The female body faces changes every month. Hormonal levels change, which often affects the condition of the fair sex and the occurrence of certain problems and deviations from the norm. One of the disorders in the reproductive system is bleeding between periods, heavy and not very heavy. Many women face such unpleasant situations. However, few of them know that this is not always dangerous. Therefore, before you start to panic and run to the gynecologist, it is better to understand and find out what caused the blood.
Discharge in the middle of the cycle often causes anxiety
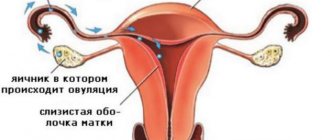
When discharge is a result of ovulation
Intermenstrual bleeding in the middle of the cycle is often observed in girls who have increased levels of estrogen and lutein-stimulating hormone, which are responsible for the release of an egg from the ovary. Bleeding is usually observed 14–16 days after the start of the menstrual cycle. These few days are the period of ovulation, when the egg is ready to “multiply”.
If this is the reason, blood is released in very scanty quantities and women do not feel pain or other signs of discomfort. Occasionally, slightly unpleasant but tolerable pain may occur in the left or right lower abdomen, depending on which ovary the egg comes from.
https://youtu.be/-HllvvAQArw
What you should know about discharge with traces of blood outside of your period
The appearance of bloody vaginal discharge in the interval between regular periods may represent a variant of the norm, but at the same time, in some cases, serve as a signal of problems in the woman’s body. These discharges usually differ from metrorrhagia (another name is intermenstrual bleeding) in their scarcity and relative short duration, and most often do not require the use of additional hygiene products. During this period, a woman can easily get by with pads intended for daily use.
In approximately every third woman of reproductive age, such discharge occurs with a certain frequency in the interval between regular periods. Here it must be said that they are usually not accompanied by a temperature reaction or pain and, as a rule, do not lead to a significant deterioration in the woman’s general well-being.
Physiological secretions
In the following cases, a woman should not worry, since discharge that appears in the middle of the cycle can be explained by physiological conditions:
- Scanty spotting, brownish in color, usually appears one or two days before the start or the same period of time after the end of menstruation. They are explained by preliminary rejection of the endometrium (the mucous layer lining the uterine cavity from the inside) or residual removal of blood after the completion of menstrual bleeding.
- Minor spotting on the 10th–14th day of the cycle. They can be associated with the ovulatory release of an egg from a mature follicle, are explained by changes in the concentration of estrogen, have a small volume, and usually disappear in one to two days.
- Bloody discharge of low intensity. They may be the result of taking certain contraceptives (means to prevent unplanned pregnancy) or placing an IUD inside the uterus to prevent conception. They are explained by changes in hormonal levels. The norm is the persistence of discharge with traces of blood during the first two months, while the hormonal levels are being updated.
- The discharge of a small amount of blood from the vagina can be observed after sexual intercourse due to insufficient production of moisturizing mucus, and can also be based on a discrepancy in the sizes of male and female genitalia, or excessive sexual activity of the partner. It should be noted that repeated discharge mixed with blood after sexual intercourse should necessarily alert a woman and force her to consult a gynecologist, because these symptoms may serve as evidence of the onset of the development of cervical pathologies.
- The appearance of intermenstrual vaginal discharge with traces of blood can also be observed against the background of stress, a change in location, or a sudden change in climatic conditions. In such a situation, we are talking about a temporary disruption of the regularity of the monthly cycle.
Spotting in the middle of the cycle is normally light, practically painless, and does not have an unpleasant odor.
Sometimes the appearance of spotting before the expected start of the next menstruation may be the first and at that time the only sign of pregnancy, which is caused by implantation of the egg after fertilization into the mucous layer of the uterus . It usually occurs on the 6th–7th day after fertilization, when neither the results of an ultrasound nor an examination by a gynecologist allow one to suspect the fact of pregnancy. A pregnancy test may also be negative due to a fairly low level of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin, a hormone whose detection in the blood allows confirmation of pregnancy).
In subsequent stages of pregnancy, the appearance of any bloody vaginal discharge is a serious symptom and requires immediate attention to a gynecologist.
Bloody discharge as a sign of pathology
The development of pathological processes in the female body can be suspected if the discharge:
- quite abundant;
- lead to a drop in hemoglobin levels;
- accompanied by pain of varying degrees of intensity;
- have an unpleasant odor;
- observed over a long period of time;
- are noted regularly.
Similar bloody discharge may occur in the following conditions:
- Inflammatory processes affecting the female genital organs, which are usually caused by gram-positive or opportunistic microflora (in particular, E. coli), are characterized by the appearance of: quite pronounced nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- an increase in body temperature to 38–39 degrees;
- changes in the nature of the discharge - they can become serous-purulent (cloudy, yellowish-greenish) and bloody in nature as a result of damage to the vascular wall by the inflammatory process.
- have a brownish color;
- sexual contact;
Cervical erosion is an ulcerative defect of the vaginal mucosa of the cervix
A separate point should be made on the sudden appearance of bleeding in women during the premenopausal period. In this condition, the duration of menstrual bleeding is reduced, while the intervals between them increase, and in such a case, the appearance of brownish discharge of a liquid consistency may be observed against the background of delayed menstruation. Such bleeding can be observed for several weeks and is a consequence of hormonal changes in an elderly body. In this situation, a woman should be concerned and wary of the fact that the discharge described above appears against the background of a long (more than a year) menopause, accompanied by a complete absence of menstruation.
Video: possible causes of vaginal discharge with traces of blood in the middle of the cycle
Could the blood be the result of progesterone deficiency?
Insufficient production of progesterone by the corpus luteum can also cause bleeding between periods. This happens if the function of the corpus luteum is reduced, and it is not able to produce a sufficient amount of progesterone necessary for the second - luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
If your blood levels of progesterone are low, problems may arise.
Such disorders are not often diagnosed, as they are easily confused with other pathologies and forms of hormonal imbalance.
This is useful: methods for restoring hormonal balance.
Progesterone deficiency is mainly detected in young girls aged 18 to 25 years.
Endometrial pathologies
In some women, intermenstrual bleeding occurs due to diseases of the endometrium (the inner mucous membrane of the uterine body).
Endometriosis
This is a common gynecological pathology characteristic of women of reproductive age. This disease is based on hormonal disorders, due to which there is excessive production of estrogens, which support the first half of the menstrual cycle, and insufficient production of progesterone. It is under the influence of estrogens that intermenstrual bleeding (sometimes very heavy) may appear.
Endometrial polyps
Endometrial polyps are benign neoplasms on a stalk, penetrated by blood vessels. According to most experts, they are one of the manifestations of hyperplasia (growth of the inner layer of the uterus). Polyps occur against the background of hormonal and non-hormonal disorders, and can also cause intermenstrual spotting and bleeding.
What hormonal diseases can there be?
If women experience bleeding between periods, they may be caused by hormonal disorders associated with:
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland, since the reproductive and endocrine systems are closely interconnected;
- starting or stopping oral contraceptives;
- regular stress, emotional turmoil;
- sudden weight loss, weight gain;
- pregnancy;
- endometriosis – excessive production of estrogen and progesterone deficiency and others.
Hormonal imbalance can occur for a variety of reasons and lead to the most unexpected and unpleasant consequences, including bleeding between periods.
Diagnostics
To identify the cause of bleeding and spotting in the middle of the cycle, a woman is prescribed a comprehensive examination. In addition to the standard examination, questioning and smear, an ultrasound is performed.
Attention! An examination may reveal damage or tears to the cervix and vagina. If genital injuries are detected, no other examinations are required.
In other cases, if in the middle of the cycle there is noticeable discharge streaked with blood, the doctor may perform a colposcopy of the cervix and take a biopsy of its tissue. If necessary, the following diagnostic procedures are also prescribed:
- hysteroscopy,
- diagnostic curettage,
- MRI,
- blood tests, including coagulation tests, hormone tests and urogenital infections.
If you have an unpleasant vaginal odor or yellow-green discharge, you should first be checked for infectious diseases.
When blood indicates vaginal damage
The reason why discharge appears in women between periods may be damage to the vagina. A similar problem occurs in a number of cases:
- during sex;
Blood after intimacy may indicate damage to the vaginal mucosa
- after an abortion or other gynecological surgery;
- when using certain contraceptives.
Most often, such bleeding is light and does not pose a serious danger. However, if additional unpleasant symptoms occur, for example, severe abdominal pain or any other pain, as well as heavy discharge or prolonged bleeding, you must visit the gynecological office and see a doctor. Only a gynecologist can determine how dangerous the situation is and say what caused such a problem.
What other reasons could there be?
There are other causes of bleeding between periods:
- inflammation of the endometrium due to the spread of pathogenic microorganisms in the uterus;
- infectious diseases of the cervix and vagina;
- excessively high dosage of contraceptives;
- use of intrauterine contraception;
- the formation of benign and malignant tumors (fibroids, fibroids and others) on the walls of the uterus;
- the appearance of endometrial polyps.
Bleeding is possible with an overdose of birth control pills.
Any impact on the female genital organs can lead to bleeding in the middle of the menstrual cycle and cause pain and discomfort.
To avoid serious complications, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist regularly. This will allow you to identify the disease early and deal with it faster.
Bloody discharge: normal variant
Menstrual blood is bright scarlet. And during ovulation, it acquires specific shades: pinkish (a mixture of blood with fluids of the vagina and cervix) and brown (“residues” of previous menstruation). The intensity of blood discharge also varies: from a couple of drops to mild hemorrhage. They last up to two days and are not a cause for particular concern.
Scanty bleeding in the middle of the monthly cycle is called ovulatory syndrome. Unpleasant symptoms of the condition usually disappear by the 17th day of the cycle.
Before ovulation, luteinizing hormone interacts with the follicle, which is located in the ovary. The wall of the follicle weakens, allowing the egg to exit unimpeded. This will release some blood. Sometimes minor bleeding causes complete destruction of the connective tissue of the follicle as the egg moves through the fallopian tube. The resulting discharge is cervical fluid with a small admixture of blood.
Hormonal shifts
After ovulation, bleeding is sometimes triggered by minor hormonal imbalances. Before the release of the egg, the level of estrogen in the female body increases. They stimulate the active release of luteinizing hormone, which causes ovulation. After ovulation, accompanied by a sharp decrease in estrogen levels in the blood, the concentration of progesterone sometimes increases very slowly. Until it returns to normal, there may be some slight bleeding.
Blood discharge in the middle of the monthly cycle can also be observed during pregnancy. The phenomenon is called “implantation bleeding” and is often confused with ovulation discharge. However, it does not occur in every pregnancy.
Comparative assessment of blood discharge during the release of a mature egg and during its implantation
| Index | Ovulation | Egg implantation |
| Time of occurrence | Mid-cycle (plus or minus three days) | After ovulation (on days 6-12) |
| Nature of the discharge | Slight, light brown or pinkish, no clots | |
| Duration | From several hours to two days | |
| Condition of cervical fluid | Transparent, watery, egg white consistency | Thick, sticky |
| Basal temperature (lowest resting temperature) | Promoted | Remains elevated until 12 days after ovulation |
| Characteristic state | “Fertile window” – the best time to conceive | Early pregnancy |
Once conception has occurred, a pregnancy test can be negative or positive. To clarify the condition, you must consult a doctor.
A number of factors influence changes in hormonal levels that can provoke bleeding after ovulation:
- presence of children;
- age;
- sexual activity;
- taking certain medications and oral contraceptives;
- stability of the menstrual cycle;
- use of a fallopian device;
- emotional overstrain, the occurrence of stressful situations.
If the phenomenon causes concern to a woman, she is prescribed sedatives and dietary supplements that stabilize the concentration of estrogen in the blood. If necessary, cancel contraceptives, including intrauterine ones. Adequate rest and limiting stressful situations are recommended.
What are the symptoms of pathology
Depending on the type of disorder, problem, symptoms may vary slightly and have their own characteristics, which is reflected in the table.
| Pathology | Symptoms |
| Inflammatory process | Excessive bleeding, abdominal pain, itching, discomfort |
| Infection | Brown discharge, unpleasant odor |
| Tumor compactions | Frequent bleeding, prolonged menstruation, a large number of passing clots |
| Endometriosis | Blood clots |
| Cervical diseases | Minor but regular bleeding |
If you experience bleeding between periods without pain, you should not immediately sound the alarm and panic. Most often this is due to hormonal levels and disruptions in it. However, to be on the safe side and rule out any serious diseases, you can always consult a specialist. After all, only he will be able to give an accurate answer and make a specific diagnosis based on the examination and examination.
To learn more about bleeding between periods, watch this video:
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Bloody discharge that appears between cycles makes girls worry and go to the gynecologist. In turn, the doctor, after a conversation with the patient and a gynecological examination on the chair, usually prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures:
- blood and urine tests to determine whether there is an inflammatory process in the body;
- biochemistry analysis - protein content;
- bacterial urine analysis, which determines the causative agent of the infection;
- collection of smears from the vagina, cervix;
- urine collection using the Nechiporenko method;
- colposcopy;
- collection and examination of secreted blood;
- histological examination of tissues;
- CT;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system;
- urethroscopy;
- X-ray of genital organs, kidneys;
- cystoscopy.
Only a comprehensive examination can give the most accurate picture and determine the cause of bleeding.
Bleeding in the middle of the cycle - definition and causes.
Mid-cycle bleeding can be defined as heavy uterine or vaginal bleeding that occurs between periods or earlier than expected.
Mid-cycle bleeding is heavy uterine or vaginal bleeding that occurs between periods, either earlier or later than your expected period. Intermenstrual bleeding in most cases is observed 10-16 days after the end of menstruation. This bleeding is not profuse (daily pads are enough) and lasts about 12 - 72 hours. If the amount of blood lost does not increase, there is usually nothing to worry about. If, over time, more blood flows out or the bleeding continues for more than 3 days, then you should go to see a gynecologist. In emergency cases, you need to call an ambulance. It very rarely happens that after conception, women have their last menstruation and do not even know they are pregnant. Therefore, if bleeding is accompanied by pain, there may be a suspicion of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, etc. Bleeding in the middle of the cycle occurs in almost a third of women and is considered normal. It occurs due to an increase or decrease in estrogen levels during ovulation, which weakens the endometrium and causes bleeding. Typically, in this case, the woman is prescribed hormonal medications to regulate hormone levels. Intermenstrual bleeding also occurs in women who are diagnosed with frequent disorders of the genitourinary system, then the bleeding is more intense. There are two main types of bleeding in the period between menstruation: 1) Intermenstrual bleeding - bleeding between two menstruation. 2) Metrorrhagia - severe uterine bleeding.
The following are the causes of intermenstrual bleeding:
- Changes in the body's hormonal levels
- Low thyroid hormone levels
- Miscarriage
- Presence of an intrauterine device
- Starting or stopping birth control pills
- Starting or stopping taking estrogen hormone supplements
- Gynecological procedures, such as cauterization (burning) of the cervix or cervical biopsy
- Taking certain medications
- Vaginal infections or trauma to the vagina
- Stress or depression If you have intermenstrual bleeding, doctors advise devoting more time to rest and avoiding stress and depression.
If the bleeding is caused by related diseases, then proper treatment is prescribed.
What treatment
Therapeutic measures for each woman are prescribed individually, based, first of all, on the nature of the pathology, characteristics of the body, age and other factors. For example, discharge between menstruation after 40 years, as a rule, does not indicate pathology, but about changes occurring in the body due to aging. However, this does not mean that the fair sex does not need help. In such cases, doctors often prescribe medications that make menopause easier to bear.
Read also: what are the signs to determine menopause.
Only a doctor should select and prescribe medications
It’s another matter if girls develop diseases of the genitourinary system. This is often indicated by brown spotting between periods. To eliminate them, conservative or surgical treatment is possible. Therapeutic measures are mainly carried out in a comprehensive manner:
- medications are prescribed to help contract the uterus and stop bleeding;
- hormonal medications are prescribed;
- general strengthening medications are prescribed;
- It is recommended to reduce emotional and physical stress.
In very severe cases, women require surgery.
What should normal discharge look like?
If a little blood is released, it is a sign that hormone levels are changing and the uterus is preparing for a possible pregnancy.
If blood began to flow on the day of ovulation, then the nature of the process can be determined taking into account the color, quantity, duration of discharge, as well as other signs of egg release.
- Color
Bloody discharge during ovulation is usually very slight; cervical mucus with small amounts of blood is often detected. The color of the discharge is light pink or brown, while typical menstrual bleeding is bright scarlet.
- Intensity
Such discharge lasts 1 day, and many women do not notice it, or it appears only as a small strip on toilet paper or a panty liner.
- Time of bleeding
A little blood is released during ovulation, more precisely - on the day of its occurrence and the next 1-2 days after it. If bloody discharge appears a week after the oocyte is released, this is a sign of pathology that requires consultation with a gynecologist.
Also in the section: The nature of discharge during ovulation