-containing cyst, inflammation may occur, which in most cases does not cause any discomfort, does not form a malignant tumor and is not a concern during lactation. Accordingly, such cysts cannot be treated surgically. Most often, the presence of a fatty cyst is detected during a mammogram.
https://youtu.be/uEG24O8hUvQ
Description
A breast cyst is a pathological cavity inside the mammary gland that has walls and liquid contents.
As a rule, it is formed due to fibrocystic mastopathy.
In the breasts of sick women, there may be several cysts at once, or maybe only one. These formations can have different sizes and shapes, and be located in different places. Thus, in some patients the cysts reach only a few millimeters, while others measure in centimeters (usually up to 5 cm). In severe cases, cysts can occupy half the volume of the breast.
The most common breast duct cyst encountered in medical practice.
However, a fatty cyst can also form, which is in no way connected with the secretory tissue. It occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous gland on the skin of the breast and its overflow with secretions.
Almost always the cyst has smooth and even walls. However, with atypical breast cysts, there are growths on the walls of the formations that go inward.
With polycystic disease, women develop multiple cysts of the mammary glands, which are small in size and interconnected.
According to statistics, every third woman has a breast cyst and does not even know it, because patients may not have any symptoms for a long time, which makes timely diagnosis difficult. And only after some time, patients begin to feel a burning sensation and discomfort in the chest, which especially intensifies before the onset of menstruation.
Often, breast cysts become inflamed, and their internal contents suppurate (purulent breast cyst).
Normally, the cyst tissue contains benign cells, although in some cases malignant ones may also be present.
As a rule, breast cysts are combined with other pathologies in the female genital area.
Causes of breast cysts
Hormonal disorders in modern women are observed very often. As a rule, hormonal imbalance consists of increased production of estrogen, the main female sex hormone. At the same time, the level of other hormones may be normal or even reduced.
As a result, the epithelium that makes up the ducts of the mammary gland grows, and the mammary gland tissue swells. In this case, some of the ducts become blocked. This is how cysts form.
It is worth noting that the hormonal system of women is neurohumoral, that is, all the processes occurring in it depend on the nervous system. With any, even the slightest negative effect on the central nervous system, a malfunction may occur in the hormonal system.
The psycho-emotional factor has the strongest influence on a woman’s neurohumoral system.
This means that the hormonal system and the development of cysts are affected by:
- mental fatigue;
- prolonged emotional stress;
- constant worries and chronic stress;
- The woman is too susceptible to any problems.
Abortions also cause no less damage to the hormonal system. They can cause a huge number of different malfunctions and diseases in the body. At the same time, frequent abortions have a direct effect on the ovaries, provoke increased production of estrogen and, as a result, cause the formation of cysts.
In addition, an increase in estrogen levels will sooner or later lead to weight gain, or even obesity. And since adipose tissue also produces estrogens, overweight women have a significantly increased chance of getting a breast cyst.
Nutrition also has a great influence on a woman’s hormonal background.
Various thermal procedures, as well as procedures that use ultraviolet light, can stimulate the release of female sex hormones.
Injuries, even the most minor ones, can provoke the formation of cysts. The risk of a cyst increases many times after surgery.
The use of hormonal contraceptives, especially if a woman chose them on her own without first consulting a doctor, can also provoke the appearance of cysts in the mammary glands.
Often, breast cysts are discovered during menopause if the doctor incorrectly administers hormone replacement therapy to a woman.
Can a breast cyst resolve on its own?
A cyst in the mammary gland can sometimes resolve on its own. However, this happens quite rarely, so you shouldn’t count on a miracle. Even small cysts almost never disappear on their own, but require the use of conservative treatment methods.
If the size of the cyst reaches 1.5 cm, then doctors perform a puncture, after which air is injected into it. With such a size of the formation, it is incredibly important to smooth out its walls.
Folk remedies and home treatment on your own are simply unacceptable in this case! So, many patients, having discovered a cyst, begin to massage it, which is not recommended. It is also unacceptable to engage in self-diagnosis and expect that education will go away on its own. Only a specialist after a thorough diagnosis will be able to carry out treatment.
Breast cysts are treated by an endocrinologist, mammologist and gynecologist. Although in some cases you may also need the help of a nutritionist, psychotherapist, neurologist and surgeon.
Why is a breast cyst dangerous?
Breast cysts are absolutely safe for the lives of patients. However, sometimes they can become infected and, as a result, fester. In more rare cases, they grow to enormous volumes and cause deformation of the mammary glands.
It is worth noting that a breast cyst can negatively affect a woman’s quality of life and interfere with normal sports activities.
Can a breast cyst turn into cancer?
Breast cyst cancer in women is diagnosed extremely rarely. At the same time, doctors often fail to find out whether the cyst itself has grown into cancer, or whether the cancer was near the cyst, and over time it simply grew into it.
However, statistics show that women who have breast cysts are slightly more likely to develop breast cancer.
Many women, upon learning about the presence of a cyst in their breast, begin to panic and fear cancer. However, this is not necessary. With timely treatment, a woman will not experience any unpleasant consequences. Moreover, the importance of treatment lies not so much in removing the cyst itself, but in eliminating the cause that caused it.
Breast cyst during lactation
Breast cysts appear quite often during breastfeeding. This type of formation is called galactocele. This is a special benign fatty cyst. The flesh of this formation is always supplemented by the thoracic lobes, which contain coagulated milk.
As a rule, such cysts develop if a woman suddenly stops breastfeeding. Although in some cases the formation appears 8-10 months after the end of lactation.
It is imperative to treat such a cyst, and only by an experienced and qualified specialist, because in the absence of therapy or if it is carried out incorrectly, the formation can cause mastitis or even an abscess.
It is worth noting that with galactocele, a woman can continue breastfeeding.
Reasons for development
Hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body is not uncommon. At such a moment, the ovaries secrete a higher than normal amount of estrogens, the main female sex hormones. This is what leads to tissue proliferation under the influence of estrogens, the epithelium of the mammary gland ducts, and swelling of its tissues. Such processes clog some ducts and form cysts.
In practice, a cyst is the main element of fibrocystic mastopathy. If the disease is diffuse in nature, i.e. equally distributed in the mammary glands, many small cysts appear. Nodular mastopathy is characterized by large nodes.
The female hormonal system is neurohumoral and controlled by the central nervous system. Any impact may cause the system to malfunction. The neurohumoral system is most sensitive to all kinds of psycho-emotional stress. First of all, the development of cysts is influenced by:
- Long-term intellectual loads.
- Constant emotional stress.
- Frequent worries and stress.
- Sensitivity to problems.
Abortion deals the biggest blow to the endocrine system. They are the ones who can cause problems in a woman’s body. Frequent abortions disrupt the functioning of the ovaries, provoke the release of large amounts of estrogens, and the maturation of cysts.
An increase in estrogen can cause excess weight, especially obesity. Since adipose tissue cells promote the production of estrogen, in obese women, the chances of developing hormone-dependent diseases increase.
Poor nutrition is another main cause of hormonal imbalance. Poor nutrition causes metabolic disorders, which sooner or later will affect the neuroendocrine system. Other endocrine glands and their work also affect the condition and activity of the mammary gland.
Any thermal procedures and ultraviolet rays stimulate the production of estrogen.
The formation of a cyst in the mammary glands can be caused by any injury. The risk of neoplasms also increases after surgery. Since breast tissue is very thin, it reacts to any physical impact. The use of oral contraceptives is a predisposing and common factor in the development of cysts.
Causes of cysts in the breast
There are a number of factors that provoke the development of cysts. The main reasons for the appearance of neoplasms:
- genetic predisposition;
- regular stressful situations;
- gynecological pathologies: endometritis (inflammation of the uterine lining), oophoritis (inflammation of the ovaries), salpingitis (damage to the fallopian tubes), adenomyosis (overgrowth of the endometrium - the lining of the uterus);
- diseases of the biliary tract, liver (cirrhosis, cholecystitis, hepatitis, cholelithiasis, fatty liver);
- disorders in the reproductive system: early menstruation, numerous abortions, late first birth, prolonged breastfeeding or lack thereof, absence of pregnancy and labor in a woman;
- diseases of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus;
- nuances of sexual life: anorgasmia, regular interruption of sexual intercourse as a method of contraception.
Classification
The following types of breast cysts are distinguished:
- Atypical cyst . In this case, a breast cyst is formed when fluid accumulates in the duct. Such a cyst has a fibrous capsule of round or oval shape of various diameters. An atypical breast cyst is a benign cyst with growths that protrude into the cavity.
- Fibrous cyst . This type of cyst occupies a central place in oncology. Such a cyst can be proliferative or non-proliferative. As a rule, such cysts develop in tissue during menopause due to hormonal imbalances. A factor in the development of fibrous cysts can also be disruptions in the functioning of the immune system, as well as disruptions in the functioning of individual organs and systems.
- Solitary cyst . This is a benign breast cyst that does not pose a threat to a woman’s health. The solitary cyst has a round shape and elastic consistency. It is a swelling that is filled with fluid. The longer the cyst exists, the denser its capsule. A solitary cyst usually manifests itself as pain in the chest, which intensifies in the second phase of menstruation. When menstruation stops, the pain subsides.
- Ductal cyst . Such a cyst can develop at any age, but most often it occurs after 48 years. A ductal cyst is a precancerous condition and accounts for 1% of all breast tumors. A ductal cyst is nothing more than an intraductal papilloma - small growths inside the mammary gland.
- Multilocular cyst . This is a multiple cyst that initially develops as a single neoplasm, but then new cysts appear next to it. This is a dangerous disease that can turn into cancer.
Symptoms
The formations in question in the mammary gland may not bother the woman at all for a long time, but as soon as the size of the cyst begins to increase, the following symptoms will occur:
- Burning, soreness at the location of the cyst, nagging pain - these signs indicate a large cyst. If the mammary gland is palpated, the presence of a cyst will be “given away” by pronounced irregularities/tubercles.
- In some cases, the cyst is manifested by discharge from the nipples, which indicates that the formation in question has a direct connection with the milk ducts.
- If the size of the cyst is too large, the breast begins to deform and the color of the skin changes, becoming red and even bluish.
- High body temperature, redness of the mammary gland, enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit area, these signs will indicate developing inflammation in the cyst cavity.
If the cyst is small in size, then it does not cause any problems for a woman in the period between menstruation, but a large cyst has pronounced symptoms, regardless of the menstrual cycle.
Are there any complications?
In fact, a breast cyst is not considered too serious a disease. The appearance of such neoplasms in medicine is not regarded as a threat to the patient’s life. In 90% of cases, you can get rid of the disease quickly and painlessly.
However, some complications are still possible. The most common of these is inflammation of a breast cyst. This pathology is accompanied by the onset of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the neoplasm, which leads to the accumulation of purulent masses. This complication is accompanied by fever, severe chest pain, as well as redness and swelling of the skin. In such cases, patients need immediate assistance from a specialist.
We should not forget that the possibility of malignant tissue degeneration in this case is also not excluded. Of course, such a complication is rare. But it is worth remembering that the presence of cysts in the glandular tissues of the mammary gland increases the risk of developing cancer. Therefore, women with this diagnosis are advised not to miss routine examinations with a gynecologist and mammologist.
On the other hand, the cyst can greatly increase in size, especially if we are talking about a multi-chamber formation. The presence of such a structure brings a lot of problems into a woman’s life, including pain, discomfort and dissatisfaction with the shape of her own breasts.
Why is a breast cyst dangerous?
A breast tumor is not life-threatening for a woman. Of course, it can reduce the quality of life with certain symptoms, but it is rarely a pathology that degenerates into a cancerous tumor. Despite this, its nodular forms are capable of stimulating a malignant tumor. Quite often, a breast cyst, taking into account the risk factors for mastopathy, and the entire danger of a malignant process, represents a background for cancer development.
According to statistics, every third woman has a cyst in the mammary gland, and many do not even know about it. Faced with the disease, representatives of the fair sex begin to panic, in fear that cancer may develop. There is no need to do this, you just need to start treatment in a timely manner. If the disease is detected in a timely manner, it is necessary to have time to eliminate the cause and carry out complex therapy.
Reviews about the treatment
Olga, 38 years old: “I encountered this disease. Everything became clear during the examination. They said that this is an early stage of the disease and should be treated immediately. Retinol was recommended. I used it as stated in the instructions. It became easier after a month. Repeated examination showed that the disease was not only stopped, but also eliminated. I am very grateful for this tool.”
Yana, 30 years old: “In the hospital I learned about the presence of this disease. I was very upset. I was advised to use beets as a compress. I performed the procedure regularly. Gradually the pain disappeared and my condition improved. Upon re-examination, it turned out that the disease had been eliminated. The medicine turned out to be very effective.”
Daria, 27 years old: “I was very upset when the hospital told me about this disease. I understood that I needed treatment immediately. Doctors advised using burdock root tincture and following a therapeutic diet. I followed their recommendations. It got easier pretty quickly. I visited the doctor two weeks later. He said that the disease was stopped and disappeared. I’m very happy about this, now I lead a healthier lifestyle than before.”
Diagnostics
Differential diagnosis of breast cysts is carried out with
- fibroadenoma of the breast
- breast cancer.
It is quite difficult to distinguish a cyst from a fibroadenoma by palpation, so additional examination methods (ultrasound of the mammary glands, mammography) are used to make a diagnosis.
Breast cancer is characterized not only by the presence of a formation, but also by changes in the skin and nipple of the affected breast, as well as enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes.
In addition to palpation of the mammary glands and examination, the diagnosis of this disease also includes instrumental examination methods:
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands allows you to distinguish a solid formation (fibroadenoma or cancer) from a cystic one, as well as study the nature of the inner wall of the cyst capsule;
- mammography – x-ray examination of the mammary glands in two projections, provides information about the size, quantity and shape of formations;
- pneumocystography provides information about the condition of the inner wall of the cyst;
- aspiration of cyst contents and histological examination.
In addition, laboratory tests are prescribed: OBC, OAM, blood for hormones and others according to indications.
Diagnosis of a cyst
In order to diagnose a medium-sized breast cyst, standard palpation is sometimes sufficient for the doctor. If the formation is smaller, then an ultrasound or mammography will be required.
These two diagnostic methods differ from each other not only in the way they are performed, but also in the results that the doctor receives. Thus, ultrasound makes it possible to clarify whether there are cystic growths inside the mammary gland, and it is also possible to distinguish between a cyst and fibroadenoma. Based on the results of mammography, a conclusion can be made about their size, shape and exact quantity.
In addition, the patient may be recommended to undergo an MRI, however, this is performed only in severe cases. After all, there are still disputes between physicists regarding the safety of this procedure for the human body. Although everywhere this method is positioned as absolutely harmless.
In this regard, before going for diagnostics using a tomograph, you should make sure that it is really needed. If the doctor is not principled in this matter, then it is better to stop at mammography or ultrasound. This will definitely relieve the body of excess stress.
A biopsy is performed when there are papillomas inside the formation. A biopsy is performed under ultrasound control. This method is necessary to enable further histological examination. Based on its results, a cancerous tumor can be suspected (if the substance taken for examination is brown or brown in color, and also if a large number of epithelial cells are detected).
Treatment of breast cyst
A breast cyst is a benign tumor that rarely develops into a malignant one. But according to statistics, it is these women who suffer from cancer in the future. Therefore, if you suspect a cyst, you should contact a mammologist or if the cyst is small, he may prescribe the following treatment:
- to eliminate hormonal imbalances, medications are prescribed to improve the functioning of the thyroid gland and ovaries;
- anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out;
- homeopathic medications can be prescribed that cause minimal harm to the female body and cope well with this ailment;
- drugs to enhance immunity;
- painkillers and decongestants;
- psychotherapy.
During the treatment period, the patient is under constant supervision of a doctor, who determines whether there are positive changes from the treatment or not. If the cyst does not resolve, then a decision is made about surgical intervention. At the same time, it is necessary to eliminate inflammation in the body.
After treatment, the patient must take additional medications to prevent inflammation, immunostimulating, and hormonal medications.
Treatment
Photo: medcentr-diana-spb.ru
How to treat a breast cyst:
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- the use of drugs that normalize hormonal levels;
- psychotherapy;
- the use of medications that improve the functioning of the thyroid gland and ovaries;
- resorption therapy;
- surgical removal of the tumor;
- use of homeopathy;
- sclerotherapy of breast cysts;
- vacuum biopsy;
- balanced diet and an active lifestyle.
Treatment of breast cysts with a variety of medications or folk remedies at home is possible if it does not reach a large size. During palpation, the formation should not be felt. Such cysts are diagnosed exclusively using ultrasound or mammography.
The woman is examined comprehensively. Several specialists are involved in this - mammologist, gynecologist, endocrinologist, oncologist, surgeon. The treatment method depends on the size of the tumor, the age and health of the woman. The presence of factors that can improve or worsen the current situation is also taken into account. Only after this is a decision made on methods of treating cysts in the mammary gland.
Is it necessary to treat a breast cyst?
A breast cyst is a benign neoplasm that rarely degenerates into malignant. But still, women who suffer from this disease are more susceptible to cancer. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you need to contact a mammologist. If these breast formations are small and do not pose a danger, the following comprehensive treatment is prescribed:
- medications are used that normalize the activity of the thyroid gland and ovaries. This allows you to eliminate hormonal imbalances, which may cause the appearance of cysts;
- anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed;
- homeopathy in the presence of mammary gland cysts is one of the non-hormonal treatment methods that shows good results and does not harm the woman’s body;
- hormone replacement therapy, which eliminates the deficiency of certain hormones and the excess of others;
- drugs with immunomodulatory effects are used;
- decongestants and painkillers are prescribed to eliminate the main symptoms of the disease;
- psychotherapy is used, which is aimed at normalizing the psycho-emotional state of a woman. Often it is chronic stress that causes this disease;
- resorption therapy is used.
During such conservative treatment with medications, the doctor periodically performs additional examination of the breast. In this way, the dynamics of the process are determined. It is important to understand how effective this therapy was. If the cysts have enlarged, most often a decision is made about surgical intervention. It is important to eliminate the source of inflammation, which is the source of infection in the body.
After using any of the methods of cyst removal, the woman still takes medications for some time that help minimize relapse - anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating, hormonal and others.
Sclerosis of breast cyst
This treatment method is an excellent alternative to surgery. When used, the mammary gland is minimally injured and neoplasms are effectively eliminated. It is shown if:
- neoplasms no larger than 2 cm in size;
- recurrence of cysts in the mammary gland;
- cystic formations with anechoic appearance;
- unilocular cysts.
Contraindications to this procedure are the presence of neoplasms that contain dense particles or bone tissue growths inside. In this case, it is better to remove them surgically. Also, sclerotherapy is not recommended if there is a suspicion of the development of oncology.
Sclerotherapy is performed by a surgeon or mammologist. This procedure includes several steps:
- puncture of the formation is performed through the skin of the mammary gland. It is done under general or local anesthesia and under ultrasound control, since this procedure is quite painful;
- aspiration of breast cysts occurs - pumping out of accumulated fluid;
- injection of an antiseptic into a breast cyst. Special sclerosant preparations are also used. They promote gluing of the neoplasm, which eliminates relapse.
After taking fluid from the cyst, it is sent for cytological analysis. The presence or absence of a malignant process in the mammary gland is determined. If all is well, the woman should undergo a preventive examination every six months by a mammologist, endocrinologist and gynecologist to monitor the dynamics of recovery. In practice, there are cases when cysts develop again, which requires taking appropriate measures.
Removal of a breast cyst
Removal of a cyst in the mammary gland is indicated in the presence of the following factors:
- formation of multilocular cysts;
- if breast cancer is suspected;
- in the presence of a large number of cystic formations;
- if the neoplasms have thickened walls;
- when there are epithelial growths in the cyst cavity.
Sectoral resection is used when tests indicate the presence of a malignant tumor. In this case, the cyst and surrounding breast tissue are removed. The resulting material is sent for cytological analysis, which accurately determines the presence or absence of oncology.
Removal of a cyst from the mammary gland most often occurs under general anesthesia by an experienced surgeon. This is done under ultrasound control with preliminary marking. This reduces trauma to the breast because the incisions are made accurately and are of a minimal size. After such a procedure, in case of successful recovery, when the woman followed all the doctors’ recommendations, you can even breastfeed.
Complications of sectoral resection or conventional removal of a cystic formation are:
- wound suppuration:
- formation of hematomas;
- breast deformation.
Despite this, removal of cysts is one of the best methods of treating this disease, especially if the formation reaches a large size.
Vacuum breast biopsy
Vacuum biopsy can be performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, depending on the nature of the formation. If there is a risk of developing malignant tumors or cysts, then this procedure is performed to collect tissue samples from the breast.
Vacuum biopsy is performed under the guidance of ultrasound or x-ray equipment. The advantage of this technique is that in a short period of time in one procedure you can obtain a large volume of tissue for examination or remove a cyst. Vacuum biopsy is less traumatic than traditional surgery. Moreover, it can be performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the woman’s condition and the nature of the formation in the breast.
Most often this procedure is carried out as follows:
- The woman sits on a couch, where her breasts are treated with a special antiseptic solution.
- Under ultrasound guidance, a puncture is made using a special biopsy needle in the area of the breast where the cystic formation is located.
- With the help of a vacuum, the necessary tissues are suctioned, and a special blade excises them from the mammary gland.
This treatment method should not be used if the development of cancer has been confirmed.
Prevention of breast cysts
To prevent the development of cysts and other formations in the mammary gland, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- choose underwear that fits your size, does not pinch, does not rub, and supports the gland well. This is especially true for those with large breasts, since in this case the risk of sagging increases;
- do not abuse alcoholic beverages or caffeine. In order not to harm your health, you can drink no more than 150-200 g of dry red wine per day and 1-2 cups of coffee;
- stop smoking, as it negatively affects both the condition of the breast and the body as a whole;
- reduce the amount of salt in your daily diet. In addition, it retains fluid in the body and negatively affects kidney function;
- stick to a balanced diet - eat small portions 5-6 times a day, don’t overeat at night, don’t forget about breakfast. You also need to give up smoked foods, too fatty foods, fast food, and minimize the amount of confectionery and fried foods. Your diet should consist of vegetables and fruits depending on the season, lean meats, fish, cereals, vegetable fats, milk and other healthy foods;
- play sports and do exercises in the morning;
- try to avoid injury to the mammary gland;
- If possible, minimize the use of hormonal drugs. If your doctor prescribed them to you, then follow his instructions completely and do not change the dosage: either down or up.
According to recent studies, women who breastfed for at least 2-3 months are less susceptible to a variety of breast diseases. Therefore, giving birth to a child and breastfeeding until 1 year of age will be an excellent prevention for the formation of cysts.
It is also necessary to regularly undergo preventive examinations with a mammologist 1-2 times a year (regardless of age). Identifying small cysts will help to avoid surgical intervention and quickly get rid of this problem using conservative treatment methods.
Drug treatment
Treatment of breast cysts without surgery is possible if the formation has a smooth inner surface and responds well to medication. In this case, it is necessary that no atypical cells are found in the aspiration material after a fine-needle biopsy - a sign of a cancerous tumor.
Drugs for the treatment of breast cysts act on the main links in the pathogenesis of the disease:
- sedatives (valerian, motherwort, Novo-passit) and adaptogens (schisandra, Eleutherococcus, Rhodiola rosea) in courses of 4 months with a break of 2 months, the duration of treatment is 2 years;
- vitamins A (has an anti-estrogenic effect), E (increases the effects of progesterone), B6 (reduces the concentration of prolactin in the blood), P and C (improves microcirculation and relieves tissue swelling);
- hepatoprotectors, for example, the herbal preparation Hofitol, which protects and restores liver cells, improves fat metabolism, and increases the emotional background;
- diuretics a week before the start of menstruation to prevent engorgement of the gland - lingonberry, kidney tea, Hypothiazide, Triampur, small doses of Furosemide as prescribed by a doctor;
- hormonal therapy, in particular, the use of gestagens for local use (Progestogel gel), and, if necessary, drugs in tablet form (Utrozhestan), implantable and long-acting injectable forms (Norplant, Depo-Provera);
- According to indications, Danazol, combined oral contraceptives, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (Zoladex), dopamine agonists (Parlodel) can be prescribed.
Previously, iodine preparations were widely recommended, but due to the spread of thyroid diseases, in which these drugs can disrupt the balance of thyroid hormones, the use of iodine is abandoned or prescribed only after consultation with an endocrinologist.
After six months of conservative therapy, mammography or ultrasound examination is repeated. If sclerosis of the breast cyst has occurred, that is, its walls have collapsed, there is no cavity, conservative treatment is continued. If aspiration of the cyst was ineffective and fluid has accumulated again, surgery is prescribed.
Can a cyst in the mammary gland resolve on its own and how to treat it?
The materials are published for informational purposes only and are not a prescription for treatment! We recommend that you consult an endocrinologist at your medical institution!
Co-author: Galina Vasnetsova, endocrinologist
A breast cyst is a hollow formation filled with fluid. Self-examination at the initial stage of cyst development does not always give results. A neoplasm can be diagnosed after a woman undergoes an ultrasound. Timely consultation with a doctor allows you to select effective drug treatment.
Breast diseases are becoming increasingly common and are experienced by many women of all ages. A breast cyst is a pathological formation that can be multiple or single. The neoplasm has the shape of a capsule filled with liquid. It is impossible to independently diagnose a lump in the first stages of its occurrence, so if you experience a deterioration in your health, you should consult a doctor.
Cysts are clearly visible on breast ultrasound
Characteristics of the disease
A cyst in the chest is a stationary spherical compaction of various sizes, causing discomfort and even pain.
For your information. A solitary breast cyst is a neoplasm that is localized in one breast, but multiple lumps can affect both breasts, in which case we should talk about multiple cysts.
The dimensions of such a seal may vary. In the initial stages, the cyst reaches only a few millimeters in diameter, it cannot be felt with fingers, and it is detected only with the help of ultrasound. If the formation has already reached several centimeters in size, then it can be felt independently without the help of additional examinations.
A preventive examination by a mammologist allows you to monitor your health and identify the disease at the initial stage of its development.
Cysts in the mammary glands are localized in the ducts and have the following characteristics:
- The neoplasm is a capsule filled with non-inflammatory fluid.
- The capsule is formed due to the expansion of the mammary gland ducts and the gradual accumulation of a specific secretion inside it. If a cyst occurs at the end of the milk duct, then after some time it becomes isolated and is no longer connected to the duct.
- The neoplasm inside is filled with liquid, which can have a different color.
By the color of the discharge from the nipple, a specialist can determine how long ago the tumor appeared in the breast
- The density of the tumor capsule is directly related to the duration of its development. The walls of a seal that has just begun to develop will be thin; later they become denser.
- Symptoms of a breast cyst may not appear at all at first; after some time, an inflammatory process develops, which may be accompanied by suppuration.
- The disease is most often accompanied by a number of diseases provoked by hormonal imbalance in the body.
- The size of the cyst may vary at different stages of its development. In advanced cases, a large tumor becomes the cause of deformation of the mammary gland. Numerous cysts lead to polycystic disease, with more than half of the entire breast affected.
Note! Women aged 35 to 60 who do not have children are at risk of developing breast cysts.
- The cyst capsule usually contains only benign cells, but in some cases malignant neoplasms can develop from it.
Causes of the disease
Experts say that the main reason for the development of the disease is a sharp change in hormonal balance. There are several main factors that cause the development of cysts:
- Mastopathy leads to the formation of a cyst in every third woman.
- Those women who have not given birth before the age of 30 are also at risk.
- An excess of estrogen in the body also increases the possibility of developing a cyst. Some experts argue that this is directly related to long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, which a woman uses without prior examination, conducting the necessary tests and consulting a doctor. Other doctors refute this theory. The possibility of malignant formations in the breast after taking oral contraceptives persists for more than 5 years.
Uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives is strictly prohibited. The drug is individually selected by the doctor after the woman has undergone the necessary examinations and tests.
- During menopause, many women are prescribed hormone replacement therapy - this can also cause the development of cysts. The drugs directly affect breast tissue, often triggering the development of new tissue and increasing cell growth. To avoid unpleasant consequences, during this period women are recommended to undergo a preventive examination by a mammologist and x-ray monitoring once every six months.
- The emotional and psychological state of a woman is also directly related to the possibility of developing a cyst. A state of constant stress causes hormonal imbalance.
Note! You can stabilize your psycho-emotional state by taking sedatives. It is not recommended to use such drugs on your own; they are prescribed by a doctor after examination. Most often, therapy includes taking motherwort and valerian tincture.
Taking sedatives based on herbal components does not affect the level of hormones in the body and allows you to normalize your emotional state in a short time
- Disruption of metabolic processes can cause the appearance of a neoplasm. Sudden weight gain causes hormonal imbalance. To normalize the condition, special attention should be paid to proper nutrition and acceptable physical activity.
- Thyroid disease is another cause of breast cysts.
The strongest hormonal stress for the body is abortion, after which the functioning of almost all organs occurs. It can cause cysts to form in the breast.
- Osteochondrosis of the spine is another reason for the possible appearance of a cyst.
Note! One of the reasons for the appearance of a tumor in the breast may be a disruption in the functioning of the gallbladder, as well as the biliary tract.
Symptoms of the disease
Cyst formations in the mammary gland may initially be asymptomatic. Only when the lump increases in size does it cause pain and discomfort in the chest. A mammologist can diagnose the presence of a neoplasm after examination. Pain in the mammary glands due to a cyst bothers a woman only during menstruation, but it can disappear after a short time.
A gradual increase in the size of the compaction provokes compression of the tissues around it. During this period, the woman almost constantly feels discomfort and periodic pain in the chest.
Experts also identify a number of other characteristic symptoms that accompany this disease:
- Burning and pain in the place where the cyst is located. A woman may feel a nagging, aching pain. The tissue surrounding the tumor gradually deforms and becomes uneven.
- Another characteristic symptom is nipple discharge, which can be of different colors.
- Pain from a breast cyst most often appears before the onset of menstruation. A large tumor constantly causes discomfort.
- The breast begins to gradually deform if the lump has increased significantly in size.
A large tumor can cause the skin of the breast to change color. You can observe redness in the area where the cyst is located; in advanced situations, the skin takes on a bluish tint.
- The inflammatory process developing in the neoplasm is accompanied by elevated body temperature, redness of the skin of the chest and enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes.
- In some cases, a cyst can transform into a malignant formation, breast cancer.
Diagnosis
At the appointment, the doctor examines the patient, collects anamnesis and prescribes the necessary examination. A medium-sized lump can be easily felt during palpation; a small-diameter cyst can only be diagnosed using ultrasound. If it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis, a woman should undergo a breast MRI.
A puncture of a breast cyst is prescribed by a specialist in order to study the composition of the cyst cells and select the correct treatment. During the procedure, the doctor punctures the cyst and takes out its contents. The resulting biological material is sent for cytological examination - this allows us to exclude the presence of malignant cells.
Breast ultrasound allows you to diagnose the development of a neoplasm in the early stages, this allows the doctor to select effective treatment therapy and speed up the recovery process
Note! After the puncture, a woman may experience bleeding in the area of the breast puncture. It is forbidden to take painkillers containing aspirin. You can reduce swelling of the mammary gland by applying a piece of ice to it.
Treatment
Treatment of breast cysts without surgery gives good results if you consult a specialist in a timely manner. Therapy is carried out using homeopathic medicines, which are combined with each other. Mastodinon, a product developed based on natural ingredients, may be prescribed. The drug suppresses the production of the hormone prolactin. The result of this therapy is a reduction or complete cessation of cell growth in the breast.
Treatment of breast cysts is also carried out using drugs containing iodine - Iodomarin, Iodaktiv. They help normalize the functioning of the thyroid gland. If necessary, herbal medicines (dietary supplements) are also used - Fitolon, Indinol, Klamin. They have an anti-inflammatory effect and help normalize estrogen levels in the body.
On the recommendation of a doctor, taking medications is supplemented by taking herbal decoctions
Doctors will advise how to treat breast cysts using herbal remedies. A decoction should be prepared from dry mint leaves, valerian and chamomile flowers, and fennel seeds. The components should be taken in equal proportions, pour boiling water over them and leave until cool, then strain. Take half a glass 3 times a day. The decoction will serve as an addition to taking medications.
To relieve pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - Diclofenac, Dicloberl, Nimesulide, etc. If necessary, plant-based sedatives are prescribed - Tenoten, valerian tincture, motherwort.
They supplement medication and herbal medicine with vitamin complexes. This allows you to normalize the functioning of the entire body.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes hormonal treatment in small dosages. Duphaston, Progestogel, Jeannine can be used. Such medications can be prescribed after determining the hormonal background of a woman’s body.
Note! It is strictly prohibited to use hormonal drugs on your own or change the dosage of medications prescribed by your doctor. This may worsen the course of the disease.
Conclusion
A breast cyst is a hollow formation in the breast filled with fluid. Its timely diagnosis allows the doctor to select effective therapy and quickly relieve the woman of the problem. Breast cysts respond well to treatment, so when the first alarming symptoms appear, you should definitely go to the doctor, undergo an examination and follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Paying attention to your health is the key to good health.
Co-author: Galina Vasnetsova, endocrinologist
Rate the material
pozhelezam.ru
Nutrition
The diet of women who have a cyst should be adjusted. It has been proven that in some patients cysts are sensitive to the consumption of chocolate, coffee, tea and other products containing xanthines. After excluding them from the diet, the well-being of such patients improved, in particular, pain in the gland before menstruation ceased to bother them. However, another part of the patients with cysts did not respond to such changes. Therefore, it is worth limiting the listed products for 2-3 months, and if there is no effect, then they will not harm you, of course, with moderate use.
Patients with breast cysts need to normalize the condition of the liver and biliary tract and lose weight. They are recommended to follow diet No. 5 with a limit on fried and fatty foods and animal fats. It is recommended to steam food with a predominance of fish, dairy products, and vegetables (except legumes and cabbage).
It is necessary to normalize intestinal function and avoid constipation. For example, oat bran will help with this; it is very useful to eat 100 grams per day. If eating them in their pure form is not very pleasant, you can add bran to porridge or a glass of kefir.
You should wisely limit the amount of calories and reduce the salt content in your food. This will help reduce the severity of premenstrual syndrome and chest pain.
Laparoscopic cyst removal
Modern medicine is often faced with the impossibility of curing the disease in question using therapeutic methods. In this case, the woman may be prescribed surgical removal of the breast cyst, but there is no need to panic - such interventions are carried out with preservation of the organ, so there will not be any aesthetic/moral inconvenience.
What you need to know about the operation:
- The intervention is carried out using anesthesia, which can be general or local - this is determined on an individual basis. During the operation, an anesthesiologist is always present with the patient.
- Small measurements are made on the chest wall to provide access to the formation. A laparoscope with a built-in video camera is inserted into one incision, and a special instrument designed specifically for the operation is inserted into the other.
- The image is transmitted to the monitor, which allows surgeons to control their own work - puncturing the cyst, drawing out fluid from it and introducing a special solution that destroys the walls of the formation.
Laparoscopy is considered a full-fledged surgical procedure, so the patient must prepare for it - pass all tests, undergo an ECG and refrain from eating 8 hours before the appointed hour. This method of surgical treatment of the disease in question has great advantages:
- minimal trauma;
- no complications (in 98% of cases);
- small, miniature incisions remain on the mammary gland;
- wounds after surgery heal very quickly.
Medicine knows of cases when a breast cyst resolves on its own, but in any case it needs to be treated! You cannot hope for a miracle and wait for an independent recovery - the resorption of a cyst is an exception, not a pattern. A woman should not rely on traditional medicine, although it will be useful for her to take herbal decoctions that increase immunity. It is strictly forbidden to make compresses, as this can provoke the growth of formation, although herbal lotions are quite acceptable. But any appointments must be made by a mammologist - from diagnostic procedures to surgical intervention. And a woman should not break this rule, because the risk of a benign tumor degenerating into a malignant one remains very high.
Does a breast cyst resolve on its own?
It is quite a rare occurrence when a mammary cyst resolves on its own, therefore, the disease should not be started. Even small cysts do not resolve on their own, but are treated conservatively. If the cyst is 1.5 centimeters in size, then a puncture is prescribed to collect the contents and introduce ozone or air into the cavity. With a given size of the cyst, it is necessary to smooth out its walls.
Any self-medication (herbs and compresses), in the hope that the cyst will resolve on its own, is unacceptable. Only a doctor prescribes treatment, carefully monitoring the dynamics of the cysts. Self-treatment without a diagnosis is also unacceptable. Experimenting with your health in the expectation that the lump will resolve is unacceptable.
Is it possible to massage the mammary gland?
The mammary gland has very delicate tissues and it is impossible to perform an intense massage of the breast in order to squeeze out fluid through the nipple, it is very dangerous, the mammary gland should not be touched again, let alone intensively massaged. Under no circumstances should this be done.
Try not to injure the mammary glands with underwear, try to prevent bruises, treat the skin on your chest with care, as you age, you can lubricate it with olive oil, this will make it more elastic and not so dry. It’s a completely different matter if a woman has given birth and her breasts are filled with milk 2-3 days after birth, this is an exception when massaging is simply necessary to avoid stagnation and lactation mastitis.
Are saunas and tanning allowed if you have a breast cyst?
Almost all doctors are now talking about the dangers of a strong tan. It is not worth being topless in the sun or sunbathing in the middle of the day, when the sun is especially active. Lovers of saunas and baths also need to be careful. Overheating of the body not only promotes the growth of cysts, but also gives impetus to the development of malignant processes (not only in the breast, but also in many other organs).
Removal of the tumor
If conservative treatment does not produce results, sclerotherapy is initially prescribed, which involves puncture followed by injection of sclerosant. This technique will be justified only when simple cysts are detected, in which there are no malignant processes or papillomas. During puncture of the cyst, it is pierced with a thin needle, which sucks out the entire contents of the capsule. Instead, it is filled with air or ozone; previously, ethyl alcohol served as a sclerosant, but the use of such a substance is considered unsafe for the health of patients and is fraught with the development of tissue necrosis, so the use of air would be preferable. A puncture is also performed when a parietal cystic tumor is detected; the procedure allows one to determine the presence of atypical cells in the aspirate. If the oncological process is not confirmed, the woman is offered to remove the cystic formation in the mammary gland through a vacuum biopsy. This procedure takes no more than 30 minutes and is done under local anesthesia.
If the presence of atypical cells in the tumor is confirmed or there are multiple formations in the breast, and other treatment methods are ineffective, they are removed during surgery. Depending on the patient’s condition, either low-traumatic laparoscopy or extensive surgery, up to resection of the entire gland followed by prosthetics using a silicone implant, may be prescribed.
If laparoscopy is prescribed, the patient is immersed in general anesthesia, a small incision is made on the chest wall, where special instruments are inserted, and an optical device is inserted into the second puncture, the image from which is shown on the computer screen. Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a series of diagnostic procedures and does not eat for about 8 hours. This is a low-traumatic procedure, after which the wounds heal quickly, and the likelihood of complications is minimal.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies is advisable only as an adjuvant therapy during drug treatment. With their help it is possible to alleviate symptoms. Several effective recipes:
- St. John's wort infusion. To prepare, you need to take 25 g of dry grass, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for 3 hours. Then strain and use to apply a compress.
- Compress made from cabbage and butter. To prepare, take a fresh cabbage leaf and brush it with melted butter. The compress should be secured with a bandage and placed on the affected area of the chest overnight.
- Medicine for oral use. Used as an antioxidant. 10 cloves of garlic must be minced and mixed with 200 ml of olive oil. Take 1 tsp. within a month.
- Soothing mint tea. It should be brewed at the rate of 1 tsp. mint per glass of boiling water.
All of the above remedies can be prepared at home. However, before using them, it is recommended to consult your doctor.
Non-drug treatment of cysts
Physiotherapy
A breast cyst can be treated with physical therapy, but such a program should be approached with great caution. The main condition is the absence of malignant neoplasms, pain and swelling.
For treatment, two methods can be used:
- Electrophoresis - used in low doses and under the strict supervision of the attending physician. During the procedures, medications are applied to the skin, which, under the influence of weak electrical impulses, are absorbed into the parenchyma of the gland. In 10-15 sessions, swelling and inflammation are relieved, immunity is increased, and with full conservative therapy, cysts resolve.
- Radon baths - before using these procedures, a woman should definitely visit a doctor; if there is a risk of tumor formation, treatment is excluded. In other cases, such physiotherapy will be beneficial - it will relieve pastiness, activate blood flow, and create conditions for the resorption of compactions.
Other physical procedures are strictly prohibited. If necessary, they can be replaced with therapeutic exercises.
Exercise therapy
If the disease is in remission, physical therapy can be included in the program. Exercises should be light and not overload a weakened body.
There are two types of exercises you can do at home:
- Wall push-ups are done measuredly and accurately, with a straight back and straight legs. It is optimal to do 2-3 approaches 5-8 times.
- Raising arms fastened into a lock - perform with moderate effort for 1-3 minutes.
These exercises are aimed at training the pectoral muscles and activating blood circulation.
Prevention
Although a cyst is not as dangerous to a woman’s health as a malignant tumor, it must be treated. And in order to prevent its development or at least minimize the risk, you need to follow the rules of prevention.
- First of all, it is worth remembering the need to regularly visit specialists such as a mammologist and gynecologist. You need to undergo examination at least twice a year.
- If there is a genetically determined predisposition to the development of tumors, it is necessary to additionally undergo ultrasound and mammography.
- To avoid the formation of cancer cells, do not expose the breast area to direct ultraviolet rays.
- Also, for prevention, hormonal diseases should be treated in a timely manner, and when taking oral contraceptives, periodically consult a gynecologist.
- It is important to avoid stressful conditions and strengthen the immune system.
- From time to time, in addition to attending routine examinations, you need to conduct independent diagnostics. To do this, you need to gently, carefully palpate the mammary glands, checking whether new growths have appeared in them. You should also pay attention to the condition of the skin of the breast, its shape, and symmetry. It is also necessary to monitor whether there is any discharge from the nipples.
The fundamental factor in the formation and growth of mammary cysts is hormonal fluctuations. The female body is very susceptible to various changes and reacts to this by changing hormonal levels. To minimize the risk of tumors, you need to carefully monitor its condition, especially if there is a congenital tendency to form tumors. An integral component of the preventive system also includes giving up bad habits, adhering to the principles of a healthy lifestyle, and regular visits to specialists for routine examinations.
Thyroid cyst: symptoms and treatment Bartholinitis Pancreatitis Hypothyroidism Prostate adenoma - what is it? Symptoms and treatment Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis)
Hormonal drugs for mastopathy
These medications are prescribed only by a gynecologist (or mammologist). He also selects an individual dosage. It should be remembered that thoughtless and incorrect use of hormonal drugs can lead to disastrous consequences. Hormonal drugs include:
- Tamoxifen is an effective and inexpensive drug for the treatment of breast cysts.
This drug belongs to the antitumor antiestrogenic drugs. It is used mainly by women during menopause both for fibrocystic mastopathy and breast cancer. The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation (for this you need to undergo a gynecologist examination in a chair), as well as with a history of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Tamoxifen has many side effects, so if your legs begin to swell, you experience shortness of breath or bleeding from the genital tract, you should stop treatment and consult a doctor. When taking tamoxifen, the likelihood of becoming pregnant increases, so women of childbearing age are recommended to use reliable condoms during treatment. The course of treatment is long, at least 3 months, until stable regression (reduction) of cystic cavities under ultrasound control.
- Femoden or Gastarella is a modern hormonal contraceptive drug that contains estrogen and gestagen.
The use of this drug for cystic mastopathy gives almost 100% recovery. Clinical studies have shown that cysts have decreased significantly after just 2 months of using the drug. These tablets are prescribed only to young women. During menopause, the use of hormonal contraceptives of this group is prohibited. Taking these drugs is contraindicated in cases of deep vein thrombosis, angina pectoris, pulmonary embolism and a history of stroke, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis, renal and liver failure, hormone-dependent malignancies, obesity, pregnancy and lactation. There are also a huge number of side effects. In connection with the above data, treatment is prescribed only by a gynecologist, and regular examinations are carried out, at least once a month.
- Orgametril is an expensive and very effective hormonal drug for the treatment of fibrocystic mastopathy.
It has practically no side effects characteristic of other hormonal drugs. The list of contraindications is also much smaller: hypertension and type 1 diabetes, pregnancy. The course of treatment not only reduces the size of cysts, but also reduces the risk of developing cancer and cystic diseases of the breast and genital organs for 5-7 years, i.e. has a preventive effect.